Identification of Novel Substrates for cGMP Dependent Protein Kinase (PKG) through Kinase Activity Profiling to Understand Its Putative Role in Inherited Retinal Degeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Modulation of PKG Activity and Substrate Identification
2.1.1. Effect of cGMP and cAMP on PKG Activity
2.1.2. Effect of PKG Activator and Inhibitors on PKG Activity
2.1.3. PKGI and PKGII Substrate Identification
| Peptides on STK PamChip® | Hits after Blasting | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | UniProt ID | Sequence | Protein Name | UniProt ID | Sequence |
| KAPCG_192_206 | P22612 | VKGRTWTLCGTPEYL | cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit α cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit β | P17612 P22694 | VKGRTWTLCGTPEYL VKGRTWTLCGTPEYL |
| KPCB_19_31_A25S | P05771 | RFARKGSLRQKNV | Protein kinase C α type | P17252 | RFARKGSLRQKNV |
| H32_3_18 | Q71DI3 | RTKQTARKSTGGKAPR | Histone H3.1 Histone H3.3 Histone H3.3C Histone H3.t | P68431 P84243 Q6NXT2 Q16695 | RTKQTARKSTGGKAPR RTKQTARKSTGGKAPR RTKQTARKSTGGKAPR RTKQTARKSTGGKAPR |
| RAF1_253_265 | P04049 | QRQRSTSTPNVHM | Serine/Threonine-protein kinase A-Raf | P10398 | QRIRSTSTPNVHM |
| PPR1A_28_40 | Q13522 | QIRRRRPTPATLV | Protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 1C | Q8WVI7 | QIRKRRPTPASLV |
| NCF1_296_308 | P14598 | RGAPPRRSSIRNA | Putative neutrophil cytosol factor 1C | A8MVU1 | RGAPPRRSSIRNA |
| ADDB_706_718 | P35612 | KKKFRTPSFLKKS | α-adducin | P35611 | KKKFRTPSFLKKS |
| RAP1B_172_184 | P61224 | PGKARKKSSCQLL | Ras-related protein Rap-1-b-like protein | A6NIZ1 | PGKARKKSSCQLL |
| CREB1_126_138 | P16220 | EILSRRPSYRKIL | cAMP-responsive element modulator | Q03060 | EILSRRPSYRKIL |
| DESP_2842_2854 | P15924 | RSGSRRGSFDATG | Plectin | Q15149 | RAGSRRGSFDATG |
2.2. Modulation of Kinase Activity in Retinal 661W Cells
2.2.1. Effect of Modulators on Kinase Activity in 661W Cells
2.2.2. Not PKG but PKA Is Modulated in 661W Cells
3. Discussion
Role of PKG Activation in Retinal Cells
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture and Lysis Procedure
4.3. Kinase Activity Measurements
4.4. Instrumentation
4.5. Data Analysis
4.6. Blast
4.7. Substrate Identification
4.8. Substrate Motifs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| cAMP | 3′,5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| cGMP | 3′,5′-cyclic guanosine monophosphate |
| CNG | cyclic nucleotide gated |
| IRD | inherited retinal degeneration |
| Ka | activation Constant |
| PKA | cAMP-dependent protein kinase A |
| PKAi | PKA inhibitor peptide |
| PKG | cGMP-dependent protein kinase G |
References
- Retinal Information Network (RetNet). Available online: https://sph.uth.edu/retnet (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Tolone, A.; Belhadj, S.; Rentsch, A.; Schwede, F.; Paquet-Durand, F. The cGMP Pathway and Inherited Photoreceptor Degeneration: Targets, Compounds, and Biomarkers. Genes 2019, 10, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Cote, R.H. cGMP signaling in vertebrate retinal photoreceptor cells. Front. Biosci. 2005, 10, 1191–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lolley, R.N.; Farber, D.B.; Rayborn, M.E.; Hollyfield, J.G. Cyclic GMP accumulation causes degeneration of photoreceptor cells: Simulation of an inherited disease. Science 1977, 196, 664–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farber, D.B.; Lolley, R.N. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate: Elevation in degenerating photoreceptor cells of the C3H mouse retina. Science 1974, 186, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, M.; Das, S.; Schütze, K.; Marigo, V.; Ekström, P.; Paquet-Durand, F. Cellular mechanisms of hereditary photoreceptor degeneration–focus on cGMP. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2020, 74, 100772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, F.; Feil, R.; Kleppisch, T.; Schlossmann, J. Function of cGMP-dependent protein kinases as revealed by gene deletion. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquet-Durand, F.; Hauck, S.M.; Van Veen, T.; Ueffing, M.; Ekström, P. PKG activity causes photoreceptor cell death in two retinitis pigmentosa models. J. Neurochem. 2009, 108, 796–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vighi, E.; Trifunović, D.; Veiga-Crespo, P.; Rentsch, A.; Hoffmann, D.; Sahaboglu, A.; Strasser, T.; Kulkarni, M.; Bertolotti, E.; Van Den Heuvel, A. Combination of cGMP analogue and drug delivery system provides functional protection in hereditary retinal degeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E2997–E3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Tsang, S.H.; Chen, J. Two pathways of rod photoreceptor cell death induced by elevated cGMP. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 2299–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, D.; Rentsch, A.; Vighi, E.; Bertolotti, E.; Comitato, A.; Schwede, F.; Genieser, H.G.; Marigo, V. New dimeric cGMP analogues reduce proliferation in three colon cancer cell lines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 141, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Browning, D.D. Protein kinase G as a therapeutic target for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2008, 12, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deguchi, A.; Thompson, W.J.; Weinstein, I.B. Activation of protein kinase G is sufficient to induce apoptosis and inhibit cell migration in colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3966–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fallahian, F.; Karami-Tehrani, F.; Salami, S.; Aghaei, M. Cyclic GMP induced apoptosis via protein kinase G in oestrogen receptor-positive and-negative breast cancer cell lines. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 3360–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, E.L.; Wong, J.C.; Johlfs, M.G.; Tsang, B.K.; Fiscus, R.R. Protein kinase G type Iα activity in human ovarian cancer cells significantly contributes to enhanced Src activation and DNA synthesis/cell proliferation. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 578–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vighi, E.; Rentsch, A.; Henning, P.; Comitato, A.; Hoffmann, D.; Bertinetti, D.; Bertolotti, E.; Schwede, F.; Herberg, F.W.; Genieser, H.G.; et al. New cGMP analogues restrain proliferation and migration of melanoma cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wheway, G.; Nazlamova, L.; Turner, D.; Cross, S. 661W photoreceptor cell line as a cell model for studying retinal ciliopathies. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comitato, A.; Subramanian, P.; Turchiano, G.; Montanari, M.; Becerra, S.P.; Marigo, V. Pigment epithelium-derived factor hinders photoreceptor cell death by reducing intracellular calcium in the degenerating retina. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hilhorst, R.; Houkes, L.; Mommersteeg, M.; Musch, J.; van den Berg, A.; Ruijtenbeek, R. Peptide microarrays for profiling of serine/threonine kinase activity of recombinant kinases and lysates of cells and tissue samples. In Gene Regulation; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 259–271. [Google Scholar]
- Poppe, H.; Rybalkin, S.D.; Rehmann, H.; Hinds, T.R.; Tang, X.B.; Christensen, A.E.; Schwede, F.; Genieser, H.G.; Bos, J.L.; Doskeland, S.O.; et al. Cyclic nucleotide analogs as probes of signaling pathways. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, R.; Bertinetti, D.; Herberg, F.W. cAMP-dependent protein kinase and cGMP-dependent protein kinase as cyclic nucleotide effectors. In Non-Canonical Cyclic Nucleotides; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 105–122. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.J.; Lorenz, R.; Arold, S.T.; Reger, A.S.; Sankaran, B.; Casteel, D.E.; Herberg, F.W.; Kim, C. Crystal structure of PKG I: cGMP complex reveals a cGMP-mediated dimeric interface that facilitates cGMP-induced activation. Structure 2016, 24, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francis, S.H.; Poteet-Smith, C.; Busch, J.L.; Richie-Jannetta, R.; Corbin, J.D. Mechanisms of autoinhibition in cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. Front. Biosci. 2002, 7, d580–d592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, S.H.; Blount, M.A.; Zoraghi, R.; Corbin, J.D. Molecular properties of mammalian proteins that interact with cGMP: Protein kinases, cation channels, phosphodiesterases, and multi-drug anion transporters. Front. Biosci. 2005, 10, 2097–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campbell, J.C.; Kim, J.J.; Li, K.Y.; Huang, G.Y.; Reger, A.S.; Matsuda, S.; Sankaran, B.; Link, T.M.; Yuasa, K.; Ladbury, J.E.; et al. Structural basis of cyclic nucleotide selectivity in cGMP-dependent protein kinase II. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 5623–5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pöhler, D.; Butt, E.; Meiβner, J.; Müller, S.; Lohse, M.; Walter, U.; Lohmann, S.M.; Jarchau, T. Expression, purification, and characterization of the cGMP-dependent protein kinases Iβ and II using the baculovirus system. FEBS Lett. 1995, 374, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williamson, E.A.; Wray, J.W.; Bansal, P.; Hromas, R. Overview for the histone codes for DNA repair. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 110, pp. 207–227. [Google Scholar]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR signaling at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 3589–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, E.; Ding, X.Q.; Saadi, A.; Agarwal, N.; Naash, M.I.; Al-Ubaidi, M.R. Expression of cone-photoreceptor–specific antigens in a cell line derived from retinal tumors in transgenic mice. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mencl, S.; Trifunović, D.; Zrenner, E.; Paquet-Durand, F. PKG-Dependent Cell Death in 661W Cone Photoreceptor-like Cell Cultures (Experimental Study). In Retinal Degenerative Diseases; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 511–517. [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln, T.M.; Cornwell, T.L. Intracellular cyclic GMP receptor proteins. FASEB J. 1993, 7, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haushalter, K.J.; Casteel, D.E.; Raffeiner, A.; Stefan, E.; Patel, H.H.; Taylor, S.S. Phosphorylation of protein kinase A (PKA) regulatory subunit RIα by protein kinase G (PKG) primes PKA for catalytic activity in cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 4411–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zor, T.; Selinger, Z. Linearization of the Bradford protein assay increases its sensitivity: Theoretical and experimental studies. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 236, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chirumamilla, C.S.; Fazil, M.H.U.T.; Perez-Novo, C.; Rangarajan, S.; de Wijn, R.; Ramireddy, P.; Verma, N.K.; Berghe, W.V. Profiling activity of cellular kinases in migrating T-cells. In T-Cell Motility; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 99–113. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, W.R. Selecting the right similarity-scoring matrix. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2013, 43, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
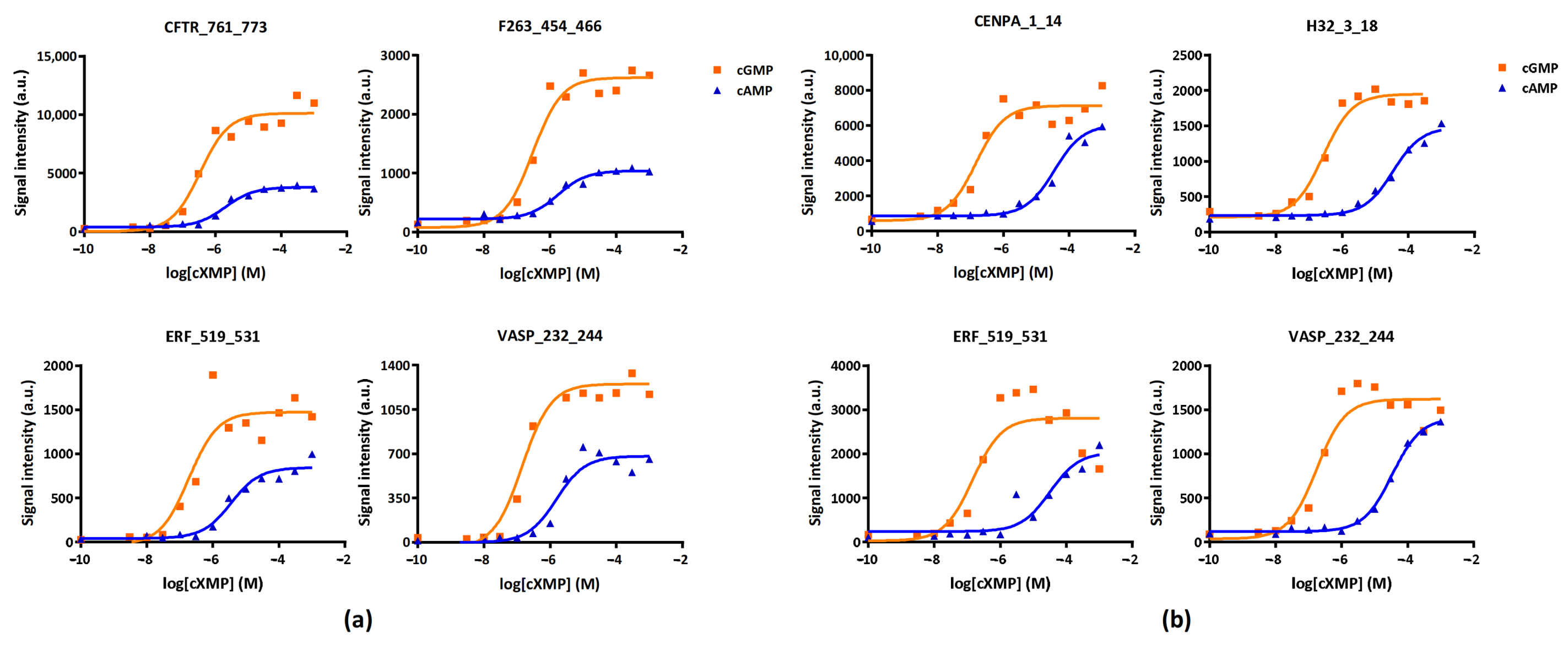



| cXMP | PKGI Ka (µM) | PKGII Ka (µM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured | Literature | Measured | Literature | |
| cGMP | 0.26 | 0.1–0.2 [20,21,22,23,24] | 1.6 | 0.04–0.8 [20,24,25,26] |
| cAMP | 22.4 | 7.6–39 [20,21] | 27 | ~12 [20] |
| Peptide ID | UniProt ID | Peptide Sequence | Description | PKGI Score | PKGII Score | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERF_519_531 | P50548 | GEAGGPLTPRRVS | ETS domain-containing transcription factor ERF | 10 | 9 | |
| VASP_232_244 | P50552 | GAKLRKVSKQEEA | Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein | 10 | 8 | A (PKGI) |
| CREB1_126_138 | P16220 | EILSRRPSYRKIL | cAMP response element-binding protein | 10 | 6 | A, B, C (PKGI) |
| CSF1R_701_713 | P07333 | NIHLEKKYVRRDS | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor precursor | 10 | 7 | |
| EPB42_241_253 | P16452 | LLNKRRGSVPILR | Erythrocyte membrane protein band 4.2 | 9 | 7 | |
| GBRB2_427_439 | P47870 | SRLRRRASQLKIT | Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit beta-2 precursor | 10 | 6 | |
| GPSM2_394_406 | P81274 | PKLGRRHSMENME | G-protein-signaling modulator 2 | 10 | 7 | |
| GRIK2_708_720 | Q13002 | FMSSRRQSVLVKS | Glutamate receptor, ionotropic kainate 2 precursor | 10 | 4 | |
| PDE5A_95_107 | Q76074 | GTPTRKISASEFD | cGMP-specific 3’,5’-cyclic phosphodiesterase | 10 | 6 | |
| PTN12_32_44 | Q05209 | FMRLRRLSTKYRT | Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 12 | 10 | 5 | |
| RS6_228_240 | P62753 | IAKRRRLSSLRAS | 40S ribosomal protein S6 | 10 | 5 | |
| RYR1_4317_4329 | P21817 | VRRLRRLTAREAA | Ryanodine receptor 1 | 9 | 5 | |
| VTNC_390_402 | P04004 | NQNSRRPSRATWL | Vitronectin precursor | 10 | 4 | |
| CFTR_761_773 | P13569 | LQARRRQSVLNLM | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | 10 | 3 | A, B (PKGI) |
| F263_454_466 | Q16875 | NPLMRRNSVTPLA | 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3 | 10 | 3 | |
| KPB1_1011_1023 | P46020 | QVEFRRLSISAES | Phosphorylase b kinase regulatory subunit alpha, skeletal muscle isoform | 9 | 3 | |
| MYPC3_268_280 | Q14896 | LSAFRRTSLAGGG | Myosin-binding protein C, cardiac-type | 10 | 4 | |
| TY3H_65_77 | P07101 | FIGRRQSLIEDAR | Tyrosine 3-monooxygenase | 9 | 3 | |
| VASP_271_283 | P50552 | LARRRKATQVGEK | Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein | 8 | 3 | A (PKGI) |
| ANXA1_209_221 | P04083 | AGERRKGTDVNVF | Annexin A1 | 7 | 9 | |
| GPR6_349_361 | P46095 | QSKVPFRSRSPSE | Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor GPR6 | 9 | 8 | |
| KIF2C_105_118_S106G | Q99661 | EGLRSRSTRMSTVS | Kinesin-like protein KIF2C | 9 | 7 | |
| ADDB_706_718 | P35612 | KKKFRTPSFLKKS | Beta-adducin | 8 | 7 | |
| CAC1C_1974_1986 | Q13936 | ASLGRRASFHLEC | Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit α-1C | 9 | 7 | |
| KAP2_92_104 | P13861 | SRFNRRVSVCAET | cAMP-dependent protein kinase type II-alpha regulatory subunit | 6 | 5 | |
| KCNA2_442_454 | P16389 | PDLKKSRSASTIS | Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 2 | 9 | 7 | |
| NCF1_296_308 | P14598 | RGAPPRRSSIRNA | Neutrophil cytosol factor 1 | 9 | 7 | |
| MPIP1_172_184 | P30304 | FTQRQNSAPARML | M-phase inducer phosphatase 1 | 9 | 4 | |
| ART_025_ CXGLRRWSLGGLRRWSL | Na | GLRRWSLGGLRRWSL | Peptide based on kemptide sequence | 8 | 4 | |
| CDN1A_139_151 | P38936 | GRKRRQTSMTDFY | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 | 6 | 3 | |
| KCNA6_504_516 | P17658 | ANRERRPSYLPTP | Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 6 | 9 | 3 | |
| ERBB2_679_691 | P04626 | QQKIRKYTMRRLL | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 precursor | 7 | 8 | A (PKGII) |
| DESP_2842_2854 | P15924 | RSGSRRGSFDATG | Desmoplakin | 8 | 7 | |
| KCNA3_461_473 | P22001 | EELRKARSNSTLS | Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 3 | 8 | 7 | |
| RAF1_253_265 | P04049 | QRQRSTSTPNVHM | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase | 8 | 7 | |
| RAP1B_172_184 | P61224 | PGKARKKSSCQLL | Ras-related protein Rap-1b precursor | 7 | 7 | |
| KAP3_107_119 | P31323 | NRFTRRASVCAEA | cAMP-dependent protein kinase type II-beta regulatory subunit | 8 | 4 | |
| TOP2A_1463_1475 | P11388 | RRKRKPSTSDDSD | DNA topoisomerase 2-alpha | 6 | 5 | |
| ADRB2_338_350 | P07550 | ELLCLRRSSLKAY | Beta-2 adrenergic receptor | 8 | 4 | |
| ANDR_785_797 | P10275 | VRMRHLSQEFGWL | Androgen receptor | 6 | 4 | |
| REL_260_272 | Q04864 | KMQLRRPSDQEVS | C-Rel proto-oncogene protein | 6 | 4 | |
| VASP_150_162 | P50552 | EHIERRVSNAGGP | Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein | 8 | 4 | A (PKGI) |
| PTK6_436_448 | Q13882 | ALRERLSSFTSYE | Tyrosine-protein kinase 6 | 7 | 1 | |
| KPCB_19_31_A25S | P05771 | RFARKGSLRQKNV | Protein kinase C β | 5 | 8 | |
| PLM_76_88 | O00168 | EEGTFRSSIRRLS | Phospholemman precursor | 7 | 7 | |
| FRAP_2443_2455 | P42345 | RTRTDSYSAGQSV | FKBP12-rapamycin complex-associated protein (mTOR) | 7 | 7 | |
| LIPS_944_956 | Q05469 | GFHPRRSSQGATQ | Hormone-sensitive lipase | 7 | 7 | A (PKGI) |
| PPR1A_28_40 | Q13522 | QIRRRRPTPATLV | Protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 1A | 4 | 7 | |
| GYS2_1_13 | P54840 | MLRGRSLSVTSLG | Glycogen synthase, liver | 5 | 4 | |
| STK6_283_295 | O14965 | SSRRTTLCGTLDY | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 6 (Aurora A) | 5 | 3 | |
| PDPK1_27_39 | O15530 | SMVRTQTESSTPP | 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 | 3 | 9 | |
| BAD_69_81 | Q92934 | IRSRHSSYPAGTE | Bcl2 antagonist of cell death | 5 | 8 | A(PKGI) |
| H2B1B_ 27_40 | P33778 | GKKRKRSRKESYSI | Histone H2B type 1-B | 3 | 8 | |
| NMDZ1_890_902 | Q05586 | SFKRRRSSKDTST | Glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit zeta-1 precursor | 4 | 8 | |
| NOS3_1171_1183 | P29474 | SRIRTQSFSLQER | Nitric oxide synthase, endothelial | 6 | 8 | A (PKGI) |
| PLEK_106_118 | P08567 | GQKFARKSTRRSI | Pleckstrin | 4 | 8 | |
| H32_3_18 | Q71DI3 | RTKQTARKSTGGKAPR | Histone H3.2 | 4 | 9 | |
| CENPA_1_14 | P49450 | MGPRRRSRKPEAPR | Histone H3-like centromeric protein A | 3 | 7 | |
| RBL2_655_667 | Q08999 | GLGRSITSPTTLY | Retinoblastoma-like protein 2 | 1 | 8 | |
| KAPCG_192_206 | P22612 | VKGRTWTLCGTPEYL | cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit γ | 0 | 7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roy, A.; Groten, J.; Marigo, V.; Tomar, T.; Hilhorst, R. Identification of Novel Substrates for cGMP Dependent Protein Kinase (PKG) through Kinase Activity Profiling to Understand Its Putative Role in Inherited Retinal Degeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031180
Roy A, Groten J, Marigo V, Tomar T, Hilhorst R. Identification of Novel Substrates for cGMP Dependent Protein Kinase (PKG) through Kinase Activity Profiling to Understand Its Putative Role in Inherited Retinal Degeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(3):1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031180
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoy, Akanksha, John Groten, Valeria Marigo, Tushar Tomar, and Riet Hilhorst. 2021. "Identification of Novel Substrates for cGMP Dependent Protein Kinase (PKG) through Kinase Activity Profiling to Understand Its Putative Role in Inherited Retinal Degeneration" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 3: 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031180
APA StyleRoy, A., Groten, J., Marigo, V., Tomar, T., & Hilhorst, R. (2021). Identification of Novel Substrates for cGMP Dependent Protein Kinase (PKG) through Kinase Activity Profiling to Understand Its Putative Role in Inherited Retinal Degeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(3), 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031180






