Type 2 Transglutaminase in Coeliac Disease: A Key Player in Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Coeliac Disease (CD)
2.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Manifestations of CD
2.2. The Main Environmental Trigger in CD: Gluten
2.3. The Genetics of CD
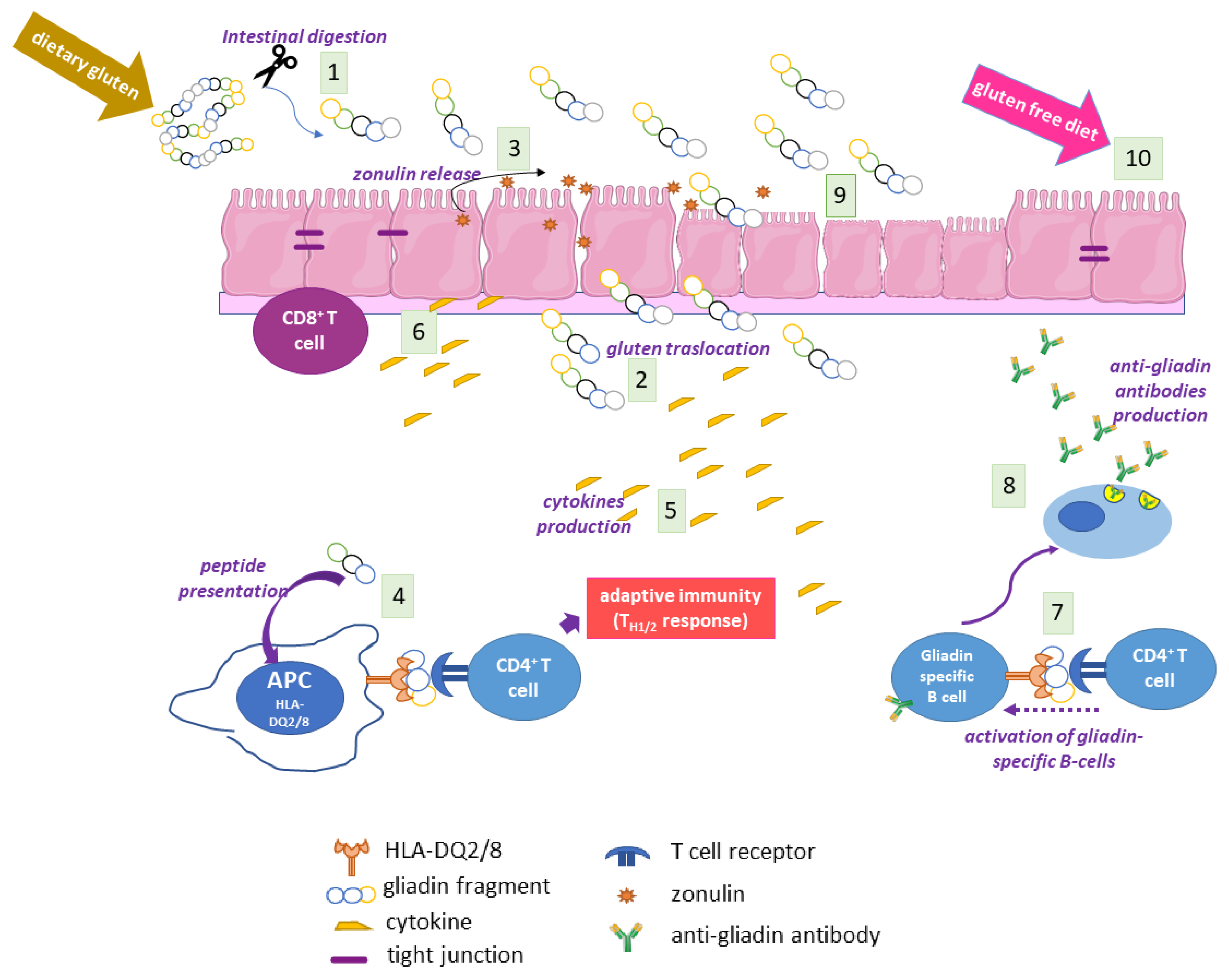
2.4. The Adaptive and Innate Immune Response in CD
2.5. Autoimmunity in CD
2.6. The Coeliac Cellular Phenotype
2.7. CD Diagnosis
Enzymatic and Immunofluorescence Assays
2.8. CD Therapy
3. TG2
3.1. TG Family and TG Canonical Enzymatic Reactions
3.2. TG2 Expression, Localisation and Enzymatic Activities
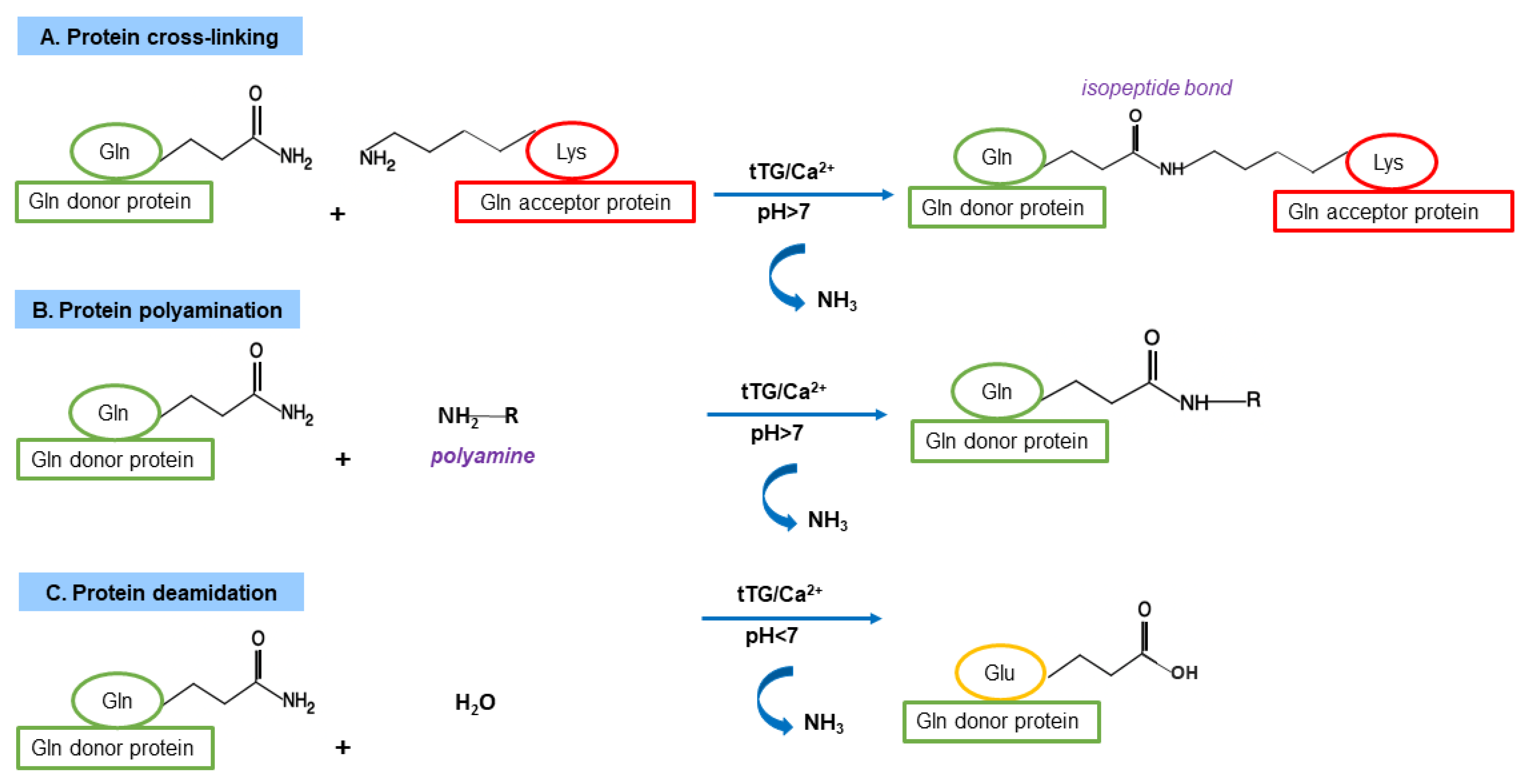
3.3. TG2 Functions as Cross-Linking Enzyme
3.4. TG2 Functions as Non-Crosslinking Enzyme
4. TG2 in CD Pathogenesis
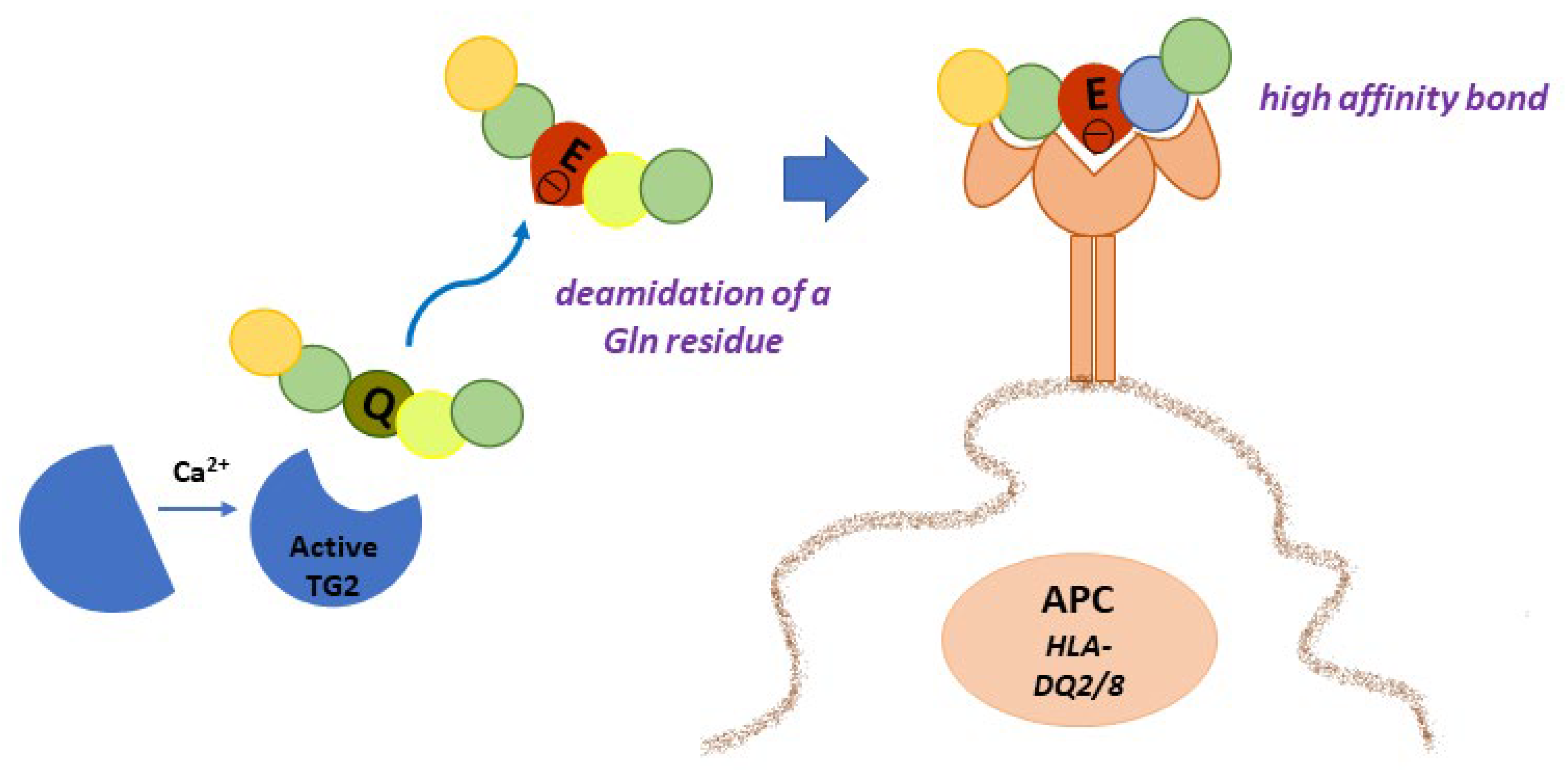
4.1. Gluten Modification: Deamidation
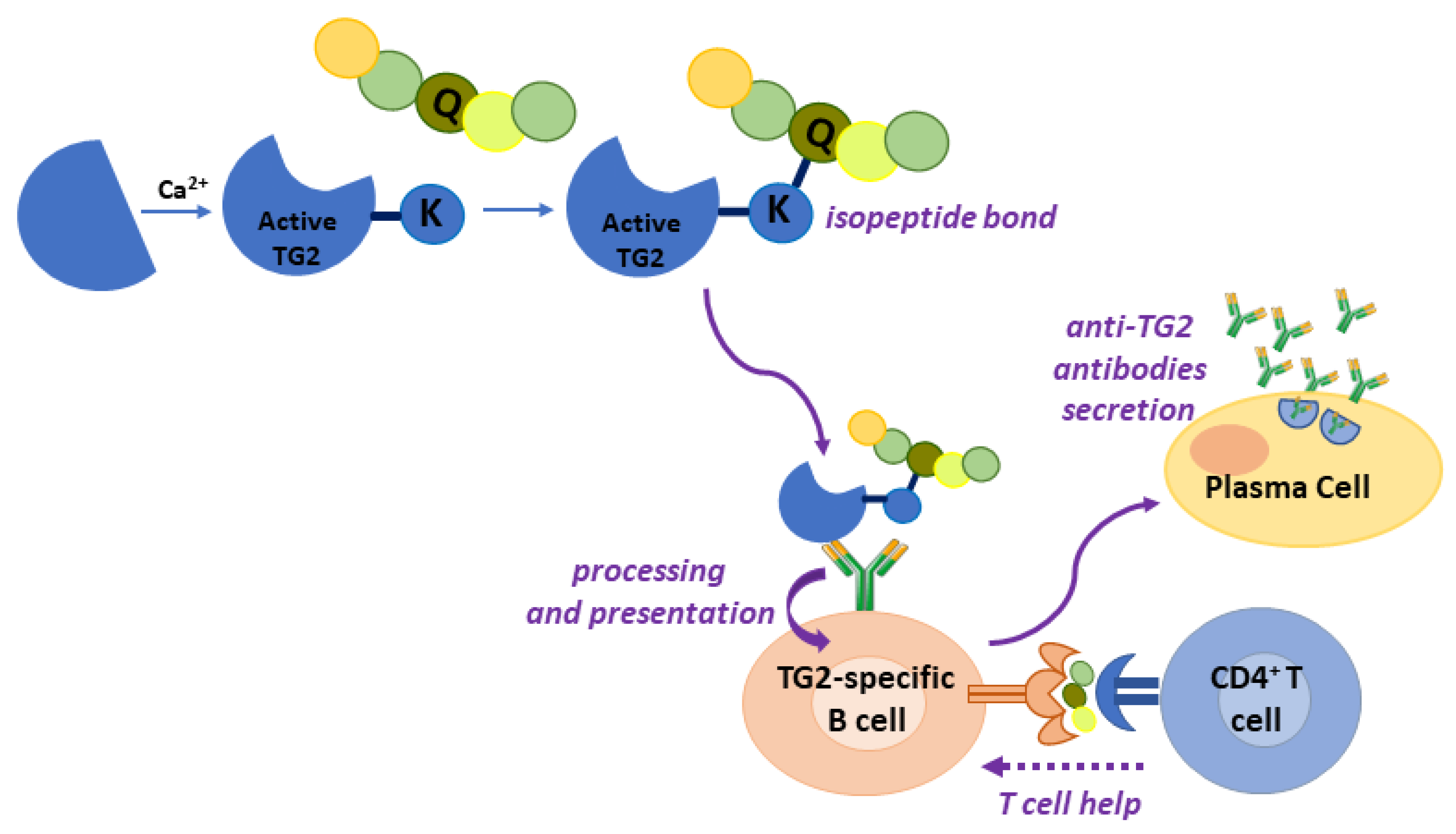
4.2. Gluten Modification: Mechanism of Anti-TG2 Antibody Production
4.3. Other TGs in CD
4.3.1. TG3 and TG6
4.3.2. TGm
4.4. Potential Pathogenetic Role of Anti-TG2 Antibodies
| Observed Biological Effect | Study Model for Anti-TG2 Antibodies | Study Model for P31–43 |
|---|---|---|
| increased proliferation | Caco-2 cells [97]; enterocyte from CD patients on gluten-free diet [87] | Caco-2 cells [97]; enterocyte from CD patients on gluten-free diet [98] |
| reduced epithelial growth factor (EGF) endocytosis | Caco-2 cells [97] | Caco-2 cells [98] |
| increased ERK phosphorylation | Caco-2 cells [97] | Caco-2 cells [98] |
| actin rearrangement | Caco-2 cells [97] | Caco-2 cells [98]; enterocyte from CD patients on gluten-free diet [98] |
| Ca2+ mobilisation from ER and mitochondria | Caco-2 cells [91] | Caco-2 cells [99] |
| intracellular TG2 activation | Caco-2 cells [91] | Caco-2 cells [99] |
4.5. TG2 and Gliadin Handling by Cells
4.6. TG2 Contribution to Coeliac Cellular Phenotype
5. TG2 in CD Diagnosis
5.1. EMA and ELISA Tests for TG2
5.2. Detection of Intestinal Anti-TG2 Antibodies
5.3. Anti-TG3 and Anti-TG6 Antibodies in Clinical Practice
6. TG2 in CD Therapy
6.1. Studies on In Vitro TG2 Inhibition
6.2. Studies on In Vivo TG2 Inhibition
6.3. Anti-TG2 Antibodies as Blocking Agents
6.4. TG2 Inhibition in Clinical Trials
7. Gluten Transamidation as a Detoxification Strategy for Therapeutical Approach
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APCs | antigen-presenting cells |
| CD | coeliac disease |
| DH | dermatitis herpetiformis |
| DPG | deamidated gliadin peptides |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| EMA | anti-endomysial antibodies |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| HLA | human leukocyte antigen |
| IFA | indirect immunofluorescence assay |
| IL | interleukin |
| INFγ | interferon-γ |
| NFkB | nuclear factor k-B |
| P31–43 | α-gliadin peptide 31–43 |
| TG | transglutaminase |
| TG2 | type 2 transglutaminase |
| TG3 | type 3 transglutaminase |
| TG6 | type 6 transglutaminase |
| TGF-β1 | transforming growth factor β1 |
| TGm | microbial transglutaminase |
References
- Lorand, L.; Graham, R.M. Transglutaminases: Crosslinking enzymes with pleiotropic functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 4, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sollid, L.M.; Jabri, B. Celiac disease and transglutaminase 2: A model for posttranslational modification of antigens and HLA association in the pathogenesis of auto-immune disorders. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2011, 23, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, R.; Khosla, C. Substrates, inhibitors, and probes of mammalian transglutaminase 2. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 591, 113560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luongo, D.; Bonavita, R.; Rossi, S.; Aufiero, V.R.; Feliciello, N.R.; Maurano, F.; Iaquinto, G.; Mazzarella, G.; Rossi, M. Tailoring the immune response to wheat gliadin by enzymatic transamidation. Cytokine 2019, 117, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollid, L.M. Molecular basis of celiac disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 53–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caio, C.; Volta, U.; Sapone, A.; Leffler, D.A.; De Giorgio, R.; Catassi, C.; Alessio, F. Celiac disease: A comprehensive current review. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durazzo, M.; Ferro, A.; Brascugli, I.; Mattivi, S.; Fagoonee, S.; Pellicano, R. Extra-Intestinal Manifestations of Celiac Disease: What Should We Know in 2022? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, H. Chemistry of gluten proteins. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, M.; Bromilow, S.N.; Nitride, C.; Shewry, P.R.; Gethings, L.A.; Mills, E.N.C. Mapping Coeliac Toxic Motifs in the Prolamin Seed Storage Proteins of Barley, Rye, and Oats Using a Curated Sequence Database. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollid, L.M.; Tye-Din, J.A.; Qiao, S.W.; Anderson, R.P.; Gianfrani, C.; Koning, F. Update 2020: Nomenclature and listing of celiac disease-relevant gluten epitopes recognized by CD4(+) T cells. Immunogenetics 2020, 72, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Molberg, Ø.; Parrot, I.; Hausch, F.; Filiz, F.; Gray, G.M.; Sollid, L.M.; Khosla, C. Structural basis for gluten intolerance in celiac sprue. Science 2002, 297, 2275–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisine, J.; Abadie, V. Interplay Between Gluten, HLA, Innate and Adaptive Immunity Orchestrates the Development of Coeliac Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 674313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodkhe, R.; Shetty, S.A.; Dhotre, D.P.; Verma, A.K.; Bhatia, K.; Mishra, A.; Kaur, G.; Pande, P.; Bangarusamy, D.K.; Santosh, B.P.; et al. Comparison of small gut and whole gut microbiota of first-degree relatives with adult celiac disease patients and controls. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemppainen, K.M.; Lynch, K.F.; Liu, E.; Lönnrot, M.; Simell, V.; Briese, T.; Koletzko, S.; Hagopian, W.; Rewers, M.; She, J.X.; et al. Factors that increase risk of celiac disease autoimmunity after a gastrointestinal infection in early life. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 694–702.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollid, L.M. The roles of MHC class II genes and post-translational modification in celiac disease. Immunogenetics 2017, 69, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kårhus, L.L.; Thuesen, B.H.; Skaaby, T.; Rumessen, J.J.; Linneberg, A. The distribution of HLA DQ2 and DQ8 haplotypes and their association with health indicators in a general Danish population. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2018, 6, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Santisteban, I.; Romero-Garmendia, I.; Cilleros-Portet, A.; Bilbao, J.R.; Fernandez-Jimenez, N. Celiac disease susceptibility: The genome and beyond. Int. Rev. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2021, 358, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammers, K.M.; Lu, R.; Brownley, J.; Lu, B.; Gerard, C.; Thomas, K.; Rallabhandi, P.; Shea-Donohue, T.; Tamiz, A.; Alkan, S.; et al. Gliadin induces an increase in intestinal permeability and zonulin release by binding to the chemokine receptor CXCR3. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 194–204.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirdo, F.G.; Auricchio, S.; Troncone, R.; Barone, M.V. The gliadin p31-43 peptide: Inducer of multiple proinflammatory effects. Int. Rev. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2021, 358, 165–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, W.; Ehnis, T.; Bauer, M.; Donner, P.; Volta, U.; Riecken, E.O.; Schuppan, D. Identification of tissue transglutaminase as the autoantigen of celiac disease. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaukinen, K.; Peräaho, M.; Collin, P.; Partanen, J.; Woolley, N.; Kaartinen, T.; Nuutinen, T.; Halttunen, T.; Mäki, M.; Korponay-Szabo, I. Small-bowel mucosal transglutaminase 2-specific IgA deposits in coeliac disease without villous atrophy: A prospective and randomized clinical study. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 40, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korponay-Szabó, I.R.; Halttunen, T.; Szalai, Z.; Laurila, K.; Király, R.; Kovács, J.B.; Fésüs, L.; Mäki, M. In vivo targeting of intestinal and extraintestinal transglutaminase 2 by coeliac auto-antibodies. Gut 2004, 53, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardy, M.; Karpati, S.; Merkl, B.; Paulsson, M.; Smyth, N. Epidermal transglutaminase (TGase 3) is the autoantigen of dermatitis herpetiformis. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjivassiliou, M.; Aeschlimann, P.; Strigun, A.; Sanders, D.S.; Woodroofe, N.; Aeschlimann, D. Auto-antibodies in gluten ataxia recognize a novel neuronal transglutaminase. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayakkara, M.; Lania, G.; Maglio, M.; Kosova, R.; Sarno, M.; Gaito, A.; Discepolo, V.; Troncone, R.; Auricchio, S.; Auricchio, R.; et al. Enterocyte proliferation and signaling are constitutively altered in celiac disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lania, G.; Nanayakkara, M.; Maglio, M.; Auricchio, R.; Porpora, M.; Conte, M.; De Matteis, M.M.; Rizzo, R.; Luini, A.; Discepolo, V.; et al. Constitutive alterations in vesicular trafficking increase the sensitivity of cells from celiac disease patients to gliadin. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolella, G.; Nanayakkara, M.; Sposito, S.; Lepretti, M.; Auricchio, S.; Esposito, C.; Barone, M.V.; Martucciello, S.; Caputo, I. Constitutive differential features of type 2 transglutaminase in cells derived from celiac patients and from healthy subjects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Discepolo, V.; Lania, G.; Ten Eikelder, M.L.G.; Nanayakkara, M.; Sepe, L.; Tufano, R.; Troncone, R.; Auricchio, S.; Auricchio, R.; Paolella, G.; et al. Pediatric Celiac Disease Patients Show Alterations of Dendritic Cell Shape and Actin Rearrangement. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porpora, M.; Conte, M.; Lania, G.; Bellomo, C.; Rapacciuolo, L.; Chirdo, F.G.; Auricchio, R.; Troncone, R.; Auricchio, S.; Barone, M.V.; et al. Inflammation Is Present, Persistent and More Sensitive to Proinflammatory Triggers in Celiac Disease Enterocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandini, A.; Gededzha, M.P.; De Maayer, T.; Barrow, P.; Mayne, E. Diagnosing coeliac disease: A literature review. Hum. Immunol. 2021, 82, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, I.L.; Coutinho de Almeida, R.; Modderman, R.; Stachurska, A.; Dekens, J.; Barisani, D.; Meijer, C.R.; Roca, M.; Martinez-Ojinaga, E.; Shamir, R.; et al. Circulating miRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Celiac Disease Development. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 734763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volta, U.; Fabbri, A.; Parisi, C.; Piscaglia, M.; Caio, G.; Tovoli, F.; Fiorini, E. Old and new serological tests for celiac disease screening. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 4, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauhavirta, T.; Hietikko, M.; Salmi, T.; Lindfors, K. Transglutaminase 2 and Transglutaminase 2 Autoantibodies in Celiac Disease: A Review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 57, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choung, R.S.; Khaleghi Rostamkolaei, S.; Ju, J.M.; Marietta, E.V.; Van Dyke, C.T.; Rajasekaran, J.J.; Jayaraman, V.; Wang, T.; Bei, K.; Rajasekaran, K.E.; et al. Synthetic Neoepitopes of the Transglutaminase-Deamidated Gliadin Complex as Biomarkers for Diagnosing and Monitoring Celiac Disease. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 582–591.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladinser, B.; Rossipal, E.; Pittschieler, K. Endomysium antibodies in coeliac disease: An improved method. Gut 1994, 35, 776–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakireva, A.V.; Zamyatnin, A.A. Properties of Gluten Intolerance: Gluten Structure, Evolution, Pathogenicity and Detoxification Capabilities. Nutrients 2016, 8, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetcuti Zammit, S.; Sanders, D.S.; Sidhu, R. Refractory coeliac disease: What should we be doing different? Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2020, 36, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klonarakis, M.; Andrews, C.N.; Raman, M.; Panaccione, R.; Ma, C. Review article: Therapeutic targets for the pharmacologic management of coeliac disease-the future beyond a gluten-free diet. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 55, 1277–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenard, P.; Bates, M.K.; Aeschlimann, D. Evolution of transglutaminase genes: Identification of a transglutaminase gene cluster on human chromosome 15q15. Structure of the gene encoding transglutaminase X and a novel gene family member, transglutaminase Z. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 33066–33078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, R.L.; Kaartinen, M.T.; Nurminskaya, M.; Belkin, A.M.; Colak, G.; Johnson, G.V.; Mehta, K. Transglutaminase regulation of cell function. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 383–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ientile, R.; Ientile, D.; Griffin, M. Tissue transglutaminase and the stress response. Amino Acids 2007, 33, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Choi, S.S.; Ha, K.S. Transglutaminase 2: A multi-functional protein in multiple subcellular compartments. Amino Acids 2010, 39, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurminskaya, M.V.; Belkin, A.M. Cellular functions of tissue transglutaminase. Int. Rev. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2012, 294, 1–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemskov, E.A.; Mikhailenko, I.; Hsia, R.C.; Zaritskaya, L.; Belkin, A.M. Unconventional secretion of tissue transglutaminase involves phospholipid-dependent delivery into recycling endosomes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkas, D.M.; Strop, P.; Brunger, A.T.; Khosla, C. Transglutaminase 2 undergoes a large conformational change upon activation. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.E.; Park, H.H. Structures of Human Transglutaminase 2: Finding Clues for Interference in Cross-linking Mediated Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plugis, N.M.; Palanski, B.A.; Weng, C.H.; Albertelli, M.; Khosla, C. Thioredoxin-1 Selectively Activates Transglutaminase 2 in the Extracellular Matrix of the Small Intestine: Implication for Celiac Disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 2000–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.C.; Melkonian, A.V.; Ousey, J.A.; Khosla, C. Endoplasmic reticulum-resident protein 57 (ERp57) oxidatively inactivates human transglutaminase 2. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 2640–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsukawa, H.; Hitomi, K. Role of Transglutaminase 2 in Cell Death, Survival, and Fibrosis. Cells 2021, 10, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fésüs, L.; Szondy, Z. Transglutaminase 2 in the balance of cell death and survival. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 3297–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Eletto, M.; Rossin, F.; Fedorova, O.; Farrace, M.G.; Piacentini, M. Transglutaminase type 2 in the regulation of proteostasis. Biol. Chem. 2019, 400, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, T.S.; Lin, C.J.; Greenberg, C.S. Role of tissue transglutaminase-2 (TG2)-mediated aminylation in biological processes. Amino Acids 2017, 49, 501–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, T.S.; Lin, C.J.; Wu, Y.T.; Wu, C.J. Tissue transglutaminase (TG2) and mitochondrial function and dysfunction. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2017, 22, 1114–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szondy, Z.; Korponay-Szabó, I.; Király, R.; Sarang, Z.; Tsay, G.J. Transglutaminase 2 in human diseases. Biomedicine 2017, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tempest, R.; Guarnerio, S.; Maani, R.; Cooper, J.; Peake, N. The Biological and Biomechanical Role of Transglutaminase-2 in the Tumour Microenvironment. Cancers 2021, 13, 2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Ma, J.; Chi, J.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, J. Roles and potential clinical implications of tissue transglutaminase in cardiovascular diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 177, 106085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martucciello, S.; Sposito, S.; Esposito, C.; Paolella, G.; Caputo, I. Interplay between Type 2 Transglutaminase (TG2), Gliadin Peptide 31-43 and Anti-TG2 Antibodies in Celiac Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iversen, R.; Amundsen, S.F.; Kleppa, L.; du Pré, M.F.; Stamnaes, J.; Sollid, L.M. Evidence That Pathogenic Transglutaminase 2 in Celiac Disease Derives from Enterocytes. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 788–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciacchi, L.; Reid, H.H.; Rossjohn, J. Structural bases of T cell antigen receptor recognition in celiac disease. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2022, 74, 102349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöck, C.; Diraimondo, T.R.; Khosla, C. Role of transglutaminase 2 in celiac disease pathogenesis. Semin. Immunopathol. 2012, 34, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollid, L.M.; Molberg, Ø.; McAdam, S.; Lundin, K.E.A. Auto-antibodies in celiac disease: Tissue transglutaminase–guilt by association? Gut 1997, 41, 851–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lexhaller, B.; Ludwig, C.; Scherf, K.A. Identification of Isopeptides Between Human Tissue Transglutaminase and Wheat, Rye, and Barley Gluten Peptides. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Pré, M.F.; Blazevski, J.; Dewan, A.E.; Stamnaes, J.; Kanduri, C.; Sandve, G.K.; Johannesen, M.K.; Lindstad, C.B.; Hnida, K.; Fugger, L.; et al. B cell tolerance and antibody production to the celiac disease autoantigen transglutaminase 2. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamnaes, J.R.; du Pré, M.F.; Chen, X.; Sollid, L.M. Enhanced B-cell receptor recognition of the autoantigen transglutaminase 2 by efficient catalytic self-multimerization. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaedini, A.; Green, P.H. Auto-antibodies in celiac disease. Autoimmunity 2008, 41, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, R.; du Pré, M.F.; Di Niro, R.; Sollid, L.M. Igs as substrates for transglutaminase 2: Implications for autoantibody production in celiac disease. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 5159–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, R.; Roy, B.; Stamnaes, J.; Høydahl, L.S.; Hnida, K.; Neumann, R.S.; Korponay-Szabó, I.R.; Lundin, K.E.A.; Sollid, L.M. Efficient T cell-B cell collaboration guides autoantibody epitope bias and onset of celiac disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 15134–15139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, J.; Ciacchi, L.; Tran, M.T.; Loh, K.L.; Kooy-Winkelaar, Y.; Croft, N.P.; Hardy, M.Y.; Chen, Z.; McCluskey, J.; Anderson, R.P.; et al. T cell receptor cross-reactivity between gliadin and bacterial peptides in celiac disease. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziberna, F.; De Lorenzo, G.; Schiavon, V.; Arnoldi, F.; Quaglia, S.; De Leo, L.; Vatta, S.; Martelossi, S.; Burrone, O.R.; Ventura, A.; et al. Lack of evidence of rotavirus-dependent molecular mimicry as a trigger of coeliac disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 186, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitomi, K. Transglutaminases in skin epidermis. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2005, 15, 313–319. [Google Scholar]
- Chermnykh, E.S.; Alpeeva, E.V.; Vorotelyak, E.A. Transglutaminase 3: The Involvement in Epithelial Differentiation and Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaunisto, H.; Salmi, T.; Lindfors, K.; Kemppainen, E. Antibody Responses to Transglutaminase 3 in Dermatitis Herpetiformis: Lessons from Celiac Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, H.; Beck, K.; Adamczyk, M.; Aeschlimann, P.; Langley, M.; Oita, R.C.; Thiebach, L.; Hils, M.; Aeschlimann, D. Transglutaminase 6: A protein associated with central nervous system development and motor function. Amino Acids 2013, 44, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze-Krebs, A.; Canneva, F.; Stemick, J.; Plank, A.C.; Harrer, J.; Bates, G.P.; Aeschlimann, D.; Steffan, J.S.; von Hörsten, S. Transglutaminase 6 Is Colocalized and Interacts with Mutant Huntingtin in Huntington Disease Rodent Animal Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, D.; Umar, S.; Muhammad, H.; Nikfekr, E.; Rostami, K.; Ishaq, S. Neurological manifestation of coeliac disease with particular emphasis on gluten ataxia and immunological injury: A review article. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench. 2021, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Hadjivassiliou, M.; Reunala, T.; Hervonen, K.; Aeschlimann, P.; Aeschlimann, D. TG6 Auto-Antibodies in Dermatitis Herpetiformis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamnaes, J.; Dorum, S.; Fleckenstein, B.; Aeschlimann, D.; Sollid, L.M. Gluten T cell epitope targeting by TG3 and TG6; implications for dermatitis herpetiformis and gluten ataxia. Amino Acids 2010, 39, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankari, H.; Hietikko, M.; Kurppa, K.; Kaukinen, K.; Mansikka, E.; Huhtala, H.; Laurila, K.; Reunala, T.; Hervonen, K.; Salmi, T.; et al. Intestinal TG3- and TG2-specific plasma cell responses in Dermatitis Herpetiformis patients undergoing a gluten challenge. Nutrients 2020, 12, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, N. Innovation in the food industry using microbial transglutaminase: Keys to success and future prospects. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 597, 113638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, A.; Aminov, R.; Matthias, T. Transglutaminases in dysbiosis as potential environmental drivers of autoimmunity. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stricker, S.; de Laffolie, J.; Rudloff, S.; Komorowski, L.; Zimmer, K.P. Intracellular Localization of Microbial Transglutaminase and Its Influence on the Transport of Gliadin in Enterocytes. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 68, e43–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthias, T.; Jeremias, P.; Neidhöfer, S.; Lerner, A. The industrial food additive microbial transglutaminase, mimics the tissue transglutaminase and is immunogenic in celiac disease patients. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agardh, D.; Matthias, T.; Wusterhausen, P.; Neidhöfer, S.; Heller, A.; Lerner, A. Antibodies against neo-epitope of microbial and human transglutaminase complexes as biomarkers of childhood celiac disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 199, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taavela, J.; Kurppa, K.; Collin, P.; Lähdeaho, M.L.; Salmi, T.; Saavalainen, P.; Haimila, K.; Huhtala, H.; Laurila, K.; Sievänen, H.; et al. Degree of damage to the small bowel and serum antibody titers correlate with clinical presentation of patients with celiac disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martucciello, S.; Paolella, G.; Esposito, C.; Lepretti, M.; Caputo, I. Anti-type 2 transglutaminase antibodies as modulators of type 2 transglutaminase functions: A possible pathological role in celiac disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 4107–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindstad, C.B.; du Pré, M.F.; Stamnaes, J.; Sollid, L.M. Injection of prototypic celiac anti-transglutaminase 2 antibodies in mice does not cause enteropathy. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, M.V.; Caputo, I.; Ribecco, M.T.; Maglio, M.; Marzari, R.; Sblattero, D.; Troncone, R.; Auricchio, S.; Esposito, C. Humoral immune response to tissue transglutaminase is related to epithelial cell proliferation in celiac disease. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halttunen, T.; Mäki, M. Serum immunoglobulin A from patients with celiac disease inhibits human T84 intestinal crypt epithelial cell differentiation. Gastroenterology 1999, 116, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoni, G.; Navone, R.; Lunardi, C.; Tridente, G.; Bason, C.; Sivori, S.; Beri, R.; Dolcino, M.; Valletta, E.; Corrocher, R.; et al. In celiac disease, a subset of autoantibodies against transglutaminase binds toll-like receptor 4 and induces activation of monocytes. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolella, G.; Caputo, I.; Marabotti, A.; Lepretti, M.; Salzano, A.M.; Scaloni, A.; Vitale, M.; Zambrano, N.; Sblattero, D.; Esposito, C. Celiac anti-type 2 transglutaminase antibodies induce phosphoproteome modification in intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, I.; Lepretti, M.; Secondo, A.; Martucciello, S.; Paolella, G.; Sblattero, D.; Barone, M.V.; Esposito, C. Anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies activate intracellular tissue transglutaminase by modulating cytosolic Ca2+ homeostasis. Amino Acids 2013, 44, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalliokoski, S.; Sulic, A.M.; Korponay-Szabó, I.R.; Szondy, Z.; Frias, R.; Perez, M.A.; Martucciello, S.; Roivainen, A.; Pelliniemi, L.J.; Esposito, C.; et al. Celiac disease-specific TG2-targeted auto-antibodies inhibit angiogenesis ex vivo and in vivo in mice by interfering with endothelial cell dynamics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalliokoski, S.; Piqueras, V.O.; Frías, R.; Sulic, A.M.; Määttä, J.A.; Kähkönen, N.; Viiri, K.; Huhtala, H.; Pasternack, A.; Laurila, K.; et al. Transglutaminase 2-specific coeliac disease auto-antibodies induce morphological changes and signs of inflammation in the small-bowel mucosa of mice. Amino Acids 2017, 49, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscolo, S.; Lorenzon, A.; Sblattero, D.; Florian, F.; Stebel, M.; Marzari, R.; Not, T.; Aeschlimann, D.; Ventura, A.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; et al. Anti transglutaminase antibodies cause ataxia in mice. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zone, J.J.; Schmidt, L.A.; Taylor, T.B.; Hull, C.M.; Sotiriou, M.C.; Jaskowski, T.D.; Hill, H.R.; Meyer, L.J. Dermatitis herpetiformis sera or goat anti-transglutaminase-3 transferred to human skin-grafted mice mimics dermatitis herpetiformis immunopathology. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 4474–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglia, S.; Ferrara, F.; De Leo, L.; Ziberna, F.; Vatta, S.; Marchiò, S.; Sblattero, D.; Ventura, A.; Not, T. A functional idiotype/anti-idiotype network is active in genetically gluten-intolerant individuals negative for both celiac disease-related intestinal damage and serum autoantibodies. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, I.; Barone, M.V.; Lepretti, M.; Martucciello, S.; Nista, I.; Troncone, R.; Auricchio, S.; Sblattero, D.; Esposito, C. Celiac anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies interfere with the uptake of alpha gliadin peptide 31–43 but not of peptide 57–68 by epithelial cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barone, M.V.; Gimigliano, A.; Castoria, G.; Paolella, G.; Maurano, F.; Paparo, F.; Maglio, M.; Mineo, A.; Miele, E.; Nanayakkara, M.; et al. Growth factor-like activity of gliadin, an alimentary protein: Implications for coeliac disease. Gut 2007, 56, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, I.; Secondo, A.; Lepretti, M.; Paolella, G.; Auricchio, S.; Barone, M.V.; Esposito, C. Gliadin peptides induce tissue transglutaminase activation and ER-stress through Ca2+ mobilization in Caco-2 cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauhavirta, T.; Qiao, S.W.; Jiang, Z.; Myrsky, E.; Loponen, J.; Korponay-Szabó, I.R.; Salovaara, H.; Garcia-Horsman, J.A.; Venäläinen, J.; Männistö, P.T.; et al. Epithelial transport and deamidation of gliadin peptides: A role for coeliac disease patient immunoglobulin A. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 164, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolella, G.; Lepretti, M.; Martucciello, S.; Nanayakkara, M.; Auricchio, S.; Esposito, C.; Barone, M.V.; Caputo, I. The toxic alpha-gliadin peptide 31-43 enters cells without a surface membrane receptor. Cell. Biol. Int. 2018, 42, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolella, G.; Lepretti, M.; Barone, M.V.; Nanayakkara, M.; Di Zenzo, M.; Sblattero, D.; Auricchio, S.; Esposito, C.; Caputo, I. Celiac anti-type 2 transglutaminase antibodies induce differential effects in fibroblasts from celiac disease patients and from healthy subjects. Amino Acids 2017, 49, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, M.S.; Mooney, P.D.; White, W.L.; Rees, M.A.; Wong, S.H.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Green, P.H.R.; Lebwohl, B.; Sanders, D.S. Office-Based Point of Care Testing (IgA/IgG-Deamidated Gliadin Peptide) for Celiac Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 3, 1238–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husby, S.; Koletzko, S.; Korponay-Szabó, I.; Kurppa, K.; Mearin, M.L.; Ribes-Koninckx, C.; Shamir, R.; Troncone, R.; Auricchio, R.; Castillejo, G.; et al. European Society Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Guidelines for Diagnosing Coeliac Disease 2020. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 70, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maglio, M.; Troncone, R. Intestinal Anti-tissue Transglutaminase2 Autoantibodies: Pathogenic and Clinical Implications for Celiac Disease. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, M.; Donat, E.; Masip, E.; Ballester, V.; Gómez, I.; San Felix, M.; Ramos, D.; Calvo-Lerma, J.; Giner-Pérez, L.; Bolonio, M.; et al. Intestinal anti-tissue transglutaminase IgA deposits as a complementary method for the diagnostic evaluation of celiac disease in patients with low-grade histological lesions. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2022, 207, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, M.; Maglio, M.; Korponay-Szabó, I.R.; Vass, V.; Mearin, M.L.; Meijer, C.; Niv-Drori, H.; Ribes-Koninckx, C.; Roca, M.; Shamir, R.; et al. Intestinal anti-transglutaminase 2 immunoglobulin A deposits in children at risk for coeliac disease (CD): Data from the PreventCD study. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2018, 191, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, M.; Maglio, M.; Agnese, M.; Paparo, F.; Gentile, S.; Colicchio, B.; Tosco, A.; Auricchio, R.; Troncone, R. High density of intraepithelial gammadelta lymphocytes and deposits of immunoglobulin (Ig)M anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies in the jejunum of coeliac patients with IgA deficiency. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2010, 160, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.N.; Kim, S.J. Dermatitis Herpetiformis: An Update on Diagnosis, Disease Monitoring, and Management. Medicina 2021, 57, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zis, P.; Rao, D.G.; Sarrigiannis, P.G.; Aeschlimann, P.; Aeschlimann, D.P.; Sanders, D.; Grünewald, R.A.; Hadjivassiliou, M. Transglutaminase 6 antibodies in gluten neuropathy. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, C.; Caputo, I.; Troncone, R. New therapeutic strategies for coeliac disease: Tissue transglutaminase as a target. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 2572–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molberg, O.; McAdam, S.; Lundin, K.E.; Kristiansen, C.; Arentz-Hansen, H.; Kett, K.; Sollid, L.M. T cells from celiac disease lesions recognize gliadin epitopes deamidated in situ by endogenous tissue transglutaminase. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauhavirta, T.; Oittinen, M.; Kivistö, R.; Männistö, P.T.; Garcia-Horsman, J.A.; Wang, Z.; Griffin, M.; Mäki, M.; Kaukinen, K.; Lindfors, K. Are transglutaminase 2 inhibitors able to reduce gliadin-induced toxicity related to celiac disease? A proof-of-concept study. J. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 33, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausch, F.; Halttunen, T.; Mäki, M.; Khosla, C. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of gluten peptide analogs as selective inhibitors of human tissue transglutaminase. Chem. Biol. 2003, 10, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, R.E.; Siegel, M.; Khosla, C. Structure-activity relationship analysis of the selective inhibition of transglutaminase 2 by dihydroisoxazoles. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 7493–7501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöck, C.; Herrera, Z.; Albertelli, M.; Khosla, C. Discovery of potent and specific dihydroisoxazole inhibitors of human transglutaminase 2. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 9042–9064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, N.M.R.; Gates, E.W.J.; Firoozi, N.; Cundy, N.J.; Leccese, J.; Eisinga, S.; Tyndall, J.D.A.; Adhikary, G.; Eckert, R.L.; Keillor, J.W. Structure-activity relationships of N-terminal variants of peptidomimetic tissue transglutaminase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 232, 114172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafik, L.; Albertelli, M.; Stamnaes, J.; Sollid, L.M.; Khosla, C. Activation and inhibition of transglutaminase 2 in mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, M.A.E.; Sajko, K.; Hils, M.; Pasternack, R.; Greinwald, R.; Tewes, B.; Schuppan, D. The oral transglutaminase 2 (TG2) inhibitor Zed1227 blocks TG2 activity in a mouse model of intestinal inflammation. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 31861–31864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büchold, C.; Hils, M.; Gerlach, U.; Weber, J.; Pelzer, C.; Heil, A.; Aeschlimann, D.; Pasternack, R. Features of ZED1227: The First-In-Class Tissue Transglutaminase Inhibitor Undergoing Clinical Evaluation for the Treatment of Celiac Disease. Cells 2022, 11, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadie, V.; Kim, S.M.; Lejeune, T.; Palanski, B.A.; Ernest, J.D.; Tastet, O.; Voisine, J.; Discepolo, V.; Marietta, E.V.; Hawash, M.B.F.; et al. IL-15, gluten and HLA-DQ8 drive tissue destruction in coeliac disease. Nature 2020, 578, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maamra, M.; Benayad, O.M.; Matthews, D.; Kettleborough, C.; Atkinson, J.; Cain, K.; Bon, H.; Brand, H.; Parkinson, M.; Watson, P.F.; et al. Transglutaminase 2: Development of therapeutic antibodies reveals four inhibitory epitopes and confirms extracellular function in fibrotic remodelling. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 179, 2697–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuppan, D.; Mäki, M.; Lundin, K.E.A.; Isola, J.; Friesing-Sosnik, T.; Taavela, J.; Popp, A.; Koskenpato, J.; Langhorst, J.; Hovde, Ø.; et al. A Randomized Trial of a Transglutaminase 2 Inhibitor for Celiac Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pultz, I.S.; Hill, M.; Vitanza, J.M.; Wolf, C.; Saaby, L.; Liu, T.; Winkle, P.; Leffler, D.A. Gluten degradation, pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of TAK-062, an engineered enzyme to treat celiac disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 81–93.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treppiccione, L.; Picarelli, A.; Rossi, M. Beneficial Role of Microbial Transglutaminase in the Pathogenetic Mechanisms of Coeliac Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2022, 74, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leszczyńska, J.; Łącka, A.; Bryszewska, M. The use of transglutaminase in the reduction of immunoreactivity of wheat flour. Food Agric. Immunol. 2007, 17, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianfrani, C.; Siciliano, R.A.; Facchiano, A.M.; Camarca, A.; Mazzeo, M.F.; Costantini, S.; Salvati, V.M.; Maurano, F.; Mazzarella, G.; Iaquinto, G.; et al. Transamidation of wheat flour inhibits the response to gliadin of intestinal T cells in celiac disease. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elli, L.; Roncoroni, L.; Hils, M.; Pasternack, R.; Barisani, D.; Terrani, C.; Vaira, V.; Ferrero, S.; Bardella, M.T. Immunological effects of transglutaminase-treated gluten in coeliac disease. Hum. Immunol. 2012, 73, 992–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, M.; Nunes, F.M.; Guedes, S.; Domingues, P.; Silva, A.M.; Carrillo, J.M.; Rodriguez-Quijano, M.; Branlard, G.; Igrejas, G. Efficient chemo-enzymatic gluten detoxification: Reducing toxic epitopes for celiac patients improving functional properties. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzeo, M.F.; Bonavita, R.; Maurano, F.; Bergamo, P.; Siciliano, R.A.; Rossi, M. Biochemical modifications of gliadins induced by microbial transglutaminase on wheat flour. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 5166–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, E.; Maurano, F.; Bergamo, P.; Bozzella, G.; Luongo, D.; Mazzarella, G.; Capobianco, F.; Rotondi Aufiero, V.; Iaquinto, G.; Rossi, M. Selective inhibition of gliadin immune reactivity by transamidation of wheat flour with microbial transglutaminase. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 93, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, S.; Giordano, D.; Mazzeo, M.F.; Maurano, F.; Luongo, D.; Facchiano, A.; Siciliano, R.A.; Rossi, M. Transamidation Down-Regulates Intestinal Immunity of Recombinant α-Gliadin in HLA-DQ8 Transgenic Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, M.; Casale, R.; Borghini, R.; Di Nardi, S.; Donato, G.; Angeloni, A.; Moscaritolo, S.; Grasso, L.; Mazzarella, G.; Di Tola, M.; et al. The effects of modified versus unmodified wheat gluten administration in patients with celiac disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 47, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzarella, G.; Salvati, V.M.; Iaquinto, G.; Stefanile, R.; Capobianco, F.; Luongo, D.; Bergamo, P.; Maurano, F.; Giardullo, N.; Malamisura, B.; et al. Reintroduction of gluten following flour transamidation in adult celiac patients: A randomized, controlled clinical study. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 329150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene Name | Protein Name | Localisation | Biological Functions |
|---|---|---|---|
| TGM1 | keratinocyte or type 1 TG (TG1) | keratinocytes (cytosol and plasma membrane) | cornified envelope formation |
| TGM2 | tissue or type 2 TG (TG2) | ubiquitarian (cytosol, nucleus, membranes, mitochondria, ECM) | signalling, differentiation, apoptosis, ECM stabilisation, tissue repair |
| TGM3 | epidermal or type 3 TG (TG3) | epidermal cells and hair follicles (cytosol) | cornified envelope formation |
| TGM4 | prostate or type 4 TG (TG4) | prostate and prostatic fluids (secreted) | semen coagulation |
| TGM5 | type 5 TG (TG5) or TGx | mainly in epithelial and skeletal muscle cells (cytosol) | cornified envelope formation |
| TGM6 | type 6 TG (TG6) or TGy | nervous, lung and testis cells | nervous system development |
| TGM7 | type 7 TG (TG7) or TGz | quite ubiquitarian, mainly in lung and testis cells | unknown |
| FXIIIA1 | plasma TG or Factor XIIIa | mainly in macrophages and platelets (extracellular) | blood clotting, tissue repair |
| EPB42 | band 4.2 (B4.2) or erythrocyte membrane protein B4.2 | mainly in erythrocytes (surface membrane bound) | structural, in plasma membrane |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paolella, G.; Sposito, S.; Romanelli, A.M.; Caputo, I. Type 2 Transglutaminase in Coeliac Disease: A Key Player in Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147513
Paolella G, Sposito S, Romanelli AM, Caputo I. Type 2 Transglutaminase in Coeliac Disease: A Key Player in Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(14):7513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147513
Chicago/Turabian StylePaolella, Gaetana, Silvia Sposito, Antonio Massimiliano Romanelli, and Ivana Caputo. 2022. "Type 2 Transglutaminase in Coeliac Disease: A Key Player in Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Therapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 14: 7513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147513
APA StylePaolella, G., Sposito, S., Romanelli, A. M., & Caputo, I. (2022). Type 2 Transglutaminase in Coeliac Disease: A Key Player in Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(14), 7513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147513






