Bone-Targeting Nanoparticles of a Dendritic (Aspartic acid)3-Functionalized PEG-PLGA Biopolymer Encapsulating Simvastatin for the Treatment of Osteoporosis in Rat Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification of dAsp3-PEG-PLGA and PEG-PLGA
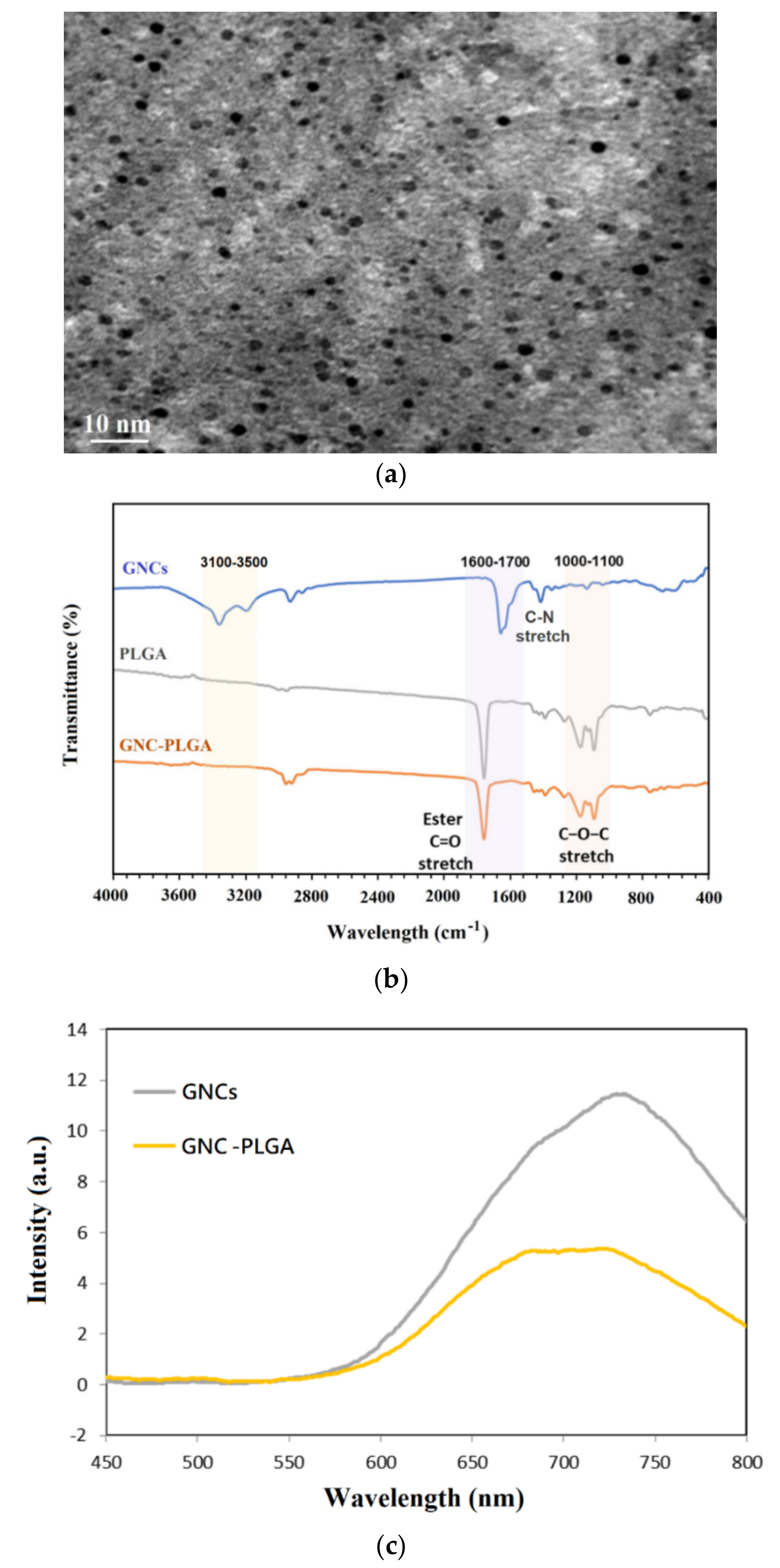
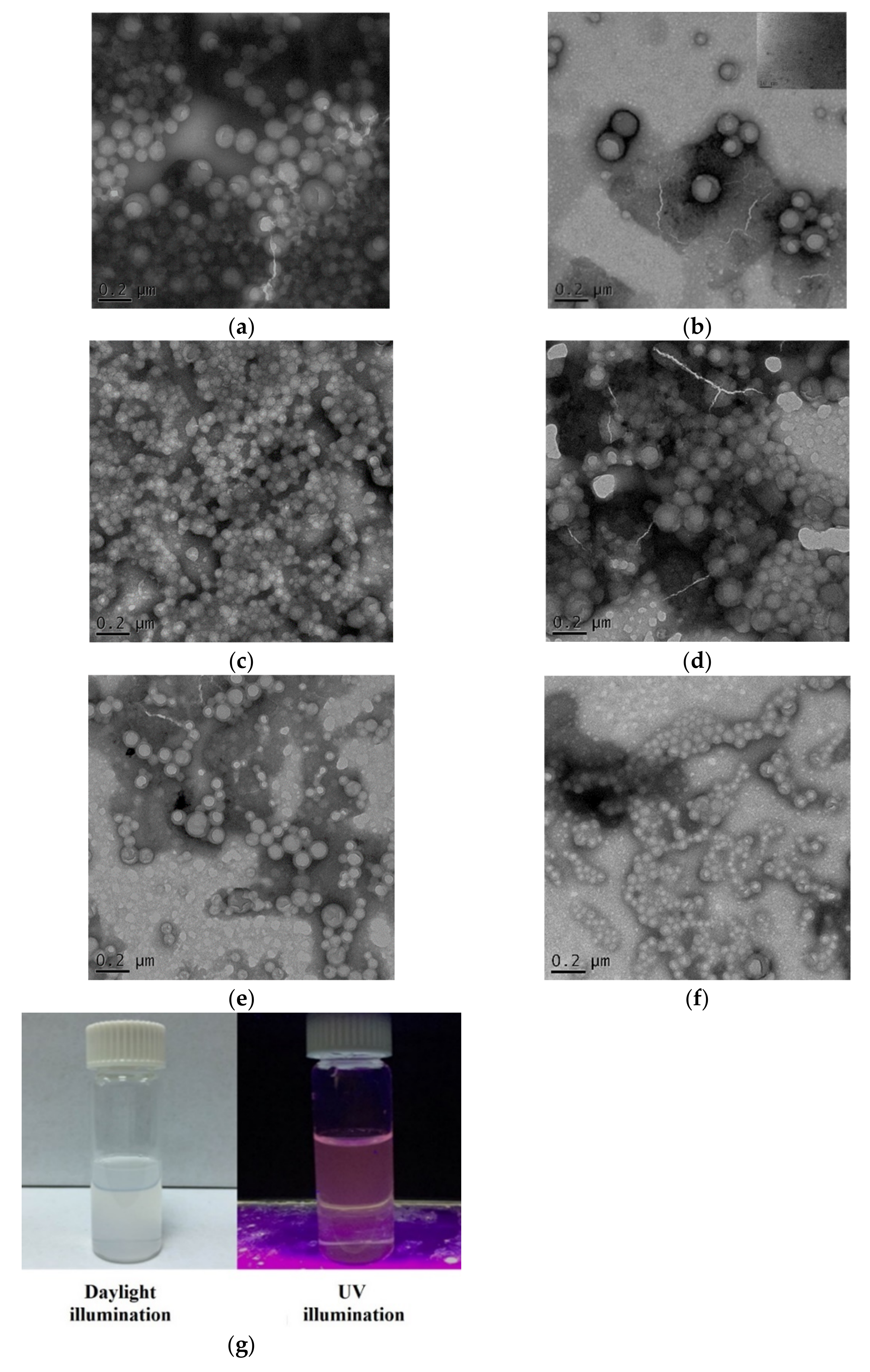
2.2. Evaluation of GNCs and GNC Coupling with PLGA
2.3. Characterization of the Fluorescent NPs
2.4. Characterization of the SIM-Loaded APP NPs and PP NPs
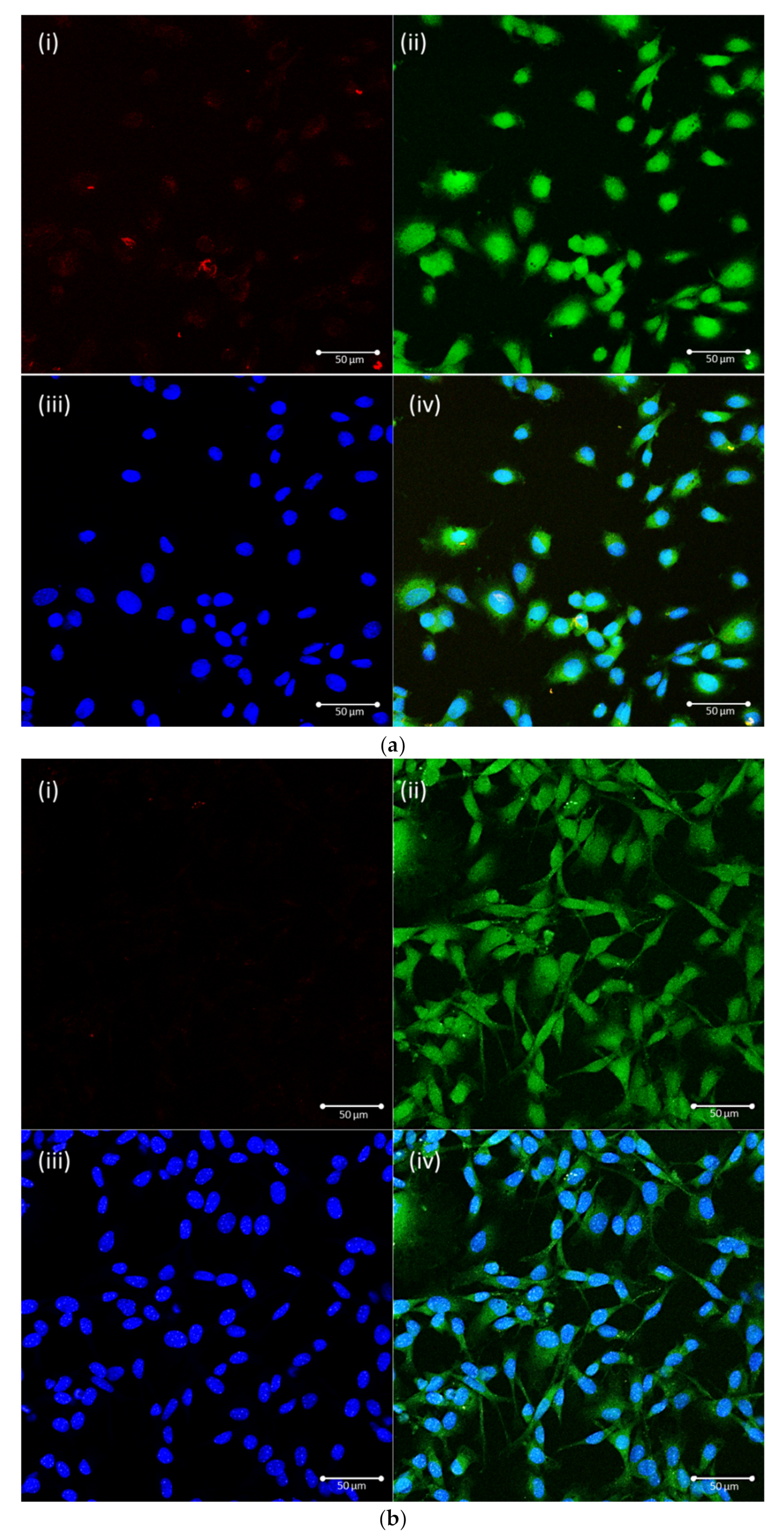
2.5. Evaluation of the Cellular Uptake Pathway
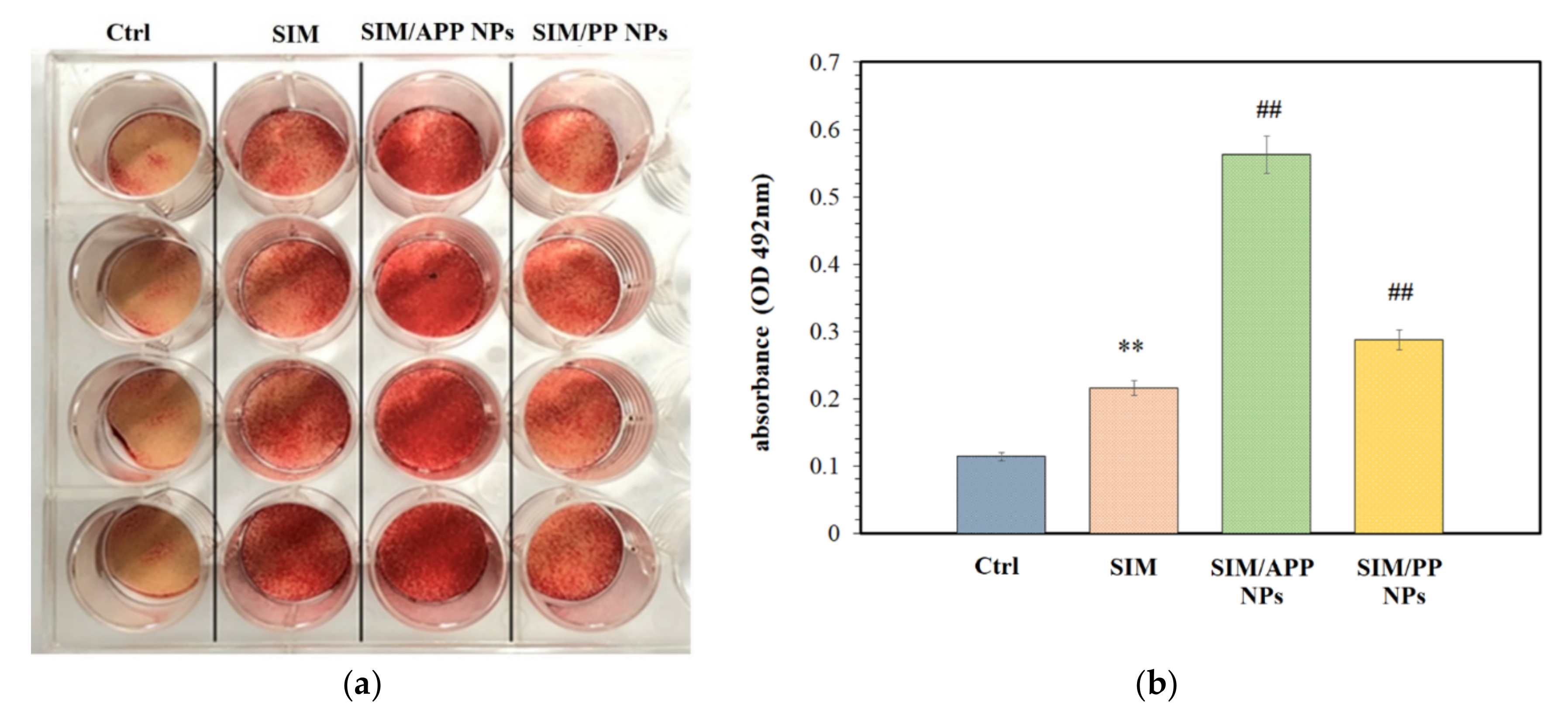
2.6. Effects of the Formation of Mineralized Nodules
2.7. In Vivo Distribution Assay in Rats
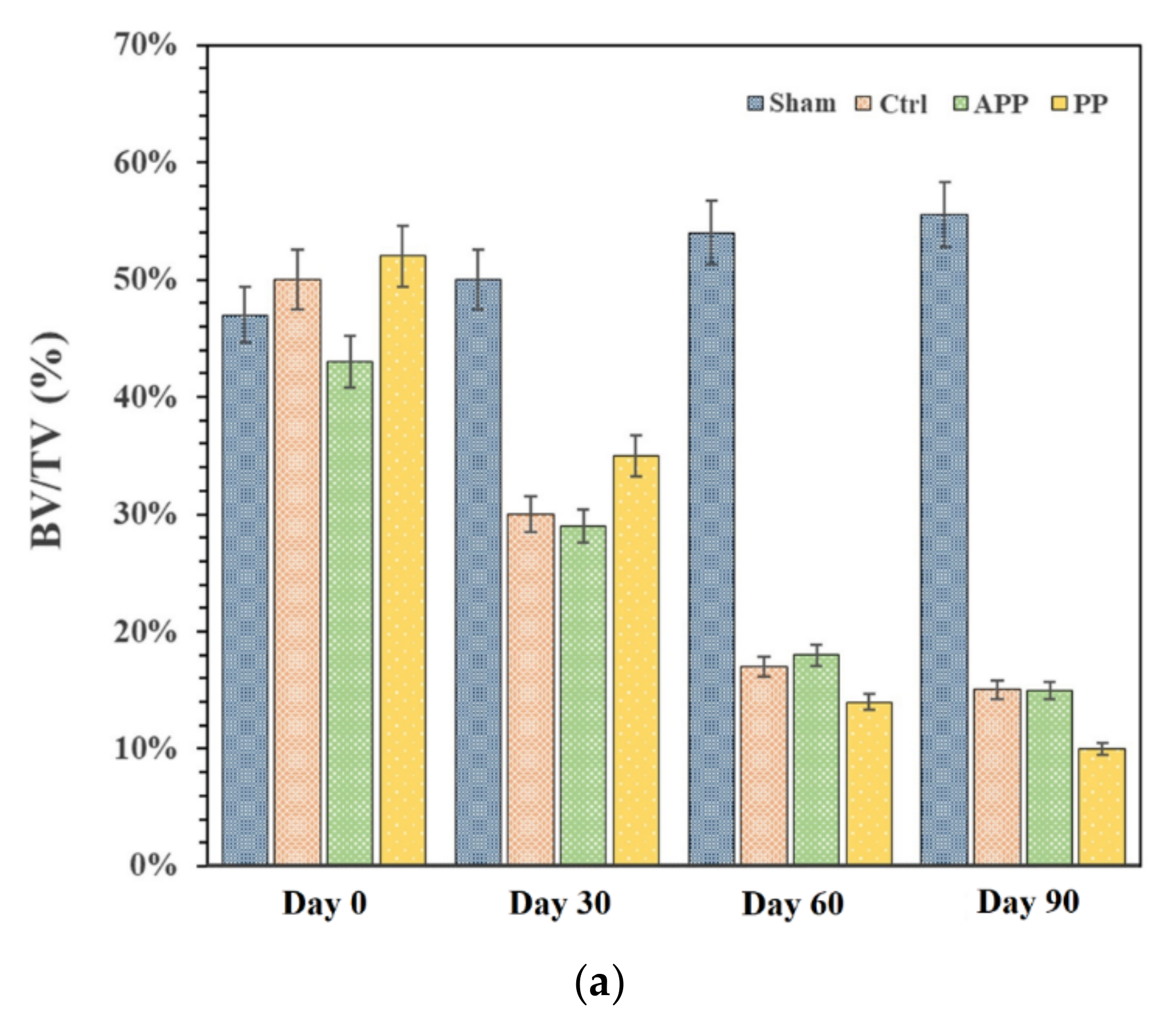
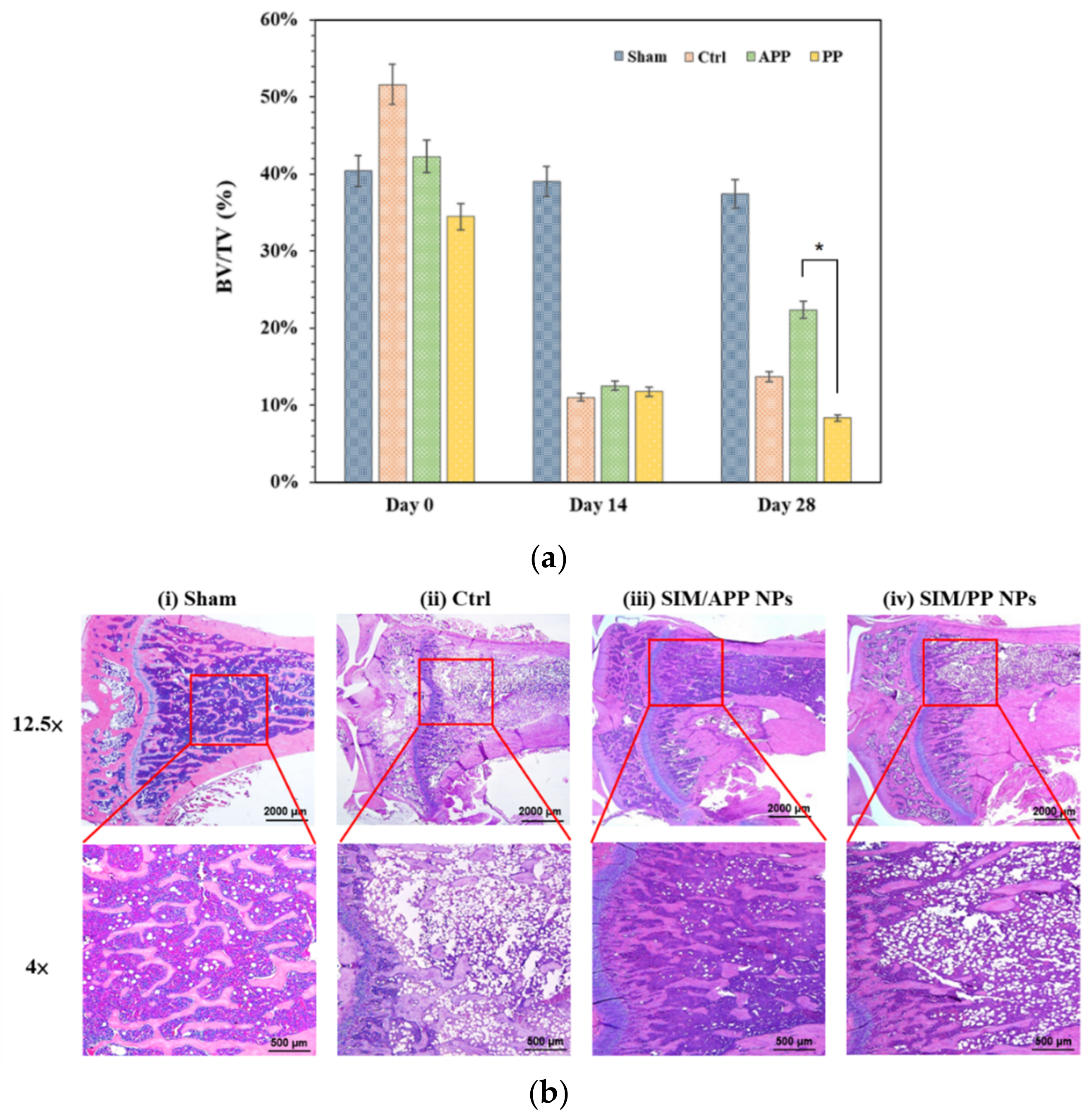
2.8. In Vivo Experiments with OPs Models in Rats
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of dAsp3-PEG-PLGA and PEG-PLGA
3.3. Preparation of GNCs, Florescence NPs, and SIM NPs
3.4. Cell Culture and Related Evaluations
3.4.1. Cellular Uptake Pathway Study
3.4.2. In Vitro Analysis of SIM NPs on the Formation of Mineralized Nodules
3.5. In Vivo Distribution Assay and OP Treatment Models in Rats
3.5.1. In Vivo Distribution Assay of GNC-PLGA/APP NPs and GNC-PLGA/PP NPs in Rats
3.5.2. In Vivo Experiments with Rat OP Models
3.5.3. Postmenopausal OP
3.5.4. Disuse OP
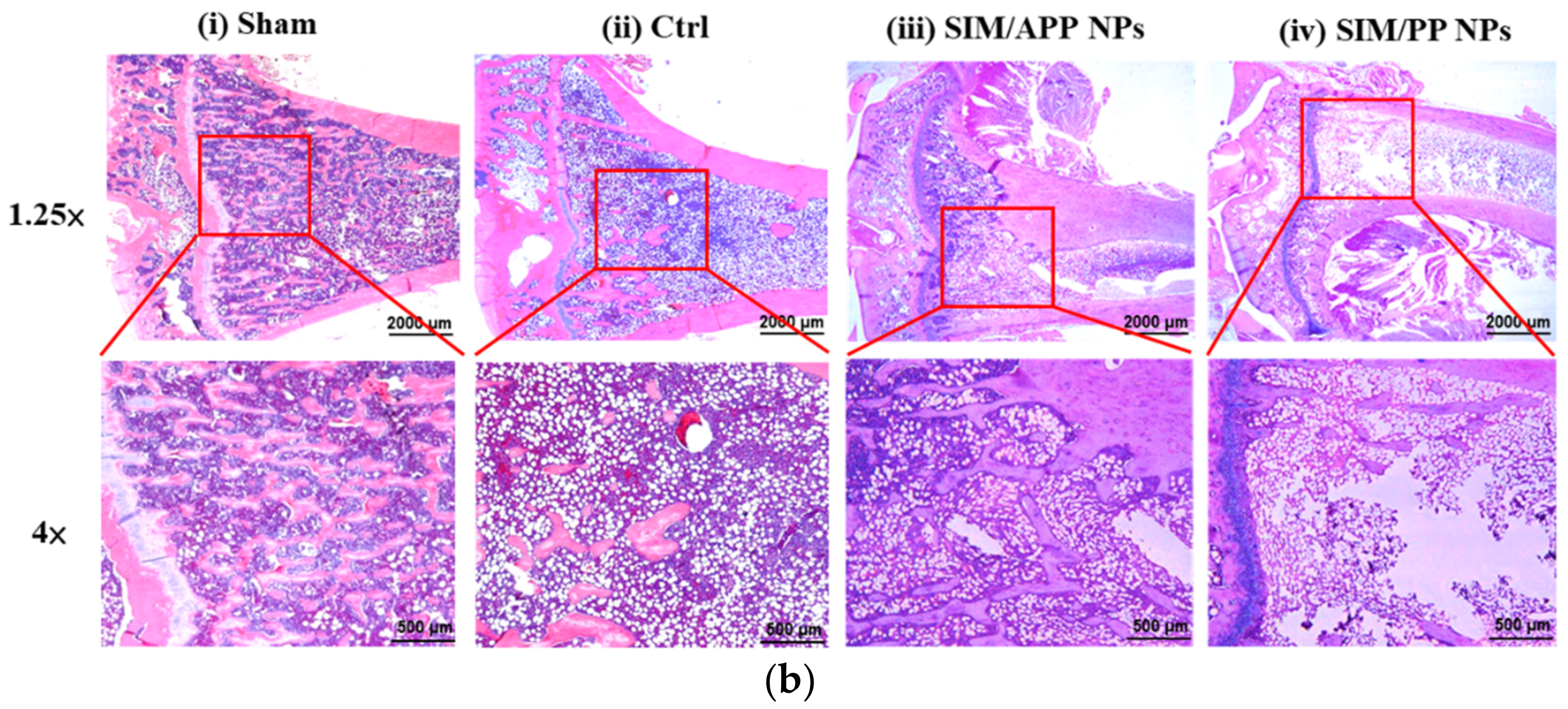
3.6. Histological Analysis of Bone Tissue
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, X.; Mcdonald, J.M. Disorders of Bone Remodeling. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2011, 6, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melton, L.J.; Cooper, C. Magnitude and Impact of Osteoporotic Fractures. In Osteoporosis, 2nd ed.; Marcus, R., Feldman, D., Kelsey, J., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Fuggle, N.R.; Curtis, E.M.; Ward, K.A.; Harvey, N.C.; Dennison, E.M.; Cooper, C. Fracture Prediction, Imaging and Screening in Osteoporosis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luhmann, T.; Germershaus, O.; Groll, J.; Meinel, L. Bone Targeting for the Treatment of Osteoporosis. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernlund, E.; Svedbom, A.; Ivergård, M.; Compston, J.; Cooper, C.; Stenmark, J.; Mccloskey, E.V.; Jönsson, B.; Kanis, J.A. Osteoporosis in the European Union: Medical Management, Epidemiology and Economic Burden. Arch. Osteoporos. 2013, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Cornelissen, D.; Silverman, S.; Pinto, D.; Si, L.; Kremer, I.; Bours, S.; de Bot, R.; Boonen, A.; Evers, S.; et al. An Updated Systematic Review of Cost-Effectiveness Analyses of Drugs for Osteoporosis. Pharmacoeconomics 2021, 39, 181–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, P. Overview of Osteoporosis. Orthop. Rheumatol. Open Access J. 2017, 5, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, R.J.; Gazit, D.; Kahn, A.J.; Gruber, H.; McDougall, S.; Hahn, T.J. Age-Related Changes in Osteogenic Stem Cells in Mice. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1996, 11, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, B.L.; Melton, L.J., 3rd. Evidence for Two Distinct Syndromes of Involutional Osteoporosis. Am. J. Med. 1983, 75, 899–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, A.H.; Murray, I.R. Main Differences in Osteoporotic Fracture Models: Which Should I Use? Injury 2016, 47, S15–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, R.Y.-C.; Guo, X. A Review on Current Osteoporosis Research: With Special Focus on Disuse Bone Loss. J. Osteoporos. 2011, 2011, 293808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A. Coding for Bone Diseases. Record 2011, 23, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Laib, A.; Barou, O.; Vico, L.; Lafage-Proust, M.; Alexandre, C.; Rügsegger, P. 3D Micro-Computed Tomography of Trabecular and Cortical Bone Architecture with Application to a Rat Model of Immobilisation Osteoporosis. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2000, 38, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klibanski, A.; Adams-Campbell, L.; Bassford, T.; Blair, S.N.; Boden, S.D.; Dickersin, K.; Gifford, D.R.; Glasse, L.; Goldring, S.R.; Hruska, K. Osteoporosis Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapy. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2001, 285, 785–795. [Google Scholar]
- Sheweita, S. Calcium Metabolism and Oxidative Stress in Bone Fractures: Role of Antioxidants. Curr. Drug Metab. 2007, 8, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marie, P.J. Strontium Ranelate: A Physiological Approach for Optimizing Bone Formation and Resorption. Bone 2006, 38 (Suppl. S1), 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodsman, A.B.; Bauer, D.C.; Dempster, D.W.; Dian, L.; Hanley, D.A.; Harris, S.T.; Kendler, D.L.; McClung, M.R.; Miller, P.D.; Olszynski, W.P.; et al. Parathyroid Hormone and Teriparatide for the Treatment of Osteoporosis: A Review of the Evidence and Suggested Guidelines for Its Use. Endocr. Rev. 2005, 26, 688–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundy, G.; Garrett, R.; Harris, S.; Chan, J.; Chen, D.; Rossini, G.; Boyce, B.; Zhao, M.; Gutierrez, G. Stimulation of Bone Formation In Vitro and in Rodents by Statins. Science 1999, 286, 1946–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, M.; Otsuka, F.; Mukai, T.; Otani, H.; Inagaki, K.; Miyoshi, T.; Goto, J.; Yamamura, M.; Makino, H. Simvastatin Antagonizes Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Inhibition of Bone Morphogenetic Proteins-2-Induced Osteoblast Differentiation by Regulating Smad Signaling and Ras/Rho-Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 196, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Z.; Fu, Y.-C.; Jian, S.-C.; Wang, Y.-H.; Liu, P.-L.; Ho, M.-L.; Wang, C.-K. Synthesis and Characterization of Cationic Polymeric Nanoparticles as Simvastatin Carriers for Enhancing the Osteogenesis of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2014, 432, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Z.; Wang, Y.-H.; Lin, C.-W.; Lee, T.-C.; Fu, Y.-C.; Ho, M.-L.; Wang, C.-K. Combination of a Bioceramic Scaffold and Simvastatin Nanoparticles as a Synthetic Alternative to Autologous Bone Grafting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, A.R.; Thorat, M.S. Clinical Effect of Subgingivally Delivered Simvastatin in the Treatment of Patients with Chronic Periodontitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Periodontol. 2010, 81, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oryan, A.; Kamali, A.; Moshiri, A. Potential Mechanisms and Applications of Statins on Osteogenesis: Current Modalities, Conflicts and Future Directions. J. Control. Release 2015, 215, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagnani, A.; Gonnelli, S.; Cepollaro, C.; Pacini, S.; Campagna, M.S.; Franci, M.B.; Lucani, B.; Gennari, C. Effect of Simvastatin Treatment on Bone Mineral Density and Bone Turnover in Hypercholesterolemic Postmenopausal Women: A 1-Year Longitudinal Study. Bone 2003, 32, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Lillard, J.W. Nanoparticle-Based Targeted Drug Delivery. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 86, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, K.; Paliwal, S. A Review on Targeted Drug Delivery: Its Entire Focus on Advanced Therapeutics and Diagnostics. Sch. J. App. Med. Sci. 2014, 2, 328–331. [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan, D.; Anitha, A.; Jayakumar, R.; Chennazhi, K.P. In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Osteoporosis Therapeutic Peptide PTH 1-34 Loaded Pegylated Chitosan Nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 4159–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahana, H.; Khajuria, D.K.; Razdan, R.; Mahapatra, D.R.; Bhat, M.R.; Suresh, S.; Rao, R.R.; Mariappan, L. Improvement in Bone Properties by Using Risedronate Adsorbed Hydroxyapatite Novel Nanoparticle Based Formulation in a Rat Model of Osteoporosis. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Tao, S.; Chai, G.; Wang, J.; Hu, F.-Q.; Yuan, H. Tetracycline-Grafted PLGA Nanoparticles as Bone-Targeting Drug Delivery System. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 5671–5685. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, S.; Chen, S.-Q.; Zhou, W.-T.; Yu, F.-Y.; Bao, L.; Qiu, G.-X.; Qiao, Q.; Hu, F.-Q.; Wang, J.-W.; Yuan, H. Correction: A Novel Biocompatible, Simvastatin-Loaded, Bone-Targeting Lipid Nanocarrier for Treating Osteoporosis More Effectively. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 26699–26700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarbrough, D.K.; Hagerman, E.; Eckert, R.; He, J.; Choi, H.; Cao, N.; Le, K.; Hedger, J.; Qi, F.; Anderson, M. Specific Binding and Mineralization of Calcified Surfaces by Small Peptides. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2010, 86, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.B.; Hartgerink, J.D.; Goepferich, A.; Mikos, A.G. Synthesis and In Vitro Hydroxyapatite Binding of Peptides Conjugated to Calcium-Binding Moieties. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2237–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirian, J.; Tripathi, G.; Kang, H.J.; Lee, B.T. Porous BMP-2 Immobilized PLGA/Glycol Chitosan Scaffold with Enhanced Hydrophilicity, Mineralization and Osteogenesis. Mater. Lett. 2022, 308, 131140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, A.; Makkar, P.; Amirian, J.; Lee, B.T. A Novel Hybrid Multichannel Biphasic Calcium Phosphate Granule-Based Composite Scaffold for Cartilage Tissue Regeneration. J. Biomater. Appl. 2018, 32, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.-C.; Fu, T.-F.; Wang, H.-J.; Lin, C.-W.; Lee, G.-H.; Wu, S.-C.; Wang, C.-K. Aspartic Acid-Based Modified PLGA-PEG Nanoparticles for Bone Targeting: In Vitro and in vivo Evaluation. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 4583–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, I.-C.; Fu, Y.-C.; Wang, C.-K.; Chang, J.-K.; Ho, M.-L. Local Delivery of Controlled-Release Simvastatin/PLGA/HAp Microspheres Enhances Bone Repair. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 3895–3904. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.-C.; Wang, Y.-H.; Huang, S.-H.; Chen, C.-H.; Ho, M.-L.; Fu, Y.-C.; Wang, C.-K. Evaluations of Clinical-Grade Bone Substitute-Combined Simvastatin Carriers to Enhance Bone Growth: In Vitro and In Vivo Analyses. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2018, 33, 160–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.; Singh, B.; Paul, A.; Tyagi, S. Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of Trinitrotoluene Using Cysteine-Capped Gold Nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 4398–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchemin, R.; N’soukpoé-Kossi, C.N.; Thomas, T.J.; Thomas, T.; Carpentier, R.; Tajmir-Riahi, H.A. Polyamine Analogues Bind Human Serum Albumin. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3177–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.T.; Faria, M.; Crampin, E.J. An Analytical Approach for Quantifying the Influence of Nanoparticle Polydispersity on Cellular Delivered Dose. J. R. Soc. Interface 2018, 15, 20180364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, D.E., 3rd; Peppas, N.A. Opsonization, Biodistribution, and Pharmacokinetics of Polymeric Nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 307, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of Nanoparticle Design for Overcoming Biological Barriers to Drug Delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.S.; Liu, W.; Misra, P.; Tanaka, E.; Zimmer, J.P.; Itty Ipe, B.; Bawendi, M.G.; Frangioni, J.V. Renal Clearance of Quantum Dots. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braet, F.; Wisse, E.; Bomans, P.; Frederik, P.; Geerts, W.; Koster, A.; Soon, L.; Ringer, S. Contribution of High-Resolution Correlative Imaging Techniques in the Study of the Liver Sieve in Three-Dimensions. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2007, 70, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.T.; Weiss, L. The Role of the Sinus Wall in the Passage of Erythrocytes through the Spleen. Blood 1973, 41, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexis, F.; Pridgen, E.; Molnar, L.K.; Farokhzad, O.C. Factors Affecting the Clearance and Biodistribution of Polymeric Nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Nagasaki, Y.; Kato, Y.; Sugiyama, Y.; Kataoka, K. Long-Circulating Poly(Ethylene Glycol)-Poly(D,L-Lactide) Block Copolymer Micelles with Modulated Surface Charge. J. Control. Release 2001, 77, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhou, R.; Wu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, R.; Li, X.; Huang, Y. Nanoparticles with Surface Features of Dendritic Oligopeptides as Potential Oral Drug Delivery Systems. J. Mater. Chem. B Mater. Biol. Med. 2020, 8, 2636–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phanse, Y.; Lueth, P.; Ramer-Tait, A.E.; Carrillo-Conde, B.R.; Wannemuehler, M.J.; Narasihan, B.; Bellaire, B.H. Cellular Internalization Mechanisms of Polyanhydride Particles: Implications for Rational Design of Drug Delivery Vehicles. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 1544–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, P.J.; Fromigué, O. Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Regen. Med. 2006, 1, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onak, G.; Şen, M.; Horzum, N.; Ercan, U.K.; Yaralı, Z.B.; Garipcan, B.; Karaman, O. Aspartic and Glutamic Acid Templated Peptides Conjugation on Plasma Modified Nanofibers for Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Comparative Study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A.S.; Beniash, E. Bioinspired Synthesis of Mineralized Collagen Fibrils. Cryst. Growth Des. 2008, 8, 3084–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haute, D.V.; Berlin, J.M. Challenges in Realizing Selectivity for Nanoparticle Biodistribution and Clearance: Lessons from Gold Nanoparticles. Ther. Deliv. 2017, 8, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshiri, A.; Sharifi, A.M.; Oryan, A. Role of Simvastatin on Fracture Healing and Osteoporosis: A Systematic Review on in vivo Investigations. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2016, 43, 659–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, W.; Farmer, R.; Cooper, R.; Chmielewski, P.A.; Tian, X.Y.; Setterberg, R.B.; Jee, W.S.S.; Lundy, M.W. Simvastatin Did Not Prevent nor Restore Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss in Adult Rats. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2006, 6, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ho, M.-L.; Chen, Y.-H.; Liao, H.-J.; Chen, C.-H.; Hung, S.-H.; Lee, M.-J.; Fu, Y.-C.; Wang, Y.-H.; Wang, G.-J.; Chang, J.-K. Simvastatin Increases Osteoblasts and Osteogenic Proteins in Ovariectomized Rats. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 39, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Song, Q.-S.; Wang, J.-Y.; Leng, H.-J.; Chen, Z.-Q.; Liu, Z.-J.; Dang, G.-T.; Song, C.-L. Simvastatin Induces Estrogen Receptor-Alpha Expression in Bone, Restores Bone Loss, and Decreases ERα Expression and Uterine Wet Weight in Ovariectomized Rats. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2011, 29, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milsom, S.; Lin, S.; Cornish, J.; Sharma, S. Disuse Osteoporosis: A Better Understanding of Pathophysiology May Lead to Potential Therapies. J. Diabetol. Endocrinol. 2016, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandre, C.; Vico, L. Pathophysiology of Bone Loss in Disuse Osteoporosis. Jt. Bone Spine 2011, 78, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wronski, T.; Morey-Holton, E. Skeletal Response to Simulated Weightlessness: A Comparison of Suspension Techniques. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 1987, 58, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Libouban, H.; Blouin, S.; Moreau, M.-F.; Baslé, M.F.; Audran, M.; Chappard, D. Effects of Risedronate in a Rat Model of Osteopenia Due to Orchidectomy and Disuse: Densitometric, Histomorphometric and Microtomographic Studies. Micron 2008, 39, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Azadfar, N.; Stockmar, F.; Send, W.; Trouillet, V.; Bruns, M.; Gerthsen, D.; Nienhaus, G.U. One-Pot Synthesis of near-Infrared Fluorescent Gold Clusters for Cellular Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging. Small 2011, 7, 2614–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fessi, H.; Puisieux, F.; Devissaguet, J.P.; Ammoury, N.; Benita, S. Nanocapsule Formation by Interfacial Polymer Deposition Following Solvent Displacement. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 55, R1–R4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Jin, Y.; Shan, W.; Huang, Y. Mechanism Study of Cellular Uptake and Tight Junction Opening Mediated by Goblet Cell-Specific Trimethyl Chitosan Nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 1520–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morey-Holton, E.R.; Globus, R.K. Hindlimb Unloading Rodent Model: Technical Aspects. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 92, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, E.; Souza, F., Jr.; Santana, C.; Soares, D.; Lemos, A.; Menezes, L. Influence of magnetic field on the dissolution profile of cotrimoxazole inserted into poly(lactic acid-co-glycolic acid) and maghemite nanocomposites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2013, 53, 2308–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Nanoparticles (NPs) | APP | GNC-PLGA/APP | PP | GNC-PLGA/PP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average size (nm) | 213.5 | 247.8 | 130.5 | 225.5 |
| Polydispersity index (PDI) | 0.116 | 0.029 | 0.024 | 0.005 |
| SIM Nanocarriers | Average Size (nm) | Polydispersity Index (PDI) | Zeta Potential (mV) | EE% | DL (μg/mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIM/APP NPs | 196.8 | 0.474 | −35.5 ± 1.2 | 72.48% | 0.28 |
| SIM/PP NPs | 103.8 | 0.121 | −25.2 ± 0.5 | 76.29% | 0.31 |
| Animal Model | Treatment Strategy | Dose and Duration | Main Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rat [OVX] | Simvastatin (PO) | 0.3 to 10 mg/kg per day for 60 days | Simvastatin had no role in new bone formation and resorption. | Yao et al., 2006 [57] |
| Rat [OVX] | Simvastatin (PO) | 10 and 20 mg/kg per day for 42 days | Simvastatin increased bone volume, osteoblast number, BMP-2, collagen type I, and osteocalcin. | Ho et al., 2009 [58] |
| Rat [OVX] | Simvastatin (per oral) + 17-b-estradiol (IP) | 5 or 10 mg/kg per day for 42 days | Simvastatin improved lumbar vertebral bone mineral density and mechanical properties. Simvastatin exerted opposing modulatory effects on estrogen receptor-alpha (Erα) expression on bone and uterus in ovariectomized rats. | Li et al., 2011 [59] |
| Rat [OVX] | SIM-loaded TC-PLGA NPs (IV) | 0.5 mg/kg/2 days for 60 days | The SIM-loaded TC-PLGA NPs can improve the curative effects of SIM on the recovery of bone mineral density compared to either SIM-loaded PLGA NPs or SIM alone. | Wang et al., 2015 [29] |
| Rat [OVX] | SIM/ASP6-LNPs (IV) | 1 mg/kg per 2 days for 60 days | SIM/ASP6-LNP nanocarriers can significantly improve the efficacy of SIM in the recovery of bone mineral density when compared with either SIM/LNPs or SIM alone. | Tao et al., 2020 [30] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.-W.; Lee, C.-Y.; Lin, S.-Y.; Kang, L.; Fu, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-H.; Wang, C.-K. Bone-Targeting Nanoparticles of a Dendritic (Aspartic acid)3-Functionalized PEG-PLGA Biopolymer Encapsulating Simvastatin for the Treatment of Osteoporosis in Rat Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10530. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810530
Lin C-W, Lee C-Y, Lin S-Y, Kang L, Fu Y-C, Chen C-H, Wang C-K. Bone-Targeting Nanoparticles of a Dendritic (Aspartic acid)3-Functionalized PEG-PLGA Biopolymer Encapsulating Simvastatin for the Treatment of Osteoporosis in Rat Models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(18):10530. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810530
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Che-Wei, Chih-Yun Lee, Sung-Yen Lin, Lin Kang, Yin-Chih Fu, Chung-Hwan Chen, and Chih-Kuang Wang. 2022. "Bone-Targeting Nanoparticles of a Dendritic (Aspartic acid)3-Functionalized PEG-PLGA Biopolymer Encapsulating Simvastatin for the Treatment of Osteoporosis in Rat Models" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 18: 10530. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810530
APA StyleLin, C.-W., Lee, C.-Y., Lin, S.-Y., Kang, L., Fu, Y.-C., Chen, C.-H., & Wang, C.-K. (2022). Bone-Targeting Nanoparticles of a Dendritic (Aspartic acid)3-Functionalized PEG-PLGA Biopolymer Encapsulating Simvastatin for the Treatment of Osteoporosis in Rat Models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(18), 10530. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810530







