Ligandability Assessment of Human Glutathione Transferase M1-1 Using Pesticides as Chemical Probes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
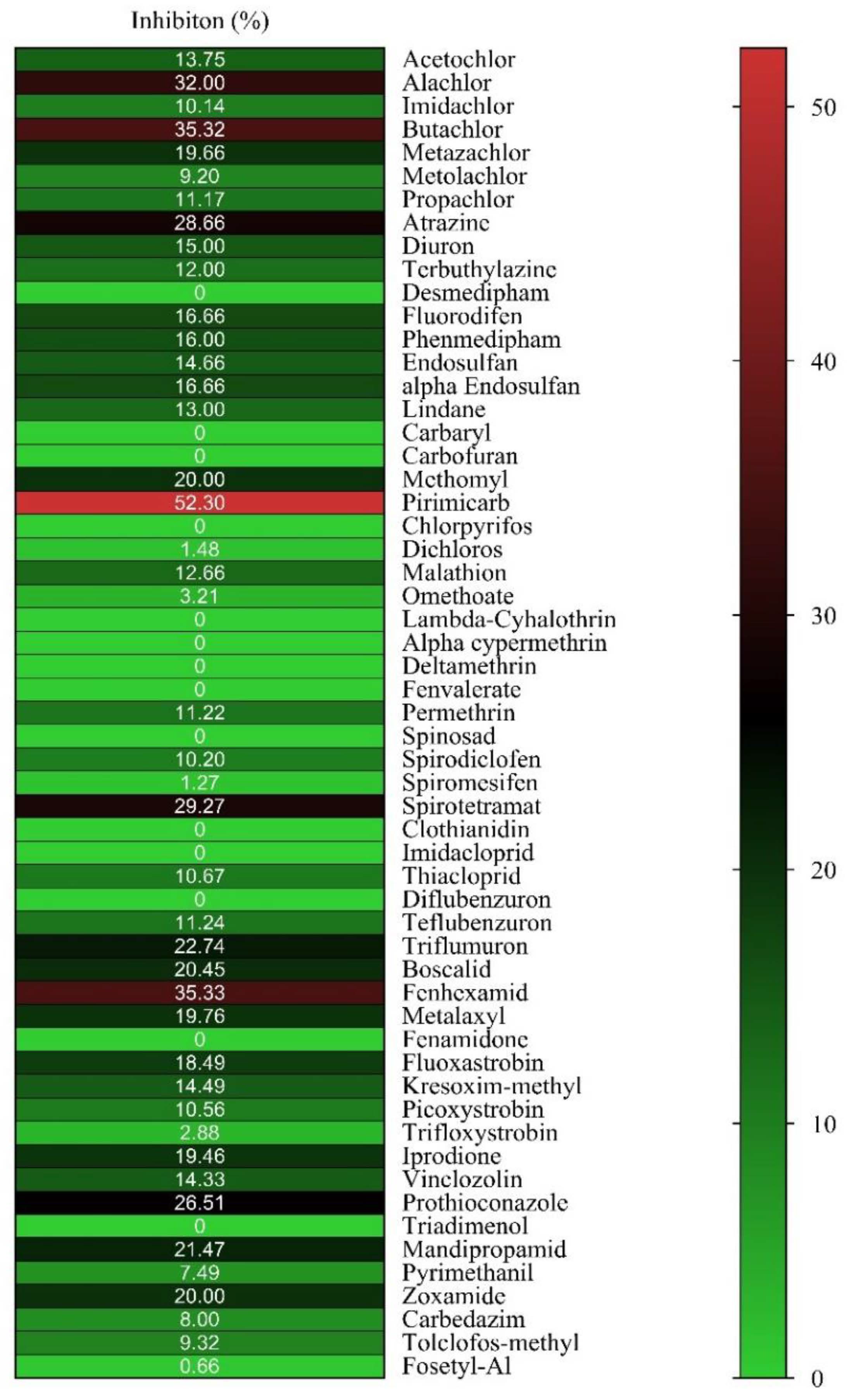
2.1. Ligandability Assessment of hGSTM1-1 by Inhibition Analysis
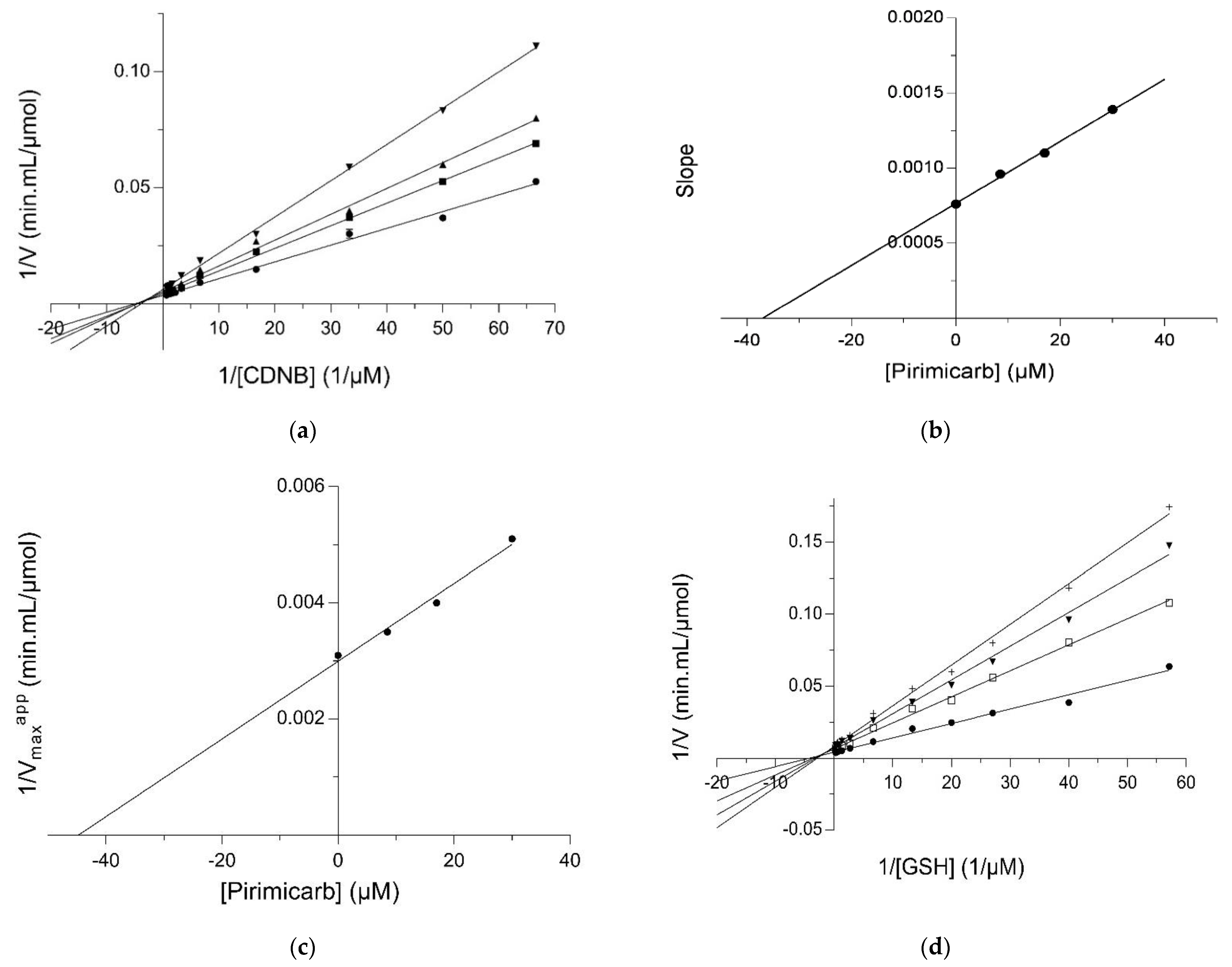
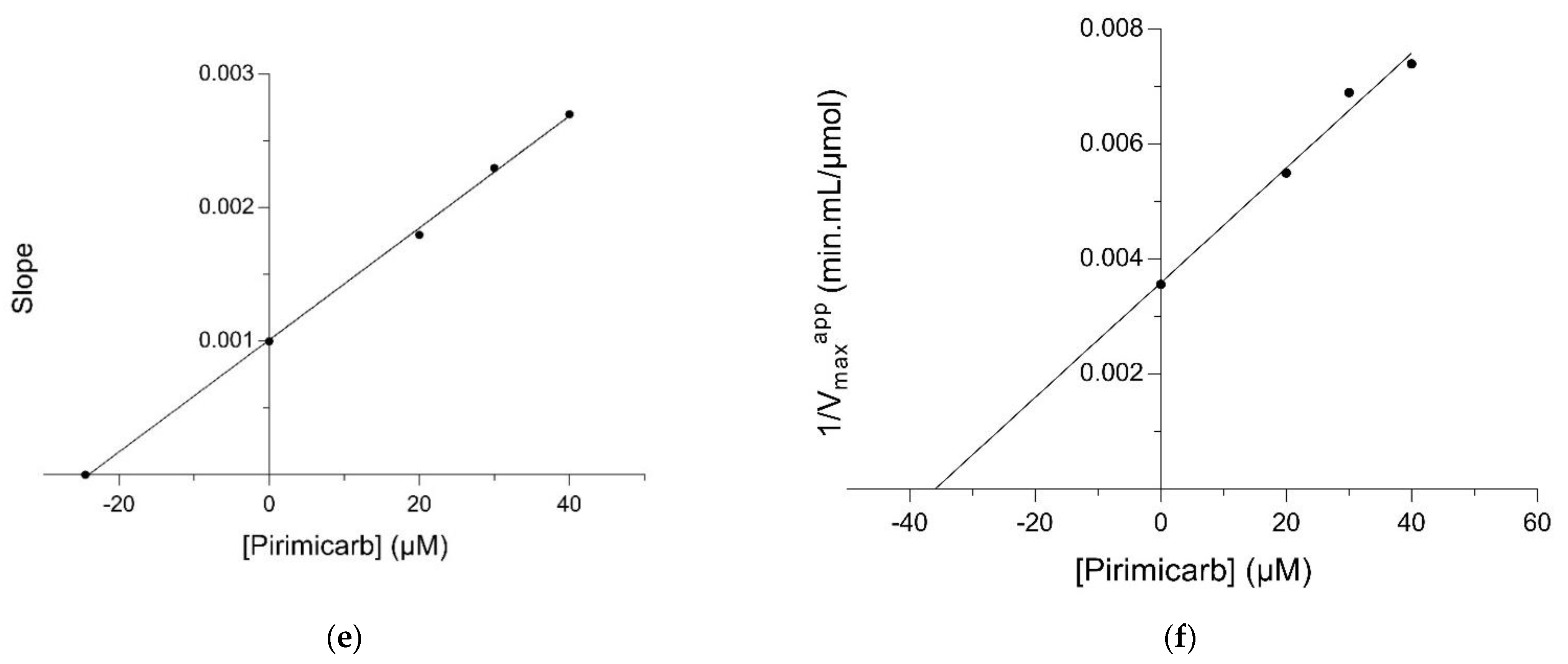
2.2. Kinetic Inhibition Study of the hGSTM1-1 with the Insecticide Pirimicarb
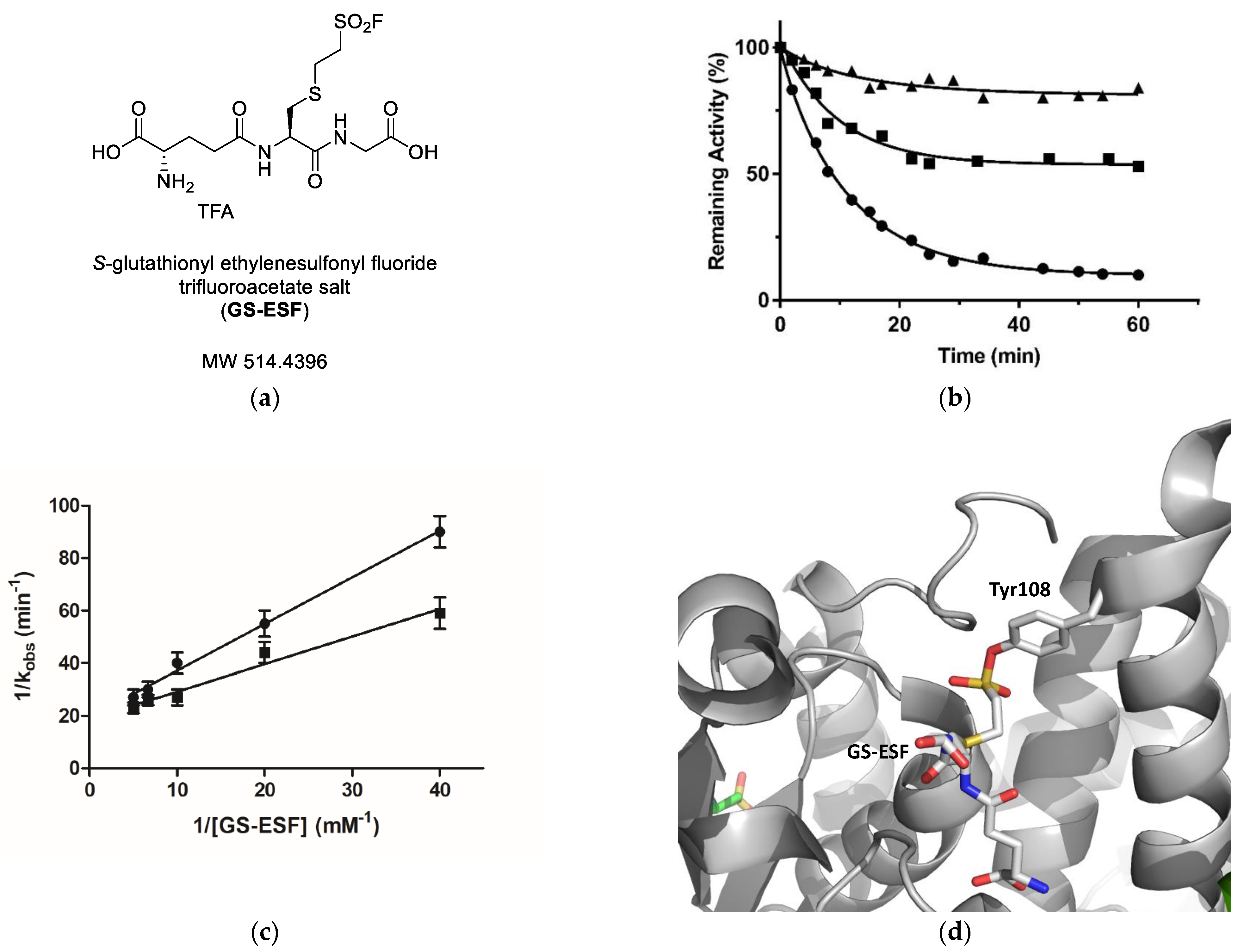
2.3. Irreversible Inactivation of hGSTM1-1 by S-Glutathionyl Ethylenesulfonyl Fluoride (GS-ESF)
2.4. The Crystal Structure of hGSTM1-1
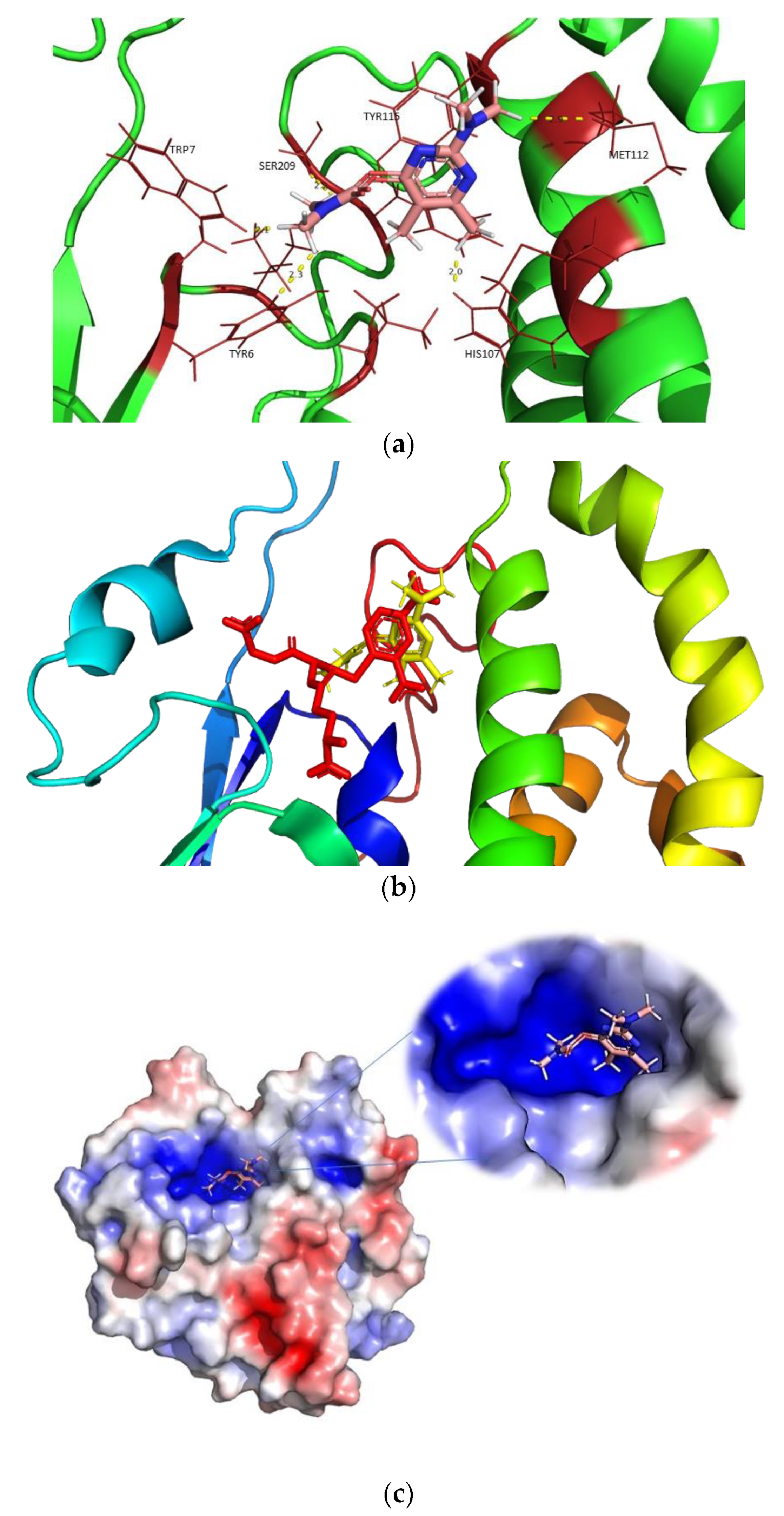
2.5. Prediction of the Pirimicarb Binding Site by Molecular Docking
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Heterologous Expression, Purification of hGSTM1-1 in E. coli and Protein Determination
3.3. Assay of Enzyme Activity and Inhibition Analysis
3.4. Kinetic Inhibition Study with the Insecticide Pirimicarb
3.5. Crystallization and Structure Determination
3.6. Docking of Insecticide Pirimicarb into the hGSTM1-1 Binding Site
3.7. Irreversible Inactivation of hGSTM1-1 by S-glutathionyl Ethylenesulfonyl Fluoride (GS-ESF)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Townsend, D.M.; Tew, K.D. The role of glutathione-S-transferase in anti-cancer drug resistance. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, G.N.; Surapaneni, S. Role of drug metabolism in drug discovery and development. Med. Res. Rev. 2001, 21, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, J.D.; Flanagan, J.U.; Jowsey, I.R. Glutathione Transferases. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2005, 45, 51–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoli, P.; Axarli, I.A.; Platis, D.; Fragoulaki, M.; Paine, M.; Hemingway, J.; Vontas, J.; Labrou, N.E. Engineering sensitive glutathione transferase for the detection of xenobiotics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chronopoulou, E.; Labrou, N. Glutathione Transferases: Emerging Multidisciplinary Tools in Red and Green Biotechnology. Recent Pat. Biotechnol. 2009, 3, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Dong, D. Human cytosolic glutathione transferases: Structure, function, and drug discovery. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 656–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.S.; Kuhnert, D.C.; Sayed, Y.; Dirr, H.W. The intersubunit lock-and-key motif in human glutathione transferase A1-1: Role of the key residues Met51 and Phe52 in function and dimer stability. Biochem. J. 2006, 393, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, Y.; Wallace, L.A.; Dirr, H.W. The hydrophobic lock-and-key intersubunit motif of glutathione transferase A1-1: Implications for catalysis, ligandin function and stability. FEBS Lett. 2000, 465, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossjohn, J.; McKinstry, W.J.; Oakley, A.J.; Verger, D.; Flanagan, J.; Chelvanayagam, G. Human theta class glutathione transferase: The crystal structure reveals a sulfate-binding pocket within a buried active site. Structure 1998, 6, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chronopoulou, E.; Kontouri, K.; Chantzikonstantinou, M.; Pouliou, F.; Perperopoulou, F.; Voulgari, G.; Bosmali, E.; Axarli, I.; Nianiou-Obeidat, I.; Madesis, P.; et al. Plant glutathione transferases: Structure, antioxidant catalytic function and in planta protective role in biotic and abiotic stress. Curr. Chem. Biol. 2014, 8, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pljesa-Ercegovac, M.; Savic-Radojevic, A.; Matic, M.; Coric, V.; Djukic, T.; Radic, T.; Simic, T. Glutathione Transferases: Potential Targets to Overcome Chemoresistance in Solid Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McIlwain, C.C.; Townsend, D.M.; Tew, K.D. Glutathione S-transferase polymorphisms: Cancer incidence and therapy. Oncogene 2006, 25, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albarakati, N.; Khayyat, D.; Dallol, A.; Al-Maghrabi, J.; Nedjadi, T. The prognostic impact of GSTM1/GSTP1 genetic variants in bladder cancer. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tew, K.D.; Manevich, Y.; Grek, C.; Xiong, Y.; Uys, J.; Townsend, D.M. The role of glutathione S-transferase P in signaling pathways and S-glutathionylation in cancer. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Economopoulos, K.P.; Sergentanis, T.N. GSTM1, GSTT1, GSTP1, GSTA1 and colorectal cancer risk: A comprehensive meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 1617–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, L.; Sterzo, C.L.; Pezzola, S.; Di Matteo, A.; Scaloni, F.; Federici, G.; Caccuri, A.M. Structural basis for the binding of the anticancer compound 6-(7-Nitro-2,1,3-Benzoxadiazol-4-Ylthio)hexanol to human glutathione S-transferases. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8025–8034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Lin, L.; Song, G.; Deng, T. GSTM1 Null Genotype and GSTP1 Ile105Val Polymorphism Are Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarian, Z.; Saliminejad, K.; Kamali, K.; Ohadi, M.; Kowsari, A.; Nasehi, L.; Khorram, H.R. Association of glutathione S-transferases M1, P1 and T1 variations and risk of late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol. Res. 2018, 40, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakis, N.D.; Karagiannopoulos, D.A.; Thireou, T.N.; Eliopoulos, E.E.; Labrou, N.E.; Tsoungas, P.G.; Koutsilieris, M.N.; Clonis, Y.D. Concluding the trilogy: The interaction of 2, 2′-dihydroxy-benzophenones and their carbonyl N-analogues with human glutathione transferase M1-1 face to face with the P1-1 and A1-1 isoenzymes involved in MDR. Chem. Biol. Drug. Des. 2017, 90, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Board, P.; Menon, D. Glutathione transferases, regulators of cellular metabolism and physiology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Bioenerg. 2013, 1830, 3267–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppugunduri, C.R.S.; Muthukumaran, J.; Robin, S.; Santos-Silva, T.; Ansari, M. In silico and in vitro investigations on the protein-protein interactions of glutathione S-transferases with mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robin, S.; Ben Hassine, K.; Mlakar, S.J.; Mlakar, V.; Ansari, M.; Uppugunduri, C.R.S. The Catalytic Activity of GSTM1 In vitro is Independent of MAPK8. Drug Metab. Lett. 2021, 14, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, M.; Dutta, S.; Tew, K.D. Inhibitors of glutathione S-transferases as therapeutic agents. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 26, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvoix, A.; Morceau, F.; Delhalle, S.; Schmitz, M.; Schnekenburger, M.; Galteau, M.-M.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Induction of apoptosis by curcumin: Mediation by glutathione S-transferase P1-1 inhibition. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 66, 1475–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqarni, M.H.; Foudah, A.I.; Muharram, M.M.; Labrou, N.E. The Interaction of the Flavonoid Fisetin with Human Glutathione Transferase A1-1. Metabolites 2021, 11, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulaksiz-Erkmen, G.; Dalmizrak, O.; Dincsoy-Tuna, G.; Dogan, A.; Ogus, I.H.; Ozer, N. Amitriptyline may have a supportive role in cancer treatment by inhibiting glutathione S-transferase pi (GST-π) and alpha (GST-α). J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2011, 28, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luisi, G.; Mollica, A.; Carradori, S.; Lenoci, A.; De Luca, A.; Caccuri, A.M. Nitrobenzoxadiazole-based GSTP1-1 inhibitors containing the full peptidyl moiety of (pseudo) glutathione. Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2016, 6, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shishido, Y.; Tomoike, F.; Kuwata, K.; Fujikawa, H.; Sekido, Y.; Murakami-Tonami, Y. A Covalent Inhibitor for Glutathione S-Transferase Pi (GSTP1-1) in Human Cells. ChemBioChem 2019, 20, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpakom, S.; Iorio, F.; Eyers, P.A.; Escott, K.J.; Hopper, S.; Wells, A.; Doig, A.; Guilliams, T.; Latimer, J.; McNamee, C.; et al. Drug repurposing: Progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouliou, F.M.; Thireou, T.N.; Eliopoulos, E.E.; Tsoungas, P.G.; Labrou, N.E.; Clonis, Y.D. Isoenzyme-and Allozyme-Specific Inhibitors: 2, 2′-Dihydroxybenzophenones and Their Carbonyl N-Analogues that Discriminate between Human Glutathione Transferase A1-1 and P1-1 Allozymes. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2015, 86, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perperopoulou, F.D.; Tsoungas, P.G.; Thireou, T.N.; Rinotas, V.E.; Douni, E.K.; Eliopoulos, E.E.; Labrou, N.E.; Clonis, Y.D. 2, 2′-Dihydroxybenzophenones and their carbonyl N-analogues as inhibitor scaffolds for MDR-involved human glutathione transferase isoenzyme A1-1. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 3957–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perperopoulou, F.; Ataya, F.S.; Fouad, D.; Malik, A.; Saeed, H.M.; Labrou, N.E. Biochemical characterization of the detoxifying enzyme glutathione transferase P1-1 from the camel Camelus dromedarius. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 4, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, U.; Breeze, A.L. “Ligandability” of drug targets: Assessment of chemical tractability via experimental and in silico approaches. Lead Generation 2016, 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitz, R.; Wilson, I.B. Esters of methanesulfonic acid as irreversible inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. J. Biol. Chem. 1962, 237, 3245–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralat, L.A.; Manevich, Y.; Fisher, A.B.; Colman, R.F. Direct evidence for the formation of a complex between 1-cysteine peroxiredoxin and glutathione S-transferase π with activity changes in both enzymes. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqarni, M.H.; Foudah, A.I.; Muharram, M.M.; Labrou, N.E. The Interaction of Human Glutathione Transferase GSTA1-1 with Reactive Dyes. Molecules 2021, 26, 2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platis, M.; Vlachakis, D.; Foudah, A.I.; Muharram, M.M.; Alqarni, M.H.; Papageorgiou, A.C.; Labrou, N.E. The interaction of Schistosoma japonicum glutathione transferase with Cibacron blue 3GA and its fragments. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 17, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patskovsky, Y.V.; Patskovska, L.N.; Listowsky, I. Functions of His107 in the catalytic mechanism of human glutathione S-transferase hGSTM1a-1a. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, M.K.; Wu, T.C.; Hsieh, C.H.; Chou, C.C.; Liu, L.F.; Kuan, I.C. Tyr115, gln165 and trp209 contribute to the 1, 2-epoxy-3-(p-nitrophenoxy) propane-conjugating activity of glutathione S-transferaSE CgSTM1-1. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 300, 1257–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearne, J.L.; Colman, R.F. Delineation of xenobiotic substrate sites in rat glutathione S-transferase M1-1. Protein Sci. 2005, 14, 2526–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shishido, Y.; Tomoike, F.; Kimura, Y.; Kuwata, K.; Yano, T.; Fukui, K.; Fujikawa, H.; Sekido, Y.; Murakami-Tonami, Y.; Kameda, T.; et al. A covalent G-site inhibitor for glutathione S-transferase Pi (GSTP1-1). Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 11138–11141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surade, S.; Blundell, T.L. Structural biology and drug discovery of difficult targets: The limits of ligandability. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dang, C.V.; Reddy, E.P.; Shokat, K.M.; Soucek, L. Drugging the undruggable cancer targets. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabsch, W. Xds. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Evans, P.R.; Murshudov, G.N. How good are my data and what is the resolution? Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2013, 69, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, A.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Adams, P.D.; Winn, M.D.; Storoni, L.C.; Read, R.J. Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liebschner, D.; Afonine, P.V.; Baker, M.L.; Bunkóczi, G.; Chen, V.B.; Croll, T.I. Macromolecular structure determination using X-rays, neutrons and electrons: Recent developments in Phenix. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Struct. Biol. 2019, 75, 861–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butt, S.S.; Badshah, Y.; Shabbir, M.; Rafiq, M. Molecular Docking Using Chimera and Autodock Vina Software for Nonbioinformaticians. Bioinform. Biotechnol. 2020, 1, 14232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Wavelength (Å) | 1.033 |
| Resolution range | 52.8–1.59 (1.65–1.59) |
| Space group | P21 |
| Unit cell | 49.12 211.19 49.44 90 116.23 90 |
| Total reflections | 310250 |
| Unique reflections | 112127 (8772) |
| Multiplicity | 2.8 (2.1) |
| Completeness (%) | 93.36 (73.05) |
| Mean I/sigma(I) | 10.6 (2.0) |
| Wilson B-factor (Å2) | 20.74 |
| R-meas | 0.064 (0.466) |
| R-pim | 0.045 (0.330) |
| CC1/2 | 1.0 (0.78) |
| Reflections used in refinement | 112117 (8772) |
| Reflections used for R-free | 5544 (495) |
| R-work/R-free | 0.1983 (0.2844)/0.2358 (0.3190) |
| Number of non-hydrogen atoms | 8454 |
| macromolecules | 7258 |
| ligands (Na atoms) | 7 |
| solvent | 1149 |
| Protein residues | 872 |
| RMS in bonds (Å) | 0.007 |
| RMS in angles (°) | 0.90 |
| Ramachandran favored (%) | 98.50 |
| Ramachandran allowed (%) | 1.39 |
| Ramachandran outliers (%) | 0.12 |
| Rotamer outliers (%) | 0.00 |
| Clashscore | 5.72 |
| Average B-factor (Å2) | 25.39 |
| macromolecules | 23.99 |
| ligands | 37.86 |
| solvent | 33.88 |
| PDB id | 7beu |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bodourian, C.S.; Poudel, N.; Papageorgiou, A.C.; Antoniadi, M.; Georgakis, N.D.; Abe, H.; Labrou, N.E. Ligandability Assessment of Human Glutathione Transferase M1-1 Using Pesticides as Chemical Probes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073606
Bodourian CS, Poudel N, Papageorgiou AC, Antoniadi M, Georgakis ND, Abe H, Labrou NE. Ligandability Assessment of Human Glutathione Transferase M1-1 Using Pesticides as Chemical Probes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(7):3606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073606
Chicago/Turabian StyleBodourian, Charoutioun S., Nirmal Poudel, Anastassios C. Papageorgiou, Mariana Antoniadi, Nikolaos D. Georgakis, Hiroshi Abe, and Nikolaos E. Labrou. 2022. "Ligandability Assessment of Human Glutathione Transferase M1-1 Using Pesticides as Chemical Probes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 7: 3606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073606
APA StyleBodourian, C. S., Poudel, N., Papageorgiou, A. C., Antoniadi, M., Georgakis, N. D., Abe, H., & Labrou, N. E. (2022). Ligandability Assessment of Human Glutathione Transferase M1-1 Using Pesticides as Chemical Probes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(7), 3606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073606








