Small-Molecule RAS Inhibitors as Anticancer Agents: Discovery, Development, and Mechanistic Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Classification of RAS Protein Superfamily
2.1. RAS Subfamily
2.2. Rho Subfamily
2.3. Rab Subfamily
2.4. Ran Subfamily
2.5. Arf Subfamily
- The Arfs
- The Arf-like (Arls) proteins
- The Secretion-associated RAS-related (SARs) proteins
- The single Tripartite protein 23, also known as TRIM23.
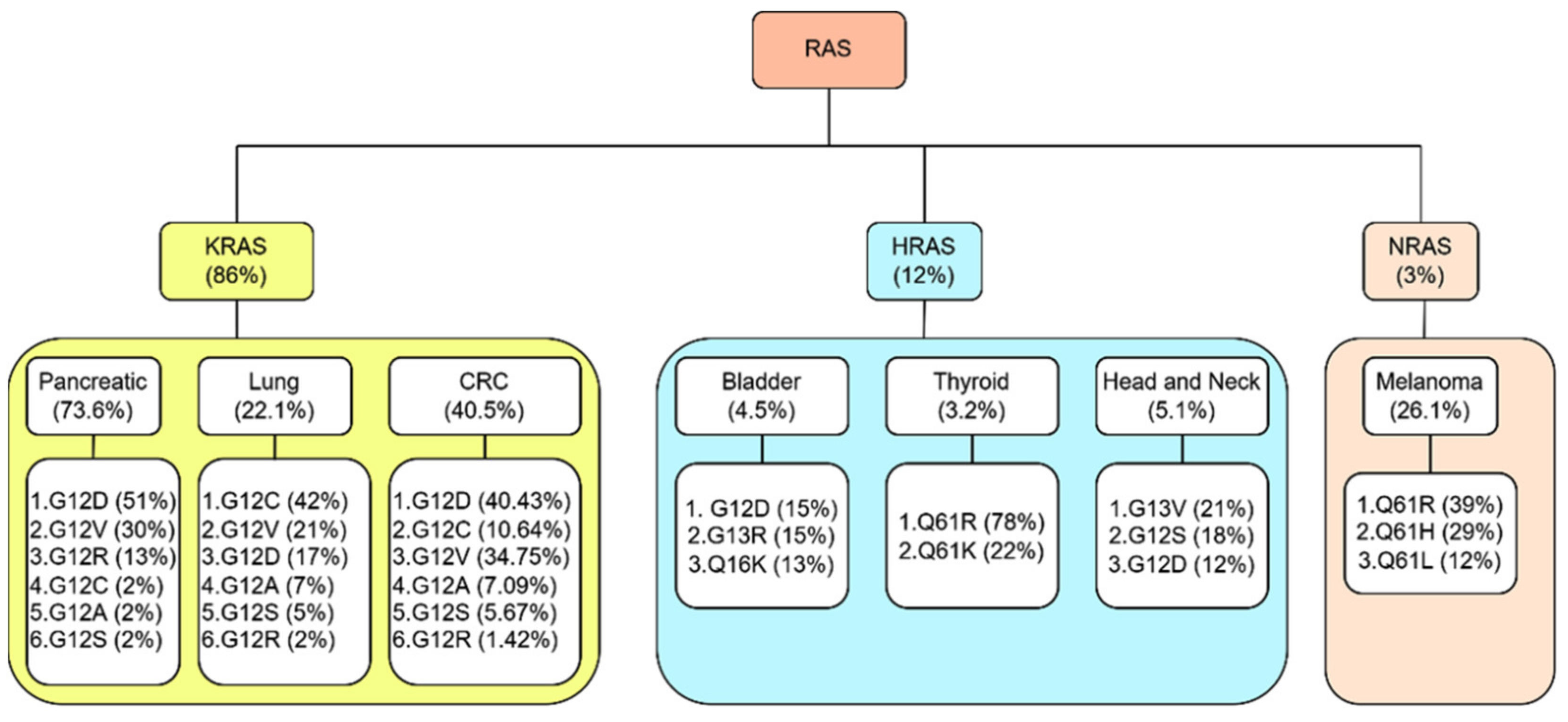
2.6. KRAS, HRAS, and NRAS
2.6.1. KRAS
2.6.2. HRAS
2.6.3. NRAS
3. RAS and Cancers
3.1. Pancreatic Cancer
3.2. Lung Cancer
3.3. Colorectal Cancer
3.4. Other Cancers
4. Small-Molecule RAS Inhibitors
4.1. Classification of Small-Molecule RAS Inhibitors Based on Their Structure
4.1.1. Ganetespib
4.1.2. Apatinib
4.1.3. Oncrasin-1
4.1.4. N-(1-Acryloylazetidin-3-yl)-2-(5-bromo-3-(5-methoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-2-carbonyl)-1H-indol-1-yl) Acetamide
4.1.5. 2-((4-((1-(2-(2,4-Dichlorophenoxy) acetyl) piperidin-4-yl) amino)-4-oxobutyl) disulfaneyl)-N,N-dimethylethan-1-aminium
4.1.6. GDC-0449 (Vismodegib)
4.2. Aza Heterocyclic Small-Molecule RAS Inhibitors with More Than One Nitrogen Atom
4.2.1. ARS-1620
4.2.2. ARS-853
4.2.3. AMG 510 (Lumakras or Sotorasib)
4.2.4. MRTX849 (Adagrasib)
4.2.5. 1-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-4-(2-Methyl-3,5-Diphenylpyrazolo[1,5-a] Pyrimidin-7-yl) Piperazin-1-ium
4.2.6. BGB324 (Bemcentinib)
4.2.7. ABT-737
4.2.8. AZD6244 (Selumetinib)
4.2.9. NVP-BEZ235 (Dactolisib)
4.2.10. R115777 (Zarnestra or Tipifarnib)
4.2.11. PPIN-1, PPIN-2
4.2.12. pan-RAS Inhibitor 3144 (RAS-IN-3144)
4.2.13. Deltarasin
4.2.14. (2. R,4aR)-3-Acryloyl-11-chloro-9-fluoro-10-(6-fluoro-2-hydroxycyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-yl)-2,6-dimethyl-2,3,4,4a-tetrahydro-1H-pyrazino [1’,2’:4,5] Pyrazino[2,3-c] Quinolin-5(6H)-one
4.2.15. SML-8-73-1 and SML-10-70-1
4.3. Oxoheterocyclic Small-Molecule RAS Inhibitors
4.3.1. NHTD
4.3.2. PD98059
4.3.3. Wortmannin
4.4. Mixed Heterocyclic Small-Molecule RAS Inhibitors
4.4.1. Talniflumate + Gefitinib
4.4.2. CPD0857 and KY1022
4.4.3. KYA1797K
4.4.4. 0375-0604
4.4.5. 7773
4.4.6. NSC-658497
4.4.7. JNJ-74699157
4.5. Carbocyclic Small-Molecule RAS Inhibitors
4.5.1. PKF115-584 (Calphostin C)
4.5.2. Kobe0065 + Kobe2602
4.5.3. 3,3’-(Ethylazanediyl)bis(N-phenylpropanamide)
4.5.4. Salirasib + FTS, Salirasib
4.6. Miscellaneous Small-Molecule RAS Inhibitors
4.6.1. ML264
4.6.2. GDC-6036
4.6.3. LY3499446
4.6.4. D-1553
5. Small-Molecule Natural Products as RAS Inhibitors
5.1. Natural Product RAS Inhibitors with Heterocyclic Skeleton
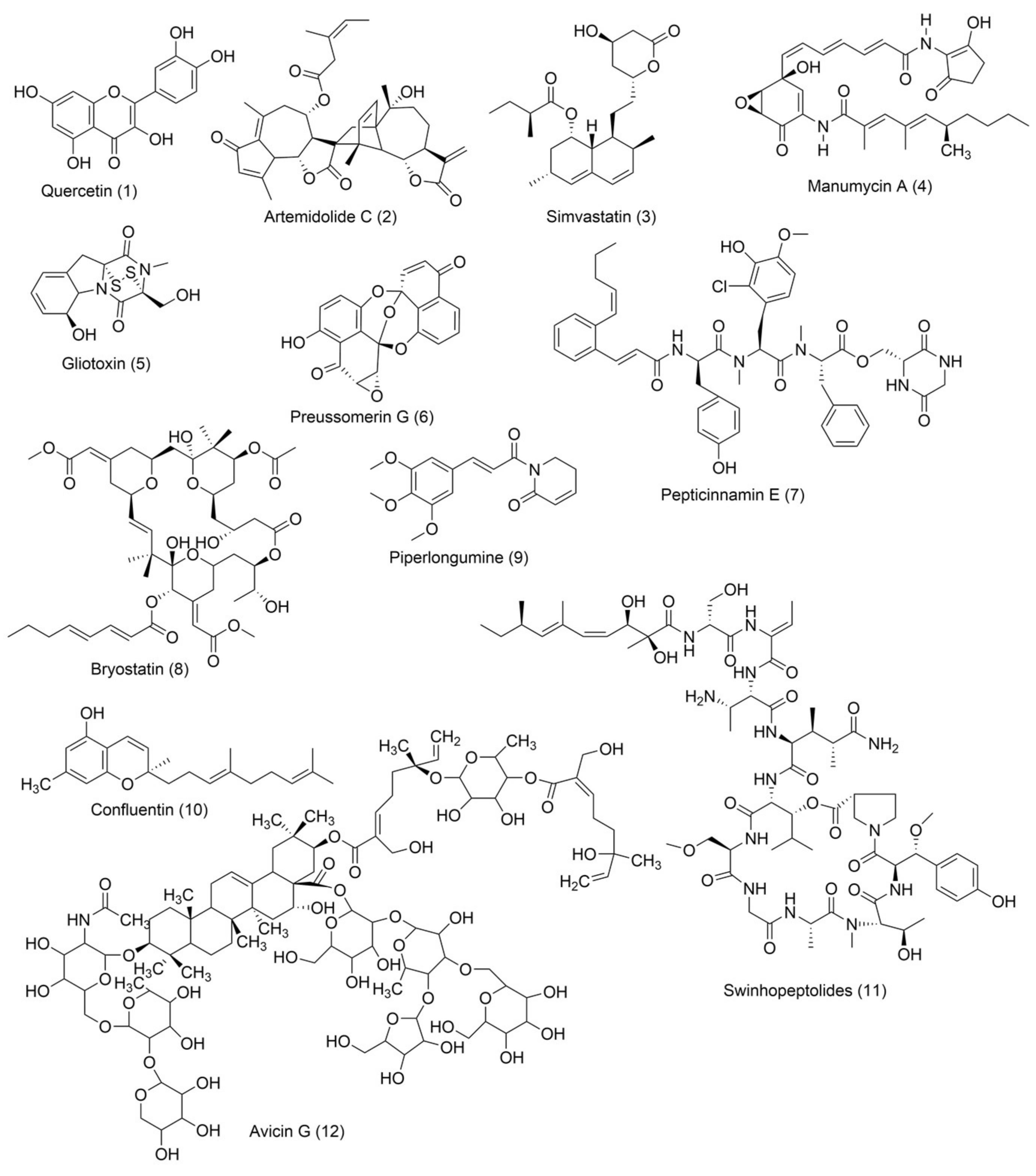
5.1.1. Quercetin
5.1.2. Artemidolide C
5.1.3. Statins
5.1.4. Manumycin A
5.1.5. Gliotoxin
5.1.6. Preussomerin G
5.1.7. Pepticinnamin E
5.1.8. Bryostatin-1
5.1.9. Piperlongumine
5.1.10. Confluentin
5.1.11. Swinhopeptolides
5.1.12. Avicin G
5.2. Natural Product RAS Inhibitor with Carbocyclic Skeleton
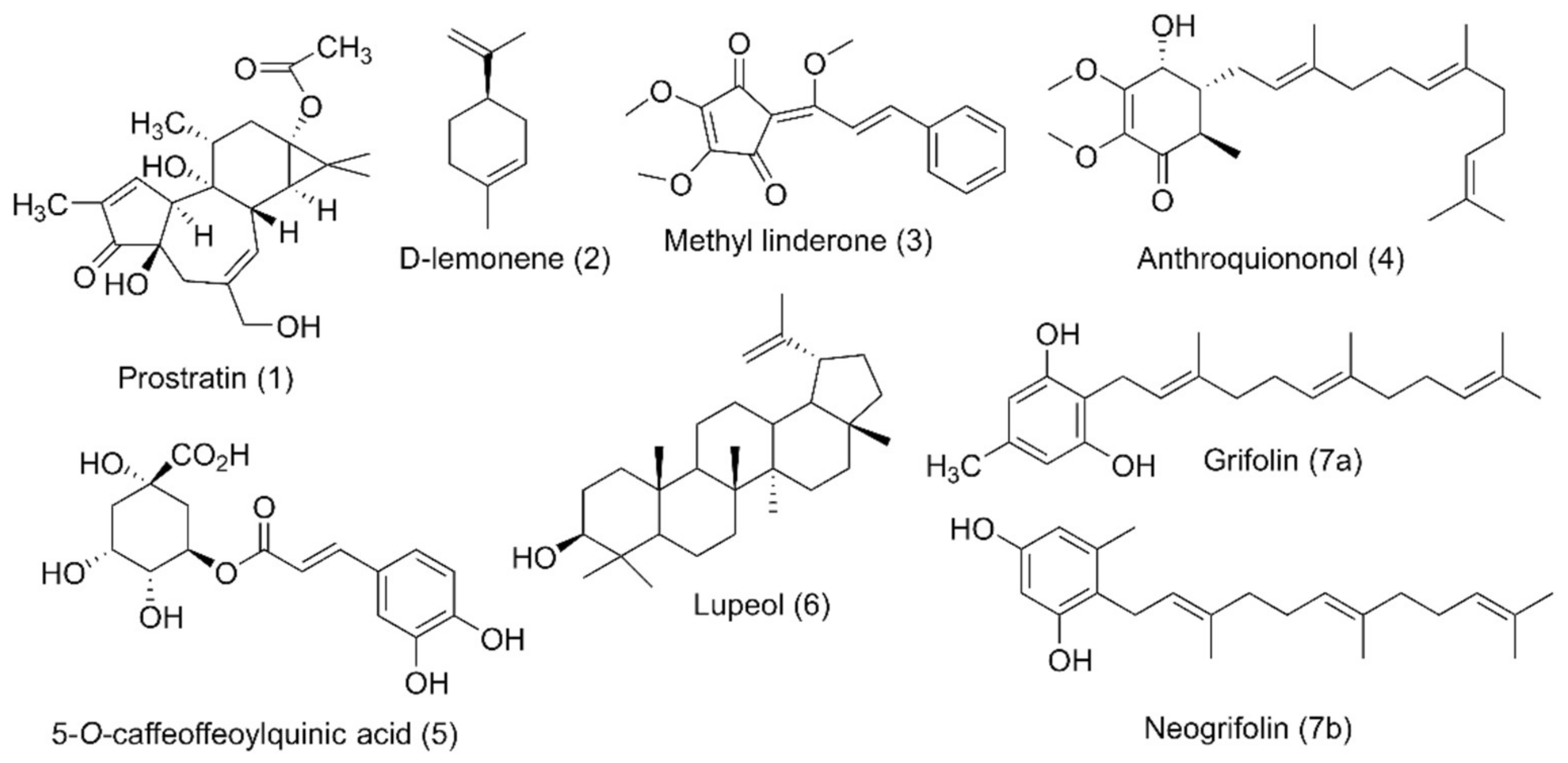
5.2.1. Prostratin
5.2.2. D-Limonene
5.2.3. Methyl Linderone
5.2.4. Antroquinonol
5.2.5. 5-CQA (5-O-Caffeoylquinic Acid)
5.2.6. Lupeol
5.2.7. Grifolin and Neogrifolin
5.3. Natural Product RAS Inhibitor with Acyclic Skeleton
Chaethomellic Acids A
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karnoub, A.E.; Weinberg, R.A. Ras oncogenes: Split personalities. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, A.D.; Der, C.J. Ras history: The saga continues. Small GTPases 2010, 1, 2–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.; Ward, E.; Hao, Y.; Xu, J.; Thun, M.J. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2009, 59, 225–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Targeting the untargetable KRAS in cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simanshu, D.K.; Nissley, D.V.; McCormick, F. RAS Proteins and Their Regulators in Human Disease. Cell 2017, 170, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennerberg, K.; Rossman, K.L.; Der, C.J. The Ras superfamily at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, A.M.; Fuentes, G.; Rausell, A.; Valencia, A. The Ras protein superfamily: Evolutionary tree and role of conserved amino acids. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colicelli, J. Human RAS superfamily proteins and related GTPases. Sci. STKE 2004, 250, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repasky, G.A.; Chenette, E.J.; Der, C.J. Renewing the conspiracy theory debate: Does Raf function alone to mediate Ras oncogenesis? Trends Cell Biol. 2004, 14, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perucho, M.; Goldfarb, M.; Shimizu, K.; Lama, C.; Fogh, J.; Wigler, M. Human-tumor-derived cell lines contain common and different transforming genes. Cell 1981, 27, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittinghofer, A.; Vetter, I.R. Structure-function relationships of the G domain, a canonical switch motif. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2011, 80, 943–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krontiris, T.G.; Cooper, G.M. Transforming activity of human tumor DNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 1181–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, C.; Padhy, L.C.; Murray, M.; Weinberg, R.A. Transforming genes of carcinomas and neuroblastomas introduced into mouse fibroblasts. Nature 1981, 290, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakhaei-Rad, S.; Haghighi, F.; Nouri, P.; Rezaei Adariani, S.; Lissy, J.; Kazemein Jasemi, N.S.; Dvorsky, R.; Ahmadian, M.R. Structural fingerprints, interactions, and signaling networks of RAS family proteins beyond RAS isoforms. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 53, 130–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, S.; Tamanoi, F. Fighting cancer by disrupting C-terminal methylation of signaling proteins. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 513–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvius, J.R. Mechanisms of Ras protein targeting in mammalian cells. J. Membr. Biol. 2002, 190, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwong, L.; Wozniak, M.A.; Collins, A.S.; Wilson, S.D.; Keely, P.J. R-Ras promotes focal adhesion formation through focal adhesion kinase and p130(Cas) by a novel mechanism that differs from integrins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 933–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhjelm, J.; Peränen, J. The C-terminal end of R-Ras contains a focal adhesion targeting signal. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 3729–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reedquist, K.A.; Ross, E.; Koop, E.A.; Wolthuis, R.M.; Zwartkruis, F.J.; van Kooyk, Y.; Salmon, M.; Buckley, C.D.; Bos, J.L. The small GTPase, Rap1, mediates CD31-induced integrin adhesion. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 148, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, Y.; White, M.A. RAL GTPases are linchpin modulators of human tumour-cell proliferation and survival. EMBO Rep. 2003, 4, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipitsin, M.; Feig, L.A. RalA but not RalB enhances polarized delivery of membrane proteins to the basolateral surface of epithelial cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 5746–5756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, G.J.; Kinch, M.S.; Rogers-Graham, K.; Sebti, S.M.; Hamilton, A.D.; Der, C.J. The Ras-related protein Rheb is farnesylated and antagonizes Ras signaling and transformation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 10608–10615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, E.; von Lintig, F.C.; Chen, J.; Zhuang, S.; Qui, W.; Chowdhury, S.; Worley, P.F.; Boss, G.R.; Pilz, R.B. Rheb is in a high activation state and inhibits B-Raf kinase in mammalian cells. Oncogene 2002, 21, 6356–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etienne-Manneville, S.; Hall, A. Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature 2002, 420, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heasman, S.J.; Ridley, A.J. Mammalian Rho GTPases: New insights into their functions from in vivo studies. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, N.; Seiler, S. The RHO1-specific GTPase-activating Protein LRG1 Regulates Polar Tip Growth in Parallel to Ndr Kinase Signaling in Neurospora. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 4554–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulloy, J.C.; Cancelas, J.A.; Filippi, M.D.; Kalfa, T.A.; Guo, F.; Zheng, Y. Rho GTPases in hematopoiesis and hemopathies. Blood 2010, 115, 936–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlessinger, K.; Hall, A.; Tolwinski, N. Wnt signaling pathways meet Rho GTPases. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boureux, A.; Vignal, E.; Faure, S.; Fort, P. Evolution of the Rho family of ras-like GTPases in eukaryotes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosaddeghzadeh, N.; Ahmadian, M.R. The RHO Family GTPases: Mechanisms of Regulation and Signaling. Cells 2021, 10, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touchot, N.; Chardin, P.; Tavitian, A. Four additional members of the ras gene superfamily isolated by an oligonucleotide strategy: Molecular cloning of YPT-related cDNAs from a rat brain library. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 8210–8214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenmark, H. Rab GTPases as coordinators of vesicle traffic. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Leal, J.B.; Seabra, M.C. Evolution of the Rab family of small GTP-binding proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 313, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerial, M.; McBride, H. Rab proteins as membrane organizers. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.S.; Blobel, G. A G protein involved in nucleocytoplasmic transport: The role of Ran. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1994, 19, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, K. Regulating access to the genome: Nucleocytoplasmic transport throughout the cell cycle. Cell 2003, 112, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Cao, K.; Zheng, Y. Ran in the spindle checkpoint: A new function for a versatile GTPase. Trends Cell Biol. 2003, 13, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, J. Ran at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 3481–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kahn, R.A.; Gilman, A.G. Purification of a protein cofactor required for ADP-ribosylation of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by cholera toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 6228–6234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewell, J.L.; Kahn, R.A. Sequences of the bovine and yeast ADP-ribosylation factor and comparison to other GTP-binding proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 4620–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, S.R.; Nightingale, M.; Tsai, S.C.; Williamson, K.C.; Adamik, R.; Chen, H.C.; Moss, J.; Vaughan, M. Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins that enhance choleragen ADP-ribosyltransferase activity: Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence of an ADP-ribosylation factor cDNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 5488–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargová, R.; Wideman, J.G.; Derelle, R.; Klimeš, V.; Kahn, R.A.; Dacks, J.B.; Eliáš, M. A Eukaryote-Wide Perspective on the Diversity and Evolution of the ARF GTPase Protein Family. Genome Biol. Evol. 2021, 13, evab157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.W.; Gasilina, A.; Yadav, M.P.; Randazzo, P.A. Control of cell signaling by Arf GTPases and their regulators: Focus on links to cancer and other GTPase families. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2022, 1869, 119171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzny, D.M.; Bainbridge, M.N.; Chang, K.; Dinh, H.H.; Drummond, J.A.; Fowler, G.; Kovar, C.L.; Lewis, L.R.; Morgan, M.B.; Newsham, I.F.; et al. Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature 2012, 487, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, P.; Chang, D.K.; Nones, K.; Johns, A.L.; Patch, A.M.; Gingras, M.C.; Miller, D.K.; Christ, A.N.; Bruxner, T.J.; Quinn, M.C.; et al. Genomic analyses identify molecular subtypes of pancreatic cancer. Nature 2016, 531, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.D.; Alexandrov, A.; Kim, J.; Wala, J.; Berger, A.H.; Pedamallu, C.S.; Shukla, S.A.; Guo, G.; Brooks, A.N.; Murray, B.A.; et al. Distinct patterns of somatic genome alterations in lung adenocarcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeton, A.B.; Salter, E.A.; Piazza, G.A. The RAS-Effector Interaction as a Drug Target. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adderley, H.; Blackhall, F.H.; Lindsay, C.R. KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer: Converging small molecules and immune checkpoint inhibition. EBioMedicine 2019, 41, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Medarde, A.; Santos, E. Ras in cancer and developmental diseases. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, K.L.; Mancias, J.D.; Kimmelman, A.C.; Der, C.J. KRAS: Feeding pancreatic cancer proliferation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfredini, S.; Thapa, A.; O’Neill, E. RAS in pancreatic cancer. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 47, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schutte, M.; Hruban, R.H.; Geradts, J.; Maynard, R.; Hilgers, W.; Rabindran, S.K.; Moskaluk, C.A.; Hahn, S.A.; Schwarte-Waldhoff, I.; Schmiegel, W.; et al. Abrogation of the Rb/p16 tumor-suppressive pathway in virtually all pancreatic carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 3126–3130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Waters, A.M.; Der, C.J. KRAS: The Critical Driver and Therapeutic Target for Pancreatic Cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a031435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordelas, L.; Rebmann, V.; Ludwig, A.K.; Radtke, S.; Ruesing, J.; Doeppner, T.R.; Epple, M.; Horn, P.A.; Beelen, D.W.; Giebel, B. MSC-derived exosomes: A novel tool to treat therapy-refractory graft-versus-host disease. Leukemia 2014, 28, 970–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamerkar, S.; LeBleu, V.S.; Sugimoto, H.; Yang, S.; Ruivo, C.F.; Melo, S.A.; Lee, J.J.; Kalluri, R. Exosomes facilitate therapeutic targeting of oncogenic KRAS in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2017, 546, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorde Khvalevsky, E.; Gabai, R.; Rachmut, I.H.; Horwitz, E.; Brunschwig, Z.; Orbach, A.; Shemi, A.; Golan, T.; Domb, A.J.; Yavin, E.; et al. Mutant KRAS is a druggable target for pancreatic cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20723–20728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosolits, S.; Ullenhag, G.; Mellstedt, H. Therapeutic vaccination in patients with gastrointestinal malignancies. A review of immunological and clinical results. Ann. Oncol. 2005, 16, 847–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quandt, J.; Schlude, C.; Bartoschek, M.; Will, R.; Cid-Arregui, A.; Schölch, S.; Reissfelder, C.; Weitz, J.; Schneider, M.; Wiemann, S.; et al. Long-peptide vaccination with driver gene mutations in p53 and Kras induces cancer mutation-specific effector as well as regulatory T cell responses. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1500671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Pei, L.; Xia, H.; Tang, Q.; Bi, F. Role of oncogenic KRAS in the prognosis, diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karachaliou, N.; Mayo, C.; Costa, C.; Magrí, I.; Gimenez-Capitan, A.; Molina-Vila, M.A.; Rosell, R. KRAS Mutations in Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2013, 14, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.; Martin-Zanca, D.; Reddy, E.P.; Pierotti, M.A.; Della Porta, G.; Barbacid, M. Malignant activation of a K-ras oncogene in lung carcinoma but not in normal tissue of the same patient. Science 1984, 223, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodenhuis, S.; van de Wetering, M.L.; Mooi, W.J.; Evers, S.G.; van Zandwijk, N.; Bos, J.L. Mutational activation of the K-ras oncogene. A possible pathogenetic factor in adenocarcinoma of the lung. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 317, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dearden, S.; Stevens, J.; Wu, Y.L.; Blowers, D. Mutation incidence and coincidence in non small-cell lung cancer: Meta-analyses by ethnicity and histology (mutMap). Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2371–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liang, S.Q.; Schmid, R.A.; Peng, R.W. New Horizons in KRAS-Mutant Lung Cancer: Dawn After Darkness. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matikas, A.; Mistriotis, D.; Georgoulias, V.; Kotsakis, A. Targeting KRAS mutated non-small cell lung cancer: A history of failures and a future of hope for a diverse entity. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 110, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrendt, S.A.; Decker, P.A.; Alawi, E.A.; Zhu Yr, Y.R.; Sanchez-Cespedes, M.; Yang, S.C.; Haasler, G.B.; Kajdacsy-Balla, A.; Demeure, M.J.; Sidransky, D. Cigarette smoking is strongly associated with mutation of the K-ras gene in patients with primary adenocarcinoma of the lung. Cancer 2001, 92, 1525–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Goding Sauer, A.; Fedewa, S.A.; Butterly, L.F.; Anderson, J.C.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, J.L.; Fearon, E.R.; Hamilton, S.R.; Verlaan-de Vries, M.; van Boom, J.H.; van der Eb, A.J.; Vogelstein, B. Prevalence of ras gene mutations in human colorectal cancers. Nature 1987, 327, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelstein, B.; Fearon, E.R.; Hamilton, S.R.; Kern, S.E.; Preisinger, A.C.; Leppert, M.; Nakamura, Y.; White, R.; Smits, A.M.; Bos, J.L. Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 319, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, J.; Zeindl-Eberhart, E.; Kirchner, T.; Jung, A. Frequency and type of KRAS mutations in routine diagnostic analysis of metastatic colorectal cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2009, 205, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sveen, A.; Kopetz, S.; Lothe, R.A. Biomarker-guided therapy for colorectal cancer: Strength in complexity. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- . Lavanya, V.; Mohamed, A.A.A.; Ahmed, N.; Rishi, A.K.; Jamal, S. Small molecule inhibitors as emerging cancer therapeutics. Integr. Cancer Sci. Ther. 2014, 1, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, D.; Banik, B.K. Microwave-assisted synthesis of medicinally privileged heterocycles. In Green Synthetic Approaches for Biologically Relevant Heterocycles, 2nd ed.; Brahmachari, G., Ed.; Advanced Synthetic Techniques; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2021; Volume 1, Chapter 3; pp. 49–110. ISBN 978-0-12-820586-0. [Google Scholar]
- Cercek, A.; Shia, J.; Gollub, M.; Chou, J.F.; Capanu, M.; Raasch, P.; Reidy-Lagunes, D.; Proia, D.A.; Vakiani, E.; Solit, D.B.; et al. Ganetespib, a novel Hsp90 inhibitor in patients with KRAS mutated and wild type, refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2014, 13, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acquaviva, J.; Smith, D.L.; Sang, J.; Friedland, J.C.; He, S.; Sequeira, M.; Zhang, C.; Wada, Y.; Proia, D.A. Targeting KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer with the Hsp90 inhibitor ganetespib. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 2633–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, D.-X.; Wang, C.-G.; Huang, J.-A.; Jiang, J.-H. Apatinib in the treatment of advanced lung adenocarcinoma with KRAS mutation. Onco. Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 4269–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guo, W.; Wu, S.; Liu, J.; Fang, B. Identification of a small molecule with synthetic lethality for K-ras and protein kinase C iota. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7403–7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.; Jeong, J.W.; Wurz, R.P.; Achanta, P.; Arvedson, T.; Bartberger, M.D.; Campuzano, I.D.G.; Fucini, R.; Hansen, S.K.; Ingersoll, J.; et al. Discovery of N-(1-Acryloylazetidin-3-yl)-2-(1H-indol-1-yl)acetamides as Covalent Inhibitors of KRASG12C. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrem, J.M.; Peters, U.; Sos, M.L.; Wells, J.A.; Shokat, K.M. K-Ras(G12C) inhibitors allosterically control GTP affinity and effector interactions. Nature 2013, 503, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Mondal, G.; Slavik, P.; Rachagani, S.; Batra, S.K.; Mahato, R.I. Codelivery of small molecule hedgehog inhibitor and miRNA for treating pancreatic cancer. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mulla, F.; Milner-White, E.J.; Going, J.J.; Birnie, G.D. Structural differences between valine-12 and aspartate-12 Ras proteins may modify carcinoma aggression. J. Pathol. 1999, 187, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticone, M.; Biollo, E.; Maffei, M.; Donadini, A.; Romeo, F.; Storlazzi, C.T.; Giaretti, W.; Castagnola, P. Gene expression deregulation by KRAS G12D and G12V in a BRAF V600E context. Mol. Cancer 2008, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Qin, S.; Xu, J.; Guo, W.; Xiong, J.; Bai, Y.; Sun, G.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, N.; et al. Apatinib for chemotherapy-refractory advanced metastatic gastric cancer: Results from a randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-arm, phase II trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3219–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, B.; Jiang, Z.; Ragaz, J.; Tong, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Pang, D.; et al. Multicenter phase II study of apatinib, a novel VEGFR inhibitor in heavily pretreated patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinni, S.R.; Li, Y.; Upadhyay, S.; Koppolu, P.K.; Sarkar, F.H. Indole-3-carbinol (I3C) induced cell growth inhibition, G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 2001, 20, 2927–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlanson, D.A.; Braisted, A.C.; Raphael, D.R.; Randal, M.; Stroud, R.M.; Gordon, E.M.; Wells, J.A. Site-directed ligand discovery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 9367–9372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.M.; Liu, S.; Rybkin, I.; Arbour, K.C.; Dilly, J.; Zhu, V.W.; Johnson, M.L.; Heist, R.S.; Patil, T.; Riely, G.J.; et al. Acquired Resistance to KRAS(G12C) Inhibition in Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2382–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giroux-Leprieur, E.; Costantini, A.; Ding, V.W.; He, B. Hedgehog Signaling in Lung Cancer: From Oncogenesis to Cancer Treatment Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrisani, J.; Bournet, B.; du Rieu, M.C.; Bouisson, M.; Souque, A.; Escourrou, J.; Buscail, L.; Cordelier, P. let-7 MicroRNA transfer in pancreatic cancer-derived cells inhibits in vitro cell proliferation but fails to alter tumor progression. Hum. Gene Ther. 2009, 20, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, M.R.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.S.; Hansen, R.; Peters, U.; Guo, X.; Chen, Y.; Babbar, A.; Firdaus, S.J.; Darjania, L.; et al. Targeting KRAS Mutant Cancers with a Covalent G12C-Specific Inhibitor. Cell 2018, 172, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patricelli, M.P.; Janes, M.R.; Li, L.S.; Hansen, R.; Peters, U.; Kessler, L.V.; Chen, Y.; Kucharski, J.M.; Feng, J.; Ely, T.; et al. Selective Inhibition of Oncogenic KRAS Output with Small Molecules Targeting the Inactive State. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canon, J.; Rex, K.; Saiki, A.Y.; Mohr, C.; Cooke, K.; Bagal, D.; Gaida, K.; Holt, T.; Knutson, C.G.; Koppada, N.; et al. The clinical KRAS(G12C) inhibitor AMG 510 drives anti-tumour immunity. Nature 2019, 575, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallin, J.; Engstrom, L.D.; Hargis, L.; Calinisan, A.; Aranda, R.; Briere, D.M.; Sudhakar, N.; Bowcut, V.; Baer, B.R.; Ballard, J.A.; et al. The KRAS(G12C) Inhibitor MRTX849 Provides Insight toward Therapeutic Susceptibility of KRAS-Mutant Cancers in Mouse Models and Patients. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, M.J.; Pagba, C.V.; Prakash, P.; Naji, A.K.; van der Hoeven, D.; Liang, H.; Gupta, A.K.; Zhou, Y.; Cho, K.J.; Hancock, J.F.; et al. Discovery of High-Affinity Noncovalent Allosteric KRAS Inhibitors That Disrupt Effector Binding. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 2921–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, K.F.; Du, W.; Sorrelle, N.B.; Wnuk-Lipinska, K.; Topalovski, M.; Toombs, J.E.; Cruz, V.H.; Yabuuchi, S.; Rajeshkumar, N.V.; Maitra, A.; et al. Small-Molecule Inhibition of Axl Targets Tumor Immune Suppression and Enhances Chemotherapy in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabusa, H.; Brooks, T.; Massey, A.J. Knockdown of PAK4 or PAK1 inhibits the proliferation of mutant KRAS colon cancer cells independently of RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tentler, J.J.; Nallapareddy, S.; Tan, A.C.; Spreafico, A.; Pitts, T.M.; Morelli, M.P.; Selby, H.M.; Kachaeva, M.I.; Flanigan, S.A.; Kulikowski, G.N.; et al. Identification of predictive markers of response to the MEK1/2 inhibitor selumetinib (AZD6244) in K-ras-mutated colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 3351–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, J.A.; Chen, L.; Tan, X.; Crosby, K.; Guimaraes, A.R.; Upadhyay, R.; Maira, M.; McNamara, K.; Perera, S.A.; Song, Y.; et al. Effective use of PI3K and MEK inhibitors to treat mutant Kras G12D and PIK3CA H1047R murine lung cancers. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaupre, D.M.; Cepero, E.; Obeng, E.A.; Boise, L.H.; Lichtenheld, M.G. R115777 induces Ras-independent apoptosis of myeloma cells via multiple intrinsic pathways. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 179–186. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Migoni, A.; Canning, P.; Quevedo, C.E.; Bataille, C.J.R.; Bery, N.; Miller, A.; Russell, A.J.; Phillips, S.E.V.; Carr, S.B.; Rabbitts, T.H. Structure-based development of new RAS-effector inhibitors from a combination of active and inactive RAS-binding compounds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 2545–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsch, M.E.; Kaplan, A.; Chambers, J.M.; Stokes, M.E.; Bos, P.H.; Zask, A.; Zhang, Y.; Sanchez-Martin, M.; Badgley, M.A.; Huang, C.S.; et al. Multivalent Small-Molecule Pan-RAS Inhibitors. Cell 2017, 168, 878–889.e829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, E.L.; Luo, L.X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Li, L.L.; Shi, D.F.; Xie, Y.; Huang, M.; Lu, L.L.; Duan, F.G.; et al. Identification of a new inhibitor of KRAS-PDEδ interaction targeting KRAS mutant nonsmall cell lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 1334–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettle, J.G.; Bagal, S.K.; Bickerton, S.; Bodnarchuk, M.S.; Breed, J.; Carbajo, R.J.; Cassar, D.J.; Chakraborty, A.; Cosulich, S.; Cumming, I.; et al. Structure-Based Design and Pharmacokinetic Optimization of Covalent Allosteric Inhibitors of the Mutant GTPase KRASG12C. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 4468–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.M.; Westover, K.D.; Ficarro, S.B.; Harrison, R.A.; Choi, H.G.; Pacold, M.E.; Carrasco, M.; Hunter, J.; Kim, N.D.; Xie, T.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of oncogenic K-Ras by a covalent catalytic site inhibitor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Román, M.; Baraibar, I.; López, I.; Nadal, E.; Rolfo, C.; Vicent, S.; Gil-Bazo, I. KRAS oncogene in non-small cell lung cancer: Clinical perspectives on the treatment of an old target. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, H.; Logsdon, C.D.; Rashid, A.; Fleming, J.B.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Gomez, H.F.; Evans, D.B.; Wang, H. Overexpression of receptor tyrosine kinase Axl promotes tumor cell invasion and survival in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer 2011, 117, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leconet, W.; Larbouret, C.; Chardès, T.; Thomas, G.; Neiveyans, M.; Busson, M.; Jarlier, M.; Radosevic-Robin, N.; Pugnière, M.; Bernex, F.; et al. Preclinical validation of AXL receptor as a target for antibody-based pancreatic cancer immunotherapy. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5405–5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, C.M.; Jones, G.E. The emerging importance of group II PAKs. Biochem. J. 2010, 425, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.H.; Zheng, M.H.; Luo, Q.; Ye, Q.; Feng, B.; Lu, A.G.; Wang, M.L.; Chen, X.H.; Su, L.P.; Liu, B.Y. P21-activated protein kinase 1 induces colorectal cancer metastasis involving ERK activation and phosphorylation of FAK at Ser-910. Int. J. Oncol. 2010, 37, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, E.R.; Eblen, S.T.; Catling, A.D. MEK1 activation by PAK: A novel mechanism. Cell Signal. 2007, 19, 1488–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, H.; Cheng, M.; Zhao, D.; Li, F. LCH-7749944, a novel and potent p21-activated kinase 4 inhibitor, suppresses proliferation and invasion in human gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2012, 317, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, M.; Hayne, C.; Luo, Z. Interaction between active Pak1 and Raf-1 is necessary for phosphorylation and activation of Raf-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 4395–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, W.; Sachidanandam, K.; Stratman, A.N.; Sacharidou, A.; Mayo, A.M.; Murphy, E.A.; Cheresh, D.A.; Davis, G.E. Formation of endothelial lumens requires a coordinated PKCepsilon-, Src-, Pak- and Raf-kinase-dependent signaling cascade downstream of Cdc42 activation. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 1812–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bardelli, A.; Silliman, N.; Ptak, J.; Szabo, S.; Yan, H.; Gazdar, A.; Powell, S.M.; Riggins, G.J.; et al. High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science 2004, 304, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, Q.B.; Solit, D.B.; Ye, Q.; O’Reilly, K.E.; Lobo, J.; Rosen, N. The BAD protein integrates survival signaling by EGFR/MAPK and PI3K/Akt kinase pathways in PTEN-deficient tumor cells. Cancer Cell 2005, 8, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelman, J.A. The role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway inhibitors in the treatment of lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4637s–4640s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.C.; Marsh, V.; Bernat, B.A.; Ballard, J.; Colwell, H.; Evans, R.J.; Parry, J.; Smith, D.; Brandhuber, B.J.; Gross, S.; et al. Biological characterization of ARRY-142886 (AZD6244), a potent, highly selective mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1576–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaupre, D.M.; McCafferty-Grad, J.; Bahlis, N.J.; Boise, L.H.; Lichtenheld, M.G. Farnesyl transferase inhibitors enhance death receptor signals and induce apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells. Leuk. Lymphoma 2003, 44, 2123–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hengartner, M.O. The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 2000, 407, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, N.; Hata, H.; Yoshida, M.; Soniki, T.; Nagasaki, A.; Kuribayashi, N.; Kimura, T.; Matsuzaki, H.; Mitsuya, H. Expression of Bcl-2 family of proteins in fresh myeloma cells. Leukemia 1998, 12, 1817–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miguel-García, A.; Orero, T.; Matutes, E.; Carbonell, F.; Miguel-Sosa, A.; Linares, M.; Tarín, F.; Herrera, M.; García-Talavera, J.; Carbonell-Ramón, F. bcl-2 expression in plasma cells from neoplastic gammopathies and reactive plasmacytosis: A comparative study. Haematologica 1998, 83, 298–304. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, A.D.; Fesik, S.W.; Kimmelman, A.C.; Luo, J.; Der, C.J. Drugging the undruggable RAS: Mission possible? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 828–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gysin, S.; Salt, M.; Young, A.; McCormick, F. Therapeutic strategies for targeting ras proteins. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, G.; Schultz-Fademrecht, C.; Küchler, P.; Murarka, S.; Ismail, S.; Triola, G.; Nussbaumer, P.; Wittinghofer, A.; Waldmann, H. Structure guided design and kinetic analysis of highly potent benzimidazole inhibitors targeting the PDEδ prenyl binding site. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 5435–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, G.; Papke, B.; Ismail, S.; Vartak, N.; Chandra, A.; Hoffmann, M.; Hahn, S.A.; Triola, G.; Wittinghofer, A.; Bastiaens, P.I.; et al. Small molecule inhibition of the KRAS-PDEδ interaction impairs oncogenic KRAS signalling. Nature 2013, 497, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghimessy, A.; Radeczky, P.; Laszlo, V.; Hegedus, B.; Renyi-Vamos, F.; Fillinger, J.; Klepetko, W.; Lang, C.; Dome, B.; Megyesfalvi, Z. Current therapy of KRAS-mutant lung cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 1159–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, E.L.H.; Luo, L.X.; Liu, Z.Q.; Wong, V.K.W.; Lu, L.L.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, N.; Qu, Y.Q.; Fan, X.X.; Li, Y.; et al. Inhibition of KRAS-dependent lung cancer cell growth by deltarasin: Blockage of autophagy increases its cytotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Mizukami, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jo, W.S.; Chung, D.C. Oncogenic K-ras stimulates Wnt signaling in colon cancer through inhibition of GSK-3beta. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialkowska, A.B.; Du, Y.; Fu, H.; Yang, V.W. Identification of novel small-molecule compounds that inhibit the proproliferative Kruppel-like factor 5 in colorectal cancer cells by high-throughput screening. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papke, B.; Murarka, S.; Vogel, H.A.; Martín-Gago, P.; Kovacevic, M.; Truxius, D.C.; Fansa, E.K.; Ismail, S.; Zimmermann, G.; Heinelt, K.; et al. Identification of pyrazolopyridazinones as PDEδ inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geltz, N.R.; Augustine, J.A. The p85 and p110 subunits of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-alpha are substrates, in vitro, for a constitutively associated protein tyrosine kinase in platelets. Blood 1998, 91, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.O.; Rittenhouse, S.E.; Tsichlis, P.N. AKT/PKB and other D3 phosphoinositide-regulated kinases: Kinase activation by phosphoinositide-dependent phosphorylation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1999, 68, 965–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michl, P.; Downward, J. Mechanisms of disease: PI3K/AKT signaling in gastrointestinal cancers. Z. Gastroenterol. 2005, 43, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, C.V.; Janakiram, N.B.; Madka, V.; Kumar, G.; Scott, E.J.; Pathuri, G.; Bryant, T.; Kutche, H.; Zhang, Y.; Biddick, L.; et al. Small-Molecule Inhibition of GCNT3 Disrupts Mucin Biosynthesis and Malignant Cellular Behaviors in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 1965–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.K.; Cho, H.; Moon, B.S. Small Molecule Destabilizer of β-Catenin and Ras Proteins Antagonizes Growth of K-Ras Mutation-Driven Colorectal Cancers Resistant to EGFR Inhibitors. Target. Oncol. 2020, 15, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.K.; Cho, Y.H.; Cha, P.H.; Yoon, J.S.; Ro, E.J.; Jeong, W.J.; Park, J.; Kim, H.; Il Kim, T.; Min, D.S.; et al. A small molecule approach to degrade RAS with EGFR repression is a potential therapy for KRAS mutation-driven colorectal cancer resistance to cetuximab. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Li, Y.; Li, L.L.; Fan, X.X.; Wang, Y.W.; Wei, C.L.; Liu, L.; Leung, E.L.H.; Yao, X.J. Identification of a New Potent Inhibitor Targeting KRAS in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, N.; Oberman, F.; Shurrush, K.; Germain, N.; Greenwald, G.; Gershon, T.; Pearl, T.; Abis, G.; Singh, V.; Singh, A.; et al. Small molecule inhibitor of Igf2bp1 represses Kras and a pro-oncogenic phenotype in cancer cells. RNA Biol. 2022, 19, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evelyn, C.R.; Duan, X.; Biesiada, J.; Seibel, W.L.; Meller, J.; Zheng, Y. Rational design of small molecule inhibitors targeting the Ras GEF, SOS1. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 1618–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, S.; Kumar, S.; Momi, N.; Sasson, A.R.; Batra, S.K. Mucins in pancreatic cancer and its microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, K.; Horinouchi, M.; Saitou, M.; Higashi, M.; Nomoto, M.; Goto, M.; Yonezawa, S. Mucin expression profile in pancreatic cancer and the precursor lesions. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Surg. 2007, 14, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniaux, N.; Andrianifahanana, M.; Brand, R.E.; Batra, S.K. Multiple roles of mucins in pancreatic cancer, a lethal and challenging malignancy. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 91, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, M.P.; Chakraborty, S.; Souchek, J.; Batra, S.K. Mucin-based targeted pancreatic cancer therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 2472–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, B.S.; Jeong, W.J.; Park, J.; Kim, T.I.; Min, D.S.; Choi, K.Y. Role of oncogenic K-Ras in cancer stem cell activation by aberrant Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, djt373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.H.; Cha, P.H.; Kaduwal, S.; Park, J.C.; Lee, S.K.; Yoon, J.S.; Shin, W.; Kim, H.; Ro, E.J.; Koo, K.H.; et al. KY1022, a small molecule destabilizing Ras via targeting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, inhibits development of metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 81727–81740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degrauwe, N.; Suvà, M.L.; Janiszewska, M.; Riggi, N.; Stamenkovic, I. IMPs: An RNA-binding protein family that provides a link between stem cell maintenance in normal development and cancer. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 2459–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Smaill, J.B.; Liu, T.; Ding, K.; Lu, X. Small-Molecule Inhibitors Directly Targeting KRAS as Anticancer Therapeutics. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 14404–14424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, W.; Yang, Z.; Kocher, G.J.; Dorn, P.; Peng, R.W. A Breakthrough Brought about by Targeting KRAS(G12C): Nonconformity Is Punished. Cancers 2022, 14, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mologni, L.; Brussolo, S.; Ceccon, M.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C. Synergistic effects of combined Wnt/KRAS inhibition in colorectal cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shima, F.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Ye, M.; Araki, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Liao, J.; Hu, L.; Sugimoto, T.; Ijiri, Y.; Takeda, A.; et al. In silico discovery of small-molecule Ras inhibitors that display antitumor activity by blocking the Ras-effector interaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8182–8187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín-Ramos, N.I.; Balabasquer, M.; Ortega-Nogales, F.J.; Torrecillas, I.R.; Gil-Ordóñez, A.; Marcos-Ramiro, B.; Aguilar-Garrido, P.; Cushman, I.; Romero, A.; Medrano, F.J.; et al. A Potent Isoprenylcysteine Carboxylmethyltransferase (ICMT) Inhibitor Improves Survival in Ras-Driven Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 6035–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, S.; Enokida, H.; Yoshino, H.; Miyamoto, K.; Yonemori, M.; Sakaguchi, T.; Osako, Y.; Nakagawa, M. HRAS as a potential therapeutic target of salirasib RAS inhibitor in bladder cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, L.; Haklai, R.; Bauer, V.; Heiss, A.; Kloog, Y. New derivatives of farnesylthiosalicylic acid (salirasib) for cancer treatment: Farnesylthiosalicylamide inhibits tumor growth in nude mice models. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, L.D.; Parsons, D.W.; Jones, S.; Lin, J.; Sjöblom, T.; Leary, R.J.; Shen, D.; Boca, S.M.; Barber, T.; Ptak, J.; et al. The genomic landscapes of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science 2007, 318, 1108–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöblom, T.; Jones, S.; Wood, L.D.; Parsons, D.W.; Lin, J.; Barber, T.D.; Mandelker, D.; Leary, R.J.; Ptak, J.; Silliman, N.; et al. The consensus coding sequences of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science 2006, 314, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, T.; Garrenton, L.S.; Oh, A.; Pitts, K.; Anderson, D.J.; Skelton, N.J.; Fauber, B.P.; Pan, B.; Malek, S.; Stokoe, D.; et al. Small-molecule ligands bind to a distinct pocket in Ras and inhibit SOS-mediated nucleotide exchange activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5299–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Casey, P.J. Protein prenylation: Unique fats make their mark on biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, A.G.; Esposito, D.; Bagni, R.K.; McCormick, F. Dragging ras back in the ring. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandith, A.A.; Shah, Z.A.; Khan, N.P.; Baba, K.M.; Wani, M.S.; Siddiqi, M.A. HRAS T81C polymorphism modulates risk of urinary bladder cancer and predicts advanced tumors in ethnic Kashmiri population. Urol. Oncol. 2013, 31, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz de Sabando, A.; Wang, C.; He, Y.; García-Barros, M.; Kim, J.; Shroyer, K.R.; Bannister, T.D.; Yang, V.W.; Bialkowska, A.B. ML264, A Novel Small-Molecule Compound That Potently Inhibits Growth of Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannoura, S.F.; Uddin, M.H.; Nagasaka, M.; Fazili, F.; Al-Hallak, M.N.; Philip, P.A.; El-Rayes, B.; Azmi, A.S. Targeting KRAS in pancreatic cancer: New drugs on the horizon. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021, 40, 819–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debasish Bandyopadhyay, V.G.; Gonzales, F. Anti-Cancer Agents from Natural Sources. In Promising Drug Molecules of Natural Origin, 1st ed.; Dutt, R., Sharma, A.K., Keservani, K.R., Garg, V., Eds.; Bioscience, Medicine, Dentistry, Nursing & Allied Health; Apple Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2020; p. 80. [Google Scholar]
- Debasish Bandyopadhyay, V.G.; Gonzales, F. Heterocyclic Drugs from Plants. In Promising Drug Molecules of Natural Origin, 1st ed.; Dutt, R., Sharma, A.K., Keservani, K.R., Garg, V., Eds.; Bioscience, Medicine, Dentistry, Nursing & Allied Health; Apple Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2020; p. 56. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranelletti, F.O.; Maggiano, N.; Serra, F.G.; Ricci, R.; Larocca, L.M.; Lanza, P.; Scambia, G.; Fattorossi, A.; Capelli, A.; Piantelli, M. Quercetin inhibits p21-RAS expression in human colon cancer cell lines and in primary colorectal tumors. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 85, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z. Quercetin Enhances Cisplatin Sensitivity of Human Osteosarcoma Cells by Modulating microRNA-217-KRAS Axis. Mol. Cells 2015, 38, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Feng, Z.; Huang, Z.a.; Wang, H.; Lu, W. MicroRNA-217 functions as a tumour suppressor gene and correlates with cell resistance to cisplatin in lung cancer. Mol. Cells 2014, 37, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, M.-Y.; Kang, H.-M.; Han, D.C.; Son, K.-H.; Yang, D.C.; Sung, N.-D.; Lee, C.W.; Kim, H.M.; Kwon, B.-M. Anti-tumor activity of the farnesyl-protein transferase inhibitors arteminolides, isolated from Artemisa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 4545–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, J.B.; Oliff, A. The potential of farnesyltransferase inhibitors as cancer chemotherapeutics. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1997, 37, 143–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.K.; Seo, J.M.; Kang, H.M.; Kim, J.H.; Son, K.H.; Lee, H.; Kwon, B.M.; Shin, J.; Seo, Y. Arteminolides B, C, and D, new inhibitors of farnesyl protein transferase from Artemisia argyi. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 7670–7675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbelcová, H.; Rimpelová, S.; Knejzlík, Z.; Šáchová, J.; Kolář, M.; Strnad, H.; Repiská, V.; D’Acunto, W.C.; Ruml, T.; Vítek, L. Isoprenoids responsible for protein prenylation modulate the biological effects of statins on pancreatic cancer cells. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minciacchi, V.R.; Freeman, M.R.; Di Vizio, D. Extracellular vesicles in cancer: Exosomes, microvesicles and the emerging role of large oncosomes. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 40, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoorvogel, W. Resolving sorting mechanisms into exosomes. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 531–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, A.; Kim, H.; Lal, M.; McGee, L.; Johnson, A.; Moustafa, A.A.; Jones, J.C.; Mondal, D.; Ferrer, M.; Abdel-Mageed, A.B. Manumycin A suppresses exosome biogenesis and secretion via targeted inhibition of Ras/Raf/ERK1/2 signaling and hnRNP H1 in castration-resistant prostate cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2017, 408, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.; Nandi, D. Farnesyltransferase inhibitors reduce Ras activation and ameliorate acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angamuthu, V.; Shanmugavadivu, M.; Nagarajan, G.; Velmurugan, B.K. Pharmacological activities of antroquinonol- Mini review. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 297, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, H.A.; Gloer, J.B. The preussomerins: Novel antifungal metabolites from the coprophilous fungus Preussia isomera Cain. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 4355–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.B.; Zink, D.L.; Liesch, J.M.; Ball, R.G.; Goetz, M.A.; Bolessa, E.A.; Giacobbe, R.A.; Silverman, K.C.; Bills, G.F. Preussomerins and Deoxypreussomerins: Novel Inhibitors of Ras Farnesyl-Protein Transferase. J. Org. Chem. 1994, 59, 6296–6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Õmura, S.; Tomoda, H. Microbial metabolites affecting lipid biosynthesis. Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 2267–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Santa Maria, K.C.; Chan, A.N.; O’Neill, E.M.; Li, B. Targeted Rediscovery and Biosynthesis of the Farnesyl-Transferase Inhibitor Pepticinnamin E. Chembiochem 2019, 20, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thutewohl, M.; Kissau, >L.; Popkirova, B.; Karaguni, I.M.; Nowak, T.; Bate, M.; Kuhlmann, J.; Müller, O.; Waldmann, H. Identification of mono- and bisubstrate inhibitors of protein farnesyltransferase and inducers of apoptosis from a pepticinnamin E library. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 2617–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivona, T.G.; Quatela, S.E.; Bodemann, B.O.; Ahearn, I.M.; Soskis, M.J.; Mor, A.; Miura, J.; Wiener, H.H.; Wright, L.; Saba, S.G.; et al. PKC regulates a farnesyl-electrostatic switch on K-Ras that promotes its association with Bcl-XL on mitochondria and induces apoptosis. Mol. Cell 2006, 21, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, G.R.; Herald, C.L.; Doubek, D.L.; Herald, D.L.; Arnold, E.; Clardy, J. Isolation and structure of bryostatin 1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, 6846–6848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortmansky, J.; Schwartz, G.K. Bryostatin-1: A novel PKC inhibitor in clinical development. Cancer Investig. 2003, 21, 924–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Agnihotri, N. Piperlongumine, a piper alkaloid targets Ras/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling axis to inhibit tumor cell growth and proliferation in DMH/DSS induced experimental colon cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1462–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, A.; Li, W.M.; Liu, V.; Wang, C.; Mackedenski, S.; Tackaberry, L.E.; Massicotte, H.B.; Egger, K.N.; Reimer, K.; Lee, C.H. Grifolin, neogrifolin and confluentin from the terricolous polypore Albatrellus flettii suppress KRAS expression in human colon cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.-K.; Wang, D.; Bokesch, H.R.; Fuller, R.W.; Smith, E.; Henrich, C.J.; Durrant, D.E.; Morrison, D.K.; Bewley, C.A.; Gustafson, K.R. Swinhopeptolides A and B: Cyclic Depsipeptides from the Sponge Theonella swinhoei That Inhibit Ras/Raf Interaction. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, C.M.; Henkels, K.M.; Rehl, K.M.; Liang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Gutterman, J.U.; Cho, K.J. Avicin G is a potent sphingomyelinase inhibitor and blocks oncogenic K- and H-Ras signaling. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, R.M.; Stoykova, S.; Nicolay, B.N.; Ross, K.N.; Fitamant, J.; Boukhali, M.; Lengrand, J.; Deshpande, V.; Selig, M.K.; Ferrone, C.R.; et al. Transcriptional control of autophagy–lysosome function drives pancreatic cancer metabolism. Nature 2015, 524, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, N.H.; Olsen, O.D.; Groth-Pedersen, L.; Ellegaard, A.M.; Bilgin, M.; Redmer, S.; Ostenfeld, M.S.; Ulanet, D.; Dovmark, T.H.; Lønborg, A.; et al. Transformation-associated changes in sphingolipid metabolism sensitize cells to lysosomal cell death induced by inhibitors of acid sphingomyelinase. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.T.; Holderfield, M.; Galeas, J.; Delrosario, R.; To, M.D.; Balmain, A.; McCormick, F. K-Ras Promotes Tumorigenicity through Suppression of Non-canonical Wnt Signaling. Cell 2015, 163, 1237–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yano, Y.; Hasuma, T.; Yoshimata, T.; Yinna, W.; Otani, S. Inhibition of farnesyl protein transferase and P21ras memebrane association by d-limonene in human pancreas tumor cells in vitro. Chin. Med. Sci. J. 1999, 14, 138–144. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, S.C.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Athar, M.; Alam, M.S. D-Limonene modulates inflammation, oxidative stress and Ras-ERK pathway to inhibit murine skin tumorigenesis. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2012, 31, 798–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afaq, F.; Saleem, M.; Krueger, C.G.; Reed, J.D.; Mukhtar, H. Anthocyanin- and hydrolyzable tannin-rich pomegranate fruit extract modulates MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways and inhibits skin tumorigenesis in CD-1 mice. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 113, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Pham, T.H.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Ryu, H.W.; Oh, S.R.; Oh, J.W.; Yoon, D.Y. Methyl Linderone Suppresses TPA-Stimulated IL-8 and MMP-9 Expression Via the ERK/STAT3 Pathway in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.L.; Wang, J.L.; Lee, C.C.; Cheng, H.Y.; Wen, W.C.; Cheng, H.H.; Chen, M.C. Antroquinonol blocks Ras and Rho signaling via the inhibition of protein isoprenyltransferase activity in cancer cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2014, 68, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.B.; Yuan, T.C.; Liou, J.W.; Yang, C.J.; Sung, P.J.; Weng, C.F. Antroquinonol inhibits NSCLC proliferation by altering PI3K/mTOR proteins and miRNA expression profiles. Mutat. Res. 2011, 707, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmioli, A.; Sacco, E.; Abraham, S.; Thomas, C.J.; Di Domizio, A.; De Gioia, L.; Gaponenko, V.; Vanoni, M.; Peri, F. First experimental identification of Ras-inhibitor binding interface using a water-soluble Ras ligand. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 4217–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmioli, A.; Ciaramelli, C.; Tisi, R.; Spinelli, M.; De Sanctis, G.; Sacco, E.; Airoldi, C. Natural Compounds in Cancer Prevention: Effects of Coffee Extracts and Their Main Polyphenolic Component, 5-O-Caffeoylquinic Acid, on Oncogenic Ras Proteins. Chem. Asian J. 2017, 12, 2457–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganaie, A.A.; Siddique, H.R.; Sheikh, I.A.; Parray, A.; Wang, L.; Panyam, J.; Villalta, P.W.; Deng, Y.; Konety, B.R.; Saleem, M. A novel terpenoid class for prevention and treatment of KRAS-driven cancers: Comprehensive analysis using in situ, in vitro, and in vivo model systems. Mol. Carcinog. 2020, 59, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, J.B.; Pompliano, D.L.; Mosser, S.D.; Rands, E.; Lingham, R.B.; Singh, S.B.; Scolnick, E.M.; Kohl, N.E.; Oliff, A. Selective inhibition of farnesyl-protein transferase blocks ras processing in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 7617–7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, A.; Vala, H.; Vasconcelos-Nóbrega, C.; Faustino-Rocha, A.I.; Pires, C.A.; Colaço, A.; Oliveira, P.A.; Pires, M.J. Long-term treatment with chaethomellic acid A reduces glomerulosclerosis and arteriolosclerosis in a rat model of chronic kidney disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Krepinsky, J.C.; Li, Y.; Chang, Y.; Liu, L.; Peng, F.; Wu, D.; Tang, D.; Scholey, J.; Ingram, A.J. Akt mediates mechanical strain-induced collagen production by mesangial cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 1661–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Peña, A.B.; Grande, M.T.; Eleno, N.; Arévalo, M.; Guerrero, C.; Santos, E.; López-Novoa, J.M. Activation of Erk1/2 and Akt following unilateral ureteral obstruction. Kidney Int. 2008, 74, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandyopadhyay, D.; Lopez, G.; Cantu, S.; Balboa, S.; Garcia, A.; Silva, C.; Valdes, V. Chemistry Research and Applications: Organic and Medicinal Chemistry; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1, Chapter 9; ISBN 978-1-53614-855-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay, D. Preparation of Substituted Pyridinyl Azetidinone Derivatives for Use in Treating Cancer and Other Diseases. WO2019227040A1, 25 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay, D. Farmer to pharmacist: Curcumin as an anti-invasive and antimetastatic agent for the treatment of cancer1. Front. Chem. 2014, 2, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Compound Name | Structure | Major Pharmacophore(s) | Cancer Type | Targeted Enzyme M/A | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ganetespib |  | Indole, Triazolone, Resorcinol | Lung cancer/colorectal cancer | Inhibits heat-shock protein 90 (Hsp90) | [74] [75] |
| Apatinib |  | Pyridine | Metastatic lung cancer/breast cancer/gastric cancer | Inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) | [76] |
| Oncrasin-1 |  | Indole, Chlorophenyl | Lung cancer | Inhibits K-RAS/PKCι pathway | [77] |
| † | 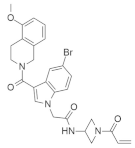 | Indole, Azetidine, Isoquinoline | Unknown | Inhibits KRASG12C mutation | [78] |
| †† | 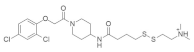 | Piperidine, Disulfide linkage | Unknown | Inhibits KRASG12C mutation | [79] |
| GDC-0449 (Vismodegib) combined with miRNA |  | Pyridine, Chlorobenzene, Sulfonyl | Pancreatic cancer | Hedgehog (Hh) inhibitor | [80] |
| Compound Name | Structure | Major Pharmacophore(s) | Cancer Type | Targeted Enzyme (M/A) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARS-1620 | 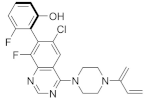 | 6-chloro-8-fluoroquinazoline, Piperizine | Unknown | KRASG12C inhibitor | [90] |
| ARS-853 | 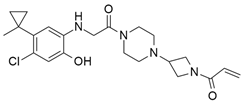 | Chlorophenol, Piperazine, Azetidine | Unknown | KRASG12C inhibitor | [91] |
| AMG 510 (Lumakras or Sotorasib) | 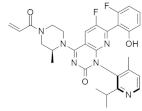 | Piperazine, Fluorophenol, Fluoropyrimidinone | Pancreatic cancer/Lung cancer | KRASG12C inhibitor | [92] |
| MRTX849 (Adagrasib) | 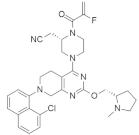 | Piperizine, Chloronaphthalene, Tetrahydropyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidine | Pancreatic cancer/Lung cancer | KRASG12C inhibitor | [93] |
| ††† | 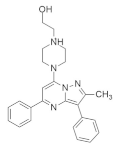 | Piperazine, Pyrazolopyrimidine | Pancreatic cancer | Inhibits MAPK/RAF signaling | [94] |
| BGB324 (Bemcentinib) | 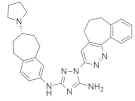 | Cycloheptapyridazine, Pyrrolidine, Triazole | Pancreatic cancer | Axl kinase inhibitor | [95] |
| ABT-737 |  | Chlorobiphenyl, Piperazine | Colon cancer | Represses Bcl-2/Bcl-XL, resulting in inhibition of the RNAi of PAK4 and PAK1 | [96] |
| AZD6244 (Selumetinib) |  | Quinoline, Imidazoquinoline | Colorectal cancer | Downregulation of MEK1/2 pathway inhibits KRAS mutation | [97] |
| NVP-BEZ235 (Dactolisib) in Combination with AZD6244 (Selumetinib) | 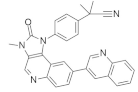 | Quinoline, Phenylpropanenitrile, Imidazoquinolinone | Lung cancer | Dual pan PI3K/MEK inhibitor | [98] |
| R115777 (Zarnestra or Tipifarnib) | 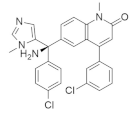 | Chlorophenyl, Imidazole, Quinolinone | Myeloma | Inhibits farnesyl transferase signaling | [99] |
| PPIN-1 PPIN-2 | 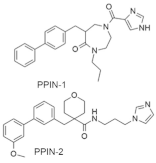 | Biphenyl, Imidazole, N-propyldiazepanone, Tetrahydropyran | Unknown | PPI inhibitor | [100] |
| pan-RAS inhibitor 3144 (RAS-IN-3144) | 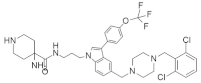 | Indole, Piperazine, Trifluoromethoxyphenyl | Unknown | Downregulates PI3K/AKT, RAF/MEK/ERK signaling | [101] |
| Deltarasin |  | Benzimidazole, Piperidine | Pancreatic cancer/Lung cancer | Downregulates RAS/RAF signaling pathway | [102] |
| †††† |  | Fluoroquinoline, Fluorophenol, Piperazine, Piperazinone | Unknown | KRASG12C inhibitor | [103] |
| SML-8-73-1 SML-10-70-1 | 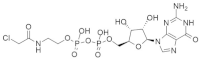 SML-8-73-1 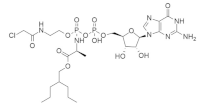 SML-10-70-1 | Purine, Tetrahydrofuran | Unknown | Inhibits KRASG12C binding with guanine-binding site | [104] |
| Cancer Type | Compound Name | Structure | Major Pharmacophore(s) | Biomolecular Target (M/A) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lung cancer | NHTD | 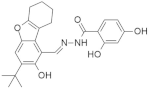 | Tetrahydrodibenzofuran, 2,4-Dihydroxybenzohydrazide | Inhibits tumor progression, decreasing CRAF, ERK, and AKT phosphorylation | [102] |
| Unknown | PD98059 |  | Chromenone | MEK inhibitor | [128] |
| Colorectal cancer | Wortmannin | 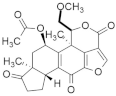 | Furoindenoisochromene | Suppresses upregulation of PI3K | [129] |
| Compound Name | Structure | Major Pharmacophore(s) | Cancer Type | Targeted Enzyme (M/A) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Talniflumate + Gefitinib | 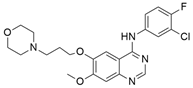 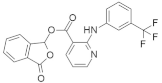 | Chlorofluorophenyl, Morpholine, Quinazoline, Pyridine, Benzofuranone | Pancreatic cancer | Inhibition of 2 β-1,6 N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (GCNT3) | [134] |
| CPD-0857 and KY1022 | 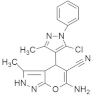 & 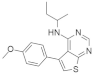 | Pyrazole, Pyran, Thienopyrimidine | Colorectal cancer | Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin, RAS/ERK, and PI3K/AKT | [135] |
| KYA1797K (ab229170) |  | Nitrophenyl, Furan, Thioxothiazolidin-4-one | Colorectal cancer | Unknown | [136] |
| 0375-0604 (KRAS inhibitor-9 or DUN09716) |  | Benzothiazolylthio-3-chloroaniline | Unknown | Inhibition of KRAS mutation by downregulating RAF/MEK/ERK and RAF/PI3K/AKT signaling pathways | [137] |
| 7773 | 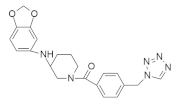 | Tetrazole, Piperidine, Benzodioxole | Lung cancer | Binding with hydrophobic surface of Igf2bp1 in KH3 and KH4 domain inhibits KRAS mutation. | [138] |
| NSC-658497 |  | Thioxothiazolidine, Chromane-2,4-dione, Nitrophenyl | Unknown | Binding with hydrophobic pocket downregulates pERK1/2 and pAKT signaling | [139] |
| JNJ-74699157 | 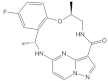 | Pyrazolopyrimidine, Benzocyclononaphanone | Unknown | KRASG12C inhibitor | Phase I Clinical trial completed |
| ID | Structure | Major Pharmacophore(s) | Cancer Type | Biomolecular Target (M/A) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PKF115-584 (Calphostin C) | 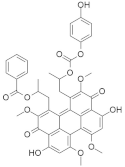 | Tetramethoxy-3,10-dioxo-3,10-dihydroperylen-1-yl) propan-2-yl benzoate | Colorectal cancer | Downregulates MAPK and RalA signaling | [149] |
| Kobe0065 + Kobe2602 | 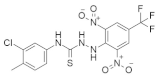 Kobe0065 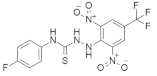 Kobe2602 | 2,6-dinitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl, Carbothioamide, Halophenyl | Unknown | Inhibits HRASG12V and KRASG12V mutation | [150] |
| ††††† | 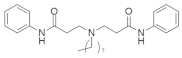 | Phenylacetamide | Myeloid leukemia | Inhibits isoprenylcysteine carboxylmethyltransferase (ICMT) | [151] |
| Salirasib + FTS, Salirasib | 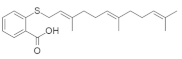 Salirasib 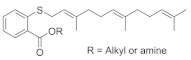 FTS, Salirasib | Trimethyldodecatrienylthiobenzoic acid | Bladder cancer (salirasib) | Inhibits glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation pathways | [152] [153] |
| ID | Structure | Major Pharmacophore(s) | Cancer Type | Targeted Enzyme/ (M/A) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ML264 | 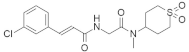 | Dioxidotetrahydro-2H-thiopyran, Chlorophenyl | Colorectal cancer | KLF5 inhibitor | [160] |
| GDC-6036 | Unpublished | Unpublished | KRASG12C inhibitor | Phase I Clinical trial (Genentech Inc) | |
| LY3499446 | Unpublished | Unpublished | KRASG12C inhibitor | Phase I and II Clinical trial (Eli Lilly) | |
| D-1553 | Unpublished | Unpublished | KRASG12C inhibitor | Phase I Clinical trial (InventisBio Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shetu, S.A.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Small-Molecule RAS Inhibitors as Anticancer Agents: Discovery, Development, and Mechanistic Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3706. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073706
Shetu SA, Bandyopadhyay D. Small-Molecule RAS Inhibitors as Anticancer Agents: Discovery, Development, and Mechanistic Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(7):3706. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073706
Chicago/Turabian StyleShetu, Shaila A., and Debasish Bandyopadhyay. 2022. "Small-Molecule RAS Inhibitors as Anticancer Agents: Discovery, Development, and Mechanistic Studies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 7: 3706. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073706
APA StyleShetu, S. A., & Bandyopadhyay, D. (2022). Small-Molecule RAS Inhibitors as Anticancer Agents: Discovery, Development, and Mechanistic Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(7), 3706. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073706