Mono-Sized Anion-Exchange Magnetic Microspheres for Protein Adsorption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
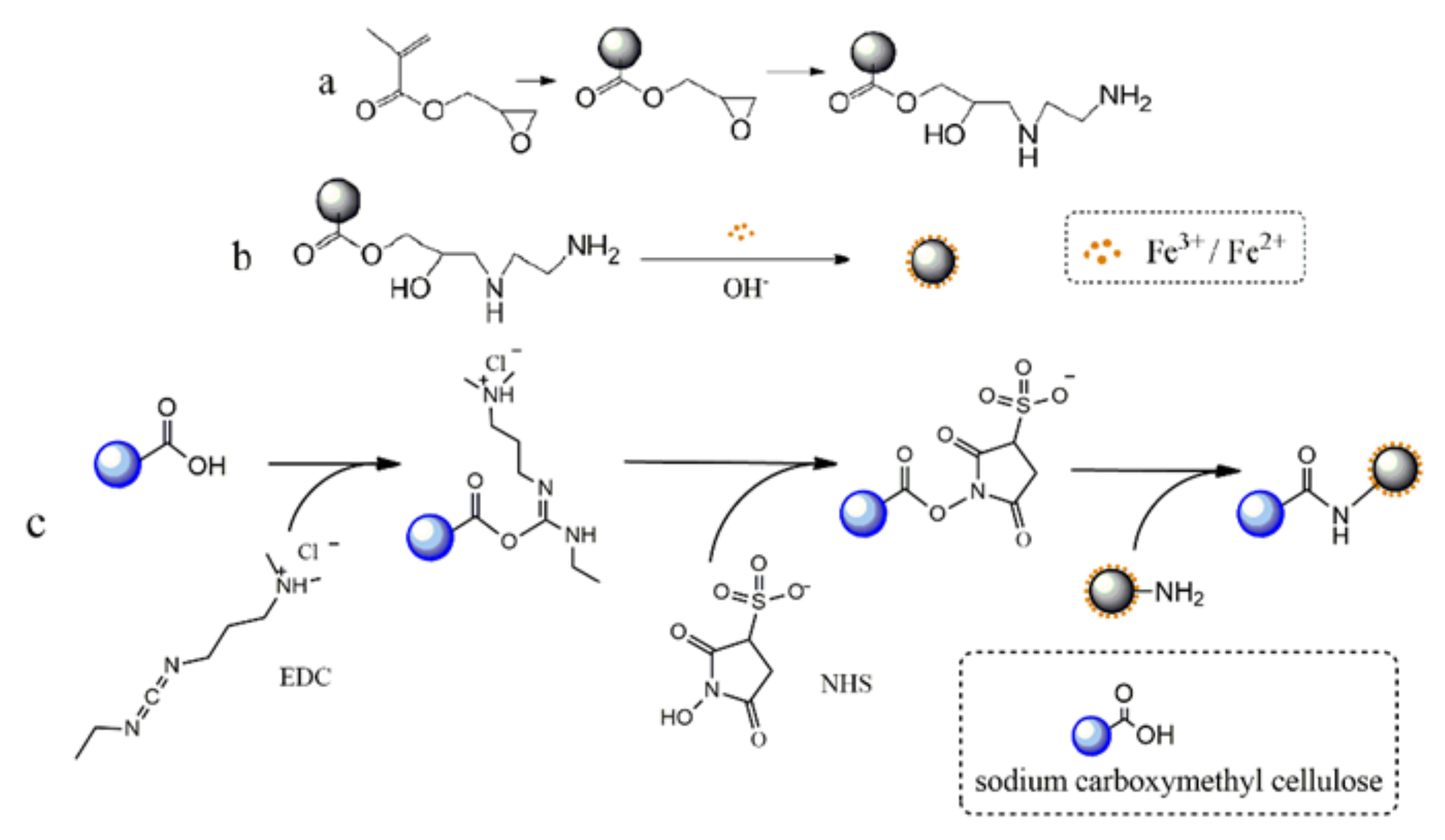
2.1. Synthesis of Anion-Exchange Magnetic Microspheres
2.2. Characterization of the Magnetic Microspheres
2.3. Binding Capability of Magnetic Microspheres
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of PGMA Microspheres
3.3. Synthesis of Amino Magnetic Microspheres
3.4. Synthesis of Carboxyl Magnetic Microspheres
3.5. Characterizations of the Magnetic Microspheres
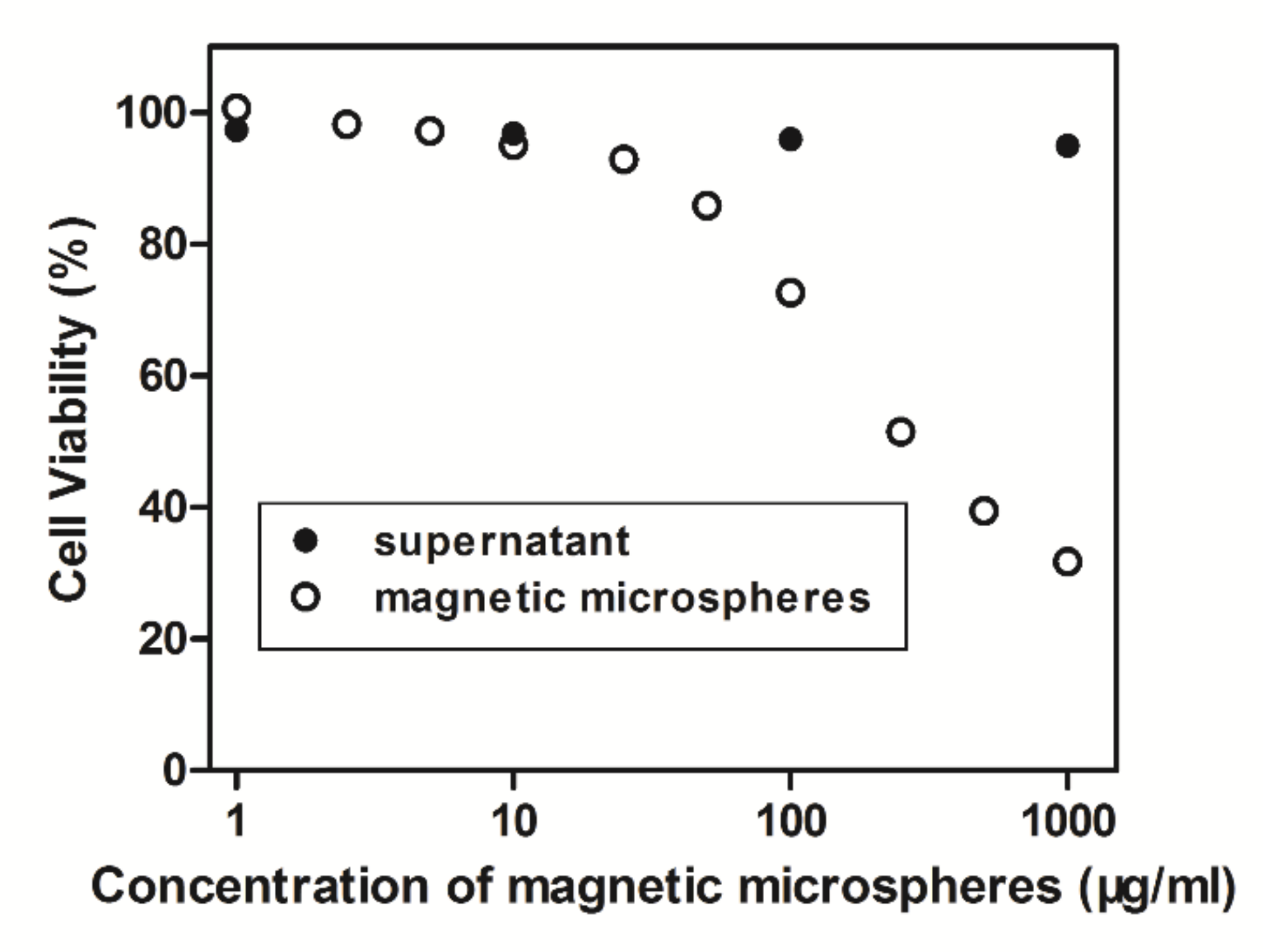
3.6. Cytotoxicity Test of the Carboxyl Magnetic Microspheres
3.7. Binding Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schmelter, C.; Funke, S.; Treml, J.; Beschnitt, A.; Perumal, N.; Manicam, C.; Pfeiffer, N.; Grus, F. Comparison of Two Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE) Methods for the Identification and Quantification of Porcine Retinal Protein Markers by LC-MS/MS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karakus, C.; Uslu, M.; Yazici, D.; Salih, B.A. Evaluation of immobilized metal affinity chromatography kits for the purification of histidine-tagged recombinant CagA protein. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1021, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keilhauer, E.C.; Hein, M.Y.; Mann, M. Accurate Protein Complex Retrieval by Affinity Enrichment Mass Spectrometry (AE-MS) Rather than Affinity Purification Mass Spectrometry (AP-MS). Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2015, 14, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, T.; Iqbal, M.Z.; Yang, F.; Hampp, N.; Wu, A.; Luo, L. Applications of magnetic materials separation in biological nanomedicine. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 2011–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaminger, S.P.; Blank-Shim, S.A.; Scheifele, I.; Pipich, V.; Fraga-García, P.; Berensmeier, S. Design of Interactions Between Nanomaterials and Proteins: A Highly Affine Peptide Tag to Bare Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Magnetic Protein Separation. Biotechnol. J. 2019, 14, 1800055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, Z.; Rasekh, B.; Yazdian, F.; Maghsoudi, A.; Soleimani, M.; Mohammadnejad, J. One-step separation of the recombinant protein by using the amine-functionalized magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles; an efficient and facile approach. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Gao, P.; Sun, S.; Du, Q.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y. Preparation of Fe3O4@PMAA@Ni Microspheres towards the Efficient and Selective Enrichment of Histidine-Rich Proteins. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 11166–11176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Lan, F.; Ma, S.; Xie, L.; He, B.; Gu, Z. Hollow superparamagnetic PLGA/Fe3O4 composite microspheres for lysozyme adsorption. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 085702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.; Sun, L.; Luo, A. Preparation and evaluation of Fe3O4 nanoparticles incorporated molecularly imprinted polymers for protein separation. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 51, 937–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.W.; Kim, J.I.; Choi, I.; Sung, J.; Hong, J.-I.; Yeo, W.-S. Zinc Ion-immobilized Magnetic Microspheres for Enrichment and Identification of Multi-phosphorylated Peptides by Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Sci. 2017, 33, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, J.; Chen, T.; Li, D.; Shen, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, Z. Fe3O4@PANI: A magnetic polyaniline nanomaterial for highly efficient and handy enrichment of intact N-glycopeptides. Analyst 2021, 146, 4261–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.X.; Kang, N.; Ke, X.B.; Bi, S.L.; Ren, L. Efficient Encapsulation of Fe3O4Nanoparticles into Genetically Engineered Hepatitis B Core Virus-Like Particles Through a Specific Interaction for Potential Bioapplications. Small 2015, 11, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, J.; Chen, J.; Ren, L.; Jiang, B.; Zhao, J. Synthesis of Monodisperse, Hierarchically Mesoporous, Silica Microspheres Embedded with Magnetic Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2735–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, L.; Du, L.; Gao, P.; Liang, N.; Wu, S.; Minami, T.; Zang, L.; Yu, C.; Xu, X. Preparation of Polyaniline/Emulsion Microsphere Composite for Efficient Adsorption of Organic Dyes. Polymers 2020, 12, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, B.; Zeng, C.; Yu, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L. Preparation of hollow zeolite NaA/chitosan composite microspheres via in situ hydrolysis-gelation-hydrothermal synthesis of TEOS. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 257, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.H.; Chen, D.H. Fast and efficient adsorption/desorption of protein by a novel magnetic nano-adsorbent. Biotechnol. Lett. 2002, 24, 1913–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heebøll-Nielsen, A.; Dalkiær, M.; Hubbuch, J.J.; Thomas, O.R.T. Superparamagnetic adsorbents for high-gradient magnetic fishing of lectins out of legume extracts. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 87, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.P.; Bai, S.; Xu, L.; Sun, Y. Fabrication of mono-sized magnetic anion exchange beads for plasmid DNA purification. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.Y.; Bai, S.; Sun, Y. Fabrication and characterization of rigid magnetic monodisperse microspheres for protein adsorption. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 852, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavinia, G.R.; Soleymani, M.; Etemadi, H.; Sabzi, M.; Atlasi, Z. Model protein BSA adsorption onto novel magnetic chitosan/PVA/laponite RD hydrogel nanocomposite beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Tang, Y.; Hao, Y.; He, G.; Gao, R.; Tang, X. Selective adsorption of protein by a high-efficiency Cu2+-cooperated magnetic imprinted nanomaterial. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 2876–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Chen, T.; Cui, K. Constituting of a new surface-initiating system on polymeric microspheres and preparation of basic protein surface-imprinted material in aqueous solution. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saçlıgil, D.; Şenel, S.; Yavuz, H.; Denizli, A. Purification of transferrin by magnetic immunoaffinity beads. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 2729–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Guan, Y.; Liu, H. Synthesis and characterization of micron-sized monodisperse superparamagnetic polymer particles with amino groups. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2005, 43, 3433–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Magnetic Microspheres | Protein | Maximum Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|
| Thepreparedmagnetmicrospheres | Hb | 217 |
| Chitosan-based magnetic beads byin situmethod [20] | BSA | 240.5 |
| Cu2+-cooperated magnetic imprinted nanomaterial [21] | Hb | 116.3 |
| surface-imprinted polyvinyl alcohol microspheres [22] | papain | 44 |
| magnetic immunoaffinity beads by dispersion polymerization [23] | Anti-Tf | 2.0 |
| Fe3O4@PMAA@Ni microspheres with flower-like Ni nanofoams [7] | Hb | 2660 |
| Adsorbents | Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm | Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | R2 | 1/n | R2 | |||
| amino magnetic microspheres | 131.27 | 1.4837 | 0.9966 | 52.55 | 0.5342 | 0.9427 |
| carboxyl magnetic microspheres | 215.74 | 0.4282 | 0.9997 | 48.41 | 0.6603 | 0.9750 |
| Amino Magnetic Microspheres | Carboxyl Magnetic Microspheres | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | R2 | |||||
| Lagergren first-order rate kinetics | 0.2660 | 166.05 | 0.9209 | 0.1143 | 153.33 | 0.9767 |
| Lagergren second-order rate kinetics | 2.352 | 119.05 | 0.9981 | 0.0010 | 172.41 | 0.9911 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Meng, Z.; Xue, M. Mono-Sized Anion-Exchange Magnetic Microspheres for Protein Adsorption. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094963
Wang Z, Wang W, Meng Z, Xue M. Mono-Sized Anion-Exchange Magnetic Microspheres for Protein Adsorption. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(9):4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094963
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhe, Wei Wang, Zihui Meng, and Min Xue. 2022. "Mono-Sized Anion-Exchange Magnetic Microspheres for Protein Adsorption" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 9: 4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094963
APA StyleWang, Z., Wang, W., Meng, Z., & Xue, M. (2022). Mono-Sized Anion-Exchange Magnetic Microspheres for Protein Adsorption. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(9), 4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094963






