An Inverse Agonist GSK5182 Increases Protein Stability of the Orphan Nuclear Receptor ERRγ via Inhibition of Ubiquitination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
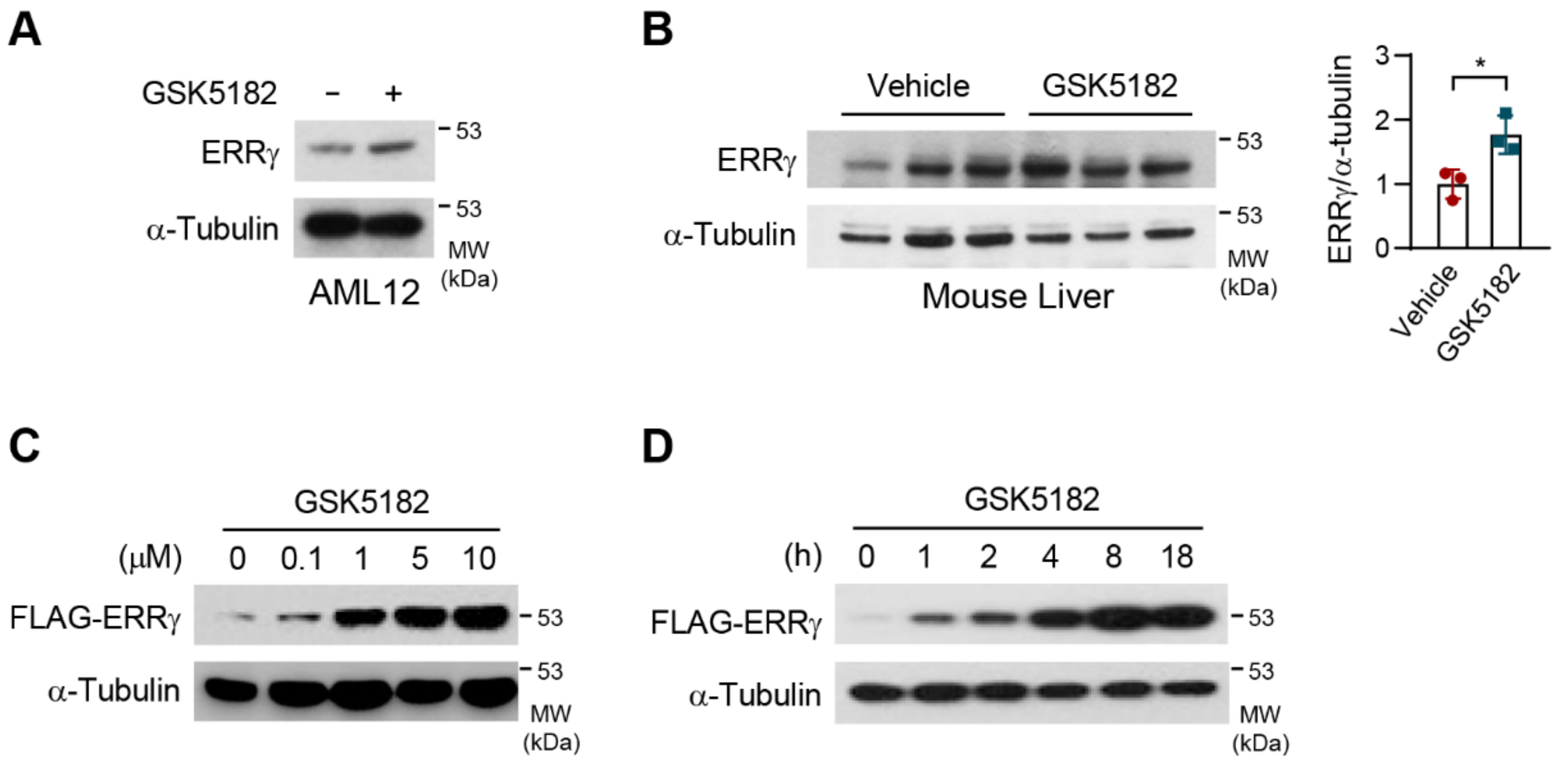
2.1. An Inverse Agonist, GSK5182, Stabilizes the ERRγ Protein
2.2. Different Effect of Ligands on ERRγ Protein
2.3. Protein Stability Due to GSK5182 Requires Y326 of ERRγ
2.4. GSK5182 Stabilizes ERRγ by Extending Its Half-Life
2.5. GSK5182 Prevents ERRγ Ubiquitination by Inhibiting Its Association with the E3 Ligase Parkin
2.6. GSK5182 Promotes Recruitment of the Corepressor SMILE to ERRγ
2.7. The AF-2 Domain of ERRγ Is Crucial for Protein Turnover
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Plasmids, DNA Constructs, and Recombinant Adenoviruses
4.3. Cell Culture, Transient Transfection, and Luciferase Assay
4.4. Animal Experiments
4.5. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Assay
4.6. Pulse Labeling
4.7. Confocal Microscopy
4.8. Immunoblotting
4.9. Nuclear/Cytosol Fractionation
4.10. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bookout, A.L.; Jeong, Y.; Downes, M.; Yu, R.T.; Evans, R.M.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Anatomical profiling of nuclear receptor expression reveals a hierarchical transcriptional network. Cell 2006, 126, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crevet, L.; Vanacker, J.M. Regulation of the expression of the estrogen related receptors (ERRs). Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 4573–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, J.; Kim, D.K.; Choi, H.S. ERRgamma: A Junior Orphan with a Senior Role in Metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.K.; Gang, G.T.; Ryu, D.; Koh, M.; Kim, Y.N.; Kim, S.S.; Park, J.; Kim, Y.H.; Sim, T.; Lee, I.K.; et al. Inverse agonist of nuclear receptor ERRgamma mediates antidiabetic effect through inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3093–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, D.K.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, K.S.; Park, S.H.; Kim, Y.D.; Koh, M.; Shin, M.; Jung, Y.S.; Kim, H.S.; et al. Inverse agonist of estrogen-related receptor gamma controls Salmonella typhimurium infection by modulating host iron homeostasis. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, K.; Kim, Y.H.; Jung, Y.S.; Kim, D.K.; Na, S.Y.; Lim, D.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.S.; Choy, H.E.; et al. Orphan nuclear receptor ERR-gamma regulates hepatic FGF23 production in acute kidney injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2022841118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Radhakrishnan, K.; Kim, J.; Lee, I.K.; Cho, S.J.; Kim, D.K.; Dooley, S.; Lee, C.H.; Choi, H.S. Orphan nuclear receptor ERR gamma regulates hepatic TGF-beta 2 expression and fibrogenic response in CCl4-induced acute liver injury. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 3071–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greschik, H.; Wurtz, J.M.; Sanglier, S.; Bourguet, W.; van Dorsselaer, A.; Moras, D.; Renaud, J.P. Structural and functional evidence for ligand-independent transcriptional activation by the estrogen-related receptor 3. Mol. Cell. 2002, 9, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coward, P.; Lee, D.; Hull, M.V.; Lehmann, J.M. 4-Hydroxytamoxifen binds to and deactivates the estrogen-related receptor gamma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8880–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, E.Y.; Collins, J.L.; Gaillard, S.; Miller, A.B.; Wang, L.; Orband-Miller, L.A.; Nolte, R.T.; McDonnell, D.P.; Willson, T.M.; Zuercher, W.J. Structure-guided synthesis of tamoxifen analogs with improved selectivity for the orphan ERRgamma. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zuercher, W.J.; Consler, T.G.; Lambert, M.H.; Miller, A.B.; Orband-Miller, L.A.; McKee, D.D.; Willson, T.M.; Nolte, R.T. X-ray crystal structures of the estrogen-related receptor-gamma ligand binding domain in three functional states reveal the molecular basis of small molecule regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 37773–37781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.C.; Puigserver, P.; Chen, G.; Donovan, J.; Wu, Z.; Rhee, J.; Adelmant, G.; Stafford, J.; Kahn, C.R.; Granner, D.K.; et al. Control of hepatic gluconeogenesis through the transcriptional coactivator PGC-1. Nature 2001, 413, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.B.; Lee, O.H.; Nedumaran, B.; Seong, H.A.; Lee, K.M.; Ha, H.; Lee, I.K.; Yun, Y.; Choi, H.S. SMILE, a new orphan nuclear receptor SHP-interacting protein, regulates SHP-repressed estrogen receptor transactivation. Biochem. J. 2008, 416, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.B.; Nedumaran, B.; Choi, H.S. Molecular characterization of SMILE as a novel corepressor of nuclear receptors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 4100–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Seo, W.Y.; Han, H.S.; Oh, K.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, D.K.; Choi, S.; Choi, B.H.; Harris, R.A.; Lee, C.H.; et al. Insulin-Inducible SMILE Inhibits Hepatic Gluconeogenesis. Diabetes 2016, 65, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, W.; Feng, J. Parkin suppresses the expression of monoamine oxidases. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 8591–8599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Jiang, H.; Ma, D.; Nakaso, K.; Feng, J. Parkin degrades estrogen-related receptors to limit the expression of monoamine oxidases. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 1074–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Peng, L.; Lv, M.; Ding, K. Recent advance in the design of small molecular modulators of estrogen-related receptors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 3421–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayanagi, S.; Tokunaga, T.; Liu, X.; Okada, H.; Matsushima, A.; Shimohigashi, Y. Endocrine disruptor bisphenol A strongly binds to human estrogen-related receptor gamma (ERRgamma) with high constitutive activity. Toxicol Lett. 2006, 167, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Ryu, D.; Koh, M.; Lee, M.W.; Lim, D.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Cho, W.J.; Lee, C.H.; Park, S.B.; et al. Orphan nuclear receptor estrogen-related receptor gamma (ERRgamma) is key regulator of hepatic gluconeogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 21628–21639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, M.C.; Askari, H.; O’Neill, J.; Klinger, A.L.; Milligan, C.; Lewandowski, F.; Springer, B.; Spurlino, J.; Rentzeperis, D. Structural determination of estrogen-related receptor gamma in the presence of phenol derivative compounds. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 108, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.; Nawaz, Z. Nuclear hormone receptor degradation and gene transcription: An update. IUBMB Life 2005, 57, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarid, E.T. Lives and times of nuclear receptors. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 1972–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonard, D.M.; Nawaz, Z.; Smith, C.L.; O’Malley, B.W. The 26S proteasome is required for estrogen receptor-alpha and coactivator turnover and for efficient estrogen receptor-alpha transactivation. Mol. Cell. 2000, 5, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Yoon, J.M.; Choi, A.H.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, G.Y.; Kim, J.B. Liver X receptor ligands suppress ubiquitination and degradation of LXRalpha by displacing BARD1/BRCA1. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 23, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genini, D.; Catapano, C.V. Block of nuclear receptor ubiquitination. A mechanism of ligand-dependent control of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 11776–11785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayaratne, A.L.; McDonnell, D.P. The human estrogen receptor-alpha is a ubiquitinated protein whose stability is affected differentially by agonists, antagonists, and selective estrogen receptor modulators. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 35684–35692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, J.; Kim, D.K.; Jung, Y.S.; Kim, H.B.; Kim, Y.H.; Yoo, E.K.; Kim, B.G.; Kim, S.; Lee, I.K.; Harris, R.A.; et al. O-GlcNAcylation of Orphan Nuclear Receptor Estrogen-Related Receptor gamma Promotes Hepatic Gluconeogenesis. Diabetes 2016, 65, 2835–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Kim, J.R.; Koh, M.; Kim, Y.D.; Lee, J.M.; Chanda, D.; Park, S.B.; Min, J.J.; Lee, C.H.; Park, T.S.; et al. Estrogen-related receptor gamma (ERRgamma) is a novel transcriptional regulator of phosphatidic acid phosphatase, LIPIN1, and inhibits hepatic insulin signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 38035–38042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Jang, H.H.; Park, J.; Kim, J.R.; Koh, M.; Jeong, W.I.; Koo, S.H.; Park, T.S.; Yun, C.H.; et al. Estrogen-related receptor gamma controls hepatic CB1 receptor-mediated CYP2E1 expression and oxidative liver injury by alcohol. Gut 2013, 62, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, J.M.; Park, S.B.; Jeong, W.I.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, I.K.; Lee, C.H.; Chiang, J.Y.; Choi, H.S. Orphan nuclear receptor oestrogen-related receptor gamma (ERRgamma) plays a key role in hepatic cannabinoid receptor type 1-mediated induction of CYP7A1 gene expression. Biochem. J. 2015, 470, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Metivier, R.; Penot, G.; Hubner, M.R.; Reid, G.; Brand, H.; Kos, M.; Gannon, F. Estrogen receptor-alpha directs ordered, cyclical, and combinatorial recruitment of cofactors on a natural target promoter. Cell 2003, 115, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greschik, H.; Flaig, R.; Renaud, J.P.; Moras, D. Structural basis for the deactivation of the estrogen-related receptor gamma by diethylstilbestrol or 4-hydroxytamoxifen and determinants of selectivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 33639–33646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Woo, S.Y.; Im, C.Y.; Yoo, E.K.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.J.; Hwang, H.J.; Cho, J.H.; Lee, W.S.; Yoon, H.; et al. Insights of a Lead Optimization Study and Biological Evaluation of Novel 4-Hydroxytamoxifen Analogs as Estrogen-Related Receptor gamma (ERRgamma) Inverse Agonists. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 10209–10227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Chandra, V.; Rastinejad, F. Structural overview of the nuclear receptor superfamily: Insights into physiology and therapeutics. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 247–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, S.; Adelmant, G.; Sarraf, P.; Wright, H.M.; Mueller, E.; Spiegelman, B.M. Degradation of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma is linked to ligand-dependent activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 18527–18533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, M.; Tarrade, A.; Nigro, E.A.; Garattini, E.; Rochette-Egly, C. The AF-1 and AF-2 domains of RAR gamma 2 and RXR alpha cooperate for triggering the transactivation and the degradation of RAR gamma 2/RXR alpha heterodimers. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 34458–34466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arao, Y.; Hamilton, K.J.; Coons, L.A.; Korach, K.S. Estrogen receptor alpha L543A,L544A mutation changes antagonists to agonists, correlating with the ligand binding domain dimerization associated with DNA binding activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 21105–21116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.D.; Huss, J.M.; Li, H.; Forman, B.M. Identification of novel inverse agonists of estrogen-related receptors ERRgamma and ERRbeta. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 1585–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, N.Y.; Lee, S.; Byun, J.K.; Yun, J.W.; Lee, J.; Jin, J.; Chin, J.; Cho, S.J.; et al. DN200434, an orally available inverse agonist of estrogen-related receptor gamma, induces ferroptosis in sorafenib-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma. BMB Rep. 2022, 55, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, S.N.; McMeekin, L.J.; Savage, C.H.; Joyce, K.L.; Boas, S.M.; Simmons, M.S.; Farmer, C.B.; Ryan, J.; Pereboeva, L.; Becker, K.; et al. Estrogen-related receptor gamma regulates mitochondrial and synaptic genes and modulates vulnerability to synucleinopathy. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2022, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.I.; Lim, J.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, H.J. ERRgamma Ligand Regulates Adult Neurogenesis and Depression-like Behavior in a LRRK2-G2019S-associated Young Female Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neurotherapeutics 2022, 19, 1298–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Chin, J.; Im, C.Y.; Yoo, E.K.; Woo, S.; Hwang, H.J.; Cho, J.H.; Seo, K.A.; Song, J.; Hwang, H.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 4-hydroxytamoxifen analogs as estrogen-related receptor gamma inverse agonists. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 120, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Song, J.; Ji, H.D.; Yoo, E.K.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, S.B.; Oh, J.M.; Lee, S.; Hwang, J.S.; Yoon, H.; et al. Discovery of Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable Estrogen-Related Receptor-gamma Inverse Agonists To Restore the Sodium Iodide Symporter Function in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 1837–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Takeda, J.; Lee, Y.K.; Moore, D.D.; Choi, H.S. Differential regulation of the orphan nuclear receptor small heterodimer partner (SHP) gene promoter by orphan nuclear receptor ERR isoforms. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Na, S.-Y.; Kim, K.-S.; Jung, Y.S.; Kim, D.-K.; Kim, J.; Cho, S.J.; Lee, I.-K.; Chung, J.; Kim, J.-S.; Choi, H.-S. An Inverse Agonist GSK5182 Increases Protein Stability of the Orphan Nuclear Receptor ERRγ via Inhibition of Ubiquitination. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010096
Na S-Y, Kim K-S, Jung YS, Kim D-K, Kim J, Cho SJ, Lee I-K, Chung J, Kim J-S, Choi H-S. An Inverse Agonist GSK5182 Increases Protein Stability of the Orphan Nuclear Receptor ERRγ via Inhibition of Ubiquitination. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(1):96. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010096
Chicago/Turabian StyleNa, Soon-Young, Ki-Sun Kim, Yoon Seok Jung, Don-Kyu Kim, Jina Kim, Sung Jin Cho, In-Kyu Lee, Jongkyeong Chung, Jeong-Sun Kim, and Hueng-Sik Choi. 2023. "An Inverse Agonist GSK5182 Increases Protein Stability of the Orphan Nuclear Receptor ERRγ via Inhibition of Ubiquitination" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 1: 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010096
APA StyleNa, S.-Y., Kim, K.-S., Jung, Y. S., Kim, D.-K., Kim, J., Cho, S. J., Lee, I.-K., Chung, J., Kim, J.-S., & Choi, H.-S. (2023). An Inverse Agonist GSK5182 Increases Protein Stability of the Orphan Nuclear Receptor ERRγ via Inhibition of Ubiquitination. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(1), 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010096







