Targeting Stage-Specific Embryonic Antigen 4 (SSEA-4) in Triple Negative Breast Cancer by CAR T Cells Results in Unexpected on Target/off Tumor Toxicities in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
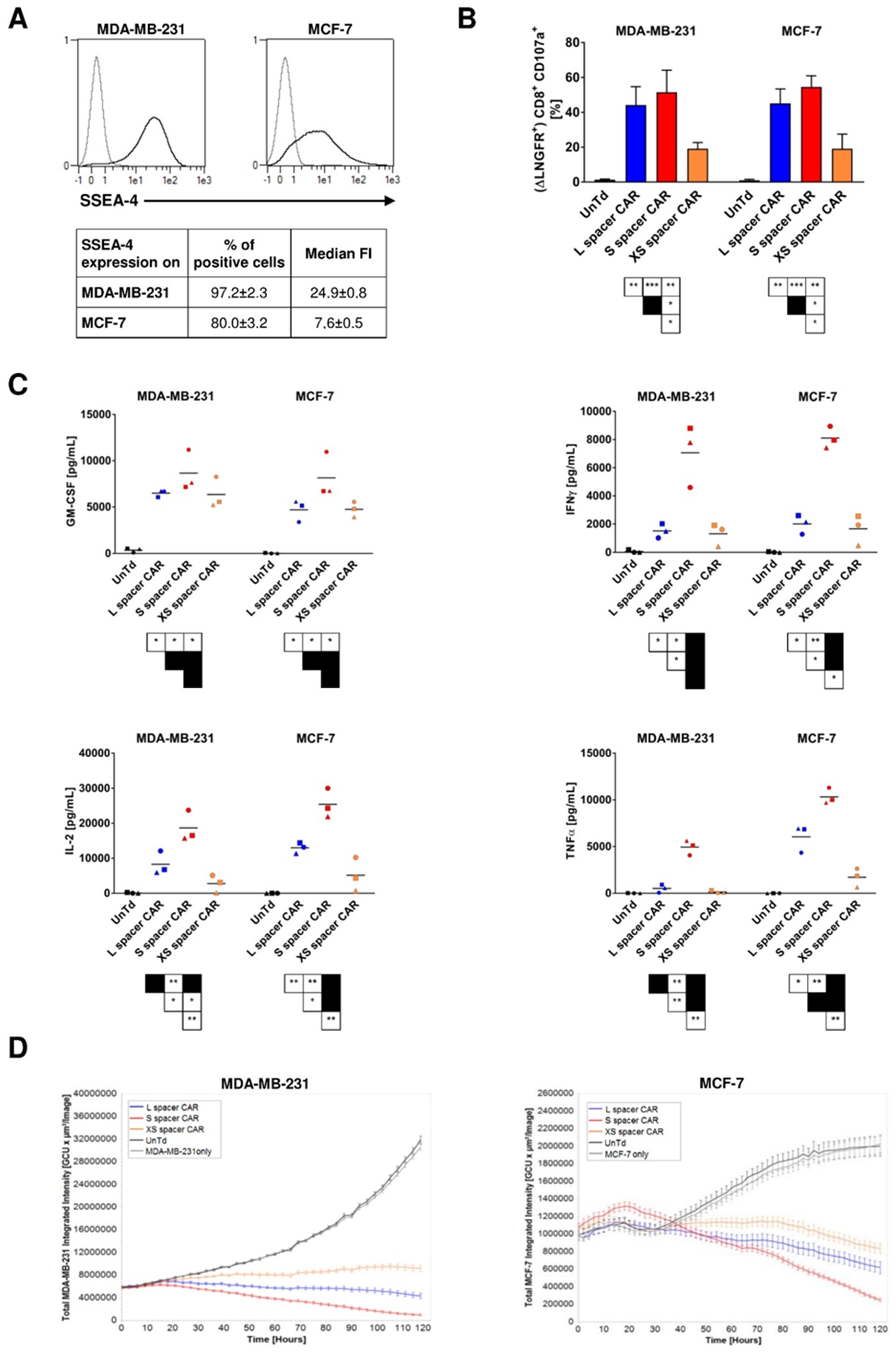
2.1. Construction of SSEA-4-Directed CARs, T Cell Engineering, and Functional In Vitro Characterization
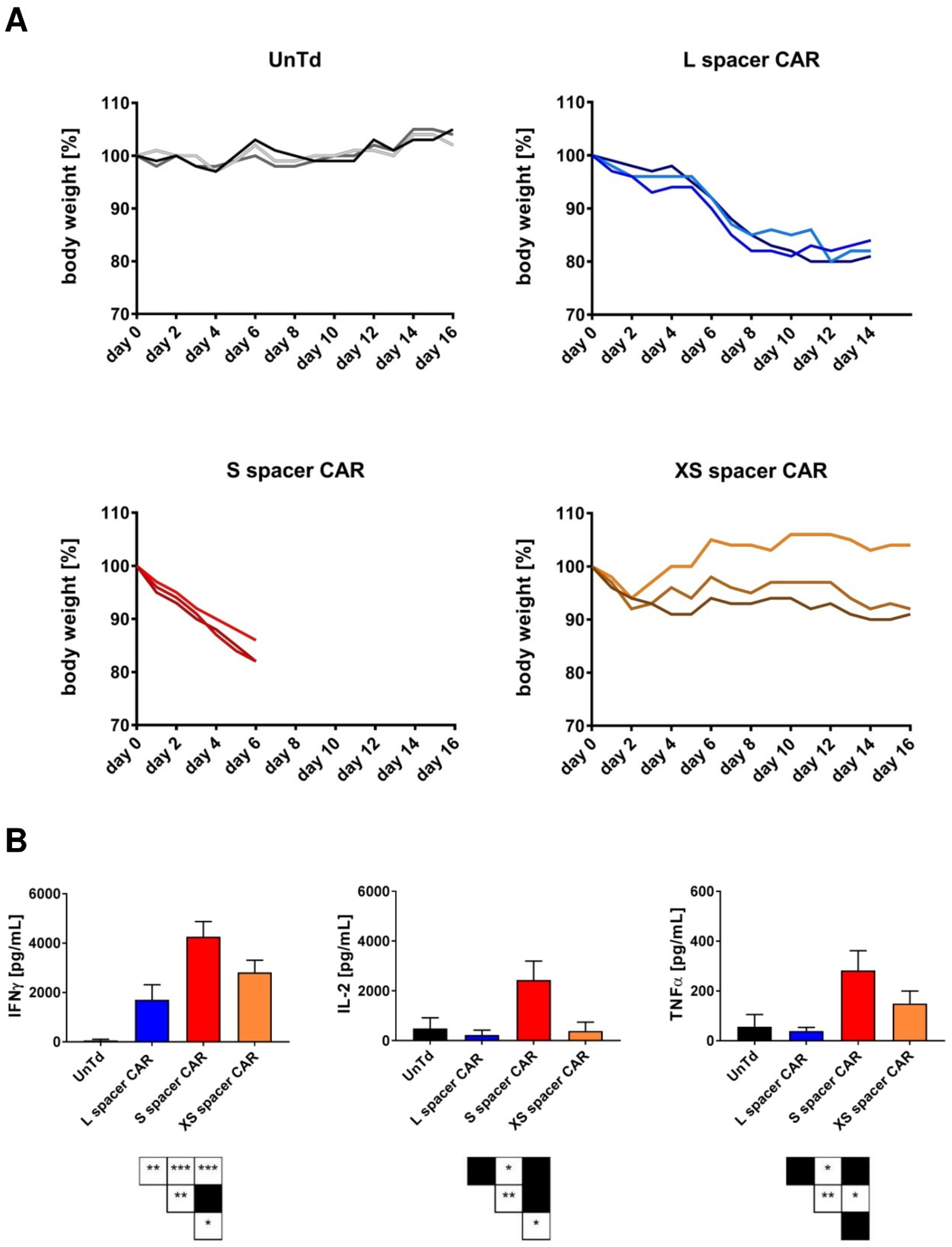
2.2. Targeting SSEA-4-Positive Tumors In Vivo
2.3. Characterization of the In Vivo Toxicities Mediated by CAR T Cells
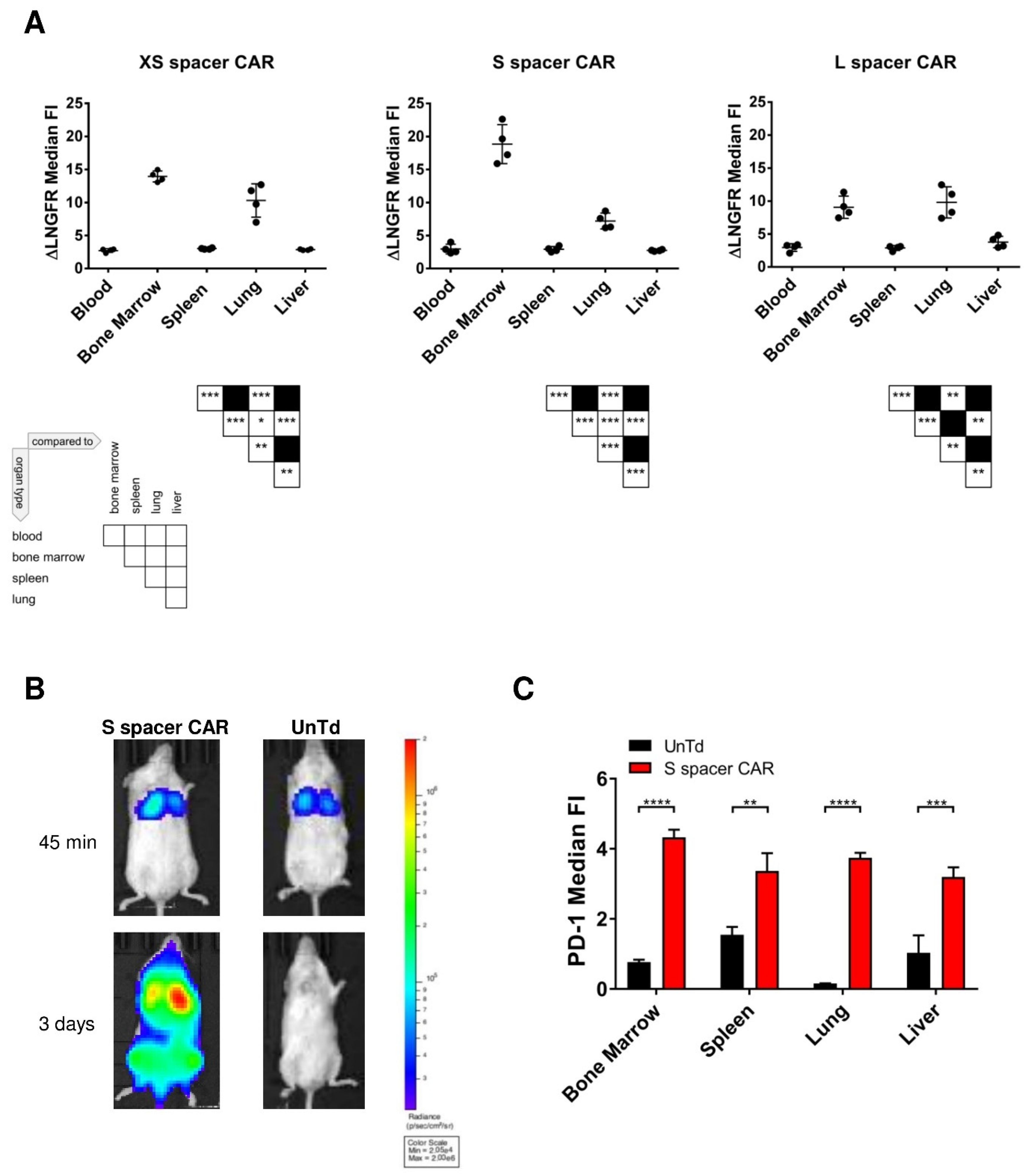
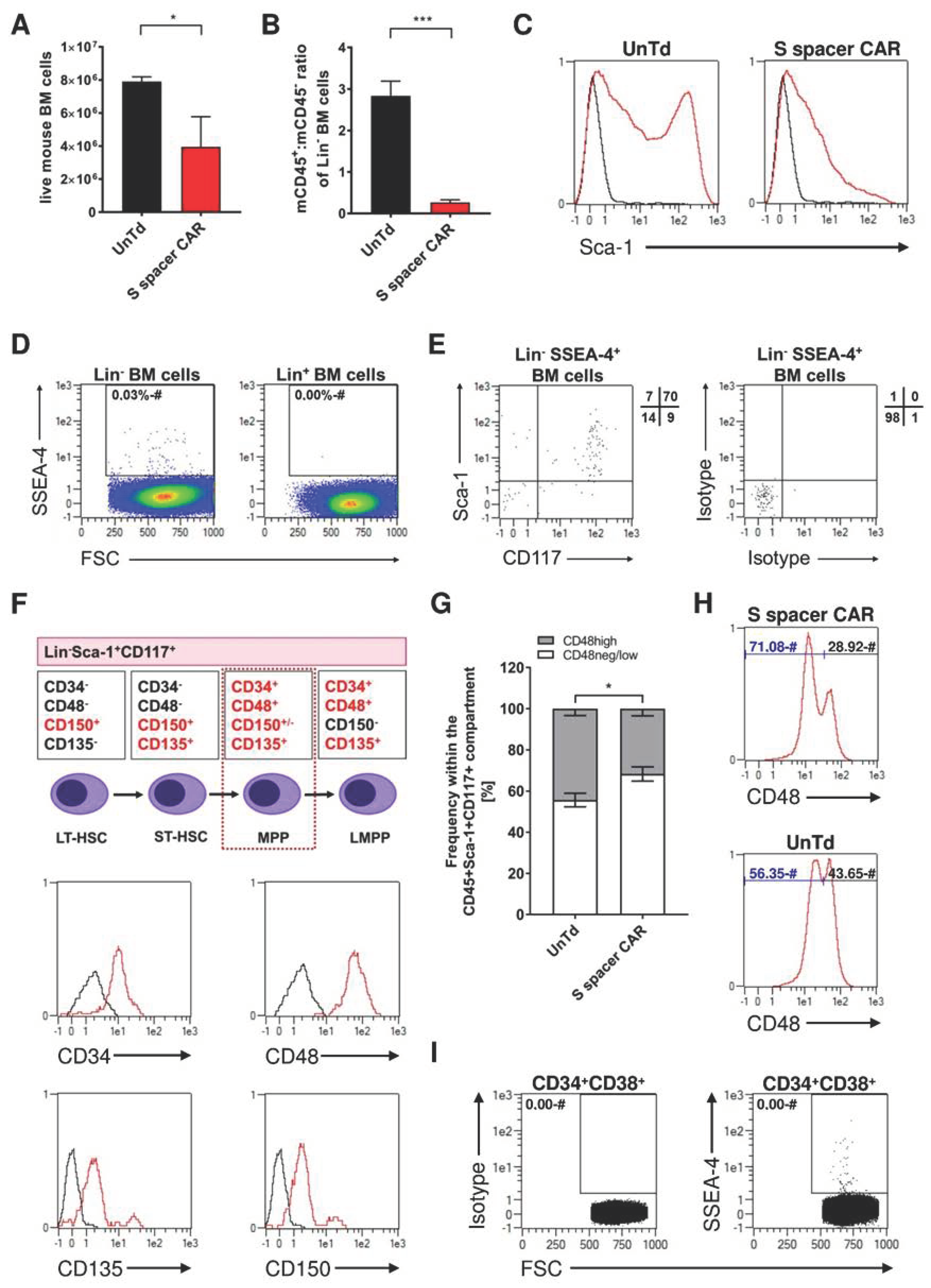
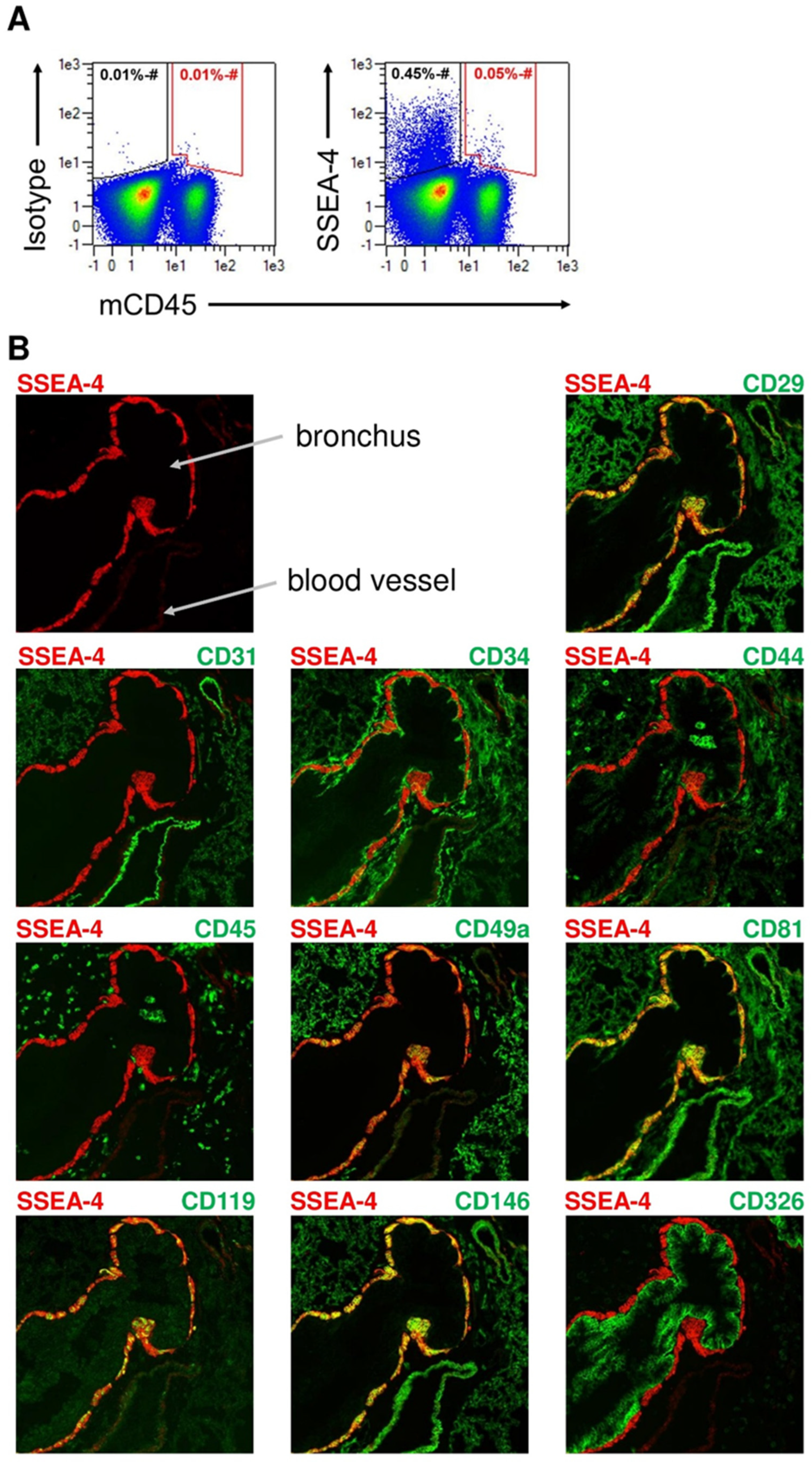
2.4. Identification of SSEA-4-Expressing Cells in Bone Marrow
2.5. Identification of SSEA-4-Expressing Cells in the Lung
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells and Culture Conditions
4.2. Construction of SSEA-4 CARs
4.3. Lentiviral Vector Production
4.4. T Cell Isolation, Transduction, and ΔLNGFR Enrichment
4.5. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.6. CAR T Cell Functional Assays
4.7. In Vivo Studies
4.8. Ex Vivo Organ Preparation
4.9. MACSima™ Imaging for Lung Tissue Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, B.O.; Shyyan, R.; Eniu, A.; Smith, R.A.; Yip, C.-H.; Bese, N.S.; Chow, L.W.C.; Masood, S.; Ramsey, S.D.; Carlson, R.W. Breast cancer in limited-resource countries: An overview of the Breast Health Global Initiative 2005 guidelines. Breast J. 2006, 12, S3–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; McCarron, P.; Parkin, D.M. The changing global patterns of female breast cancer incidence and mortality. Breast Cancer Res. BCR 2004, 6, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoncheh, M.; Pournamdar, Z.; Salehiniya, H. Incidence and Mortality and Epidemiology of Breast Cancer in the World. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2016, 17, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korde, L.A.; Zujewski, J.A.; Kamin, L.; Giordano, S.; Domchek, S.; Anderson, W.F.; Bartlett, J.M.; Gelmon, K.; Nahleh, Z.; Bergh, J.; et al. Multidisciplinary meeting on male breast cancer: Summary and research recommendations. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2114–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, K.R.; Brown, M.; Cress, R.D.; Parise, C.A.; Caggiano, V. Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor (ER)-negative, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, and HER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple-negative phenotype: A population-based study from the California cancer Registry. Cancer 2007, 109, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, R.; Hanna, W.M.; Trudeau, M.; Rawlinson, E.; Sun, P.; Narod, S.A. Pattern of metastatic spread in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2009, 115, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.K.; Mortimer, J. Triple-negative breast cancer: Novel therapies and new directions. Maturitas 2009, 63, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balko, J.M.; Giltnane, J.M.; Wang, K.; Schwarz, L.J.; Young, C.D.; Cook, R.S.; Owens, P.; Sanders, M.E.; Kuba, M.G.; Sánchez, V.; et al. Molecular profiling of the residual disease of triple-negative breast cancers after neoadjuvant chemotherapy identifies actionable therapeutic targets. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liedtke, C.; Mazouni, C.; Hess, K.R.; André, F.; Tordai, A.; Mejia, J.A.; Symmans, W.F.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Hennessy, B.; Green, M.; et al. Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, H.; Masuda, N.; Kodama, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Karita, M.; Yamamura, J.; Tsukuda, K.; Doihara, H.; Miyoshi, S.; Mano, M.; et al. Predictive factors for the effectiveness of neoadjuvant chemotherapy and prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer patients. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 67, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloia, A.; Petrova, E.; Tomiuk, S.; Bissels, U.; Déas, O.; Saini, M.; Zickgraf, F.M.; Wagner, S.; Spaich, S.; Sütterlin, M.; et al. The sialyl-glycolipid stage-specific embryonic antigen 4 marks a subpopulation of chemotherapy-resistant breast cancer cells with mesenchymal features. Breast Cancer Res. BCR 2015, 17, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannagi, R.; Cochran, N.; Ishigami, F.; Hakomori, S.; Andrews, P.; Knowles, B.; Solter, D. Stage-specific embryonic antigens (SSEA-3 and -4) are epitopes of a unique globo-series ganglioside isolated from human teratocarcinoma cells. EMBO J. 1983, 2, 2355–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breimer, M.E.; Saljo, K.; Barone, A.; Teneberg, S. Glycosphingolipids of human embryonic stem cells. Glycoconj. J. 2017, 34, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, E.J.; Bosnakovski, D.; Figueiredo, C.A.; Visser, J.W.; Perlingeiro, R.C.R. SSEA-4 identifies mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow. Blood 2007, 109, 1743–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittenger, M.F.; Mackay, A.M.; Beck, S.C.; Jaiswal, R.K.; Douglas, R.; Mosca, J.D.; Moorman, M.A.; Simonetti, D.W.; Craig, S.; Marshak, D.R. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 1999, 284, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riekstina, U.; Cakstina, I.; Parfejevs, V.; Hoogduijn, M.; Jankovskis, G.; Muiznieks, I.; Muceniece, R.; Ancans, J. Embryonic stem cell marker expression pattern in human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue, heart and dermis. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2009, 5, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, S.; Orikasa, S.; Satoh, M.; Ohyama, C.; Ito, A.; Takahashi, T. Expression of globo-series gangliosides in human renal cell carcinoma. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. Gann. 1997, 88, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschling, S.; Jensen, K.; Warth, A.; Herth, F.J.; Thomas, M.; Schnabel, P.A.; Herpel, E. Stage-specific embryonic antigen-4 is expressed in basaloid lung cancer and associated with poor prognosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Hu, Y.; Chen, H. Stage-specific embryonic antigen 4 expression in epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer Off. J. Int. Gynecol. Cancer Soc. 2010, 20, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noto, Z.; Yoshida, T.; Okabe, M.; Koike, C.; Fathy, M.; Tsuno, H.; Tomihara, K.; Arai, N.; Noguchi, M.; Nikaido, T. CD44 and SSEA-4 positive cells in an oral cancer cell line HSC-4 possess cancer stem-like cell characteristics. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Y.-W.; Wang, P.-Y.; Yeh, S.-C.; Chuang, P.-K.; Li, S.-T.; Wu, C.-Y.; Khoo, K.-H.; Hsiao, M.; Hsu, T.-L.; Wong, C.-H. Stage-specific embryonic antigen-4 as a potential therapeutic target in glioblastoma multiforme and other cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2482–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasubramaniyan, K.; Harichandan, A.; Schilbach, K.; Mack, A.F.; Bedke, J.; Stenzl, A.; Kanz, L.; Niederfellner, G.; Bühring, H.-J. Expression of stage-specific embryonic antigen-4 (SSEA-4) defines spontaneous loss of epithelial phenotype in human solid tumor cells. Glycobiology 2015, 25, 902–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, S.; Gray, R.J.; Demaria, S.; Goldstein, L.; Perez, E.A.; Shulman, L.N.; Martino, S.; Wang, M.; Jones, V.E.; Saphner, T.J.; et al. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancers from two phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trials: ECOG 2197 and ECOG 1199. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 2959–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, E.M.; Al-Foheidi, M.E.; Al-Mansour, M.M.; Kazkaz, G.A. The prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 148, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loi, S.; Michiels, S.; Salgado, R.; Sirtaine, N.; Jose, V.; Fumagalli, D.; Kellokumpu-Lehtinen, P.-L.; Bono, P.; Kataja, V.; Desmedt, C.; et al. Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes are prognostic in triple negative breast cancer and predictive for trastuzumab benefit in early breast cancer: Results from the FinHER trial. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2014, 25, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, S.; Sirtaine, N.; Piette, F.; Salgado, R.; Viale, G.; Van Eenoo, F.; Rouas, G.; Francis, P.; Crown, J.P.; Hitre, E.; et al. Prognostic and predictive value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in a phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trial in node-positive breast cancer comparing the addition of docetaxel to doxorubicin with doxorubicin-based chemotherapy: BIG 02-98. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guest, R.D.; Hawkins, R.E.; Kirillova, N.; Cheadle, E.J.; Arnold, J.; O’Neill, A.; Irlam, J.; Chester, K.A.; Kemshead, J.T.; Shaw, D.M.; et al. The role of extracellular spacer regions in the optimal design of chimeric immune receptors: Evaluation of four different scFvs and antigens. J. Immunother. 2005, 28, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haso, W.; Lee, D.W.; Shah, N.N.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; Yuan, C.M.; Pastan, I.H.; Dimitrov, D.S.; Morgan, R.A.; Fitzgerald, D.J.; Barrett, D.M.; et al. Anti-CD22-chimeric antigen receptors targeting B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2013, 121, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudecek, M.; Sommermeyer, D.; Kosasih, P.L.; Silva-Benedict, A.; Liu, L.; Rader, C.; Jensen, M.C.; Riddell, S.R. The nonsignaling extracellular spacer domain of chimeric antigen receptors is decisive for in vivo antitumor activity. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Künkele, A.; Johnson, A.J.; Rolczynski, L.S.; Chang, C.A.; Hoglund, V.; Kelly-Spratt, K.S.; Jensen, M.C. Functional Tuning of CARs Reveals Signaling Threshold above Which CD8+ CTL Antitumor Potency Is Attenuated due to Cell Fas-FasL-Dependent AICD. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefrançais, E.; Ortiz-Muñoz, G.; Caudrillier, A.; Mallavia, B.; Liu, F.; Sayah, D.M.; Thornton, E.E.; Headley, M.B.; David, T.; Coughlin, S.R.; et al. The lung is a site of platelet biogenesis and a reservoir for haematopoietic progenitors. Nature 2017, 544, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Djamgoz, M.B.A. Triple negative breast cancer: Emerging therapeutic modalities and novel combination therapies. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 62, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Terakura, S.; Martens, A.C.; van Meerten, T.; Uchiyama, S.; Imai, M.; Sakemura, R.; Goto, T.; Hanajiri, R.; Imahashi, N.; et al. Target antigen density governs the efficacy of anti-CD20-CD28-CD3 zeta chimeric antigen receptor-modified effector CD8+ T cells. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrikanova, I.; Kayali, A.; Lopez, A.; Hayek, A. Is stage-specific embryonic antigen 4 a marker for human ductal stem/progenitor cells? BioRes. Open Access 2012, 1, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hishikawa, K.; Takase, O.; Yoshikawa, M.; Tsujimura, T.; Nangaku, M.; Takato, T. Adult stem-like cells in kidney. World J. Stem Cells 2015, 7, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Meirelles, L.; Chagastelles, P.C.; Nardi, N.B. Mesenchymal stem cells reside in virtually all post-natal organs and tissues. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119 Pt 11, 2204–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, R.A.; Yang, J.C.; Kitano, M.; Dudley, M.E.; Laurencot, C.M.; Rosenberg, S.A. Case report of a serious adverse event following the administration of T cells transduced with a chimeric antigen receptor recognizing ERBB2. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2010, 18, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turatti, F.; Figini, M.; Balladore, E.; Alberti, P.; Casalini, P.; Marks, J.D.; Canevari, S.; Mezzanzanica, D. Redirected activity of human antitumor chimeric immune receptors is governed by antigen and receptor expression levels and affinity of interaction. J. Immunother. 2007, 30, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.D.; Aggen, D.H.; Schietinger, A.; Schreiber, H.; Kranz, D.M. A sensitivity scale for targeting T cells with chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) and bispecific T-cell Engagers (BiTEs). Oncoimmunology 2012, 1, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamers, C.H.; Sleijfer, S.; van Steenbergen, S.; van Elzakker, P.; van Krimpen, B.; Groot, C.; Vulto, A.; Bakker, M.D.; Oosterwijk, E.; Debets, R.; et al. Treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma with CAIX CAR-engineered T cells: Clinical evaluation and management of on-target toxicity. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2013, 21, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamers, C.H.J.; Sleijfer, S.; Vulto, A.G.; Kruit, W.H.J.; Kliffen, M.; Debets, R.; Gratama, J.W.; Stoter, G.; Oosterwijk, E. Treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma with autologous T-lymphocytes genetically retargeted against carbonic anhydrase IX: First clinical experience. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, e20–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamers, C.H.; Langeveld, S.C.; Groot-van Ruijven, C.M.; Debets, R.; Sleijfer, S.; Gratama, J.W. Gene-modified T cells for adoptive immunotherapy of renal cell cancer maintain transgene-specific immune functions in vivo. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 2007, 56, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fesnak, A.D.; June, C.H.; Levine, B.L. Engineered T cells: The promise and challenges of cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 566–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Rawashdeh, W.; Zuo, S.; Melle, A.; Appold, L.; Koletnik, S.; Tsvetkova, Y.; Beztsinna, N.; Pich, A.; Lammers, T.; Kiessling, F.; et al. Noninvasive Assessment of Elimination and Retention using CT-FMT and Kinetic Whole-body Modeling. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pfeifer, R.; Al Rawashdeh, W.; Brauner, J.; Martinez-Osuna, M.; Lock, D.; Herbel, C.; Eckardt, D.; Assenmacher, M.; Bosio, A.; Hardt, O.T.; et al. Targeting Stage-Specific Embryonic Antigen 4 (SSEA-4) in Triple Negative Breast Cancer by CAR T Cells Results in Unexpected on Target/off Tumor Toxicities in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119184
Pfeifer R, Al Rawashdeh W, Brauner J, Martinez-Osuna M, Lock D, Herbel C, Eckardt D, Assenmacher M, Bosio A, Hardt OT, et al. Targeting Stage-Specific Embryonic Antigen 4 (SSEA-4) in Triple Negative Breast Cancer by CAR T Cells Results in Unexpected on Target/off Tumor Toxicities in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(11):9184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119184
Chicago/Turabian StylePfeifer, Rita, Wa’el Al Rawashdeh, Janina Brauner, Manuel Martinez-Osuna, Dominik Lock, Christoph Herbel, Dominik Eckardt, Mario Assenmacher, Andreas Bosio, Olaf T. Hardt, and et al. 2023. "Targeting Stage-Specific Embryonic Antigen 4 (SSEA-4) in Triple Negative Breast Cancer by CAR T Cells Results in Unexpected on Target/off Tumor Toxicities in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 11: 9184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119184
APA StylePfeifer, R., Al Rawashdeh, W., Brauner, J., Martinez-Osuna, M., Lock, D., Herbel, C., Eckardt, D., Assenmacher, M., Bosio, A., Hardt, O. T., & Johnston, I. C. D. (2023). Targeting Stage-Specific Embryonic Antigen 4 (SSEA-4) in Triple Negative Breast Cancer by CAR T Cells Results in Unexpected on Target/off Tumor Toxicities in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(11), 9184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119184




