Current Indications and Future Landscape of Bispecific Antibodies for the Treatment of Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Approvals in Oncology
3. Bispecific Antibodies for the Treatment of Lung Cancer
3.1. Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
3.2. Small-Cell Lung Cancer
3.3. Toxicity of Bispecific Antibodies
4. Future Areas of Development
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salvador, J.-P.; Vilaplana, L.; Marco, M.-P. Nanobody: Outstanding features for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muyldermans, S. A guide to: Generation and design of nanobodies. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 2084–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steeland, S.; Vandenbroucke, R.E.; Libert, C. Nanobodies as therapeutics: Big opportunities for small antibodies. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 1076–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovcevska, I.; Muyldermans, S. The Therapeutic Potential of Nanobodies. BioDrugs 2020, 34, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyldermans, S. Nanobodies: Natural Single-Domain Antibodies. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 775–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamers-Casterman, C.; Atarhouch, T.; Muyldermans, S.; Robinson, G.; Hammers, C.; Songa, E.B.; Bendahman, N.; Hammers, R. Naturally occurring antibodies devoid of light chains. Nature 1993, 363, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Numair, N.S.; Theyab, A.; Alzahrani, F.; Shams, A.M.; Al-Anazi, I.O.; Oyouni, A.A.A.; Al-Amer, O.M.; Mavromatis, C.; Saadeldin, I.M.; Abdali, W.A.; et al. Camels’ biological fluids contained nanobodies: Promising avenue in cancer therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, L.; Jin, D.; Liu, Y. Nanobody—A versatile tool for cancer diagnosis and therapeutics. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 13, e1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, C.; Muyldermans, S. Nanobody-Based Delivery Systems for Diagnosis and Targeted Tumor Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dummer, R.; Ascierto, P.A.; Gogas, H.J.; Arance, A.; Mandala, M.; Liszkay, G.; Garbe, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Krajsova, I.; Gutzmer, R.; et al. Encorafenib plus binimetinib versus vemurafenib or encorafenib in patients with BRAF -mutant melanoma (COLUMBUS): A multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutzmer, R.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Gogas, H.; Robert, C.; Lewis, K.; Protsenko, S.; Pereira, R.P.; Eigentler, T.; Rutkowski, P.; Demidov, L.; et al. Atezolizumab, vemurafenib, and cobimetinib as first-line treatment for unresectable advanced BRAFV600 mutation-positive melanoma (IMspire150): Primary analysis of the randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1835–1844, Erratum in Lancet 2020, 396, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, J.; Ascierto, P.A.; Dréno, B.; Atkinson, V.; Liszkay, G.; Maio, M.; Mandalà, M.; Demidov, L.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Thomas, L.; et al. Combined Vemurafenib and Cobimetinib in BRAF-Mutated Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, J.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Gonzalez, R.; Grob, J.-J.; Rutkowski, P.; Lao, C.D.; Cowey, C.L.; Schadendorf, D.; Wagstaff, J.; Dummer, R.; et al. Five-Year Survival with Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Ciuleanu, T.-E.; Cobo, M.; Schenker, M.; Zurawski, B.; Menezes, J.; Richardet, E.; Bennouna, J.; Felip, E.; Juan-Vidal, O.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab combined with two cycles of chemotherapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 9LA): An international, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 198–211, Erratum in Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, e92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, C.; Grob, J.J.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Karaszewska, B.; Hauschild, A.; Levchenko, E.; Chiarion Sileni, V.; Schachter, J.; Garbe, C.; Bondarenko, I.; et al. Five-Year Outcomes with Dabrafenib plus Trametinib in Metastatic Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, M.; Ren, F.; Meng, X.; Yu, J. The landscape of bispecific T cell engager in cancer treatment. Biomark. Res. 2021, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarjian, H.; Stein, A.; Gökbuget, N.; Fielding, A.K.; Schuh, A.C.; Ribera, J.-M.; Wei, A.; Dombret, H.; Foà, R.; Bassan, R.; et al. Blinatumomab versus Chemotherapy for Advanced Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 836–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budde, L.E.; Sehn, L.H.; Matasar, M.; Schuster, S.J.; Assouline, S.; Giri, P.; Kuruvilla, J.; Canales, M.; Dietrich, S.; Fay, K.; et al. Safety and efficacy of mosunetuzumab, a bispecific antibody, in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma: A single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 1055–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keam, S.J. Cadonilimab: First Approval. Drugs 2022, 82, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ji, J.; Lou, H.; Li, Y.; Feng, M.; Xu, N.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Lou, G.; et al. Efficacy and safety of cadonilimab, an anti-PD-1/CTLA4 bi-specific antibody, in previously treated recurrent or metastatic (R/M) cervical cancer: A multicenter, open-label, single-arm, phase II trial (075). Gynecol. Oncol. 2022, 166, S47–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, S.; Lipfert, L.; Chevalier, K.; Bushey, B.S.; Henley, B.; Lenhart, R.; Sendecki, J.; Beqiri, M.; Millar, H.J.; Packman, K.; et al. Amivantamab (JNJ-61186372), an Fc Enhanced EGFR/cMet Bispecific Antibody, Induces Receptor Downmodulation and Antitumor Activity by Monocyte/Macrophage Trogocytosis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 2044–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Haura, E.B.; Leighl, N.B.; Mitchell, P.; Shu, C.A.; Girard, N.; Viteri, S.; Han, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, C.K.; et al. Amivantamab in EGFR Exon 20 Insertion–Mutated Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Progressing on Platinum Chemotherapy: Initial Results from the CHRYSALIS Phase I Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3391–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, C.A.; Goto, K.; Ohe, Y.; Besse, B.; Lee, S.-H.; Wang, Y.; Griesinger, F.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Felip, E.; Sanborn, R.E.; et al. Amivantamab and lazertinib in patients with EGFR-mutant non–small cell lung (NSCLC) after progression on osimertinib and platinum-based chemotherapy: Updated results from CHRYSALIS-2. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.C.; Felip, E.; Hayashi, H.; Thomas, M.; Lu, S.; Besse, B.; Sun, T.; Martinez, M.; Sethi, S.N.; Shreeve, S.M.; et al. MARIPOSA: Phase 3 study of first-line amivantamab + lazertinib versus osimertinib in EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Futur. Oncol. 2022, 18, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, L.; Mansfield, A.S.; Szczęsna, A.; Havel, L.; Krzakowski, M.; Hochmair, M.J.; Huemer, F.; Losonczy, G.; Johnson, M.L.; Nishio, M.; et al. First-Line Atezolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2220–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Dvorkin, M.; Chen, Y.; Reinmuth, N.; Hotta, K.; Trukhin, D.; Statsenko, G.; Hochmair, M.J.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Ji, J.H.; et al. Durvalumab plus platinum–etoposide versus platinum–etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, D.H.; Giffin, M.J.; Bailis, J.M.; Smit, M.-A.D.; Carbone, D.P.; He, K. DLL3: An emerging target in small cell lung cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owonikoko, T.K.; Champiat, S.; Johnson, M.L.; Govindan, R.; Izumi, H.; Lai, W.V.V.; Borghaei, H.; Boyer, M.J.; Boosman, R.J.; Hummel, H.-D.; et al. Updated results from a phase 1 study of AMG 757, a half-life extended bispecific T-cell engager (BiTE) immuno-oncology therapy against delta-like ligand 3 (DLL3), in small cell lung cancer (SCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 8510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Champiat, S.; Lai, W.V.; Izumi, H.; Govindan, R.; Boyer, M.; Hummel, H.-D.; Borghaei, H.; Johnson, M.L.; Steeghs, N.; et al. Tarlatamab, a First-In-Class DLL3-Targeted Bispecific T-Cell Engager, in Recurrent Small Cell Lung Cancer: An Open-Label, Phase I Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2893–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, A.J.; Chan, J.M.; Kubota, D.; Sato, H.; Rizvi, H.; Daneshbod, Y.; Chang, J.C.; Paik, P.K.; Offin, M.; Arcila, M.E.; et al. Tumor Analyses Reveal Squamous Transformation and Off-Target Alterations as Early Resistance Mechanisms to First-line Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2654–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Deng, C.; Qiu, Z.; Cao, C.; Wu, F. The Resistance Mechanisms and Treatment Strategies for ALK-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 713530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, N.-W.; Kim, S.; Kim, M.; Ahn, Y.-O.; Keam, B.; Heo, D.S. Acquired Resistance of MET-Amplified Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells to the MET Inhibitor Capmatinib. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 51, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recondo, G.; Bahcall, M.; Spurr, L.F.; Che, J.; Ricciuti, B.; Leonardi, G.C.; Lo, Y.-C.; Li, Y.Y.; Lamberti, G.; Nguyen, T.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Acquired Resistance to MET Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Patients with MET Exon 14–Mutant NSCLC. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2615–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.M.; Liu, S.; Rybkin, I.I.; Arbour, K.C.; Dilly, J.; Zhu, V.W.; Johnson, M.L.; Heist, R.S.; Patil, T.; Riely, G.J.; et al. Acquired Resistance to KRASG12C Inhibition in Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2382–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Liu, S.; McCoach, C.; Zhu, V.; Tan, A.; Yoda, S.; Peterson, J.; Do, A.; Prutisto-Chang, K.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; et al. Mechanisms of resistance to selective RET tyrosine kinase inhibitors in RET fusion-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1725–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, E.Y.; Won, H.H.; Zheng, Y.; Cocco, E.; Selcuklu, D.; Gong, Y.; Friedman, N.D.; de Bruijn, I.; Sumer, O.; Bielski, C.M.; et al. The evolution of RET inhibitor resistance in RET-driven lung and thyroid cancers. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Paz-Ares, L.; Bernabe Caro, R.; Zurawski, B.; Kim, S.-W.; Carcereny Costa, E.; Park, K.; Alexandru, A.; Lupinacci, L.; de la Mora Jimenez, E.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab in Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2020–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.L.; Cho, B.C.; Luft, A.; Alatorre-Alexander, J.; Geater, S.L.; Laktionov, K.; Kim, S.-W.; Ursol, G.; Hussein, M.; Lim, F.L.; et al. Durvalumab with or without Tremelimumab in Combination with Chemotherapy as First-Line Therapy for Metastatic Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: The Phase III POSEIDON Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1213–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.C.; Abreu, D.R.; Hussein, M.; Cobo, M.; Patel, A.J.; Secen, N.; Lee, K.H.; Massuti, B.; Hiret, S.; Yang, J.C.H.; et al. Tiragolumab plus atezolizumab versus placebo plus atezolizumab as a first-line treatment for PD-L1-selected non-small-cell lung cancer (CITYSCAPE): Primary and follow-up analyses of a randomised, double-blind, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felip, E.; Majem, M.; Doger, B.; Clay, T.D.; Carcereny, E.; Bondarenko, I.; Peguero, J.A.; Cobo-Dols, M.; Forster, M.; Ursol, G.; et al. A phase II study (TACTI-002) in first-line metastatic non–small cell lung carcinoma investigating eftilagimod alpha (soluble LAG-3 protein) and pembrolizumab: Updated results from a PD-L1 unselected population. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.-J.; Kim, S.-W.; Costa, E.C.; Rodríguez, L.; Oliveira, J.; Molla, M.I.; Majem, M.; Costa, L.; Su, W.-C.; Lee, K.; et al. LBA56 MEDI5752 or pembrolizumab (P) plus carboplatin/pemetrexed (CP) in treatment-naïve (1L) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A phase Ib/II trial. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33 (Suppl. 7), S808–S869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodi, F.S.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Gonzalez, R.; Grob, J.-J.; Rutkowski, P.; Cowey, C.L.; Lao, C.D.; Schadendorf, D.; Wagstaff, J.; Dummer, R.; et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab or nivolumab alone versus ipilimumab alone in advanced melanoma (CheckMate 067): 4-year outcomes of a multicentre, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1480–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawbi, H.A.; Schadendorf, D.; Lipson, E.J.; Ascierto, P.A.; Matamala, L.; Gutiérrez, E.C.; Rutkowski, P.; Gogas, H.J.; Lao, C.D.; De Menezes, J.J.; et al. Relatlimab and Nivolumab versus Nivolumab in Untreated Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
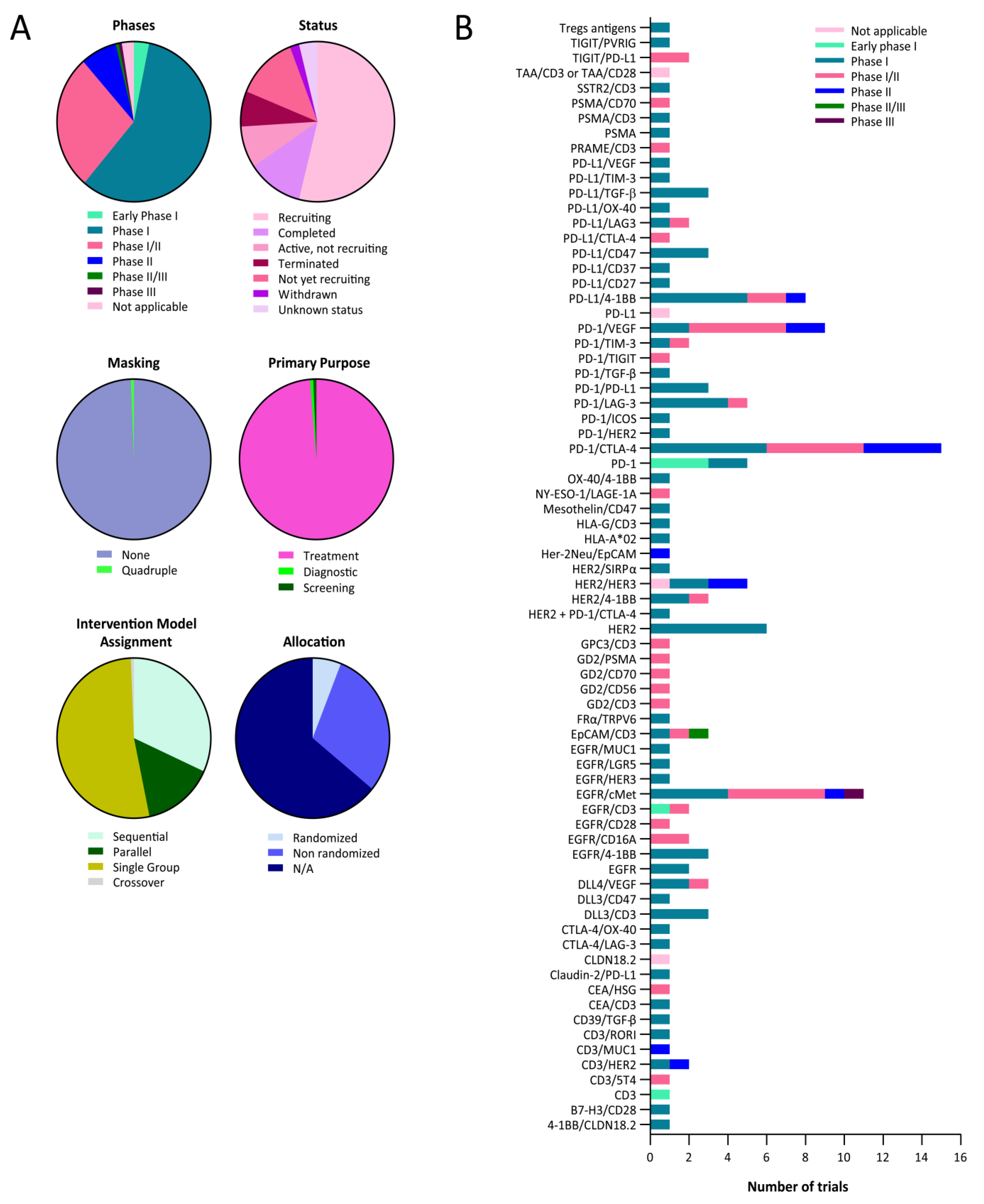
| Target | NCT Number | Phase | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4-1BB/CLDN18.2 | NCT04900818 | Phase 1 | TJ033721 |
| B7-H3/CD28 | NCT05585034 | Phase 1 | XmAb®808 |
| CD3 | NCT04076137 | Phase 1 | T-cell armed with bispecific antibody |
| CD3/EGFR | NCT01081808 | Phase 1 | T cells armed with EGFR-bispecific |
| CD3/HER2 | NCT02829372 | Phase 1 | CD3/HER2 bispecific antibody |
| CD3/HER2 | NCT04501770 | Phase 1 | M802 |
| CD3/RORI | NCT05607498 | Phase 1 | EMB07 |
| CD39/TGF-β | NCT05381935 | Phase 1 | ES014 |
| CEA/CD3 | NCT02324257 | Phase 1 | RO6958688 |
| Claudin-2/PD-L1 | NCT04856150 | Phase 1 | Q-1802 |
| CTLA-4/LAG-3 | NCT03849469 | Phase 1 | XmAb®22841 |
| CTLA-4/OX-40 | NCT03782467 | Phase 1 | ATOR-1015 |
| DLL3/CD3 | NCT03319940 | Phase 1 | AMG 757 |
| DLL3/CD3 | NCT05461287 | Phase 1 | QLS31904 |
| DLL3/CD47 | NCT05652686 | Phase 1 | PT217 |
| DLL4/VEGF | NCT02298387 | Phase 1 | OMP-305B83 |
| DLL4/VEGF | NCT03292783 | Phase 1 | NOV1501 (ABL001) |
| DLL3/CD3 | NCT05361395 | Phase 1 | Tarlatamab |
| EGFR | NCT02687386 | Phase 1 | Mitoxantrone packaged EDV |
| EGFR | NCT02369198 | Phase 1 | TargomiRs |
| EGFR/4-1BB | NCT05442996 | Phase 1 | HLX35 |
| EGFR/4-1BB | NCT05360381 | Phase 1 | HLX35 |
| EGFR/4-1BB | NCT05150457 | Phase 1 | BNA035 |
| EGFR/cMet | NCT04606381 | Phase 1 | Amivantamab |
| EGFR/cMet | NCT02609776 | Phase 1 | Amivantamab |
| EGFR/cMet | NCT04077463 | Phase 1 | Amivantamab |
| EGFR/CD3 | NCT05387265 | Phase 1 | CX-904 |
| EGFR/HER3 | NCT04603287 | Phase 1 | SI-B001 |
| EGFR/LGR5 | NCT03526835 | Phase 1 | MCLA-158 |
| EGFR/cMet | NCT02221882 | Phase 1 | LY3164530 |
| EGFR/MUC1 | NCT04695847 | Phase 1 | M1231 |
| EpCAM/CD3 | NCT04501744 | Phase 1 | M701 |
| FRα/TRPV6 | NCT04740398 | Phase 1 | CBP-1008 |
| GPC3/CD3 | NCT02748837 | Phase 1 | ERY974 |
| HER2 | NCT03842085 | Phase 1 | MBS301 |
| HER2 | NCT05320874 | Phase 1 | KM257 |
| HER2 | NCT04040699 | Phase 1 | KN026 and KN046 |
| HER2 | NCT03821233 | Phase 1 | ZW49 |
| HER2 | NCT02892123 | Phase 1 | Zanidatamab |
| HER2 | NCT05380882 | Phase 1 | TQB2930 |
| HER2 + PD-1/CTLA-4 | NCT02760199 | Phase 1 | 89Zr-AMG211 |
| HER2/4-1BB | NCT03330561 | Phase 1 | PRS-343 |
| HER2/4-1BB | NCT03650348 | Phase 1 | PRS-343 |
| HER2/HER3 | NCT00911898 | Phase 1 | MM-111 |
| HER2/HER3 | NCT01304784 | Phase 1 | MM-111 |
| HER2/SIRPα | NCT05076591 | Phase 1 | IMM2902 |
| HLA-A*02 | NCT05359445 | Phase 1 | IMA401 |
| HLA-G/CD3 | NCT04991740 | Phase 1 | JNJ-78306358 |
| Mesothelin/CD47 | NCT05403554 | Phase 1 | NI-1801 |
| OX-40/4-1BB | NCT04648202 | Phase 1 | FS120 |
| PD-1 | NCT05263180 | Phase 1 | EMB-09 |
| PD-1 | NCT05089266 | Phase 1 | CAR T cells |
| PD-1 | NCT05373147 | Phase 1 | PD1-MSLN-CAR T cells |
| PD-1 | NCT04503980 | Phase 1 | PD1-MSLN-CAR T cells |
| PD-1 | NCT04489862 | Phase 1 | PD1-MSLN-CAR T cells |
| PD-1/CTLA-4 | NCT04606472 | Phase 1 | SI-B003 |
| PD-1/CTLA-4 | NCT04572152 | Phase 1 | AK104 |
| PD-1/CTLA-4 | NCT05293496 | Phase 1 | Lorigerlimab |
| PD-1/CTLA-4 | NCT03530397 | Phase 1 | MEDI5752 |
| PD-1/CTLA-4 | NCT03761017 | Phase 1 | Lorigerlimab |
| PD-1/CTLA-4 | NCT03517488 | Phase 1 | XmAb20717 |
| PD-1/HER2 | NCT04162327 | Phase 1 | IBI315 |
| PD-1/ICOS | NCT03752398 | Phase 1 | XmAb23104 |
| PD-1/LAG-3 | NCT04140500 | Phase 1 | RO7247669 |
| PD-1/LAG-3 | NCT03219268 | Phase 1 | Tebotelimab |
| PD-1/LAG-3 | NCT05645276 | Phase 1 | AK129 |
| PD-1/LAG-3 | NCT05577182 | Phase 1 | INCA32459-101 |
| PD-1/PD-L1 | NCT03936959 | Phase 1 | LY3434172 |
| PD-1/PD-L1 | NCT04672928 | Phase 1 | IBI318 |
| PD-1/PD-L1 | NCT04777084 | Phase 1 | IBI318 |
| PD-1/TGF-β | NCT05028556 | Phase 1 | Y101D |
| PD-1/TIM-3 | NCT03708328 | Phase 1 | RO7121661 |
| PD-1/TIM-3 | NCT05357651 | Phase 1 | LB1410 |
| PD-1/VEGF | NCT04047290 | Phase 1 | AK112 |
| PD-1/VEGF | NCT05116007 | Phase 1 | AK112 |
| PD-L1/4-1BB | NCT04009460 | Phase 1 | ES101 |
| PD-L1/4-1BB | NCT04762641 | Phase 1 | ABL503 |
| PD-L1/4-1BB | NCT03809624 | Phase 1 | INBRX-105 |
| PD-L1/4-1BB | NCT04740424 | Phase 1 | FS222 |
| PD-L1/4-1BB | NCT03922204 | Phase 1 | MCLA-145 |
| PD-L1/CD27 | NCT04440943 | Phase 1 | CDX-527 |
| PD-L1/CD37 | NCT04881045 | Phase 1 | PF-07257876 |
| PD-L1/CD47 | NCT04912466 | Phase 1 | IBI322 |
| PD-L1/CD47 | NCT04328831 | Phase 1 | IBI322 |
| PD-L1/CD47 | NCT05200013 | Phase 1 | BAT7104 |
| PD-L1/LAG3 | NCT05101109 | Phase 1 | BL501 |
| PD-L1/OX-40 | NCT05638334 | Phase 1 | S09501 |
| PD-L1/TGF-β | NCT04958434 | Phase 1 | TST005 |
| PD-L1/TGF-β | NCT05537051 | Phase 1 | PM8001 |
| PD-L1/TGF-β | NCT04954456 | Phase 1 | QLS31901 |
| PD-L1/TIM-3 | NCT03752177 | Phase 1 | LY3415244 |
| PD-L1/VEGF | NCT05650385 | Phase 1 | B1962 |
| PSMA | NCT03927573 | Phase 1 | GEM3PSCA |
| SSTR2/CD3 | NCT03411915 | Phase 1 | XmAb18087 |
| TIGIT/PVRIG | NCT05607563 | Phase 1 | PM1009 |
| Tregs antigens | NCT04156100 | Phase 1 | AGEN1223 |
| CD3/5T4 | NCT04424641 | Phase 1/2 | GEN1044 |
| CD3/5T4 | NCT05180474 | Phase 1/2 | GEN1047 |
| CD3/GD2 | NCT04750239 | Phase 1/2 | Nivatrotamab |
| CEA/HSG | NCT01221675 | Phase 1/2 | TF2 |
| DLL4/VEGF | NCT04492033 | Phase 1/2 | CTX-009 (ABL001) |
| EGFR/CD16A | NCT05099549 | Phase 1/2 | AFM24 |
| EGFR/CD16A | NCT04259450 | Phase 1/2 | AFM24 |
| EGFR/CD28 | NCT04626635 | Phase 1/2 | REGN7075 |
| EGFR/CD3 | NCT04844073 | Phase 1/2 | MVC-101 (TAK-186) |
| EGFR/cMet | NCT04868877 | Phase 1/2 | MCLA-129 |
| EGFR/cMet | NCT04930432 | Phase 1/2 | MCLA-129 |
| EGFR/cMET | NCT05498389 | Phase 1/2 | EMB-01 |
| EGFR/cMET | NCT04590781 | Phase 1/2 | XmAb18087 |
| EGFR/Cmet | NCT03797391 | Phase 1/2 | EMB-01 |
| EpCAM/CD3 | NCT05543330 | Phase 1/2 | M701 |
| GD2/CD3 | NCT03860207 | Phase 1/2 | 3F8 |
| GD2/CD56 | NCT05437328 | Phase 1/2 | bi-4SCAR GD2/CD56 T cells |
| GD2/CD70 | NCT05438368 | Phase 1/2 | bi-4SCAR GD2/CD70 T cells |
| GD2/PSMA | NCT05437315 | Phase 1/2 | bi-4SCAR GD2/PSMA T cells |
| HER2/4-1BB | NCT05523947 | Phase 1/2 | YH32367 |
| NY-ESO-1/LAGE-1A | NCT03515551 | Phase 1/2 | IMCnyeso |
| PD-1/CTLA-4 | NCT04172454 | Phase 1/2 | AK104 |
| PD-1/CTLA-4 | NCT03852251 | Phase 1/2 | AK104 |
| PD-1/CTLA-4 | NCT05559541 | Phase 1/2 | AK104 |
| PD-1/CTLA-4 | NCT05235542 | Phase 1/2 | AK104 |
| PD-1/CTLA-4 | NCT05505825 | Phase 1/2 | AK104 |
| PD-1/LAG-3 | NCT04618393 | Phase 1/2 | EMB-02 |
| PD-1/TIGIT | NCT04995523 | Phase 1/2 | AZD2936 |
| PD-1/TIM-3 | NCT04931654 | Phase 1/2 | AZD7789 |
| PD-1/VEGF | NCT04597541 | Phase 1/2 | Ivonescimab |
| PD-1/VEGF | NCT05689853 | Phase 1/2 | Ivonescimab |
| PD-1/VEGF | NCT05229497 | Phase 1/2 | Ivonescimab |
| PD-1/VEGF | NCT05214482 | Phase 1/2 | Ivonescimab |
| PD-1/VEGF | NCT04900363 | Phase 1/2 | Ivonescimab |
| PD-L1/4-1BB | NCT05159388 | Phase 1/2 | PRS-344/S095012 |
| PD-L1/4-1BB | NCT04841538 | Phase 1/2 | ES101 |
| PD-L1/CTLA-4 | NCT05425602 | Phase 1/2 | MAX-40279-01 |
| PD-L1/LAG-3 | NCT03440437 | Phase 1/2 | FS118 |
| PRAME/CD3 | NCT04262466 | Phase 1/2 | IMC-F106C |
| PSMA/CD3 | NCT04496674 | Phase 1/2 | CC-1 |
| PSMA/CD70 | NCT05437341 | Phase 1/2 | bi-4SCAR PSMA/CD70 |
| TIGIT/PD-L1 | NCT05102214 | Phase 1/2 | HLX301 |
| TIGIT/PD-L1 | NCT05390528 | Phase 1/2 | HLX301 |
| CD3/MUC1 | NCT03501056 | Phase 2 | CD3-MUC1 Bispecific Antibody |
| EGFR/Cmet | NCT05299125 | Phase 2 | Amivantamab |
| HER2/HER3 | NCT02912949 | Phase 2 | Zenocutuzumab |
| HER2/HER3 | NCT05588609 | Phase 2 | Zenocutuzumab |
| Her-2Neu/EpCAM | NCT00149019 | Phase 2 | Cell therapy |
| PD-1/CTLA-4 | NCT04547101 | Phase 2 | AK104 |
| PD-1/CTLA-4 | NCT05377658 | Phase 2 | AK104 |
| PD-1/CTLA-4 | NCT05420220 | Phase 2 | KN046 |
| PD-1/CTLA-4 | NCT05215067 | Phase 2 | AK104 |
| PD-1/VEGF | NCT04736823 | Phase 2 | AK112 |
| PD-1/VEGF | NCT05247684 | Phase 2 | AK112 |
| PD-L1/4-1BB | NCT05117242 | Phase 2 | GEN1046 |
| EpCAM/CD3 | NCT00836654 | Phase 2/3 | Catumaxomab |
| EGFR/CMET | NCT05388669 | Phase 3 | Amivantamab |
| CLDN18.2 | NCT05436093 | Not applicable | 18F-FDG |
| HER2/HER3 | NCT04100694 | Not applicable | MCLA-128 |
| PD-L1 | NCT05156515 | Not applicable | 68Ga-THP-APN09 |
| TAA/CD3 or CD28 | NCT05119257 | Not applicable |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arasanz, H.; Chocarro, L.; Fernández-Rubio, L.; Blanco, E.; Bocanegra, A.; Echaide, M.; Labiano, I.; Huerta, A.E.; Alsina, M.; Vera, R.; et al. Current Indications and Future Landscape of Bispecific Antibodies for the Treatment of Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9855. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129855
Arasanz H, Chocarro L, Fernández-Rubio L, Blanco E, Bocanegra A, Echaide M, Labiano I, Huerta AE, Alsina M, Vera R, et al. Current Indications and Future Landscape of Bispecific Antibodies for the Treatment of Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(12):9855. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129855
Chicago/Turabian StyleArasanz, Hugo, Luisa Chocarro, Leticia Fernández-Rubio, Ester Blanco, Ana Bocanegra, Miriam Echaide, Ibone Labiano, Ana Elsa Huerta, Maria Alsina, Ruth Vera, and et al. 2023. "Current Indications and Future Landscape of Bispecific Antibodies for the Treatment of Lung Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 12: 9855. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129855
APA StyleArasanz, H., Chocarro, L., Fernández-Rubio, L., Blanco, E., Bocanegra, A., Echaide, M., Labiano, I., Huerta, A. E., Alsina, M., Vera, R., Escors, D., & Kochan, G. (2023). Current Indications and Future Landscape of Bispecific Antibodies for the Treatment of Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(12), 9855. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129855







