Vaccine-Induced Immunity Elicited by Microneedle Delivery of Influenza Ectodomain Matrix Protein 2 Virus-like Particle (M2e VLP)-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
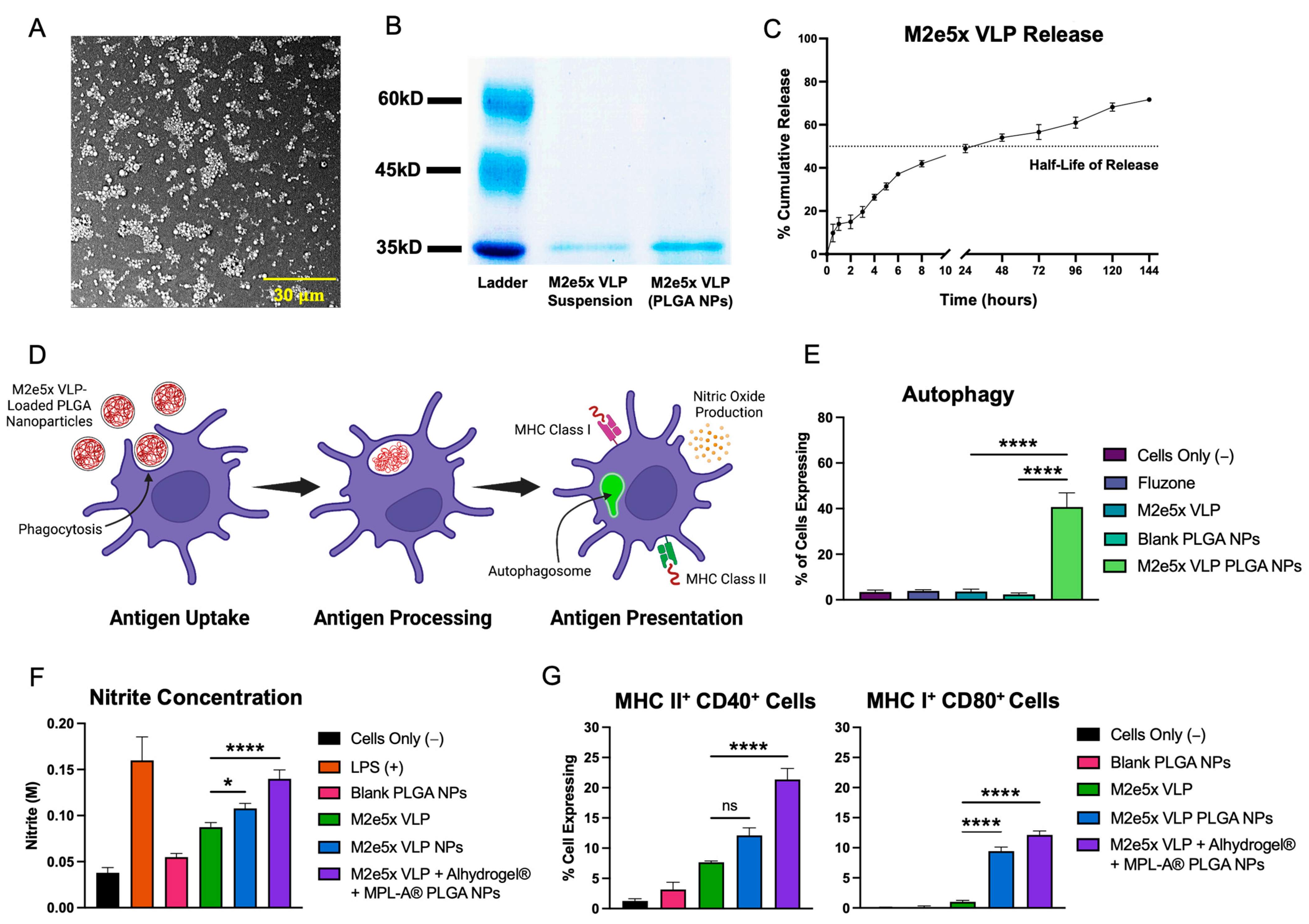
2.1. Physical Characterization of Vaccine Nanoparticles
2.2. Vaccine Nanoparticles Elicit In Vitro Immunogenicity in Antigen-Presenting Cells
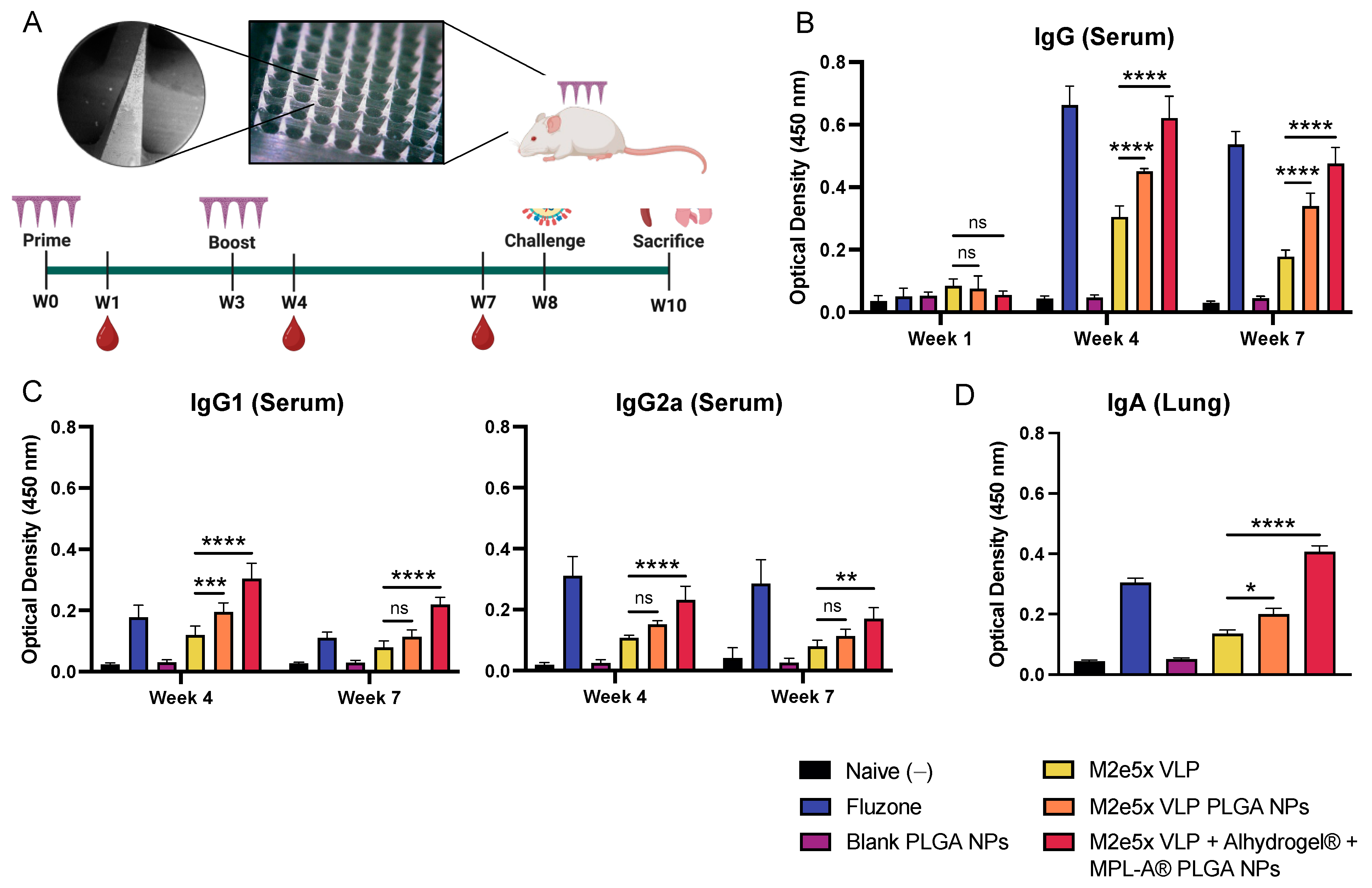
2.3. Vaccine Nanoparticles Administered Using Dissolving Microneedles Induce M2e-Specific Antibody Responses in Mice
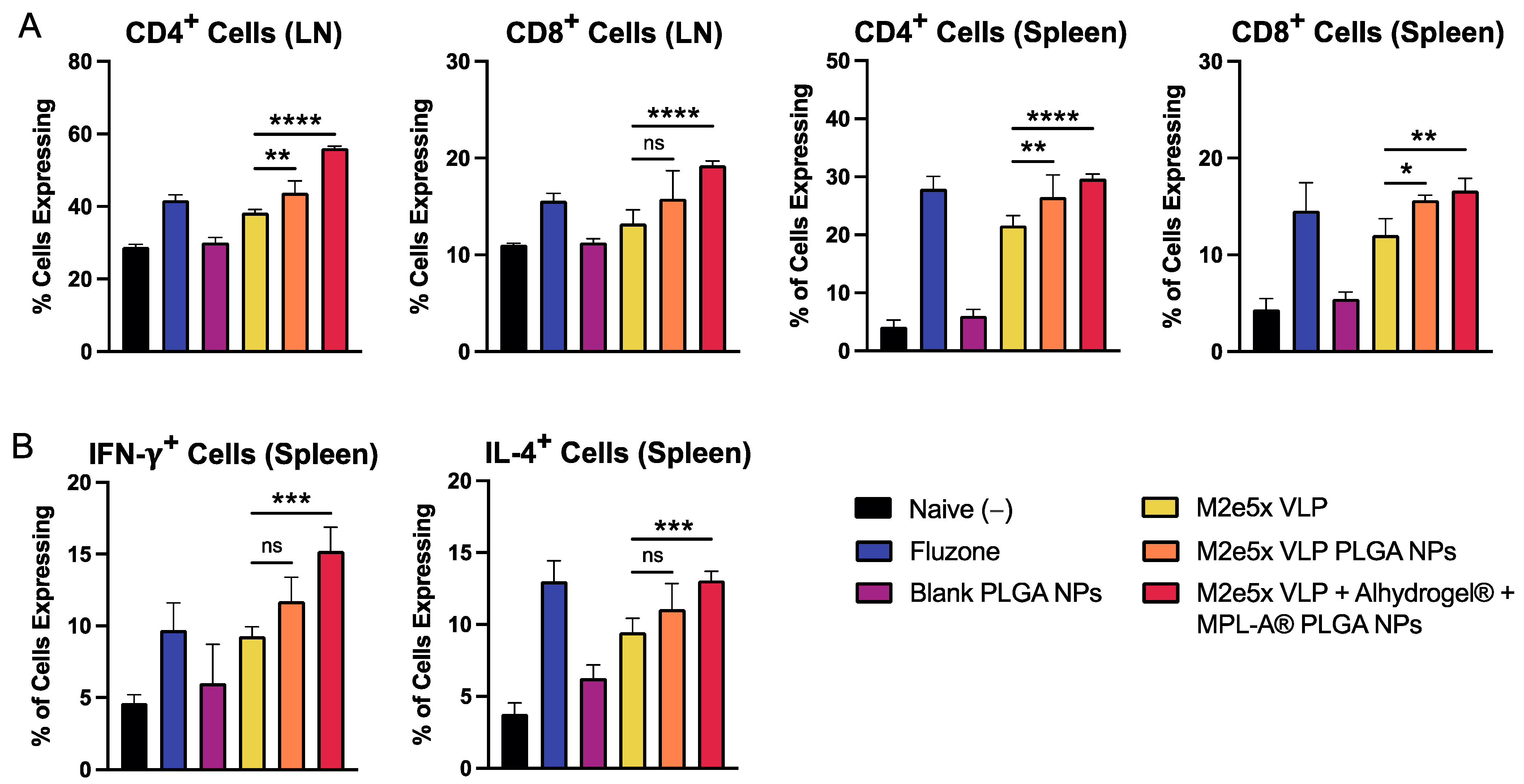
2.4. Vaccine Nanoparticles Administered in Mice Using Dissolving Microneedles Induce T Cell Responses in Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Formulation of M2e5x VLP-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles
4.2. Particle Yield, Size, Charge, and Morphology
4.3. Antigen Encapsulation Efficiency, Integrity, and Release
4.4. Formulation and Characterization of Vaccine Nanoparticle-Loaded Microneedles
4.5. Induction of Autophagy
4.6. Nitrite Production
4.7. Surface Expression of Antigen-Presenting Molecules in Dendritic Cells
4.8. Immunization, Blood Collection, and Challenge
4.9. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) to Evaluate M2e-Specific Antibody Responses
4.10. Evaluation of T Cell Responses in Immune Organs
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Influenza (Seasonal). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/influenza-(seasonal) (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Dou, D.; Revol, R.; Östbye, H.; Wang, H.; Daniels, R. Influenza A Virus Cell Entry, Replication, Virion Assembly and Movement. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhauer, D.A.; Skehel, J.J. Genetics of influenza viruses. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2002, 36, 305–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondy, M.; El Omeiri, N.; Thompson, M.G.; Levêque, A.; Moren, A.; Sullivan, S.G. Effectiveness of influenza vaccines in preventing severe influenza illness among adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of test-negative design case-control studies. J. Infect. 2017, 75, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sridhar, S.; Brokstad, K.A.; Cox, R.J. Influenza Vaccination Strategies: Comparing Inactivated and Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccines. Vaccines 2015, 3, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Webster, R.G.; Govorkova, E.A. Continuing challenges in influenza. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1323, 115–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, S.-S.; Webby, R.J. Traditional and New Influenza Vaccines. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 476–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Does Repeated Influenza Vaccination Attenuate Effectiveness? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis–The Lancet Respiratory Medicine. Available online: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanres/article/PIIS2213-2600(22)00266-1/fulltext (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Murray, T. Repeated flu shots may blunt effectiveness. CMAJ Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2015, 187, E180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, L.; Cho, K.J.; Fiers, W.; Saelens, X. M2e-Based Universal Influenza A Vaccines. Vaccines 2015, 3, 105–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kavishna, R.; Kang, T.Y.; Vacca, M.; Chua, B.Y.L.; Park, H.-Y.; Tan, P.S.; Alonso, S. A single-shot vaccine approach for the universal influenza A vaccine candidate M2e. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2025607119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezhenskaya, D.; Isakova-Sivak, I.; Rudenko, L. M2e-based universal influenza vaccines: A historical overview and new approaches to development. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomes, K.B.; Menon, I.; Bagwe, P.; Bajaj, L.; Kang, S.-M.; D’Souza, M.J. Enhanced Immunogenicity of an Influenza Ectodomain Matrix-2 Protein Virus-like Particle (M2e VLP) Using Polymeric Microparticles for Vaccine Delivery. Viruses 2022, 14, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.J.; Schepens, B.; Seok, J.H.; Kim, S.; Roose, K.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, K.H. Structure of the Extracellular Domain of Matrix Protein 2 of Influenza A Virus in Complex with a Protective Monoclonal Antibody. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3700–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, K.J.; Schepens, B.; Moonens, K.; Deng, L.; Fiers, W.; Remaut, H.; Saelens, X. Crystal Structure of the Conserved Amino Terminus of the Extracellular Domain of Matrix Protein 2 of Influenza A Virus Gripped by an Antibody. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kwon, Y.-M.; Lee, Y.-T.; Kim, M.-C.; Hwang, H.S.; Ko, E.-J.; Kang, S.M. Virus-Like Particles Are a Superior Platform for Presenting M2e Epitopes to Prime Humoral and Cellular Immunity against Influenza Virus. Vaccines 2018, 6, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, H.-J.; Chu, K.-B.; Lee, D.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Park, B.R.; Kim, M.-C.; Quan, F.S. Influenza M2 virus-like particle vaccination enhances protection in combination with avian influenza HA VLPs. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohsen, M.O.; Bachmann, M.F. Virus-like particle vaccinology, from bench to bedside. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 993–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hagan, D.T.; Singh, M.; Ulmer, J.B. Microparticle-based technologies for vaccines. Methods San Diego Calif. 2006, 40, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.L.; Soema, P.C.; Slütter, B.; Ossendorp, F.; Jiskoot, W. PLGA particulate delivery systems for subunit vaccines: Linking particle properties to immunogenicity. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2016, 12, 1056–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagwe, P.; Bajaj, L.; Gala, R.P.; D’Souza, M.J.; Zughaier, S.M. Assessment of In Vitro Immunostimulatory Activity of an Adjuvanted Whole-Cell Inactivated Neisseria gonorrhoeae Microparticle Vaccine Formulation. Vaccines 2022, 10, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyewumi, M.O.; Kumar, A.; Cui, Z. Nano-microparticles as immune adjuvants: Correlating particle sizes and the resultant immune responses. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2010, 9, 1095–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, B.; Sun, R.; Liu, W.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C. PLGA-based biodegradable microspheres in drug delivery: Recent advances in research and application. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 1397–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grego, E.A.; Siddoway, A.C.; Uz, M.; Liu, L.; Christiansen, J.C.; Ross, K.A.; Narasimhan, B. Polymeric Nanoparticle-Based Vaccine Adjuvants and Delivery Vehicles. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2021, 433, 29–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braz, G.K.; D’Sa, S.; Allotey-Babington, G.L.; Kang, S.-M.; D’Souza, M.J. Transdermal Vaccination with the Matrix-2 Protein Virus-like Particle (M2e VLP) Induces Immunity in Mice against Influenza A Virus. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhydrogel® Adjuvant 2%. InvivoGen 2016. Available online: https://www.invivogen.com/alhydrogel (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- He, P.; Zou, Y.; Hu, Z. Advances in aluminum hydroxide-based adjuvant research and its mechanism. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2015, 11, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awate, S.; Babiuk, L.A.; Mutwiri, G. Mechanisms of Action of Adjuvants. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salkowski, C.A.; Detore, G.R.; Vogel, S.N. Lipopolysaccharide and monophosphoryl lipid A differentially regulate interleukin-12, gamma interferon, and interleukin-10 mRNA production in murine macrophages. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 3239–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casella, C.R.; Mitchell, T.C. Putting endotoxin to work for us: Monophosphoryl lipid A as a safe and effective vaccine adjuvant. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2008, 65, 3231–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernandez-Davies, J.E.; Dollinger, E.P.; Pone, E.J.; Felgner, J.; Liang, L.; Strohmeier, S.; Davies, D.H. Magnitude and breadth of antibody cross-reactivity induced by recombinant influenza hemagglutinin trimer vaccine is enhanced by combination adjuvants. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Mikszta, J.A.; Cormier, M.; Andrianov, A.K. Microneedle-based vaccines. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 333, 369–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kale, A.; Joshi, D.; Menon, I.; Bagwe, P.; Patil, S.; Vijayanand, S.; D’Souza, M. Novel microparticulate Zika vaccine induces a significant immune response in a preclinical murine model after intramuscular administration. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 624, 121975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayanand, S.; Patil, S.; Menon, I.; Braz, G.K.; Kale, A.; Bagwe, P.; D’Souzaal, M.J. An Adjuvanted Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Microparticulate Vaccine Delivered Using Microneedles Induces a Robust Immune Response in Vaccinated Mice. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, I.; Bagwe, P.; Gomes, K.B.; Bajaj, L.; Gala, R.; Uddin, M.N.; Zughaier, S.M. Microneedles: A New Generation Vaccine Delivery System. Micromachines 2021, 12, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, I.; Kang, S.M.; Gomes, K.B.; Uddin, M.N.; D’Souza, M. Laser-assisted intradermal delivery of a microparticle vaccine for respiratory syncytial virus induces a robust immune response. Vaccine 2023, 41, 1209–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayanand, S.; Patil, S.; Joshi, D.; Menon, I.; Gomes, B.K.; Kale, A.; D’Souza, M.J. Microneedle Delivery of an Adjuvanted Microparticulate Vaccine Induces High Antibody Levels in Mice Vaccinated against Coronavirus. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Vijayanand, S.; Joshi, D.; Menon, I.; Braz, G.K.; Kale, A.; D’Souza, M.J. Subunit microparticulate vaccine delivery using microneedles trigger significant SARS-spike-specific humoral and cellular responses in a preclinical murine model. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 632, 122583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gala, R.P.; Zaman, R.U.; D’Souza, M.J.; Zughaier, S.M. Novel Whole-Cell Inactivated Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Microparticles as Vaccine Formulation in Microneedle-Based Transdermal Immunization. Vaccines 2018, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vo, T.P.; Panicker, G.; Braz-Gomes, K.; Parenky, A.C.; Rajbhandari, I.; Rajeevan, M.S.; Uddin, M.N. Enhanced Immunogenicity of Adjuvanted Microparticulate HPV16 Vaccines Administered via the Transdermal Route. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waeckerlemen, Y.; Groettrup, M. PLGA microspheres for improved antigen delivery to dendritic cells as cellular vaccines. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabata, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Ikada, Y. Size effect on systemic and mucosal immune responses induced by oral administration of biodegradable microspheres. Vaccine 1996, 14, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Roche, P.A. Macropinocytosis in phagocytes: Regulation of MHC class-II-restricted antigen presentation in dendritic cells. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, V.B.; Geary, S.M.; Salem, A.K. Biodegradable Particles as Vaccine Delivery Systems: Size Matters. AAPS J. 2012, 15, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peptide/Protein Vaccine Delivery System Based on PLGA Particles–PMC. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4964737/ (accessed on 9 May 2023).
- Koerner, J.; Horvath, D.; Groettrup, M. Harnessing Dendritic Cells for Poly (D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) Microspheres (PLGA MS)—Mediated Anti-tumor Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Didierlaurent, A.M.; Morel, S.; Lockman, L.; Giannini, S.L.; Bisteau, M.; Carlsen, H.; Garçon, N. AS04, an aluminum salt-and TLR4 agonist-based adjuvant system, induces a transient localized innate immune response leading to enhanced adaptive immunity. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6186–6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giannini, S.L.; Hanon, E.; Moris, P.; Van Mechelen, M.; Morel, S.; Dessy, F.; Wettendorff, M.A. Enhanced humoral and memory B cellular immunity using HPV16/18 L1 VLP vaccine formulated with the MPL/aluminium salt combination (AS04) compared to aluminium salt only. Vaccine 2006, 24, 5937–5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ita, K. Dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug delivery: Advances and challenges. Biomed. Pharm. 2017, 93, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-N.; Kim, M.-C.; Lee, Y.-T.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kang, S.-M. Mechanisms of Cross-protection by Influenza Virus M2-based Vaccines. Immune. Netw. 2015, 15, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tay, M.Z.; Wiehe, K.; Pollara, J. Antibody-Dependent Cellular Phagocytosis in Antiviral Immune Responses. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stepanova, L.A.; Kotlyarov, R.Y.; Kovaleva, A.A.; Potapchuk, M.V.; Korotkov, A.V.; Sergeeva, M.V.; Kiselev, O.I. Protection against Multiple Influenza A Virus Strains Induced by Candidate Recombinant Vaccine Based on Heterologous M2e Peptides Linked to Flagellin. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantis, N.J.; Rol, N.; Corthésy, B. Secretory IgA’s complex roles in immunity and mucosal homeostasis in the gut. Mucosal Immunol. 2011, 4, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corthesy, B. Multi-Faceted Functions of Secretory IgA at Mucosal Surfaces. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eliasson, D.G.; Omokanye, A.; Schön, K.; Wenzel, U.A.; Bernasconi, V.; Bemark, M.; Sprent, J. M2e-tetramer-specific memory CD4 T cells are broadly protective against influenza infection. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.-C.; Lee, J.W.; Choi, H.-J.; Lee, Y.-N.; Hwang, H.S.; Lee, J.; Kang, S.M. Microneedle patch delivery to the skin of virus-like particles containing heterologous M2e extracellular domains of influenza virus induces broad heterosubtypic cross-protection. J. Control. Release 2015, 210, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braz, G.K.; D’Souza, B.; Vijayanand, S.; Menon, I.; D’Souza, M.J. A dual-delivery platform for vaccination using antigen-loaded nanoparticles in dissolving microneedles. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 613, 121393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Braz Gomes, K.; Vijayanand, S.; Bagwe, P.; Menon, I.; Kale, A.; Patil, S.; Kang, S.-M.; Uddin, M.N.; D’Souza, M.J. Vaccine-Induced Immunity Elicited by Microneedle Delivery of Influenza Ectodomain Matrix Protein 2 Virus-like Particle (M2e VLP)-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10612. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310612
Braz Gomes K, Vijayanand S, Bagwe P, Menon I, Kale A, Patil S, Kang S-M, Uddin MN, D’Souza MJ. Vaccine-Induced Immunity Elicited by Microneedle Delivery of Influenza Ectodomain Matrix Protein 2 Virus-like Particle (M2e VLP)-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(13):10612. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310612
Chicago/Turabian StyleBraz Gomes, Keegan, Sharon Vijayanand, Priyal Bagwe, Ipshita Menon, Akanksha Kale, Smital Patil, Sang-Moo Kang, Mohammad N. Uddin, and Martin J. D’Souza. 2023. "Vaccine-Induced Immunity Elicited by Microneedle Delivery of Influenza Ectodomain Matrix Protein 2 Virus-like Particle (M2e VLP)-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 13: 10612. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310612
APA StyleBraz Gomes, K., Vijayanand, S., Bagwe, P., Menon, I., Kale, A., Patil, S., Kang, S.-M., Uddin, M. N., & D’Souza, M. J. (2023). Vaccine-Induced Immunity Elicited by Microneedle Delivery of Influenza Ectodomain Matrix Protein 2 Virus-like Particle (M2e VLP)-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(13), 10612. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310612










