Antibacterial MccM as the Major Microcin in Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 against Pathogenic Enterobacteria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Result
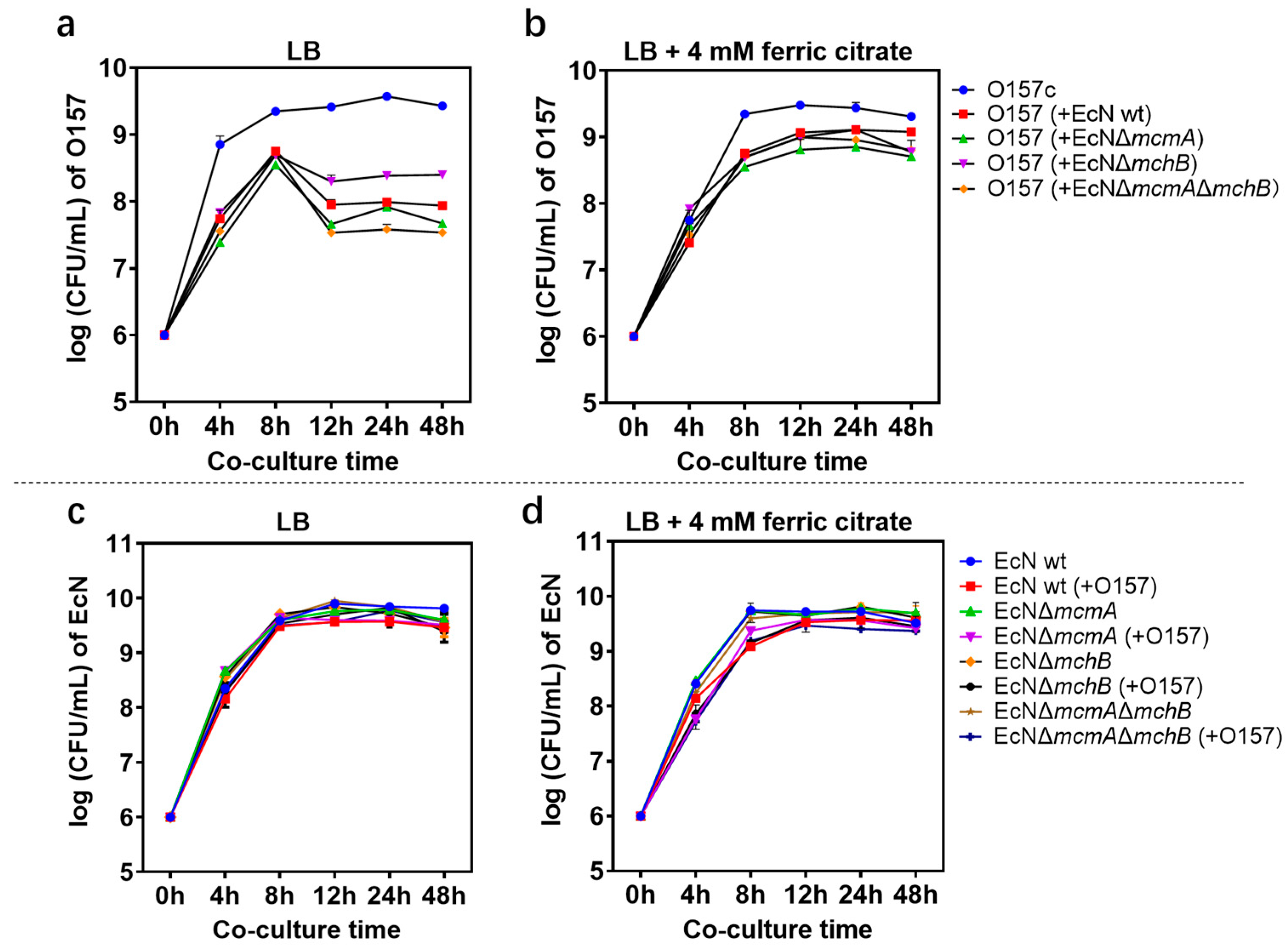
2.1. Effect of Probiotic EcN on EHEC O157: H7 Growth and Stx Gene Expression
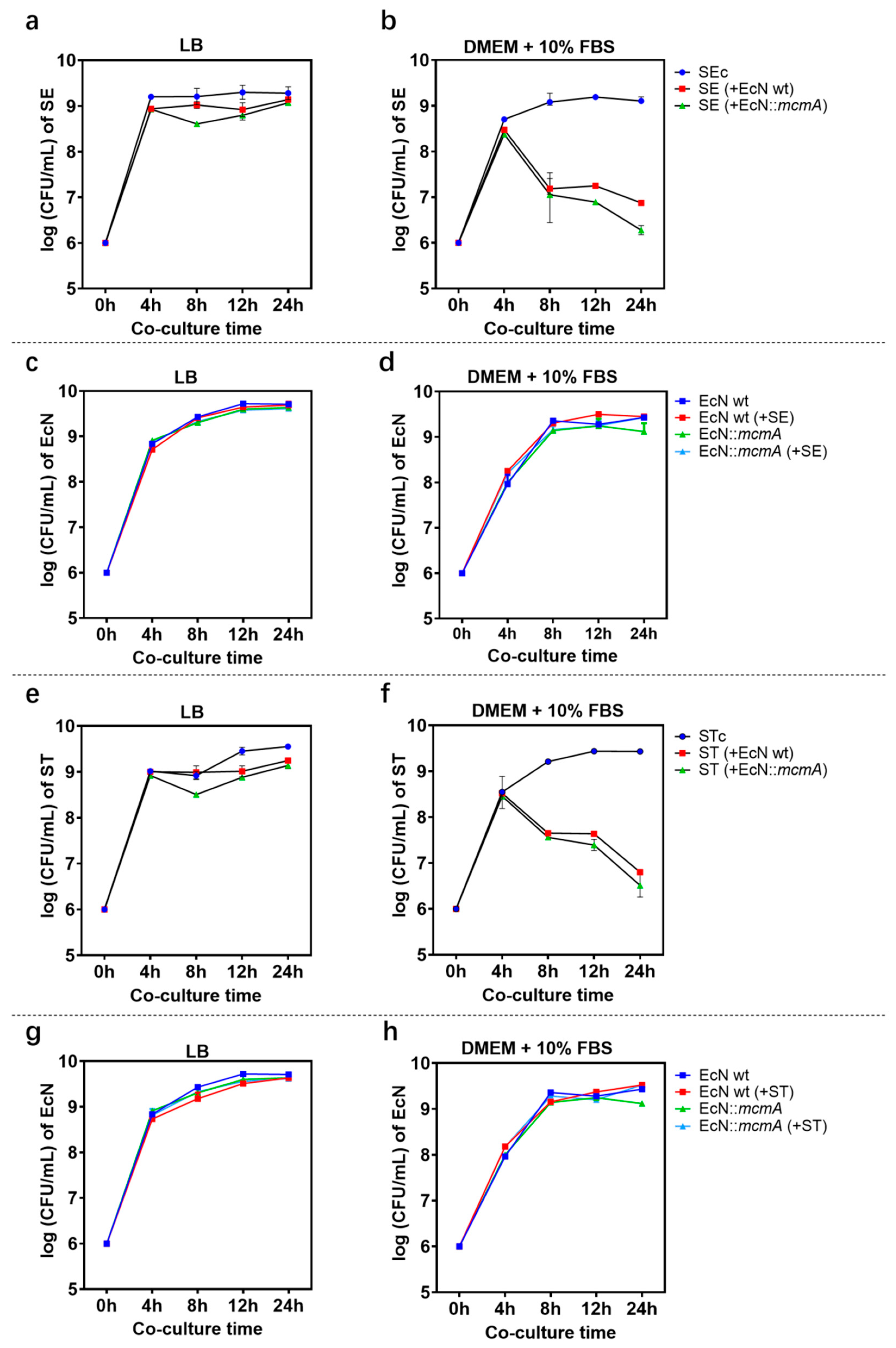
2.2. E. coli Nissle 1917 Significantly Reduced the Growth of Salmonella in Iron-Limited Media
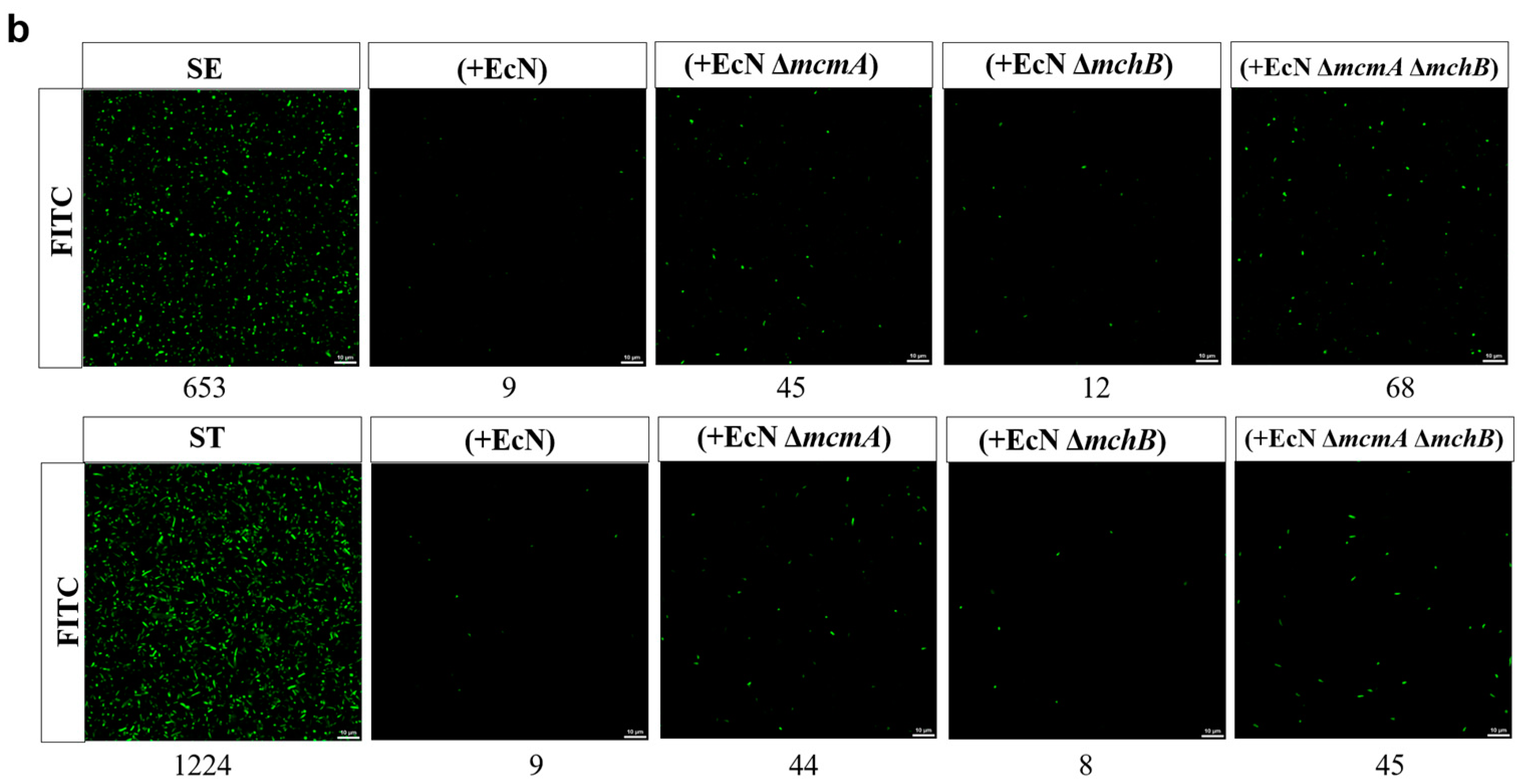
2.3. The Engineered Strain EcN::mcmA Significantly Reduced the Growth of Salmonella in Iron-Limited Media
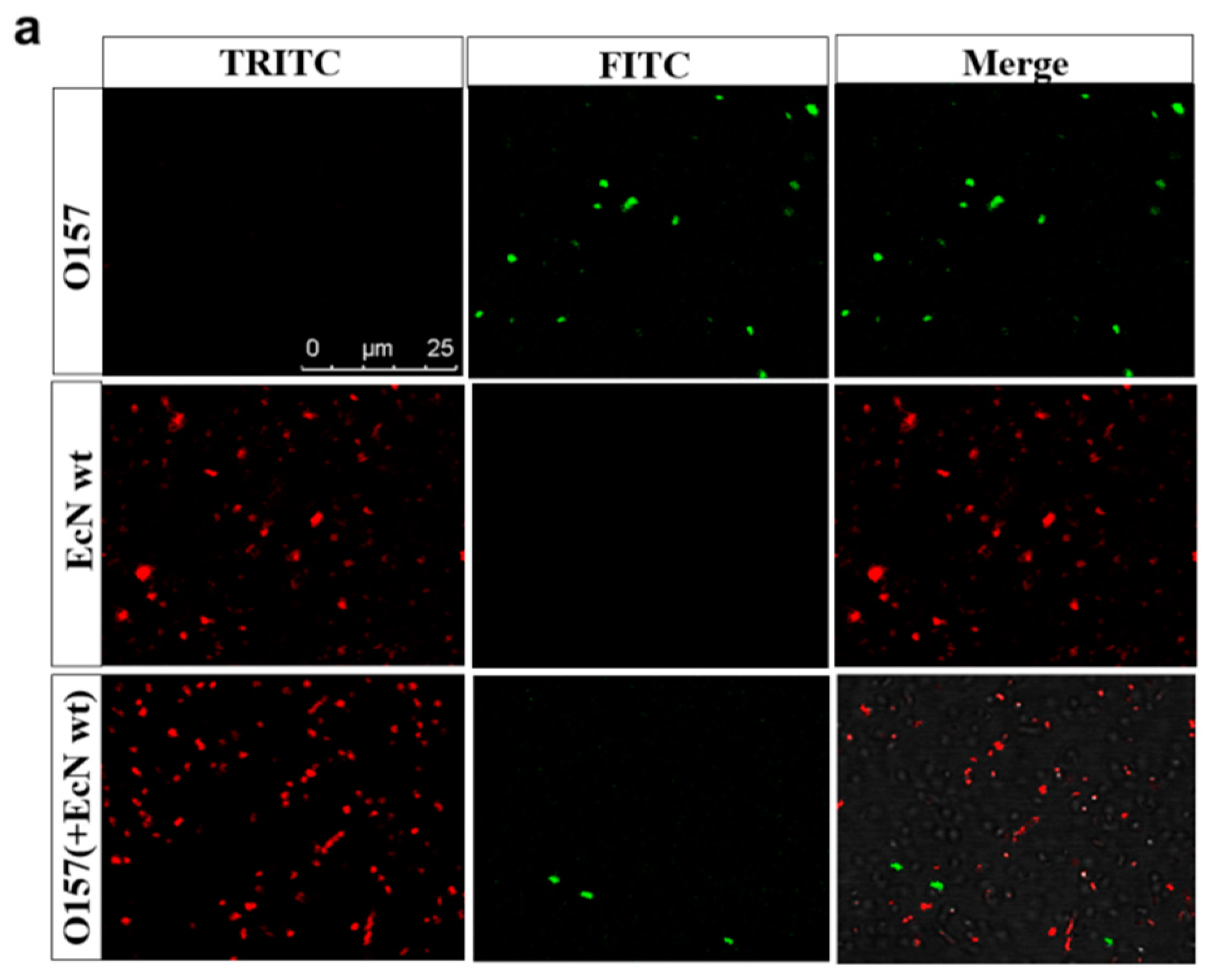
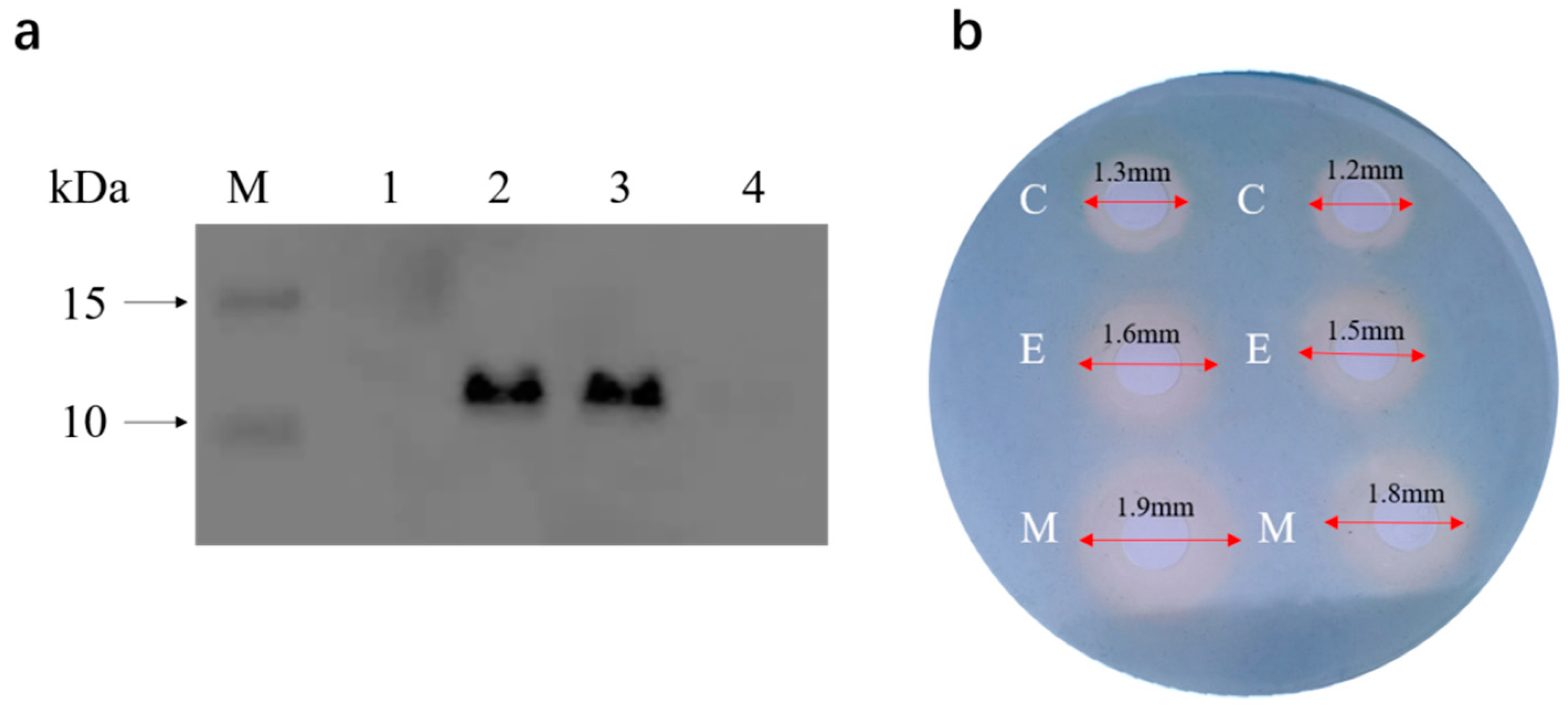
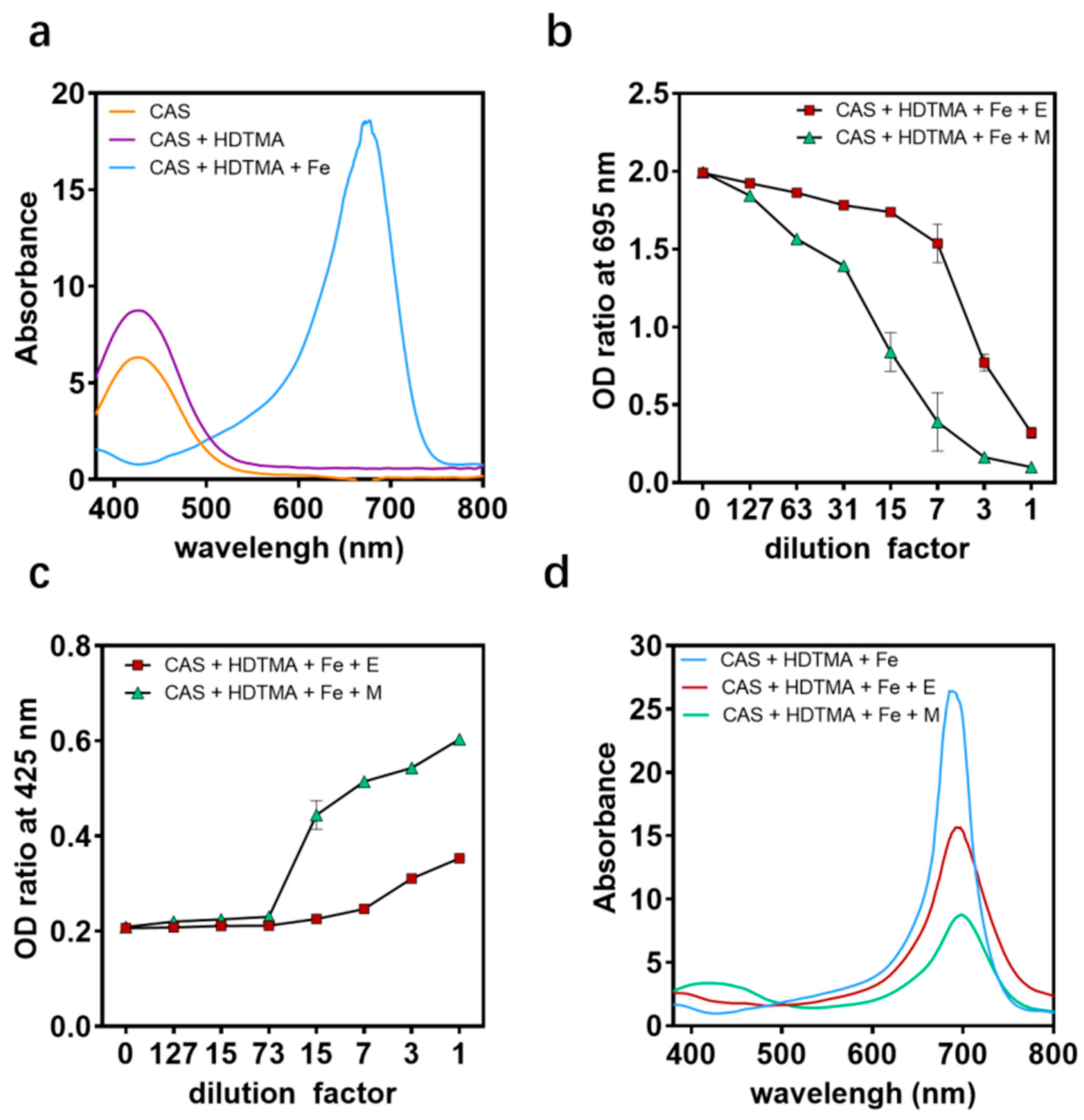
2.4. Antibacterial Mechanism of the Engineered Strain EcN::mcmA
2.5. The Engineered Strain EcN::mcmA Significantly Inhibited the Adhesion and Invasion of Salmonella to Intestinal Epithelial Cells
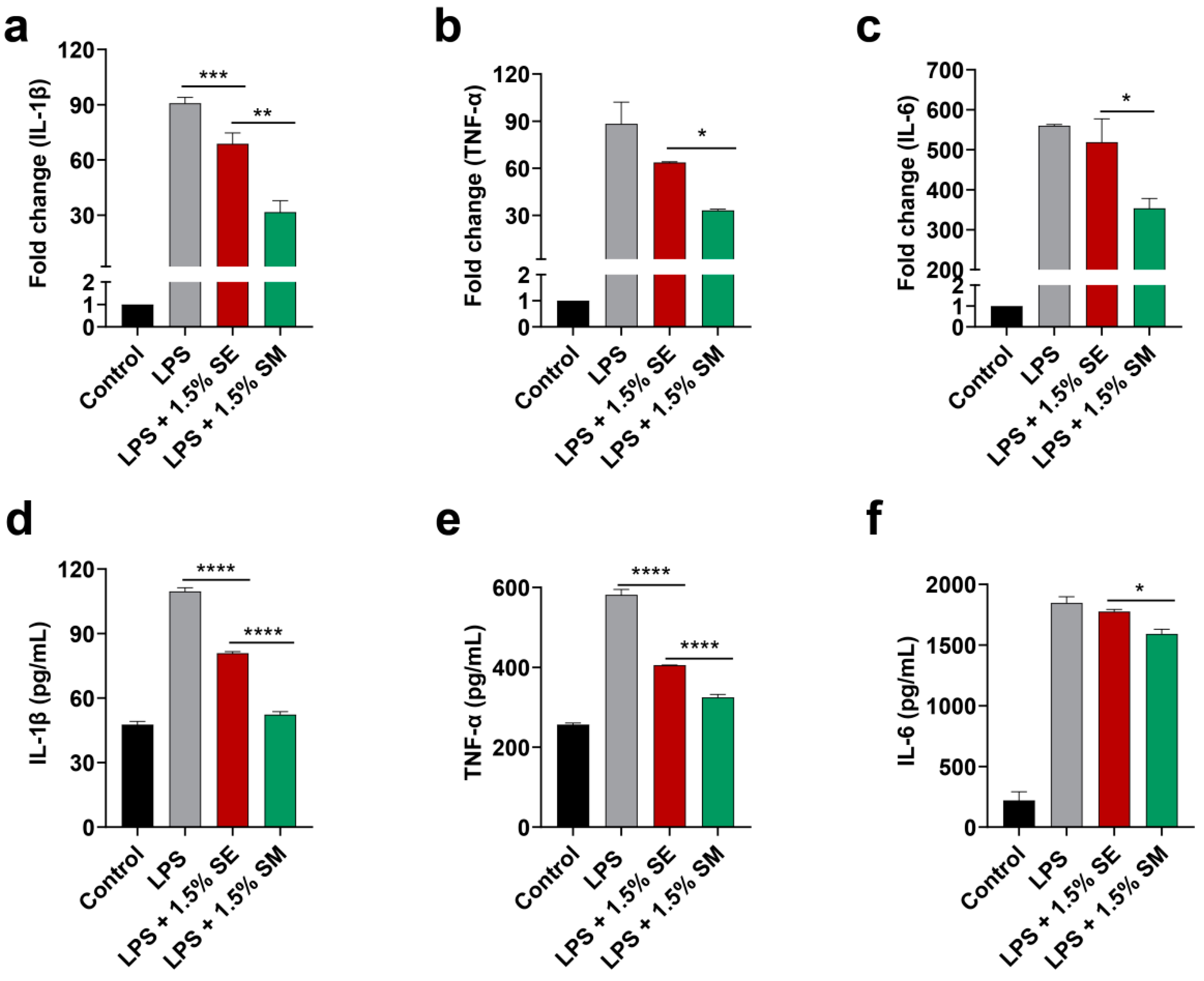
2.6. The Engineered Strain EcN::mcmA Significantly Inhibited the Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strains, Plasmids and Culture Conditions
4.2. Generation of Bacterial Mutants
4.3. In Vitro Growth Assays
4.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.5. Spectrofluorometric Assays
4.6. Protein Overexpression and Western Blot Analysis
4.7. CAS Agar Diffusion Assay (CASDA)
4.8. CAS Assay Methods
4.9. Adhesion and Invasion Inhibition Assays
4.10. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of E. coli Nissle 1917
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, Z.H.; Daliri, E.B.M.; Wang, J.; Liu, D.H.; Chen, S.G.; Ye, X.Q.; Ding, T. Inhibitory Effect of Lactic Acid Bacteria on Foodborne Pathogens: A Review. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezfulian, A.; Ardekani, A.; Aslani, M.M.; Dabiri, H.; Zali, M.R. Influence of the probiotic Escherichia coli strain Nissle 1917 on the growth of different pathogenic bacteria isolated from patients with diarrhea. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2008, 1, 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Konowalchuk, J.; Speirs, J.I.; Stavric, S. Vero response to a cytotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1977, 18, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dunkley, K.D.; Callaway, T.R.; Chalova, V.I.; Mcreynolds, J.L.; Hume, M.E.; Dunkley, C.S.; Kubena, L.F.; Nisbet, D.J.; Ricke, S.C. Foodborne Salmonella ecology in the avian gastrointestinal tract. Anaerobe 2009, 15, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiennimitr, P.; Winter, S.E.; Bäumler, A.J. Salmonella, the host and its microbiota. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 15, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.Z.; Jellbauer, S.; Poe, A.J.; Ton, V.; Pesciaroli, M.; Kehl-Fie, T.E.; Restrepo, N.A.; Hosking, M.P.; Edwards, R.A.; Battistoni, A.; et al. Zinc Sequestration by the Neutrophil Protein Calprotectin Enhances Salmonella Growth in the Inflamed Gut. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 11, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen-Wester, I.; Hensel, M. Salmonella pathogenicity islands encoding type III secretion systems. Microb. Infect. 2001, 3, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraga, A.; Ohlson, M.B.; Miller, S.I. Salmonellae interplay with host cells. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltby, R.; Leatham-Jensen, M.P.; Gibson, T.; Cohen, P.S.; Conway, T. Nutritional basis for colonization resistance by human commensal Escherichia coli strains HS and Nissle 1917 against E. coli O157:H7 in the mouse intestine. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Kim, Y.; Yoon, S.H. Development of a Genome-Scale Metabolic Model and Phenome Analysis of the Probiotic Escherichia coli Strain Nissle 1917. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenborn, U. Escherichia coli strain Nissle 1917-from bench to bedside and back: History of a special Escherichia coli strain with probiotic properties. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2016, 363, fnw212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dsc, B.S.; Vmd, S.D.; Vmd, S.B.; Vmd, R.B.; Vmd, A.D.G.; Vmd, S.D.; Vdm, G.B. Preventive Effects of the Probiotic Escherichia coli Strain Nissle 1917 on Acute Secretory Diarrhea in a Pig Model of Intestinal Infection. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2006, 51, 724–731. [Google Scholar]
- Schroder, N.C.H.; Korsa, A.; Wami, H.; Mantel, O.; Dobrindt, U.; Kurtz, J. Serial passage in an insect host indicates genetic stability of the human probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917. Evol. Med. Public Health 2022, 10, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobi, C.A.; Malfertheiner, P. Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (Mutaflor): New Insights into an Old Probiotic Bacterium. Dig. Dis. 2011, 29, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leatham, M.P.; Banerjee, S.; Autieri, S.M.; Mercado-Lubo, R.; Conway, T.; Cohen, P.S. Precolonized Human Commensal Escherichia coli Strains Serve as a Barrier to E-coli O157:H7 Growth in the Streptomycin-Treated Mouse Intestine. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 2876–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, C.S.; Mooney, J.C.; Brandt, J.R.; Staples, A.O.; Jelacic, S.; Boster, D.R.; Watkins, S.L.; Tarr, P.I. Risk factors for the hemolytic uremic syndrome in children infected with Escherichia coli O157:H7: A multivariable analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleta, S.; Nordhoff, M.; Tedin, K.; Wieler, L.H.; Kolenda, R.; Oswald, S.; Oelschlaeger, T.A.; Bleiss, W.; Schierack, P. Role of F1C fimbriae, flagella, and secreted bacterial components in the inhibitory effect of probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 on atypical enteropathogenic E. coli infection. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 1801–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asensio, C.; Perez-Diaz, J.C. A new family of low molecular weight antibiotics from enterobacteria. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1976, 69, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duquesne, S.; Destoumieux-Garzon, D.; Peduzzi, J.; Rebuffat, S. Microcins, gene-encoded antibacterial peptides from enterobacteria. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007, 24, 708–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischbach, M.A.; Lin, H.; Liu, D.R.; Walsh, C.T. How pathogenic bacteria evade mammalian sabotage in the battle for iron. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, H. Molecular genetics of fungal siderophore biosynthesis and uptake: The role of siderophores in iron uptake and storage. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 62, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, F.; Lima, T.; Correia, A.; Silva, A.M.; Soares, C.; Morais, S.; Weißelberg, S.; Vilanova, M.; Rohde, H.; Cerca, N. Siderophore-Mediated Iron Acquisition Plays a Critical Role in Biofilm Formation and Survival of Staphylococcus epidermidis Within the Host. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 799227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miethke, M.; Marahiel, M.A. Siderophore-based iron acquisition and pathogen control. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 413–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.P.; Liu, Z.Z.; Yu, F.; Zhu, J.P.; Chen, Y.; Tao, T. Siderophore-modified Fenton-like system for the degradation of propranolol in aqueous solutions at near neutral pH values. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 229, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deriu, E.; Liu, J.Z.; Pezeshki, M.; Edwards, R.A.; Ochoa, R.J.; Contreras, H.; Libby, S.J.; Fang, F.C.; Raffatellu, M. Probiotic bacteria reduce salmonella typhimurium intestinal colonization by competing for iron. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vassiliadis, G.; Destoumieux-Garzón, D.; Lombard, C.; Rebuffat, S.; Peduzzi, J. Isolation and characterization of two members of the siderophore-microcin family, microcins M and H47. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 54, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patzer, S.I.; Baquero, M.R.; Bravo, D.; Moreno, F.; Hantke, K. The colicin G, H and X determinants encode microcins M and H47, which might utilize the catecholate siderophore receptors FepA, Cir, Fiu and IroN. Microbiology 2003, 149, 2557–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rebuffat, S. Microcins in action: Amazing defence strategies of Enterobacteria. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2012, 40, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haywood, J.; Vadlamani, G.; Stubbs, K.A.; Mylne, J.S. Antibiotic resistance lessons for the herbicide resistance crisis. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 3807–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimi, S.; Zirah, S.; Hammami, R.; Fernandez, B.; Rebuffat, S.; Fliss, I. Fate and Biological Activity of the Antimicrobial Lasso Peptide Microcin J25 Under Gastrointestinal Tract Conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geldart, K.G.; Kommineni, S.; Forbes, M.; Hayward, M.; Dunny, G.M.; Salzman, N.H.; Kaznessis, Y.N. Engineered E. coli Nissle 1917 for the reduction of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus in the intestinal tract. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2018, 3, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ou, B.M.; Yang, Y.; Tham, W.L.; Chen, L.; Guo, J.T.; Zhu, G.Q. Genetic engineering of probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 for clinical application. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 8693–8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, T.; Elias, W.P.; Scaletsky, I.; Guth, B.; Rodrigues, J.F.; Piazza, R.; Ferreira, L.; Martinez, M.B. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47 (Suppl. S1), S3–S30. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsin, M.; Guenther, S.; Schierack, P.; Tedin, K.; Wieler, L.H. Probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 reduces growth, Shiga toxin expression, release and thus cytotoxicity of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 305, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rund, S.A.; Rohde, H.; Sonnenborn, U.; Oelschlaeger, T.A. Antagonistic effects of probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 on EHEC strains of serotype O104:H4 and O157:H7. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 303, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargun, A.; Gerner, R.R.; Raffatellu, M.; Nolan, E.M. Harnessing Iron Acquisition Machinery to Target Enterobacteriaceae. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 223 (Suppl. S2), S307–S313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosso, H.M.; Xiaoli, L.; Banerjee, K.; Hoffmann, M.; Yao, K.; Dudley, E.G. A Putative Microcin Amplifies Shiga Toxin 2a Production of Escherichia coli O157:H7. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 202, e00353-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crichton, R.R.; Ward, R.J. Iron homeostasis. Met. Ions Biol. Syst. 1998, 35, 633. [Google Scholar]
- Ganz, T. Hepcidin, a key regulator of iron metabolism and mediator of anemia of inflammation. Blood 2003, 102, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massip, C.; Branchu, P.; Bossuet-Grief, N.; Chagneau, C.V.; Gaillard, D.; Martin, P.; Boury, M.; Secher, T.; Dubois, D.; Nougayrede, J.P.; et al. Deciphering the interplay between the genotoxic and probiotic activities of Escherichia coli Nissle 1917. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1008029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azpiroz, M.F.; Lavina, M. Involvement of Enterobactin Synthesis Pathway in Production of Microcin H47. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palmer, J.D.; Piattelli, E.; McCormick, B.A.; Silby, M.W.; Brigham, C.J.; Bucci, V. Engineered Probiotic for the Inhibition of Salmonella via Tetrathionate-Induced Production of Microcin H47. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K.; Kizhakkekalam, V.K.; Joy, M.; Chakraborty, R.D. Bacillibactin class of siderophore antibiotics from a marine symbiotic Bacillus as promising antibacterial agents. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 106, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massip, C.; Oswald, E. Siderophore-Microcins inEscherichia coli: Determinants of Digestive Colonization, the First Step Toward Virulence. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, C.; Murphy, L.; Flynn, S.; O’Mahony, L.; O’Halloran, S.; Feeney, M.; Morrissey, D.; Thornton, G.; Fitzgerald, G.; Daly, C.; et al. Probiotics: From myth to reality. Demonstration of functionality in animal models of disease and in human clinical trials. Antonie Leeuwenhoek Int. J. Gen. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 76, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeser, J.R.; Granato, D.; Rouvet, M.; Servin, A.; Teneberg, S.; Karlsson, E.A. Lactobacillus johnsonii Lal shares carbohydrate-binding specificities with several enteropathogenic bacteria. Glycobiology 2000, 10, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kamada, N.; Maeda, K.; Inoue, N.; Hisamatsu, T.; Okamoto, S.; Hong, K.S.; Yamada, T.; Watanabe, N.; Tsuchimoto, K.; Ogata, H.; et al. Nonpathogenic Escherichia coli strain Nissle 1917 inhibits signal transduction in intestinal epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karancsi, Z.; Moritz, A.V.; Lewin, N.; Veres, A.M.; Jerzsele, A.; Farkas, O. Beneficial Effect of a Fermented Wheat Germ Extract in Intestinal Epithelial Cells in case of Lipopolysaccharide-Evoked Inflammation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1482482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Lilo, S.; Mena, P.; Bliska, J.B. YopJ-Induced Caspase-1 Activation in Yersinia-Infected Macrophages: Independent of Apoptosis, Linked to Necrosis, Dispensable for Innate Host Defense. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, S.R.; Naus, C.C. RF-Cloning.org: An online tool for the design of restriction-free cloning projects. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W209–W213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.W.; Wang, A.; Li, K.; Wang, B.; Jin, S.; Reiser, M.; Lockey, R.F. CRISPR/Cas9 nuclease cleavage combined with Gibson assembly for seamless cloning. BioTechniques 2015, 58, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, H.; Du, Y.; Liu, S.; Ni, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; SI, W.; Yang, J.; Ling, J. Development and evaluation of an indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of antibodies against Campylobacter fetus in cattle. Res. Vet. Sci. 2010, 88, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwyn, B.; Neilands, J.B. Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 160, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Materials | Description | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Strains | ||
| DH5α | Plasmid amplification host | Our lab |
| EcN | E. coli Nissle 1917, wt | Our lab |
| EcN ΔmcmA | Knockout of EcN Microcin M precursor, mutant strain | Our study |
| EcN ΔmchB | Knockout of EcN Microcin H47 precursor, mutant strain | Our study |
| EcN ΔmcmAΔmchB | Knockout of EcN Microcin M and H47 precursor, mutant strain | Our study |
| EcN::mcmA | Overexpression of EcN Microcin M precursor, engineered strain | Our study |
| EHEC O157:H7 | Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) O157:H7 ATCC 35150 | Our lab |
| SE | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Pullorum str. ATCC 9120 | Our lab |
| ST | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium ATCC 14028 | Our lab |
| Plasmids | ||
| pUC19 | Expressing GFP (green) or mCherry (red) fluorescent proteins, Overexpression vector | Our lab |
| pTargetF | Plasmid for CRISPR-Cas9 | Our lab |
| pCas | Plasmid for CRISPR-Cas9 | Our lab |
| Primers | ||
| A20-F | GGATGATAATCCTATACCTGgttttagagctagaaatagca | |
| A20-R | CAGGTATAGGATTATCATCCactagtattatacctaggact | |
| B20-F | GTTAAGATATATTTCCGGGGgttttagagctagaaatagca | |
| B20-R | CCCCGGAAATATATCTTAACactagtattatacctaggact | |
| AH1-F | agagtcgacctgcagaagcttGGGGTATGAAACGTTAATAGGT | |
| AH1-R | taaggtTTCAACACCTTCGCTATAAGATT | |
| AH2-F | gcgaaggtgttgaaACCTTATATTGTTAATGAAGCACC | |
| AH2-R | ggagctgcacatgaactcgagTTTTATGGATTAATATATTTTCTTCTGT | |
| BH1-F | agagtcgacctgcagaagcttGACTTTATATGGACAATATGACACTTT | |
| BH1-R | aaatataaATAAACTCCATCATATTTAACTTCC | |
| BH2-F | gatggagtttatTTATATTTTTATTTATTTTACAGGTACTTT | |
| BH2-R | ggagctgcacatgaactcgagAACGTGCACCACCTCCAT | |
| Δ mcmA-F | GAAGAAAAGAAACCGGAAATT | |
| Δ mcmA-R | ACTTCTTGTTCCTGTATATGAAGAGA | |
| Δ mchB-F | GTTTGCAAAAATGTTTGTTATAGG | |
| Δ mchB-R | AACGTGCACCACCTCCAT | |
| pUC19-F | ATGACCATGATTACGCCAAG | |
| pUC19-R | AGCTGTTTCCTGTGTGAAATTG | |
| pUC -mcmA-F | ttcacacaggaaacagctATGAGAAAACTATCTGAAAATGAAAT | |
| pUC -mcmA-R | tggcgtaatcatggtcatTTAGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGACTTCCACTCCCCGC | |
| STX1-SG-F | CATTACAGACTATTTCATCAGGAGGTA | |
| STX1-SG-R | TCGTTCAACAATAAGCCGTAGATTA | |
| STX2-SG-F | GCGGTTTTATTTGCATTAGC | |
| STX2-SG-R | TCCCGTCAACCTTCACTGTA | |
| IC-1F | GACCACTACCAGCAGAAC | |
| IC-10R | CTTGTACAGCTCGTCCATGC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Fu, W.; Hong, B.; Wang, X.; Jiang, S.; Wang, J. Antibacterial MccM as the Major Microcin in Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 against Pathogenic Enterobacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11688. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411688
Ma Y, Fu W, Hong B, Wang X, Jiang S, Wang J. Antibacterial MccM as the Major Microcin in Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 against Pathogenic Enterobacteria. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(14):11688. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411688
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yi, Wei Fu, Bin Hong, Xinfeng Wang, Shoujin Jiang, and Jufang Wang. 2023. "Antibacterial MccM as the Major Microcin in Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 against Pathogenic Enterobacteria" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 14: 11688. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411688
APA StyleMa, Y., Fu, W., Hong, B., Wang, X., Jiang, S., & Wang, J. (2023). Antibacterial MccM as the Major Microcin in Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 against Pathogenic Enterobacteria. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(14), 11688. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411688






