Molecular Characteristics of Catalytic Nitrogen Removal from Coal Tar Pitch over γ-Alumina-Supported NiMo and CoMo Catalysts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Overall Reactivity
2.2. Reactivities of the Molecular Classes
2.3. CcHh Class
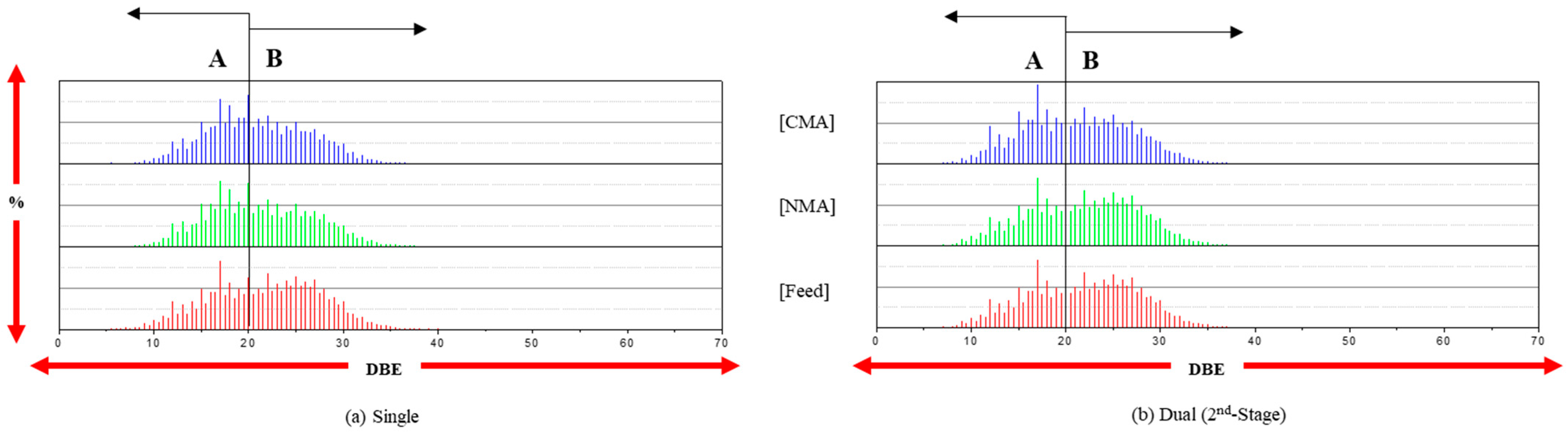
2.4. Subclasses of Nitrogen
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Hydrotreatment Apparatus
3.3. Bulk Analysiss
3.4. FT-ICR MS
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gabdulkhakov, R.R.; Rudko, V.A.; Pyagay, I.N. Methods for modifying needle coke raw materials by introducing additives of various origin (review). Fuel 2022, 310, 122265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, K.; Liu, D.; Lou, B.; Li, M.; Guo, S.; Yu, R.; Wu, B.; Gong, X.; Li, G. Comparative study of the carbonization process and structural evolution during needle coke preparation from petroleum and coal feedstock. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 156, 105097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, X.-M.; Cui, L.-W.; Fan, X.-Y.; Shi, J.-H.; Xu, X.; Tian, J.-Y.; Tian, Y.-C.; Zheng, J.-X.; Li, D. Effect of raw material composition on the structure of needle coke. J. Fuel. Chem. Technol. 2021, 49, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochida, I.; Oyama, T.; Fei, Y.Q.; Furuno, T.; Korai, Y. Optimization of carbonization conditions for needle coke production from a low-sulphur petroleum vacuum residue. J. Mater. Sci. 1988, 23, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershaw, J.R.; Black, K.J. Structural characterization of coal-tar and petroleum pitches. Energy Fuels 1993, 7, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, M.F. Nitrogenous chemicals from carbon based materials. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2005, 23, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochida, I.; Fei, Y.Q.; Sakanishi, K.; Korai, Y.; Usuba, H.; Miura, K. Carbonization of coal tar pitch denitrogenated by metal sulfates. Carbon 1992, 30, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adschiri, T.; Suzuki, T.; Arai, K. Catalytic reforming of coal tar pitch in supercritical fluid. Fuel 1991, 70, 1483–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Mukherji, S. Desorption kinetics of soil sorbed carbazole, fluorene, and dibenzothiophene by P. aeruginosa RS1 from single and multicomponent systems and elucidation of their interaction effects. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 180, 108367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosberg, R.H.; Scouten, C.G. Removal of Phenols from Phenol-Containing Streams. U.S. Patent 4,256,568, 17 March 1981. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/biblio/6357608 (accessed on 3 January 2021).
- Zhang, L.; Xu, D.; Gao, J.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Z. Extraction and mechanism for the separation of neutral N-compounds from coal tar by ionic liquids. Fuel 2017, 194, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adschiri, T.; Okazaki, S.; Mochiduki, M.; Kurosawa, S.; Arai, K. Hydrogenation through Partial Oxidation of Hydrocarbons in Supercritical Water. Int. J. Soc. Mater. Eng. Resour. 1999, 7, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Ding, M.; Xu, Z. Study of oxidization of coal–pitch by O3. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2016, 26, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochida, I.; Fei, Y.Q.; Sakanishi, K.; Usuba, H.; Miura, K. Capture and Recovery of Basic Nitrogen Species in Coal Tar Pitch, Using Nickel Sulfate as Adsorbent. Chem. Lett. 1990, 19, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochida, I.; Sakanishi, K.; Usuba, H.; Miura, K. Removal of basic nitrogen species in coal-tar pitch by metal sulphates supported on silica gel. Fuel 1991, 70, 761–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeja, M. Adsorptive Removal of Nitrogen from Coal-Based Needle Coke Feedstocks using Activated Carbon. Ph.D. Thesis, West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV, USA, 2009; p. 1478762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Kang, H.-C.; Kim, Y.-S.; Jeong, H.-J. Liquid membrane permeation of nitrogen heterocyclic compounds contained in model coal tar fraction. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, 31, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habaki, H.; Shimada, Y.; Egashira, R. Separation of coal tar absorption oil by an ionic liquid supported liquid membrane. Solvent Extr. Res. Dev. Jpn. 2013, 20, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gole, A.; Andersson, J.T. Group-type separation of nitrogen containing aromatic compounds in coal tar pitch on a hafnium modified silica HPLC phase. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2015, 35, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Andersson, J.T.; Räder, H.J.; Müllen, K. Molecular characterization of large polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in solid petroleum pitch and coal tar pitch by high resolution MALDI ToF MS and insights from ion mobility separation. Carbon 2015, 95, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reckendorf, R.M.Z. Identification of phenyl-substituted polycyclic aromatic compounds in ring furnace gases using GC-MS and GC-AED. Chromatographia 1997, 45, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammann, A.A. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP MS): A versatile tool. J. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 42, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, E.J.; Na, J.-G.; Chung, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.H. Identification of about 30 000 Chemical Components in Shale Oils by Electrospray Ionization (ESI) and Atmospheric Pressure Photoionization (APPI) Coupled with 15 T Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry (FT-ICR MS) and a Comparison to Conventional Oil. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 2563–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Hong, I.; Son, S.; An, J.-C.; Kim, S. Molecular-level investigation of coal-tar pitch treated by air blowing: Revealing the restructure of aromatic compounds via radical reactions. Carbon 2023, 203, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón-Patiño, M.L.; Rowland, S.M.; Rodgers, R.P. The Compositional and Structural Continuum of Petroleum from Light Distillates to Asphaltenes: The Boduszynski Continuum Theory as Revealedby FT-ICR Mass Spectrometry. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 6, 113–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.I.; Nakano, K.; Kim, Y.K.; Miyawaki, J.; Yoon, S.H.; Mochida, I. Characteristics on HDS over amorphous silica-alumina in single and dual catalytic bed system for gas oil. Catal. Today 2011, 164, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, M.S.; AL-Mutairi, A.; Jung, H.K.; Hong, I.P.; An, J.C.; Park, C.I.; Kim, D.W.; Jeon, Y.; Marafi, A.M.; Ma, X.; et al. Molecular characteristics of light cycle oil hydrodesulfurization over silica-alumina supported NiMo catalysts. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 29746–29754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Riches, E.; Palmer, M.; Giles, K.; Ujima, J.; Kim, S.H. Isolation of Crude Oil Peaks Differing by m/z ∼0.1 via Tandem Mass Spectrometry Using a Cyclic Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4268–14274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Feed | Single-Stage Reaction | Dual-Stage Reaction | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMA | Change (%) | CMA | Change (%) | DM5CQ (1st Stage) | Change (%) | NMA (2nd Stage) | Change (%) | CMA (2nd Stage) | Change (%) | ||
| C/H | 18.8 | 15.8 | −15.9 | 16.1 | −14.3 | 15.9 | −15.4 | 14.8 | −21.3 | 14.8 | −21.3 |
| Total S (wt%) | 0.415 | 0.056 | −86.5 | 0.022 | −94.7 | 0.053 | −87.2 | - | −100 | - | −100 |
| Total N (wt%) | 1.33 | 0.97 | −26.8 | 0.94 | −29.2 | 1.04 | −21.8 | 0.71 | −46.4 | 0.68 | −48.7 |
| Heteroatoms | Feed | NMA | Change, % | CMA | Change, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CcHh | 54.379 | 67.217 | 23.6 | 67.936 | 24.9 |
| CcHh-Nn | 20.610 | 17.072 | −17.2 | 16.381 | −20.5 |
| CcHh-SS | 1.942 | 0.336 | −82.7 | 0.179 | −90.8 |
| CcHh-OO | 10.900 | 7.650 | −29.8 | 7.673 | −29.6 |
| CcHh-NnOO | 6.472 | 2.774 | −57.1 | 2.885 | −55.4 |
| CcHh-NnSS | 2.043 | 2.200 | 7.7 | 2.294 | 12.3 |
| CcHh-OOSS | 1.500 | 1.006 | −32.9 | 0.867 | −42.2 |
| CcHh-NnOOSS | 0.974 | 0.656 | −32.6 | 0.649 | −33.4 |
| Heteroatoms | Feed | DM5CQ (1st Stage) | Change, % | NMA (2nd Stage) | Change, % | CMA (2nd Stage) | Change, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CcHh | 54.379 | 62.567 | 15.1 | 74.682 | 37.3 | 74.463 | 36.9 |
| CcHh-Nn | 20.610 | 17.553 | −14.8 | 14.111 | −31.5 | 12.053 | −41.5 |
| CcHh-SS | 1.942 | 0.514 | −73.5 | 0.118 | −93.9 | 0.138 | −92.9 |
| CcHh-OO | 10.900 | 7.293 | −33.1 | 5.284 | −51.5 | 7.309 | −32.9 |
| CcHh-NnOO | 6.472 | 3.879 | −40.1 | 2.313 | −64.3 | 2.709 | −58.1 |
| CcHh-NnSS | 2.043 | 3.861 | 89.0 | 1.033 | −49.4 | 1.018 | −50.2 |
| CcHh-OOSS | 1.500 | 2.117 | 41.1 | 0.632 | −57.9 | 0.551 | −63.3 |
| CcHh-NnOOSS | 0.974 | 1.095 | 12.4 | 0.606 | −37.8 | 0.549 | −43.6 |
| Heteroatoms | Feed | Single-Stage Reaction | Dual-Stage Reaction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMA | CMA | DM5CQ (1st Stage) | NMA (2nd Stage) | CMA (2nd Stage) | ||
| CcHh-Nn | 20.610 | 17.072 | 16.381 | 17.553 | 14.111 | 12.053 |
| N1 | 18.473 | 16.029 | 15.262 | 16.137 | 13.594 | 11.471 |
| N2 | 2.053 | 0.985 | 1.058 | 1.358 | 0.426 | 0.278 |
| N3 | 0.061 | 0.024 | 0.032 | 0.030 | 0.055 | 0.043 |
| N4 | 0.020 | 0.031 | 0.026 | 0.026 | 0.034 | 0.026 |
| N5 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.006 |
| CcHh-NnOO | 6.472 | 2.774 | 2.885 | 3.879 | 2.313 | 2.709 |
| N1O1 | 4.710 | 2.136 | 2.135 | 2.326 | 1.808 | 1.986 |
| N1O2 | 0.745 | 0.141 | 0.104 | 0.184 | 0.180 | 0.279 |
| N2O1 | 0.570 | 0.062 | 0.184 | 0.113 | 0.035 | 0.026 |
| N2O2 | 0.280 | 0.283 | 0.352 | 1.154 | 0.188 | 0.293 |
| N2O3 | 0.049 | 0.013 | 0.008 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.019 |
| CcHh-NnSS | 2.043 | 2.200 | 2.294 | 3.861 | 1.033 | 1.018 |
| N1S1 | 0.912 | 0.167 | 0.200 | 0.288 | 0.092 | 0.130 |
| N1S3 | 0.129 | 0.437 | 0.330 | 0.604 | 0.144 | 0.181 |
| N1S4 | 0.607 | 1.010 | 1.228 | 2.072 | 0.470 | 0.405 |
| N2S2 | 0.089 | 0.101 | 0.097 | 0.112 | 0.084 | 0.096 |
| N3S1 | 0.082 | 0.244 | 0.206 | 0.442 | 0.039 | 0.034 |
| CcHh-NnOOSS | 0.974 | 0.656 | 0.649 | 1.095 | 0.606 | 0.549 |
| N1O1S1 | 0.173 | 0.070 | 0.072 | 0.069 | 0.070 | 0.070 |
| N1O1S2 | 0.045 | 0.046 | 0.057 | 0.076 | 0.059 | 0.046 |
| N1O1S4 | 0.120 | 0.035 | 0.031 | 0.169 | 0.011 | 0.006 |
| N1O2S1 | 0.025 | 0.012 | 0.010 | 0.021 | 0.007 | 0.007 |
| N1O3S1 | 0.029 | 0.025 | 0.030 | 0.039 | 0.013 | 0.005 |
| Softening Point (°C) | Toluene Insoluble (%) | Quinoline Insoluble (%) | Beta-Resin (%) | Ash (%) | Viscosity at 0.84 s−1, cP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 170 °C | 190 °C | 230 °C | ||||||
| CTP, as-received | 110–120 | 25.4 | 4.9 | 20.5 | 0.24 | 1860 | 460 | 54.4 |
| Characteristics | Unit | Catalysts (Single/Dual Stage) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Stage | 2nd Stage | |||
| DM5CQ | NMA | CMA | ||
| Bulk density | g/cc | 0.43 | 0.61 | 0.60 |
| Surface area | m2/g | 178 | 232 | 228 |
| Average pore diameter | nm | 17.4 | 9.8 | 10.2 |
| Active metal | Mo | Ni-Mo | Co-Mo | |
| Metal contents | ||||
| Mo | wt. % | 2.7 | 7.6 | 7.7 |
| Ni | wt. % | - | 2.5 | - |
| Co | wt. % | - | - | 2.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, K.-H.; Seo, D.-J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Cho, S.-S.; Han, Y.-J.; Yang, I.; Kim, C.-W.; Oh, K.; An, J.-C.; Park, J.-I. Molecular Characteristics of Catalytic Nitrogen Removal from Coal Tar Pitch over γ-Alumina-Supported NiMo and CoMo Catalysts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11793. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411793
Choi K-H, Seo D-J, Kim Y-J, Cho S-S, Han Y-J, Yang I, Kim C-W, Oh K, An J-C, Park J-I. Molecular Characteristics of Catalytic Nitrogen Removal from Coal Tar Pitch over γ-Alumina-Supported NiMo and CoMo Catalysts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(14):11793. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411793
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Kyoung-Hwan, Dong-Jin Seo, Yu-Jin Kim, San-Seong Cho, Yu-Jin Han, Inchan Yang, Chel-Woo Kim, Kyeongseok Oh, Jung-Chul An, and Joo-Il Park. 2023. "Molecular Characteristics of Catalytic Nitrogen Removal from Coal Tar Pitch over γ-Alumina-Supported NiMo and CoMo Catalysts" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 14: 11793. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411793
APA StyleChoi, K.-H., Seo, D.-J., Kim, Y.-J., Cho, S.-S., Han, Y.-J., Yang, I., Kim, C.-W., Oh, K., An, J.-C., & Park, J.-I. (2023). Molecular Characteristics of Catalytic Nitrogen Removal from Coal Tar Pitch over γ-Alumina-Supported NiMo and CoMo Catalysts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(14), 11793. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411793







