Interactions of the N- and C-Terminal SH3 Domains of Drosophila Drk with the Proline-Rich Peptides from Sos and Dos
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The NMR Titration Experiments of Two SH3 Domains of Drk with Sos- and Dos-Derived Peptides
2.2. Docking Simulations of Sos and Dos-Derived Peptides on Drk-NSH3 and Drk-CSH3
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Purification of Drk-NSH3 and Drk-CSH3
4.2. NMR Spectroscopy
4.3. Molecular Docking
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jorissen, R.N.; Walker, F.; Pouliot, N.; Garrett, T.P.; Ward, C.W.; Burgess, A.W. Epidermal growth factor receptor: Mechanisms of activation and signalling. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 284, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, G.; Whyte, D.B.; Martinez, R.; Hunter, T.; Sudarsanam, S. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science 2002, 298, 1912–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musacchio, A.; Saraste, M.; Wilmanns, M. High-resolution crystal structures of tyrosine kinase SH3 domains complexed with proline-rich peptides. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1994, 1, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionne, U.; Percival, L.J.; Chartier, F.J.M.; Landry, C.R.; Bisson, N. SRC homology 3 domains: Multifaceted binding modules. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2022, 47, 772–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume-Jensen, P.; Hunter, T. Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature 2001, 411, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, T.J.; Jang, H.; Nussinov, R.; Fushman, D. High-Affinity Interactions of the nSH3/cSH3 Domains of Grb2 with the C-Terminal Proline-Rich Domain of SOS1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 3401–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenstein, E.; Daly, R.; Batzer, A.; Li, W.; Margolis, B.; Lammers, R.; Ullrich, A.; Skolnik, E.; Bar-Sagi, D.; Schlessinger, J. The SH2 and SH3 domain-containing protein GRB2 links receptor tyrosine kinases to ras signaling. Cell 1992, 70, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.A.; Batzer, A.; Daly, R.; Yajnik, V.; Skolnik, E.; Chardin, P.; Bar-Sagi, D.; Margolis, B.; Schlessinger, J. Guanine-nucleotide-releasing factor hSos1 binds to Grb2 and links receptor tyrosine kinases to Ras signalling. Nature 1993, 363, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holgado-Madruga, M.; Emlet, D.R.; Moscatello, D.K.; Godwin, A.K.; Wong, A.J. A Grb2-associated docking protein in EGF-and insulin-receptor signalling. Nature 1996, 379, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yu, D.-H.; Shen, R.; Feng, G.-S. Gab2, a new pleckstrin homology domain-containing adapter protein, acts to uncouple signaling from ERK kinase to Elk-1. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 19649–19654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raabe, T.; Olivier, J.P.; Dickson, B.; Liu, X.; Gish, G.D.; Pawson, T.; Hafen, E. Biochemical and genetic analysis of the Drk SH2/SH3 adaptor protein of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 2509–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feller, S.M.; Wecklein, H.; Lewitzky, M.; Kibler, E.; Raabe, T. SH3 domain-mediated binding of the Drk protein to Dos is an important step in signaling of Drosophila receptor tyrosine kinases. Mech. Dev. 2002, 116, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, O.; Kay, L.E.; Olivier, J.P.; Forman-Kay, J.D. Backbone 1 H and 15 N resonance assignments of the N-terminal SH3 domain of drk in folded and unfolded states using enhanced-sensitivity pulsed field gradient NMR techniques. J. Biomol. NMR 1994, 4, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, O.; Forman-Kay, J.D. Structural characterization of folded and unfolded states of an SH3 domain in equilibrium in aqueous buffer. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 6784–6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, J.P.; Raabe, T.; Henkemeyer, M.; Dickson, B.; Mbamalu, G.; Margolis, B.; Schlessinger, J.; Hafen, E.; Pawson, T. A Drosophila SH2-SH3 adaptor protein implicated in coupling the sevenless tyrosine kinase to an activator of Ras guanine nucleotide exchange, Sos. Cell 1993, 73, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayeesh, P.M.; Ikeya, T.; Sugasawa, H.; Watanabe, R.; Mishima, M.; Inomata, K.; Ito, Y. Insight into the C-terminal SH3 domain mediated binding of Drosophila Drk to Sos and Dos. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 625, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadmiller, S.S.; Aguilar, J.S.; Parnham, S.; Pielak, G.J. Protein-Peptide Binding Energetics under Crowded Conditions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 9297–9309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezsonova, I.; Singer, A.; Choy, W.Y.; Tollinger, M.; Forman-Kay, J.D. Structural comparison of the unstable drkN SH3 domain and a stable mutant. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 15550–15560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, O.; Forman-Kay, J.D. NMR studies of unfolded states of an SH3 domain in aqueous solution and denaturing conditions. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 3959–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sanner, M.F. AutoDock CrankPep: Combining folding and docking to predict protein-peptide complexes. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 5121–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanner, M.F. A component-based software environment for visualizing large macromolecular assemblies. Structure 2005, 13, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, T.; Li, L.; Li, S.S. The SH3 domain--a family of versatile peptide- and protein-recognition module. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 4938–4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoelz, A.; Janz, J.M.; Lawrie, S.D.; Corwin, B.; Lee, A.; Sakmar, T.P. Crystal structure of the SH3 domain of betaPIX in complex with a high affinity peptide from PAK2. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 358, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, M.; Goudreau, N.; Cornille, F.; Cussac, D.; Gincel, E.; Garbay, C. Molecular and cellular analysis of Grb2 SH3 domain mutants: Interaction with Sos and dynamin. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 290, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkiolaki, M.; Tsirka, T.; Lewitzky, M.; Simister, P.C.; Joshi, D.; Bird, L.E.; Jones, E.Y.; O’Reilly, N.; Feller, S.M. Distinct binding modes of two epitopes in Gab2 that interact with the SH3C domain of Grb2. Structure 2009, 17, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Dunker, A.K.; Uversky, V.N. Orderly order in protein intrinsic disorder distribution: Disorder in 3500 proteomes from viruses and the three domains of life. J Biomol Struct Dyn 2012, 30, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.E.; Dyson, H.J. Intrinsically disordered proteins in cellular signalling and regulation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranken, W.F.; Boucher, W.; Stevens, T.J.; Fogh, R.H.; Pajon, A.; Llinas, M.; Ulrich, E.L.; Markley, J.L.; Ionides, J.; Laue, E.D. The CCPN data model for NMR spectroscopy: Development of a software pipeline. Proteins 2005, 59, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, M.P. Using chemical shift perturbation to characterise ligand binding. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2013, 73, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
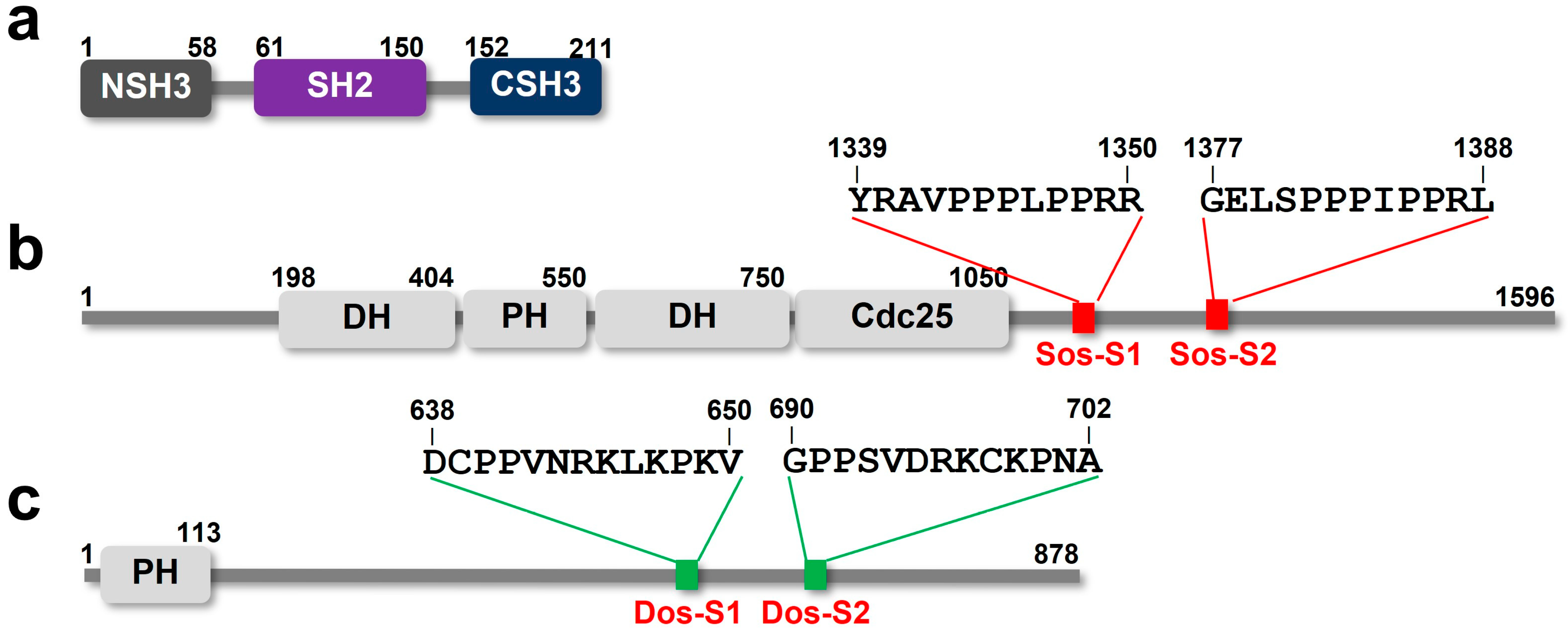
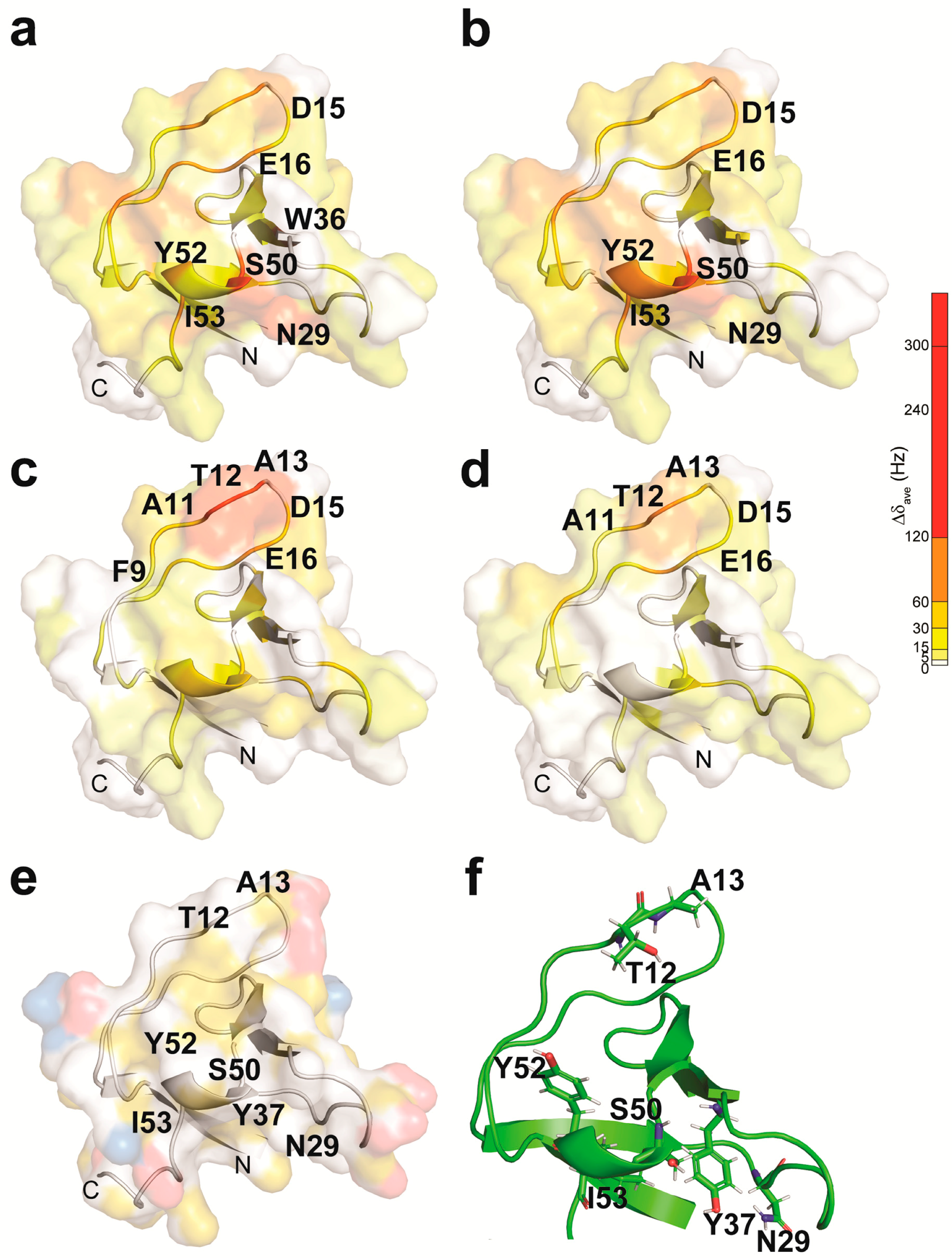
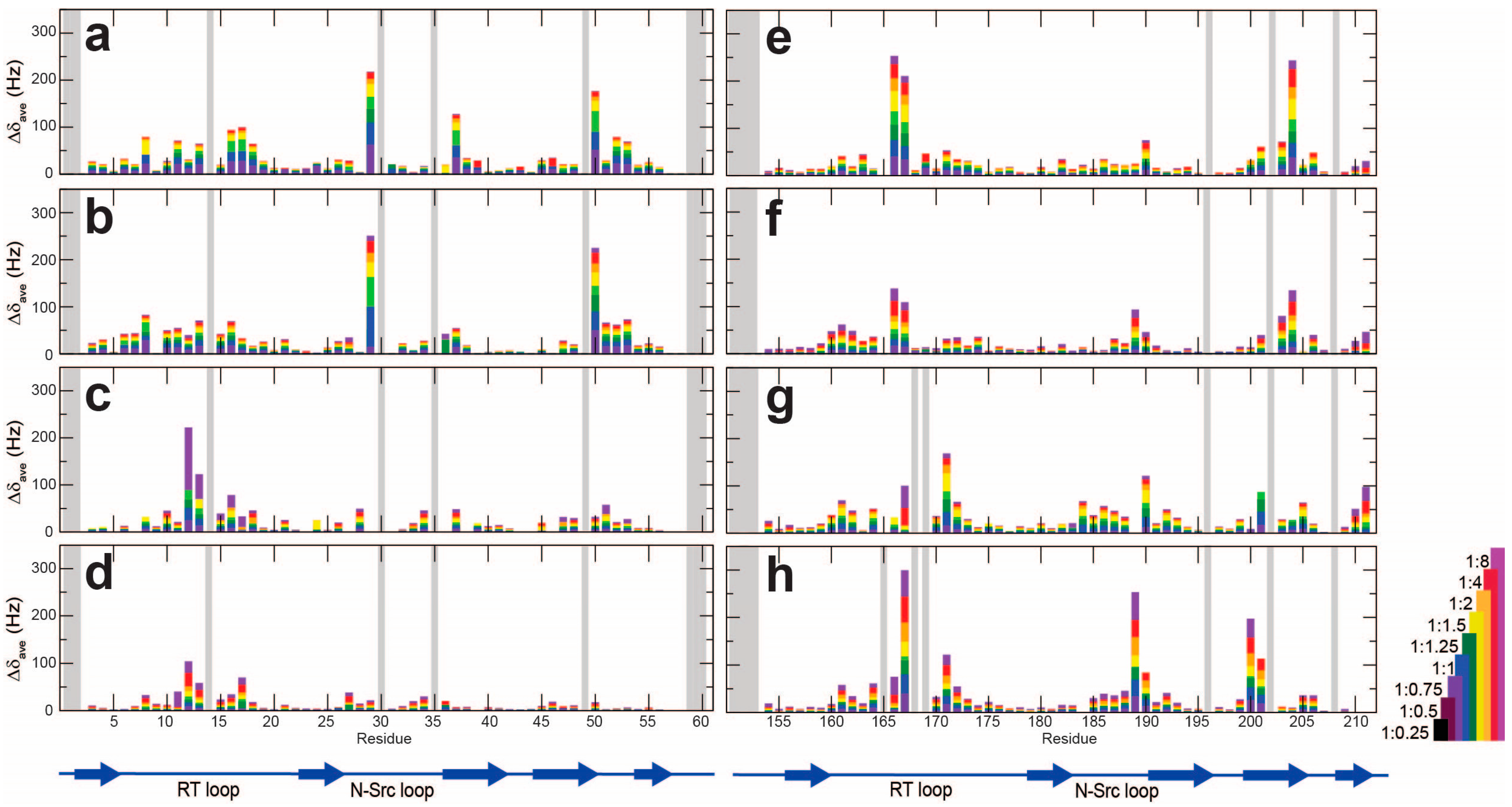
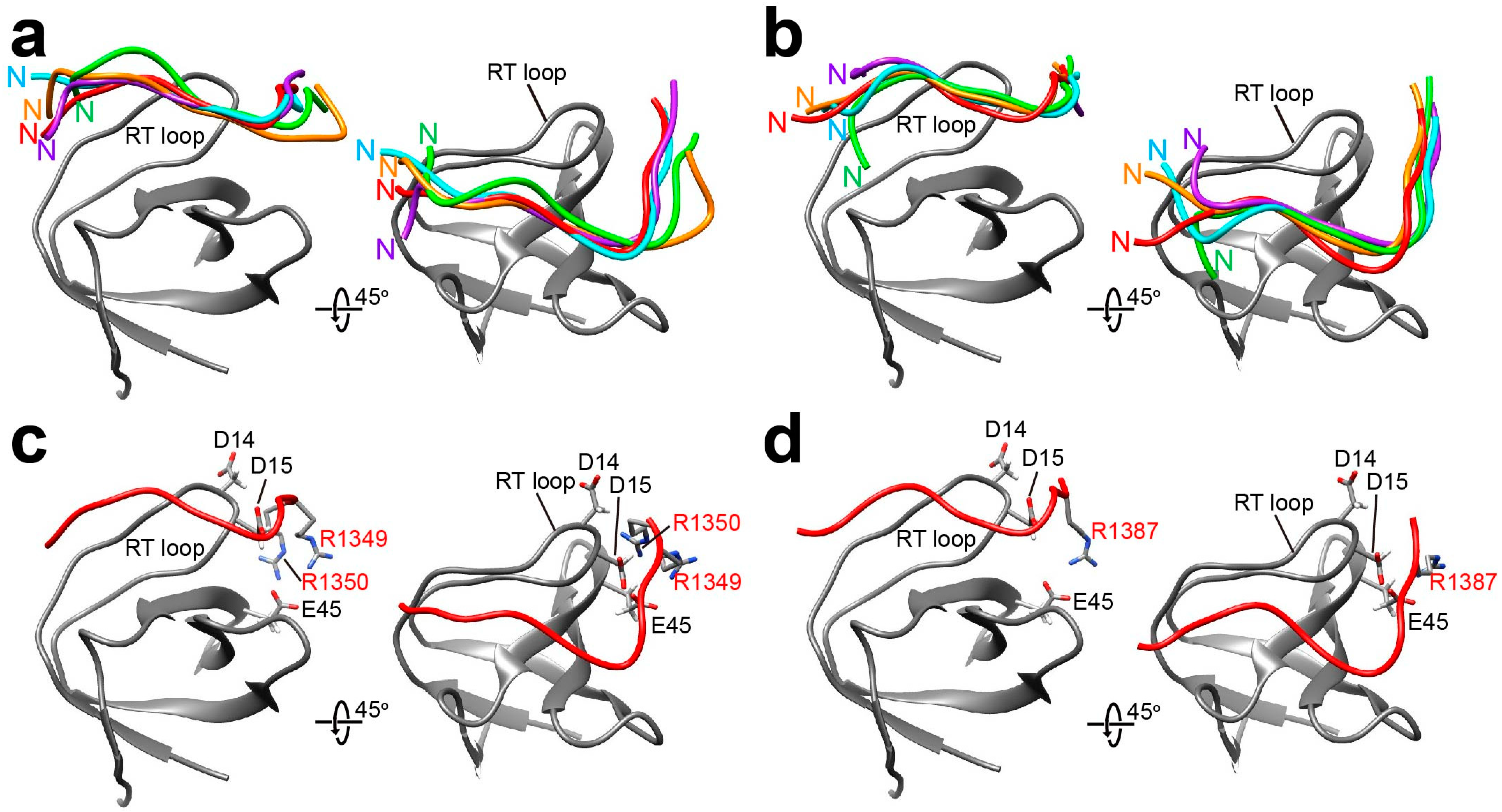


| Peptide | Sequence | Motif | Drk-NSH3 | Drk-CSH3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sos-S1 | YRAVPPPLPPRR (1339–1350) | PxxPxR | 13.24 ± 0.704 μM (Kf = 0.9589 ± 0.0044) | 157.57 ± 8.405 μM |
| Sos-S2 | GELSPPPIPPRL (1377–1389) | PxxPxR | 41.44 ± 8.429 μM (Kf = 0.8813 ± 0.0435) | 457.40 ± 17.334 μM |
| Dos-S1 | DCPPVNRKLKPKV (638–650) | PxxxRxxKP | 82.89 ± 4.535 μM (Kf = 0.4741 ± 0.026) | 124.73 ± 14.724 μM |
| Dos-S2 | GPPSVDRKCKPNA (690–702) | PxxxRxxKP | 242.11 ± 11.608 μM (Kf = 0.6154 ± 0.0178) | 250.17 ± 21.498 μM |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sayeesh, P.M.; Iguchi, M.; Suemoto, Y.; Inoue, J.; Inomata, K.; Ikeya, T.; Ito, Y. Interactions of the N- and C-Terminal SH3 Domains of Drosophila Drk with the Proline-Rich Peptides from Sos and Dos. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241814135
Sayeesh PM, Iguchi M, Suemoto Y, Inoue J, Inomata K, Ikeya T, Ito Y. Interactions of the N- and C-Terminal SH3 Domains of Drosophila Drk with the Proline-Rich Peptides from Sos and Dos. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(18):14135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241814135
Chicago/Turabian StyleSayeesh, Pooppadi Maxin, Mayumi Iguchi, Yusuke Suemoto, Jin Inoue, Kohsuke Inomata, Teppei Ikeya, and Yutaka Ito. 2023. "Interactions of the N- and C-Terminal SH3 Domains of Drosophila Drk with the Proline-Rich Peptides from Sos and Dos" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 18: 14135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241814135
APA StyleSayeesh, P. M., Iguchi, M., Suemoto, Y., Inoue, J., Inomata, K., Ikeya, T., & Ito, Y. (2023). Interactions of the N- and C-Terminal SH3 Domains of Drosophila Drk with the Proline-Rich Peptides from Sos and Dos. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(18), 14135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241814135







