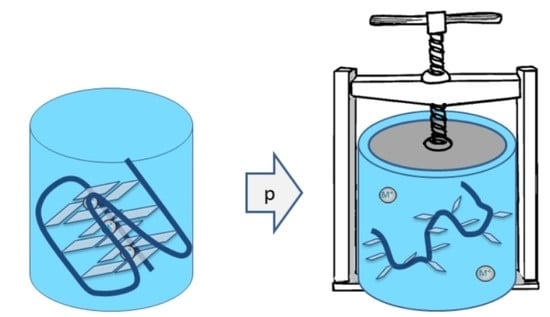
Pressure Tuning Studies of Four-Stranded Nucleic Acid Structures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The G-Quadruplex
3. The i-Motif
4. High Pressure
5. Experimental Methods to Study the Phase Transitions of Nucleic Acids under Pressure
6. Nucleic Acids and Pressure
7. GQ and Pressure
8. i-Motif under Pressure
9. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sugimoto, N. Noncanonical structures and their thermodynamics of DNA and RNA under molecular crowding: Beyond the Watson-Crick double helix. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 307, 205–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightfoot, H.L.; Hagen, T.; Tatum, N.J.; Hall, J. The diverse structural landscape of quadruplexes. FEBS Lett. 2019, 593, 2083–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, F.B. Fundamentals of G-quadruplex biology. Annu. Rep. Med. Chem. 2020, 54, 3–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou Assi, H.; Garavis, M.; Gonzalez, C.; Damha, M.J. i-Motif DNA: Structural features and significance to cell biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 8038–8056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Antonio, M.; Ponjavic, A.; Radzevicius, A.; Ranasinghe, R.T.; Catalano, M.; Zhang, X.; Shen, J.; Needham, L.M.; Lee, S.F.; Klenerman, D.; et al. Single-molecule visualization of DNA G-quadruplex formation in live cells. Nat. Chem. 2020, 12, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeraati, M.; Langley, D.B.; Schofield, P.; Moye, A.L.; Rouet, R.; Hughes, W.E.; Bryan, T.M.; Dinger, M.E.; Christ, D. I-motif DNA structures are formed in the nuclei of human cells. Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, F.Y.; Jiang, Z.Z.; Guo, M.; Tan, X.Z.; Chen, F.; Xi, X.G.; Xu, Y. G-quadruplex DNA: A novel target for drug design. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 6557–6583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D. G-Quadruplex DNA and RNA. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 2035, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, J.; Maizels, N. Gene function correlates with potential for G4 DNA formation in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 3887–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavezzo, E.; Berselli, M.; Frasson, I.; Perrone, R.; Palu, G.; Brazzale, A.R.; Richter, S.N.; Toppo, S. G-quadruplex forming sequences in the genome of all known human viruses: A comprehensive guide. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranathan, N.; Vivekanandan, P. G-Quadruplexes: More Than Just a Kink in Microbial Genomes. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harris, L.M.; Merrick, C.J. G-quadruplexes in pathogens: A common route to virulence control? PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molnar, O.R.; Vegh, A.; Somkuti, J.; Smeller, L. Characterization of a G-quadruplex from hepatitis B virus and its stabilization by binding TMPyP4, BRACO19 and PhenDC3. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somkuti, J.; Molnar, O.R.; Grad, A.; Smeller, L. Pressure Perturbation Studies of Noncanonical Viral Nucleic Acid Structures. Biology 2021, 10, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panera, N.; Tozzi, A.E.; Alisi, A. The G-Quadruplex/Helicase World as a Potential Antiviral Approach Against COVID-19. Drugs 2020, 80, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, E.; Richter, S.N. G-quadruplexes and G-quadruplex ligands: Targets and tools in antiviral therapy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 3270–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruggiero, E.; Zanin, I.; Terreri, M.; Richter, S.N. G-Quadruplex Targeting in the Fight against Viruses: An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Manisegaran, M.; Campanile, M.; Del Vecchio, P.; Petraccone, L.; Winter, R. Binding Properties of RNA Quadruplex of SARS-CoV-2 to Berberine Compared to Telomeric DNA Quadruplex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Qin, G.; Niu, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Targeting RNA G-Quadruplex in SARS-CoV-2: A Promising Therapeutic Target for COVID-19? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2021, 60, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, D.; Arachchilage, G.M.; Basu, S. Metal Cations in G-Quadruplex Folding and Stability. Front. Chem. 2016, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Sugimoto, N. New Insights into the Functions of Nucleic Acids Controlled by Cellular Microenvironments. Top. Curr. Chem. 2021, 379, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, R.J.; Minton, A.P. Cell biology: Join the crowd. Nature 2003, 425, 27–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, M.L.; Kunkel, J.; Long, S.; Asuri, P. Combined Effects of Confinement and Macromolecular Crowding on Protein Stability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julius, K.; Weine, J.; Gao, M.; Latarius, J.; Elbers, M.; Paulus, M.; Tolan, M.; Winter, R. Impact of Macromolecular Crowding and Compression on Protein-Protein Interactions and Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation Phenomena. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 1772–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schummel, P.H.; Anders, C.; Jaworek, M.W.; Winter, R. Cosolvent and Crowding Effects on the Temperature- and Pressure-Dependent Dissociation Process of the/-Tubulin Heterodimer. Chemphyschem 2019, 20, 1098–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Sugimoto, N. Effect of Pressure on the Stability of G-Quadruplex DNA: Thermodynamics under Crowding Conditions. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2013, 52, 13774–13778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergny, J.L. Fluorescence energy transfer as a probe for tetraplex formation: The i-motif. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somkuti, J.; Molnar, O.R.; Smeller, L. Revealing unfolding steps and volume changes of human telomeric i-motif DNA. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 23816–23823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergny, J.L.; Lacroix, L.; Han, X.G.; Leroy, J.L.; Helene, C. Intramolecular Folding of Pyrimidine Oligodeoxynucleotides into an I-DNA Motif. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 8887–8898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B. The RNA i-Motif in the Primordial RNA World. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 2019, 49, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.L.; Kendrick, S. The i-Motif as a Molecular Target: More Than a Complementary DNA Secondary Structure. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, M.; Fatma, K.; Dash, J. Chemical Regulation of DNA i-Motifs for Nanobiotechnology and Therapeutics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 2942–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeller, L. Biomolecules under Pressure: Phase Diagrams, Volume Changes, and High Pressure Spectroscopic Techniques. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, W.F.; Stadtmuller, A.A. Experimental Techniques in High-Pressure Research; Wiley: Chichester West Sussex, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1987; 471p. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, R. Interrogating the Structural Dynamics and Energetics of Biomolecular Systems with Pressure Modulation. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2019, 48, 441–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heremans, K.; Smeller, L. Protein structure and dynamics at high pressure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1998, 1386, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, M.P.; Kitahara, R. Characterization of low-lying excited states of proteins by high-pressure NMR. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta-Proteins Proteom. 2019, 1867, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, C.A. Revisiting volume changes in pressure-induced protein unfolding. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 2002, 1595, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauro, F.M.; Bartlett, D.H. Prokaryotic lifestyles in deep sea habitats. Extremophiles 2008, 12, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, J.M.; Mukherjee, S.; Jaworek, M.W.; Kriegler, S.; Manisegaran, M.; Fetahaj, Z.; Ostermeier, L.; Oliva, R.; Gault, S.; Cockell, C.S.; et al. Life in Multi-Extreme Environments: Brines, Osmotic and Hydrostatic Pressure horizontal line A Physicochemical View. Chem. Rev. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurel, M.C.; Leclerc, F.; Herve, G. Ribozyme Chemistry: To Be or Not To Be under High Pressure. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 4898–4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, F. Molecular Responses to High Hydrostatic Pressure in Eukaryotes: Genetic Insights from Studies on Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biology 2021, 10, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penhallurick, R.W.; Ichiye, T. Pressure Adaptations in Deep-Sea Moritella Dihydrofolate Reductases: Compressibility versus Stability. Biology 2021, 10, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahmidi-Azizi, N.; Oliva, R.; Gault, S.; Cockell, C.S.; Winter, R. The Effects of Temperature and Pressure on Protein-Ligand Binding in the Presence of Mars-Relevant Salts. Biology 2021, 10, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonanno, A.; Chong, P.L.G. Certain, but Not All, Tetraether Lipids from the Thermoacidophilic Archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius Can Form Black Lipid Membranes with Remarkable Stability and Exhibiting Mthk Channel Activity with Unusually High Ca2+ Sensitivity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.Y.; Shek, Y.L.; Amiri, A.; Dubins, D.N.; Heerklotz, H.; Macgregor, R.B.; Chalikian, T.V. Volumetric Characterization of Sodium-Induced G-Quadruplex Formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 4518–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R.; Winter, R. Cold- and pressure-induced dissociation of protein aggregates and amyloid fibrils. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2008, 47, 6518–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacic, M.; Podbevsek, P.; Tateishi-Karimata, H.; Takahashi, S.; Sugimoto, N.; Plavec, J. Thrombin binding aptamer G-quadruplex stabilized by pyrene-modified nucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 3975–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baiz, C.R.; Blasiak, B.; Bredenbeck, J.; Cho, M.; Choi, J.H.; Corcelli, S.A.; Dijkstra, A.G.; Feng, C.J.; Garrett-Roe, S.; Ge, N.H.; et al. Vibrational Spectroscopic Map, Vibrational Spectroscopy, and Intermolecular Interaction. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 7152–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taillandier, E.; Liquier, J. Vibrational spectroscopy of nucleic acids. In Handbook of Vibrational Spectroscopy; Griffiths, P., Chalmers, J.M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 3465–3480. [Google Scholar]
- Somkuti, J.; Adanyi, M.; Smeller, L. Self-crowding influences the temperature—Pressure stability of the human telomere G-quadruplex. Biophys. Chem. 2019, 254, 106248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Zhu, L.J.; Li, S.T.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Liu, S.Y.; Huang, K.L.; Xu, W.T. Fluorescent functional nucleic acid: Principles, properties and applications in bioanalyzing. Trac-Trend Anal. Chem. 2021, 141, 116292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, P.; Budhathoki, J.B.; Roy, W.A.; Balci, H. A practical guide to studying G-quadruplex structures using single-molecule FRET. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2017, 292, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; You, H. Characterization of G-Quadruplexes Folding/Unfolding Dynamics and Interactions with Proteins from Single-Molecule Force Spectroscopy. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, Y.; Itoh, T. Reaction Volume of Protonic Ionization for Buffering Agents—Prediction of Pressure Dependence of pH and pOH. J. Solut. Chem. 1987, 16, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, K.J.; Morrison, J.F. Buffers of constant ionic strength for studying pH-dependent processes. Methods Enzymol. 1982, 87, 405–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Sugimoto, N. Pressure-dependent formation of i-motif and G-quadruplex DNA structures. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 31004–31010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepper, C.P.; Williams, M.A.K.; Edwards, P.J.B.; Filichev, V.V.; Jameson, G.B. Effects of Pressure and pH on the Physical Stability of an I-Motif DNA Structure. Chemphyschem 2019, 20, 1567–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubins, D.N.; Lee, A.; Macgregor, R.B., Jr.; Chalikian, T.V. On the stability of double stranded nucleic acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 9254–9259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niven, G.W.; Miles, C.A.; Mackey, B.M. The effects of hydrostatic pressure on ribosome conformation in Escherichia coli: And in vivo study using differential scanning calorimetry. Microbiology 1999, 145 Pt 2, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chalikian, T.V.; Macgregor, R.B. Volumetric Properties of Four-Stranded DNA Structures. Biology 2021, 10, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, O.R.; Somkuti, J.; Smeller, L. Negative volume changes of human G-quadruplexes at unfolding. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shek, Y.L.; Noudeh, G.D.; Nazari, M.; Heerklotz, H.; Abu-Ghazalah, R.M.; Dubins, D.N.; Chalikian, T.V. Folding Thermodynamics of the Hybrid-1 Type Intramolecular Human Telomeric G-Quadruplex. Biopolymers 2014, 101, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.T.; Scott, L.; Kume, T.; Chalikian, T.V. Volumetric Interplay between the Conformational States Adopted by DNA Strands from the Promoter Region of the c-MYC Oncogene. Biophys. J. 2021, 120, 218a–219a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, N.; Kume, T.; Feroze, U.N.; Macgregor, R.B., Jr. The Pressure Dependence of the Stability of the G-quadruplex Formed by d(TGGGGT). Life 2022, 12, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Y.; Dubins, D.N.; Le, D.M.N.T.; Leung, K.; Macgregor, R.B. The role of loops and cation on the volume of unfolding of G-quadruplexes related to HTel. Biophys. Chem. 2017, 231, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.T.; Scott, L.; Tariq, N.; Kume, T.; Dubins, D.N.; Macgregor, R.B.; Chalikian, T.V. Volumetric Interplay between the Conformational States Adopted by Guanine-Rich DNA from the c-MYC Promoter. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 7406–7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riccardi, C.; Napolitano, E.; Platella, C.; Musumeci, D.; Montesarchio, D. G-quadruplex-based aptamers targeting human thrombin: Discovery, chemical modifications and antithrombotic effects. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 217, 107649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Sugimoto, N. Effect of Pressure on Thermal Stability of G-Quadruplex DNA and Double-Stranded DNA Structures. Molecules 2013, 18, 13297–13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, Y.; Kan, Z.Y.; Wang, Q.; Yao, Y.; Liu, J.; Hao, Y.H.; Tan, Z. Human telomeric DNA forms parallel-stranded intramolecular G-quadruplex in K+ solution under molecular crowding condition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 11185–11191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, A.T.; Kuryavyi, V.; Luu, K.N.; Patel, D.J. Structure of two intramolecular G-quadruplexes formed by natural human telomere sequences in K+ solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 6517–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smeller, L. Pressure-temperature phase diagrams of biomolecules. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Protein Struct. Molec. Enzymol. 2002, 1595, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, G.A.P.; Marques, M.A.; Pedrote, M.M.; Silva, J.L. High pressure studies on the misfolding and aggregation of p53 in cancer and of -synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. High Press. Res. 2019, 39, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, A.T.; Kuryavyi, V.; Burge, S.; Neidle, S.; Patel, D.J. Structure of an unprecedented G-quadruplex scaffold in the human c-kit promoter. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 4386–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biswas, B.; Kandpal, M.; Vivekanandan, P. A G-quadruplex motif in an envelope gene promoter regulates transcription and virion secretion in HBV genotype B. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 11268–11280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guedin, A.; Gros, J.; Alberti, P.; Mergny, J.L. How long is too long? Effects of loop size on G-quadruplex stability. Nucleic Acids Rese. 2010, 38, 7858–7868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, T.Q.N.; Lim, K.W.; Phan, A.T. Folding Kinetics of G-Quadruplexes: Duplex Stem Loops Drive and Accelerate G-Quadruplex Folding. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 5122–5130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Sugimoto, N. Volumetric contributions of loop regions of G-quadruplex DNA to the formation of the tertiary structure. Biophys. Chem. 2017, 231, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Bhowmik, S.; Sugimoto, N. Volumetric analysis of formation of the complex of G-quadruplex DNA with hemin using high pressure. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2017, 166, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, J.M.; Patra, S.; Harish, B.; Royer, C.A.; Winter, R. The Deep Sea Osmolyte Trimethylamine N-Oxide and Macromolecular Crowders Rescue the Antiparallel Conformation of the Human Telomeric G-Quadruplex from Urea and Pressure Stress. Chem.-Eur. J. 2018, 24, 14346–14351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Kim, B.G.; Feroze, U.; Macgregor, R.B., Jr.; Chalikian, T.V. Probing the Ionic Atmosphere and Hydration of the c-MYC i-Motif. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 2229–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.K.; Knop, J.M.; Oliva, R.; Mobitz, S.; Winter, R. Untangling the interaction of alpha-synuclein with DNA i-motifs and hairpins by volume-sensitive single-molecule FRET spectroscopy. RSC Chem. Biol. 2021, 2, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeller, L.; Meersman, F.; Tolgyesi, F.; Bode, C.; Fidy, J.; Heremans, K. From aggregation to chaperoning: Pressure effect on intermolecular interactions of proteins. High Press. Res. 2002, 22, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccirilli, F.; Plotegher, N.; Ortore, M.G.; Tessari, I.; Brucale, M.; Spinozzi, F.; Beltramini, M.; Mariani, P.; Militello, V.; Lupi, S.; et al. High-Pressure-Driven Reversible Dissociation of alpha-Synuclein Fibrils Reveals Structural Hierarchy. Biophys. J. 2017, 113, 1685–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Name | Sequence |
|---|---|
| c-MYC | d[TGAGGGTGGGTAGGGTGGGTAA] |
| HepB1 | d[GGC TGG GGC TTG GTC ATG GGC CAT CAG] |
| HepB2 | d[GGG AGT GGG AGC ATT CGG GCC AGG G] |
| HepB3 | d[TTG GGT GGC TTT GGG GCA TGG AC] |
| Htel22 | d[AGGGTTAGGGTTAGGGTTAGGG] |
| Htel26 | d[AAAGGGTTAGGGTTAGGGTTAGGGAA] |
| KIT | d[AGGGAGGGCGCTGGGAGGAGGG] |
| Pu22T12T13 | d[CGGGGCGGGCCTTGGGCGGGGT] |
| TBA | d[GGTTGGTGTGGTTGG] |
| TG4T | d[TGGGGGT] tetramolecular |
| VEGF | d[TTGGGGCGGGCCGGGGGGCGGGGTT] |
| c-MYC iM | d[TTACCCACCCTACCCACCCTCA] |
| Htel-iM | d[CCCTAACCCTAACCCTAACCC] |
| Name | Cation | Cation Conc. | ΔV (cm3/mol) | Tm at 1bar (°C) | Oligomer Conc. (μM) | N | Topology | pH | Buffer | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TBA | K+ | 100 mM | −54.6 ± 4.2 | 52.6 ± 3.4 | 40 | 15 | AP | - | TRIS 30 mM | [26] |
| Htel22 | Na+ | 100 mM | −38.4 ± 10.1 | 54.6 ± 0.9 | 20 | 22 | AP | 7.4 | TRIS 10 mM | [66] |
| Htel22 | Na+ | 2 0mM | −68 ± 2 1 | 39.6 ± 0.7 1 | 10–300 4 | 22 | AP | 7.0 | Na phosph 10mM | [46] |
| Htel22 | Na+ | 50 mM | −60 ± 2 1 | 47.9 ± 0.7 1 | 10–300 4 | 22 | AP | 7.0 | Na phosph 10mM | [46] |
| Htel22 | Na+ | 100 mM | −56 ± 2 1 | 54.9 ± 0.6 1 | 10–300 4 | 22 | AP | 7.0 | Na phosph 10mM | [46] |
| Htel22 | K+ | 100 mM | −42.7 ± 6.7 | 64.6 ± 2.2 | 20 | 22 | H | 7.4 | Tris 10 mM | [66] |
| c-MYC | K+ | 170 mM | −16.9 ± 1.8 | 83.4 ± 1.3 | 2 | 22 | P | 7.4 | K-phosph 100 mM | [62] |
| KIT | K+ | 170 mM | −6.2 ± 0.9 | 58.5 ± 0.4 | 2 | 22 | P | 7.4 | K-phosph 100 mM | [62] |
| VEGF | K+ | 170 mM | −18.1 ± 4.6 | 78.8 ± 1.1 | 2 | 24 | P | 7.4 | K-phosph 100 mM | [62] |
| Htel26 | K+ | 20 mM | −69 ± 7 2 | NA | 300 | 26 | H | 7.0 | tetrabutylammonium phosphate | [63] |
| c-MYC | K+ | 0.1 mM | −30 ± 4 | 59.1 | 25 | 22 | P | 7.0 | Cs-phosp 10 mM | [67] |
| HepB1 | K+ | 140 mM | 17.8 ± 3.8 | NA | 1 | 27 | NA | 7.4 3 | K-phosp/TRIS | [14] |
| HepB1 | K+ | 100 mM | 16.1 ± 2.0 | 53.8 | 2400 | 27 | NA | 7.4 | Bis-TRIS 100 mM | [14] |
| HepB2 | K+ | 140 mM | −3.7 ± 0.6 | 51.9 | 1 | 25 | NA | 7.4 3 | K-phosp/TRIS | [14] |
| HepB3 | K+ | 140 mM | 2.0 ± 1.1 | 41.4 | 1 | 23 | NA | 7.4 3 | K-phosp/TRIS | [14] |
| TBA (+PEG) | K+ | 100 mM | −13.1 ± 1.0 | 60.6 ± 3.2 | 40 | 15 | AP | 7.0 | TRIS 30 mM | [26] |
| Htel22 | K+ | 170 mM | −19 ± 3 | 63 | 10 | 21 | H | 7.4 | K-phosph 100 mM | [51] |
| Htel22 | K+ | 200 mM | 6.4 ± 1 | NA | 9400 | 21 | P? | 7.4 | Bis-TRIS 200 mM | [51] |
| TG4T | Na+ | 1 M | 1.5 ± 2.3 | 68.9 | 100 | 4 × 7 | P | 7.5 | TRIS 10 mM | [65] |
| Pu22T12T13 | K+ | 2 mM | −38 ± 10 | 71.8 | 100 | 22 | P | 7.0 | tetrabutylammonium phosphate | [65] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smeller, L. Pressure Tuning Studies of Four-Stranded Nucleic Acid Structures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021803
Smeller L. Pressure Tuning Studies of Four-Stranded Nucleic Acid Structures. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(2):1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021803
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmeller, László. 2023. "Pressure Tuning Studies of Four-Stranded Nucleic Acid Structures" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 2: 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021803
APA StyleSmeller, L. (2023). Pressure Tuning Studies of Four-Stranded Nucleic Acid Structures. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(2), 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021803