Exploring the Role of the Plant Actin Cytoskeleton: From Signaling to Cellular Functions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Identification and Annotation of Arabidopsis Actin Family
2.1. Tissue-Specific Expression of Arabidopsis Actin Genes
2.2. Subcellular Localization of Actin
2.3. Diverse Functions of Actin Isoforms in Plants
3. Structure and Evolution of the ARP Superfamily
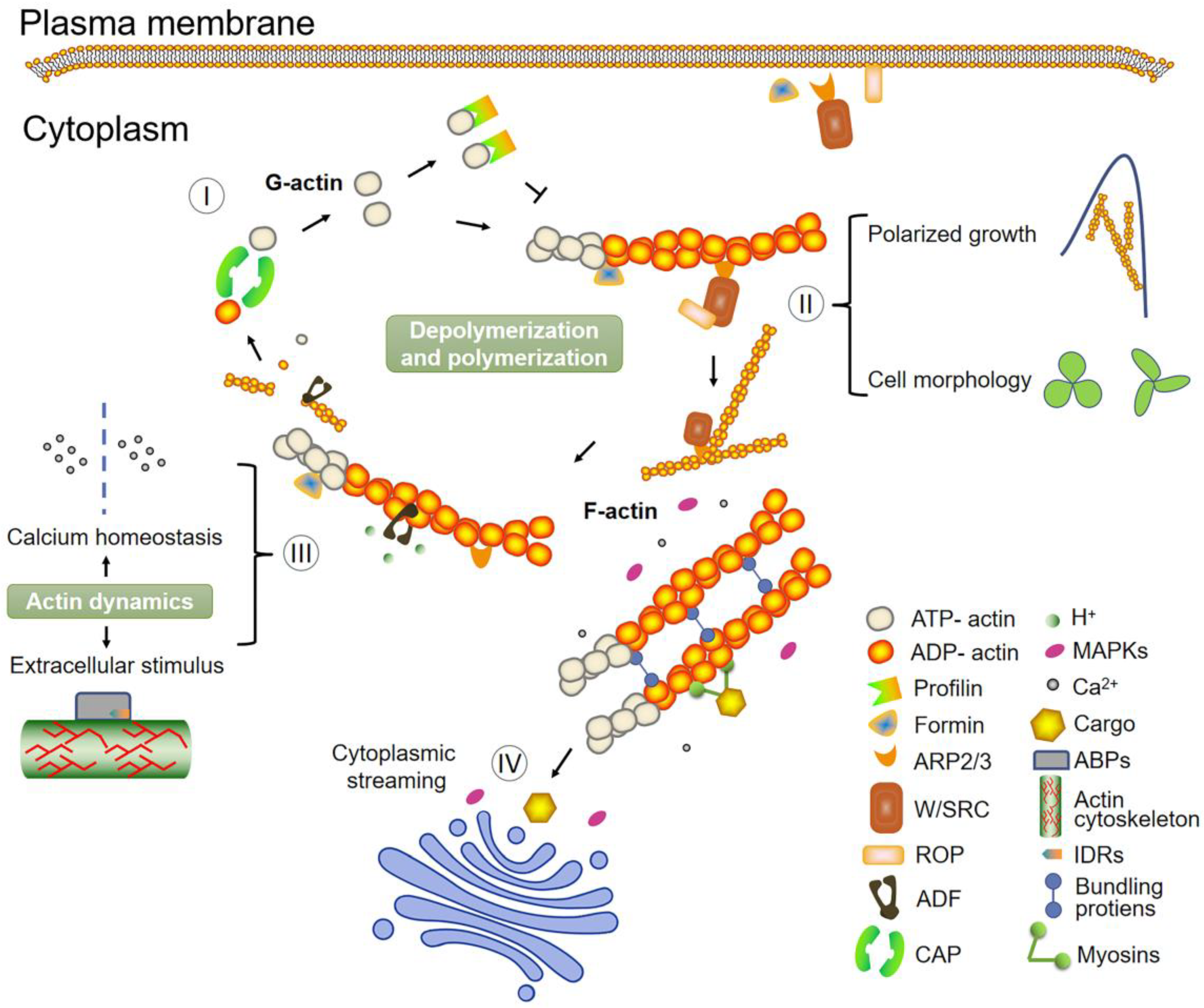
4. Role of ABPs: An Accurate Network Controller of Plant Actin Dynamics
4.1. Fimbrin
4.2. Formin
4.3. Capping Protein
4.4. Villin
4.5. LIM Domain-Containing Protein
4.6. Myosin
4.7. Profilin
4.8. Cyclase-Associated Protein
4.9. Actin-Depolymerizing Factor
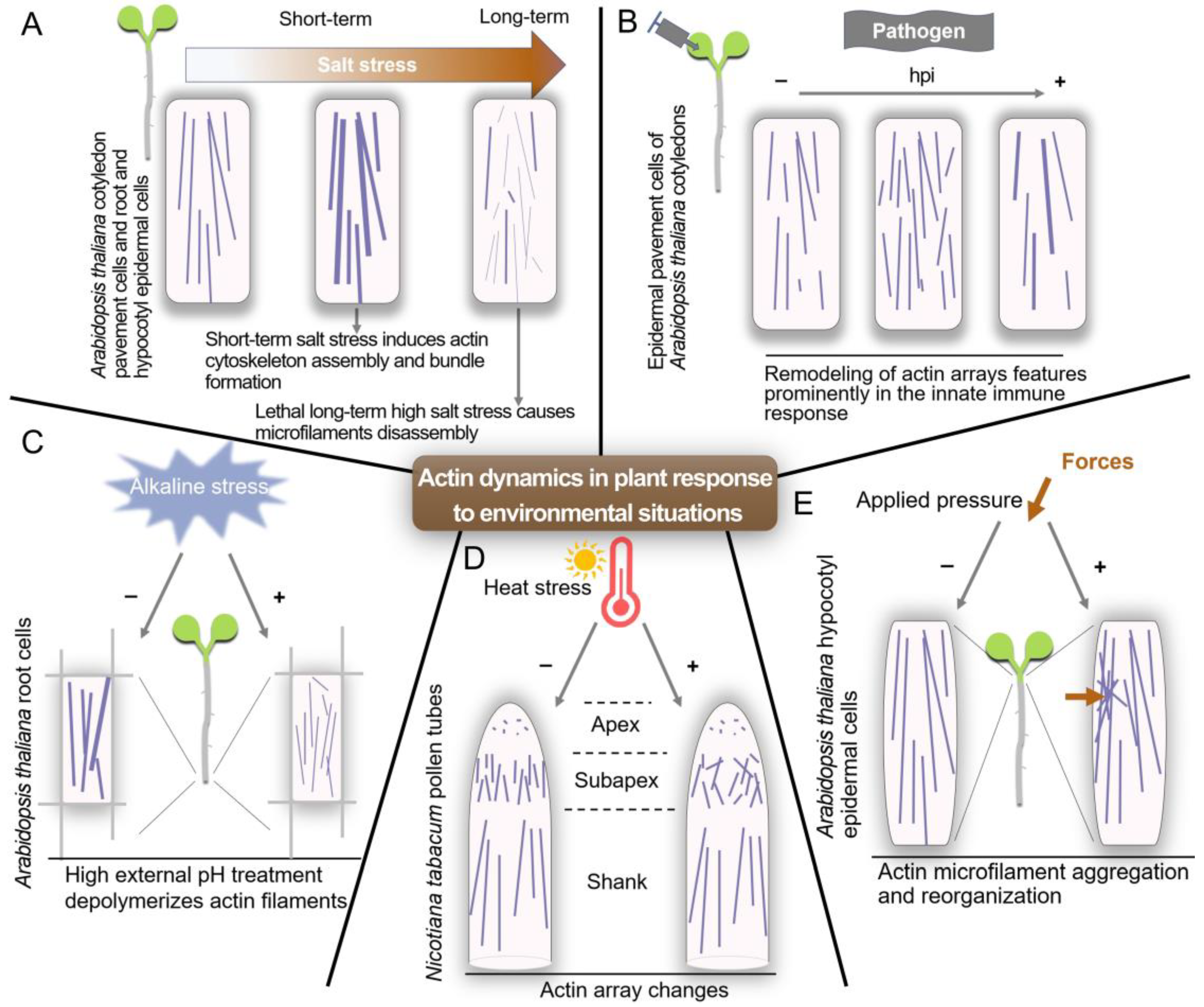
5. Signals and Pathways Regulating the Actin Cytoskeleton
6. Support for In-Depth Investigation on Plant Actin
7. The Coordinating Effect of Microtubules and Microfilaments
8. Conclusions and Future Outlines
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blanchoin, L.; Boujemaa-Paterski, R.; Sykes, C.; Plastino, J. Actin dynamics, architecture, and mechanics in cell motility. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 235–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, T.D.; Cooper, J.A. Actin, a central player in cell shape and movement. Science 2009, 326, 1208–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peremyslov, V.V.; Cole, R.A.; Fowler, J.E.; Dolja, V.V. Myosin-powered membrane compartment drives cytoplasmic streaming, cell expansion and plant development. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymanski, D.; Staiger, C.J. The actin cytoskeleton: Functional arrays for cytoplasmic organization and cell shape control. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, N.; Wang, X.W.; Jing, Y.P.; Lin, J.X. Regulation of cytoskeleton-associated protein activities: Linking cellular signals to plant cytoskeletal function. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y.Y.; Du, F.; Cao, L.J.; Dong, H.J.; Ren, H. Arabidopsis VILLIN4 is involved in root hair growth through regulating actin organization in a Ca2+-dependent manner. New Phytol. 2011, 190, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchoin, L.; Boujemaa-Paterski, R.; Henty, J.L.; Khurana, P.; Staiger, C.J. Actin dynamics in plant cells: A team effort from multiple proteins orchestrates this very fast-paced game. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2010, 13, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, T.D.; Borisy, G.G. Cellular motility driven by assembly and disassembly of actin filaments. Cell 2003, 112, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodson, H.V.; Hawse, W.F. Molecular evolution of the actin family. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 2619–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, D.A.; Schroer, T.A. Actin-related proteins. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1999, 15, 341–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinney, E.C.; Kandasamy, M.K.; Meagher, R.B. Arabidopsis contains ancient classes of differentially expressed actin-related protein genes. Plant Physiol. 2002, 128, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, T.D.; Beltzner, C.C. Structure and function of the Arp2/3 complex. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2002, 12, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olave, I.A.; Reck-Peterson, S.L.; Crabtree, G.R. Nuclear actin and actin-related proteins in chromatin remodeling. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 755–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fyodorov, D.V.; Kadonaga, J.T. The many faces of chromatin remodeling: SWItching beyond transcription. Cell 2001, 106, 523–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caillaud, M.C. Methods to visualize the actin cytoskeleton during plant cell division. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2382, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nick, P. Microtubules, signalling and abiotic stress. Plant J. 2013, 75, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, M.; Kong, S.G. Actin-mediated movement of chloroplasts. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs210310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedbrook, J.C. MAPs in plant cells: Delineating microtubule growth dynamics and organization. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, Y. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt-stress responses. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meagher, R.B.; McKinney, E.C.; Vitale, A.V. The evolution of new structures: Clues from plant cytoskeletal genes. Trends Genet. 1999, 15, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, R.T.; Shah, D.M.; Eckenrode, V.K.; Meagher, R.B. Multigene family of actin-related sequences isolated from a soybean genomic library. DNA 1981, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, Y.; Katsumaru, H. Nuclear actin bundles in Amoeba, Dictyostelium and human HeLa cells induced by dimethyl sulfoxide. Exp. Cell Res. 1979, 120, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, T.G.; Rosenbaum, J.L. An actin filament matrix in hand-isolated nuclei of X. laevis oocytes. Cell 1979, 18, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettinger, B.T.; Gilbert, D.M.; Amberg, D.C. Actin up in the nucleus. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheer, U.; Hinssen, H.; Franke, W.W.; Jockusch, B.M. Microinjection of actin-binding proteins and actin antibodies demonstrates involvement of nuclear actin in transcription of lampbrush chromosomes. Cell 1984, 39, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasser, M.; Chia, W. The EAST protein of drosophila controls an expandable nuclear endoskeleton. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rando, O.J.; Zhao, K.; Janmey, P.; Crabtree, G.R. Phosphatidylinositol-dependent actin filament binding by the SWI/SNF-like BAF chromatin remodeling complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2824–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Fan, X.Y.; Ding, M.; Li, R.F.; Shao, S.P.; Hou, Y.P.; Meng, S.S.; Tang, F.C.; Li, C.; Sun, Y.J. Nuclear actin regulates inducible transcription by enhancing RNA polymerase II clustering. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, P.; Shen, X. Mechanisms of nuclear actin in chromatin-remodeling complexes. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percipalle, P. Co-transcriptional nuclear actin dynamics. Nucleus 2013, 4, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, W.A.; Stojiljkovic, L.; Fuchsova, B.; Vargas, G.M.; Mavrommatis, E.; Philimonenko, V.; Kysela, K.; Goodrich, J.A.; Lessard, J.L.; Hope, T.J.; et al. Actin is part of pre-initiation complexes and is necessary for transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philimonenko, V.V.; Zhao, J.; Iben, S.; Dingova, H.; Kysela, K.; Kahle, M.; Zentgraf, H.; Hofmann, W.A.; de Lanerolle, P.; Hozak, P.; et al. Nuclear actin and myosin I are required for RNA polymerase I transcription. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vartiainen, M.K.; Guettler, S.; Larijani, B.; Treisman, R. Nuclear actin regulates dynamic subcellular localization and activity of the SRF cofactor MAL. Science 2007, 316, 1749–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dundr, M.; Ospina, J.K.; Sung, M.H.; John, S.; Upender, M.; Ried, T.; Hager, G.L.; Matera, A.G. Actin-dependent intranuclear repositioning of an active gene locus in vivo. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 179, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baarlink, C.; Plessner, M.; Sherrard, A.; Morita, K.; Misu, S.; Virant, D.; Kleinschnitz, E.M.; Harniman, R.; Alibhai, D.; Baumeister, S.; et al. A transient pool of nuclear F-actin at mitotic exit controls chromatin organization. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrank, B.R.; Aparicio, T.; Li, Y.; Chang, W.; Chait, B.T.; Gundersen, G.G.; Gottesman, M.E.; Gautier, J. Nuclear ARP2/3 drives DNA break clustering for homology-directed repair. Nature 2018, 559, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caridi, C.P.; D’Agostino, C.; Ryu, T.; Zapotoczny, G.; Delabaere, L.; Li, X.; Khodaverdian, V.Y.; Amaral, N.; Lin, E.; Rau, A.R.; et al. Nuclear F-actin and myosins drive relocalization of heterochromatic breaks. Nature 2018, 559, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percipalle, P.; Zhao, J.; Pope, B.; Weeds, A.; Lindberg, U.; Daneholt, B. Actin bound to the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein hrp36 is associated with Balbiani ring mRNA from the gene to polysomes. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 153, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukalev, A.; Nord, Y.; Palmberg, C.; Bergman, T.; Percipalle, P. Actin and hnRNP U cooperate for productive transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, M.K.; McKinney, E.C.; Meagher, R.B. Differential sublocalization of actin variants within the nucleus. Cytoskeleton 2010, 67, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijima, S.T.; Staiger, C.J.; Katoh, K.; Nagasaki, A.; Ito, K.; Uyeda, T.Q.P. Arabidopsis vegetative actin isoforms, AtACT2 and AtACT7, generate distinct filament arrays in living plant cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.F.; Fatema, U.; Peng, X.B.; Hacker, S.W.; Maruyama, D.; Sun, M.X.; Kawashima, T. ARP2/3-independent WAVE/SCAR pathway and class XI myosin control sperm nuclear migration in flowering plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 32757–32763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.J.; Liu, J.Y.; Xue, X.H.; Tan, K.; Wang, C.B.; Su, H. The migration direction of hair cell nuclei is closely related to the perinuclear actin filaments in Arabidopsis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 519, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitzalis, N.; Heinlein, M. The roles of membranes and associated cytoskeleton in plant virus replication and cell-to-cell movement. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.G.; Barton, D.A. The cytoskeleton in plasmodesmata: A role in intercellular transport? J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 5249–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.Z.; Liu, Z.H.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Miao, L.; Wang, X.C.; Yuan, M. Cucumber mosaic virus movement protein severs actin filaments to increase the plasmodesmal size exclusion limit in tobacco. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 1373–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, C.R.; Blackman, L.M.; Collings, D.A.; Cordwell, S.J.; Overall, R.L. Anti-tropomyosin antibodies co-localise with actin microfilaments and label plasmodesmata. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 88, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, M.J.; Calcutt, J.R.; Ingle, E.K.; Hawkins, T.J.; Chapman, S.; Richardson, A.C.; Mentlak, D.A.; Dixon, M.R.; Cartwright, F.; Smertenko, A.P.; et al. A superfamily of actin-binding proteins at the actin-membrane nexus of higher plants. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 1595–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, M.K.; McKinney, E.C.; Meagher, R.B. Functional nonequivalency of actin isovariants in Arabidopsis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, M.K.; Burgos-Rivera, B.; McKinney, E.C.; Ruzicka, D.R.; Meagher, R.B. Class-specific interaction of profilin and ADF isovariants with actin in the regulation of plant development. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 3111–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Ahn, J.; Bong, H.; Wada, M.; Kong, S.G. ACTIN2 functions in chloroplast photorelocation movement in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Plant Biol. 2020, 63, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheahan, M.B.; Collings, D.A.; Rose, R.J.; McCurdy, A.D.W. ACTIN7 is required for perinuclear clustering of chloroplasts during Arabidopsis protoplast culture. Plants 2020, 9, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendrinna, A.; Persson, S. Root hair growth: It’s a one way street. F1000Prime Rep. 2015, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, J.; Mathur, N.; Kirik, V.; Kernebeck, B.; Srinivas, B.P.; Hulskamp, M. Arabidopsis CROOKED encodes for the smallest subunit of the ARP2/3 complex and controls cell shape by region specific fine F-actin formation. Development 2003, 130, 3137–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.L.; Bi, S.T.; Wang, L.; Li, H.P.; Gao, B.A.; Huang, S.J.; Qu, X.L.; Cheng, J.N.; Wang, S.C.; Liu, C.Y.; et al. GLABRA2 regulates actin bundling protein VILLIN1 in root hair growth in response to osmotic stress. Plant Physiol. 2020, 184, 176–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringli, C.; Baumberger, N.; Diet, A.; Frey, B.; Keller, B. ACTIN2 is essential for bulge site selection and tip growth during root hair development of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, M.K.; McKinney, E.C.; Meagher, R.B. A single vegetative actin isovariant overexpressed under the control of multiple regulatory sequences is sufficient for normal Arabidopsis development. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 701–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Yokota, E.; Wada, T.; Shimmen, T.; Okada, K. An Arabidopsis ACT2 dominant-negative mutation, which disturbs F-actin polymerization, reveals its distinctive function in root development. Plant Cell Physiol. 2003, 44, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, M.; Garcia-Ponce, B.; Castrillo, G.; Catarecha, P.; Sauer, M.; Rodriguez-Serrano, M.; Paez-Garcia, A.; Sanchez-Bermejo, E.; T C, M.; Leo del Puerto, Y.; et al. Role of actin cytoskeleton in brassinosteroid signaling and in its integration with the auxin response in plants. Dev. Cell 2012, 22, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliland, L.U.; Pawloski, L.C.; Kandasamy, M.K.; Meagher, R.B. Arabidopsis actin gene ACT7 plays an essential role in germination and root growth. Plant J. 2003, 33, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliland, L.U.; McKinney, E.C.; Asmussen, M.A.; Meagher, R.B. Detection of deleterious genotypes in multigenerational studies. I. Disruptions in individual Arabidopsis actin genes. Genetics 1998, 149, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasik, J.; Micieta, K.; Siao, W.; Voigt, B.; Stuchlik, S.; Schmelzer, E.; Turna, J.; Baluška, F. Actin3 promoter reveals undulating F-actin bundles at shanks and dynamic F-actin meshworks at tips of tip-growing pollen tubes. Plant Signal Behav. 2016, 11, e1146845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketelaar, T.; de Ruijter, N.C.A.; Emons, A.M.C. Unstable F-actin specifies the area and microtubule direction of cell expansion in Arabidopsis root hairs. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymanski, D.B.; Cosgrove, D.J. Dynamic coordination of cytoskeletal and cell wall systems during plant cell morphogenesis. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, R800–R811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tominaga, M.; Kojima, H.; Yokota, E.; Nakamori, R.; Anson, M.; Shimmen, T.; Oiwa, K. Calcium-induced mechanical change in the neck domain alters the activity of plant myosin XI. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 30711–30718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruta, M.; Sabat, G.; Stecker, K.; Minkoff, B.B.; Sussman, M.R. A peptide hormone and its receptor protein kinase regulate plant cell expansion. Science 2014, 343, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsuka, H.; Umeda, M. Hormonal control of cell division and elongation along differentiation trajectories in roots. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 2633–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, S.S.; Mao, T.L.; Qu, X.L.; Cao, W.H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; He, L.; Li, S.D.; Ren, S.L.; et al. The plant-specific actin binding protein SCAB1 stabilizes actin filaments and regulates stomatal movement in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 2314–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsuka, H.; Higaki, T.; Umeda, M. Actin reorganization triggers rapid cell elongation in roots. Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 1130–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, J.; Mathur, N.; Kernebeck, B.; Hulskamp, M. Mutations in actin-related proteins 2 and 3 affect cell shape development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1632–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.B.; Fan, X.P.; Wang, X.L.; Cai, L.; Yang, W.C. The cotton ACTIN1 gene is functionally expressed in fibers and participates in fiber elongation. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 859–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.W.; Liang, W.H.; Shen, W.J.; Feng, H.; Chen, J.D.; Si, Z.F.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, T.Z. G65V substitution in actin disturbs polymerization leading to inhibited cell elongation in Cotton. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, M.K.; Gilliland, L.U.; McKinney, E.C.; Meagher, R.B. One plant actin isovariant, ACT7, is induced by auxin and required for normal callus formation. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 1541–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numata, T.; Sugita, K.; Rahman, A.A.; Rahman, A. Actin isovariant ACT7 controls root meristem development in Arabidopsis through modulating auxin and ethylene responses. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 6255–6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, M.; Ge, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fan, J.; Ruan, Y.; Cui, Z.; Tong, S.; Zhang, S. The microfilament cytoskeleton plays a vital role in salt and osmotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Biol. 2010, 12, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, Z.J.; Guo, G.Q.; Guo, Y. Microfilament dynamics is required for root growth under alkaline stress in Arabidopsis. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2010, 52, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrotta, L.; Faleri, C.; Cresti, M.; Cai, G. Heat stress affects the cytoskeleton and the delivery of sucrose synthase in tobacco pollen tubes. Planta 2016, 243, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, R.; Pearsall, E.J.; Rundle, C.A.; White, R.G.; Bradby, J.E.; Hardham, A.R. Quantifying the plant actin cytoskeleton response to applied pressure using nanoindentation. Protoplasma 2017, 254, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Staiger, C.J. Understanding cytoskeletal dynamics during the plant immune response. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2018, 56, 513–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.A.; Schafer, D.A. Control of actin assembly and disassembly at filament ends. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2000, 12, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.H. The sugar kinase/heat shock protein 70/actin superfamily: Implications of conserved structure for mechanism. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1996, 25, 137–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Hendrickson, W.A. Insights into Hsp70 chaperone activity from a crystal structure of the yeast Hsp110 Sse1. Cell 2007, 131, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shida, M.; Arakawa, A.; Ishii, R.; Kishishita, S.; Takagi, T.; Kukimoto-Niino, M.; Sugano, S.; Tanaka, A.; Shirouzu, M.; Yokoyama, S. Direct inter-subdomain interactions switch between the closed and open forms of the Hsp70 nucleotide-binding domain in the nucleotide-free state. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.M.; Kirley, T.L. Site-directed mutagenesis of a human brain ecto-apyrase: Evidence that the E-type ATPases are related to the actin/heat shock 70/sugar kinase superfamily. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettigrew, D.W. Amino acid substitutions in the sugar kinase/hsp70/actin superfamily conserved ATPase core of E. coli glycerol kinase modulate allosteric ligand affinity but do not alter allosteric coupling. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 481, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, M.K.; Deal, R.B.; McKinney, E.C.; Meagher, R.B. Silencing the nuclear actin-related protein AtARP4 in Arabidopsis has multiple effects on plant development, including early flowering and delayed floral senescence. Plant J. 2005, 41, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, M.K.; McKinney, E.C.; Meagher, R.B. Cell cycle-dependent association of Arabidopsis actin-related proteins AtARP4 and AtARP7 with the nucleus. Plant J. 2003, 33, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, M.K.; McKinney, E.C.; Deal, R.B.; Smith, A.P.; Meagher, R.B. Arabidopsis actin-related protein ARP5 in multicellular development and DNA repair. Dev. Biol. 2009, 335, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.J.; Zhang, C.; An, Z.X.; Shen, W.H.; Zhu, Y. AtINO80 and AtARP5 physically interact and play common as well as distinct roles in regulating plant growth and development. New Phytol. 2019, 223, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, M.K.; McKinney, E.C.; Deal, R.B.; Meagher, R.B. Arabidopsis ARP7 is an essential actin-related protein required for normal embryogenesis, plant architecture, and floral organ abscission. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 2019–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meagher, R.B.; Kandasarny, M.K.; Deal, R.B.; McKinney, E.C. Actin-related proteins in chromatin-level control of the cell cycle and developmental transitions. Trends Cell Biol. 2007, 17, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, M.K.; Deal, R.B.; McKinney, E.C.; Meagher, R.B. Plant actin-related proteins. Trends Plant Sci. 2004, 9, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidali, L.; Hepler, P.K. Actin and pollen tube growth. Protoplasma 2001, 215, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Mallery, E.L.; Szymanski, D.B. ARP2/3 localization in Arabidopsis leaf pavement cells: A diversity of intracellular pools and cytoskeletal interactions. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgs, H.N.; Blanchoin, L.; Pollard, T.D. Influence of the C terminus of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASp) and the Arp2/3 complex on actin polymerization. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 15212–15222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campellone, K.G.; Welch, M.D. A nucleator arms race: Cellular control of actin assembly. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.J.; Zheng, Z.Y.; Xue, S.; Li, H.H.; Wang, Y.R.; Le, J. The role of Arabidopsis Actin-Related Protein 3 in amyloplast sedimentation and polar auxin transport in root gravitropism. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 5325–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifrova, P.; Oulehlova, D.; Kollarova, E.; Martinek, J.; Rosero, A.; Zarsky, V.; Schwarzerova, K.; Cvrckova, F. Division of labor between two actin nucleators-the formin FH1 and the ARP2/3 complex-in Arabidopsis epidermal cell morphogenesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Liu, L.J.; Tu, J.Y.; Yang, G.G.; Wang, S.; Quilichini, T.D.; Gao, P.; Wang, H.; Peng, G.; Blancaflor, E.B.; et al. The ARP2/3 complex, acting cooperatively with Class I formins, modulates penetration resistance in Arabidopsis against powdery mildew invasion. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 3151–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Sorefan, K.; Deeks, M.J.; Bevan, M.; Hussey, P.J.; Hetherington, A.M. The ARP2/3 complex mediates guard cell actin reorganization and stomatal movement in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 2031–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Huang, S.; Yuan, M.; Schumaker, K.S.; et al. The actin-related Protein2/3 complex regulates mitochondrial-associated calcium signaling during salt stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 4544–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, R.; Holmes, K.C. Actin structure and function. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2011, 40, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Deng, L.; Chang, D.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Kang, Z. TaADF3, an actin-depolymerizing factor, negatively modulates wheat resistance against Puccinia striiformis. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunning, P.W.; Ghoshdastider, U.; Whitaker, S.; Popp, D.; Robinson, R.C. The evolution of compositionally and functionally distinct actin filaments. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 2009–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCurdy, D.W.; Kovar, D.R.; Staiger, C.J. Actin and actin-binding proteins in higher plants. Protoplasma 2001, 215, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Q.; Qian, D.; Niu, Y.; He, Y.X.; Tong, S.F.; Niu, Z.M.; Ma, J.C.; Yang, Y.; An, L.Z.; Wan, D.S.; et al. Plant actin-depolymerizing factors possess opposing biochemical properties arising from key amino acid changes throughout evolution. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozycka, M.; Khan, S.; Lopez, I.; Greenland, A.J.; Hussey, P.J. A Zea mays pollen cdna-encoding a putative actin-depolymerizing factor. Plant Physiol. 1995, 107, 1011–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, I.; Anthony, R.G.; Maciver, S.K.; Jiang, C.J.; Khan, S.; Weeds, A.G.; Hussey, P.J. Pollen specific expression of maize genes encoding actin depolymerizing factor-like proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 7415–7420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allwood, E.G.; Anthony, R.G.; Smertenko, A.P.; Reichelt, S.; Drøbak, B.K.; Doonan, J.H.; Weeds, A.G.; Hussey, P.J. Regulation of the pollen-specific actin-depolymerizing factor LlADF1. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 2915–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tholl, S.; Moreau, F.; Hoffmann, C.; Arumugam, K.; Dieterle, M.; Moes, D.; Neumann, K.; Steinmetz, A.; Thomas, C. Arabidopsis actin-depolymerizing factors (ADFs) 1 and 9 display antagonist activities. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 1821–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.H.; Cheung, A.Y.; Wu, H.M. Actin-depolymerizing factor mediates Rac/Rop GTPase-regulated pollen tube growth. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayasu, T.; Yokota, E.; Shimmen, T. Purification of an actin-binding protein composed of 115-kDa polypeptide from pollen tubes of lily. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 249, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klahre, U.; Friederich, E.; Kost, B.; Louvard, D.; Chua, N.H. Villin-like actin-binding proteins are expressed ubiquitously in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2000, 122, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Qu, X.L.; Bao, C.C.; Khurana, P.; Wang, Q.N.; Xie, Y.R.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Chen, N.Z.; Blanchoin, L.; Staiger, C.J.; et al. Arabidopsis VILLIN5, an actin filament bundling and severing protein, is necessary for normal pollen tube growth. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2749–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Robinson, R.C.; Gao, L.Y.; Matsumoto, T.; Brunet, A.; Blanchoin, L.; Staiger, C.J. Arabidopsis VILLIN1 generates actin filament cables that are resistant to depolymerization. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, A.Y.; Wu, H.M. Overexpression of an Arabidopsis formin stimulates supernumerary actin cable formation from pollen tube cell membrane. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.Y.; Xiang, Y. The function of actin-binding proteins in pollen tube growth. Protoplasma 2007, 230, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.T.; Li, S.W.; Ren, H.Y. Profilin as a regulator of the membrane-actin cytoskeleton interface in plant cells. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparkes, I. Recent advances in understanding plant myosin function: Life in the fast lane. Mol. Plant 2011, 4, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Zhu, J.S.; Cai, C.; Pei, W.K.; Wang, J.J.; Dong, H.J.; Ren, H.Y. FIMBRIN1 is involved in lily pollen tube growth by stabilizing the actin fringe. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 4539–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovar, D.R.; Staiger, C.J.; Weaver, E.A.; McCurdy, D.W. AtFim1 is an actin filament crosslinking protein from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2000, 24, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Qu, X.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, Y.; Dai, A.; Zhao, W.; Cao, D.; Lan, Y.; Yu, R.; Wang, H.; et al. The balance between actin-bundling factors controls actin architecture in pollen tubes. iScience 2019, 16, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, F.; Guerin, C.; von Witsch, M.; Blanchoin, L.; Staiger, C.J. Identification of Arabidopsis cyclase-associated protein 1 as the first nucleotide exchange factor for plant actin. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 3002–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, J. The ARP2/3 complex: Giving plant cells a leading edge. Bioessays 2005, 27, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Wan, A.R.; Jauh, G.Y. An actin-binding protein, LlLIM1, mediates calcium and hydrogen regulation of actin dynamics in pollen tubes. Plant Physiol. 2008, 147, 1619–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Hoffmann, C.; Dieterle, M.; Van Troys, M.; Ampe, C.; Steinmetz, A. Tobacco WLIM1 is a novel F-actin binding protein involved in actin cytoskeleton remodeling. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 2194–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.J.; Blanchoin, L.; Kovar, D.R.; Staiger, C.J. Arabidopsis capping protein (AtCP) is a heterodimer that regulates assembly at the barbed ends of actin filaments. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 44832–44842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.R.; Belardi, B.; Jreij, P.; Wei, K.; Shams, H.; Bausch, A.; Fletcher, D.A. Steric regulation of tandem calponin homology domain actin-binding affinity. Mol. Biol. Cell 2019, 30, 3112–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretscher, A.; Weber, K. Fimbrin, a new microfilament-associated protein present in microvilli and other cell-surface structures. J. Cell Biol. 1980, 86, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.H.; Qu, X.L.; Huang, S.J. Arabidopsis FIM5 decorates apical actin filaments and regulates their organization in the pollen tube. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 3407–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Feng, H.L.; Chao, X.T.; Ding, X.; Nan, Q.; Wen, C.X.; Liu, H.D.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, W. Fimbrins 4 and 5 act synergistically during polarized pollen tube growth to ensure fertility in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 2006–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovar, D.R.; Gibbon, B.C.; McCurdy, D.W.; Staiger, C.J. Fluorescently-labeled fimbrin decorates a dynamic actin filament network in live plant cells. Planta 2001, 213, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.H.; Chang, M.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Y.J.; Qu, X.L.; Huang, S.J. The structurally plastic CH2 domain is linked to distinct functions of fimbrins/plastins. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 17881–17896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCurdy, D.W.; Staiger, C.J. Fimbrin. In Actin: A Dynamic Framework for Multiple Plant Cell Functions; Staiger, C.J., Baluska, F., Volkmann, D., Barlow, P., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 87–102. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchoin, L.; Staiger, C.J. Plant formins: Diverse isoforms and unique molecular mechanism. BBA-Mol. Cell Res. 2010, 1803, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.X.; Liu, X.N.; Fu, Y.; Huang, S.J. Arabidopsis class I formins control membrane-originated actin polymerization at pollen tube tips. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingouff, M.; Gerald, J.N.F.; Guerin, C.; Robert, H.; Sorensen, M.B.; Van Damme, D.; Geelen, D.; Blanchoin, L.; Berger, F. Plant formin AtFH5 is an evolutionarily conserved actin nucleator involved in cytokinesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.H.; Shen, Y.A.; Cai, C.; Zhong, C.C.; Zhu, L.; Yuan, M.; Ren, H.Y. The type II Arabidopsis formin14 interacts with microtubules and microfilaments to regulate cell division. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2710–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, H.X.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Liang, W.Q.; Yuan, Z.; Hu, J.P.; Ren, H.Y.; Zhang, D.B. RICE MORPHOLOGY DETERMINANT encodes the type II formin FH5 and regulates rice morphogenesis. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 681–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favery, B.; Chelysheva, L.A.; Lebris, M.; Jammes, F.; Marmagne, A.; de Almeida-Engler, J.; Lecomte, P.; Vaury, C.; Arkowitz, R.A.; Abad, P. Arabidopsis formin AtFH6 is a plasma membrane-associated protein upregulated in giant cells induced by parasitic nematodes. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 2529–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.W.; Ren, Z.H.; Liu, C.; Du, P.Z.; Li, J.B.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhang, F.L.; Hou, H.L.; Shi, J.X.; Liang, W.Q.; et al. OsFH3 encodes a type II formin required for rice morphogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gisbergen, P.A.C.; Bezanilla, M. Plant formins: Membrane anchors for actin polymerization. Trends Cell Biol. 2013, 23, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oulehlova, D.; Kollarova, E.; Cifrova, P.; Pejchar, P.; Zarsky, V.; Cvrckova, F. Arabidopsis class I formin FH1 relocates between membrane compartments during root cell ontogeny and associates with plasmodesmata. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 1855–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, M.; Ren, S.L.; Wang, Q.N.; Qian, L.C.; Shen, J.F.; Liu, Y.L.; Huang, S.J. Arabidopsis formin 2 regulates cell-to-cell trafficking by capping and stabilizing actin filaments at plasmodesmata. eLife 2018, 7, e36316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Dong, G.J.; Wu, L.M.; Wang, X.W.; Chen, F.; Xiong, E.H.; Xiong, G.S.; Zhou, Y.H.; Kong, Z.S.; Fu, Y.; et al. Formin protein DRT1 affects gross morphology and chloroplast relocation in rice. Plant Physiol. 2023, 191, 280–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.M.; Liu, X.L.; Nath, S.; Sun, H.; Tran, T.M.; Yang, L.; Mayor, S.; Miao, Y.S. Formin nanoclustering-mediated actin assembly during plant flagellin and DSF signaling. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.M.; Sun, Y.B.; Zhu, X.L.; Yang, L.; Chen, X.; Miao, Y.S. Membrane nanodomains modulate formin condensation for actin remodeling in Arabidopsis innate immune responses. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 374–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Henty-Ridilla, J.L.; Huang, S.J.; Wang, X.; Blanchoin, L.; Staiger, C.J. Capping protein modulates the dynamic behavior of actin filaments in response to phosphatidic acid in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 3742–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Henty-Ridilla, J.L.; Staiger, B.H.; Day, B.; Staiger, C.J. Capping protein integrates multiple MAMP signalling pathways to modulate actin dynamics during plant innate immunity. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Cao, L.Y.; Staiger, C.J. Capping protein modulates actin remodeling in response to reactive oxygen species during plant innate immunity. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qian, D.; Fan, T.T.; Jia, H.L.; An, L.Z.; Xiang, Y. Arabidopsis actin capping protein (AtCP) subunits have different expression patterns, and downregulation of AtCPB confers increased thermotolerance of Arabidopsis after heat shock stress. Plant Sci. 2012, 193, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.J.; Qu, X.L.; Zhang, R.H. Plant villins: Versatile actin regulatory proteins. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2015, 57, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.; Tholl, S.; Moes, D.; Dieterle, M.; Papuga, J.; Moreau, F.; Steinmetz, A. Actin bundling in plants. Cell Motil. Cytoskel 2009, 66, 940–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, P.; Henty, J.L.; Huang, S.J.; Staiger, A.M.; Blanchoin, L.; Staiger, C.J. Arabidopsis VILLIN1 and VILLIN3 have overlapping and distinct activities in actin bundle formation and turnover. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2727–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Li, M.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Cheng, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Lv, Y.; He, M.; Cheng, X.; et al. Actin depolymerizing factor ADF7 inhibits actin bundling protein VILLIN1 to regulate root hair formation in response to osmotic stress in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2022, 18, e1010338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, M.X.; Guo, M.M.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Wang, B.X.; Pan, Q.; Li, J.J.; Zhou, J.M.; Li, J.J. MPK3-and MPK6-mediated VLN3 phosphorylation regulates actin dynamics during stomatal immunity in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Ren, H.; Li, J. An auxin transport inhibitor targets villin-mediated actin dynamics to regulate polar auxin transport. Plant Physiol. 2019, 181, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.L.; Zhang, H.; Xie, Y.R.; Wang, J.; Chen, N.Z.; Huang, S.J. Arabidopsis villins promote actin turnover at pollen tube tips and facilitate the construction of actin collars. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 1803–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Honing, H.S.; Kieft, H.; Emons, A.M.C.; Ketelaar, T. Arabidopsis VILLIN2 and VILLIN3 are required for the generation of thick actin filament bundles and for directional organ growth. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 1426–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papuga, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Dieterle, M.; Moes, D.; Moreau, F.; Tholl, S.; Steinmetz, A.; Thomas, C. Arabidopsis LIM proteins: A family of actin bundlers with distinct expression patterns and modes of regulation. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 3034–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peremyslov, V.V.; Prokhnevsky, A.I.; Dolja, V.V. Class XI myosins are required for development, cell expansion, and F-Actin organization in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 1883–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichelt, S.; Knight, A.E.; Hodge, T.P.; Baluška, F.; Šamaj, J.; Volkmann, D.; Kendrick-Jones, J. Characterization of the unconventional myosin VIII in plant cells and its localization at the post-cytokinetic cell wall. Plant J. 1999, 19, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, T.; Tominaga, M.; Matsumoto, R.; Sato, K.; Nakano, A.; Yamamoto, K.; Ito, K. Molecular characterization and subcellular localization of Arabidopsis class VIII myosin, ATM1. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 12343–12355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henn, A.; Sadot, E. The unique enzymatic and mechanistic properties of plant myosins. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2014, 22, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Henty-Ridilla, J.L.; Szymanski, D.B.; Staiger, C.J. Arabidopsis myosin XI: A motor rules the tracks. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Cai, C.; Staiger, C.J. Myosins XI are involved in exocytosis of cellulose synthase complexes. Plant Physiol. 2019, 179, 1537–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.W.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.H.; Staiger, C.J. Arabidopsis myosin XIK interacts with the exocyst complex to facilitate vesicle tethering during exocytosis. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 2454–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hepler, P.K.; Winship, L.J. The pollen tube clear zone: Clues to the mechanism of polarized growth. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2015, 57, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, M.; Kimura, A.; Yokota, E.; Haraguchi, T.; Shimmen, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Nakano, A.; Ito, K. Cytoplasmic streaming velocity as a plant size determinant. Dev. Cell 2013, 27, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. Myosin XI-B is involved in the transport of vesicles and organelles in pollen tubes of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2021, 108, 1145–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Abied, M.; Belausov, E.; Hagay, S.; Peremyslov, V.; Dolja, V.; Sadot, E. Myosin XI-K is involved in root organogenesis, polar auxin transport, and cell division. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 2869–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, R.H.; Goldschmidt-Clermont, P.J. Profilin-at the crossroads of signal-transduction and the actin cytoskeleton. Bioessays 1994, 16, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, D.K.; Chaudhary, B. Evolutionary expansion and structural functionalism of the ancient family of profilin proteins. Gene 2017, 626, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baluška, F.; von Witsch, M.; Peters, M.; Hlavacka, A.; Volkmann, D. Mastoparan alters subcellular distribution of profilin and remodels F-actin cytoskeleton in cells of maize root apices. Plant Cell Physiol. 2001, 42, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, D.K.; Chaudhary, B. Evolution of functional diversity among actin-binding profilin genes in land plants. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 588689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, S.; Christensen, H.E.M.; Ishimaru, Y.; Dong, C.H.; Chao-Ming, W.; Cleary, A.L.; Chua, N.H. Profilin plays a role in cell elongation, cell shape maintenance, and flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2000, 124, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zweifel, M.E.; Courtemanche, N. Competition for delivery of profilin-actin to barbed ends limits the rate of formin-mediated actin filament elongation. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 4513–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horan, B.G.; Zerze, G.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Vavylonis, D.; Mittal, J. Computational modeling highlights the role of the disordered Formin Homology 1 domain in profilin-actin transfer. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 1804–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.Y.; Henty-Ridilla, J.L.; Blanchoin, L.; Staiger, C.J. Profilin-dependent nucleation and assembly of actin filaments controls cell elongation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Qiao, Z.; Chua, K.P.; Tursic, A.; Liu, X.; Gao, Y.G.; Mu, Y.G.; Hou, X.L.; Miao, Y.S. Profilin negatively regulates formin-mediated actin assembly to modulate PAMP-triggered plant immunity. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 1882–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, H.Y. Profilin promotes formin-mediated actin filament assembly and vesicle transport during polarity formation in pollen. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 1252–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerst, J.E.; Ferguson, K.; Vojtek, A.; Wigler, M.; Field, J. Cap is a bifunctional component of the Saccharomyces-cerevisiae adenylyl cyclase complex. Mol. Cell Biol. 1991, 11, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perelroizen, I.; Didry, D.; Christensen, H.; Chua, N.H.; Carlier, M.F. Role of nucleotide exchange and hydrolysis in the function of profilin in actin assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 12302–12309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrero, R.A.; Umeda, M.; Yamamura, S.; Uchimiya, H. Arabidopsis CAP regulates the actin cytoskeleton necessary for plant cell elongation and division. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.X.; Chang, M.; Lan, Y.X.; Huang, S.J. Mechanism of CAP1-mediated apical actin polymerization in pollen tubes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 12084–12093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeks, M.J.; Rodrigues, C.; Dimmock, S.; Ketelaar, T.; Maciver, S.K.; Malho, R.; Hussey, P.J. Arabidopsis CAP1-a key regulator of actin organisation and development. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 2609–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, C.; Roland, J.; Boujemaa-Paterski, R.; Kang, H.; McCullough, B.R.; Reymann, A.C.; Guerin, C.; Martiel, J.L.; De La Cruz, E.M.; Blanchoin, L. Cofilin tunes the nucleotide state of actin filaments and severs at bare and decorated segment boundaries (vol 21, pg 862, 2011). Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galkin, V.E.; Orlova, A.; Kudryashov, D.S.; Solodukhin, A.; Reisler, E.; Schroder, G.F.; Egelman, E.H. Remodeling of actin filaments by ADF/cofilin proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20568–20572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzicka, D.R.; Kandasamy, M.K.; McKinney, E.C.; Burgos-Rivera, B.; Meagher, R.B. The ancient subclasses of Arabidopsis ACTIN DEPOLYMERIZING FACTOR genes exhibit novel and differential expression. Plant J. 2007, 52, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.Y.; Xie, Y.R.; Jiang, Y.X.; Qu, X.L.; Huang, S.J. Arabidopsis ACTIN-DEPOLYMERIZING FACTOR7 severs actin filaments and regulates actin cable turnover to promote normal pollen tube growth. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 3405–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, F.B.; Geitmann, A. Actin depolymerizing factors ADF7 and ADF10 play distinct roles during pollen development and pollen tube growth. Plant Signal Behav. 2012, 7, 879–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, F.B.; van Oostende, C.; Geitmann, A. Spatial and temporal expression of actin depolymerizing factors ADF7 and ADF10 during male gametophyte development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 1177–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.X.; Wang, J.; Xie, Y.R.; Chen, N.Z.; Huang, S.J. ADF10 shapes the overall organization of apical actin filaments by promoting their turnover and ordering in pollen tubes. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 3988–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Y.; Wong, E.I.; Vidali, L.; Estavillo, A.; Hepler, P.K.; Wu, H.M.; Cheung, A.Y. The regulation of actin organization by actin-depolymerizing factor in elongating pollen tubes. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 2175–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustine, R.C.; Vidali, L.; Kleinman, K.P.; Bezanilla, M. Actin depolymerizing factor is essential for viability in plants, and its phosphoregulation is important for tip growth. Plant J. 2008, 54, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.H.; Xia, G.X.; Hong, Y.; Ramachandran, S.; Kost, B.; Chua, N.H. ADF proteins are involved in the control of flowering and regulate F-actin organization, cell expansion, and organ growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos-Rivera, B.; Ruzicka, D.R.; Deal, R.B.; McKinney, E.C.; King-Reid, L.; Meagher, R.B. ACTIN DEPOLYMERIZING FACTOR9 controls development and gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2008, 68, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henty, J.L.; Bledsoe, S.W.; Khurana, P.; Meagher, R.B.; Day, B.; Blanchoin, L.; Staiger, C.J. Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor4 modulates the stochastic dynamic behavior of actin filaments in the cortical array of epidermal cells. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 3711–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.Y.; Chaudhry, F.; Ruzicka, D.R.; Meagher, R.B.; Staiger, C.J.; Day, B. Arabidopsis actin-depolymerizing factor AtADF4 mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henty-Ridilla, J.L.; Li, J.J.; Day, B.; Staiger, C.J. ACTIN DEPOLYMERIZING FACTOR4 regulates actin dynamics during innate immune signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.J.; Li, P.; Shimono, M.; Corrion, A.; Higaki, T.; He, S.Y.; Day, B. Arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinase 3 regulates actin cytoskeleton organization and immunity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, D.; Zhang, Z.; He, J.X.; Zhang, P.; Ou, X.B.; Li, T.; Niu, L.P.; Nan, Q.; Niu, Y.; He, W.L.; et al. Arabidopsis ADF5 promotes stomatal closure by regulating actin cytoskeleton remodeling in response to ABA and drought stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Qian, D.; Luo, C.; Niu, Y.; Li, T.; Li, C.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Niu, Y. Arabidopsis ADF5 acts as a downstream target gene of CBFs in response to low-temperature stress. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 635533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.B. Small GTPases: Versatile signaling switches in plants. Plant Cell 2002, 14, S375–S388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.L.; Yang, Z. The Rop GTPase: An emerging signaling switch in plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, Z.B. The ROP2 GTPase controls the formation of cortical fine F-actin and the early phase of directional cell expansion during Arabidopsis organogenesis. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 777–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wu, G.; Yang, Z.B. Rop GTPase-dependent dynamics of tip-localized F-actin controls tip growth in pollen tubes. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 152, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allwood, E.G.; Smertenko, A.P.; Hussey, P.J. Phosphorylation of plant actin-depolymerising factor by calmodulin-like domain protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 2001, 499, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smertenko, A.P.; Jiang, C.J.; Simmons, N.J.; Weeds, A.G.; Davies, D.R.; Hussey, P.J. Ser6 in the maize actin-depolymerizing factor, ZmADF3, is phosphorylated by a calcium-stimulated protein kinase and is essential for the control of functional activity. Plant J. 1998, 14, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldy, C.; Caillaud, M.C. Connecting the plant cytoskeleton to the cell surface via the phosphoinositides. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2023, 73, 102365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymanski, D.B. Breaking the WAVE complex: The point of Arabidopsis trichomes. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2005, 8, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, K.; Hirt, H. Reactive oxygen species: Metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2004, 55, 373–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, O.O.H. Effects of environmental stress factors on the actin cytoskeleton of fungi and plants: Ionizing radiation and ROS. Cytoskeleton 2023, 80, 330–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, Y.; Jeon, B.W.; Staiger, C.J.; Lee, Y. Phosphatidylinositol 3- and 4-phosphate modulate actin filament reorganization in guard cells of day flower. Plant Cell Environ. 2008, 31, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, J.H.; Wang, W.; Chen, N.Z.; Ma, T.S.; Xi, Y.N.; Zhang, X.L.; Lin, H.F.; Bai, Y.; Huang, S.J.; et al. ARP2/3 complex-mediated actin dynamics is required for hydrogen peroxide-induced stomatal closure in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 1548–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Yan, M.; Wang, R.; Wang, L.; Welti, R.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X. Phospholipase Dα1 and phosphatidic acid regulate NADPH oxidase activity and production of reactive oxygen species in ABA-mediated stomatal closure in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 2357–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.Y.; Wang, W.Y.; Zhang, W.W.; Staiger, C.J. Lipid signaling requires ROS production to elicit actin cytoskeleton remodeling during plant innate immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwah, S.; Jones, A.M.; Laxmi, A. Cytokinin-induced root growth involves actin filament reorganization. Plant Signal Behav. 2011, 6, 1848–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro, L.; Munoz, D.; Marash, I.; Gupta, R.; Anand, G.; Leibman-Markus, M.; Bar, M. Cytokinin modulates cellular trafficking and the cytoskeleton, enhancing defense responses. Cells 2021, 10, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwabuchi, K.; Takagi, S. Actin-based mechanisms for light-dependent intracellular positioning of nuclei and chloroplasts in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal Behav. 2010, 5, 1010–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwabuchi, K.; Minamino, R.; Takagi, S. Actin reorganization underlies phototropin-dependent positioning of nuclei in Arabidopsis leaf cells. Plant Physiol. 2010, 152, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadota, A.; Yamada, N.; Suetsugu, N.; Hirose, M.; Saito, C.; Shoda, K.; Ichikawa, S.; Kagawa, T.; Nakano, A.; Wada, M. Short actin-based mechanism for light-directed chloroplast movement in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13106–13111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whippo, C.W.; Khurana, P.; Davis, P.A.; DeBlasio, S.L.; DeSloover, D.; Staiger, C.J.; Hangarter, R.P. THRUMIN1 is a light-regulated actin-bundling protein involved in chloroplast motility. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.Q.; Xing, J.J.; Wan, Y.L.; Lv, X.Q.; Fan, L.S.; Zhang, Y.D.; Song, K.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.H.; Deng, X.; et al. Arabidopsis blue light receptor phototropin 1 undergoes blue light-induced activation in membrane microdomains. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 846–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzeszowiec, W.; Rajwa, B.; Dobrucki, J.; Gabrys, H. Actin cytoskeleton in Arabidopsis thaliana under blue and red light. Biol. Cell 2007, 99, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Bibeau, J.P.; Lemoi, K.P.; Tuzel, E.; Vidali, L. The kinesin-like proteins, KAC1/2, regulate actin dynamics underlying chloroplast light-avoidance in Physcomitrella patens. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2015, 57, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šamaj, J.; Ovecka, M.; Hlavacka, A.; Lecourieux, F.; Meskiene, I.; Lichtscheidl, I.; Lenart, P.; Salaj, J.; Volkmann, D.; Bogre, L.; et al. Involvement of the mitogen-activated protein kinase SIMK in regulation of root hair tip growth. Embo J. 2002, 21, 3296–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwan, V.; Orvar, B.L.; Beyerly, J.; Hirt, H.; Dhindsa, R.S. Opposite changes in membrane fluidity mimic cold and heat stress activation of distinct plant MAP kinase pathways. Plant J. 2002, 31, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šamaj, J.; Baluška, F.; Hirt, H. From signal to cell polarity: Mitogen-activated protein kinases as sensors and effectors of cytoskeleton dynamicity. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staiger, C.J.; Franklin-Tong, V.E. The actin cytoskeleton is a target of the self-incompatibility response in Papaver rhoeas. J. Exp. Bot. 2003, 54, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Qu, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, L.; Bosch, M.; Franklin-Tong, V.E.; Xue, Y.; Huang, S. Villin controls the formation and enlargement of punctate actin foci in pollen tubes. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133, jcs237404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Fan, L.M.; Zhang, W.Z.; Zhang, W.; Wu, W.H. Ca2+-permeable channels in the plasma membrane of Arabidopsis pollen are regulated by actin microfilaments. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 3892–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.S.; Han, X.M.; Zheng, L.Z.; Xie, Y.; Mu, Y.G.; Yates, J.R.; Drubin, D.G. Fimbrin phosphorylation by metaphase Cdk1 regulates actin cable dynamics in budding yeast. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.M.; Holehouse, A.S.; Pappu, R.V. Physical principles underlying the complex biology of intracellular phase transitions. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2020, 49, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Sun, J.L.; Han, X.; Tursic-Wunder, A.; Toh, J.D.W.; Hong, W.J.; Gao, Y.G.; Miao, Y.S. Polarisome scaffolder Spa2-mediated macromolecular condensation of Aip5 for actin polymerization. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.M.; Miao, Y.S. Review: F-Actin remodelling during plant signal transduction via biomolecular assembly. Plant Sci. 2020, 301, 110663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pydiura, N.; Pirko, Y.; Galinousky, D.; Postovoitova, A.; Yemets, A.; Kilchevsky, A.; Blume, Y. Genome-wide identification, phylogenetic classification, and exon-intron structure characterization of the tubulin and actin genes in flax (Linum usitatissimum). Cell Biol. Int. 2019, 43, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldspink, D.A.; Matthews, Z.J.; Lund, E.K.; Wileman, T.; Mogensen, M.M. Immuno-fluorescent labeling of microtubules and centrosomal proteins in ex vivo intestinal tissue and 3D in vitro intestinal organoids. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 13, 56662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, A.T.; Nelson, S.R.; Kennedy, G.G.; Trybus, K.M.; Walcott, S.; Warshaw, D.M. Myosin Va transport of liposomes in three-dimensional actin networks is modulated by actin filament density, position, and polarity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8326–8335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Jasnin, M. Capturing actin assemblies in cells using in situ cryo-electron tomography. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2022, 101, 151224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.Q.; Du, P.Z.; Wang, Z.X.; Sun, F.; Ren, H.Y. Cryo-EM structure of actin filaments from Zea mays pollen. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 2855–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussey, P.J.; Ketelaar, T.; Deeks, M.J. Control of the actin cytoskeleton in plant cell growth. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampathkumar, A.; Gutierrez, R.; McFarlane, H.E.; Bringmann, M.; Lindeboom, J.; Emons, A.M.; Samuels, L.; Ketelaar, T.; Ehrhardt, D.W.; Persson, S. Patterning and lifetime of plasma membrane-localized cellulose synthase is dependent on actin organization in Arabidopsis interphase cells. Plant Physiol. 2013, 162, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appenzeller-Herzog, C.; Hauri, H.P. The ER-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC): In search of its identity and function. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 2173–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.W.; Hussey, P.J. Interactions between plant endomembrane systems and the actin cytoskeleton. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monastyrska, I.; He, C.; Geng, J.F.; Hoppe, A.D.; Li, Z.J.; Klionsky, D.J. Arp2 links autophagic machinery with the actin cytoskeleton. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 1962–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monastyrska, I.; Reggiori, F.; Klionsky, D.J. Harpooning the Cvt complex to the phagophore assembly site. Autophagy 2008, 4, 914–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kast, D.J.; Zajac, A.L.; Holzbaur, E.L.F.; Ostap, E.M.; Dominguez, R. WHAMM directs the Arp2/3 complex to the ER for autophagosome biogenesis through an actin comet tail mechanism. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 1791–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Condeelis, J. Regulation of the actin cytoskeleton in cancer cell migration and invasion. BBA-Mol. Cell Res. 2007, 1773, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.H.; Mallery, E.; Reagan, S.; Boyko, V.P.; Kotchoni, S.O.; Szymanski, D.B. The endoplasmic reticulum is a reservoir for WAVE/SCAR regulatory complex signaling in the Arabidopsis leaf. Plant Physiol. 2013, 162, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.W.; Richardson, C.; Hawes, C.; Hussey, P.J. Arabidopsis NAP1 regulates the formation of autophagosomes. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 2060–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohfeld, J. Autophagy: Press and push for destruction. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R703–R705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.W.; Gao, E.L.; Hussey, P.J. Autophagosome biogenesis in plants: An actin cytoskeleton perspective. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin-Tong, V.E.; Gourlay, C.W. A role for actin in regulating apoptosis/programmed cell death: Evidence spanning yeast, plants and animals. Biochem. J. 2008, 413, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komis, G.; Novak, D.; Ovecka, M.; Samajova, O.; Šamaj, J. Advances in imaging plant cell dynamics. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conduit, P.T.; Wainman, A.; Novak, Z.A.; Weil, T.T.; Raff, J.W. Re-examining the role of Drosophila Sas-4 in centrosome assembly using two-colour-3D-SIM FRAP. eLife 2015, 4, e08483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzano, L.; Scipioni, L.; Di Bona, M.; Bianchini, P.; Bizzarri, R.; Cardarelli, F.; Diaspro, A.; Vicidomini, G. Measurement of nanoscale three-dimensional diffusion in the interior of living cells by STED-FCS. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, M.; Li, X.; Huang, S.J. Arabidopsis AIP1-1 regulates the organization of apical actin filaments by promoting their turnover in pollen tubes. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higaki, T.; Kutsuna, N.; Sano, T.; Kondo, N.; Hasezawa, S. Quantification and cluster analysis of actin cytoskeletal structures in plant cells: Role of actin bundling in stomatal movement during diurnal cycles in Arabidopsis guard cells. Plant J. 2010, 61, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Nan, Q.; Qin, T.; Qian, D.; Mao, T.; Yuan, S.; Wu, X.; Niu, Y.; Bai, Q.; An, L.; et al. Higher-ordered actin structures remodeled by Arabidopsis ACTIN-DEPOLYMERIZING FACTOR5 are important for pollen germination and pollen tube growth. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 1065–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baluška, F.; Mancuso, S. Actin cytoskeleton and action potentials: Forgotten connections. In The Cytoskeleton Diverse Roles in a Plant’s Life; Sahi, V.P., Baluška, F., Eds.; Plant Cell Monographs; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 24, pp. 63–83. [Google Scholar]
- Cvrčková, F. Formins and membranes: Anchoring cortical actin to the cell wall and beyond. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, A.Y.; Niroomand, S.; Zou, Y.J.; Wu, H.M. A transmembrane formin nucleates subapical actin assembly and controls tip-focused growth in pollen tubes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16390–16395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baluška, F.; Hlavačka, A. Plant formins come of age: Something special about cross-walls. New Phytol. 2005, 168, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeks, M.J.; Cvrcková, F.; Machesky, L.M.; Mikitová, V.; Ketelaar, T.; Zársky, V.; Davies, B.; Hussey, P.J. Arabidopsis group Ie formins localize to specific cell membrane domains, interact with actin-binding proteins and cause defects in cell expansion upon aberrant expression. New Phytol. 2005, 168, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baluška, F.; Cvrcková, F.; Kendrick-Jones, J.; Volkmann, D. Sink plasmodesmata as gateways for phloem unloading. Myosin VIII and calreticulin as molecular determinants of sink strength? Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amari, K.; Di Donato, M.; Dolja, V.V.; Heinlein, M. Myosins VIII and XI play distinct roles in reproduction and transport of Tobacco mosaic virus. PLoS Path. 2014, 10, e1004448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkmann, D.; Mori, T.; Tirlapur, U.K.; König, K.; Fujiwara, T.; Kendrick-Jones, J.; Baluška, F. Unconventional myosins of the plant-specific class VIII: Endocytosis, cytokinesis, plasmodesmata/pit-fields, and cell-to-cell coupling. Cell Biol. Int. 2003, 27, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baluška, F.; Mancuso, S. Root apex transition zone as oscillatory zone. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baluška, F.; Mancuso, S.; Volkmann, D.; Barlow, P.W. Root apex transition zone: A signalling-response nexus in the root. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goode, B.L.; Drubin, D.G.; Barnes, G. Functional cooperation between the microtubule and actin cytoskeletons. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2000, 12, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collings, D.A.; Wasteneys, G.O. Actin microfilament and microtubule distribution patterns in the expanding root of Arabidopsis thaliana. Can. J. Bot. 2005, 83, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampathkumar, A.; Lindeboom, J.J.; Debolt, S.; Gutierrez, R.; Ehrhardt, D.W.; Ketelaar, T.; Persson, S. Live cell imaging reveals structural associations between the actin and microtubule cytoskeleton in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 2302–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, J.Z.; Klemm, S.; Pain, C.; Duckney, P.; Bao, Z.R.; Stamm, G.; Kriechbaumer, V.; Burstenbinder, K.; Hussey, P.J.; Wang, P.W. A novel plant actin-microtubule bridging complex regulates cytoskeletal and ER structure at ER-PM contact sites. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.C.; Zhang, H.; Xia, Q.; Yu, J.J.; Zhu, D.Y.; Zhao, Q. ZmGLR, a cell membrane localized microtubule-associated protein, mediated leaf morphogenesis in maize. Plant Sci. 2019, 289, 110248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, T.; Liu, X.M.; Li, J.J.; Sun, J.B.; Song, L.N.; Mao, T.L. Arabidopsis microtubule-destabilizing protein 25 functions in pollen tube growth by severing actin filaments. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.J.; Wang, X.L.; Qin, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.M.; Sun, J.B.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Z.D.; Yuan, M.; et al. MDP25, a novel calcium regulatory protein, mediates hypocotyl cell elongation by destabilizing cortical microtubules in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 4411–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Jin, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Bai, X.; Xie, W.; Hu, T.; Zhao, X.; Mao, T.; Qin, T. MDP25 mediates the fine-tuning of microtubule organization in response to salt stress. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 1181–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smertenko, A.; Hewitt, S.L.; Jacques, C.N.; Kacprzyk, R.; Liu, Y.; Marcec, M.J.; Moyo, L.; Ogden, A.; Oung, H.M.; Schmidt, S.; et al. Phragmoplast microtubule dynamics-a game of zones. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs203331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, S.; Jürgens, G. Plant cytokinesis-No ring, no constriction but centrifugal construction of the partitioning membrane. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 53, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Higaki, T. Disruption of actin filaments delays accumulation of cell plate membranes after chromosome separation. Plant Signal. Behav. 2021, 16, 1873586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.Z.; Bezanilla, M. Actin and microtubule cross talk mediates persistent polarized growth. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 3531–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welf, E.S.; Driscoll, M.K.; Dean, K.M.; Schafer, C.; Chu, J.; Davidson, M.W.; Lin, M.Z.; Danuser, G.; Fiolka, R. Quantitative multiscale cell imaging in controlled 3D microenvironments. Dev. Cell 2016, 36, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, M.; Ehrhardt, D.W.; Hashimoto, T. Microtubule and katanin-dependent dynamics of microtubule nucleation complexes in the acentrosomal Arabidopsis cortical array. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, F.; Ren, H.Y. Development and application of probes for labeling the actin cytoskeleton in living plant cells. Protoplasma 2011, 248, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| ABP Types | Species | Proteins | Activities or Effects on Actin Cytoskeleton | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actin-depolymerizing factor | Arabidopsis thaliana | ADF1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 10, 11 | Severing or depolymerizing actin filaments | [106] |
| Zea mays | ADF3 | Severing or depolymerizing actin filaments | [106] | |
| Zea mays | ADF1, ADF2 | Involving in pollen actin reorganization | [107,108] | |
| Lilium longiflorum | ADF1 | Severing or depolymerizing actin filaments | [109] | |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | ADF9, ADF5 | Actin-bundling and actin-stabilizing activities | [110] | |
| Nicotiana tabacum | ADF1 | Actin-binding ability | [111] | |
| Villin | Lilium longiflorum | P-115-ABP, P-135-ABP | Actin-bundling activity | [112] |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | VLN2, VLN3, VLN4 | Being responsible for actin bundle formation | [113] | |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | VLN5 | Harbor filament bundling, barbed-end capping, and Ca2+-dependent severing activities | [114] | |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | VLN1 | Generating actin bundles and stabilize actin cables | [115] | |
| Formin | Arabidopsis thaliana | FH1 | Inducing supernumerary actin cable formation | [116] |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | FHs | Nucleating, bundling and severing actin filaments | [117] | |
| Profilin | Arabidopsis thaliana | PRF1, PRF2 | Having high affinities for both PLP and G-actin | [118] |
| Myosin | Arabidopsis thaliana | MYOSIN XI-K, XI-1, XI-2 | Cargo, actin-binding, and ATPase activities; Providing the tensile force to pull an actin filament straight | [119] |
| Fimbrin | Lilium longiflorum | FIM1 | Stabilizing the actin fringe by cross-linking actin filaments into bundles | [120] |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | FIM1 | Organizing actin filaments into loose networks | [121] | |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | FIM5 | Organizing actin filaments into tight actin bundles | [122] | |
| Cyclase-associated protein | Arabidopsis thaliana | CAP1 | Nucleotide exchange activity | [123] |
| Actin nucleation factor | Arabidopsis thaliana | Arp2/3 Complex | Enhancing actin nucleation and polymerization and initiating the formation of a dynamic, dendritic array of F-actin | [124] |
| LIM domain-containing protein | Lilium longiflorum | LIM1 | Promoting filamentous actin bundle assembly | [125] |
| Nicotiana benthamiana | WLIM1 | Promoting the recruitment of actin filaments into thick actin bundles and cables | [126] | |
| NETWORKED protein | Arabidopsis thaliana | NET1A | Coupling different membranes to the actin cytoskeleton | [48] |
| Capping protein | Arabidopsis thaliana | CP | Regulating assembly at the barbed ends of actin filaments | [127] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, G.; Gao, H.; Yang, T. Exploring the Role of the Plant Actin Cytoskeleton: From Signaling to Cellular Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015480
Yuan G, Gao H, Yang T. Exploring the Role of the Plant Actin Cytoskeleton: From Signaling to Cellular Functions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(20):15480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015480
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Guoqiang, Huanhuan Gao, and Tao Yang. 2023. "Exploring the Role of the Plant Actin Cytoskeleton: From Signaling to Cellular Functions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 20: 15480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015480
APA StyleYuan, G., Gao, H., & Yang, T. (2023). Exploring the Role of the Plant Actin Cytoskeleton: From Signaling to Cellular Functions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(20), 15480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015480





