The Effect of Fat Intake with Increased Omega-6-to-Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Ratio in Animal Models of Early and Late Alzheimer’s Disease-like Pathogenesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. General Study Observations and Body Weight
2.2. Triglycerides, Cholesterol, and Glucose Levels in HDF-Treated Animals
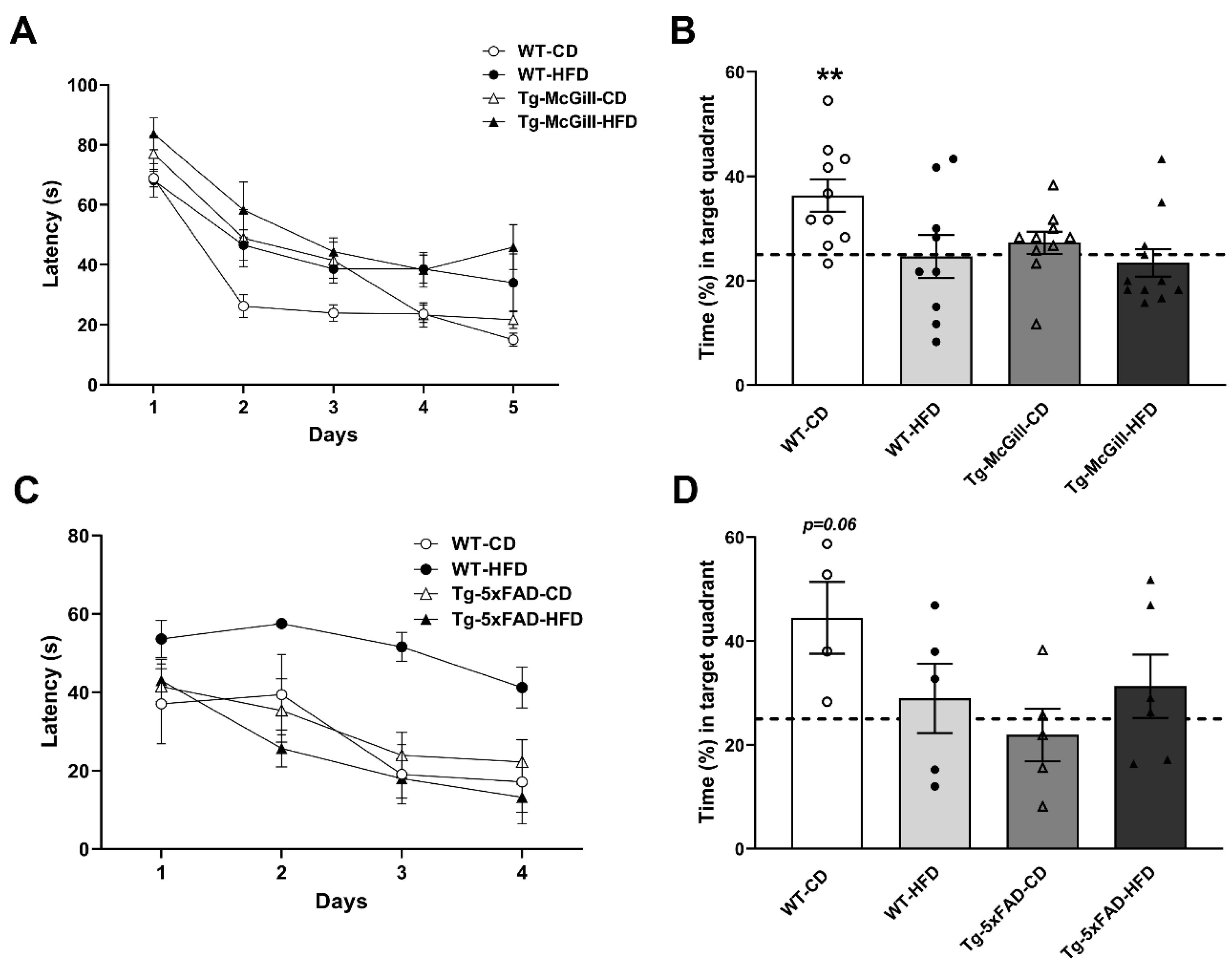
2.3. HFD Did Not Worsen Cognitive Performance in Tg Animals
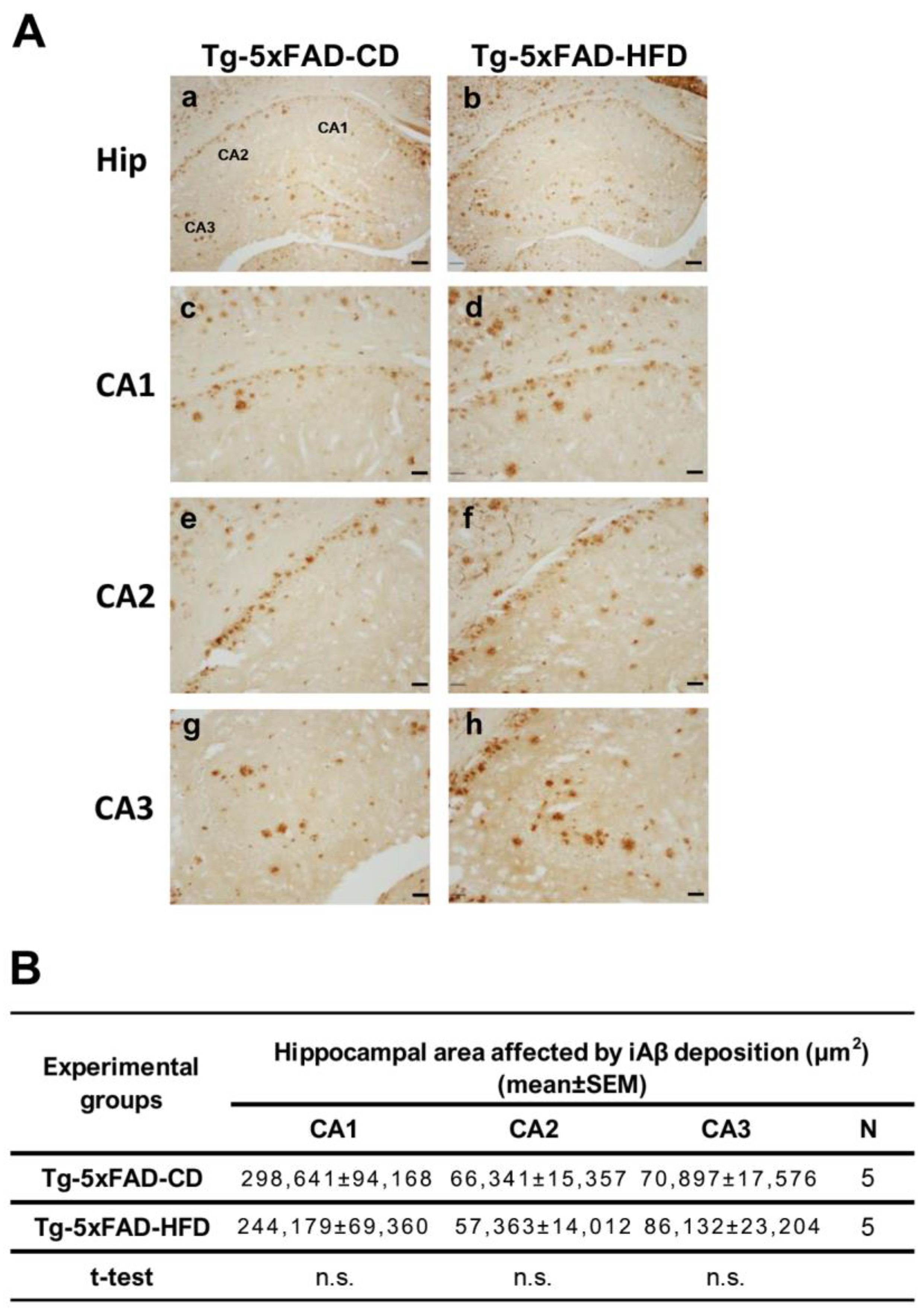
2.4. There Were No Emergent Phenotypes of Increased Hippocampal Aβ Accumulation in Tg Animals Exposed to HFD
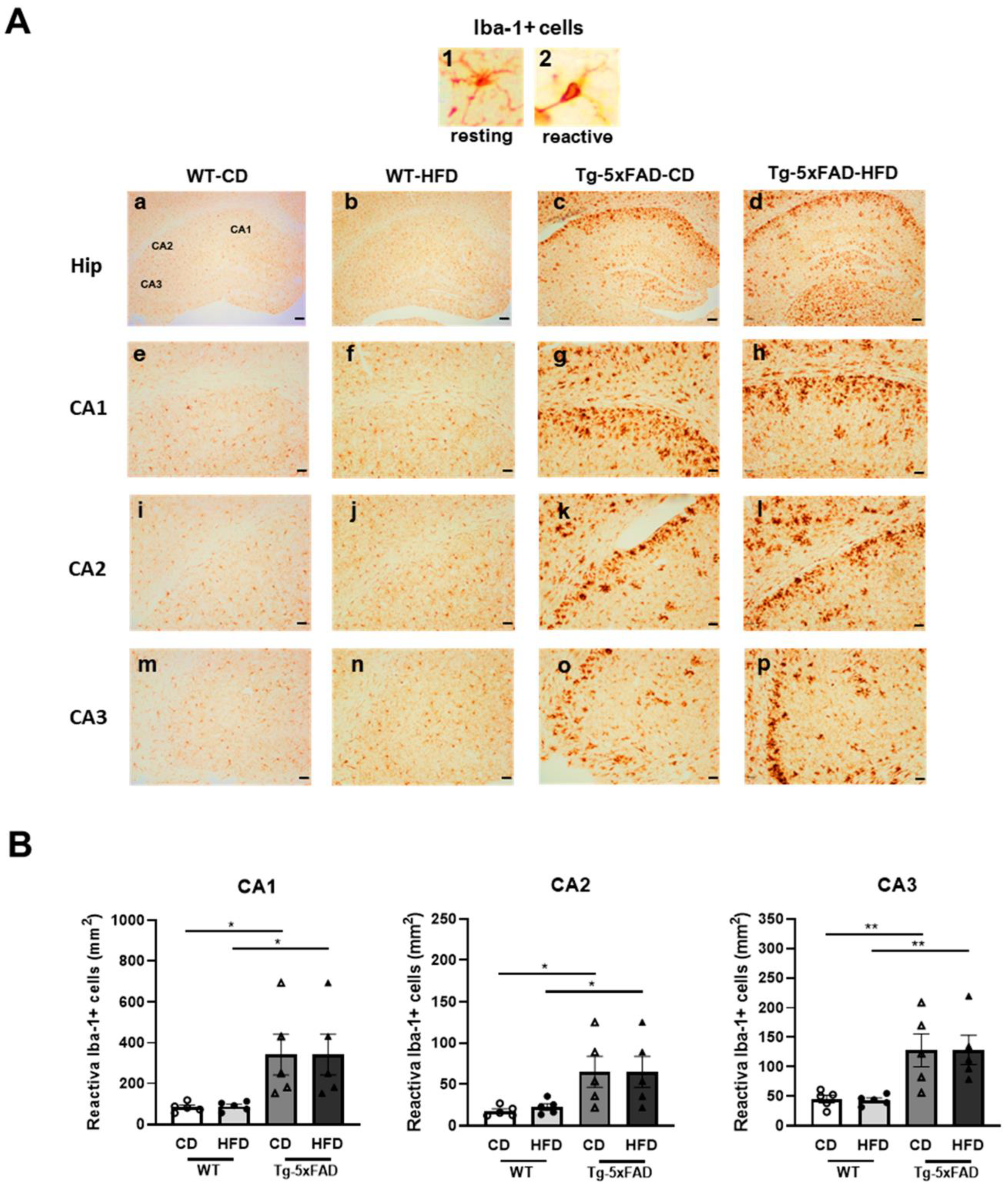
2.5. High-Fat Diet Promoted Hippocampal Microglia Activation
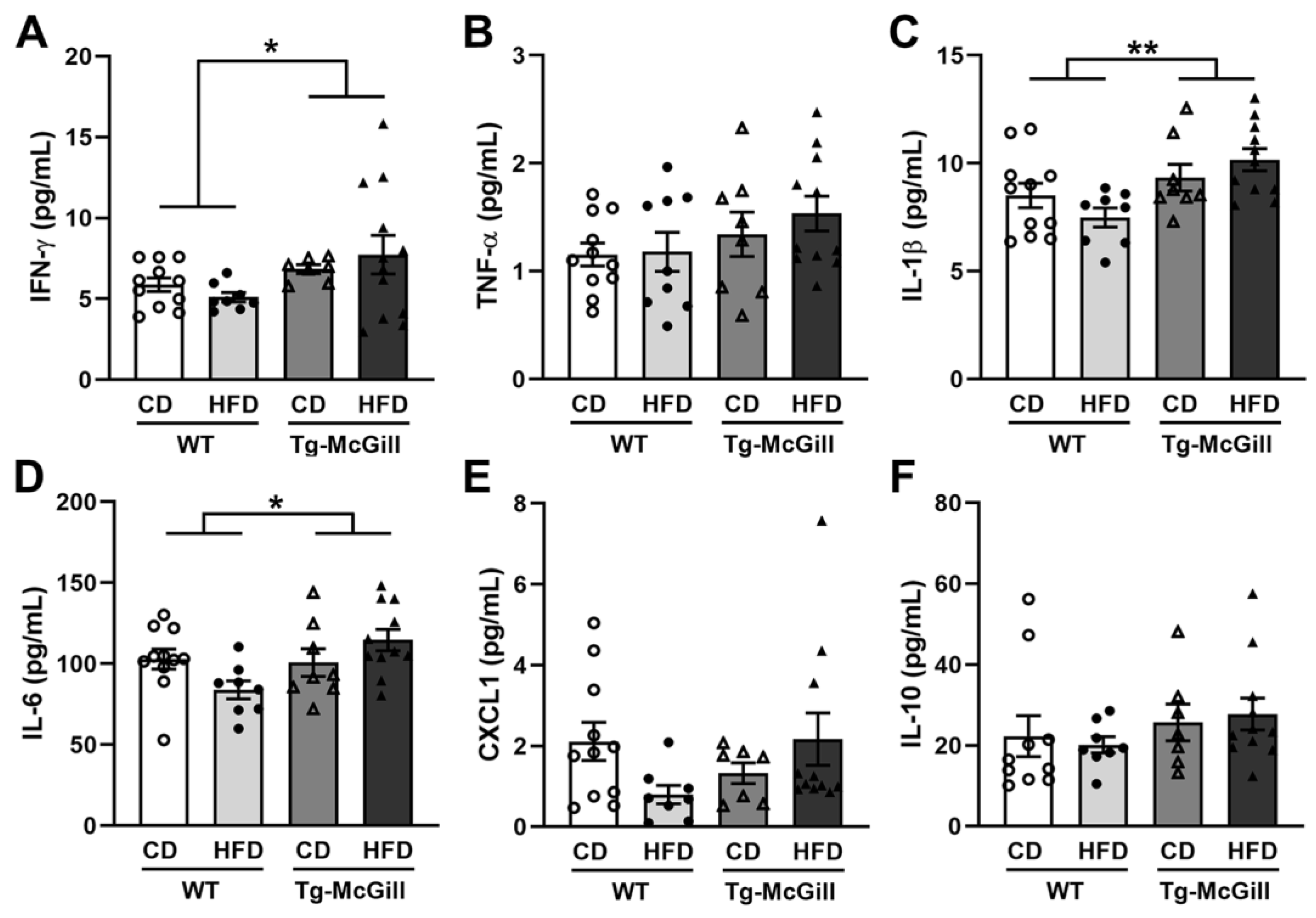
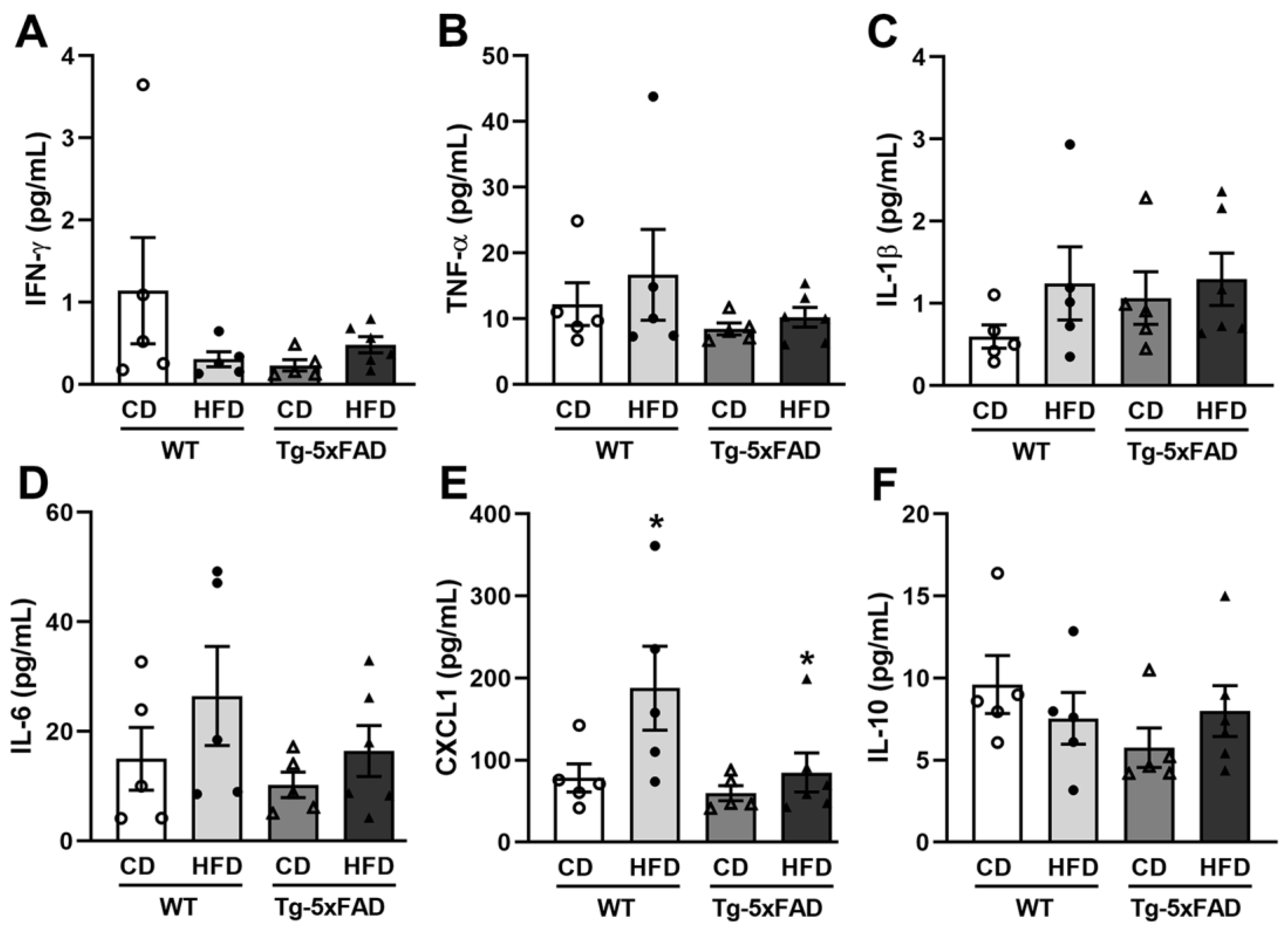
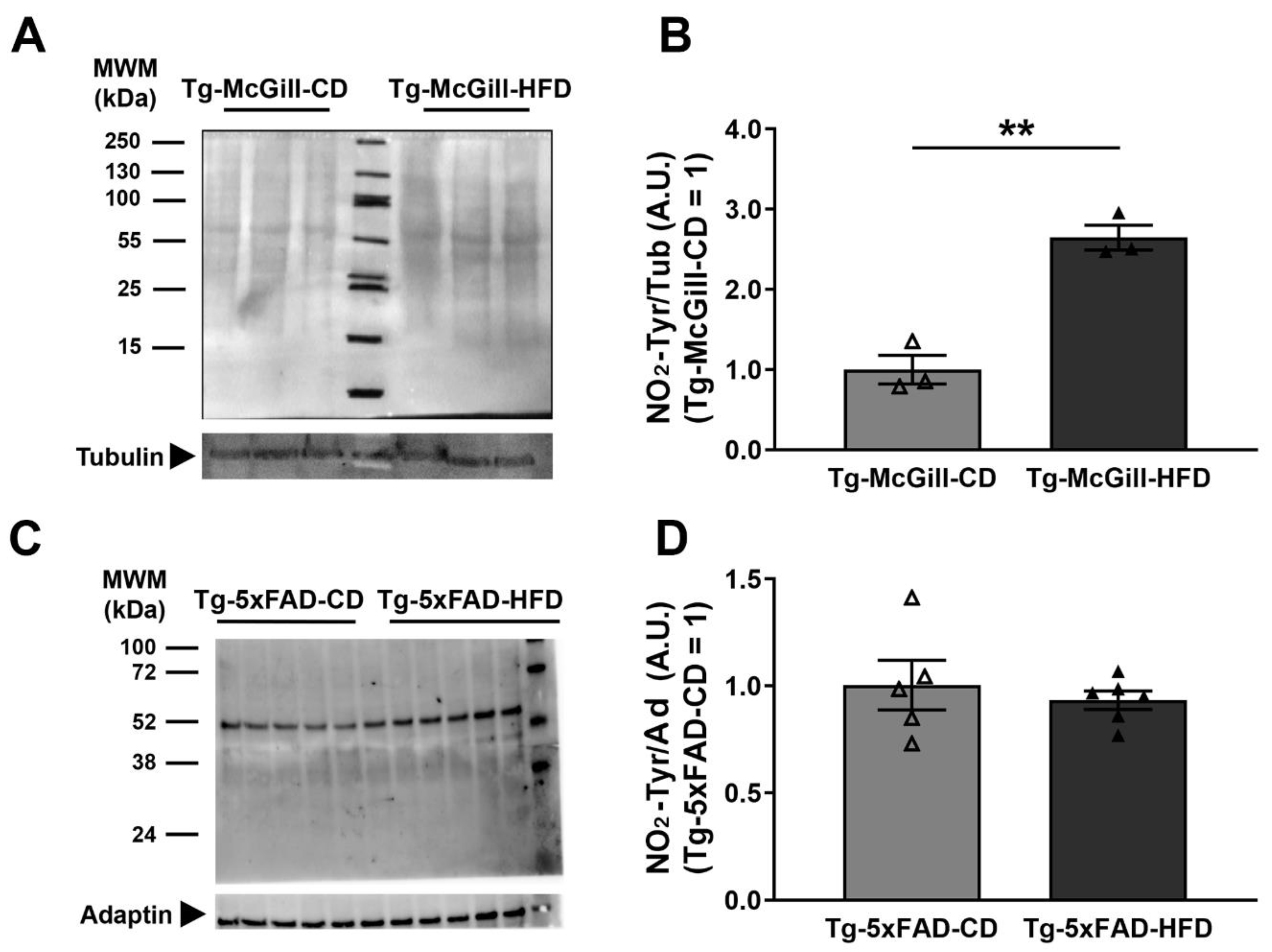
2.6. Diet-Related Expression of Nitro-Oxidative Stress Parameters in Mice and Rat Brains
3. Discussion
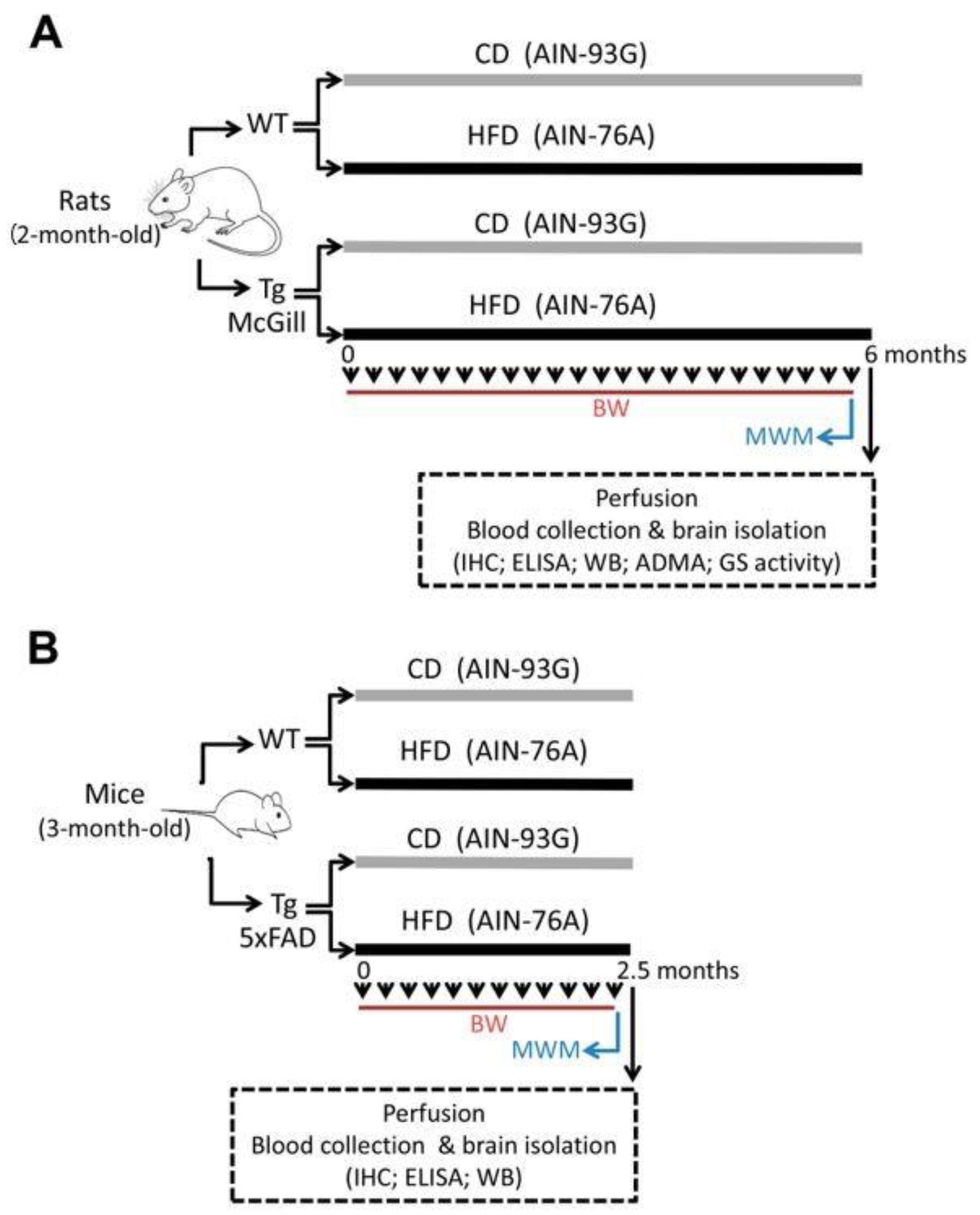
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Ethical Implications
4.2. Diets
4.3. Nutritional Protocol
4.4. Ante-Mortem Observations
4.5. Behavioral Assessment
4.6. Blood and Brain Isolation
4.7. Brain Homogenates and Western Blotting (WB)
4.8. Immunohistochemistry
4.9. Cytokine Panel Assay
4.10. Human Aβ Species Assay
4.11. Sample Preparation for 3-NO2-Tyrosine and ADMA Quantification in the Hippocampus
4.12. Quantification of Nitro-Oxidative Stress
4.13. Glutamine Synthetase (GS) Activity
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Isik, A.T. Late onset Alzheimer’s disease in older people. Clin. Interv. Aging 2010, 5, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, H.M.; Stevenson, R.J. Higher reported saturated fat and refined sugar intake is associated with reduced hippocampal-dependent memory and sensitivity to interoceptive signals. Behav. Neurosci. 2011, 125, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanoski, S.E.; Davidson, T.L. Western diet consumption and cognitive impairment: Links to hippocampal dysfunction and obesity. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 103, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beilharz, J.; Maniam, J.; Morris, M. Short-term exposure to a diet high in fat and sugar, or liquid sugar, selectively impairs hippocampal-dependent memory, with differential impacts on inflammation. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 306, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citron, M. Alzheimer’s disease: Strategies for disease modification. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karch, C.M.; Cruchaga, C.; Goate, A.M. Alzheimer’s Disease Genetics: From the Bench to the Clinic. Neuron 2014, 83, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello-Corral, L.; Sánchez-Valdeón, L.; Casado-Verdejo, I.; Seco-Calvo, J.; Fernández-Fernández, J.A.; Fernández-Martínez, M.N. The Influence of Nutrition in Alzheimer’s Disease: Neuroinflammation and the Microbiome vs. Transmissible Prion. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 677777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Sueta, G.; Campolo, N.; Trujillo, M.; Bartesaghi, S.; Carballal, S.; Romero, N.; Alvarez, B.; Radi, R. Biochemistry of Peroxynitrite and Protein Tyrosine Nitration. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 1338–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piacenza, L.; Zeida, A.; Trujillo, M.; Radi, R. The superoxide radical switch in the biology of nitric oxide and peroxynitrite. Physiol. Rev. 2022, 102, 1881–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Rodriguez, M.; Radi, R. Aconitase is readily inactivated by peroxynitrite, but not by its precursor, nitric oxide. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 29409–29415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMillan-Crow, L.; Crow, J.P.; Kerby, J.D.; Beckman, J.S.A.; Thompson, J. Nitration and inactivation of manganese superoxide dismutase in chronic rejection of human renal allografts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 11853–11858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campolo, N.; Mastrogiovanni, M.; Mariotti, M.; Issoglio, F.M.; Estrin, D.; Hägglund, P.; Grune, T.; Davies, M.J.; Bartesaghi, S.; Radi, R. Multiple oxidative post-translational modifications of human glutamine synthetase mediate peroxynitrite-dependent enzyme inactivation and aggregation. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 102941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.D.; Carney, J.M.; Starke-Reed, P.E.; Oliver, C.N.; Stadtman, E.R.; Floyd, R.A.; Markesbery, W.R. Excess brain protein oxidation and enzyme dysfunction in normal aging and in Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 10540–10543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malden, D.E.; Mangoni, A.A.; Woodman, R.J.; Thies, F.; McNeil, C.; Murray, A.D.; Soiza, R.L. Circulating asymmetric dimethylarginine and cognitive decline: A 4-year follow-up study of the 1936 Aberdeen Birth Cohort. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2020, 35, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinski, T. Nitric Oxide and Nitroxidative Stress in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2007, 11, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loef, M.; Walach, H. Midlife obesity and dementia: Meta-analysis and adjusted forecast of dementia prevalence in the united states and china. Obesity 2013, 21, E51–E55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelianchik, A.; Sweetland-Martin, L.; Norris, E.H. The effect of dietary fat consumption on Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis in mouse models. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarian, D. Perspective: Obesity—An unexplained epidemic. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 115, 1445–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedin, I.; Cederholm, T.; Levi, Y.F.; Basun, H.; Garlind, A.; Irving, G.F.; Jönhagen, M.E.; Vessby, B.; Wahlund, L.-O.; Palmblad, J. Effects of docosahexaenoic acid–rich n−3 fatty acid supplementation on cytokine release from blood mononuclear leukocytes: The OmegAD study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1616–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, W.C.; Canneva, F.; Partridge, V.; Allard, S.; Ferretti, M.T.; DeWilde, A.; Vercauteren, F.; Atifeh, R.; Ducatenzeiler, A.; Klein, W.; et al. A Novel Transgenic Rat Model with a Full Alzheimer’s-Like Amyloid Pathology Displays Pre-Plaque Intracellular Amyloid-beta-Associated Cognitive Impairment. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 20, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, H.; Cole, S.L.; Logan, S.; Maus, E.; Shao, P.; Craft, J.; Guillozet-Bongaarts, A.; Ohno, M.; Disterhoft, J.; Van Eldik, L.; et al. Intraneuronal β-Amyloid Aggregates, Neurodegeneration, and Neuron Loss in Transgenic Mice with Five Familial Alzheimer’s Disease Mutations: Potential Factors in Amyloid Plaque Formation. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 10129–10140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, E.N.; Carmo, S.D.; Welikovitch, L.A.; Hall, H.; Aguilar, L.F.; Foret, M.K.; Iulita, M.F.; Jia, D.T.; Marks, A.R.; Allard, S.; et al. NP03, a Microdose Lithium Formulation, Blunts Early Amyloid Post-Plaque Neuropathology in McGill-R-Thy1-APP Alzheimer-Like Transgenic Rats. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 73, 723–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Aguilar, L.; Hall, H.; Orciani, C.; Foret, M.K.; Kovecses, O.; Ducatenzeiler, A.; Cuello, A.C. Early loss of locus coeruleus innervation promotes cognitive and neuropathological changes before amyloid plaque deposition in a transgenic rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2022, 48, e12835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orciani, C.; Carmo, S.D.; Foret, M.K.; Hall, H.; Bonomo, Q.; Lavagna, A.; Huang, C.; Cuello, A.C. Early treatment with an M1 and sigma-1 receptor agonist prevents cognitive decline in a transgenic rat model displaying Alzheimer-like amyloid pathology. Neurobiol. Aging 2023, 132, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanzel, C.E.; Pichet-Binette, A.; Pimentel, L.S.; Iulita, M.F.; Allard, S.; Ducatenzeiler, A.; Do Carmo, S.; Cuello, A.C. Neuronal driven pre-plaque inflammation in a transgenic rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 2249–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Tian, L.; Liu, L.; Feng, Y.; Dong, Y.-B.; Li, B.; Shang, D.-S.; Fang, W.-G.; Cao, Y.-P.; Chen, Y.-H. CXCL1 Contributes to β-Amyloid-Induced Transendothelial Migration of Monocytes in Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwarawrah, Y.; Kiernan, K.; MacIver, N.J. Changes in Nutritional Status Impact Immune Cell Metabolism and Function. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zheng, H. Peripheral immune system in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2018, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.S.; Beiser, A.S.; Vasan, R.S.; Roubenoff, R.; Dinarello, C.A.; Harris, T.B.; Benjamin, E.J.; Au, R.; Kiel, D.P.; Wolf, P.A.; et al. Inflammatory markers and the risk of Alzheimer disease: The Framingham Study. Neurology 2007, 68, 1902–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, C. Systemic inflammation and delirium: Important co-factors in the progression of dementia. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batthyány, C.; Bartesaghi, S.; Mastrogiovanni, M.; Lima, A.; Demicheli, V.; Radi, R. Tyrosine-Nitrated Proteins: Proteomic and Bioanalytical Aspects. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 26, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adami, P.V.M.; Galeano, P.; Wallinger, M.L.; Quijano, C.; Rabossi, A.; Pagano, E.S.; Olivar, N.; Toso, C.R.; Cardinali, D.; Brusco, L.I.; et al. Worsening of memory deficit induced by energy-dense diet in a rat model of early-Alzheimer’s disease is associated to neurotoxic Aβ species and independent of neuroinflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, P.G.; Nielsen, F.H.; Fahey, G.C., Jr. AIN-93 Purified Diets for Laboratory Rodents: Final Report of the American Institute of Nutrition Ad Hoc Writing Committee on the Reformulation of the AIN-76A Rodent Diet. J. Nutr. 1993, 123, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihedioha, J.I.; Noel-Uneke, O.A.; Ihedioha, T.E. Reference values for the serum lipid profile of albino rats (Rattus norvegicus) of varied ages and sexes. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2013, 22, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariri, N.; Thibault, L. High-fat diet-induced obesity in animal models. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2010, 23, 270–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speakman, J.R. Use of high-fat diets to study rodent obesity as a model of human obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 1491–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viggiano, E.; Mollica, M.P.; Lionetti, L.; Cavaliere, G.; Trinchese, G.; De Filippo, C.; Chieffi, S.; Gaita, M.; Barletta, A.; De Luca, B.; et al. Effects of an High-Fat Diet Enriched in Lard or in Fish Oil on the Hypothalamic Amp-Activated Protein Kinase and Inflammatory Mediators. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beynen, A.C.; Katan, M.B. Why do polyunsaturated fatty acids lower serum cholesterol? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1985, 42, 560–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnuolo, M.S.; Iossa, S.; Cigliano, L. Sweet but Bitter: Focus on Fructose Impact on Brain Function in Rodent Models. Nutrients 2020, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beilharz, J.E.; Maniam, J.; Morris, M.J. Short exposure to a diet rich in both fat and sugar or sugar alone impairs place, but not object recognition memory in rats. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2014, 37, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, S.A.; Yamada, K.A.; Butterfield, D.A.; Abdul, H.M.; Xu, L.; Miller, N.E.; Banks, W.A.; Morley, J.E. Obesity and Hypertriglyceridemia Produce Cognitive Impairment. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 2628–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granholm, A.-C.; Bimonte-Nelson, H.A.; Moore, A.B.; Nelson, M.E.; Freeman, L.R.; Sambamurti, K. Effects of a Saturated Fat and High Cholesterol Diet on Memory and Hippocampal Morphology in the Middle-Aged Rat. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2008, 14, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, C.E.; Winocur, G. High-fat diets, insulin resistance and declining cognitive function. Neurobiol. Aging 2005, 26, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molteni, R.; Barnard, R.; Ying, Z.; Roberts, C.; Gómez-Pinilla, F. A high-fat, refined sugar diet reduces hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor, neuronal plasticity, and learning. Neuroscience 2002, 112, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancani, T.; Anderson, K.L.; Brewer, L.D.; Kadish, I.; DeMoll, C.; Landfield, P.W.; Blalock, E.M.; Porter, N.M.; Thibault, O. Effect of high-fat diet on metabolic indices, cognition, and neuronal physiology in aging F344 rats. Neurobiol. Aging 2013, 34, 1977–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stranahan, A.M.; Norman, E.D.; Lee, K.; Cutler, R.G.; Telljohann, R.S.; Egan, J.M.; Mattson, M.P. Diet-induced insulin resistance impairs hippocampal synaptic plasticity and cognition in middle-aged rats. Hippocampus 2008, 18, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemens, D.; Touma, C.; Rappeneau, V. Neurobiological Mechanisms Modulating Emotionality, Cognition and Reward-Related Behaviour in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rodents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadry, H.; Noorani, B.; Cucullo, L. A blood–brain barrier overview on structure, function, impairment, and biomarkers of integrity. Fluids Barriers CNS 2020, 17, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, B.E.; Silverman, H.A.; Robbiati, S.; Gunasekaran, M.K.; Tsaava, T.; Battinelli, E.; Stiegler, A.; Bouton, C.E.; Chavan, S.S.; Tracey, K.J.; et al. Cytokine-specific Neurograms in the Sensory Vagus Nerve. Bioelectron. Med. 2016, 3, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maesako, M.; Uemura, M.; Tashiro, Y.; Sasaki, K.; Watanabe, K.; Noda, Y.; Ueda, K.; Asada-Utsugi, M.; Kubota, M.; Okawa, K.; et al. High Fat Diet Enhances β-Site Cleavage of Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP) via Promoting β-Site APP Cleaving Enzyme 1/Adaptor Protein 2/Clathrin Complex Formation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refolo, L.M.; Pappolla, M.A.; Malestera, B.; LaFrancois, J.; Bryant-Thomas, T.; Wangc, R.; Tintd, G.S.; Sambamurtie, K.; Duff, K. Hypercholesterolemia Accelerates the Alzheimer’s Amyloid Pathology in a Transgenic Mouse Model. Neurobiol. Dis. 2000, 7, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jekabsone, A.; Mander, P.K.; Tickler, A.; Sharpe, M.; Brown, G.C. Fibrillar beta-amyloid peptide Abeta1–40 activates microglial proliferation via stimulating TNF-alpha release and H2O2 derived from NADPH oxidase: A cell culture study. J. Neuroinflammation 2006, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, E.N.; Carmo, S.D.; Iulita, M.F.; Hall, H.; Austin, G.L.; Jia, D.T.; Malcolm, J.C.; Foret, M.K.; Marks, A.R.; Butterfield, D.A.; et al. Microdose Lithium NP03 Diminishes Pre-Plaque Oxidative Damage and Neuroinflammation in a Rat Model of Alzheimer’s-like Amyloidosis. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2018, 15, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasko, I.; Ransmayr, G.; Veerhuis, R.; Eikelenboom, P.; Grubeck-Loebenstein, B. Does IFNγ play a role in neurodegeneration? J. Neuroimmunol. 2001, 116, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Zhao, Y.-F.; Zhu, S.-W.; Huang, W.-J.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Ge, L.-J.; Li, R.-S.; Wang, J.-F.; Sun, M.; et al. CXCL1 Triggers Caspase-3 Dependent Tau Cleavage in Long-Term Neuronal Cultures and in the Hippocampus of Aged Mice: Implications in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 48, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeano, P.; Calvo, E.B.; de Oliveira, D.M.; Cuenya, L.; Kamenetzky, G.V.; Mustaca, A.E.; Barreto, G.E.; Giraldez-Alvarez, L.D.; Milei, J.; Capani, F. Long-lasting effects of perinatal asphyxia on exploration, memory and incentive downshift. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2011, 29, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeano, P.; Adami, P.V.M.; Carmo, S.D.; Blanco, E.; Rotondaro, C.; Capani, F.; Castaño, E.M.; Cuello, A.C.; Morelli, L. Longitudinal analysis of the behavioral phenotype in a novel transgenic rat model of early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mañas-Padilla, M.C.; Gil-Rodríguez, S.; Sampedro-Piquero, P.; Ávila-Gámiz, F.; de Fonseca, F.R.; Santín, L.J.; Castilla-Ortega, E. Remote memory of drug experiences coexists with cognitive decline and abnormal adult neurogenesis in an animal model of cocaine-altered cognition. Addict. Biol. 2021, 26, e12886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, S.M.; Ducatenzeiler, A.; Szyf, M.; Cuello, A.C. Abeta Immunoreactive Material Is Present in Several Intracellular Compartments in Transfected, Neuronally Differentiated, P19 Cells Expressing the Human Amyloid beta-Protein Precursor. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2000, 2, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Paxinos, G.; Franklin, K.B.J. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Gamon, L.F.; Guo, C.; He, J.; Hägglund, P.; Hawkins, C.L.; Davies, M.J. Absolute quantitative analysis of intact and oxidized amino acids by LC-MS without prior derivatization. Redox Biol. 2020, 36, 101586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, S.J.; Shen, Z.; Fu, X.; Levison, B.S.; Hazen, S.L. Quantification of 3-nitrotyrosine levels using a benchtop ion trap mass spectrometry method. Methods Enzymol. 2005, 396, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galeano, P.; de Ceglia, M.; Mastrogiovanni, M.; Campanelli, L.; Medina-Vera, D.; Campolo, N.; Novack, G.V.; Rosell-Valle, C.; Suárez, J.; Aicardo, A.; et al. The Effect of Fat Intake with Increased Omega-6-to-Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Ratio in Animal Models of Early and Late Alzheimer’s Disease-like Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242317009
Galeano P, de Ceglia M, Mastrogiovanni M, Campanelli L, Medina-Vera D, Campolo N, Novack GV, Rosell-Valle C, Suárez J, Aicardo A, et al. The Effect of Fat Intake with Increased Omega-6-to-Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Ratio in Animal Models of Early and Late Alzheimer’s Disease-like Pathogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(23):17009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242317009
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaleano, Pablo, Marialuisa de Ceglia, Mauricio Mastrogiovanni, Lorenzo Campanelli, Dina Medina-Vera, Nicolás Campolo, Gisela V. Novack, Cristina Rosell-Valle, Juan Suárez, Adrián Aicardo, and et al. 2023. "The Effect of Fat Intake with Increased Omega-6-to-Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Ratio in Animal Models of Early and Late Alzheimer’s Disease-like Pathogenesis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 23: 17009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242317009
APA StyleGaleano, P., de Ceglia, M., Mastrogiovanni, M., Campanelli, L., Medina-Vera, D., Campolo, N., Novack, G. V., Rosell-Valle, C., Suárez, J., Aicardo, A., Campuzano, K., Castaño, E. M., Do Carmo, S., Cuello, A. C., Bartesaghi, S., Radi, R., Rodríguez de Fonseca, F., & Morelli, L. (2023). The Effect of Fat Intake with Increased Omega-6-to-Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Ratio in Animal Models of Early and Late Alzheimer’s Disease-like Pathogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(23), 17009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242317009








