Abstract
Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) is a potentially life-threatening systemic small-vessel vasculitis that is characterized by pauci-immune glomerulonephritis in case of kidney involvement, representing a major denominator of AAV mortality. Innate immunity with complement system activation is increasingly recognized in the pathogenesis of AAV and as an attractive therapeutic target. Although C-reactive protein (CRP) was thought to be a passive, nonspecific marker of inflammation, recent studies indicate that CRP plays a key role in the innate immune system by recognizing pathogens and altered self-determinants. Elevated baseline CRP at disease onset of AAV has already been described as a determinant of poor long-term outcomes. However, its clinical implications at disease onset of AAV, with respect to vasculitis manifestations and complement system activation that might also affect long-term outcomes, remain elusive. CRP levels were retrospectively analyzed in 53 kidney-biopsy-confirmed cases of ANCA-associated renal vasculitis; a total of 138 disease controls were also evaluated. Univariate and multivariate regression analysis was performed on clinicopathological parameters associated with CRP levels in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis. Results: Compared to disease controls, CRP elevation was common in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis and associated with de novo disease (p = 0.0169), critical illness (p = 0.0346), and severe deterioration of kidney function (p = 0.0167), independent of extrarenal disease manifestations. As confirmed by multiple regression analysis, CRP levels were correlated with active lesions predominated by interstitial arteritis in renal vasculitis, specifically with MPO-ANCA seropositivity (p = 0.0017). Based on analysis of systemic complement system activation and intrarenal complement deposits, CRP elevation was correlated specifically with complement C4 deposits in interstitial arteries in the subgroup with myeloperoxidase (MPO)-ANCA seropositivity (p = 0.039). Finally, this association was independent of systemic complement system activation, as reflected by the consumption of respective complement components. Here, we expand our current understanding of CRP in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis not only as an inflammatory marker, but potentially also as being involved in the pathogenesis of kidney injury by interaction with the complement system.
1. Introduction
Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) is a potentially life-threatening systemic small-vessel vasculitis that is characterized by pauci-immune glomerulonephritis in case of kidney involvement, representing a major denominator of AAV mortality [1,2,3,4]. Two principal antigens on neutrophils—namely, proteinase 3 (PR3) and myeloperoxidase (MPO)—provide epitopes for ANCA binding, promoting endothelial damage and vascular inflammation, culminating in necrotizing vasculitis [5,6,7]. Innate immunity with complement system activation is increasingly recognized in the pathogenesis of AAV and as an attractive therapeutic target [8,9]. Although C-reactive protein (CRP) was thought to be a passive, nonspecific marker of inflammation, recent studies indicate that CRP plays a key role in the innate immune system by recognizing pathogens and altered self-determinants [10,11]. CRP is synthesized by the liver in response to pro-inflammatory cytokines during acute inflammation and is capable of activating the classical pathway of the complement system [12,13,14]. CRP primarily binds to phosphocholine-containing molecules, and CRP–phosphocholine complexes activate the classical pathway of the complement system [15,16,17,18,19,20]. Elevated baseline CRP at disease onset of AAV has already been described as a determinant of poor long-term outcomes [21,22,23,24]. However, its clinical implications at disease onset of AAV, with respect to vasculitis manifestations and complement system activation that might also affect long-term outcomes, remain elusive. Therefore, in this study, we aimed to systematically describe clinicopathological findings associated with baseline CRP levels at disease onset of AAV in kidney-biopsy-confirmed severe ANCA-associated renal vasculitis.
2. Results
2.1. CRP Elevation Was Associated with Active ANCA-Associated Renal Vasculitis Independent of Extrarenal Disease Manifestations
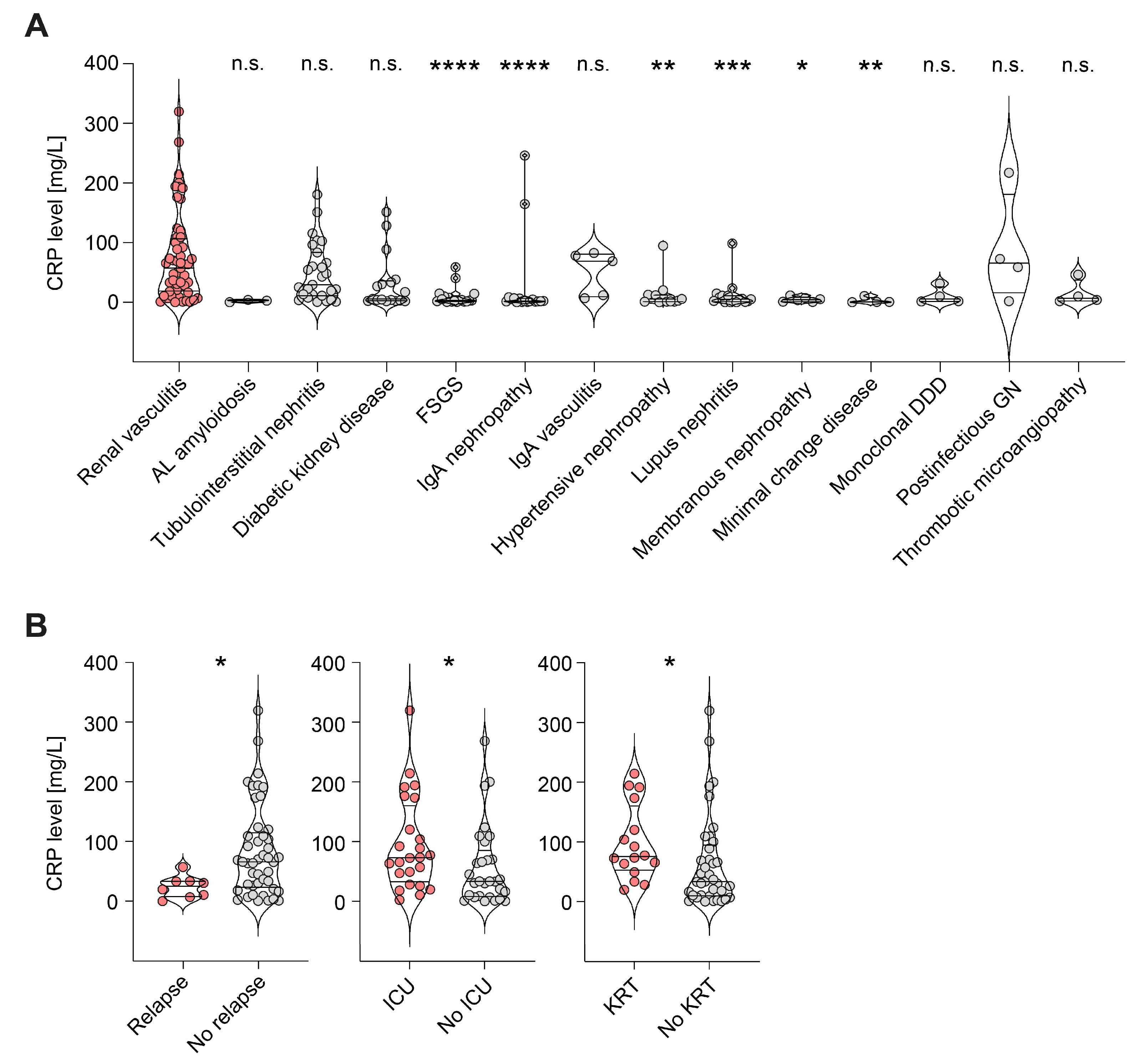
We first compared CRP levels at admission in a total of 53 patients with kidney-biopsy-confirmed ANCA-associated renal vasculitis, along with 138 disease controls. CRP levels were significantly elevated in renal vasculitis compared to focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS, p < 0.0001), immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy (p < 0.0001), hypertensive nephropathy (p = 0.0025), lupus nephritis (p = 0.0003), membranous nephropathy (p = 0.0231), and minimal change disease (p = 0.0067, Figure 1A). In contrast, AL amyloidosis (p = 0.0588), tubulointerstitial nephritis (p > 0.9999), diabetic kidney disease (p = 0.2425), IgA vasculitis (p > 0.9999), monoclonal dense deposit disease (DDD, p = 0.4730), post-infectious glomerulonephritis (GN, p > 0.9999), and thrombotic microangiopathy (p > 0.9999) presented CRP elevation that was not significantly different from that of renal vasculitis (Figure 1A). The relevance of CRP levels was confirmed by elevation in de novo disease (p = 0.0169), critical illness with requirement of intensive care unit treatment (p = 0.0346), and severe deterioration of kidney function requiring kidney replacement therapy (KRT, p = 0.0167, Figure 1B). Interestingly, there were no significant differences in CRP levels with respect to extrarenal AAV manifestations (Table 1), indicating that CRP elevation was predominantly correlated with kidney involvement. In summary, CRP elevation was common in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis and associated with de novo disease, critical illness, and severe deterioration of kidney function, independent of extrarenal disease manifestations.

Figure 1.
CRP elevation is associated with active ANCA-associated renal vasculitis: (A) Violin plots and individual data points for CRP levels are shown in renal vasculitis (n = 53) and disease controls, including AL amyloidosis (n = 3), tubulointerstitial nephritis (n = 27), diabetic kidney disease (n = 17), FSGS (n = 18), IgA nephropathy (n = 17), IgA vasculitis (n = 5), hypertensive nephropathy (n = 13), lupus nephritis (n = 16), membranous nephropathy (n = 6), minimal change disease (n = 4), monoclonal DDD (n = 4), post-infectious GN (n = 4), and thrombotic microangiopathy (n = 4). The Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple correction was performed for group comparisons (n.s. = not significant, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001). (B) CRP levels after group separations according to relapsing disease, requirement of ICU supportive care, and KRT. Group comparisons were performed with the Mann–Whitney U-test (* p < 0.05). Abbreviations: ANCA, anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; CRP, C-reactive protein; FSGS, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis; IgA, immunoglobulin A; DDD, dense deposit disease; GN, glomerulonephritis; ICU, intensive care unit; KRT, kidney replacement therapy.

Table 1.
CRP levels after group separation by extrarenal manifestations of AAV.
2.2. CRP Levels Were Correlated with Active Glomerular and Tubulointerstitial Renal Vasculitis with MPO-ANCA Seropositivity
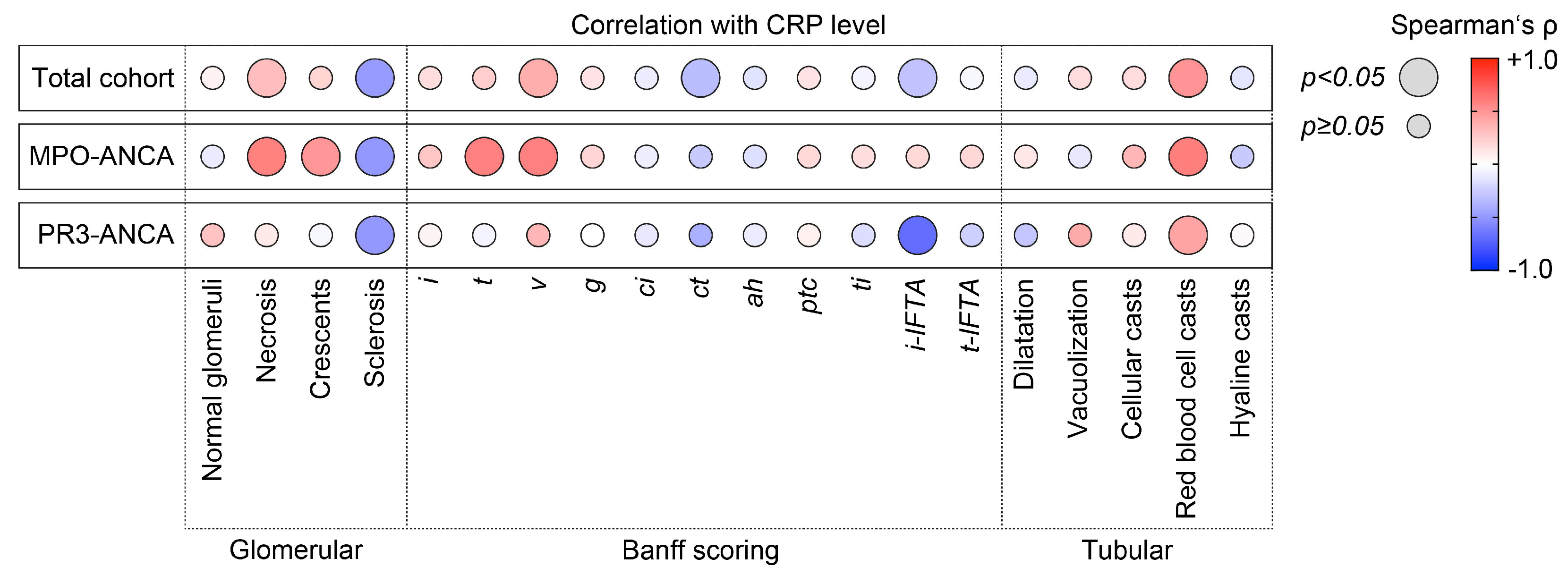
Based on our observation that elevated levels of CRP were correlated with deterioration of kidney function, we next analyzed active and chronic intrarenal lesions in association with CRP levels in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis. In the total cohort, CRP levels were positively correlated with glomerular necrosis (Spearman’s ρ = +0.32, p = 0.0212), interstitial arteritis v (ρ = +0.39, p = 0.0111), and red blood cell casts (ρ = +0.50, p = 0.0003, Figure 2). Interestingly, this association between CRP levels and active glomerular and tubulointerstitial renal vasculitis was only detectable in the subgroup with MPO-ANCA seropositivity (glomerular necrosis: ρ = +0.58, p = 0.002, crescents: ρ = +0.49, p = 0.0103, tubulitis t: ρ = +0.59, p = 0.002, interstitial arteritis v: ρ = +0.59, p = 0.0067, red blood cell casts: ρ = +0.59, p = 0.0018, Figure 2). Multiple regression analysis confirmed that interstitial arteritis v was the predominant variable associated with levels of CRP in MPO-ANCA-associated renal vasculitis (ß = +0.66, p = 0.0017, Table 2). Except for red blood cell casts (ρ = +0.43, p = 0.0429), none of these lesions were correlated with levels of CRP in the subgroup with PR3-ANCA seropositivity (Figure 2). In summary, CRP levels were correlated with active lesions predominated by interstitial arteritis in renal vasculitis, specifically with MPO-ANCA seropositivity.
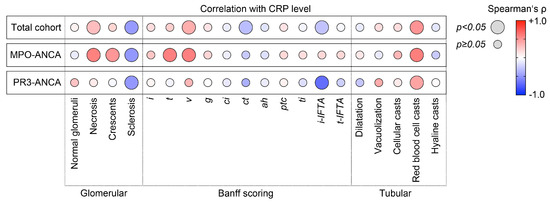
Figure 2.
CRP elevation is correlated with complement C4 deposits in interstitial arteries in MPO-ANCA-associated renal vasculitis. Correlations between CRP levels, serum C3 and C4 measurements, and intrarenal complement C3 and C4 deposits localized to different vascular compartments in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis are shown by heatmaps reflecting the mean values of Spearman’s ρ; circle size represents the significance level.

Table 2.
Multiple linear regression analyses correlating with CRP levels in MPO-ANCA-associated renal vasculitis.
2.3. CRP Elevation Was Correlated with Complement C4 Deposits in Interstitial Arteries in MPO-ANCA-Associated Renal Vasculitis
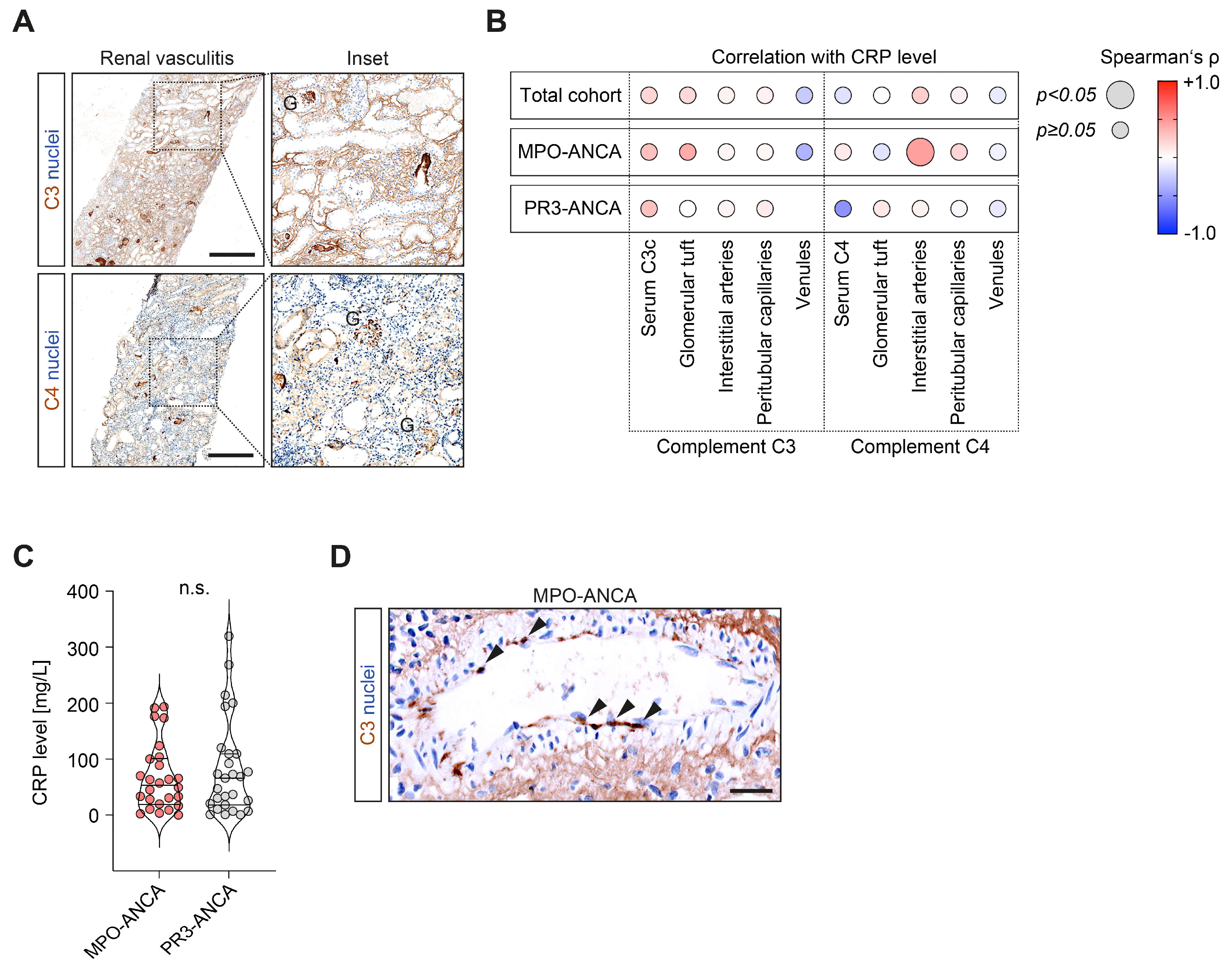
Based on our observation that elevated CRP levels were correlated with active glomerular and tubulointerstitial renal vasculitis, we finally analyzed their association with systemic complement system activation and intrarenal complement deposits (Figure 3A). We did not observe any association between CRP levels and systemic complement system activation reflected by serum C3c and C4 measurements (Figure 3B). Among intrarenal complement deposits, the only significant correlation was observed between CRP elevation and complement C4 deposits in interstitial arteries, specifically in the subgroup with MPO-ANCA seropositivity (ρ = +0.45, p = 0.039, Figure 3B,C). This observation was not attributed to significant differences in complement C4 deposits between MPO-ANCA and PR3-ANCA seropositivity per se (Table 3). In summary, CRP elevation was correlated with interstitial arteritis along with complement C4 deposits in interstitial arteries, specifically in the subgroup with MPO-ANCA seropositivity. Furthermore, this association was independent of systemic complement system activation, as reflected by the consumption of respective complement components.

Figure 3.
CRP elevation is correlated with complement C4 deposits in interstitial arteries in MPO-ANCA-associated renal vasculitis: (A) Immunostainings for intrarenal complement C3 and C4 deposits, with insets; positive glomeruli (G) are indicated (scale bars: 500 µm). (B) Correlations between CRP levels, serum C3 and C4 measurements, and intrarenal complement C3 and C4 deposits localized to different vascular compartments in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis, as shown by heatmaps reflecting the mean values of Spearman’s ρ; circle size represents the significance level. (C) CRP levels after group separations according to ANCA subtypes. Group comparisons were performed with the Mann–Whitney U-test (n.s. = not significant). (D) Representative immunostaining for intrarenal complement C4 deposits in interstitial arteries in the subgroup with MPO-ANCA seropositivity; arrowheads indicate endothelial cells positive for complement C4 (scale bar: 25 µm). Abbreviations: ANCA, anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; CRP, C-reactive protein; G, glomerulus; MPO, myeloperoxidase; PR3, proteinase 3.

Table 3.
Complement C3 and C4 deposits in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis separated by MPO-ANCA and PR3-ANCA seropositivity.
3. Discussion
CRP is part of the innate immunity involved in nonspecific opsonization and neutralization of antigens, in contrast to the antigen-specific adaptive/acquired immunity maintained by antibodies [25]. While elevated baseline CRP at disease onset of AAV has already been described as a determinant of poor long-term outcomes, its clinical implications at disease onset of AAV with respect to vasculitis manifestations and complement system activation remain elusive [21,22,23,24]. Therefore, in this study, we aimed to systematically describe clinicopathological findings in association with baseline CRP levels at disease onset of AAV in kidney-biopsy-confirmed severe ANCA-associated renal vasculitis. Baseline CRP elevation was common in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis and associated with de novo disease, critical illness, and severe deterioration of kidney function. This is especially relevant because a higher initial mortality rate of critically ill patients within the first hospital stay was observed, while the long-term mortality of hospital survivors did not differ between the ICU and non-ICU groups [26]. Regarding the kidneys, severe renal dysfunction has already been associated with poor long-term outcomes in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis [2]. Our observation that we did not find any association between CRP levels at AAV onset and extrarenal disease manifestations further supports the predominant role of CRP levels in severe kidney involvement. Furthermore, we found that CRP levels were correlated with active lesions predominated by interstitial arteritis in renal vasculitis, specifically with MPO-ANCA seropositivity. We and others have recently described how interstitial arteritis represents a subtype of ANCA-associated renal vasculitis affecting a considerable subset of patients [27,28]. In addition, the presence of interstitial arteritis was associated with poor long-term renal outcomes and significantly increased the risk prediction by established scoring systems [28,29]. Interestingly, our observations confirm those of previous reports that the presence of interstitial arteritis was correlated with higher levels of CRP [28]. Our observation that CRP elevation was also correlated with complement C4 deposits in interstitial arteries could therefore further improve our current understanding of the underlying mechanisms contributing to interstitial arteritis in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis.
Regarding the complement system, CRP can bind to the C1q globular recognition domain to activate the classical complement pathway, as well as to ficolins, mannose-binding lectins, and factor H to regulate the alternative and lectin-dependent complement pathways [25]. In kidney allografts, previous studies suggested that CRP can mediate complement activation in vivo [30]. In terms of distinct complement components, C3 is critical for activation of the complement system as a whole, while C4 is the major protein of the classical cascade [31]. Anaphylatoxin C3a stimulates inflammation by inducing an oxidative burst in macrophages, eosinophils, and neutrophils [32,33,34]. Furthermore, C3a and C5a directly activate basophils and mast cells, resulting in histamine production [35,36]. Although the pro-inflammatory effects of C3a are not in question, studies have also highlighted the anti-inflammatory role of C3a in different contexts [37]. Migration of neutrophils and degranulation are prevented in the presence of anaphylatoxin C3a, regardless of whether other granulocytes are activated by C3a [38,39]. The C4 activation product C4a has also been shown to exert a functional activity on macrophages and monocytes [40,41]. Because no C4a receptor has yet been reported, the physiological role of anaphylatoxin C4a and its contribution to autoimmune diseases such as AAV remain elusive [42]. On a mechanistic level, the ability of CRP to activate the complement system is by binding to an appropriate ligand, such as complement C4 [12,19]. We found that this association between CRP elevation, interstitial arteritis, and corresponding complement C4 deposits was specifically present in the subgroup with MPO-ANCA seropositivity. In this context, specific binding of CRP to MPO (and not PR3) has already been described and experimentally linked to complement system activation [43]. In addition, CRP is capable of stimulating the release of MPO in vitro and in vivo [44]. These findings might indicate a pathomechanistic link between MPO seropositivity and CRP in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis. The alternative pathway plays a predominant role in AAV pathogenesis, and it has already been reported that alternative pathway activation of the complement system requires the presence of C4 [45,46,47,48]. We have previously shown that intrarenal complement deposits were not associated with corresponding consumption of serum levels, supporting the concept of intrarenal synthesis of distinct complement system components [49,50]. Therefore, this study expands our current understanding of CRP in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis not only as an inflammatory marker, but also as potentially being involved in the pathogenesis of kidney injury by interaction with the complement system, and possibly local complement synthesis in the kidney. This is especially relevant because targeted therapies to block complement system activation in AAV are currently emerging.
Our study has several limitations, such as the small number of patients and the retrospective study design. Furthermore, our observations are associative and do not prove causality, which would require mechanistic studies. Nevertheless, this study provides a clinically approached link between CRP elevation, complement C4 deposits, and interstitial arteritis limited to MPO-ANCA-associated renal vasculitis, thereby broadening our current pathophysiological understanding.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population and Subgroup Formation
A cohort of 53 kidney-biopsy-confirmed cases of ANCA-associated renal vasculitis was retrospectively enrolled between 2015 and 2020 in a single-center observational study at the University Medical Center Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany [51,52,53,54,55]. In addition, a total of 138 disease controls—including AL amyloidosis, tubulointerstitial nephritis, diabetic kidney disease, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy, IgA vasculitis, hypertensive nephropathy, lupus nephritis, membranous nephropathy, minimal change disease, monoclonal dense deposit disease (DDD), post-infectious glomerulonephritis (GN), and thrombotic microangiopathy—were also evaluated. While no formal approval was required for the use of routine clinical data, a favorable ethical opinion was granted by the local ethics committee (no. 22 February 2014 and 28 September 2017). All participants provided their written informed consent for the utilization of routinely collected data for research purposes as part of their regular medical care. Medical records were used to collect data on age, sex, medication, comorbidities, and laboratory findings, including baseline CRP at the time of kidney biopsy.
4.2. ANCA Autoantibody and Complement Measurements
MPO-ANCA (reference range: <3.5 IU/mL) and PR3-ANCA autoantibodies (reference range: <2 IU/mL) were measured by immunoassay (ImmunoCAP 250, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Plasma concentrations of human complement components C3c (9D9621, Abbott, Chicago, IL, USA) and C4 (9D9721, Abbott, Chicago, IL, USA) were determined by turbidimetric measurements on the ARCHITECT-C module. Reference range plasma concentrations for circulating C3c and C4 were defined at 0.82–1.93 g/L and 0.15–0.57 g/L, respectively.
4.3. Renal Histopathology
A renal pathologist evaluated all kidney biopsies and was blinded to the clinical data analysis. Based on the current version of the Banff scoring system for renal allograft pathology, tubulointerstitial lesions were scored as previously reported: arteriolar hyalinosis (ah), arteritis (v), glomerulitis (g), inflammation in areas of interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (i-IFTA), interstitial fibrosis (ci), interstitial inflammation (i), peritubular capillaritis (ptc), total inflammation (ti), tubular atrophy (ct), tubulitis (t), and tubulitis in areas of interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (t-IFTA) [56,57]. Tubular injury lesions were systematically assessed as recently described in [58]. Briefly, tubular dilation, tubular necrosis, epithelial simplification, non-isometric cell vacuolization, and red blood cell (RBC) and necrotic casts were scored in a range from 0 to 4, depending on the fraction of affected cortical area of renal biopsy (score 0: <1%, 1: ≥1–10%, 2: ≥10–25%, 3: ≥25–50%, 4: >50%). Moreover, all injured glomeruli (crescentic and/or necrotic) were screened for the presence of a Bowman’s capsule rupture, the extent of which was further quantified as previously described in [59,60,61].
4.4. C3c and C4d Immunohistochemistry
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded kidney sections were deparaffinized in xylene and rehydrated in ethanol containing distilled water. Tissue sections were stained using antibodies against C3c (1:10,000, A0062, Agilent Dako, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and C4d (1:50, 503-17344, Zytomed, Berlin, Germany), and labeling was performed using the NovolinkTM Polymer Detection System (Leica Biosystems, Wetzlar, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Nuclear counterstaining was performed by using Mayer’s Hematoxylin Solution (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA). As previously described, kidney biopsies were evaluated for the presence/absence of C3c and C4d deposits in the glomerular tuft, interlobular arteries, peritubular capillaries, and venules [49,50].
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Normal distribution was evaluated using the Shapiro–Wilk test; statistical comparisons were not formally powered or pre-specified. Probability values (p-values) below 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant. Parameters are shown as the median and interquartile range (IQR); median comparisons were performed with the Mann–Whitney U-test. Heatmaps reflect the mean values of Spearman’s ρ in the univariate linear regression analysis; circle size represents the significance level. For stepwise multiple linear regression, covariates were retained to significant differences in the linear regression model to avoid model overfitting. Data analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism (version 9.4.1 for MacOS, GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA) and IBM SPSS Statistics (version 28.0.1.1 for MacOS, IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA).
5. Conclusions
This study expands our current understanding of CRP in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis not only as an inflammatory marker, but also as potentially being involved in the pathogenesis of kidney injury by interaction with the complement system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.T.; methodology, P.K. and B.T.; software, B.T.; validation, B.T.; formal analysis, P.K., E.B., S.H. and B.T.; investigation, P.K., E.B., S.H. and B.T.; resources, B.T.; data curation, P.K., E.B., S.H. and B.T.; writing—original draft preparation, B.T.; writing—review and editing, P.K., E.B. and S.H.; visualization, B.T.; supervision, B.T.; project administration, B.T.; funding acquisition, E.B. and B.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Else-Kröner research program entitled “molecular therapy and prediction of gastrointestinal malignancies”, grant number 7-67-1840876. We also acknowledge support by the Open Access Publication Funds of Göttingen University. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University Medical Center Göttingen, Germany (protocol code: 22/2/14, approval date 22 September 2014; and 28/09/17, approval date 17 November 2017).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent for participation was not required for this study, in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article; further data and materials are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jennette, J.C.; Nachman, P.H. ANCA Glomerulonephritis and Vasculitis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 1680–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.; Gasim, A.; Derebail, V.K.; Chung, Y.; McGregor, J.G.; Lionaki, S.; Poulton, C.J.; Hogan, S.L.; Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; et al. Predictors of treatment outcomes in ANCA-associated vasculitis with severe kidney failure. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennette, J.C.; Wilkman, A.S.; Falk, R.J. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated glomerulonephritis and vasculitis. Am. J. Pathol. 1989, 135, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flossmann, O.; Berden, A.; de Groot, K.; Hagen, C.; Harper, L.; Heijl, C.; Hoglund, P.; Jayne, D.; Luqmani, R.; Mahr, A.; et al. Long-term patient survival in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Kronbichler, A.; Park, D.D.; Park, Y.; Moon, H.; Kim, H.; Choi, J.H.; Choi, Y.; Shim, S.; Lyu, I.S.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in autoimmune diseases: A comprehensive review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 1160–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelot, J.M.; Le Goff, B.; Neel, A.; Maugars, Y.; Hamidou, M. NETosis: At the crossroads of rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and vasculitis. Joint Bone Spine 2017, 84, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangou, E.; Vassilopoulos, D.; Boletis, J.; Boumpas, D.T. An emerging role of neutrophils and NETosis in chronic inflammation and fibrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and ANCA-associated vasculitides (AAV): Implications for the pathogenesis and treatment. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimoto, Y.; Horiuchi, T. The Complement System and ANCA Associated Vasculitis in the Era of Anti-Complement Drugs. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 926044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesar, V.; Hruskova, Z. Complement Inhibition in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 888816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peisajovich, A.; Marnell, L.; Mold, C.; Du Clos, T.W. C-reactive protein at the interface between innate immunity and inflammation. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 4, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.; Agrawal, A. Evolution of C-Reactive Protein. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mold, C.; Gewurz, H.; Du Clos, T.W. Regulation of complement activation by C-reactive protein. Immunopharmacology 1999, 42, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Ngwa, D.N.; Agrawal, A. Complement Activation by C-Reactive Protein Is Critical for Protection of Mice against Pneumococcal Infection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, M.V.; Singh, S.K.; Ferguson, D.A., Jr.; Agrawal, A. Role of the property of C-reactive protein to activate the classical pathway of complement in protecting mice from pneumococcal infection. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 4369–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrive, A.K.; Cheetham, G.M.; Holden, D.; Myles, D.A.; Turnell, W.G.; Volanakis, J.E.; Pepys, M.B.; Bloomer, A.C.; Greenhough, T.J. Three dimensional structure of human C-reactive protein. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1996, 3, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, D.; Pepys, M.B.; Wood, S.P. The physiological structure of human C-reactive protein and its complex with phosphocholine. Structure 1999, 7, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillett, W.S.; Francis, T. Serological Reactions in Pneumonia with a Non-Protein Somatic Fraction of Pneumococcus. J. Exp. Med. 1930, 52, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volanakis, J.E.; Kaplan, M.H. Specificity of C-reactive protein for choline phosphate residues of pneumococcal C-polysaccharide. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1971, 136, 612–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, M.H.; Volanakis, J.E. Interaction of C-reactive protein complexes with the complement system. I. Consumption of human complement associated with the reaction of C-reactive protein with pneumococcal C-polysaccharide and with the choline phosphatides, lecithin and sphingomyelin. J. Immunol. 1974, 112, 2135–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haapasalo, K.; Meri, S. Regulation of the Complement System by Pentraxins. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.S.; Ahn, S.S.; Park, Y.B.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, S.W. C-Reactive Protein to Serum Albumin Ratio Is an Independent Predictor of All-Cause Mortality in Patients with ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. Yonsei Med. J. 2018, 59, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, N.; Yin, H.; Duan, L. Relationship between C-Reactive Protein/Serum Albumin Ratio, Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio, and ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Activity: A Retrospective Single Center Cohort Study. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 855869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGovern, D.; Williams, S.P.; Parsons, K.; Farrah, T.E.; Gallacher, P.J.; Miller-Hodges, E.; Kluth, D.C.; Hunter, R.W.; Dhaun, N. Long-term outcomes in elderly patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.L.; Liang, Q.H.; Huang, B.T.; Ding, N.; Li, B.W.; Hao, J. The plasma level of mCRP is linked to cardiovascular disease in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lech, M.; Rommele, C.; Anders, H.J. Pentraxins in nephrology: C-reactive protein, serum amyloid P and pentraxin-3. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demiselle, J.; Auchabie, J.; Beloncle, F.; Gatault, P.; Grange, S.; Du Cheyron, D.; Dellamonica, J.; Boyer, S.; Beauport, D.T.; Piquilloud, L.; et al. Patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis admitted to the intensive care unit with acute vasculitis manifestations: A retrospective and comparative multicentric study. Ann. Intensive Care 2017, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakroush, S.; Tampe, B. Incidence of Arteritis and Peritubular Capillaritis in ANCA-associated Vasculitis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 2974–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudhabhay, I.; Delestre, F.; Coutance, G.; Gnemmi, V.; Quemeneur, T.; Vandenbussche, C.; Lazareth, H.; Canaud, G.; Tricot, L.; Gosset, C.; et al. Reappraisal of Renal Arteritis in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: Clinical Characteristics, Pathology, and Outcome. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 2362–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, S.R.; Noriega, M.; Tennstedt, P.; Vettorazzi, E.; Busch, M.; Nitschke, M.; Jabs, W.J.; Ozcan, F.; Wendt, R.; Hausberg, M.; et al. Development and validation of a renal risk score in ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolbink, G.J.; Brouwer, M.C.; Buysmann, S.; ten Berge, I.J.; Hack, C.E. CRP-mediated activation of complement in vivo: Assessment by measuring circulating complement-C-reactive protein complexes. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasperska-Zajac, A.; Grzanka, A.; Machura, E.; Misiolek, M.; Mazur, B.; Jochem, J. Increased serum complement C3 and C4 concentrations and their relation to severity of chronic spontaneous urticaria and CRP concentration. J. Inflamm. 2013, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Imamichi, T.; Nagasawa, S. Characterization of C3a anaphylatoxin receptor on guinea-pig macrophages. Immunology 1993, 79, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elsner, J.; Oppermann, M.; Czech, W.; Kapp, A. C3a activates the respiratory burst in human polymorphonuclear neutrophilic leukocytes via pertussis toxin-sensitive G-proteins. Blood 1994, 83, 3324–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsner, J.; Oppermann, M.; Czech, W.; Dobos, G.; Schopf, E.; Norgauer, J.; Kapp, A. C3a activates reactive oxygen radical species production and intracellular calcium transients in human eosinophils. Eur. J. Immunol. 1994, 24, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretzschmar, T.; Jeromin, A.; Gietz, C.; Bautsch, W.; Klos, A.; Kohl, J.; Rechkemmer, G.; Bitter-Suermann, D. Chronic myelogenous leukemia-derived basophilic granulocytes express a functional active receptor for the anaphylatoxin C3a. Eur. J. Immunol. 1993, 23, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el-Lati, S.G.; Dahinden, C.A.; Church, M.K. Complement peptides C3a- and C5a-induced mediator release from dissociated human skin mast cells. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1994, 102, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulthard, L.G.; Woodruff, T.M. Is the complement activation product C3a a proinflammatory molecule? Re-evaluating the evidence and the myth. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 3542–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.J.; Mirtsos, C.; Suh, D.; Lu, Y.C.; Lin, W.J.; McKerlie, C.; Lee, T.; Baribault, H.; Tian, H.; Yeh, W.C. C5L2 is critical for the biological activities of the anaphylatoxins C5a and C3a. Nature 2007, 446, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daffern, P.J.; Pfeifer, P.H.; Ember, J.A.; Hugli, T.E. C3a is a chemotaxin for human eosinophils but not for neutrophils. I. C3a stimulation of neutrophils is secondary to eosinophil activation. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 181, 2119–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuruta, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Matsubara, S.; Nagasawa, S.; Tanase, S.; Tanaka, J.; Takagi, K.; Kambara, T. Novel function of C4a anaphylatoxin. Release from monocytes of protein which inhibits monocyte chemotaxis. Am. J. Pathol. 1993, 142, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, H.; Yu, W.; Xie, B.D. Complement anaphylatoxin C4a inhibits C5a-induced neointima formation following arterial injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnum, S.R. C4a: An Anaphylatoxin in Name Only. J. Innate Immun. 2015, 7, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.C.; Li, Z.Y.; Yang, X.W.; Zhao, M.H.; Chen, M. Myeloperoxidase influences the complement regulatory function of modified C-reactive protein. Innate Immun. 2014, 20, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, U.; Devaraj, S.; Jialal, I. C-reactive protein stimulates myeloperoxidase release from polymorphonuclear cells and monocytes: Implications for acute coronary syndromes. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.Q.; Chen, M.; Liu, G.; Heeringa, P.; Zhang, J.J.; Zheng, X.; Jie, E.; Kallenberg, C.G.; Zhao, M.H. Complement activation is involved in renal damage in human antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody associated pauci-immune vasculitis. J. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 29, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, M. Complement C4, Infections, and Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 694928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mershon-Shier, K.L.; Vasuthasawat, A.; Takahashi, K.; Morrison, S.L.; Beenhouwer, D.O. In vitro C3 deposition on Cryptococcus capsule occurs via multiple complement activation pathways. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 2009–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Ishida, Y.; Iwaki, D.; Kanno, K.; Suzuki, T.; Endo, Y.; Homma, Y.; Fujita, T. Essential role of mannose-binding lectin-associated serine protease-1 in activation of the complement factor D. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakroush, S.; Tampe, D.; Baier, E.; Kluge, I.A.; Strobel, P.; Tampe, B. Intrarenal synthesis of complement C3 localized to distinct vascular compartments in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis. J. Autoimmun. 2022, 133, 102924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakroush, S.; Kluge, I.A.; Baier, E.; Tampe, D.; Tampe, B. Relevance of Complement C4 Deposits Localized to Distinct Vascular Compartments in ANCA-Associated Renal Vasculitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakroush, S.; Kluge, I.A.; Strobel, P.; Korsten, P.; Tampe, D.; Tampe, B. Systematic Histological Scoring Reveals More Prominent Interstitial Inflammation in Myeloperoxidase-ANCA Compared to Proteinase 3-ANCA Glomerulonephritis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakroush, S.; Tampe, D.; Korsten, P.; Strobel, P.; Tampe, B. Complement Components C3 and C4 Indicate Vasculitis Manifestations to Distinct Renal Compartments in ANCA-Associated Glomerulonephritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tampe, D.; Strobel, P.; Korsten, P.; Hakroush, S.; Tampe, B. Consideration of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange in Association with Inflammatory Lesions in ANCA-Associated Glomerulonephritis: A Real-World Retrospective Study from a Single Center. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 645483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampe, D.; Korsten, P.; Strobel, P.; Hakroush, S.; Tampe, B. Comprehensive Analysis of Sex Differences at Disease Manifestation in ANCA-Associated Glomerulonephritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 736638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakroush, S.; Tampe, D.; Strobel, P.; Korsten, P.; Tampe, B. Comparative Histological Subtyping of Immune Cell Infiltrates in MPO-ANCA and PR3-ANCA Glomerulonephritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 737708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roufosse, C.; Simmonds, N.; Clahsen-van Groningen, M.; Haas, M.; Henriksen, K.J.; Horsfield, C.; Loupy, A.; Mengel, M.; Perkowska-Ptasinska, A.; Rabant, M.; et al. A 2018 Reference Guide to the Banff Classification of Renal Allograft Pathology. Transplantation 2018, 102, 1795–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loupy, A.; Haas, M.; Roufosse, C.; Naesens, M.; Adam, B.; Afrouzian, M.; Akalin, E.; Alachkar, N.; Bagnasco, S.; Becker, J.U.; et al. The Banff 2019 Kidney Meeting Report (I): Updates on and clarification of criteria for T cell- and antibody-mediated rejection. Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 20, 2318–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakroush, S.; Tampe, D.; Korsten, P.; Strobel, P.; Tampe, B. Systematic Scoring of Tubular Injury Patterns Reveals Interplay between Distinct Tubular and Glomerular Lesions in ANCA-Associated Glomerulonephritis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakroush, S.; Tampe, D.; Korsten, P.; Strobel, P.; Tampe, B. Bowman’s capsule rupture links glomerular damage to tubulointerstitial inflammation in ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. S129), 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakroush, S.; Tampe, B. Neutrophils associate with Bowman’s capsule rupture specifically in PR3-ANCA glomerulonephritis. J. Nephrol. 2022, 35, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakroush, S.; Tampe, B. Correspondence on ‘Bowman’s capsule rupture on renal biopsy improves the outcome prediction of ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis classifications’. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).