Screening of Candidate Effectors from Magnaporthe oryzae by In Vitro Secretomic Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Preparation of M. oryzae Secretome
2.2. Shotgun Analysis of M. oryzae Secretomes
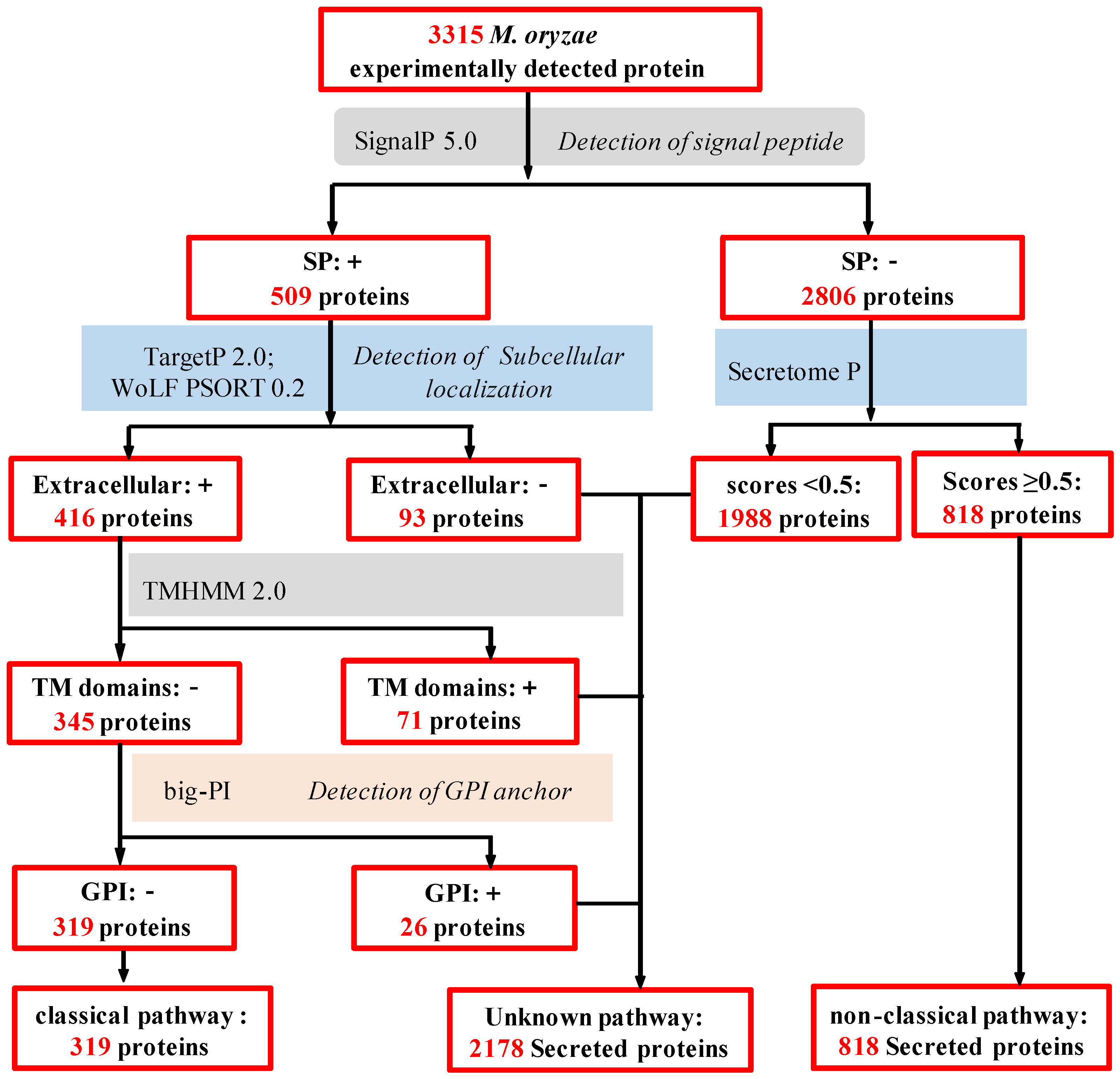
2.3. In Silico Analysis of M. oryzae Secretome
2.4. Functional Annotation and Classification of the Secreted Proteins
2.5. CAZymes and CWDE Analysis of the Secreted Protein
2.6. Effector Analysis of M. oryzae Secretome
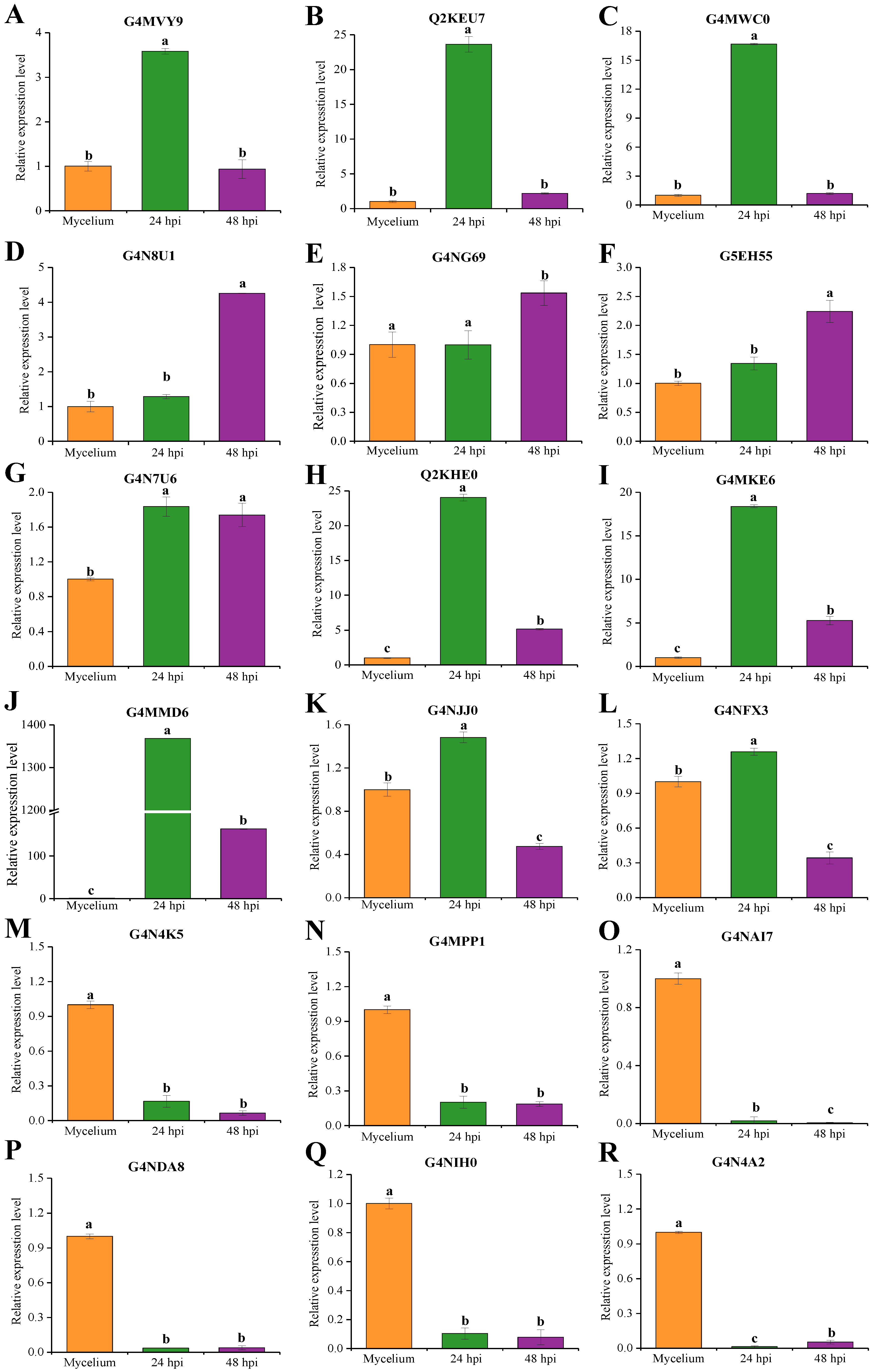
2.7. qRT-PCR Analysis of Candidate Effectors
2.8. Transient Expression Assays
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Fungi and Plants
4.2. Extraction of Secreted Proteins
4.3. Identification of Proteins by LC-MS/MS
4.4. Bioinformatics Analysis of the M. oryzae Secreted Proteins
4.5. Functional Annotation of Secreted Proteins
4.6. Prediction of CAZymes and Effectors
4.7. Quantitative Reverse Transcription (qRT-PCR) Analysis
4.8. Transient Expression of Candidate Effectors in N. benthamiana
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Z. The Magnaporthe grisea species complex and plant pathogenesis. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 17, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Kashyap, P.L.; Mahapatra, S.; Jasrotia, P.; Singh, G.P. New and emerging technologies for detecting Magnaporthe oryzae causing blast disease in crop plants. Crop Protect. 2021, 143, 105473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Nag, A.; Arya, P.; Kapoor, R.; Singh, A.; Jaswal, R.; Sharma, T.R. Prospects of understanding the molecular biology of disease resistance in rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Si, W.; Deng, Q.; Li, P.; Yang, S. Rapid evolution of avirulence genes in rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. BMC Genet. 2014, 15, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Gupta, R.; Min, C.W.; Kwon, S.W.; Wang, Y.; Je, B.I.; Kim, Y.J.; Jeon, J.S.; Agrawal, G.K.; Rakwal, R.; et al. Proteomics of rice-Magnaporthe oryzae interaction: What have we learned so far? Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhou, E.; Lee, S.; Bianco, T. Coevolutionary dynamics of rice blast resistance gene Pi-ta and Magnaporthe oryzae avirulence gene AVR-Pita 1. Phytopathology 2016, 106, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.A.; Talbot, N.J. Under pressure: Investigating the biology of plant infection by Magnaporthe oryzae. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Mireles, N.; Eseola, A.B.; Osés-Ruiz, M.; Ryder, L.S.; Talbot, N.J. From appressorium to transpressorium—Defining the morphogenetic basis of host cell invasion by the rice blast fungus. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentlak, T.A.; Kombrink, A.; Shinya, T.; Ryder, L.S.; Otomo, I.; Saitoh, H.; Terauchi, R.; Nishizawa, Y.; Shibuya, N.; Thomma, B.P.; et al. Effector-mediated suppression of chitin-triggered immunity by Magnaporthe oryzae is necessary for rice blast disease. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhuang, H.Q.; Shi, W.J.; Yang, X.F.; Qiu, D.W.; Zeng, H.M. The secreted protein MoHrip1 is necessary for the virulence of Magnaporthe oryzae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Zou, Y.; You, Y.; Yang, L.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, X.; et al. Magnaporthe oryzae auxiliary activity protein MoAa91 functions as chitin-binding protein to induce appressorium formation on artificial inductive surfaces and suppress plant immunity. mBio 2020, 11, e03304-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Chen, S.; Shirsekar, G.; Zhou, B.; Khang, C.H.; Songkumarn, P.; Afzal, A.J.; Ning, Y.; Wang, R.; Bellizzi, M.; et al. The Magnaporthe oryzae effector AvrPiz-t targets the RING E3 ubiquitin ligase APIP6 to suppress pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered immunity in rice. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 4748–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Ning, Y.; Shi, X.; He, F.; Zhang, C.; Fan, J.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Hu, Y.; et al. Immunity to rice blast disease by suppression of effector-triggered necrosis. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 2399–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera, G.; Giraldo, M.C.; Khang, C.H.; Coughlan, S.; Valent, B. Interaction transcriptome analysis identifies Magnaporthe oryzae BAS1-4 as biotrophy-associated secreted proteins in rice blast disease. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 1273–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Kim, S.G.; Tsuda, K.; Gupta, R.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, S.T.; Kang, K.Y. Magnaporthe oryzae-secreted protein MSP1 induces cell death and elicits defense responses in rice. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2016, 29, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, T.; Mochizuki, S.; Ishii-Minami, N.; Fujisawa, Y.; Kawahara, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Okada, K.; Ando, S.; Matsumura, H.; Terauchi, R.; et al. Magnaporthe oryzae glycine-rich secretion protein, Rbf1 critically participates in pathogenicity through the focal formation of the biotrophic interfacial complex. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, R.A.; Talbot, N.J.; Ebbole, D.J.; Farman, M.L.; Mitchell, T.K.; Orbach, M.J.; Thon, M.; Kulkarni, R.; Xu, J.R.; Pan, H.; et al. The genome sequence of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Nature 2005, 434, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, M.; Jing, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Global genome and transcriptome analyses of Magnaporthe oryzae epidemic isolate 98-06 uncover novel effectors and pathogenicity-related genes, revealing gene gain and lose dynamics in genome evolution. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Saitoh, H.; Fujisawa, S.; Kanzaki, H.; Matsumura, H.; Yoshida, K.; Tosa, Y.; Chuma, I.; Takano, Y.; Win, J.; et al. Association genetics reveals three novel avirulence genes from the rice blast fungal pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 1573–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraldo, M.C.; Dagdas, Y.F.; Gupta, Y.K.; Mentlak, T.A.; Yi, M.; Martinez-Rocha, A.L.; Saitoh, H.; Terauchi, R.; Talbot, N.J.; Valent, B. Two distinct secretion systems facilitate tissue invasion by the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, G.K.; Jwa, N.S.; Lebrun, M.H.; Job, D.; Rakwal, R. Plant secretome: Unlocking secrets of the secreted proteins. Proteomics 2010, 10, 799–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperschneider, J.; Dodds, P.N. EffectorP 3.0: Prediction of apoplastic and cytoplasmic effectors in fungi and oomycetes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 35, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Park, Z.Y.; Kim, S.G.; Rakwal, R.; Agrawal, G.K.; Kim, S.T.; Kang, K.Y. Comparative secretome investigation of Magnaporthe oryzae proteins responsive to nitrogen starvation. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 3136–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.H.; Jeong, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Singh, R.; Lee, J.E.; Cho, Y.S.; Agrawal, G.K.; Rakwal, R.; Jwa, N.S. Secretome analysis of Magnaporthe oryzae using in vitro systems. Proteomics 2012, 12, 878–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G.; Wang, Y.; Lee, K.H.; Park, Z.Y.; Park, J.; Wu, J.; Kwon, S.J.; Lee, Y.H.; Agrawal, G.K.; Rakwal, R.; et al. In-depth insight into in vivo apoplastic secretome of rice-Magnaporthe oryzae interaction. J. Proteom. 2013, 78, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, W.; Rabouille, C. Mechanisms of regulated unconventional protein secretion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Brink, J.; de Vries, R.P. Fungal enzyme sets for plant polysaccharide degradation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 91, 1477–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombard, V.; Golaconda Ramulu, H.; Drula, E.; Coutinho, P.M.; Henrissat, B. The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D490–D495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ospina-Giraldo, M.D.; Griffith, J.G.; Laird, E.W.; Mingora, C. The CAZyome of Phytophthora spp.: A comprehensive analysis of the gene complement coding for carbohydrate-active enzymes in species of the genus Phytophthora. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levasseur, A.; Drula, E.; Lombard, V.; Coutinho, P.M.; Henrissat, B. Expansion of the enzymatic repertoire of the CAZy database to integrate auxiliary redox enzymes. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2013, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selin, C.; de Kievit, T.R.; Belmonte, M.F.; Fernando, W.G. Elucidating the role of effectors in plant-fungal interactions: Progress and challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grynberg, P.; Coiti Togawa, R.; Dias de Freitas, L.; Antonino, J.D.; Rancurel, C.; Mota do Carmo Costa, M.; Grossi-de-Sa, M.F.; Miller, R.N.G.; Brasileiro, A.C.M.; Messenberg Guimaraes, P.; et al. Comparative genomics reveals novel target genes towards specific control of plant-parasitic nematodes. Genes 2020, 11, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, J.; Cook, D.E. Histone modification dynamics at H3K27 are associated with altered transcription of in planta induced genes in Magnaporthe oryzae. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, B.; Wu, J.; Lu, G.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, H.; et al. The Magnaporthe oryzae avirulence gene AvrPiz-t encodes a predicted secreted protein that triggers the immunity in rice mediated by the blast resistance gene Piz-t. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kim, M.S.; Huang, J.; Yan, H.; Yang, T.; Song, L.; Yu, W.; Shim, W.B. Transcriptome analysis of maize pathogen Fusarium verticillioides revealed FvLcp1, a secreted protein with type-D fungal LysM and chitin-binding domains, that plays important roles in pathogenesis and mycotoxin production. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 265, 127195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngou, B.P.M.; Ding, P.; Jones, J.D.G. Thirty years of resistance: Zig-zag through the plant immune system. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 1447–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, D.E.; Mesarich, C.H.; Thomma, B.P. Understanding plant immunity as a surveillance system to detect invasion. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2015, 53, 541–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazar Pour, F.; Pedrosa, B.; Oliveira, M.; Fidalgo, C.D.B.; Driessche, G.V.; Félix, C.; Rosa, N.; Alves, A.; Duarte, A.S.; Esteves, A.C. Unveiling the secretome of the fungal plant pathogen Neofusicoccum parvum induced by in vitro host mimicry. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, D.; Rafiqi, M.; Job, D. The multiple facets of plant-fungal interactions revealed through plant and fungal secretomics. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 10, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.S.; Kawaguchi, K.; Kikuma, T.; Takegawa, K.; Kitamoto, K.; Higuchi, Y. Analysis of an acyl-CoA binding protein in Aspergillus oryzae that undergoes unconventional secretion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chung, K.P.; Lin, W.; Jiang, L. Protein secretion in plants: Conventional and unconventional pathways and new techniques. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 69, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, T.C.; Wang, D.W.; Zheng, S.M.; Yan, Y.M.; Jiao, Y.B.; Cheng, Y.X.; Wang, F. Antifungal and wound healing promotive compounds from the resins of Dracaena cochinchinensis. Fitoterapia 2021, 151, 104904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Nie, Y. In vitro secretome analysis suggests differential pathogenic mechanisms between Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense race 1 and race 4. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.J.; Kong, W.S. Genome-wide comparison of carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes) repertoire of Flammulina ononidis. Mycobiology 2018, 46, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Assis, L.J.; Silva, L.P.; Bayram, O.; Dowling, P.; Kniemeyer, O.; Krüger, T.K.; Brakhage, A.A.; Chen, Y.; Dong, L.; Tan, K.; et al. Carbon catabolite repression in filamentous fungi is regulated by phosphorylation of the transcription factor CreA. mBio 2021, 12, e03146-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quoc, N.B.; Chau, N.N.B. The role of cell wall degrading enzymes in pathogenesis of Magnaporthe oryzae. Curr. Protein Peptide Sci. 2017, 18, 1019–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbach, M.J.; Farrall, L.; Sweigard, J.A.; Chumley, F.G.; Valent, B. A telomeric avirulence gene determines efficacy for the rice blast resistance gene Pi-ta. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 2019–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhnert, H.U.; Fudal, I.; Dioh, W.; Tharreau, D.; Notteghem, J.L.; Lebrun, M.H. A putative polyketide synthase/peptide synthetase from Magnaporthe grisea signals pathogen attack to resistant rice. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 2499–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Sweigard, J.A.; Valent, B. The PWL host specificity gene family in the blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 1995, 8, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, H.; Fujisawa, S.; Mitsuoka, C.; Ito, A.; Hirabuchi, A.; Ikeda, K.; Irieda, H.; Yoshino, K.; Yoshida, K.; Matsumura, H.; et al. Large-scale gene disruption in Magnaporthe oryzae identifies MC69, a secreted protein required for infection by monocot and dicot fungal pathogens. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhong, D.; Xie, W.; He, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Han, Y.; Tian, D.; Liu, W.; et al. Functional identification of novel cell death-inducing effector proteins from Magnaporthe oryzae. Rice 2019, 12, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, N.; Xie, X.; Yu, H.; Mei, J.; Li, Q.; Zuo, S.; Wu, H.; Liu, W.; Li, Z. Plant peroxisome-targeting effector MoPtep1 is required for the virulence of Magnaporthe oryzae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbot, N.J.; Ebbole, D.J.; Hamer, J.E. Identification and characterization of MPG1, a gene involved in pathogenicity from the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Plant Cell 1993, 5, 1575–1590. [Google Scholar]
- Rafiqi, M.; Ellis, J.G.; Ludowici, V.A.; Hardham, A.R.; Dodds, P.N. Challenges and progress towards understanding the role of effectors in plant-fungal interactions. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2012, 15, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivek-Ananth, R.P.; Mohanraj, K.; Vandanashree, M.; Jhingran, A.; Craig, J.P.; Samal, A. Comparative systems analysis of the secretome of the opportunistic pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus and other Aspergillus species. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Talbot, N.J. Investigating the cell biology of plant infection by the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 34, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Q.; Zhou, X.; Li, H.; Chen, X.L.; Li, Y. A novel elicitor MoVcpo is necessary for the virulence of Magnaporthe oryzae and triggers rice defense responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1018616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ye, Z.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.L.; Wang, Z. Comparative phosphoproteome analysis of Magnaporthe oryzae-responsive proteins in susceptible and resistant rice cultivars. J. Proteom. 2015, 115, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewski, J.R.; Zougman, A.; Mann, M. Combination of FASP and StageTip-based fractionation allows in-depth analysis of the hippocampal membrane proteome. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 5674–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Sønderby, C.; Petersen, T.N.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; Von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, P.; Park, K.J.; Obayashi, T.; Fujita, N.; Harada, H.; Adams-Collier, C.J.; Nakai, K. WOLF PSORT: Protein localization predictor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W585–W587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenhaber, B.; Bork, P.; Eisenhaber, F. Post-translational GPI lipid anchor modification of proteins in kingdoms of life: Analysis of protein sequence data from complete genomes. Protein Eng. 2001, 14, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendtsen, J.D.; Jensen, L.J.; Blom, N.; Von Heijne, G.; Brunak, S. Feature-based prediction of non-classical and leaderless protein secretion. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2004, 17, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Sun, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, J. Comparative analysis of erythrocyte proteomes of water buffalo, dairy cattle, and beef cattle by shotgun LC-MS/MS. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, F.F.; Pang, X.H.; Zhu, D.Q.; Zhu, Z.T.; Sun, S.R.; Meng, X.C. Role of the luxS gene in bacteriocin biosynthesis by Lactobacillus plantarum KLDS1.0391: A proteomic analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, Y.; Itoh, M.; Okuda, S.; Yoshizawa, A.C.; Kanehisa, M. KAAS: An automatic genome annotation and pathway reconstruction server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W182–W185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.A.; Bertazzoni, S.; Turo, C.J.; Syme, R.A.; Hane, J.K. Bioinformatic prediction of plant-pathogenicity effector proteins of fungi. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 46, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Lukasik, E.; Gawehns, F.; Takken, F.L.W. The use of agroinfiltration for transient expression of plant resistance and fungal effector proteins in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 835, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Shi, Q.; He, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhong, M.; Tong, L.; Li, H.; Nie, Y.; Li, Y. Screening of Candidate Effectors from Magnaporthe oryzae by In Vitro Secretomic Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043189
Li G, Shi Q, He Y, Zhu J, Zhong M, Tong L, Li H, Nie Y, Li Y. Screening of Candidate Effectors from Magnaporthe oryzae by In Vitro Secretomic Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(4):3189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043189
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guanjun, Qingchuan Shi, Yanqiu He, Jie Zhu, Mingluan Zhong, Lingjie Tong, Huaping Li, Yanfang Nie, and Yunfeng Li. 2023. "Screening of Candidate Effectors from Magnaporthe oryzae by In Vitro Secretomic Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 4: 3189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043189
APA StyleLi, G., Shi, Q., He, Y., Zhu, J., Zhong, M., Tong, L., Li, H., Nie, Y., & Li, Y. (2023). Screening of Candidate Effectors from Magnaporthe oryzae by In Vitro Secretomic Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(4), 3189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043189





