WNT3a Signaling Inhibits Aromatase Expression in Breast Adipose Fibroblasts—A Possible Mechanism Supporting the Loss of Estrogen Responsiveness of Triple-Negative Breast Cancers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
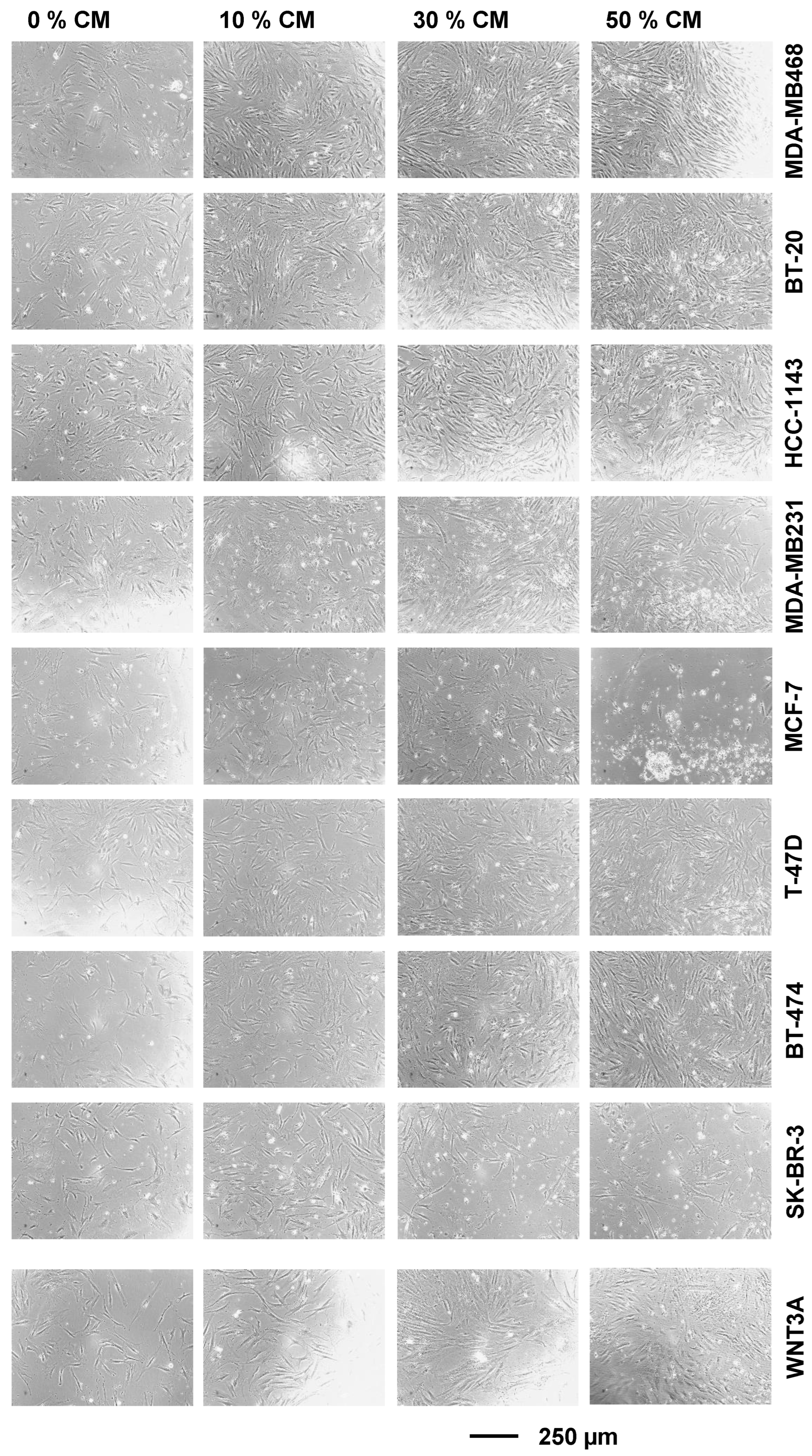
2.1. Breast Cancer Cell- and WNT3a-Conditioned Media Potentiate BAF Growth
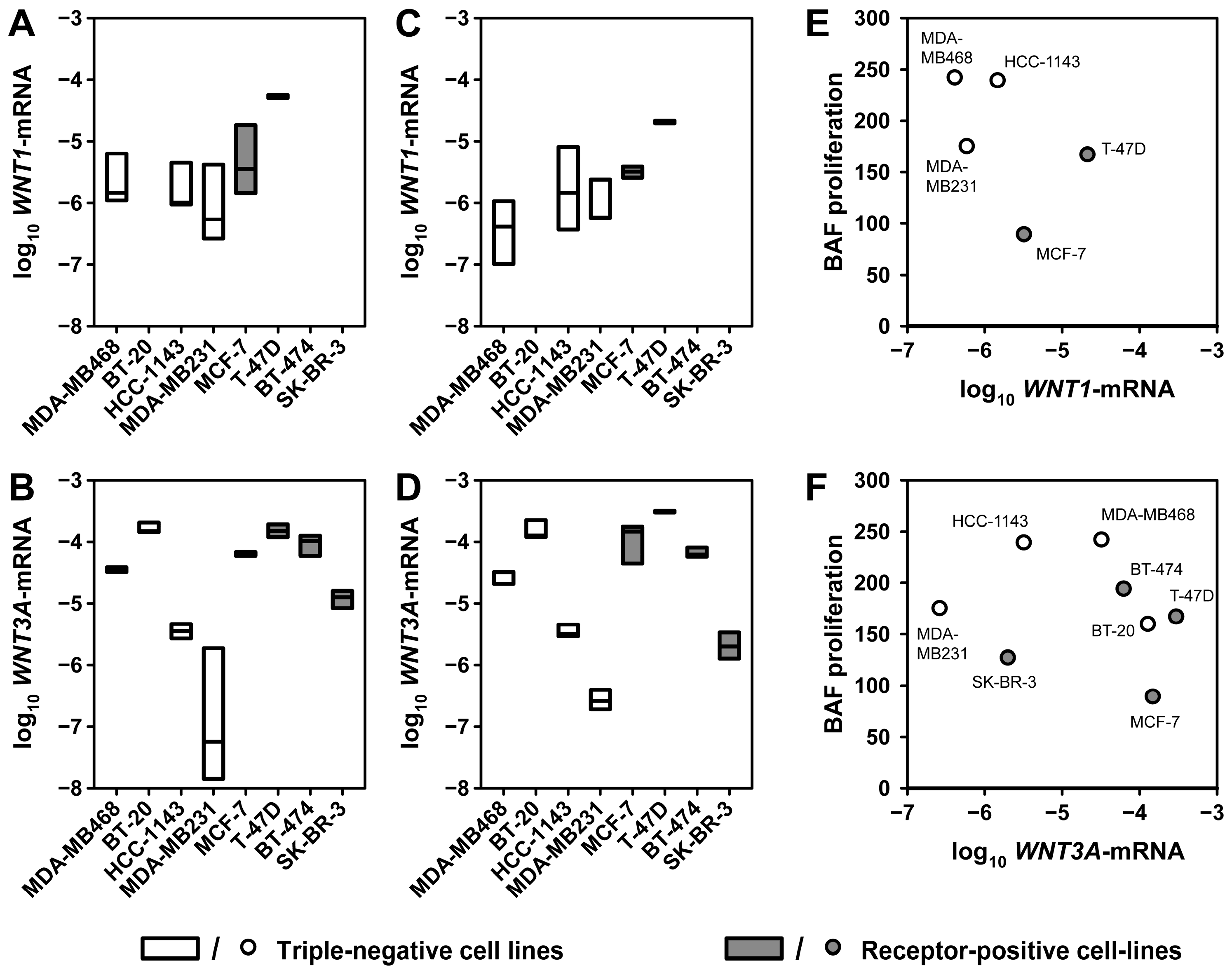
2.2. Expression of WNT1 and WNT3A in Breast Cancer Cell Lines
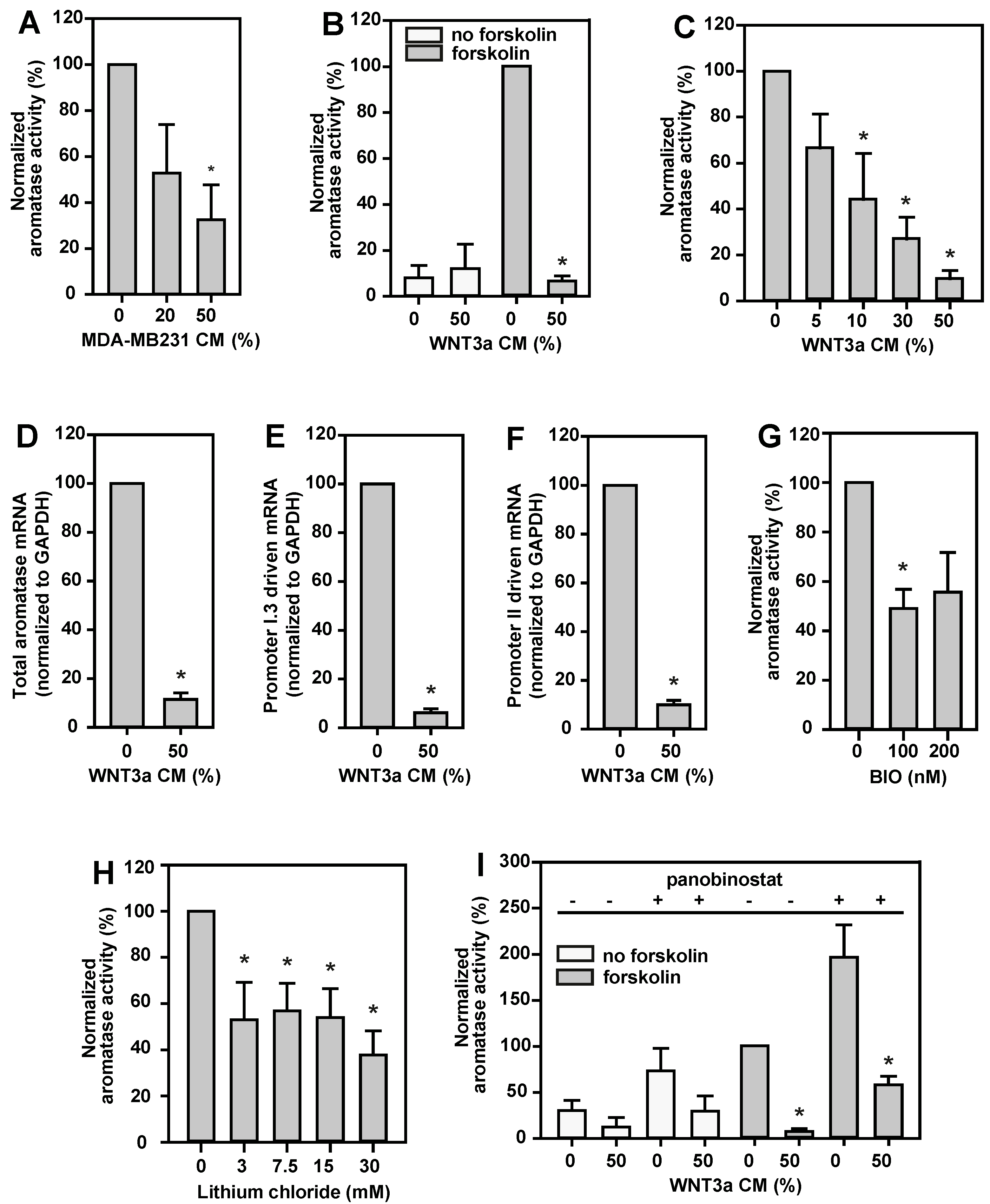
2.3. Aromatase Activity and Expression in BAFs Treated with MDA-MB231 CM or WNT3a CM
2.4. Aromatase Activity Is Inhibited by Canonical Wnt Signaling and Histone Deacetylases
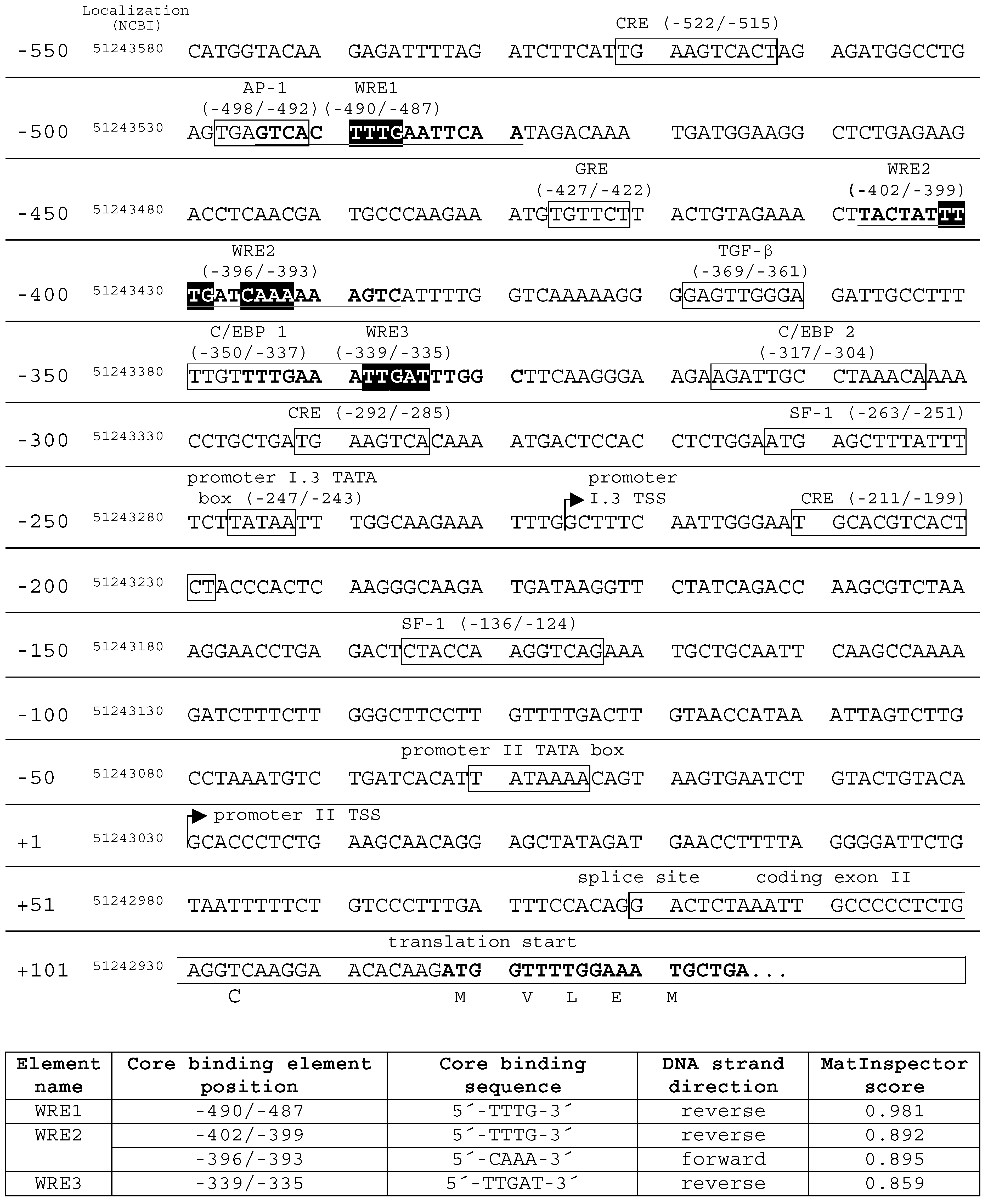
2.5. Identification of Putative Wnt Response Elements in the Aromatase Promoter I.3/II Sequence
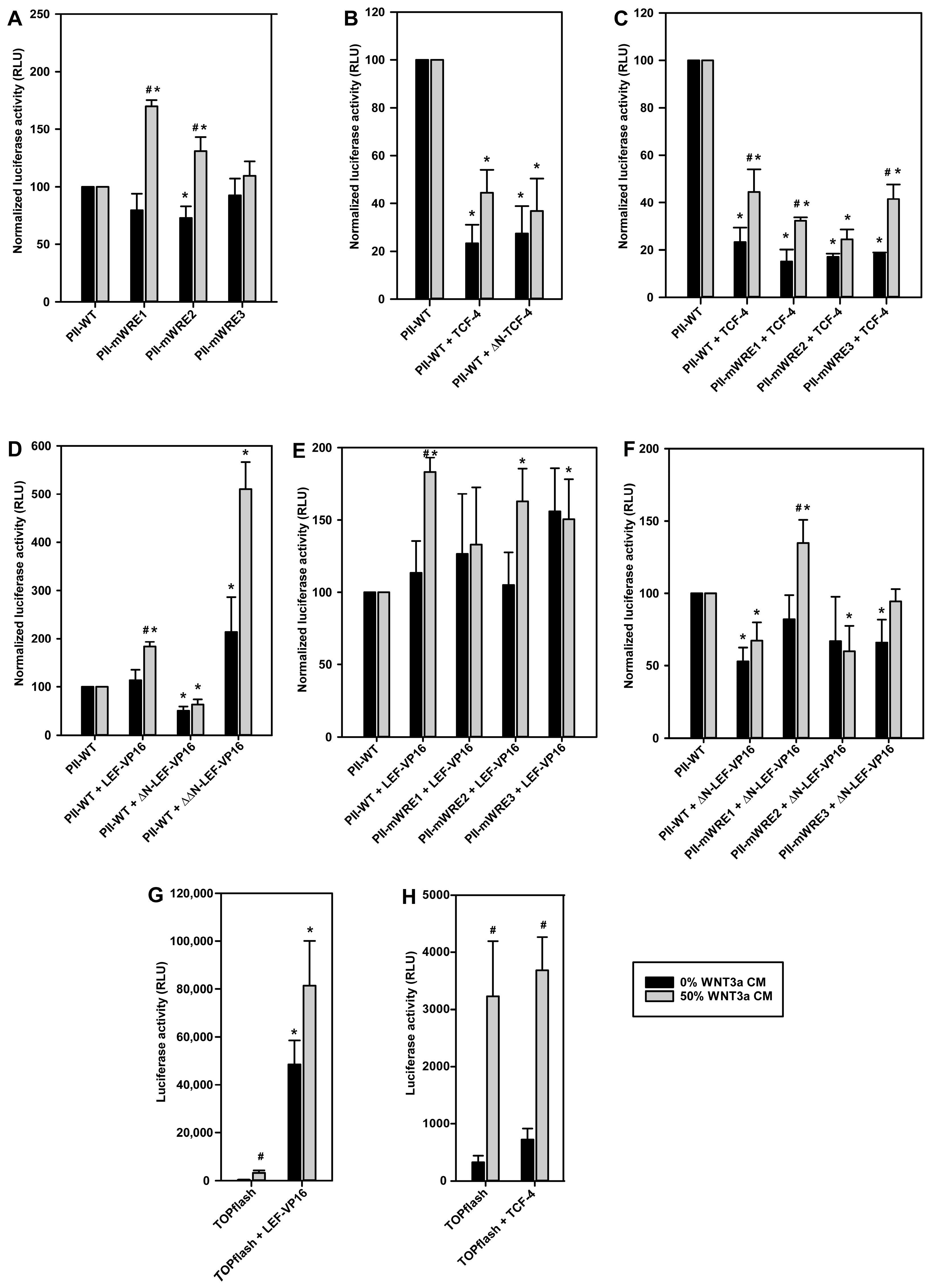
2.6. Evaluation of Putative WREs in the Aromatase Promoter I.3/II Region In Vitro
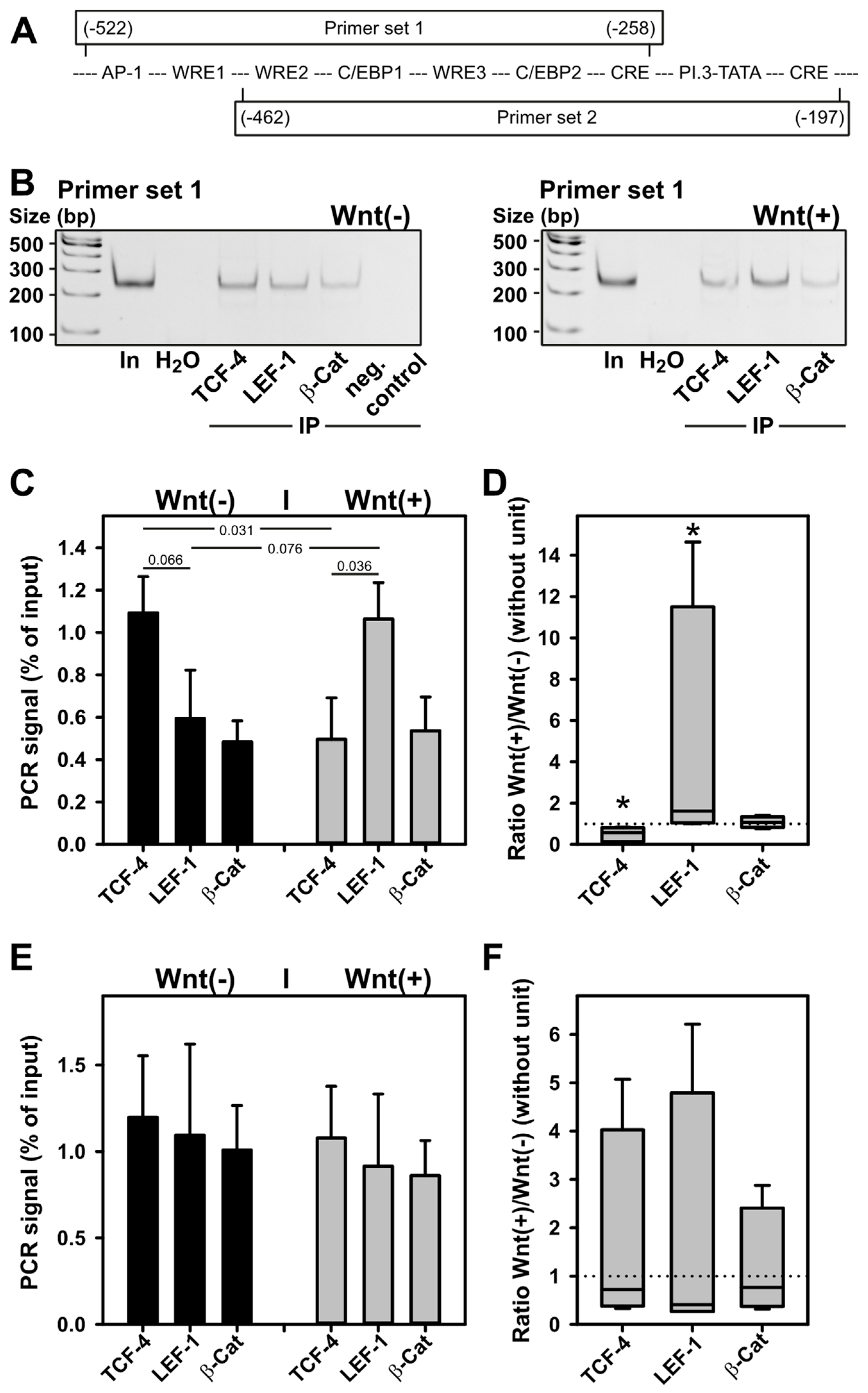
2.7. WNT3a Treatment Triggers TCF-4 Replacement by LEF-1 on WRE1 of the Aromatase Promoter I.3/II Region in BAFs
2.8. Functional Consequences of TCF-4 or LEF-1 Binding to WREs in the Aromatase Promoter I.3/II Region
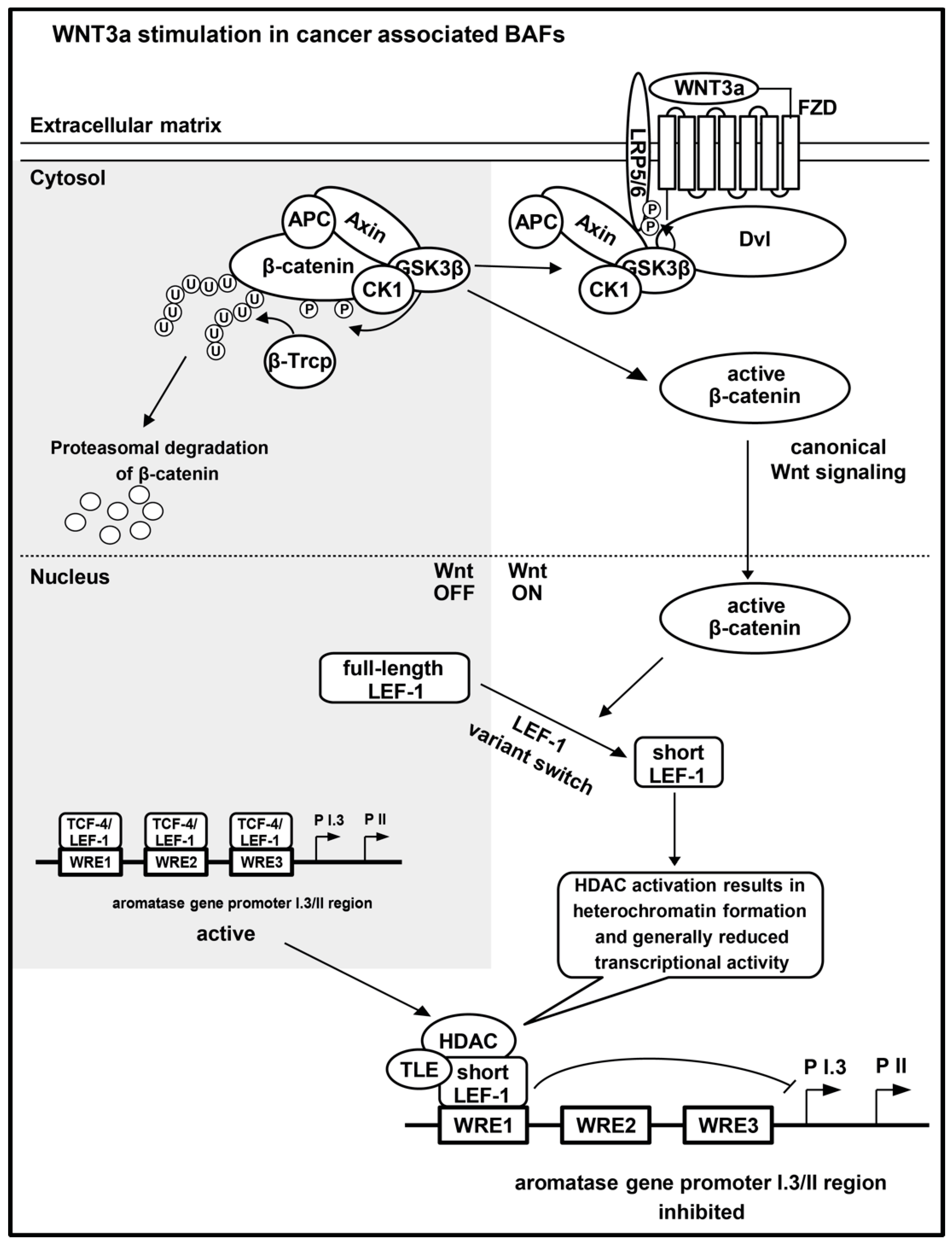
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells and Cell Culture
4.2. Viability Assay with Fluorescein Diacetate
4.3. Quantification of mRNA Expression
4.4. Aromatase Activity Testing
4.5. Preparation of Soluble Nuclear Extracts
4.6. Immunoprecipitation-Based DNA-Binding Assay
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Plasmid Mutagenesis
4.9. Transfection and Luciferase Reporter Gene Assays
4.10. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
4.11. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Chen, D.; Reierstad, S.; Lu, M.; Lin, Z.; Ishikawa, H.; Bulun, S.E. Regulation of breast cancer-associated aromatase promoters. Cancer Lett. 2009, 273, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, E.R.; Clyne, C.; Rubin, G.; Boon, W.C.; Robertson, K.; Britt, K.; Speed, C.; Jones, M. Aromatase--a brief overview. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2002, 64, 93–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, E.R.; Mahendroo, M.S.; Means, G.D.; Kilgore, M.W.; Hinshelwood, M.M.; Graham-Lorence, S.; Amarneh, B.; Ito, Y.; Fisher, C.R.; Michael, M.D.; et al. Aromatase cytochrome P450, the enzyme responsible for estrogen biosynthesis. Endocr. Rev. 1994, 15, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santen, R.J.; Brodie, H.; Simpson, E.R.; Siiteri, P.K.; Brodie, A. History of aromatase: Saga of an important biological mediator and therapeutic target. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 343–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, S.R.; Dowsett, M. Aromatase inhibitors for breast cancer: Lessons from the laboratory. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, B.T.; Tamai, K.; He, X. Wnt/β-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev. Cell 2009, 17, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, W.-H.; Fuchs, E. Wnt some lose some: Transcriptional governance of stem cells by Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Genes. Dev. 2014, 28, 1517–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niehrs, C. The complex world of WNT receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastas, J.N.; Moon, R.T. WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polakis, P. The many ways of Wnt in cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2007, 17, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadigan, K.M.; Waterman, M.L. TCF/LEFs and Wnt signaling in the nucleus. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a007906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovanes, K.; Li, T.W.; Munguia, J.E.; Truong, T.; Milovanovic, T.; Lawrence Marsh, J. β-Catenin-sensitive isoforms of lymphoid enhancer factor-1 are selectively expressed in colon cancer. Nat. Genet. 2001, 28, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Wetering, M.; Castrop, J.; Korinek, V.; Clevers, H. Extensive alternative splicing and dual promoter usage generate Tcf-protein isoforms with differential transcription control properties. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duval, A.; Rolland, S.; Tubacher, E.; Bui, H.; Thomas, G.; Hamelin, R. The human T-cell transcription factor-4 gene: Structure, extensive characterization of alternative splicings, and mutational analysis in colorectal cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 3872–3879. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geyer, F.C.; Lacroix-Triki, M.; Savage, K.; Arnedos, M.; Lambros, M.B.; MacKay, A.; Natrajan, R.; Reis-Filho, J.S. β-Catenin pathway activation in breast cancer is associated with triple-negative phenotype but not with CTNNB1 mutation. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 209–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khramtsov, A.I.; Khramtsova, G.F.; Tretiakova, M.; Huo, D.; Olopade, O.I.; Goss, K.H. Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation is enriched in basal-like breast cancers and predicts poor outcome. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 2911–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, R.; Ablett, M.P.; Spence, K.; Landberg, G.; Sims, A.H.; Clarke, R.B. Wnt pathway activity in breast cancer sub-types and stem-like cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochet, L.; Lehuédé, C.; Dauvillier, S.; Wang, Y.Y.; Dirat, B.; Laurent, V.; Dray, C.; Guiet, R.; Maridonneau-Parini, I.; Le Gonidec, S.; et al. Adipocyte-derived fibroblasts promote tumor progression and contribute to the desmoplastic reaction in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5657–5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, K.M.; Oguro, S.; Omata, F.; Kikuchi, K.; Guestini, F.; Suzuki, K.; Yang, Y.; Abe, E.; Hirakawa, H.; Brown, K.A.; et al. The presence and impact of estrogen metabolism on the biology of triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 161, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapp, A.D.; Gómez, B.I.; Gifford, C.A.; Hallford, D.M.; Hernandez Gifford, J.A. Canonical WNT signaling inhibits follicle stimulating hormone mediated steroidogenesis in primary cultures of rat granulosa cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhaj, K.; Akcali, K.C.; Ozturk, M. Redundant expression of canonical Wnt ligands in human breast cancer cell lines. Oncol. Rep. 2006, 15, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neve, R.M.; Chin, K.; Fridlyand, J.; Yeh, J.; Baehner, F.L.; Fevr, T.; Clark, L.; Bayani, N.; Coppe, J.P.; Tong, F.; et al. A collection of breast cancer cell lines for the study of functionally distinct cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Cheng, H.; Bai, Z.; Li, J. Breast Cancer Cell Line Classification and Its Relevance with Breast Tumor Subtyping. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 3131–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willert, K.; Brown, J.D.; Danenberg, E.; Duncan, A.W.; Weissman, I.L.; Reya, T.; Yates, J.R., III; Nusse, R. Wnt proteins are lipid-modified and can act as stem cell growth factors. Nature 2003, 423, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billin, A.N.; Thirlwell, H.; Ayer, D.E. β-Catenin-histone deacetylase interactions regulate the transition of LEF1 from a transcriptional repressor to an activator. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 6882–6890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosimann, C.; Hausmann, G.; Basler, K. β-Catenin hits chromatin: Regulation of Wnt target gene activation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, J.; Erdmann, M.; Mertens, M.; Eiselt, G.; Schmidt, M. Aromatase activity induction in human adipose fibroblasts by retinoic acids via retinoic acid receptor α. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 51, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, M.; Hecht, A.; Kruse, U.; Kemler, R.; Vogt, P.K. Nuclear endpoint of Wnt signaling: Neoplastic transformation induced by transactivating lymphoid-enhancing factor 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Knowles, E.; Zardawi, S.J.; McNeil, C.M.; Millar, E.K.A.; Crea, P.; Musgrove, E.A.; Sutherland, R.L.; O’Toole, S.A. Cytoplasmic localization of β-catenin is a marker of poor outcome in breast cancer patients. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2010, 19, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-Y.; Xia, W.; Wang, J.C.; Kwong, K.Y.; Spohn, B.; Wen, Y.; Pestell, R.G.; Hung, M.-C. β-Catenin, a novel prognostic marker for breast cancer: Its roles in cyclin D1 expression and cancer progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4262–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, B.; Smith, U. Activation of canonical wingless-type MMTV integration site family (Wnt) signaling in mature adipocytes increases β-catenin levels and leads to cell dedifferentiation and insulin resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 14031–14041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christodoulides, C.; Lagathu, C.; Sethi, J.K.; Vidal-Puig, A. Adipogenesis and WNT signalling. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 20, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorman, A.M.; Vink, R.; Heijmans, H.J.; van der Palen, J.; Kouwenhoven, E.A. The prognostic value of tumour-stroma ratio in triple-negative breast cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 38, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downey, C.L.; Simpkins, S.A.; White, J.; Holliday, D.L.; Jones, J.L.; Jordan, L.B.; Kulka, J.; Pollock, S.; Rajan, S.S.; Thygesen, H.H.; et al. The prognostic significance of tumour-stroma ratio in oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1744–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, M.C.; Bertolette, D.; Castro, N.P.; Klauzinska, M.; Cuttitta, F.; Salomon, D.S. Developmental signaling pathways regulating mammary stem cells and contributing to the etiology of triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 156, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Coombes, R.C. Endocrine-responsive breast cancer and strategies for combating resistance. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.D.; Gyorffy, B.; Vogel, R.; Eckert, K.; Valenti, G.; Fang, L.; Lohneis, P.; Elezkurtaj, S.; Ziebold, U.; Birchmeier, W. Combined Wnt/β-catenin, Met, and CXCL12/CXCR4 signals characterize basal breast cancer and predict disease outcome. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 1214–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Landeghem, A.A.; Poortman, J.; Nabuurs, M.; Thijssen, J.H. Endogenous concentration and subcellular distribution of estrogens in normal and malignant human breast tissue. Cancer Res. 1985, 45, 2900–2906. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Agarwal, V.R.; Mendelson, C.R.; Simpson, E.R. Estrogen biosynthesis proximal to a breast tumor is stimulated by PGE2 via cyclic AMP, leading to activation of promoter II of the CYP19 (aromatase) gene. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 5739–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Gurates, B.; Yang, S.; Sebastian, S.; Bulun, S.E. Malignant breast epithelial cells stimulate aromatase expression via promoter II in human adipose fibroblasts: An epithelial-stromal interaction in breast tumors mediated by CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 2328–2334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Löffler, G. The human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB231 produces an aromatase stimulating activity. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 63, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Renner, C.; Löffler, G. Progesterone inhibits glucocorticoid-dependent aromatase induction in human adipose fibroblasts. J. Endocrinol. 1998, 158, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Löffler, G. RU486 is a potent inhibitor of aromatase induction in human breast adipose tissue stromal cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1997, 60, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, G.L.; Duong, J.H.; Clyne, C.D.; Speed, C.J.; Murata, Y.; Gong, C.; Simpson, E.R. Ligands for the peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor gamma and the retinoid X receptor inhibit aromatase cytochrome P450 (CYP19) expression mediated by promoter II in human breast adipose. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 2863–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augsten, M. Cancer-associated fibroblasts as another polarized cell type of the tumor microenvironment. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.W.-H.; Ting, J.-H.T.; Yokoyama, N.N.; Bernstein, A.; van de Wetering, M.; Waterman, M.L. Wnt activation and alternative promoter repression of LEF1 in colon cancer. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 5284–5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce, L.; Yokoyama, N.N.; Waterman, M.L. Diversity of LEF//TCF action in development and disease. Oncogene 2006, 25, 7492–7504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantjes, H.; Roose, J.; van De Wetering, M.; Clevers, H. All Tcf HMG box transcription factors interact with Groucho-related co-repressors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 1410–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, D.L.; Weis, W.I. β-Catenin directly displaces Groucho/TLE repressors from Tcf/Lef in Wnt-mediated transcription activation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce, L.; Pate, K.T.; Waterman, M.L. Groucho binds two conserved regions of LEF-1 for HDAC-dependent repression. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, C.Y.; Nusse, R. The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 20, 781–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Semenov, M.; Tamai, K.; Zeng, X. LDL receptor-related proteins 5 and 6 in Wnt/β-catenin signaling: Arrows point the way. Development 2004, 131, 1663–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Rubin, J.S.; Kimmel, A.R. Rapid, Wnt-induced changes in GSK3β associations that regulate β-catenin stabilization are mediated by Gα proteins. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimelman, D.; Xu, W. β-Catenin destruction complex: Insights and questions from a structural perspective. Oncogene 2006, 25, 7482–7491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Mittag, S.; Schmidt, M.; Simm, A.; Horstkorte, R.; Huber, O. Wnt Glycation Inhibits Canonical Signaling. Cells 2019, 8, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Löffler, G. Induction of aromatase activity in human adipose tissue stromal cells by extracellular nucleotides. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 252, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albring, K.F.; Weidemuller, J.; Mittag, S.; Weiske, J.; Friedrich, K.; Geroni, M.C.; Lombardi, P.; Huber, O. Berberine acts as a natural inhibitor of Wnt/β-catenin signaling--identification of more active 13-arylalkyl derivatives. Biofactors 2013, 39, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, G.E.; Smith, M.E.; Mendelson, C.R.; Macdonald, P.C.; Simpson, E.R. Aromatization of androstenedione by human adipose tissue stromal cells in monolayer culture. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1981, 53, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.D.; Ackroyd, A.J.; Halford, S.E. The gel shift assay for the analysis of DNA-protein interactions. In DNA–Protein Interactions: Principles and Protocol, 1st ed.; Kneale, G.G., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 1994; Volume 30, pp. 263–279. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, O.; Huber-Wunderlich, M. Recombinant proteins. J. Chromatogr. Libr. 2000, 61, 557–586. [Google Scholar]
- Cribier, B.; Worret, W.I.; Braun-Falco, M.; Peltre, B.; Langbein, L.; Schweizer, J. Expression patterns of hair and epithelial keratins and transcription factors HOXC13, LEF1, and β-catenin in a malignant pilomatricoma: A histological and immunohistochemical study. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2006, 33, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korinek, V.; Barker, N.; Morin, P.J.; van Wichen, D.; de Weger, R.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B.; Clevers, H. Constitutive transcriptional activation by a β-catenin-Tcf complex in APC-/-colon carcinoma. Science 1997, 275, 1784–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittag, S.; Valenta, T.; Weiske, J.; Bloch, L.; Klingel, S.; Gradl, D.; Wetzel, F.; Chen, Y.; Petersen, I.; Basler, K.; et al. A novel role for the tumour suppressor Nitrilase1 modulating the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway. Cell Discov. 2016, 2, 15039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinmann, A.S.; Farnham, P.J. Identification of unknown target genes of human transcription factors using chromatin immunoprecipitation. Methods 2002, 26, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiske, J.; Huber, O. The histidine triad protein Hint1 triggers apoptosis independent of its enzymatic activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 27356–27366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Cell Line | Molecular Classification | ER | PR | HER2 | WNT | Growth Medium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDA-MB468 | TNA | - | - | - | [21] | DMEM/10% (v/v) FBS |
| BT-20 | TNA | - | - | - | [21] | DMEM/10% (v/v) FBS |
| HCC-1143 | TNA | - | - | - | DMEM/20% (v/v) FBS | |
| MDA-MB231 | TNB | - | - | - | [18] | DMEM/10% (v/v) FBS |
| MCF-7 | LA | + | + | - | [21] | DMEM/10% (v/v) FBS |
| T-47D | LA | + | + | - | [21] | RPMI/10% (v/v) FBS |
| BT-474 | LB | + | + | + | [21] | RPMI/10% (v/v) FBS |
| SK-BR-3 | H | - | - | + | RPMI/10% (v/v) FBS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaiser, A.; Eiselt, G.; Bechler, J.; Huber, O.; Schmidt, M. WNT3a Signaling Inhibits Aromatase Expression in Breast Adipose Fibroblasts—A Possible Mechanism Supporting the Loss of Estrogen Responsiveness of Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054654
Kaiser A, Eiselt G, Bechler J, Huber O, Schmidt M. WNT3a Signaling Inhibits Aromatase Expression in Breast Adipose Fibroblasts—A Possible Mechanism Supporting the Loss of Estrogen Responsiveness of Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(5):4654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054654
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaiser, Alexander, Gabriele Eiselt, Joachim Bechler, Otmar Huber, and Martin Schmidt. 2023. "WNT3a Signaling Inhibits Aromatase Expression in Breast Adipose Fibroblasts—A Possible Mechanism Supporting the Loss of Estrogen Responsiveness of Triple-Negative Breast Cancers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 5: 4654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054654
APA StyleKaiser, A., Eiselt, G., Bechler, J., Huber, O., & Schmidt, M. (2023). WNT3a Signaling Inhibits Aromatase Expression in Breast Adipose Fibroblasts—A Possible Mechanism Supporting the Loss of Estrogen Responsiveness of Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(5), 4654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054654







