The Role of IL-13 and IL-4 in Adipose Tissue Fibrosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
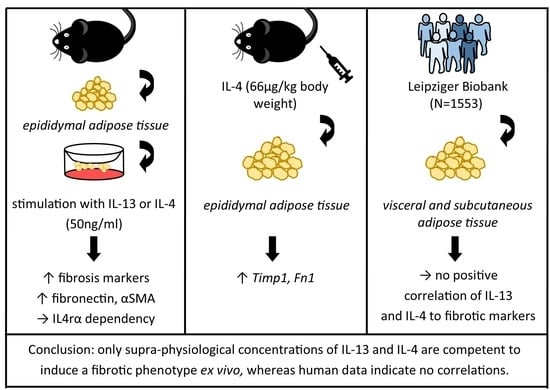
2.1. IL-13 and IL-4 Induced WAT Fibrosis
2.2. IL-4Rα-Chain Is Required for IL-13 and IL-4 Induced Fibrosis
2.3. IL-13 and IL-4 Induced Fibrosis Phenotype Depends on ATMs
2.4. IL-13 and IL-4 Do Not Positively Correlate with Fibrosis Markers and Parameters Associated with Obesity in Human WAT
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Adipose Tissue Explant Culture
4.3. Clodronate Liposomes Treatment
4.4. Culture of Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages (BMDMs)
4.5. Culture of 3T3-L1 Cells
4.6. RNA Isolation and Quantitative RT-PCR
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Collagen Content
4.9. Fibronectin Content
4.10. Immunofluorescence
4.11. RNA Bulk Sequencing from BMDMs and Differential Gene Expression Analysis
4.12. RNA Bulk Sequencing from Human Data
4.13. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, E.K.; Abbott, R.D. Adipose Tissue Paracrine-, Autocrine-, and Matrix-Dependent Signaling during the Development and Progression of Obesity. Cells 2023, 12, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakers, A.; de Siqueira, M.K.; Seale, P.; Villanueva, C.J. Adipose-tissue plasticity in health and disease. Cell 2022, 185, 419–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, R.; Podolsky, M.J.; Atabai, K. Fat fibrosis: Friend or foe? JCI Insight 2018, 3, e122289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeBari, M.K.; Abbott, R.D. Adipose Tissue Fibrosis: Mechanisms, Models, and Importance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, S.; Ohyane, C.; Kim, Y.-I.; Lin, S.; Goto, T.; Takahashi, N.; Kim, C.-S.; Kang, J.; Yu, R.; Kawada, T. Involvement of mast cells in adipose tissue fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E247–E255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keophiphath, M.; Achard, V.; Henegar, C.; Rouault, C.; Clément, K.; Lacasa, D. Macrophage-secreted factors promote a profibrotic phenotype in human preadipocytes. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 23, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borthwick, L.A.; Wynn, T.A.; Fisher, A.J. Cytokine mediated tissue fibrosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1832, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Junttila, I.S. Tuning the Cytokine Responses: An Update on Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 Receptor Complexes. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J. T helper 2 (Th2) cell differentiation, type 2 innate lymphoid cell (ILC2) development and regulation of interleukin-4 (IL-4) and IL-13 production. Cytokine 2015, 75, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zurawski, S.M.; Vega, F.; Huyghe, B.; Zurawski, G. Receptors for interleukin-13 and interleukin-4 are complex and share a novel component that functions in signal transduction. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 2663–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichtner-Feigl, S.; Strober, W.; Kawakami, K.; Puri, R.K.; Kitani, A. IL-13 signaling through the IL-13alpha2 receptor is involved in induction of TGF-beta1 production and fibrosis. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, N.; Whitters, M.J.; Jacobson, B.A.; Witek, J.; Sypek, J.P.; Kasaian, M.; Eppihimer, M.J.; Unger, M.; Tanaka, T.; Goldman, S.J.; et al. Enhanced interleukin (IL)-13 responses in mice lacking IL-13 receptor alpha 2. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernacka, A.; Dobaczewski, M.; Frangogiannis, N.G. TGF-β signaling in fibrosis. Growth Factors 2011, 29, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcelin, G.; Ferreira, A.; Liu, Y.; Atlan, M.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Pelloux, V.; Botbol, Y.; Ambrosini, M.; Fradet, M.; Rouault, C.; et al. A PDGFRα-Mediated Switch toward CD9high Adipocyte Progenitors Controls Obesity-Induced Adipose Tissue Fibrosis. Cell. Metab. 2017, 25, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cinti, S.; Mitchell, G.; Barbatelli, G.; Murano, I.; Ceresi, E.; Faloia, E.; Wang, S.; Fortier, M.; Greenberg, A.S.; Obin, M.S. Adipocyte death defines macrophage localization and function in adipose tissue of obese mice and humans. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 2347–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindhorst, A.; Raulien, N.; Wieghofer, P.; Eilers, J.; Rossi, F.M.V.; Bechmann, I.; Gericke, M. Adipocyte death triggers a pro-inflammatory response and induces metabolic activation of resident macrophages. Cell. Death Dis. 2021, 12, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcelin, G.; Gautier, E.L.; Clément, K. Adipose Tissue Fibrosis in Obesity: Etiology and Challenges. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2022, 84, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaitin, D.A.; Adlung, L.; Thaiss, C.A.; Weiner, A.; Li, B.; Descamps, H.; Lundgren, P.; Bleriot, C.; Liu, Z.; Deczkowska, A.; et al. Lipid-Associated Macrophages Control Metabolic Homeostasis in a Trem2-Dependent Manner. Cell 2019, 178, 686–698.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Ikeda, K.; Suganami, T.; Komiya, C.; Ochi, K.; Shirakawa, I.; Hamaguchi, M.; Nishimura, S.; Manabe, I.; Matsuda, T.; et al. Macrophage-inducible C-type lectin underlies obesity-induced adipose tissue fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vila, I.K.; Badin, P.-M.; Marques, M.-A.; Monbrun, L.; Lefort, C.; Mir, L.; Louche, K.; Bourlier, V.; Roussel, B.; Gui, P.; et al. Immune cell Toll-like receptor 4 mediates the development of obesity- and endotoxemia-associated adipose tissue fibrosis. Cell. Rep. 2014, 7, 1116–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingberg, F.; Hinz, B.; White, E.S. The myofibroblast matrix: Implications for tissue repair and fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2013, 229, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antar, S.A.; Ashour, N.A.; Marawan, M.E.; Al-Karmalawy, A.A. Fibrosis: Types, Effects, Markers, Mechanisms for Disease Progression, and Its Relation with Oxidative Stress, Immunity, and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomarat, P.; Banchereau, J. Interleukin-4 and interleukin-13: Their similarities and discrepancies. Int. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 17, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rooijen, N.; van Nieuwmegen, R. Elimination of phagocytic cells in the spleen after intravenous injection of liposome-encapsulated dichloromethylene diphosphonate. An enzyme-histochemical study. Cell. Tissue Res. 1984, 238, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Tordjman, J.; Clément, K.; Scherer, P.E. Fibrosis and adipose tissue dysfunction. Cell. Metab. 2013, 18, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gericke, M.; Weyer, U.; Braune, J.; Bechmann, I.; Eilers, J. A method for long-term live imaging of tissue macrophages in adipose tissue explants. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 308, E1023–E1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Arcy, Q.; Gharaee-Kermani, M.; Zhilin-Roth, A.; Macoska, J.A. The IL-4/IL-13 signaling axis promotes prostatic fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinnin, M.; Ihn, H.; Yamane, K.; Tamaki, K. Interleukin-13 stimulates the transcription of the human alpha2(I) collagen gene in human dermal fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 41783–41791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaviratne, M.; Hesse, M.; Leusink, M.; Cheever, A.W.; Davies, S.J.; McKerrow, J.H.; Wakefield, L.M.; Letterio, J.J.; Wynn, T.A. IL-13 activates a mechanism of tissue fibrosis that is completely TGF-beta independent. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 4020–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aoudjehane, L.; Pissaia, A., Jr.; Scatton, O.; Podevin, P.; Massault, P.-P.; Chouzenoux, S.; Soubrane, O.; Calmus, Y.; Conti, F. Interleukin-4 induces the activation and collagen production of cultured human intrahepatic fibroblasts via the STAT-6 pathway. Lab. Investig. 2008, 88, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, J.K.; Austin, E.; Huang, A.; Mamalis, A.; Jagdeo, J. The IL-4/IL-13 axis in skin fibrosis and scarring: Mechanistic concepts and therapeutic targets. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2020, 312, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.G.; Homer, R.J.; Zhu, Z.; Lanone, S.; Wang, X.; Koteliansky, V.; Shipley, J.M.; Gotwals, P.; Noble, P.; Chen, Q.; et al. Interleukin-13 induces tissue fibrosis by selectively stimulating and activating transforming growth factor beta(1). J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Lyons, T.; Monks, J.; Lucia, M.S.; Wilson, R.S.; Hines, L.; Man, Y.-g.; Borges, V.; Schedin, P. Alternatively activated macrophages and collagen remodeling characterize the postpartum involuting mammary gland across species. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 1241–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takemoto, R.; Kamiya, T.; Atobe, T.; Hara, H.; Adachi, T. Regulation of lysyl oxidase expression in THP-1 cell-derived M2-like macrophages. J. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 122, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa Santos, M.A.R.; Dos Reis, J.S.; do Nascimento Santos, C.A.; da Costa, K.M.; Barcelos, P.M.; de Oliveira Francisco, K.Q.; Barbosa, P.A.G.N.; da Silva, E.D.S.; Freire-de-Lima, C.G.; Morrot, A.; et al. Expression of O-glycosylated oncofetal fibronectin in alternatively activated human macrophages. Immunol. Res. 2023, 71, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, R.; Bing, R.; Gartling, G.J.; Branski, R.C. Macrophages alter inflammatory and fibrotic gene expression in human vocal fold fibroblasts. Exp. Cell. Res. 2022, 419, 113301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnik, M.; Hukara, A.; Kocherova, I.; Jordan, S.; Schniering, J.; Milleret, V.; Ehrbar, M.; Klingel, K.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.; Distler, O.; et al. Elevated Fibronectin Levels in Profibrotic CD14+ Monocytes and CD14+ Macrophages in Systemic Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 642891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munder, M.; Eichmann, K.; Morán, J.M.; Centeno, F.; Soler, G.; Modolell, M. Th1/Th2-regulated expression of arginase isoforms in murine macrophages and dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 3771–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindemann, D.; Racké, K. Glucocorticoid inhibition of interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-13 (IL-13) induced up-regulation of arginase in rat airway fibroblasts. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2003, 368, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, J.; Weyer, U.; Immig, K.; Klöting, N.; Blüher, M.; Eilers, J.; Bechmann, I. Local proliferation of macrophages in adipose tissue during obesity-induced inflammation. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichioka, M.; Suganami, T.; Tsuda, N.; Shirakawa, I.; Hirata, Y.; Satoh-Asahara, N.; Shimoda, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Kim-Saijo, M.; Miyamoto, Y.; et al. Increased expression of macrophage-inducible C-type lectin in adipose tissue of obese mice and humans. Diabetes 2011, 60, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramachandran, P.; Dobie, R.; Wilson-Kanamori, J.R.; Dora, E.F.; Henderson, B.E.P.; Luu, N.T.; Portman, J.R.; Matchett, K.P.; Brice, M.; Marwick, J.A.; et al. Resolving the fibrotic niche of human liver cirrhosis at single-cell level. Nature 2019, 575, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, M.; Kato, H.; Suganami, T.; Konuma, K.; Marumoto, Y.; Terai, S.; Sakugawa, H.; Kanai, S.; Hamaguchi, M.; Fukaishi, T.; et al. Hepatic crown-like structure: A unique histological feature in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice and humans. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marangoni, R.G.; Korman, B.D.; Wei, J.; Wood, T.A.; Graham, L.V.; Whitfield, M.L.; Scherer, P.E.; Tourtellotte, W.G.; Varga, J. Myofibroblasts in murine cutaneous fibrosis originate from adiponectin-positive intradermal progenitors. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.E.C.; Rabhi, N.; Orofino, J.; Gamini, R.; Perissi, V.; Vernochet, C.; Farmer, S.R. The Adipocyte Acquires a Fibroblast-Like Transcriptional Signature in Response to a High Fat Diet. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marangoni, R.G.; Korman, B.; Varga, J. Adipocytic Progenitor Cells Give Rise to Pathogenic Myofibroblasts: Adipocyte-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Its Emerging Role in Fibrosis in Multiple Organs. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2020, 22, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Côté, J.A.; Lessard, J.; Pelletier, M.; Marceau, S.; Lescelleur, O.; Fradette, J.; Tchernof, A. Role of the TGF-β pathway in dedifferentiation of human mature adipocytes. FEBS Open Bio 2017, 7, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, C.-H.; Shiau, M.-Y.; Chuang, P.-H.; Chang, Y.-H.; Hwang, J. Interleukin-4 regulates lipid metabolism by inhibiting adipogenesis and promoting lipolysis. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spencer, M.; Yao-Borengasser, A.; Unal, R.; Rasouli, N.; Gurley, C.M.; Zhu, B.; Peterson, C.A.; Kern, P.A. Adipose tissue macrophages in insulin-resistant subjects are associated with collagen VI and fibrosis and demonstrate alternative activation. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 299, E1016–E1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarsenbayeva, A.; Pereira, M.J.; Nandi Jui, B.; Ahmed, F.; Dipta, P.; Fanni, G.; Almby, K.; Kristófi, R.; Hetty, S.; Eriksson, J.W. Excess glucocorticoid exposure contributes to adipose tissue fibrosis which involves macrophage interaction with adipose precursor cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 198, 114976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, H.M.; Acosta, L.P.; Wu, H.W.; McGarvey, S.T.; Su, L.; Langdon, G.C.; Jiz, M.A.; Jarilla, B.; Olveda, R.M.; Friedman, J.F.; et al. Th2 cytokines are associated with persistent hepatic fibrosis in human Schistosoma japonicum infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 195, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandriani, S.; DePianto, D.J.; N’Diaye, E.N.; Abbas, A.R.; Jackman, J.; Bevers, J., III; Ramirez-Carrozzi, V.; Pappu, R.; Kauder, S.E.; Toy, K.; et al. Endogenously expressed IL-13Rα2 attenuates IL-13-mediated responses but does not activate signaling in human lung fibroblasts. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, H.; Laurent, S.; Tang, Y.; Zong, H.; Vemulapalli, P.; Pessin, J.E. Adipocyte-specific IKKβ signaling suppresses adipose tissue inflammation through an IL-13-dependent paracrine feedback pathway. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Wakkad, A.; Hassan, N.E.-M.; Sibaii, H.; El-Zayat, S.R. Proinflammatory, anti-inflammatory cytokines and adiponkines in students with central obesity. Cytokine 2013, 61, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-H.; Ho, K.-T.; Lu, S.-H.; Huang, C.-N.; Shiau, M.-Y. Regulation of glucose/lipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity by interleukin-4. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2012, 36, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasarica, M.; Gowronska-Kozak, B.; Burk, D.; Remedios, I.; Hymel, D.; Gimble, J.; Ravussin, E.; Bray, G.A.; Smith, S.R. Adipose tissue collagen VI in obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 5155–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, T.; Muise, E.S.; Iyengar, P.; Wang, Z.V.; Chandalia, M.; Abate, N.; Zhang, B.B.; Bonaldo, P.; Chua, S.; Scherer, P.E. Metabolic dysregulation and adipose tissue fibrosis: Role of collagen VI. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 1575–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braune, J.; Weyer, U.; Hobusch, C.; Mauer, J.; Brüning, J.C.; Bechmann, I.; Gericke, M. IL-6 Regulates M2 Polarization and Local Proliferation of Adipose Tissue Macrophages in Obesity. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 2927–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Rooijen, N.; Sanders, A.; van den Berg, T.K. Apoptosis of macrophages induced by liposome-mediated intracellular delivery of clodronate and propamidine. J. Immunol. Methods 1996, 193, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, J.; Arndt, L.; Kirstein, M.; Hobusch, C.; Brinker, G.; Klöting, N.; Braune, J.; Gericke, M. Myeloid Cell-Specific IL-4 Receptor Knockout Partially Protects from Adipose Tissue Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2021, 207, 3081–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braune, J.; Lindhorst, A.; Fröba, J.; Hobusch, C.; Kovacs, P.; Blüher, M.; Eilers, J.; Bechmann, I.; Gericke, M. Multinucleated Giant Cells in Adipose Tissue Are Specialized in Adipocyte Degradation. Diabetes 2021, 70, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brentnall, M.; Weir, D.B.; Rongvaux, A.; Marcus, A.I.; Boise, L.H. Procaspase-3 regulates fibronectin secretion and influences adhesion, migration and survival independently of catalytic function. J. Cell. Sci. 2014, 127, 2217–2226. [Google Scholar]
- Brinker, G.; Froeba, J.; Arndt, L.; Braune, J.; Hobusch, C.; Lindhorst, A.; Bechmann, I.; Gericke, M. CD4+ T cells regulate glucose homeostasis independent of adipose tissue dysfunction in mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 51, 1399–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimshony, T.; Senderovich, N.; Avital, G.; Klochendler, A.; de Leeuw, Y.; Anavy, L.; Gennert, D.; Li, S.; Livak, K.J.; Rozenblatt-Rosen, O.; et al. CEL-Seq2: Sensitive highly-multiplexed single-cell RNA-Seq. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aken, B.L.; Achuthan, P.; Akanni, W.; Amode, M.R.; Bernsdorff, F.; Bhai, J.; Billis, K.; Carvalho-Silva, D.; Cummins, C.; Clapham, P.; et al. Ensembl 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D635–D642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robinson, M.D.; Oshlack, A. A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Langhardt, J.; Flehmig, G.; Klöting, N.; Lehmann, S.; Ebert, T.; Kern, M.; Schön, M.R.; Gärtner, D.; Lohmann, T.; Dressler, M.; et al. Effects of Weight Loss on Glutathione Peroxidase 3 Serum Concentrations and Adipose Tissue Expression in Human Obesity. Obes. Facts 2018, 11, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klöting, N.; Blüher, M. Insulin-sensitive obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 299, E506–E515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picelli, S.; Faridani, O.R.; Björklund, A.K.; Winberg, G.; Sagasser, S.; Sandberg, R. Full-length RNA-seq from single cells using Smart-seq2. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, N.L.; Pimentel, H.; Melsted, P.; Pachter, L. Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patil, I. Visualizations with statistical details: The ‘ggstatsplot’ approach. JOSS 2021, 6, 3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Foundation for Statistical Computing. R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2022. Available online: http://www.r-project.org (accessed on 18 February 2022).






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arndt, L.; Lindhorst, A.; Neugebauer, J.; Hoffmann, A.; Hobusch, C.; Alexaki, V.-I.; Ghosh, A.; Blüher, M.; Wolfrum, C.; Glaß, M.; et al. The Role of IL-13 and IL-4 in Adipose Tissue Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065672
Arndt L, Lindhorst A, Neugebauer J, Hoffmann A, Hobusch C, Alexaki V-I, Ghosh A, Blüher M, Wolfrum C, Glaß M, et al. The Role of IL-13 and IL-4 in Adipose Tissue Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(6):5672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065672
Chicago/Turabian StyleArndt, Lilli, Andreas Lindhorst, Julia Neugebauer, Anne Hoffmann, Constance Hobusch, Vasileia-Ismini Alexaki, Adhideb Ghosh, Matthias Blüher, Christian Wolfrum, Markus Glaß, and et al. 2023. "The Role of IL-13 and IL-4 in Adipose Tissue Fibrosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 6: 5672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065672
APA StyleArndt, L., Lindhorst, A., Neugebauer, J., Hoffmann, A., Hobusch, C., Alexaki, V.-I., Ghosh, A., Blüher, M., Wolfrum, C., Glaß, M., & Gericke, M. (2023). The Role of IL-13 and IL-4 in Adipose Tissue Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(6), 5672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065672