Rivastigmine–Benzimidazole Hybrids as Promising Multitarget Metal-Modulating Compounds for Potential Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
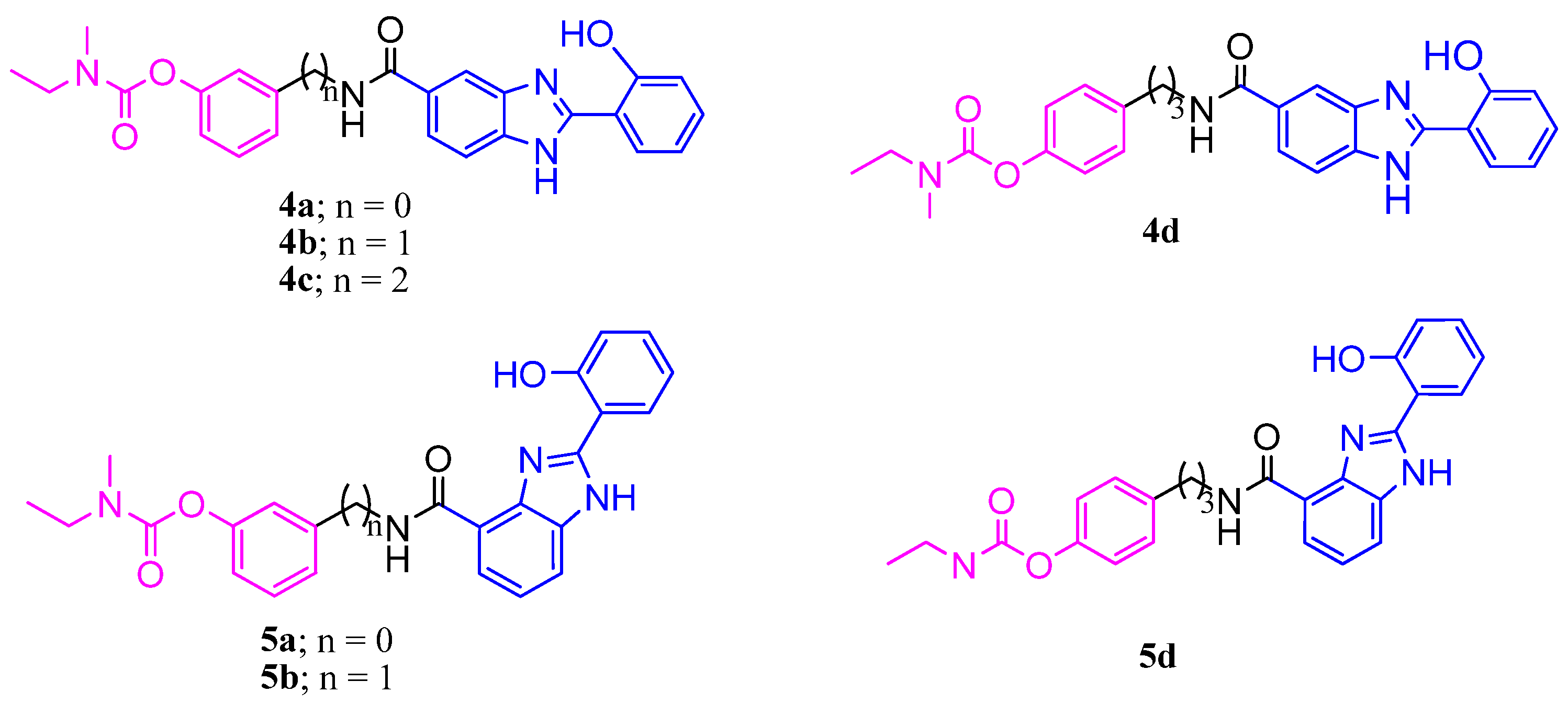
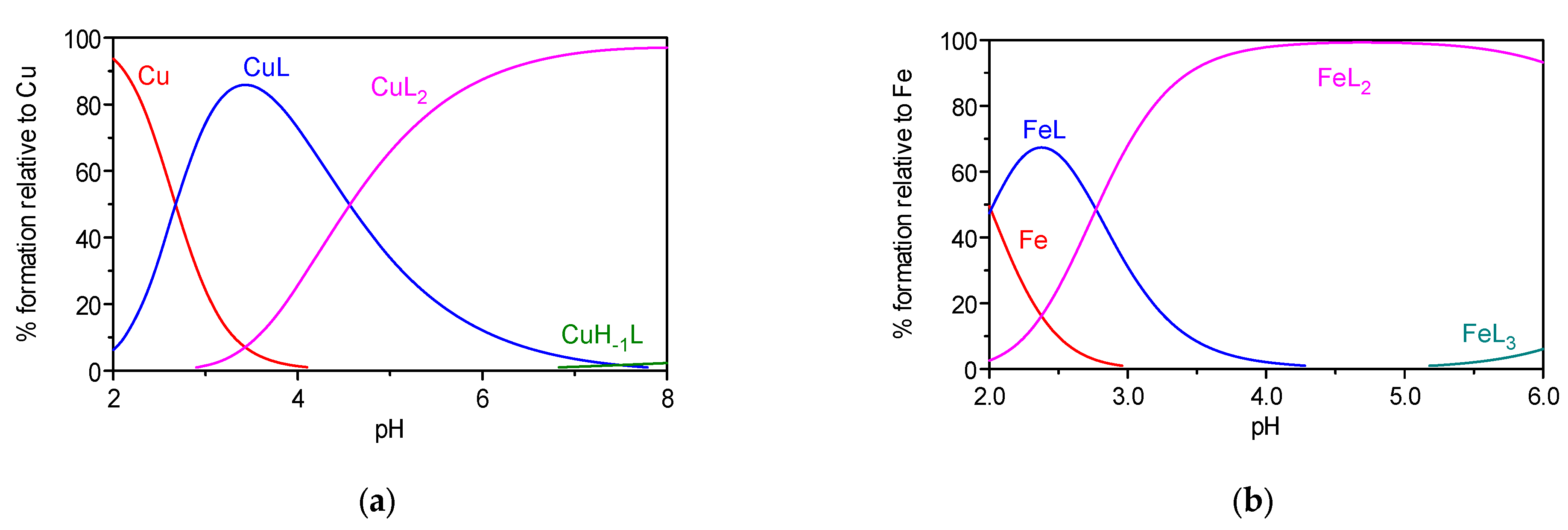
2.1. Metal Complexation Studies
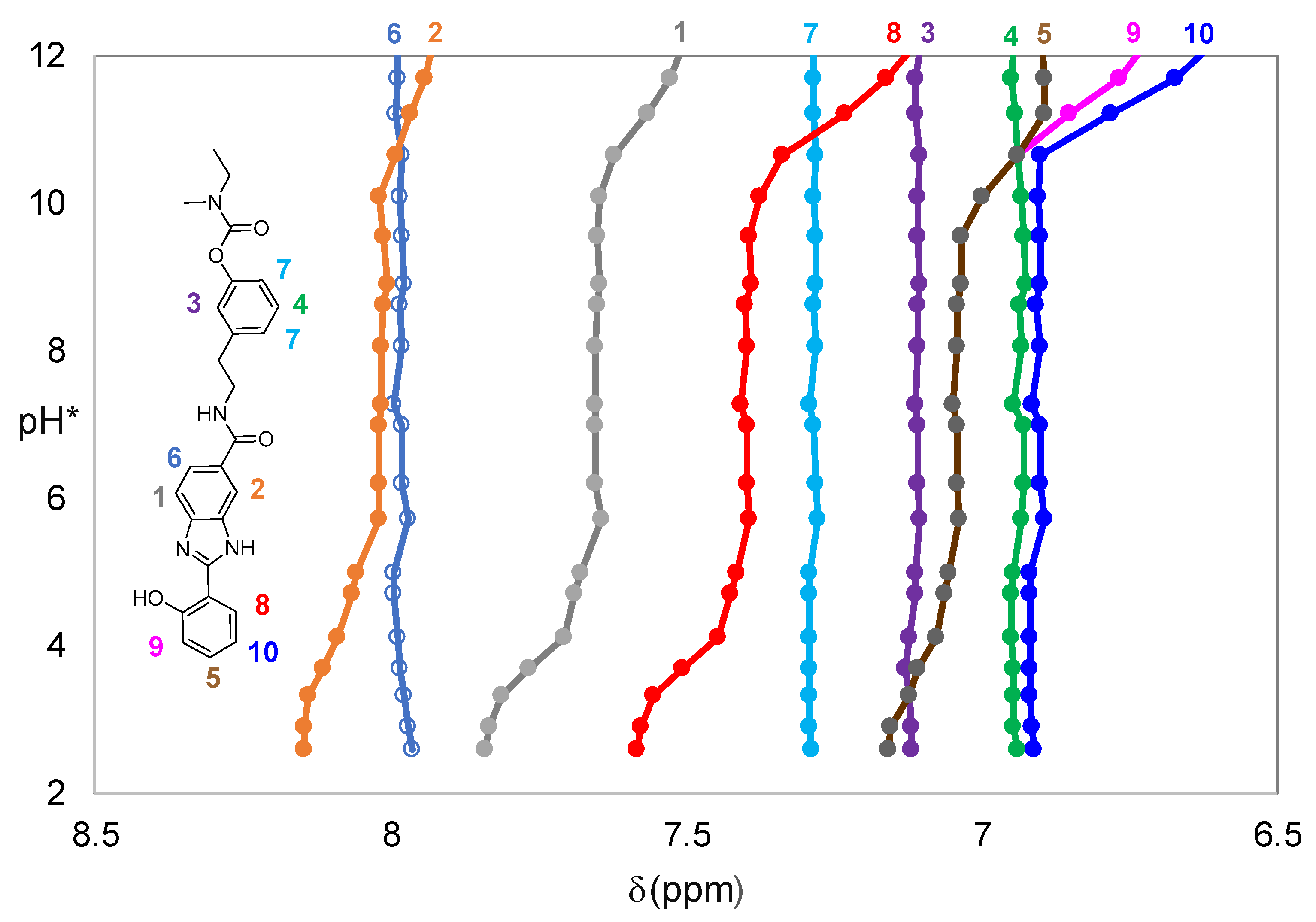
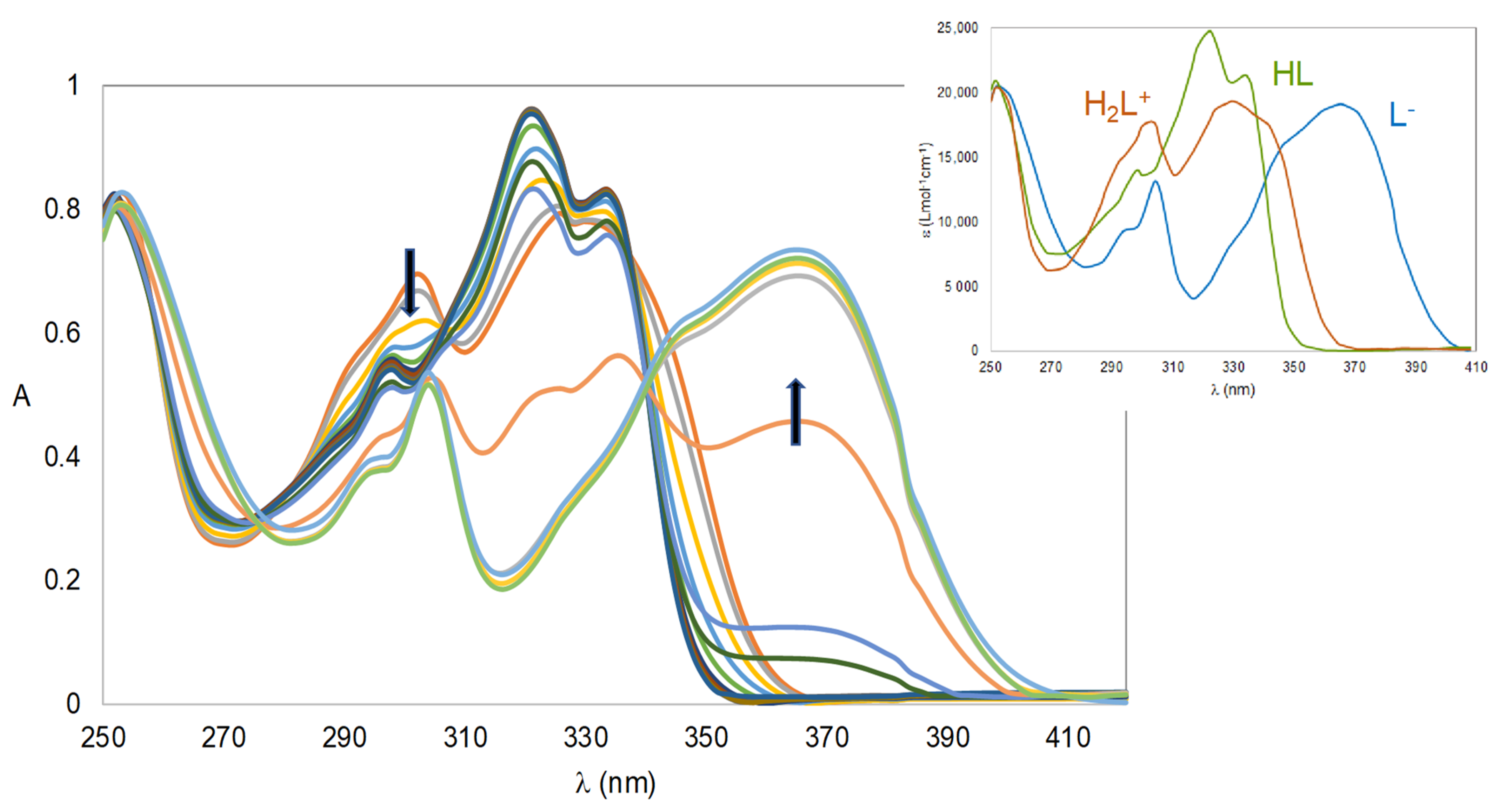
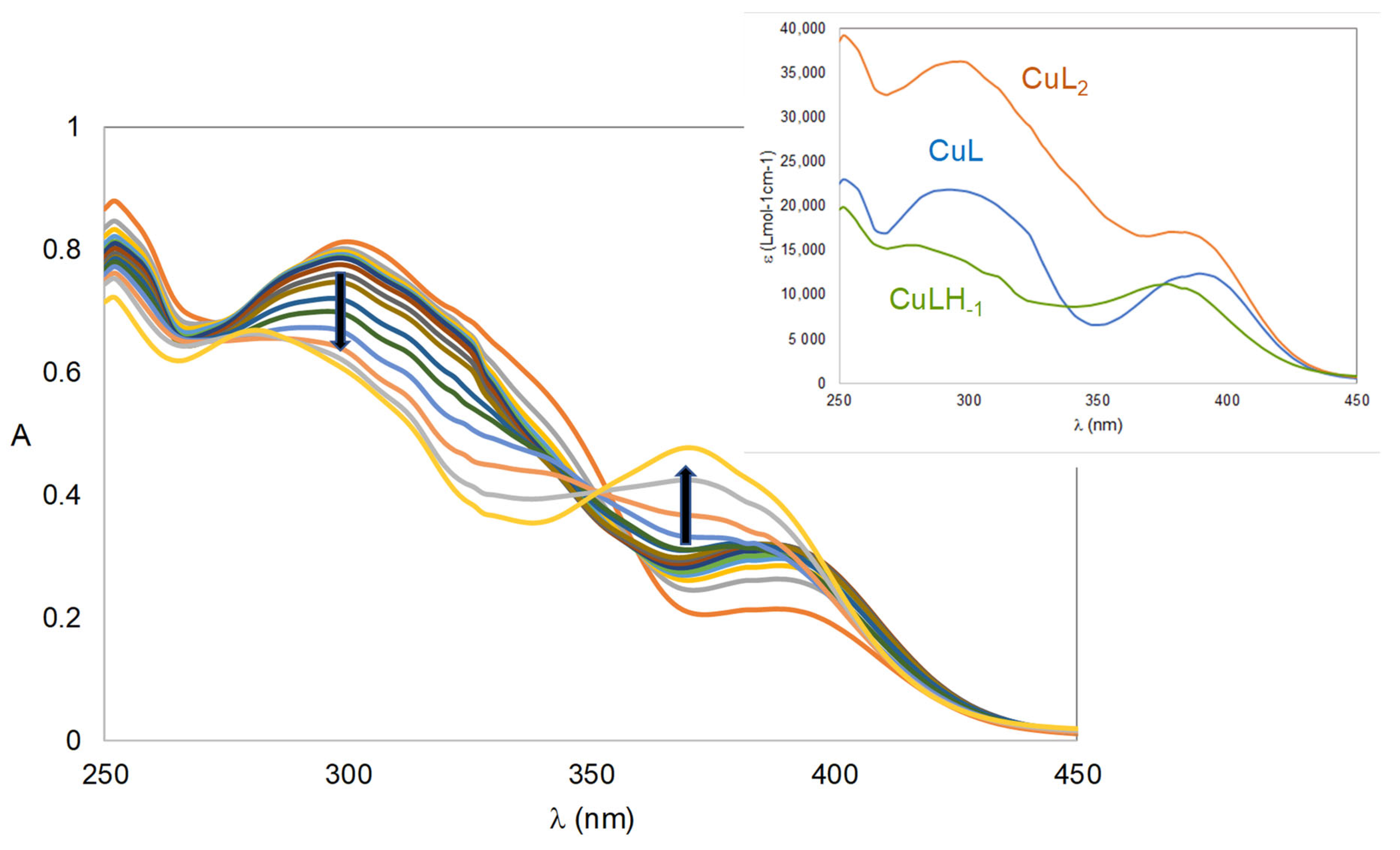
2.1.1. Solution Equilibria
Acid-Base Properties
Metal Chelation
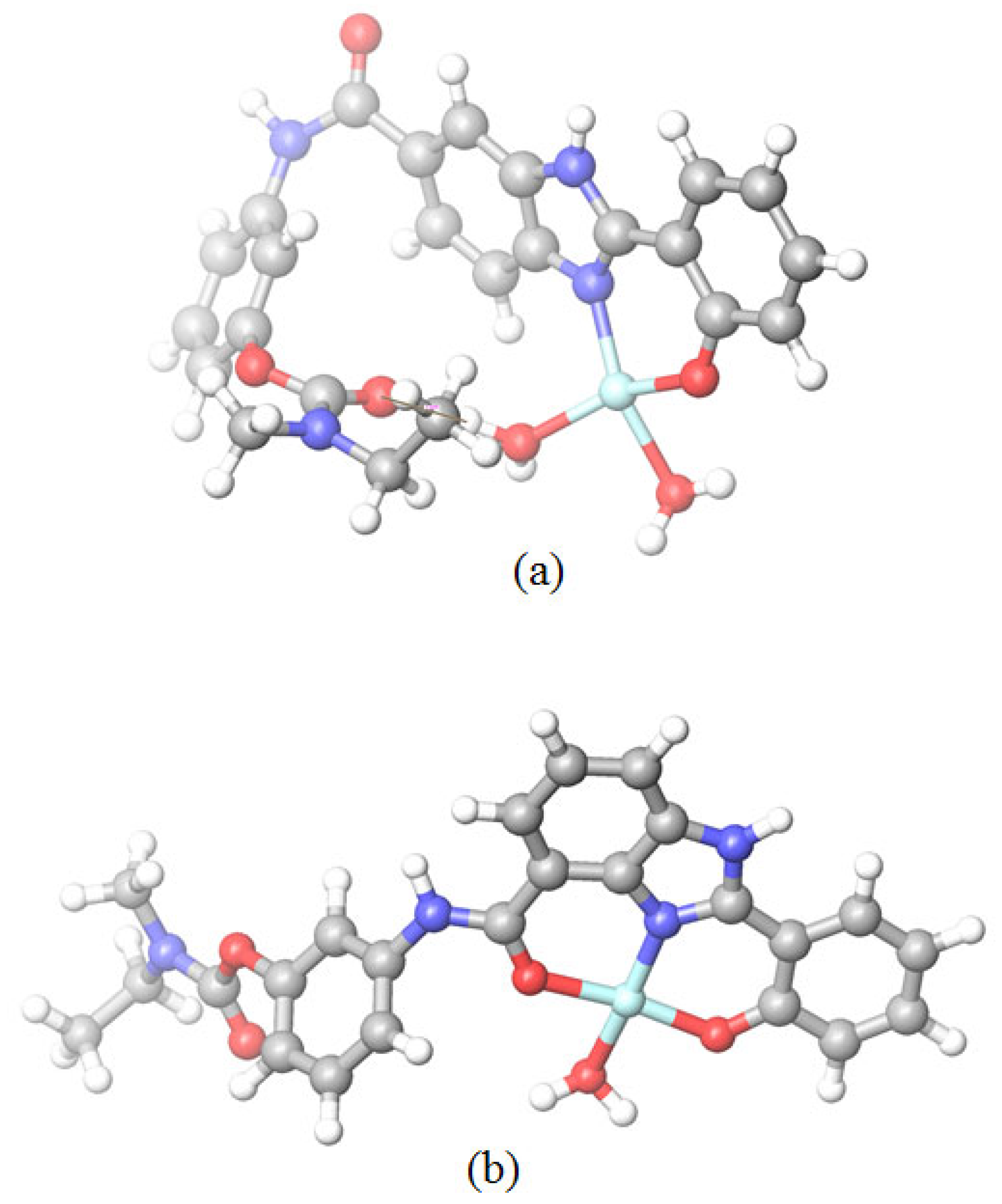
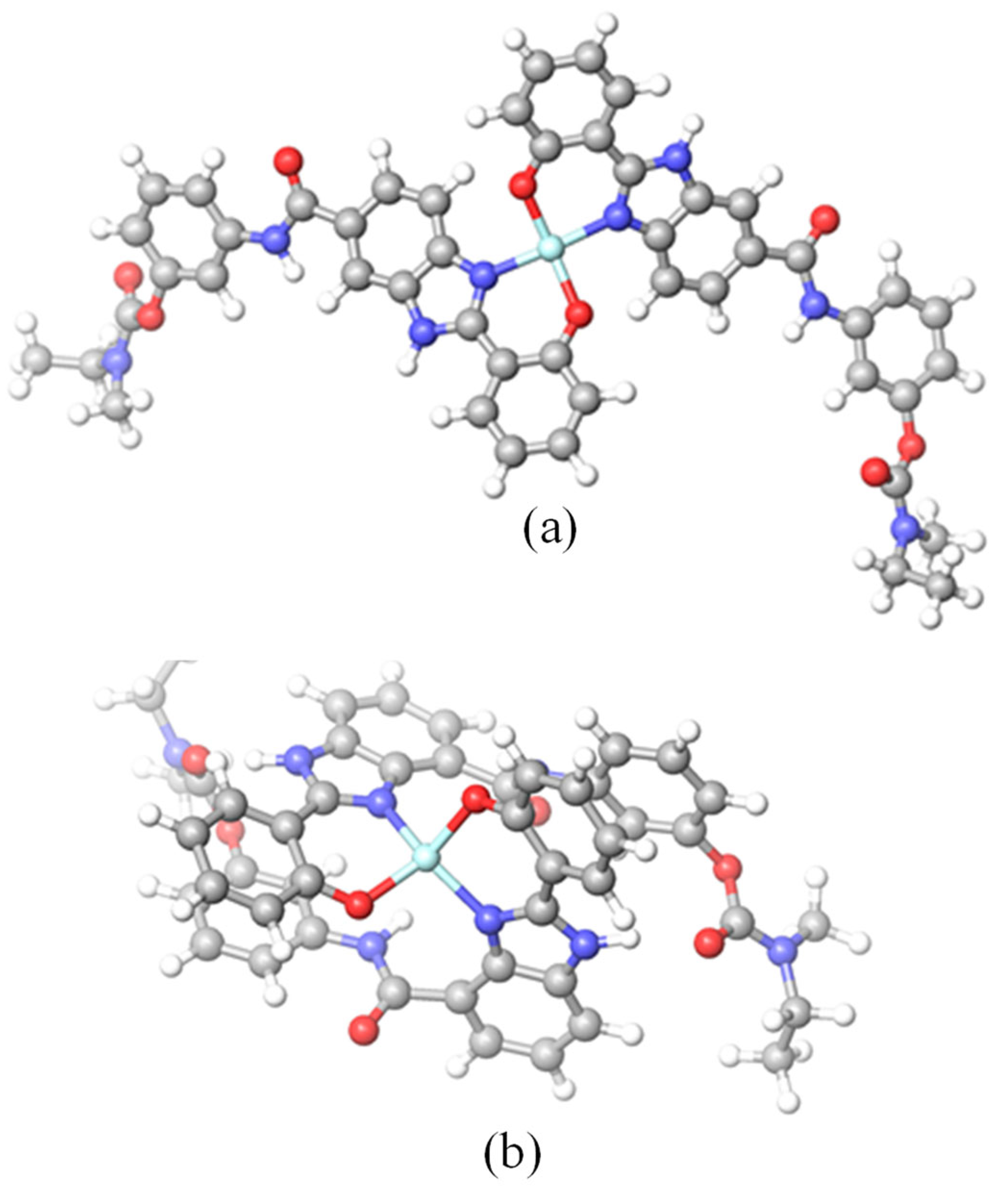
2.1.2. Molecular Modeling of the Copper Complexes
2.2. Biological Studies
2.2.1. Inhibition of Aβ Aggregation and Cu(II) Role
2.2.2. Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidases
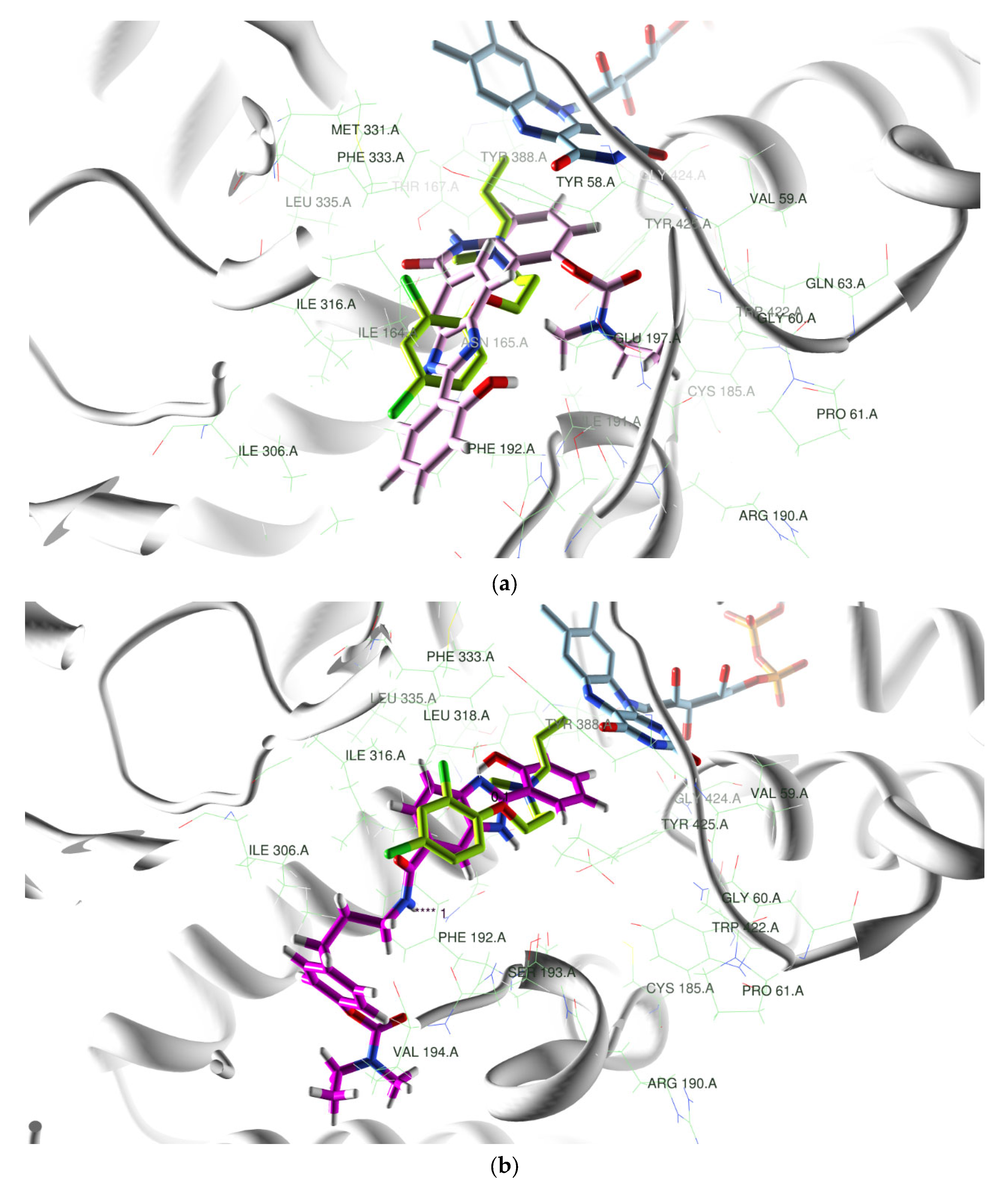
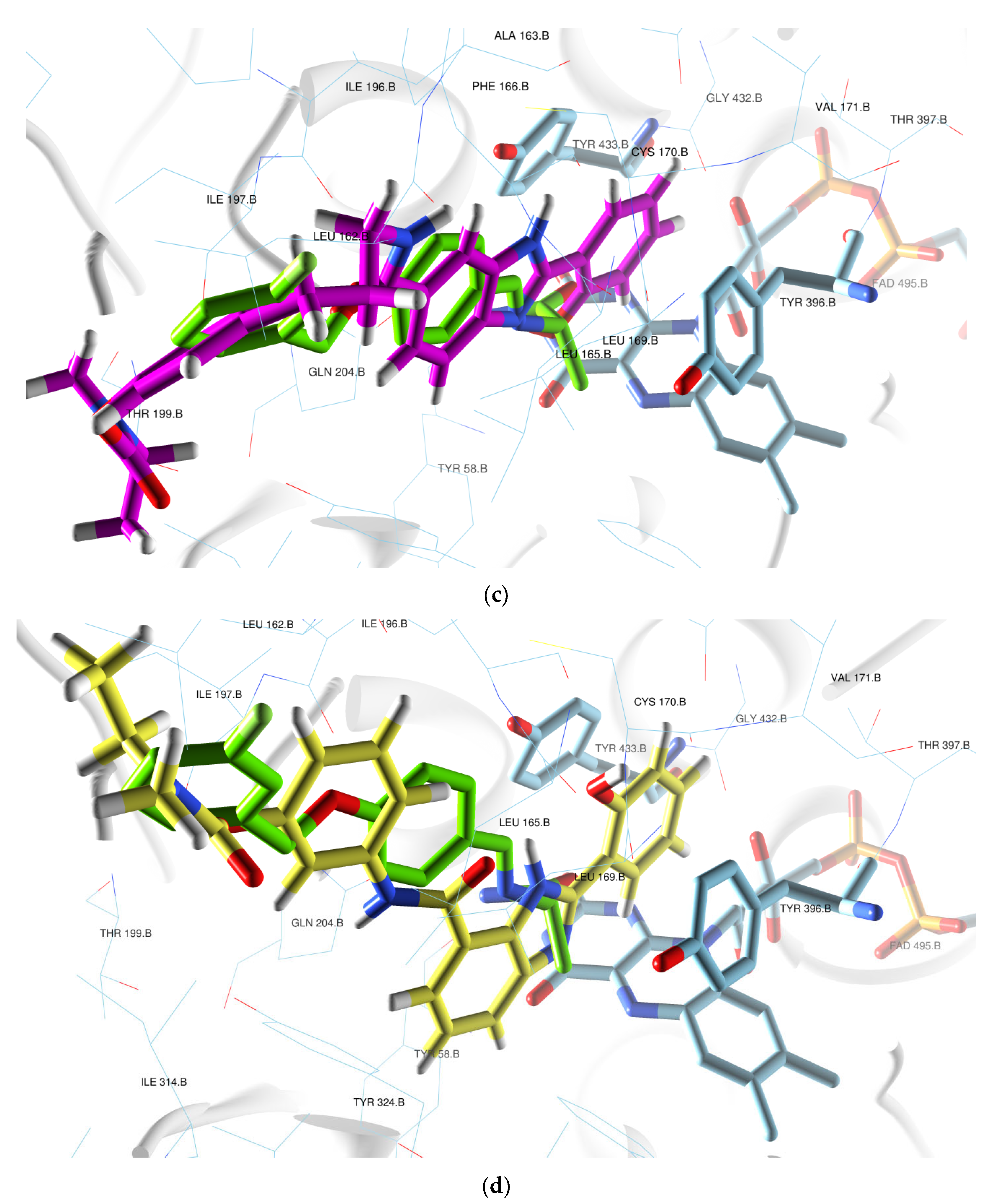
2.2.3. Docking Studies of Selected Hybrids with hMAOs
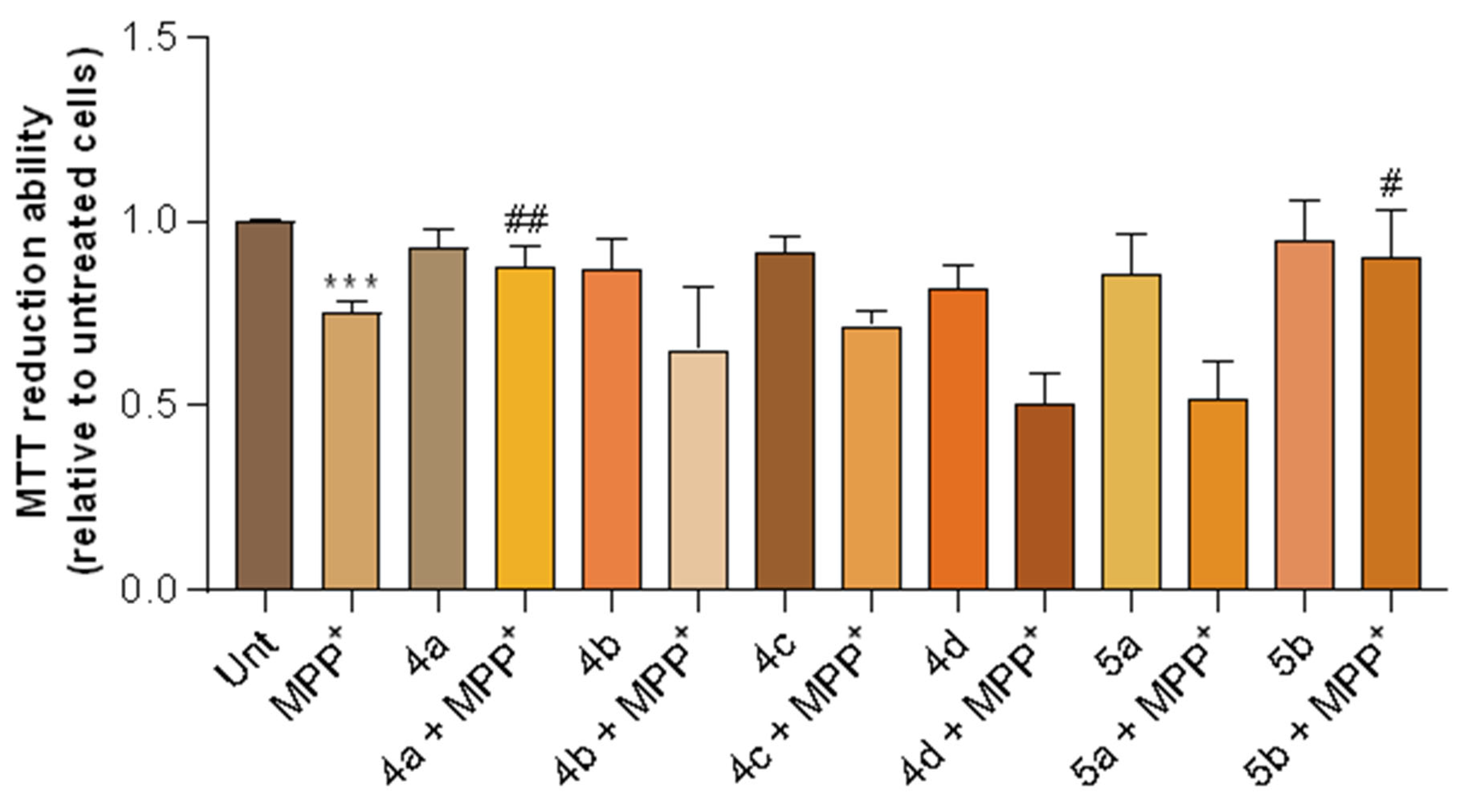
2.2.4. Cell Viability and In Vitro Neuroprotection
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Metal Complexation Studies
3.1.1. Materials and Equipment
3.1.2. Spectrophotometric Titrations
3.1.3. 1H NMR Studies
3.1.4. Molecular Modeling of the Cu(II) Complexes
3.2. Biological Assays
3.2.1. Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase
3.2.2. Cell Viability and In Vitro Neuroprotection
3.3. Molecular Docking of Monoamine Oxidases
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alzheimer’s Association. Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2021, 17, 327–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsey, E.R.; Elbaz, A.; Nichols, E.; Abbasi, N.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Adsuar, J.C.; Ansha, M.G.; Brayne, C.; Choi, J.-Y.J.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of Parkinson’s disease, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Ashoor, H.M.; Soobiah, C.; Rios, P.; Veroniki, A.A.; Hamid, J.S.; Ivory, J.D.; Khan, P.A.; Yazdi, F.; Ghassemi, M.; et al. Comparative effectiveness and safety of cognitive enhancers for treating Alzheimer’s disease: Systematic review and network metaanalysis. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2018, 66, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Mesulam, M.M.; Cuello, A.C.; Khachaturian, A.S.; Vergallo, A.; Farlow, M.R.; Snyder, P.J.; Giacobini, E.; Khachaturian, Z.S. Revisiting the cholinergic hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease: Emerging evidence from translational and clinical research. J. Prev. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 6, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeWitt, P.A.; Fahn, S. Levodopa therapy for Parkinson disease: A look backward and forward. Neurology 2016, 86, S3–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolato, M.; Chen, K.; Shih, J.C. Monoamine oxidase inactivation: From pathophysiology to therapeutics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisani, L.; Catto, M.; Leonetti, F.; Nicolotti, O.; Stefanachi, A.; Campagna, F.; Carotti, A. Targeting monoamine oxidases with multipotent ligands: An emerging strategy in the search of new drugs against neurodegenerative diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 4568–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, P.; Park, H.; Baumann, M.; Dunlop, J.; Frydman, J.; Kopito, R.; McCampbell, A.; Leblanc, G.; Venkateswaran, A.; Nurmi, A.; et al. Protein misfolding in neurodegenerative diseases: Implications and strategies. Transl. Neurodegener. 2017, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnham, K.J.; Bush, A.I. Biological metals and metal-targeting compounds in major neurodegenerative diseases. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6727–6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Nguyen, M.; Robert, A.; Meunier, B. Metal ions in Alzheimer’s disease: A key role or not? Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2026–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ricco, R.; Valensin, D.; Dell’Acqua, S.; Casella, L.; Hureau, C.; Faller, P. Copper(I/II), α/β-Synuclein and amyloid-β: Menage à trois? ChemBioChem 2015, 16, 2319–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savelieff, M.G.; Nam, G.; Kang, J.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, M.; Lim, M.H. Development of multifunctional molecules as potential therapeutic candidates for Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in the last decade. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 1221–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.A.; Chand, K.; Chaves, S. Recent progress in repositioning Alzheimer´s disease drugs based on a multitarget strategy. Future Med. Chem. 2016, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismaili, L.; Refouvelet, B.; Benchekroun, M.; Brogi, S.; Brindisi, M.; Gemma, S.; Campiani, G.; Filipic, S.; Agbaba, D.; Esteban, G.; et al. Multitarget compounds bearing tacrine- and donepezil-like structural and functional motifs for the potential treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2017, 151, 4–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeřábek, J.; Uliassi, E.; Guidotti, L.; Korábečný, J.; Soukup, O.; Sepsova, V.; Hrabinova, M.; Kuča, K.; Bartolini, M.; Peña-Altamira, L.E.; et al. Tacrine-resveratrol fused hybrids as multi-target-directed ligands against Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 127, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampietro, A.; Perez-Areales, F.J.; Martinez, P.; Arce, E.M.; Galdeano, C.; Munoz-Torrero, D. Unveiling the multitarget anti-Alzheimer drug discovery landscape: A bibliometric analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lv, Y.; Bai, R.; Xie, Y. Structural exploration of multifunctional monoamine oxidase B inhibitors as potential drug candidates against Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 114, 105070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Youdim, M.B.H. A novel neuroprotective cholinesterase-monoamine oxidase inhibitor for treatment of dementia and depression in Parkinson’s disease. Ageing Neur. Dis. 2022, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremathad, A.; Keri, R.S.; Esteves, A.R.; Cardoso, S.M.; Chaves, S.; Santos, M.A. Novel tacrine-hydroxyphenylbenzimidazole hybrids as potential multitarget drug candidates for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 148, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piemontese, L.; Tomás, D.; Hiremathad, A.; Capriati, V.; Candeias, E.; Cardoso, S.M.; Chaves, S.; Santos, M.A. Donepezil structure-based hybrids as potential multifunctional anti-Alzheimer’s drug candidates. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2018, 33, 1212–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Zurdo, D.; Rosales-Conrado, N.; León-González, M.E.; Brunetti, L.; Piemontese, L.; Pereira-Santos, A.R.; Cardoso, S.M.; Madrid, Y.; Chaves, S.; Santos, M.A. Novel rivastigmine derivatives as promising multi-target compounds for potential treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colca, J.R.; Finck, B.N. Metabolic Mechanisms connecting Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases: Potential avenues for novel therapeutic approaches. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 929328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayton, S.; Lei, P.; Bush, A.I. Metallostasis in Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 62, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, S.; Várnagy, K.; Santos, M.A. Recent multi-target approaches on the development of anti-Alzheimer’s agents integrating metal chelation activity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 7247–7277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista-Aguilera, O.M.; Esteban, G.; Chioua, M.; Nikolic, K.; Agbaba, D.; Moraleda, I.; Iriepa, I.; Soriano, E.; Samadi, A.; Unzeta, M.; et al. Multipotent cholinesterase/monoamine oxidase inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Design, synthesis, biochemical evaluation, ADMET, molecular modeling, and QSAR analysis of novel donepezil-pyridyl hybrids. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2014, 13, 81893–81910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, H.; Wu, F.; Dimitrov, M.; Osuna, G.M.G.; Fraering, P.C. Zinc and copper differentially modulate amyloid precursor protein processing by gamma-secretase and amyloid-beta peptide production. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 3751–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lei, P.; Tuo, Q.; Ayton, S.; Li, Q.X.; Moon, S.; Volitakis, I.; Liu, R.; Masters, C.L.; Finkelstein, D.I.; et al. Enduring elevations of hippocampal amyloid precursor protein and iron are features of beta-amyloid toxicity and are mediated by tau. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitazawa, M.; Hsu, H.W.; Medeiros, R. Copper exposure perturbs brain inflammatory responses and impairs clearance of amyloid-beta. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 152, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, A.; Liu, Y.; Nguyen, M.; Meunier, B. Regulation of copper and iron homeostasis by metal chelators: A possible chemotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1332–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, S.; Hiremathad, A.; Tomas, D.; Keri, R.S.; Piemontese, L.; Santos, M.A. Exploring the chelating capacity of 2-hydroxyphenyl-benzimidazole based hybrids with multi-target ability as anti-Alzheimer’s agents. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 16503–16515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekany, L.; Nagypal, I. PSEQUAD. In Computational Methods for the Determination of Formation Constants; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 291–353. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M.; Josselin, R.; Silva, D.; Cardoso, S.M.; May, N.; Chaves, S.; Santos, M.A. Donepezil-based hybrids as multifunctional anti-Alzheimer’s disease chelating agents: Effect of positional isomerization. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2020, 206, 111039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, K.N.; Carrano, C.J. Coordination chemistry and microbial iron transport. Acc. Chem. Res. 1979, 12, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Montgomery, J.A., Jr.; Vreven, T.; Kudin, K.N.; Burant, J.C.; et al. Gaussian 03, Revision C.02; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Wang, Y. Generalized gradient approximation for the exchange-correlation hole of a many-electron system. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 16533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faller, P.; Hureau, C. Bioinorganic chemistry of copper and zinc ions coordinated to amyloid-peptide. Dalton Trans. 2009, 7, 1080–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesiti, F.; Maruca, A.; Silva, V.; Rocca, R.; Fernandes, C.; Remião, F.; Uriarte, E.; Alcaro, S.; Gaspar, A.; Borges, F. 4-Oxoquinolines and monoamine oxidase: When tautomerism matters. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 213, 113183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavarria, D.; Cagide, F.; Pinto, M.; Gomes, L.R.; Low, J.N.; Borges, F. Development of piperic acid-based monoamine oxidase inhibitors: Synthesis, structural characterization and biological evaluation. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1182, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youdim, M.B.H.; Edmondson, D.; Tipton, K.F. The therapeutic potential of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carradori, S.; Petzer, J.P. Novel monoamine oxidase inhibitors: A patent review (2012–2014). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2014, 25, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, J.H.; Wilson, A.A.; Sagrati, S.; Miler, L.; Rusjan, P.; Bloomfield, P.M.; Clark, M.; Sacher, J.; Voineskos, A.N.; Houle, S. Brain monoamine oxidase A binding in major depressive disorder: Relationship to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor treatment, recovery, and recurrence. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacher, J.; Houle, S.; Parkes, J.; Rusjan, P.; Sagrati, S.; Wilson, A.A.; Meyer, J. Monoamine oxidase A inhibitor occupancy during treatment of major depressive episodes with moclobemide or St. John’s wort: An [11C]-harmine PET study. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2011, 36, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bymaster, F.P.; McNamara, R.K.; Tran, P.V. New approaches to developing antidepressants by enhancing monoaminergic neurotransmission. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2003, 12, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hely, M.A.; Reid, W.G.; Adena, M.A.; Halliday, G.M.; Morris, J.G. The Sydney multicenter study of Parkinson’s disease: The inevitability of dementia at 20 years. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, J.; Lefevre, G.; Small, G.; Appel-Dingemanse, S. Pharmacokinetic rationale for the rivastigmine patch. Neurology 2007, 69, S10–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandiah, N.; Pai, M.-C.; Senanarong, V.; Looi, I.; Ampil, E.; Park, K.W.; Karanam, A.K.; Christopher, S. Rivastigmine: The advantages of dual inhibition of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase and its role in subcortical vascular dementia and Parkinson’s disease dementia. Clin. Interv. Aging 2017, 12, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Colibus, L.; Li, M.; Binda, C.; Lustig, A.; Edmondson, D.E.; Mattevi, A. Three-dimensional structure of human monoamine oxidase A (MAO A): Relation to the structures of rat MAO A and human MAO B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12684–12689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binda, C.; Wang, J.; Pisani, L.; Caccia, C.; Carotti, A.; Salvati, P.; Edmondson, D.E.; Mattevi, M. Structures of human monoamine oxidase B complexes with selective noncovalent inhibitors: Safinamide and coumarin analogs. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5848–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, H.A.; Dhillon, S. Safinamide: A review in Parkinson’s disease. CNS Drugs 2017, 31, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yu, H.; Zhu, J.; Li, D. Protective effects and mechanisms of procyanidins on Parkinson’s disease in vivo and in vitro. Molecules 2021, 26, 5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xicoy, H.; Wieringa, B.; Martens, G.J. The SH-SY5Y cell line in Parkinson’s disease research: A systematic review. Mol. Neurodegener. 2017, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.R.; Hu, L.S.; Li, G.Y. SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell line: In vitro cell model of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Chin. Med. J. 2010, 123, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar]
- Singer, T.P.; Ramsay, R.R.; McKeown, K.; Trevor, A.; Castagnoli, N.E., Jr. Mechanism of the neurotoxicity of 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+), the toxic bioactivation product of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP). Toxicology 1988, 49, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossotti, F.J.C.; Rossotti, H. Potentiometric titrations using gran plots: A textbook omission. J. Chem. Educ. 1965, 42, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gans, P.; Sabatini, A.; Vacca, A. Investigation of equilibria in solution. Determination of equilibrium constants with the HYPERQUAD suite of programs. Talanta 1996, 43, 1739–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krezel, A.; Bal, W. A formula for correlating pKa values determined in D2O and H2O. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2004, 98, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbs, K.D.; Hehre, W.J. Molecular orbital theory of the properties of inorganic and organometallic compounds 5. Extended basis sets for first-row transition metals. J. Comp. Chem. 1987, 8, 861–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, P.C.; Pople, J.A. The influence of polarization functions on molecular orbital hydrogenation energies. Theor. Chim. Acta 1973, 28, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenow, S.; Stasiak, A.; Ramsay, R.R.; Stark, H. Ciproxifan, a histamine H3 receptor antagonist, reversibly inhibits monoamine oxidase A and B. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Inc. Maestro, Version 9.3; Schrödinger Inc.: Portland, OR, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Acton, A.; Banck, M.; Bréfort, J.; Cruz, M.; Curtis, D.; Hassinen, T.; Heikkilä, V.; Hutchison, G.; Huuskonen, J.; Jensen, J.; et al. Ghemical, Version 3.0; GPL: Burbank, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, M.; Cramer, R.D., III; Van Opdenbosch, N. Validation of the general purpose Tripos 5.2 Force Field. J. Comput. Chem. 1989, 10, 982–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.; Willett, P.; Glen, R.C.; Leach, A.R.; Taylor, R. Development and validation of a genetic algorithm for flexible docking. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 267, 727–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
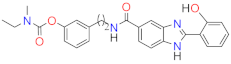
| Compound | MmHhLl (mhl) | log Ki | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | (011) | 8.98(1) | ||
| (021) | 3.48(2) | |||
| (101) | 9.09(5) | 11.57(6) | ||
| (1–11) | 3.40(5) | - | ||
| (102) | 17.16(8) | 20.35(7) | ||
| (103) | - | 28.40(6) | ||
| 4c | pM | 10.3 | 16.8 | |
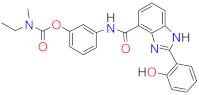 | (011) | 8.67(1) | ||
| (021) | 3.38(6) | |||
| (101) | 11.30(2) | 12.53(5) | ||
| (1–11) | 3.82(8) | - | ||
| (102) | 20.43(5) | 23.82(4) | ||
| (103) | - | 30.20(8) | ||
| 5a | pM | 13.6 | 17.4 |
| Compounds | Aβ42 Self- Aggreg. Inhib. a (%) | Aβ42 Cu-ind. Aggreg. Inhib. a (%) | IC50 (µM) or % Inhibition (at 10 µM) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hMAO-A | hMAO-B | |||
| 4a | 39.0 | 41.2 | 0.74 ± 0.07 | 28% |
| 4b | 39.6 | 48.8 | 8.6 ± 0.9 | 43% |
| 4c | 21.2 | 22.0 | 30% | 33% |
| 4d | 20.1 | 21.3 | 11 ± 1 | 43% |
| 5a | 44.5 | 45.4 | 33% | 31% |
| 5b | 58.7 | 60.8 | 22% | 34% |
| 5d | 42.1 | 40.3 | – | – |
| Curcumin | 65.7 | 62.7 | – | – |
| Safinamide | – | – | 13% | 25.3 b |
| R-(–)-Deprenyl c (Selegiline) | – | – | 20 ± 2 | 0.039 ± 0.004 |
| Clorgyline c | – | – | 0.0027 ± 0.0005 | 2.2 ± 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vicente-Zurdo, D.; Brunetti, L.; Piemontese, L.; Guedes, B.; Cardoso, S.M.; Chavarria, D.; Borges, F.; Madrid, Y.; Chaves, S.; Santos, M.A. Rivastigmine–Benzimidazole Hybrids as Promising Multitarget Metal-Modulating Compounds for Potential Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098312
Vicente-Zurdo D, Brunetti L, Piemontese L, Guedes B, Cardoso SM, Chavarria D, Borges F, Madrid Y, Chaves S, Santos MA. Rivastigmine–Benzimidazole Hybrids as Promising Multitarget Metal-Modulating Compounds for Potential Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(9):8312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098312
Chicago/Turabian StyleVicente-Zurdo, David, Leonardo Brunetti, Luca Piemontese, Beatriz Guedes, Sandra M. Cardoso, Daniel Chavarria, Fernanda Borges, Yolanda Madrid, Sílvia Chaves, and M. Amélia Santos. 2023. "Rivastigmine–Benzimidazole Hybrids as Promising Multitarget Metal-Modulating Compounds for Potential Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 9: 8312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098312
APA StyleVicente-Zurdo, D., Brunetti, L., Piemontese, L., Guedes, B., Cardoso, S. M., Chavarria, D., Borges, F., Madrid, Y., Chaves, S., & Santos, M. A. (2023). Rivastigmine–Benzimidazole Hybrids as Promising Multitarget Metal-Modulating Compounds for Potential Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(9), 8312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098312








