Vitamin Status in Patients with Phenylketonuria: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Collection Process, Extraction and Analysis
2.4. Data Item
- General information: the title of the article, journal name, main author, and publication year.
- Study characteristics: the study name and design, country (region), and sample size (total number of subjects and the number in each group who were included and completed the study).
- Study population characteristics: age, sex, body mass index (BMI, kg/m2).
- Description of dietary treatment: natural protein intake (g/day), protein substitute intake (g/day), total protein intake (g/day), phenylalanine intake (mg/d), annual mean/median phenylalanine levels (μmol/L), follow-up (yes or no), treatment adherence (yes or no), phenylalanine levels (μmol/L), tyrosine levels (μmol/L), and total protein levels (g/dL).
- Main outcomes: blood or plasma levels of folate (nmol/L), folic acid (nmol/L), erythrocyte folate (nmol/L), total folate (nmol/L), vitamin B12 (pmol/L), 25-hydroxyvitamin D (nmol/L), 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (nmol/L), cholecalciferol (nmol/L), 1,25-hydroxyvitamin D (nmol/L), vitamin A (μmol/L), beta-carotene (μmol/L), vitamin E (μmol/L), erythrocyte tocopherol (μmol/L), vitamin B6 (μmol/L), vitamin K (μmol/L), vitamin C (μmol/L), and biotin (ng/L).
2.5. Information Sources and Search Strategy
2.6. Risk of Bias of Individual Studies
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
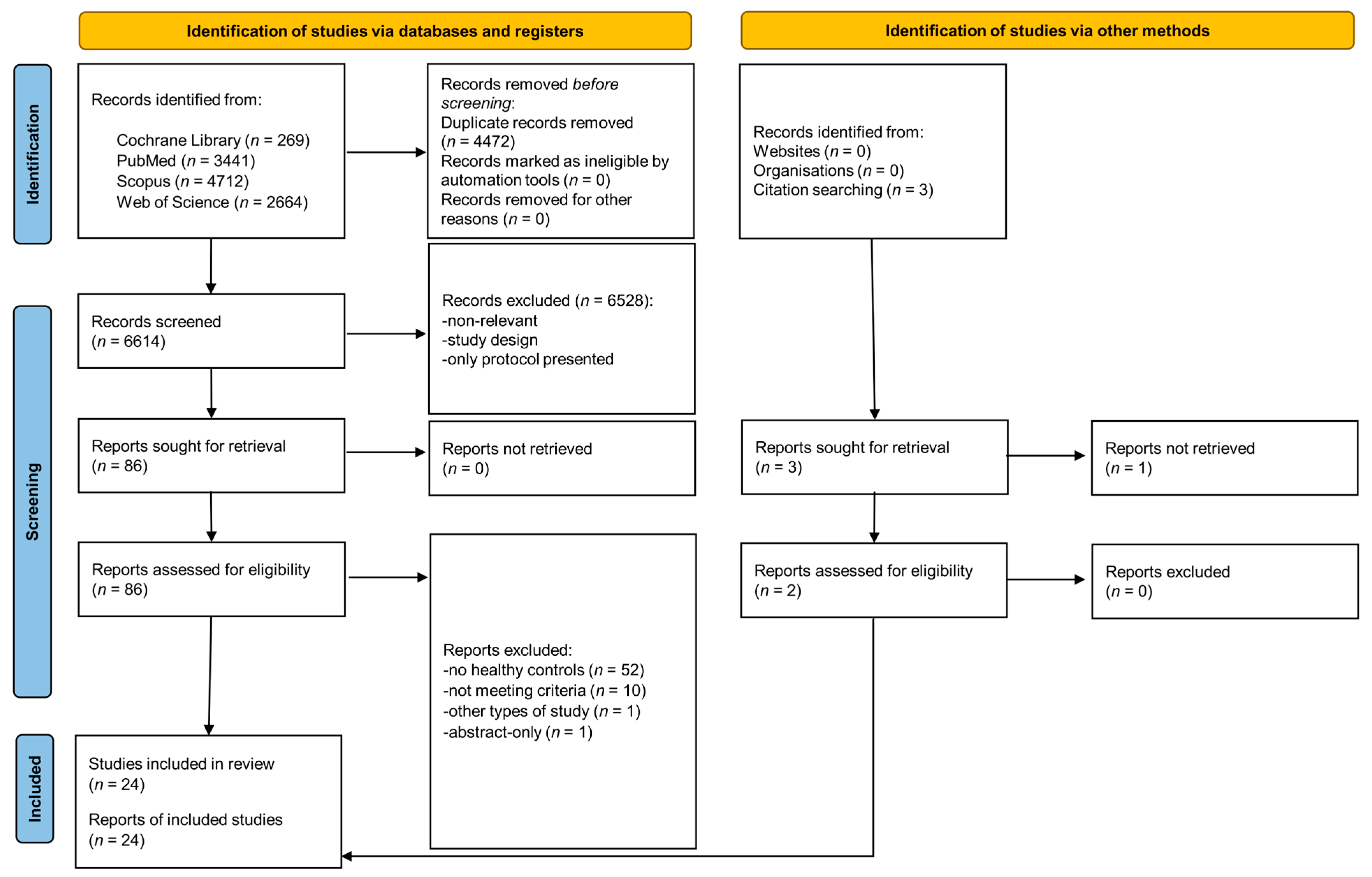
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Comparison of Folate Levels
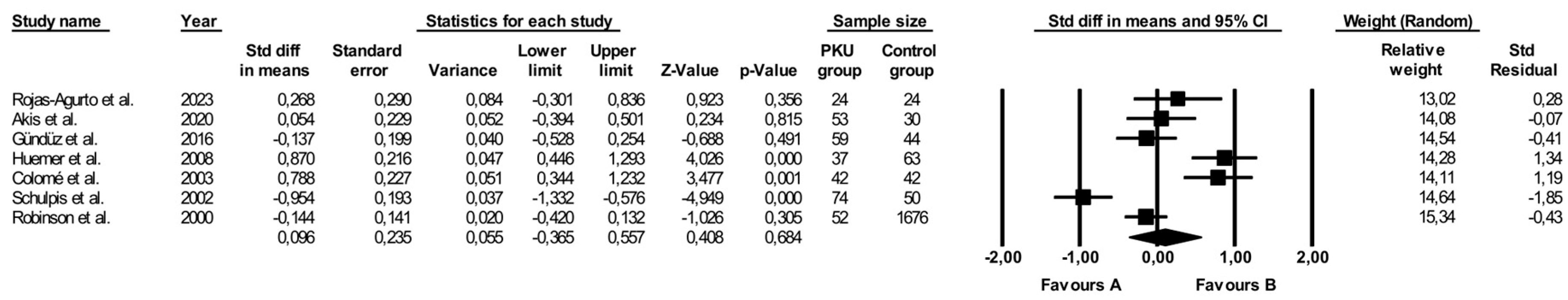
3.4. Comparison of Vitamin B12 Levels
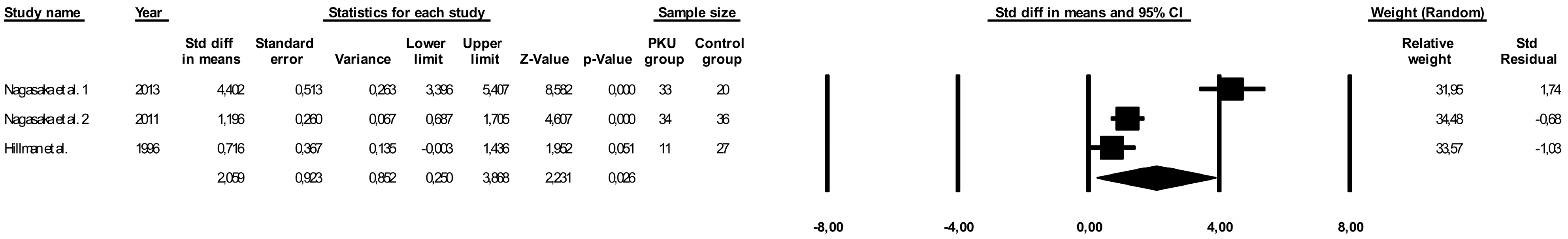
3.5. Comparison of Vitamin D Levels
3.6. Comparison of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D Levels
3.7. Comparison of Vitamin A Levels
3.8. Comparison of Vitamin E Levels
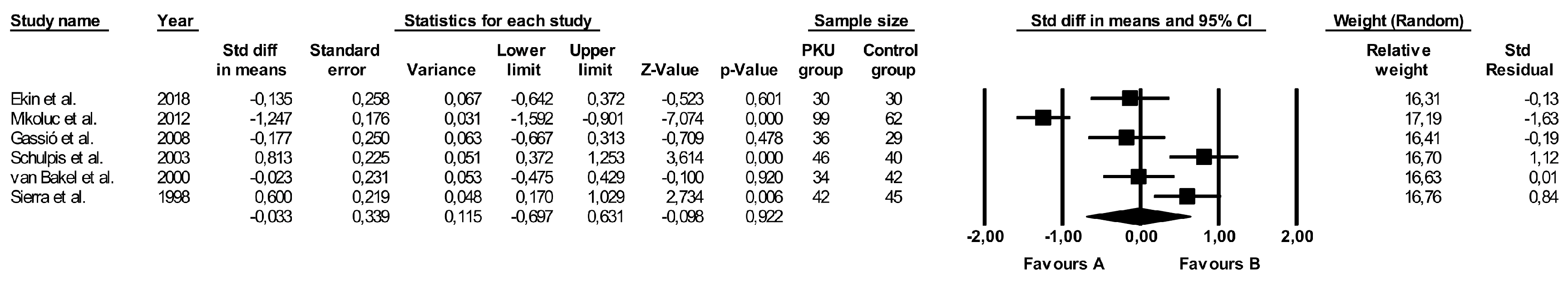
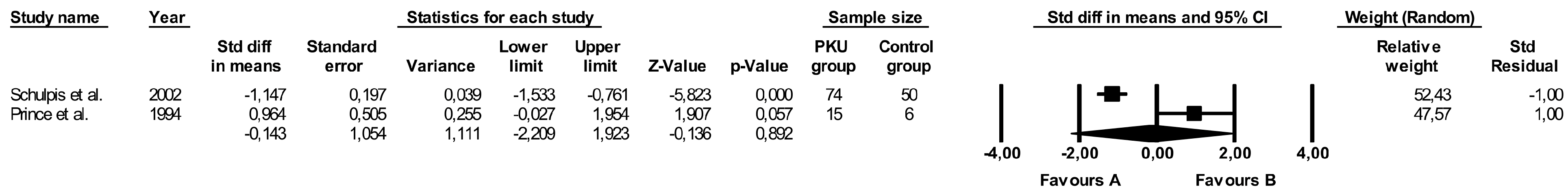
3.9. Comparison of Vitamin B6 Levels
3.10. Comparison of Other Vitamins
3.11. Subgroup Analysis
3.12. Relative Differences in Vitamin Levels across Studies
3.13. Risk of Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Al Hafid, N.; Christodoulou, J. Phenylketonuria: A Review of Current and Future Treatments. Transl. Pediatr. 2015, 4, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillert, A.; Anikster, Y.; Belanger-Quintana, A.; Burlina, A.; Burton, B.K.; Carducci, C.; Chiesa, A.E.; Christodoulou, J.; Đorđević, M.; Desviat, L.R.; et al. The Genetic Landscape and Epidemiology of Phenylketonuria. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 107, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flydal, M.I.; Martinez, A. Phenylalanine Hydroxylase: Function, Structure, and Regulation. IUBMB Life 2013, 65, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blau, N.; van Spronsen, F.J.; Levy, H.L. Phenylketonuria. Lancet 2010, 376, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickel, H.; Gerrard, J.; Hickmans, E.M. Influence of Phenylalanine Intake on Phenylketonuria. Lancet 1953, 265, 812–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Spronsen, F.J.; van Wegberg, A.M.; Ahring, K.; Bélanger-Quintana, A.; Blau, N.; Bosch, A.M.; Burlina, A.; Campistol, J.; Feillet, F.; Giżewska, M.; et al. Key European Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Patients with Phenylketonuria. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, A.; van Wegberg, A.M.J.; Ahring, K.; Beblo, S.; Bélanger-Quintana, A.; Burlina, A.; Campistol, J.; Coşkun, T.; Feillet, F.; Giżewska, M.; et al. PKU Dietary Handbook to Accompany PKU Guidelines. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Wegberg, A.M.J.; MacDonald, A.; Ahring, K.; Bélanger-Quintana, A.; Blau, N.; Bosch, A.M.; Burlina, A.; Campistol, J.; Feillet, F.; Giżewska, M.; et al. The Complete European Guidelines on Phenylketonuria: Diagnosis and Treatment. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, A.; Davies, P.; Daly, A.; Hopkins, V.; Hall, S.K.; Asplin, D.; Hendriksz, C.; Chakrapani, A. Does Maternal Knowledge and Parent Education Affect Blood Phenylalanine Control in Phenylketonuria? J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2008, 21, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkowiak, D.; Bukowska-Posadzy, A.; Kałużny, Ł.; Ołtarzewski, M.; Staszewski, R.; Musielak, M.; Walkowiak, J. Therapy Compliance in Children with Phenylketonuria Younger than 5 Years: A Cohort Study. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 28, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurecki, E.R.; Cederbaum, S.; Kopesky, J.; Perry, K.; Rohr, F.; Sanchez-Valle, A.; Viau, K.S.; Sheinin, M.Y.; Cohen-Pfeffer, J.L. Adherence to Clinic Recommendations among Patients with Phenylketonuria in the United States. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 120, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, J.H.; White, F.J. Blood Phenylalanine Control in Adolescents with Phenylketonuria. Int. J. Adolesc. Med. Health 2004, 16, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crone, M.R.; van Spronsen, F.J.; Oudshoorn, K.; Bekhof, J.; van Rijn, G.; Verkerk, P.H. Behavioural Factors Related to Metabolic Control in Patients with Phenylketonuria. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2005, 28, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, T.; Nalin, T.; Krug, B.; Bittar, C.; Netto, C.; Schwartz, I. Adherence to Treatment of Phenylketonuria: A Study in Southern Brazilian Patients. J. Inborn Errors Metab. Screen. 2015, 3, 2326409815579861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Dalei, S.; Adlakha, N. Food Regime for Phenylketonuria: Presenting Complications and Possible Solutions. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2022, 15, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walkowiak, D.; Domaradzki, J.; Mozrzymas, R.; Korycińska-Chaaban, D.; Duś-Żuchowska, M.; Didycz, B.; Mikołuć, B.; Walkowiak, J. Professional Activity, Gender and Disease-Related Emotions: The Impact on Parents’ Experiences in Caring for Children with Phenylketonuria. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2023, 36, 100992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kose, E.; Arslan, N. Vitamin/Mineral and Micronutrient Status in Patients with Classical Phenylketonuria. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Vliet, K.; Rodenburg, I.L.; van Ginkel, W.G.; Lubout, C.M.A.; Wolffenbuttel, B.H.R.; van der Klauw, M.M.; Heiner-Fokkema, M.R.; van Spronsen, F.J. Biomarkers of Micronutrients in Regular Follow-Up for Tyrosinemia Type 1 and Phenylketonuria Patients. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, J.H. Vitamin B12 Deficiency and Phenylketonuria. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 104, S52–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procházková, D.; Jarkovský, J.; Haňková, Z.; Konečná, P.; Benáková, H.; Vinohradská, H.; Mikušková, A. Long-Term Treatment for Hyperphenylalaninemia and Phenylketonuria: A Risk for Nutritional Vitamin B12 Deficiency? J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 28, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vugteveen, I.; Hoeksma, M.; Monsen, A.-L.B.; Fokkema, M.R.; Reijngoud, D.-J.; van Rijn, M.; van Spronsen, F.J. Serum Vitamin B12 Concentrations within Reference Values Do Not Exclude Functional Vitamin B12 Deficiency in PKU Patients of Various Ages. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 102, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, A.; Rocha, J.C.; van Rijn, M.; Feillet, F. Nutrition in Phenylketonuria. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 104, S10–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozrzymas, R.; Walkowiak, D.; Drzymała-Czyż, S.; Krzyżanowska-Jankowska, P.; Duś-Żuchowska, M.; Kałużny, Ł.; Walkowiak, J. Vitamin K Status in Adherent and Non-Adherent Patients with Phenylketonuria: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, S.; Daly, A.; MacDonald, J.; Preece, M.A.; Santra, S.; Vijay, S.; Chakrapani, A.; MacDonald, A. The Micronutrient Status of Patients with Phenylketonuria on Dietary Treatment: An Ongoing Challenge. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 65, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulpis, K.H.; Tsakiris, S.; Karikas, G.A.; Moukas, M.; Behrakis, P. Effect of Diet on Plasma Total Antioxidant Status in Phenylketonuric Patients. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 57, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huemer, M.; Födinger, M.; Bodamer, O.A.; Mühl, A.; Herle, M.; Weigmann, C.; Ulmer, H.; Stöckler-Ipsiroglu, S.; Möslinger, D. Total Homocysteine, B-Vitamins and Genetic Polymorphisms in Patients with Classical Phenylketonuria. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2008, 94, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulpis, K.H.; Karikas, G.A.; Papakonstantinou, E. Homocysteine and Other Vascular Risk Factors in Patients with Phenylketonuria on a Diet. Acta Paediatr. 2002, 91, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikoluc, B.; Motkowski, R.; Karpinska, J.; Amilkiewicz, J.; Didycz, B.; Gizewska, M.; Lange, A.; Milanowski, A.; Nowacka, M.; Sands, D.; et al. Impact of Lipophilic Antioxidants and Level of Antibodies against Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein in Polish Children with Phenylketonuria. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2012, 16, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasaka, H.; Okano, Y.; Kimura, A.; Mizuochi, T.; Sanayama, Y.; Takatani, T.; Nakagawa, S.; Hasegawa, E.; Hirano, K.; Mochizuki, H.; et al. Oxysterol Changes along with Cholesterol and Vitamin D Changes in Adult Phenylketonuric Patients Diagnosed by Newborn Mass-Screening. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 416, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasaka, H.; Tsukahara, H.; Takatani, T.; Sanayama, Y.; Takayanagi, M.; Ohura, T.; Sakamoto, O.; Ito, T.; Wada, M.; Yoshino, M.; et al. Cross-Sectional Study of Bone Metabolism with Nutrition in Adult Classical Phenylketonuric Patients Diagnosed by Neonatal Screening. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2011, 29, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekin, S.; Dogan, M.; Gok, F.; Karakus, Y. Assessment of Antioxidant Enzymes, Total Sialic Acid, Lipid Bound Sialic Acid, Vitamins and Selected Amino Acids in Children with Phenylketonuria. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 84, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassió, R.; Artuch, R.; Vilaseca, M.A.; Fusté, E.; Colome, R.; Campistol, J. Cognitive Functions and the Antioxidant System in Phenylketonuric Patients. Neuropsychology 2008, 22, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. (Eds.) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Version 6.4 (Updated August 2023); Cochrane: Cochrane, AB, Canada, 2023; Available online: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current (accessed on 7 February 2024).
- Bokayeva, K.; Jamka, M.; Walkowiak, D.; Duś-Żuchowska, M.; Herzig, K.-H.; Walkowiak, J. Vitamin Status in Phenylketonuria Patients. PROSPERO: International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews. Available online: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=519589 (accessed on 19 March 2024).
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Non-Randomized Studies in Meta-Analyses. Ottawa: Ottawa Hospital Research Institute. Available online: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 7 February 2024).
- Modesti, P.A.; Reboldi, G.; Cappuccio, F.P.; Agyemang, C.; Remuzzi, G.; Rapi, S.; Perruolo, E.; Parati, G.; Agostoni, P.; Barros, H.; et al. Panethnic Differences in Blood Pressure in Europe: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prince, A.P.; Leklem, J.E. Vitamin B-6 Status of School-Aged Patients with Phenylketonuria. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1994, 60, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Agurto, E.; Leal-Witt, M.J.; Arias, C.; Cabello, J.F.; Bunout, D.; Cornejo, V. Muscle and Bone Health in Young Chilean Adults with Phenylketonuria and Different Degrees of Compliance with the Phenylalanine Restricted Diet. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulpis, K.H.; Nyalala, J.O.; Papakonstantinou, E.D.; Leondiadis, L.; Livaniou, E.; Ithakisios, D.; Georgala, S. Biotin Recycling Impairment in Phenylketonuric Children with Seborrheic Dermatitis. Int. J. Dermatol. 1998, 37, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qadreh, A.; Schulpis, K.H.; Athanasopoulou, H.; Mengreli, C.; Skarpalezou, A.; Voskaki, I. Bone Mineral Status in Children with Phenylketonuria under Treatment. Acta Paediatr. 1998, 87, 1162–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akış, M.; Kant, M.; Işık, İ.; Kısa, P.T.; Köse, E.; Arslan, N.; İşlekel, H. Functional Vitamin B12 Deficiency in Phenylketonuria Patients and Healthy Controls: An Evaluation with Combined Indicator of Vitamin B12 Status as a Biochemical Index. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2020, 57, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gündüz, M.; Çakar, S.; Kuyum, P.; Makay, B.; Arslan, N. Comparison of Atherogenic Risk Factors among Poorly Controlled and Well-Controlled Adolescent Phenylketonuria Patients. Cardiol. Young 2016, 26, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomé, C.; Artuch, R.; Sierra, C.; Brandi, N.; Lambruschini, N.; Campistol, J.; Vilaseca, M.-A. Plasma Thiols and Their Determinants in Phenylketonuria. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 57, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, C.; Vilaseca, M.A.; Moyano, D.; Brandi, N.; Campistol, J.; Lambruschini, N.; Cambra, F.J.; Deulofeu, R.; Mira, A. Antioxidant Status in Hyperphenylalaninemia. Clin. Chim. Acta 1998, 276, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huemer, M.; Simma, B.; Mayr, D.; Möslinger, D.; Mühl, A.; Schmid, I.; Ulmer, H.; Bodamer, O.A. Free Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA) Is Low in Children and Adolescents with Classical Phenylketonuria (PKU). J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2012, 35, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiva, C.; Bravo, P.; Arias, C.; Cabello, J.F.; Leal-Witt, M.J.; Salazar, F.; Cornejo, V. 25 Hydroxy Vitamin D Level, Bone Health, Vitamin D and Calcium Intake in Chilean Patients with Phenylketonuria and Hyperphenylalaninemias. J. Inborn Errors Metab. Screen. 2021, 9, e20210004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucock, M.; Yates, Z.; Hall, K.; Leeming, R.; Rylance, G.; MacDonald, A.; Green, A. The Impact of Phenylketonuria on Folate Metabolism. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2002, 76, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.; White, F.J.; Cleary, M.A.; Wraith, E.; Lam, W.K.; Walter, J.H. Increased Risk of Vitamin B12 Deficiency in Patients with Phenylketonuria on an Unrestricted or Relaxed Diet. J. Pediatr. 2000, 136, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillman, L.; Schlotzhauer, C.; Lee, D.; Grasela, J.; Witter, S.; Allen, S.; Hillman, R. Decreased Bone Mineralization in Children with Phenylketonuria under Treatment. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1996, 155 (Suppl. S1), S148–S152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mütze, U.; Beblo, S.; Kortz, L.; Matthies, C.; Koletzko, B.; Bruegel, M.; Rohde, C.; Thiery, J.; Kiess, W.; Ceglarek, U. Metabolomics of Dietary Fatty Acid Restriction in Patients with Phenylketonuria. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veyrat-Durebex, C.; Debeissat, C.; Blasco, H.; Patin, F.; Henique, H.; Emond, P.; Antar, C.; Gissot, V.; Herault, O.; Maillot, F. Hyperphenylalaninemia Correlated with Global Decrease of Antioxidant Genes Expression in White Blood Cells of Adult Patients with Phenylketonuria. JIMD Rep. 2017, 37, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bakel, M.M.; Printzen, G.; Wermuth, B.; Wiesmann, U.N. Antioxidant and Thyroid Hormone Status in Selenium-Deficient Phenylketonuric and Hyperphenylalaninemic Patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya Parra, G.A.; Singh, R.H.; Cetinyurek-Yavuz, A.; Kuhn, M.; MacDonald, A. Status of Nutrients Important in Brain Function in Phenylketonuria: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2018, 13, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurry, M.P.; Chan, G.M.; Leonard, C.O.; Ernst, S.L. Bone Mineral Status in Children with Phenylketonuria--Relationship to Nutritional Intake and Phenylalanine Control. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 55, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushueva, T.V.; Ladodo, K.S.; Spirichev, V.B.; Denisova, S.N.; Rybakova, E.P. Calcium homeostasis and calcium-regulating hormones in young children with phenylketonuria. Vopr. Pitan. 1993, 3, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Colomé, C.; Artuch, R.; Vilaseca, M.-A.; Sierra, C.; Brandi, N.; Lambruschini, N.; Cambra, F.J.; Campistol, J. Lipophilic Antioxidants in Patients with Phenylketonuria. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Yao, H.-F.; Wang, C.-J. Effect of Low Phenylalanine Diet on Micro-Nutrients and Anti-Oxidative Capacity in Patients with Phenylketonuria. Matern. Child. Health Care China 2009, 29, 4539–4541. [Google Scholar]
- Dezortová, M.; Hájek, M.; Tintera, J.; Hejcmanová, L.; Syková, E. MR in Phenylketonuria-Related Brain Lesions. Acta Radiol. 2001, 42, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sijens, P.E.; Oudkerk, M.; Reijngoud, D.-J.; Leenders, K.L.; de Valk, H.W.; van Spronsen, F.J. 1H MR Chemical Shift Imaging Detection of Phenylalanine in Patients Suffering from Phenylketonuria (PKU). Eur. Radiol. 2004, 14, 1895–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmel, R. Nutritional Anemias and the Elderly. Semin. Hematol. 2008, 45, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dali-Youcef, N.; Andrès, E. An Update on Cobalamin Deficiency in Adults. QJM 2009, 102, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F.; Binkley, N.C.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Gordon, C.M.; Hanley, D.A.; Heaney, R.P.; Murad, M.H.; Weaver, C.M. Endocrine Society Evaluation, Treatment, and Prevention of Vitamin D Deficiency: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 1911–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, A.T.; Tuckey, R.C.; Jetten, A.M.; Holick, M.F. Recent Advances in Vitamin D Biology: Something New under the Sun. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 143, 2340–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Author | Year | Country (Region) | Study Design | Groups | n Included | n Completed | Age [Years] 1 | BMI [kg/m2] 1 | Sex [% of Women] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rojas-Agurto et al. [39] | 2023 | Chile | Cross-sectional | PKU 2 | 10 | 10 | 23.5 (19–26) 4 | 24.3 (22.4–28.5) 4 | 50 |
| Control | 10 | 10 | 21.5 (20–27) 4 | 24.3 (24.1–27.9) 4 | 50 | ||||
| PKU 3 | 14 | 14 | 22.5 (18.5–25.5) 4 | 26.7 (24–29.9) 4 | 36 | ||||
| Control | 14 | 14 | 23 (19–25) 4 | 27.6 (23.3–30.6) 4 | 36 | ||||
| Leiva et al. [47] | 2021 | Chile | Cross-sectional | PKU 2 | 16 | 16 | 6–23 5 | NI | 44 |
| Control | 16 | 16 | NI | NI | 44 | ||||
| Akış et al. [42] | 2020 | Turkey | Cross-sectional | PKU 6 | 31 | 31 | 9.50 (5.00–18.00) 8 | NI | 38 |
| PKU 7 | 22 | 22 | |||||||
| Control | 30 | 30 | 8.59 (5.00–17.50) 8 | NI | 53 | ||||
| Ekin et al. [31] | 2018 | Turkey | Cross-sectional | PKU 2 | 30 | 30 | 7.54 ± 0.58 9 | 16.16 ± 0.54 9 | 60 |
| Control | 30 | 30 | 7.89 ± 0.74 9 | 17.64 ± 0.53 9 | 56.6 | ||||
| Veyrat-Durebex et al. [52] | 2017 | France | Cross-sectional | PKU 10 | 10 | 9 | 31 ± 6 | 26 ± 4 | 60 |
| Control | 10 | 9 | NI | 22 ± 4 | NI | ||||
| Gündüz et al. [43] | 2016 | Turkey | Cross-sectional | PKU 11 | 24 | 24 | 13.1 ± 2.4 | 19.1 ± 2.1 | 33 |
| PKU 12 | 35 | 35 | 14.1± 2.9 | 18.9± 1.9 | 54 | ||||
| Control | 44 | 44 | 13.0 ± 2.0 | 19.7± 2.0 | 57 | ||||
| Nagasaka et al. [29] | 2013 | Japan | Cross-sectional | PKU 13 | 33 | 33 | 28.1 ± 5.1 | 23.7 ± 2.2 | 54.5 |
| Control | 20 | 20 | 28.9 ± 4.5 | 23.1 ± 1.9 | 50 | ||||
| Mikoluc et al. [28] | 2012 | Poland | Cross-sectional | PKU 14 | 107 | 107 15 | 8.8 ± 2.06 | NI | 43 |
| Control | 62 | 62 | 8.6 ± 1.1 | NI | 50 | ||||
| Mütze et al. [51] | 2012 | Germany | Cross-sectional | PKU 11 | 12 | 12 | 7.88 (5–14) 8 | 16.68/0.6 (14.51/−1.24–23.21/1.51) 8,16 | 50 |
| Control | 8 | 8 | 9.75 (5–17) 8 | 16.22/−0.1 (13.15/−1.71–22.41/1.18) 8,16 | 62.5 | ||||
| Huemer et al. [46] | 2012 | Austria | Cross-sectional | PKU 2 | 16 | 16 | 10.1 ± 5.2 | 19.5 ± 4.5 | 43.75 |
| Control | 91 | 91 | 11.6 ± 3.7 | 19.2 ± 4.3 | 35 | ||||
| Nagasaka et al. [30] | 2011 | Japan | Cross-sectional | PKU 17,18 | 21 | 21 | 27.1 ± 3.2 9 | 22.5 ± 1.5 9 | 100 |
| PKU 17,19 | 13 | 13 | 26.9 ± 3.3 9 | 24.7 ± 2.4 9 | 0 | ||||
| Control 18 | 22 | 22 | 27.9 ± 5.1 9 | 23.7 ± 2.2 9 | 100 | ||||
| Control 19 | 14 | 14 | 30.3 ± 4.5 9 | 23.5 ± 2.3 9 | 0 | ||||
| Huemer et al. [26] | 2008 | Austria | Case-control | PKU 2 | 37 | 37 | 12.3 ± 4.5 | 19.1 ± 3.3 | 35.1 |
| Control | 63 | 63 | 11.5 ± 4.1 | NI | 41.3 | ||||
| Gassió et al. [32] | 2008 | Spain | Cross-sectional | PKU 2 | 36 | 36 | 9.7 (2.7–19.4) 20 | NI | 47.2 |
| Control | 29 | 29 | 9.6 (2.5–18.8) 20 | NI | 48.3 | ||||
| Colomé et al. [44] | 2003 | Spain | Cross-sectional | PKU 2,21 | 42 | 42 | 15.3 ± 9.5 | NI | NI |
| Control | 42 | 42 | 15.7 ± 9.7 | NI | NI | ||||
| Schulpis et al. [25] | 2003 | Greece | Cross-sectional | PKU 11 | 22 | 22 | 7.7 ± 3.2 | NI | NI |
| PKU 12 | 24 | 24 | 8.0 ± 3.6 | NI | NI | ||||
| Control | 40 | 40 | 7.68 ± 2.6 | NI | NI | ||||
| Schulpis et al. [27] | 2002 | Greece | Cross-sectional | PKU 11 | 34 | 34 | 6.78 ± 1.5 | NI | NI |
| PKU 12 | 40 | 40 | 8.0 ± 3.2 | NI | NI | ||||
| Control | 50 | 50 | 7.68 ± 2.3 | NI | NI | ||||
| Lucock et al. [48] | 2002 | The United Kingdom | Cross-sectional | PKU | 16 | 16 | 26.5 (17–37) 8 | NI | NI |
| Control | 25 | 25 | 33 (25–53) 8 | NI | NI | ||||
| van Bakel et al. [53] | 2000 | Switzerland | Cross-sectional | PKU 22 | 24 | 24 | 9.65 ± 4.06 | NI | 41.7 |
| PKU 23 | 10 | 10 | 9.08 ± 5.17 | NI | 50 | ||||
| Control | 42 | 42 | 11.18 ± 4.84 | NI | 28.6 | ||||
| Robinson et al. [49] | 2000 | The United Kingdom | Cross-sectional | PKU 24 | 22 | 22 26 | 24 29 | NI | NI |
| PKU 25 | 30 | 30 27 | 21 29 | NI | NI | ||||
| Control | 1676 | 1676 28 | NI | NI | NI | ||||
| Al-Qadreh et al. [41] | 1998 | Greece | Cross-sectional | PKU | 48 | 48 | 8.86 ± 3.7 | NI | 58.3 |
| Control | 50 | 50 | 9.06 ± 3.5 | NI | 58.3 | ||||
| Schulpis et al. [40] | 1998 | Greece | Cross-sectional | PKU 11 | 21 | 21 | 4.78 ± 3.51 | NI | NI |
| PKU 12 | 26 | 26 | 7.87 ± 3.68 | NI | NI | ||||
| Control | 79 | 79 | 6.68 ± 2.3 | NI | NI | ||||
| Sierra et al. [45] | 1998 | Spain | Cross-sectional | PKU 11 | 42 | 42 | 7.12 (1 month–17 years) 20 | NI | NI |
| Control | 45 | 45 | 6.5 (1 month–17 years) 20 | NI | NI | ||||
| Hillman et al. [50] | 1996 | The USA | Cross-sectional | PKU | 11 | 11 | 10.9 ± 4.2 | NI | 54.5 |
| Control | 64 | 64 30,31 | 11.4 ± 4.2 | NI | 50 | ||||
| Prince et al. [38] | 1994 | The USA | Cross-sectional | PKU 2 | 16 | 15 | 10.5 ± 2.9 | NI | 40 |
| Control | 6 | 6 | 9.4 ± 3.3 | NI | 33.3 |
| Author | Year | Groups | Natural Protein/Protein Substitute/Total Protein Intake [g/day] 1 | Phe Intake [mg/d] | Mean/Median Phe Levels [μmol/L] 1 | Medical Control | Adherence to Treatment | Phe [μmol/L] 1 | Tyr [μmol/L] 1 | Total Protein Level [g/dL] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rojas-Agurto et al. [39] | 2023 | PKU 2 | 75.1 (57.3–78.2) 4 | 600 (400–800) 4 | NI | Yes | Yes | 260.3 (170–642) 4 | 46.6 (33.1–49.7) 4 | NI |
| Control | 84.4 (57.9–101) 4 | 3900 (2600–4900) 4 | /// | /// | 39.3 (36.3–42.4) 4 | 49.7 (44.2–60.7) 4 | ||||
| PKU 3 | 46.6 (28.9–68.7) 4 | 1200 (500–1700) 4 | No | No | 781 (636–1035.1) 4 | 35.9 (33.1–55.2) 4 | ||||
| Control | 89.6 (66.6–101.1) 4 | 4000 (3100–4500) 4 | /// | /// | 47.8 (40.6–48.4) 4 | 53 (44.2–60.7) 4 | ||||
| Leiva et al. [47] | 2021 | PKU 2 | NI | NI | NI | Yes | Yes | 310 (262; 481) 5 | NI | NI |
| Control | /// | /// | NI | |||||||
| Akış et al. [42] | 2020 | PKU 6 | NI | NI | NI | Yes | High | 357.19 (121.10–514.60) 8 | NI | NI |
| PKU 7 | Yes | Low | 696.21 (441.90–1035.20) 8 | NI | NI | |||||
| Control | /// | /// | NI | NI | NI | |||||
| Ekin et al. [31] | 2018 | PKU 2 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 269.50 ± 49.75 9 | 59.62 ± 10.58 9 | NI |
| Control | /// | /// | 51.07 ± 3.52 9 | 57.58 ± 4.45 9 | ||||||
| Veyrat-Durebex et al. [52] | 2017 | PKU 10 | NI | NI | NI | NI | No | 1449 (363;1854) 8 | 51 (30;56) 8 | NI |
| Control | /// | /// | 60 (50;95) 8 | 69 (45;77) 8 | ||||||
| Gündüz et al. [43] | 2016 | PKU 11 | 0.20–0.40/0.6–0.8/0.8–1.2 13 | 300–900 | NI | NINI | Yes | 306.1± 78.0 | NI | NI |
| PKU 12 | No | 720.8± 196.7 | ||||||||
| Control | NI | NI | /// | /// | 48.8± 12.2 | |||||
| Nagasaka et al. [29] | 2013 | PKU 14 | 50 ± 13/ /71 ± 17 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 1019 ± 380 | NI | NI |
| Control | 66 ± 14/-/80 ± 15 | /// | /// | 30 ± 15 | ||||||
| Mikoluc et al. [28] | 2012 | PKU 15 | NI | NI | NI | Yes | Yes | NI | NI | NI |
| Control | /// | /// | ||||||||
| Mütze et al. [51] | 2012 | PKU 11 | -/-/41.1 (22.5–78.3) 8 | 338 (254–690) 8 | NI | NI | Yes | 302 (72–930) 8 | NI | 7.05 (6.37–7.3) 8 |
| Control | NI | NI | NI | /// | /// | 53 (48–75) 8 | NI | NI | ||
| Huemer et al. [46] | 2012 | PKU 2 | 0.23 ± 0.11/-/1.3 ± 0.4 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 809 (400–919) 4 | NI | NI |
| Control | NI | /// | /// | 6250 ± 80 4 | NI | NI | ||||
| Nagasaka et al. [30] | 2011 | PKU 16, 17 | 40 ± 11/-/66 ± 15 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 22.3 ± 4.5 | NI | 7.2 ± 0.3 9 |
| PKU 16, 18 | 47 ± 10/-/72 ± 17 | NI | 7.3 ± 0.3 9 | |||||||
| Control 17 | 79 ± 10/-/79 ± 10 | /// | /// | NI | 7.5 ± 0.3 9 | |||||
| Control 18 | 88 ± 11/-/88 ± 11 | /// | /// | NI | 7.6 ± 0.3 9 | |||||
| Huemer et al. [26] | 2008 | PKU 2 | 0.3 ± 0.2//1.8 ± 0.3 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 620 ± 425 | NI | NI |
| Control | NI | /// | /// | /// | ||||||
| Gassió et al. [32] | 2008 | PKU 2 | NI | NI | NI | NI | Yes | NI | 57.41 ± 24.84 | NI |
| Control | /// | /// | 72 (53–87) 19 | |||||||
| Colomé et al. [44] | 2003 | PKU 2, 20 | NI | NI | NI | NI | Mixed group | NI | NI | NI |
| Control | /// | |||||||||
| Schulpis et al. [25] | 2003 | PKU 11 | -/-/70 ± 18 21 | NI | 292 ± 60 22 | Yes | NI | 115.3 ± 26.5 | NI | |
| PKU 12 | -/-/72.0 ± 20 21 | 895 ± 54 22 | No | 45.8 ± 27.5 | ||||||
| Control | -/-/73.0 ± 17 21 | NI | /// | /// | 139.6 ± 32.1 | |||||
| Schulpis et al. [27] | 2002 | PKU 11 | 6 ± 1.2/-/70 ± 13 | NI | NI | Yes | 192 ± 115 | NI | NI | |
| PKU 12 | 30 ± 1.6/-/72 ± 14 | No | 599 ± 16 | |||||||
| Control | 74 ± 15/-/74 ± 15 | /// | /// | 70.1 ± 100 | ||||||
| Lucock et al. [48] | 2002 | PKU | NI | NI | NI | No | 1037 (560–1760) 8 | NI | NI | |
| Control | /// | /// | NI | |||||||
| van Bakel et al. [53] | 2000 | PKU 23 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI |
| PKU 24 | ||||||||||
| Control | /// | /// | ||||||||
| Robinson et al. [49] | 2000 | PKU 25 | NI | NI | NI | Yes | Yes | NI | NI | NI |
| PKU 26 | Yes | No | ||||||||
| Control | /// | /// | ||||||||
| Al-Qadreh et al. [41] | 1998 | PKU | NI | NI | NI | Yes | NI | 111.3 ± 66.20 | NI | NI |
| Control | /// | /// | /// | |||||||
| Schulpis et al. [40] | 1998 | PKU 11 | 26.0 ± 7.2/42.0 ± 5.0/68.1 ± 12.9 | NI | 20 ± 9 22 | Yes | 31.0 ± 9.0 | NI | NI | |
| PKU 12 | 35.0 ± 8.2/35.0 ± 11.5/70.9 ± 19.7 | 15.87 ± 5.09 22 | No | 18.87 ± 3.09 | ||||||
| Control | -/-/72.3 ± 16.9 | NI | /// | /// | 1.2 ± 0.5 | |||||
| Sierra et al. [45] | 1998 | PKU 11 | NI | NI | NI | Yes | NI | NI | NI | |
| Control | /// | /// | ||||||||
| Hillman et al. [50] | 1996 | PKU | -/-/46.1 ± 12.1 | NI | 99.8 ± 95.4 27 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI |
| Control | NI | NI | /// | /// | ||||||
| Prince et al. [38] | 1994 | PKU 2 | -/-/44.2 ± 10 | NI | NI | Yes | No 28 | 882 ± 284 | NI | NI |
| Control | -/-/69.2 ± 17 | /// | /// | 70 ± 13 |
| Author | Year | Groups | Folate 1 | Vitamin B12 1 | Vitamin D 1 | 1,25(OH)2D Vitamin 1 | Vitamin A 1 | Beta-Carotene 1 | Vitamin E 1 | Vitamin B6 1 | Vitamin K 1 | Vitamin C 1 | Biotin 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rojas-Agurto et al. [39] | 2023 | PKU 2 | 25.69 ± 7.58 4,5,6,7 | 669.2 ± 330.4 4,6,7 | 36.97 ± 9.33 4,7,8,9 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Control | 15.72 ± 5.39 4,5,6,7 | 454 ± 216.6 4,6,7 | 29.26 ± 8.98 4,7,8,9 | ||||||||||
| PKU 3 | 23.68 ± 7.19 4,5,6,7 | 383.4 ± 253.2 4,6,7 | 24.3 ± 10.62 4,7,8,9 | ||||||||||
| Control | 16.63 ± 4.57 4,5,6,7 | 444.9 ± 134.8 4,6,7 | 30.45 ± 10.29 4,7,8,9 | ||||||||||
| Leiva et al. [47] | 2021 | PKU 2 | NA | NA | 38.61 ± 8.67 4,6,7,8 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Control | 33.84 ± 7.93 4,6,7,8 | ||||||||||||
| Akış et al. [42] | 2020 | PKU 10 | 36.39 ± 9.85 4,7,13 | 297.4 ± 126.5 4,7,15 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| PKU 11 | 37.05 (15.5–54.6) 4,13,14 | 281.2 (100–607) 4,14,15 | |||||||||||
| PKU 12 | 36.36 (12.3–54.6) 4,13,14 | 266.8 (117–568) 4,14,15 | |||||||||||
| Control | 22.61 ± 7.38 4,7,13,14 | 291.4 ± 81.6 4,7,14,15 | |||||||||||
| Ekin et al. [31] | 2018 | PKU 2 | NA | NA | 0.43 ± 0.035 4,16,17,18 | NA | 2.91 ± 0.21 4,16,18 | NA | 2.26 ± 0.19 4,16,18 | NA | 0.73 ± 0.078 4,16,18 | NA | NA |
| Control | 0.38 ± 0.033 4,16,17,18 | 3.03 ± 0.14 4,16,18 | 2.39 ± 0.16 4,16,18 | 1.01 ± 0.056 4,16,18 | |||||||||
| Veyrat-Durebex et al. [52] | 2017 | PKU 19 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1.8 (1.3;3.28) 14,18,20 | NA | 22.4 (18;36) 14,18,20 | NA | NA | 58 (20;90) 14,18,20 | NA |
| Control | 1.67 (1;2.03) 14,18,20 | 24.2 (19;32) 14,18,20 | 75 (17;102) 14,18,20 | ||||||||||
| Gündüz et al. [43] | 2016 | PKU 21 | 32.4± 9.7 4,5,13 | 256.5± 139.3 4,15 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| PKU 22 | 32.8 ± 9.0 4,5,13 | 308.8± 119.1 4,15 | |||||||||||
| Control | 22.5± 7.2 4,5,13 | 303.0± 85.8 4,15 | |||||||||||
| Nagasaka et al. [29] | 2013 | PKU 23 | NA | NA | 19.9 ± 2.1 4,6,24 | 55.5 ± 3.7 4,9 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Control | 28.9 ± 2.3 4,6,24 | 40.7 ± 2.7 4,9 | |||||||||||
| Mikoluc et al. [28] | 2012 | PKU 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3.36 ± 2.11 18,20 | NA | 9.89 ± 7.75 18,20 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Control | 2.74 ± 1.93 18,20 | 25.40 ± 17.52 18,20 | |||||||||||
| Mütze et al. [51] | 2012 | PKU 21 | 45.4 (30.3 -> 45.4) 4,13,14 | 774.8 (289.9–1229) 4,14,15 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Control | 28.1 (15.4–45.2) 4,13,14 | 352.6 (238.6–500) 4,14,15 | |||||||||||
| Huemer et al. [46] | 2012 | PKU 2 | 7.2 ± 3.2 7,13,20 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Control | 6.5 ± 2.9 7,13,20 | ||||||||||||
| Nagasaka et al. [30] | 2011 | PKU 26,27 | NA | NA | 18.7 ± 1.3 4,6,8,16 | 58.4 ± 2.7 4,9,16 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| PKU 26,28 | 22.2 ± 1.7 4,6,8,16 | 50.6 ± 2.0 4,9,16 | |||||||||||
| Control 27 | 27.6 ± 2.1 4,6,8,16 | 41.6 ± 3.1 4,9,16 | |||||||||||
| Control 28 | 30.0 ± 2.6 4,6,8,16 | 39.9 ± 2.7 4,9,16 | |||||||||||
| Huemer et al. [26] | 2008 | PKU 2 | 15.1 ± 5.1 4,6 | 783 ± 528 4,9 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 146 ± 72 4,13 | NA | NA | NA |
| Control | 7.6 ± 3.3 4,6 | 478 ± 180 4,9 | NI | ||||||||||
| Gassió et al. [32] | 2008 | PKU 2 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1.36 ± 0.38 20,29 | NA | 20 ± 4.57 20,29 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Control | 2.10 ± 4.12 20,29 | 21 ± 6.74 20,29 | |||||||||||
| Colomé et al. [44] | 2003 | PKU 2,30 | 49.1 ± 8.6 4,13 | 622 ± 253 4,15 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Control | 19.1 ± 7.5 4,13 | 455 ± 161 4,15 | |||||||||||
| Schulpis et al. [25] | 2003 | PKU 21 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.7 ± 0.09 18,20 | 34 ± 0.9 18,20 | NA | NA | 36.3 ± 1.1 18,20 | NA |
| PKU 22 | 0.49 ± 0.08 18,20 | 22.0 ± 0.6 18,20 | 34.5 ± 1.1 18,20 | ||||||||||
| Control | 0.40 ± 0.09 18,20 | 24.0 ± 1.6 18,20 | 38.2 ± 2.01 18,20 | ||||||||||
| Schulpis et al. [27] | 2002 | PKU 21 | 2.35 ± 1.3 4,13 | 98.5 ± 22.3 4,15 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10.7 ± 0.9 4,13 | NA | NA | NA |
| PKU 22,31 | 5.8 ± 2.1 4,13 | 240.8 ± 62 4,15 | 58.8 ± 9.8 4,13 | ||||||||||
| Control | 6.1 ± 2.0 4,13 | 251 ± 68 4,15 | 60.2 ± 10 4,13 | ||||||||||
| Lucock et al. [48] | 2002 | PKU | 469.1 (397.7–637.1) 4,6,32,33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Control | 363.9 (325.3–457.9) 4,6,32,33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | ||
| van Bakel et al. [53] | 2000 | PKU 34 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 21.46 ± 4.06 18,20 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| PKU 35 | 19.25 ± 2.11 18,20 | ||||||||||||
| Control | 20.93 ± 6.15 18,20 | ||||||||||||
| Robinson et al. [49] | 2000 | PKU 36 | 476 ± 258 32,38 | 468.7 ± 199.7 39,40 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| PKU 37 | 471 ± 190.5 32,38 | 332.8 ± 128 39,40 | |||||||||||
| Control | 201 ± 92.8 32,38 | 411.9 ± 148.75 39,40 | |||||||||||
| Al-Qadreh et al. [41] | 1998 | PKU | NA | NA | 45.3 ±3.8 4,8,13,16 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Control | 49.16 ±2.54 4,8,13,16 | ||||||||||||
| Schulpis et al. [40] | 1998 | PKU 21 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 636 ± 118 4,40 |
| PKU 22 | 411.9 ± 184.9 4,40 | ||||||||||||
| Control | 336.6 ± 290.6 4,40 | ||||||||||||
| Sierra et al. [45] | 1998 | PKU 21 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 30.6 ± 9.31 29,41 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Control | 26.07 ± 5.43 29,41 | ||||||||||||
| Hillman et al. [50] | 1996 | PKU | NA | NA | 28.3 ± 9.8 4,8,42 | 36.6 ± 6.7 4,42 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Control | 22.3 ± 8.5 4,8,42 | 30.4 ± 9.3 4,42 | |||||||||||
| Prince et al. [38] | 1994 | PKU 2 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 99.4 ± 54 13,20 | NA | NA | NA |
| Control | 53.5 ± 21.3 13,20 |
| Study Name | Year | PKU Group Mean | Control Group Mean | Relative Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Folate | ||||
| Rojas-Agurto et al. [39] | 2023 | 24.52 1,2,3,4 | 16.25 1,2,3,4 | 51% |
| Akış et al. [42] | 2020 | 36.39 1,5 | 22.61 1,5 | 61% |
| Gündüz et al. [43] | 2016 | 32.64 1,3,4,5 | 22.5 1,3,5 | 45% |
| Huemer et al. [46] | 2012 | 7.2 5,6 | 6.5 5,6 | 11% |
| Huemer et al. [26] | 2008 | 15.1 1,2 | 7.6 1,2 | 99% |
| Colomé et al. [44] | 2003 | 49.1 1,5 | 19.1 1,5 | 157% |
| Schulpis et al. [27] | 2002 | 4.21 1,4,5 | 6.1 1,5 | −31% |
| Lucock et al. [48] | 2002 | 469.1 1,2,7 | 363.9 1,2,7 | 29% |
| Robinson et al. [49] | 2000 | 472.72 4,7,8 | 201 7,8 | 135% |
| Vitamin B12 | ||||
| Rojas-Agurto et al. [39] | 2023 | 518 1,2,4 | 448.7 1,2 | 15% |
| Akış et al. [42] | 2020 | 297.4 1,9 | 291.4 1,9 | 2% |
| Gündüz et al. [43] | 2016 | 287.5 1,4,9 | 303 1,9 | −5% |
| Huemer et al. [26] | 2008 | 783 1,10 | 478 1,10 | 64% |
| Colomé et al. [44] | 2003 | 622 1,9 | 455 1,9 | 37% |
| Schulpis et al. [27] | 2002 | 175.4 1,9 | 251 1,9 | −30% |
| Robinson et al. [49] | 2000 | 390.3 4,11,12 | 411.9 11,12 | −5% |
| Vitamin D | ||||
| Rojas-Agurto et al. [39] | 2023 | 29.58 1,4,10,13 | 29.95 1,10,13 | −1% |
| Leiva et al. [47] | 2021 | 38.61 1,2,13 | 33.84 1,2,13 | 14% |
| Ekin et al. [31] | 2018 | 0.43 1,14,15 | 0.38 1,14,15 | 13% |
| Nagasaka et al. [29] | 2013 | 19.9 1,2,16 | 28.9 1,2,16 | −31% |
| Nagasaka et al. [30] | 2011 | 20.04 1,2,4,16 | 28.53 1,2,4,16 | −30% |
| Al-Qadreh et al. [41] | 1998 | 45.3 1,4,13 | 49.16 1,4,13 | −8% |
| Hillman et al. | 1996 | 28.3 1,13,17 | 22.3 1,13,17 | 27% |
| 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D | ||||
| Nagasaka et al. [29] | 2013 | 55.5 1,10 | 40.7 1,10 | 36% |
| Nagasaka et al. [30] | 2011 | 55.42 1,10 | 40.94 1,10 | 35% |
| Hillman et al. [50] | 1996 | 36.6 1,17 | 30.4 1,17 | 20% |
| Vitamin A | ||||
| Ekin et al. [31] | 2018 | 2.91 1,15 | 3.03 1,15 | −4% |
| Mikoluc et al. [28] | 2012 | 3.36 6,15 | 2.74 6,15 | 23% |
| Gassió et al. [32] | 2008 | 1.36 6,18 | 2.1 6,18 | −35% |
| Vitamin E | ||||
| Ekin et al. [31] | 2018 | 2.26 1,15 | 2.39 1,15 | −5% |
| Mikoluc et al. [28] | 2012 | 9.89 6,15 | 25.4 6,15 | −61% |
| Gassió et al. [32] | 2008 | 20 6,18 | 21 6,18 | −5% |
| Schulpis et al. [25] | 2003 | 27.74 4,6,15 | 24 6,15 | 16% |
| van Bakel et al. [53] | 2000 | 20.81 4,6,15 | 20.93 6,15 | −1% |
| Sierra et al. [45] | 1998 | 30.6 18,19 | 26.07 18,19 | 17% |
| Vitamin B6 | ||||
| Schulpis et al. [27] | 2002 | 36.7 1,4,5 | 60.2 1,5 | −39% |
| Prince et al. [38] | 1994 | 99.4 5,6 | 53.5 5,6 | 86% |
| Study (First Author) | Selection | Comparability | Outcome | Overall Score | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-Sectional Studies | Representativeness of the Sample | Sample Size | Non- Respondents | Ascertainment of Exposure | Based on Design and Analysis | Assessment of Outcome | Statistical Test | ||
| Rojas-Agurto et al. [39], 2023 | + | + + | + + | 5 | |||||
| Leiva et al. [47], 2021 | + | + | + | + + | + | 6 | |||
| Akış et al. [42], 2020 | + | + + | + + | 5 | |||||
| Ekin et al. [31], 2018 | + | + + | + + | 5 | |||||
| Veyrat-Durebex et al. [52], 2017 | + | + + | + + | 5 | |||||
| Gündüz et al. [43], 2016 | + | + + | + + | 5 | |||||
| Nagasaka et al. [29], 2013 | + | + + | + + | 5 | |||||
| Mikoluc et al. [28], 2012 | + | + + | + | 4 | |||||
| Mütze et al. [51], 2012 | + | + + | + + | 5 | |||||
| Huemer et al. [46], 2012 | + | + + | 3 | ||||||
| Nagasaka et al. [30], 2011 | + | + + | + + | 5 | |||||
| Gassió et al. [32], 2008 | + | + | + + | + + | 6 | ||||
| Colomé et al. [44], 2003 | + | + | + + | + | 5 | ||||
| Schulpis et al. [25], 2003 | + | + + | + + | 5 | |||||
| Schulpis et al. [27], 2002 | + | + + | + + | 5 | |||||
| Lucock et al. [48], 2002 | + | + + | 3 | ||||||
| van Bakel et al. [53], 2000 | + | + + | 3 | ||||||
| Robinson et al. [49], 2000 | 0 | ||||||||
| Al-Qadreh et al. [41], 1998 | + | 1 | |||||||
| Schulpis et al. [40], 1998 | + | + + | + + | 5 | |||||
| Sierra et al. [45], 1998 | + + | + | 3 | ||||||
| Hillman et al. [50], 1996 | + + | + + | 4 | ||||||
| Prince et al. [38], 1994 | + + | 2 | |||||||
| Study (first author) | Selection | Comparability | Exposure | ||||||
| Case-control study | Case definition adequate? | Representativeness of the cases | Selection of controls | Definition of controls | Based on design and analysis | Ascertainment of exposure | Same method for cases and controls | Non-response rate | Overall score |
| Huemer et al. [26], 2008 | + | + | + + | + | + | 6 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bokayeva, K.; Jamka, M.; Walkowiak, D.; Duś-Żuchowska, M.; Herzig, K.-H.; Walkowiak, J. Vitamin Status in Patients with Phenylketonuria: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5065. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105065
Bokayeva K, Jamka M, Walkowiak D, Duś-Żuchowska M, Herzig K-H, Walkowiak J. Vitamin Status in Patients with Phenylketonuria: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(10):5065. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105065
Chicago/Turabian StyleBokayeva, Kamila, Małgorzata Jamka, Dariusz Walkowiak, Monika Duś-Żuchowska, Karl-Heinz Herzig, and Jarosław Walkowiak. 2024. "Vitamin Status in Patients with Phenylketonuria: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 10: 5065. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105065
APA StyleBokayeva, K., Jamka, M., Walkowiak, D., Duś-Żuchowska, M., Herzig, K.-H., & Walkowiak, J. (2024). Vitamin Status in Patients with Phenylketonuria: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(10), 5065. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105065








