Redox Properties of Bacillus subtilis Ferredoxin:NADP+ Oxidoreductase: Potentiometric Characteristics and Reactions with Pro-Oxidant Xenobiotics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
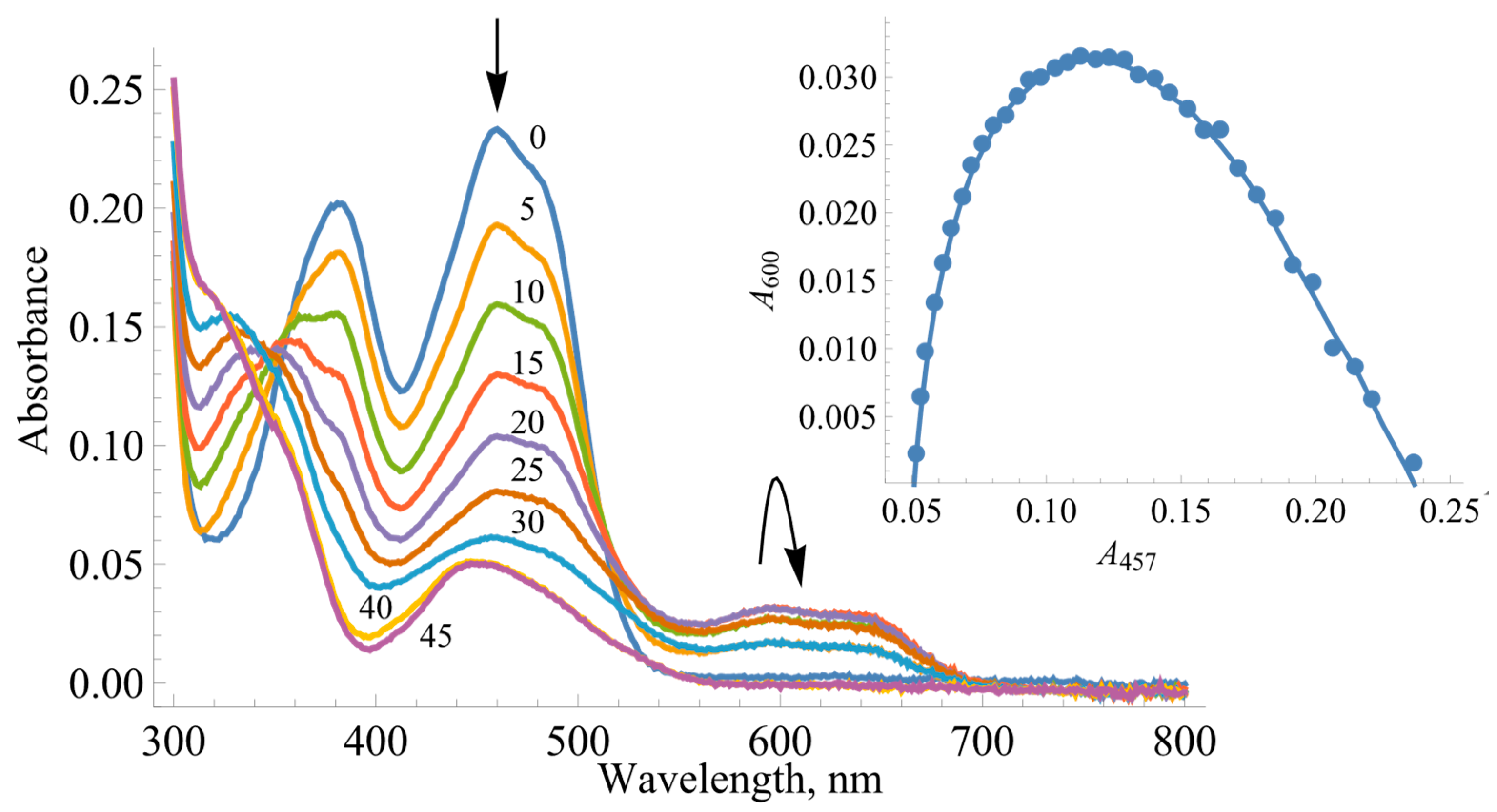
2.1. The Determination of Redox Potentials of BsFNR
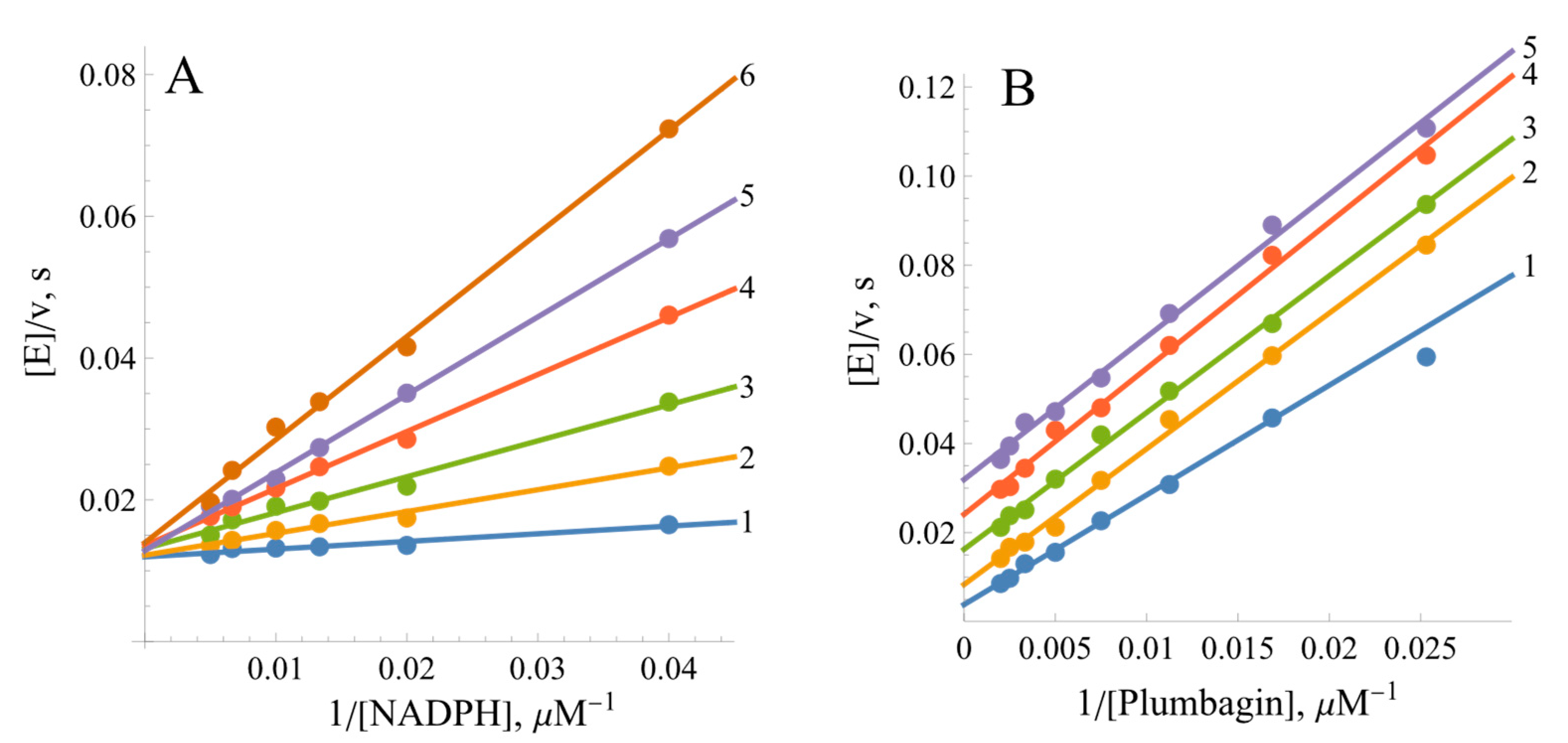
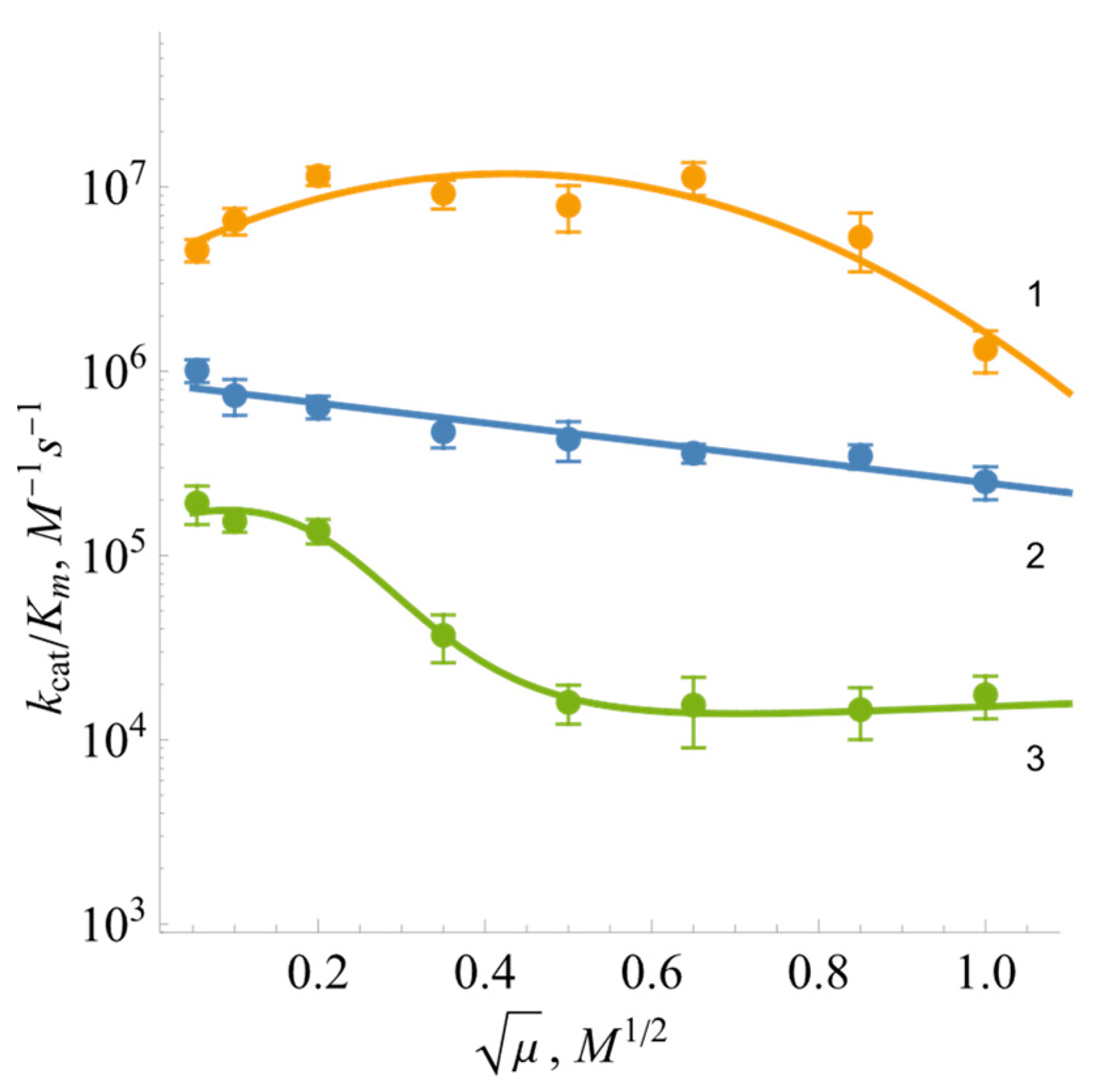
2.2. Steady-State Kinetics and Oxidant Substrate Specificity of BsFNR
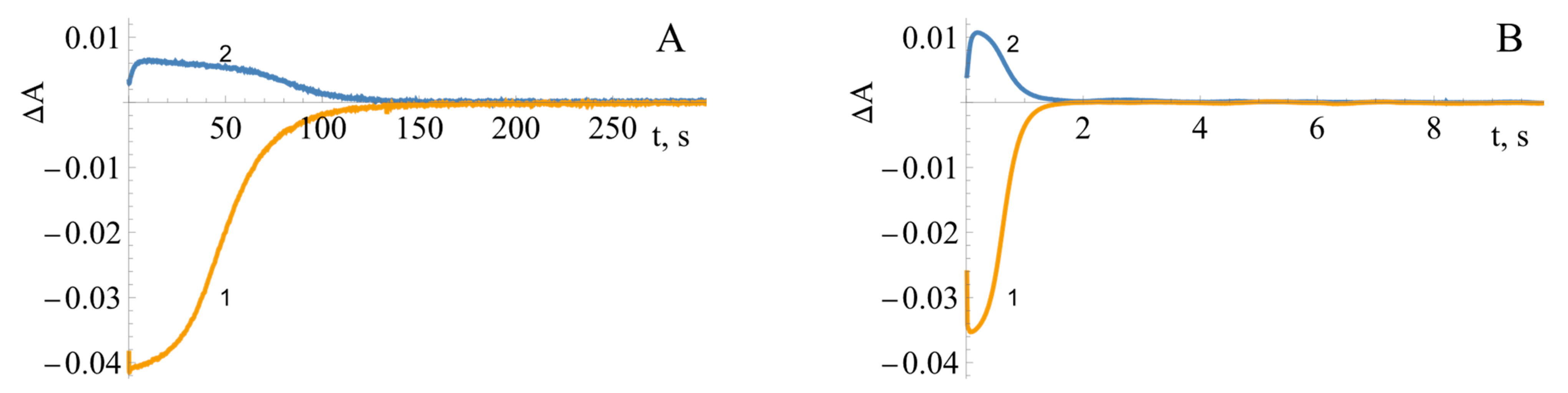
2.3. Pre-Steady-State Kinetics of BsFNR Oxidation under Multiple Turnover Conditions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Enzymes
4.2. Steady-State Kinetics
4.3. Presteady-State Kinetics
4.4. Photoreduction of BsFNR
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanke, G.T.; Kurisu, G.; Kusunoki, M.; Hase, T. Fd:FNR electron transfer complexes: Evolutionary refinement of structural interactions. Photosynth. Res. 2004, 81, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccarelli, E.A.; Arakaki, A.K.; Cortez, N.; Carrillo, N. Functional plasticity and catalytic efficiency in plant and bacterial ferredoxin-NADP(H) reductases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Proteins Proteom. 2004, 1698, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliverti, A.; Pandini, V.; Pennati, A.; de Rosa, M.; Zanetti, G. Structural and functional diversity of ferredoxin-NADP+ reductases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2008, 474, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karplus, P.A.; Daniels, M.J.; Herriott, J.R. Atomic structure of ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase: Prototype for a structurally novel flavoenzyme family. Science 1991, 251, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyanagi, T. Roles of ferredoxin-NADP+ oxidoreductase and flavodoxin in NAD(P)H-dependent electron transfer systems. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onda, Y.; Matsumura, T.; Kimata-Ariga, Y.; Sakakibara, H.; Sugiyama, T.; Hase, T. Differential interaction of maize root ferredoxin:NADP+ oxidoreductase with photosynthetic and non-photosynthetic ferredoxin isoproteins. Plant Physiol. 2000, 123, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röhrich, R.C.; Englert, N.; Troschke, K.; Reichenberg, A.; Hintz, M.; Seeber, F.; Balconi, E.; Aliverti, A.; Zanetti, G.; Köhler, U.; et al. Reconstitution of an apicoplast-localised electron transfer pathway involved in the isoprenoid biosynthesis of Plasmodium falciparum. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 6433–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogués, I.; Tejero, J.; Hurley, J.K.; Paladini, D.; Frago, S.; Tollin, G.; Mayhew, S.G.; Gómez-Moreno, C.; Ceccarelli, E.A.; Carrillo, N.; et al. Role of the C-terminal tyrosine of ferredoxin-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate reductase in the electron transfer processes with its protein partners ferredoxin and flavodoxin. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 6127–6137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, M.; Gomez-Moreno, C.; Tollin, G. Effects of chemical modification of Anabaena flavodoxin and ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase on the kinetics of interprotein electron transfer reactions. Eur. J. Biochem. 1992, 210, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuello, C.; de Miguel, R.; Martínez-Júlvez, M.; Gómez-Moreno, C.; Lostao, A. Mechanostability of the single-electron-transfer complexes of Anabaena ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase. ChemPhysChem 2015, 16, 3161–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerstad, M.; Hersleth, H.-P. Overview of structurally homologous flavoprotein oxidoreductases containing the low Mr thioredoxin reductase-like fold—A functionally diverse group. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 702, 108826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, D.; Muraki, N.; Kurisu, G. Kinetic and structural insight into a role of the re-face Tyr328 residue of the homodimer type ferredoxin-NADP+ oxidoreductase from Rhodopseudomonas palustris in the reaction with NADP+/NADPH. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Bioenerg. 2020, 1861, 148140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komori, H.; Seo, D.; Sakurai, T.; Higuchi, Y. Crystal structure analysis of Bacillus subtilis ferredoxin-NADP+ oxidoreductase and the structural basis for its substrate selectivity. Protein Sci. 2010, 19, 2279–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, E.C.; Goddard, T.D.; Pettersen, E.F.; Couch, G.S.; Pearson, Z.J.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. ChimeraX: Tools for structure building and analysis. Protein Sci. 2023, 32, e4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, D.; Soeta, T.; Sakurai, H.; Sétif, P.; Sakurai, T. Pre-steady-state kinetic studies of redox reactions catalysed by Bacillus subtilis ferredoxin-NADP+ oxidoreductase with NADP+/NADPH and ferredoxin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Bioenerg. 2016, 1857, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, D.; Asano, T.; Komori, H.; Sakurai, T. Role of the C-terminal extension stacked on the re-face of the isoalloxazine ring moiety of the flavin adenine dinucleotide prosthetic group in ferredoxin-NADP+ oxidoreductase from Bacillus subtilis. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2014, 81, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, D.; Naito, H.; Nishimura, E.; Sakurai, T. Replacement of Tyr50 stacked on the si-face of the isoalloxazine ring of the flavin adenine dinucleotide prosthetic group modulates Bacillus subtilis ferredoxin-NADP+ oxidoreductase activity toward NADPH. Photosynth. Res. 2015, 125, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, A.J.; Munro, A.W.; Cheesman, M.R.; Reid, G.A.; von Wachenfeldt, C.; Chapman, S.K. Expression, purification and characterisation of a Bacillus subtilis ferredoxin: A potential electron transfer donor to cytochrome P450 BioI. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2003, 93, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, R.J.; von Wachenfeldt, C.; Haq, I.; Perkins, J.; Munro, A.W. Expression and characterization of the two flavodoxin proteins of Bacillus subtilis, YkuN and YkuP: Biophysical properties and interactions with cytochrome P450 BioI. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 12390–12409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazarreta-Cifre, L.; Martiarena, L.; de Mendoza, D.; Altabe, S.G. Role of ferredoxin and flavodoxins in Bacillus subtilis fatty acid desaturation. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 4043–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, J.K.; Lim, N.; Poulos, T.L. Identification of redox partners and development of a novel chimeric bacterial nitric oxide synthase for structure activity analyses. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 29437–29445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebeke, M.; Pöther, D.C.; Van Duy, N.; Albrecht, D.; Becher, D.; Hochgräfe, F.; Lalk, M.; Hecker, M.; Antelmann, H. Depletion of thiol-containing proteins in response to quinones in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 69, 1513–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauber, J.P.; Schroeckh, V.; Shelest, E.; Brakhage, A.A.; Hoffmeister, D. Bacteria induce pigment formation in the basidiomycete Serpula lacrymans. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 5218–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imlay, J.A. Where in the world do bacteria experience oxidative stress? Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapley, A.; Prasad, S.; Purohit, H.J. Changes in microbial diversity in fed-batch reactor operation with wastewater containing nitroaromatic residues. Bioresource Technol. 2007, 98, 2479–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Yao, L.; Li, N.; Cao, Q.; Dai, C.; Zhang, J.; He, Q.; He, J. Biodegradation of pendimethalin by Bacillus subtilis Y3. J. Environ. Sci.—China 2016, 41, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichocki, B.A.; Donzel, M.; Heimsch, K.C.; Lesanavičius, M.; Feng, L.; Montagut, E.J.; Becker, K.; Aliverti, A.; Elhabiri, M.; Čėnas, N.; et al. Plasmodium falciparum ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase-catalyzed redox cycling of plasmodione generates both predicted key drug metabolites: Implication for antimalarial drug development. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 1996–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampropoulos, P.K.; Gkentzi, D.; Tzifas, S.; Dimitriou, G. Neonatal sepsis due to Bacillus subtilis. Cureus 2021, 13, e17692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokano, M.; Tarumoto, N.; Imai, K.; Sakai, J.; Maeda, T.; Kawamura, T.; Seo, K.; Takahashi, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Maesaki, S. Bacterial meningitis caused by Bacillus subtilis var. natto. Internal Med. 2023, 62, 1989–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfmann, C.; Zhu, B.; Stülke, J.; Halbedel, S. ListiWiki: A database for the foodborne pathogen Listeria monocytogenes. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2023, 313, 151591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesanavičius, M.; Seo, D.; Čėnas, N. Thioredoxin reductase-type ferredoxin:NADP+ oxidoreductase of Rhodopseudomonas palustris: Potentiometric characteristics and reactions with nonphysiological oxidants. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Arscott, L.D.; Ballou, D.P.; Williams, C.H. The relationship of the redox potentials of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase from Drosophila melanogaster to the enzymatic mechanism: Reduced thioredoxin is the reductant of glutathione in drosophila. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 7875–7885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, N.O.; Ciotti, M.M. Chemistry and properties of the 3-acetylpyridine analogue of diphosphopyridine nucleotide. J. Biol. Chem. 1956, 221, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D. The role of the si-face tyrosine of a homodimeric ferredoxin-NADP+ oxidoreductase from Bacillus subtilis during complex formation and redox equivalent transfer with NADP+/H and ferredoxin. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesanavičius, M.; Aliverti, A.; Šarlauskas, J.; Čėnas, N. Reactions of Plasmodium falciparum ferredoxin:NADP+ oxidoreductase with redox cycling xenobiotics: A mechanistic study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, Z.; Mahbuba, R.; Turcotte, B. The anticancer drug tirapazamine has antimicrobial activity against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium difficile. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2013, 347, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardman, P. Reduction potentials of one-electron couples involving free radicals in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1989, 18, 1637–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Buettner, G.R. Thermodynamic and kinetic considerations for the reaction of semiquinone radicals to form superoxide and hydrogen peroxide. Free Radical Bio. Med. 2010, 49, 919–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čėnas, N.; Nemeikaitė-Čėnienė, A.; Kosychova, L. Single- and two-electron reduction of nitroaromatic compounds by flavoenzymes: Mechanisms and implications for cytotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeikaitė-Čėnienė, A.; Šarlauskas, J.; Jonušienė, V.; Marozienė, A.; Misevičienė, L.; Yantsevich, A.V.; Čėnas, N. Kinetics of flavoenzyme-catalyzed reduction of tirapazamine derivatives: Implications for their prooxidant cytotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyanagi, T.; Yamazaki, I. One-electron-transfer reactions in biochemical systems V. Difference in the mechanism of quinone reduction by the NADH dehydrogenase and the NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (DT-diaphorase). Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Bioenerg. 1970, 216, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chance, B. A simple relationship for a calculation of the “on” velocity constant in enzyme reactions. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1957, 71, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balconi, E.; Pennati, A.; Crobu, D.; Pandini, V.; Cerutti, R.; Zanetti, G.; Aliverti, A. The ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase/ferredoxin electron transfer system of Plasmodium falciparum. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 3825–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batie, C.J.; Kamin, H. The relation of pH and oxidation-reduction potential to the association state of the ferredoxin•ferredoxin:NADP+ reductase complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 7756–7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, R.P.; Krey, G.D. Site-directed mutagenesis of tyrosine-98 in the flavodoxin from Desulfovibrio vulgaris (hildenborough): Regulation of oxidation-reduction properties of the bound FMN cofactor by aromatic, solvent, and electrostatic interactions. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 8505–8514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, D.; Okabe, S.; Yanase, M.; Kataoka, K.; Sakurai, T. Studies of interaction of homo-dimeric ferredoxin-NAD(P)+ oxidoreductases of Bacillus subtilis and Rhodopseudomonas palustris, that are closely related to thioredoxin reductases in amino acid sequence, with ferredoxins and pyridine nucleotide coenzymes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Proteins Proteom. 2009, 1794, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; Mcgettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valiauga, B.; Williams, E.M.; Ackerley, D.F.; Čėnas, N. Reduction of quinones and nitroaromatic compounds by Escherichia coli nitroreductase A (NfsA): Characterization of kinetics and substrate specificity. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 614, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, R.A.; Sutin, N. Electron transfers in chemistry and biology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Rev. Bioenerg. 1985, 811, 265–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardman, P.; Dennis, M.F.; Everett, S.A.; Patel, K.B.; Stratford, M.R.L.; Tracy, M. Radicals from one-electron reduction of nitro compounds, aromatic N-oxides and quinones: The kinetic basis for hypoxia-selective, bioreductive drugs. Biochem. Soc. Symp. 1995, 61, 171–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, D.E.; Tollin, G. Semiquinone formation in flavo- and metalloflavoproteins. In Topics in Current Chemistry; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 1983; Volume 108, pp. 109–138. [Google Scholar]
- Tejero, J.; Peregrina, J.R.; Martínez-Júlvez, M.; Gutiérrez, A.; Gómez-Moreno, C.; Scrutton, N.S.; Medina, M. Catalytic mechanism of hydride transfer between NADP+/H and ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase from Anabaena PCC 7119. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 459, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, T.; Sakamoto, H.; Sugiyama, T.; Yamano, T. Formation of the semiquinone form in the anaerobic reduction of adrenodoxin reductase by NADPH. Resonance Raman, EPR, and optical spectroscopic evidence. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 12075–12080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, H.; Ohta, M.; Miura, R.; Sugiyama, T.; Yamano, T.; Miyake, Y. Studies on the reaction mechanism of NADPH-adrenodoxin reductase with NADPH. J. Biochem. 1982, 92, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliverti, A.; Corrado, M.E.; Zanetti, G. Involvement of lysine-88 of spinach ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase in the interaction with ferredoxin. FEBS Lett. 1994, 343, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliverti, A.; Deng, Z.; Ravasi, D.; Piubelli, L.; Karplus, P.A.; Zanetti, G. Probing the function of the invariant glutamyl residue 312 in spinach ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 34008–34015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.K.; Hazzard, J.T.; Martínez-Júlvez, M.; Medina, M.; Gómez-Moreno, C.; Tollin, G. Electrostatic forces involved in orienting Anabaena ferredoxin during binding to Anabaena ferredoxin:NADP+ reductase: Site-specific mutagenesis, transient kinetic measurements, and electrostatic surface potentials. Protein Sci. 1999, 8, 1614–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anusevičius, Ž.; Misevičienė, L.; Medina, M.; Martinez-Julvez, M.; Gomez-Moreno, C.; Čėnas, N. FAD semiquinone stability regulates single- and two-electron reduction of quinones by Anabaena PCC7119 ferredoxin:NADP+ reductase and its Glu301Ala mutant. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 437, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauk, A.G.; Scott, R.A.; Gray, H.B. Distances of electron transfer to and from metalloprotein redox sites in reactions with inorganic complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 4360–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, R.A.; Reinbold, R.; Schofield, C.J.; Armstrong, F.A. NADP(H)-dependent biocatalysis without adding NADP(H). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2214123120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



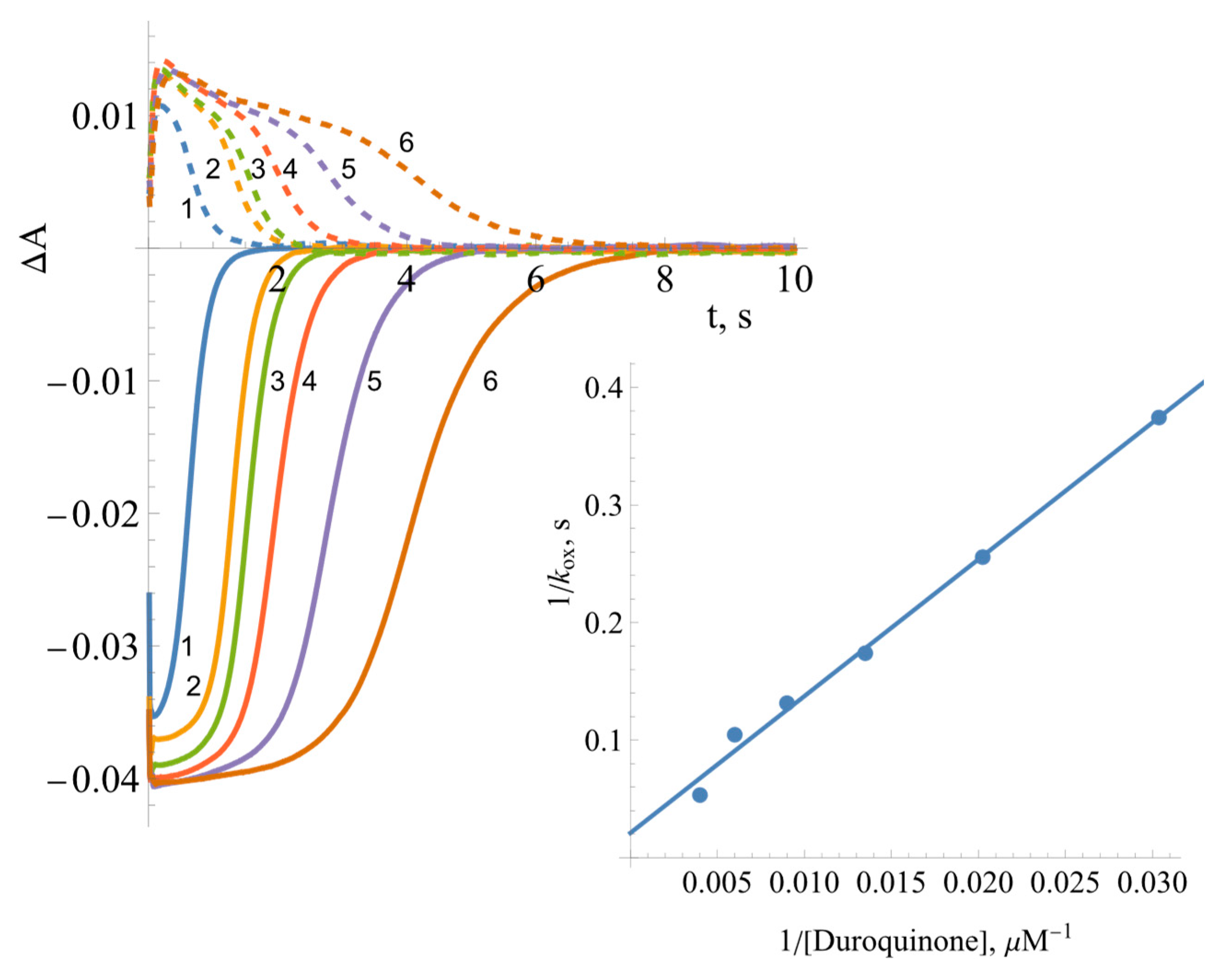
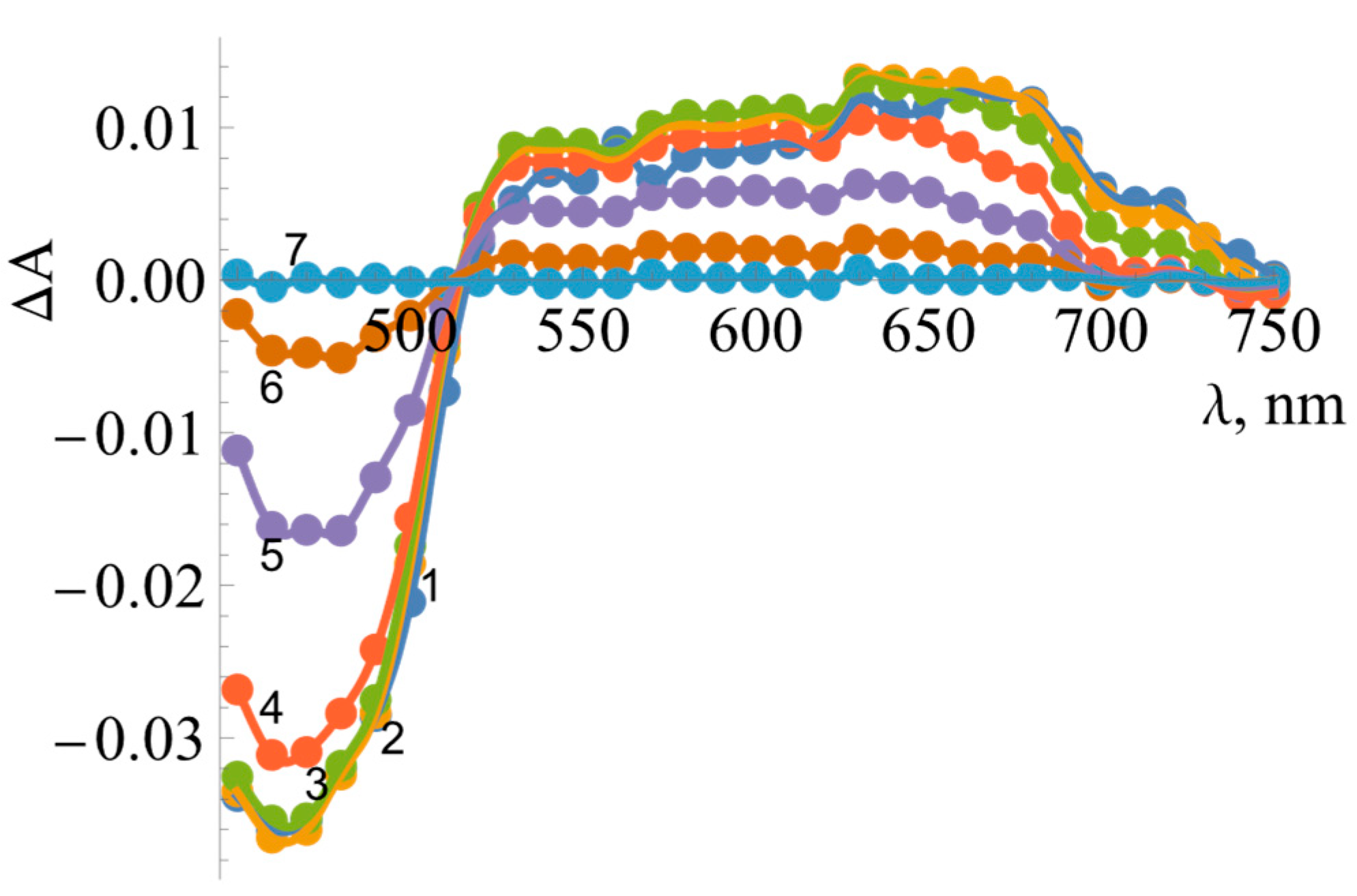

| No. | Compound | , V | , s−1 | , M−1s−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quinones | ||||
| 1 | 1,4-Benzoquinone | 0.090 | 209.8 ± 5.5 | 3.7 ± 0.4 × 106 |
| 2 | 2-Methyl-1,4-benzoquinone | 0.010 | 267.3 ± 7.8 | 2.3 ± 0.3 × 106 |
| 3 | 2,3-Dichloro-1,4-naphthoquinone | −0.036 | 58.2 ± 1.1 | 3.5 ± 0.3 × 106 |
| 4 | 2,3-Dimethyl-1,4-benzoquinone | −0.074 | 301.9 ± 19.8 | 1.1 ± 0.1 × 106 |
| 5 | 2,6-Dimethyl-1,4-benzoquinone | −0.080 | 183.1 ± 5.0 | 1.0 ± 0.1 × 106 |
| 6 | 5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone | −0.090 | 221.4 ± 2.6 | 4.4 ± 0.2 × 106 |
| 7 | 5,8-Hihydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone | −0.110 | 96.0 ± 3.5 | 5.9 ± 0.4 × 106 |
| 8 | 9,10-Phenanthrenequinone | −0.120 | 65.3 ± 2.1 | 7.5 ± 0.8 × 106 |
| 9 | 1,4-Naphthoquinone | −0.150 | 180.1 ± 28.8 | 6.5 ± 0.5 × 105 |
| 10 | 5-Hydroxy-2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone | −0.156 | 142.7 ± 8.7 | 6.0 ± 0.4 × 105 |
| 11 | 2-Methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone | −0.200 | 68.9 ± 8.3 | 1.9 ± 0.3 × 105 |
| 12 | Tetramethyl-1,4-benzoquinone | −0.260 | 13.3 ± 1.2 | 9.9 ± 0.8 × 104 |
| 13 | 9,10-Anthraquinone-2-sulphonate | −0.380 | 16.2 ± 0.6 | 6.0 ± 0.7 × 104 |
| 14 | 2-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone | −0.410 | 2.5 ± 0.4 | 1.6 ± 0.3 × 104 |
| 15 | 2-Hydroxy-3-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone | −0.460 | 5.8 ± 0.4 | 1.5 ± 0.2 × 104 |
| Nitroaromatic compounds | ||||
| 16 | 2,4,6-Trinitrophenyl-N-methylnitramine (tetryl) | −0.191 | 43.4 ± 6.0 | 6.0 ± 0.5 × 104 |
| 17 | N-methylpicramide | −0.225 | 17.5 ± 2.4 | 3.0 ± 0.2 × 104 |
| 18 | 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene (TNT) | −0.253 | 15.3 ± 0.6 | 4.0 ± 0.5 × 104 |
| 19 | Nitrofurantoin | −0.255 | 35.3 ± 7.2 | 1.8 ± 0.3 × 104 |
| 20 | Nifuroxim | −0.255 | 38.2 ± 4.0 | 4.4 ± 0.4 × 104 |
| 21 | p-Dinitrobenzene | −0.257 | 9.3 ± 0.5 | 2.3 ± 0.3 × 104 |
| 22 | o-Dinitrobenzene | −0.287 | 6.2 ± 0.4 | 1.4 ± 0.2 × 104 |
| 23 | 2-Nitrobenzaldehyde | −0.308 | 26.4 ± 2.7 | 1.1 ± 0.2 × 104 |
| 24 | 3,5-Dinitrobenzamide | −0.311 | 20.9 ± 1.3 | 1.4 ± 0.2 × 104 |
| 25 | 4-Nitrobenzaldehyde | −0.325 | 20.8 ± 1.8 | 7.6 ± 0.7 × 103 |
| 26 | 3,5-Dinitrobenzoic acid | −0.344 | 4.7 ± 0.3 | 2.5 ± 0.3 × 103 |
| 27 | m-Dinitrobenzene | −0.348 | 12.1 ± 0.7 | 6.1 ± 0.7 × 103 |
| 28 | 4-Nitroacetophenone | −0.355 | 16.2 ± 1.6 | 5.7 ± 0.4 × 103 |
| 29 | 5-(Aziridin-1-yl)-2,4-dinitrobenzamide (CB-1954) | −0.385 | 3.6 ± 0.4 | 4.3 ± 0.2 × 103 |
| 30 | 2-Amino-4,6-dinitrotoluene | −0.417 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 8.3 ± 0.9 × 103 |
| 31 | 4-Amino-2,6-dinitrotoluene | −0.449 | 0.7 ± 0.04 | 4.3 ± 0.5 × 103 |
| 32 | 3-Nitro-1,2,4-triazolone | −0.472 | 0.3 ± 0.03 | 7.3 ± 0.9 × 102 |
| 33 | 4-Nitrobenzyl alcohol | −0.475 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 8.2 ± 0.9 × 102 |
| Aromatic N-oxides | ||||
| 34 | 7-Trifluoromethoxytirapazamine | −0.345 | 5.4 ± 0.3 | 1.2 ± 0.1 × 104 |
| 35 | 7-Fluorotirapazamine | −0.400 | 6.2 ± 0.2 | 1.2 ± 0.1 × 104 |
| 36 | Tirapazamine | −0.456 | 5.6 ± 0.3 | 3.5 ± 0.4 × 103 |
| 37 | 7-Ethoxytirapazamine | −0.494 | 2.3 ± 0.4 | 5.8 ± 0.5 × 103 |
| Single-electron acceptors | ||||
| 38 | Ferricyanide a | 0.410 | 557.5 ± 18.1 | 6.3 ± 0.8 × 106 |
| 39 | FeEDTA− | 0.120 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 5.7 ± 0.6 × 103 |
| 40 | Benzyl viologen | −0.354 | 38.4 ± 3.7 | 1.9 ± 0.3 × 105 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lesanavičius, M.; Seo, D.; Maurutytė, G.; Čėnas, N. Redox Properties of Bacillus subtilis Ferredoxin:NADP+ Oxidoreductase: Potentiometric Characteristics and Reactions with Pro-Oxidant Xenobiotics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105373
Lesanavičius M, Seo D, Maurutytė G, Čėnas N. Redox Properties of Bacillus subtilis Ferredoxin:NADP+ Oxidoreductase: Potentiometric Characteristics and Reactions with Pro-Oxidant Xenobiotics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(10):5373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105373
Chicago/Turabian StyleLesanavičius, Mindaugas, Daisuke Seo, Gintarė Maurutytė, and Narimantas Čėnas. 2024. "Redox Properties of Bacillus subtilis Ferredoxin:NADP+ Oxidoreductase: Potentiometric Characteristics and Reactions with Pro-Oxidant Xenobiotics" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 10: 5373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105373
APA StyleLesanavičius, M., Seo, D., Maurutytė, G., & Čėnas, N. (2024). Redox Properties of Bacillus subtilis Ferredoxin:NADP+ Oxidoreductase: Potentiometric Characteristics and Reactions with Pro-Oxidant Xenobiotics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(10), 5373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105373








