Macrophage Polarization and Functions in Pathogenesis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pathophysiology of COPD
2.1. Airflow Limitation
2.2. Small Airway Obstruction
2.3. Emphysema
2.4. Chronic Bronchitis
2.5. Airway Mucus Hyperproduction
2.6. Impairment of Gas Exchange
3. Etiology of COPD
3.1. Oxidative Stress
3.2. Protease–Antiprotease Imbalance
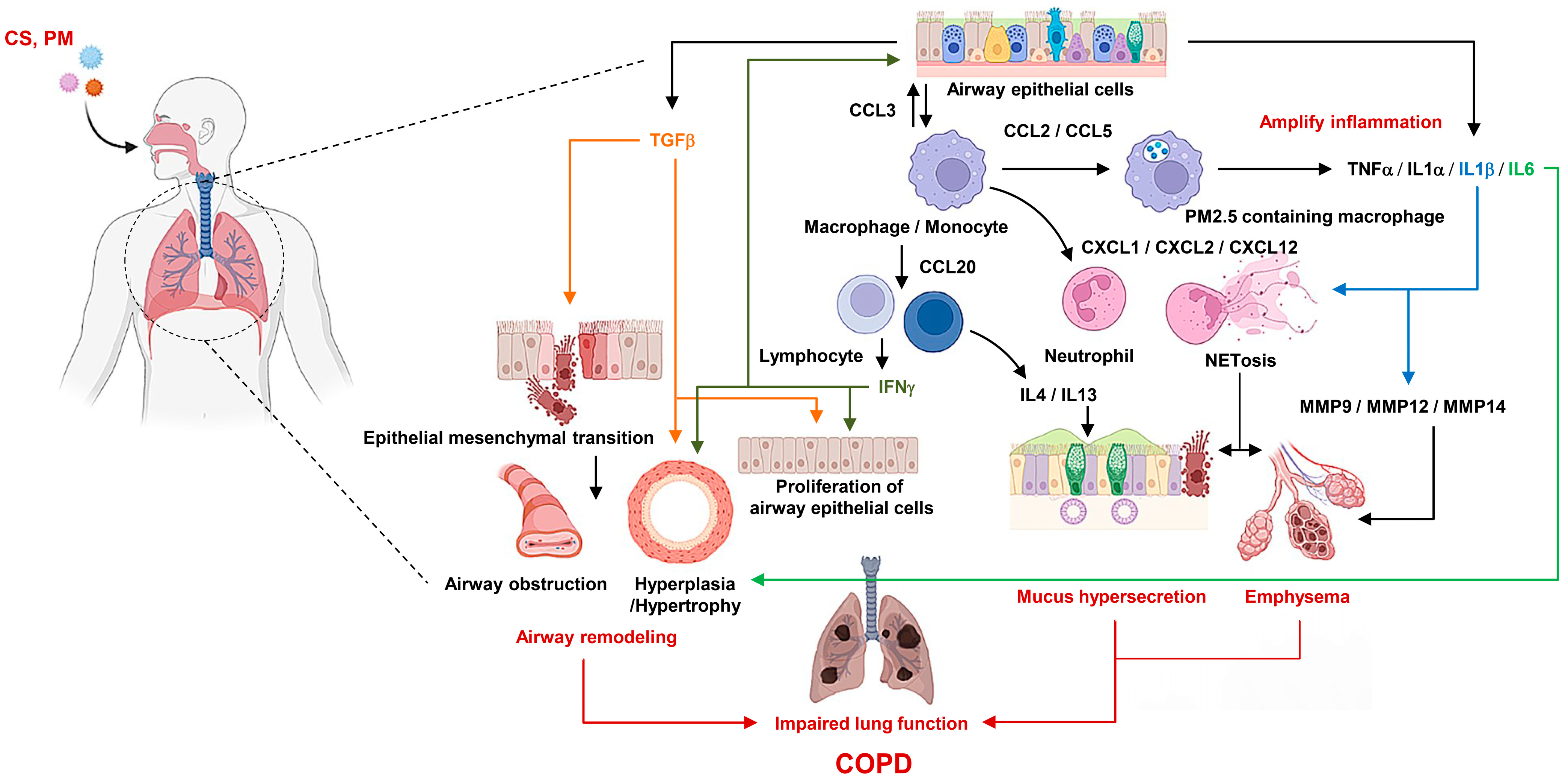
3.3. Inflammatory Mediators
3.4. Inflammatory Cells
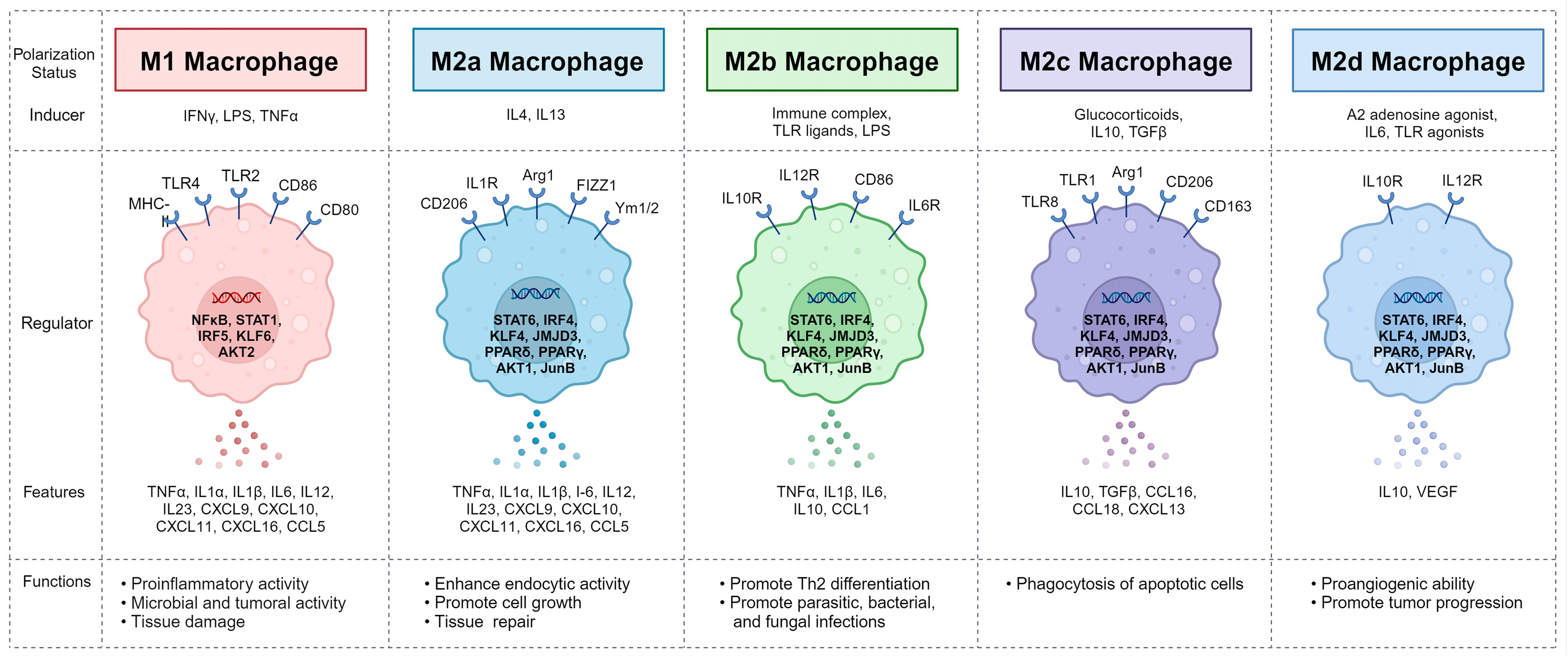
4. Macrophages and Their Polarization
5. Pulmonary Macrophage
6. Role of Macrophages and Their Polarization in COPD
7. Altered Function of Macrophage in Patients with COPD
7.1. Altered Macrophage Phenotype
7.2. Impaired Phagocytic Activity
7.3. Inflammatory Response
7.4. Lipid-Laden Foamy Macrophages
8. Macrophage-Targeting COPD Treatment
8.1. Regulation of Macrophage Phenotype
8.2. Enhanced Phagocytic Activity
8.3. Reduced Inflammatory Response
8.4. Reduced Lipid-Laden Foamy Macrophages
| Therapeutic Means | Target and Mechanisms | Effect on Macrophage Function | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plant compound (Salidroside) | JNK/c-Jun | Inhibited M1 polarization of alveolar macrophages in lung tissues of CS-induced pulmonary inflammation rat model and alveolar macrophage from BALF | [182] |
| Mycosterol (Ergosterol) | HDAC3 | Inhibited M1 polarization and increased M2 polarization in CSE-induced COPD rat model and raw cells Elevated HDAC3 activation and suppressed HAT activity and NFκB/p65 acetylation | [184] |
| Thiazolidinedione compound (Rosiglitazone) | PPARγ and RXRα | Inhibited M1 polarization in lung and BALF of CS-induced COPD model and alveolar macrophage from BALF | [185] |
| PPARγ agonist | JAK-STAT, MAPK and NFκB | Inhibited M1 polarization and increased M2 polarization in CS-induced COPD mice | [152] |
| Plant compound (ECC) | mTORC2 | Inhibited M2 macrophage polarization by inhibition of mTORC2 activity in IL4-induced polarization in MH-S cells | [191] |
| Macrolide antibiotics (Azithromycin) | Increased phagocytosis of E. coli and efferocytosis | [162,192] | |
| Nonantibiotic macrolides (GS-459755, GS-560660) | NLRP3 | Increased phagocytosis of NTHI and efferocytosis Decreased the NLRP3 and IL1β in THP-1 cells | [193] |
| Corticosteroid (Dexamethasone) | Increased efferocytosis | [194] | |
| S1PR3 and S1PR5 agonist (Suramin) | Increased efferocytosis | [165] | |
| Plant compound (Sulforaphane) | NRF2 | Increased phagocytosis of NTHI and P. aeruginosa by increasing MARCO | [197] |
| PDE4 inhibitor (Roflumilast) | Increased phagocytosis | [195] | |
| PDE4 inhibitor (CHF6001 and roflumilast) | CREB | Inhibited TNFα stimulated with LPS in alveolar macrophage and lung tissues of patients with COPD | [199] |
| Exogenous SP-D | NRF2 | Decreased lipid-laden macrophages Improved lung function and attenuated airway inflammation in ozone-exposed mice | [179] |
| miR-103a | Decreased lipid-laden macrophages | [202] |
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rabe, K.F.; Watz, H. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet 2017, 389, 1931–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, J.C. Pathophysiology of airflow limitation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet 2004, 364, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawlor, D.A.; Ebrahim, S.; Davey Smith, G. Association of birth weight with adult lung function: Findings from the British Women’s Heart and Health Study and a meta-analysis. Thorax 2005, 60, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foreman, M.G.; Zhang, L.; Murphy, J.; Hansel, N.N.; Make, B.; Hokanson, J.E.; Washko, G.; Regan, E.A.; Crapo, J.D.; Silverman, E.K.; et al. Early-onset chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is associated with female sex, maternal factors, and African American race in the COPDGene Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorheim, I.C.; Johannessen, A.; Gulsvik, A.; Bakke, P.S.; Silverman, E.K.; DeMeo, D.L. Gender differences in COPD: Are women more susceptible to smoking effects than men? Thorax 2010, 65, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, S.G.; Ge, D.; Zhu, G.; Kong, X.; Shianna, K.V.; Need, A.C.; Feng, S.; Hersh, C.P.; Bakke, P.; Gulsvik, A.; et al. A genome-wide association study in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): Identification of two major susceptibility loci. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohansal, R.; Martinez-Camblor, P.; Agusti, A.; Buist, A.S.; Mannino, D.M.; Soriano, J.B. The natural history of chronic airflow obstruction revisited: An analysis of the Framingham offspring cohort. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balmes, J.; Becklake, M.; Blanc, P.; Henneberger, P.; Kreiss, K.; Mapp, C.; Milton, D.; Schwartz, D.; Toren, K.; Viegi, G.; et al. American Thoracic Society Statement: Occupational contribution to the burden of airway disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauderman, W.J.; Avol, E.; Gilliland, F.; Vora, H.; Thomas, D.; Berhane, K.; McConnell, R.; Kuenzli, N.; Lurmann, F.; Rappaport, E.; et al. The effect of air pollution on lung development from 10 to 18 years of age. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schikowski, T.; Sugiri, D.; Ranft, U.; Gehring, U.; Heinrich, J.; Wichmann, H.E.; Kramer, U. Long-term air pollution exposure and living close to busy roads are associated with COPD in women. Respir. Res. 2005, 6, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collaborators, G.B.D.R.F. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1223–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safiri, S.; Carson-Chahhoud, K.; Noori, M.; Nejadghaderi, S.A.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Ahmadian Heris, J.; Ansarin, K.; Mansournia, M.A.; Collins, G.S.; Kolahi, A.A.; et al. Burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and its attributable risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. BMJ 2022, 378, e069679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boers, E.; Barrett, M.; Su, J.G.; Benjafield, A.V.; Sinha, S.; Kaye, L.; Zar, H.J.; Vuong, V.; Tellez, D.; Gondalia, R.; et al. Global Burden of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Through 2050. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2346598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
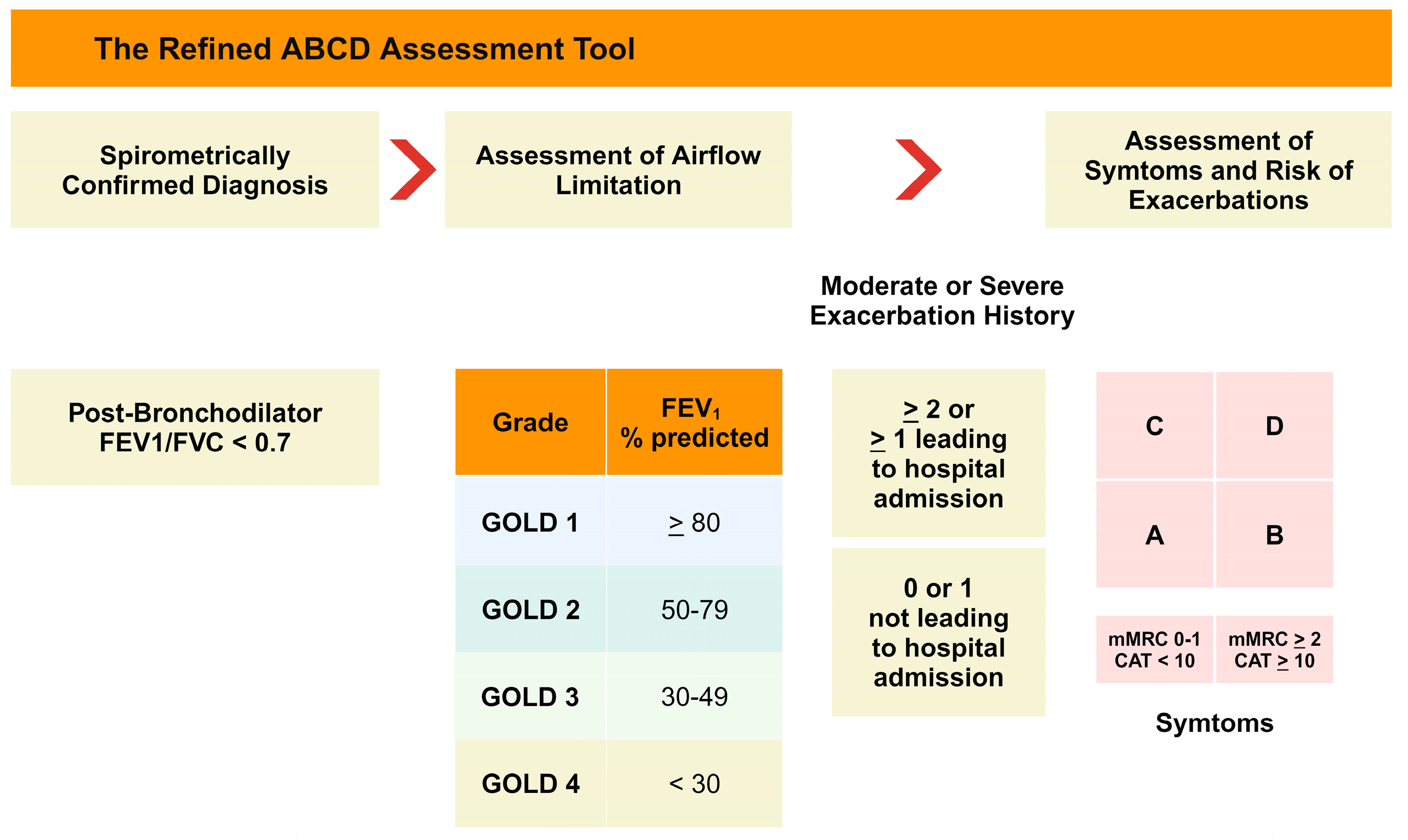
- Pauwels, R.A.; Buist, A.S.; Calverley, P.M.; Jenkins, C.R.; Hurd, S.S.; GOLD Scientific Committee. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. NHLBI/WHO Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Workshop summary. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 1256–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelmeier, C.F.; Criner, G.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Anzueto, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Bourbeau, J.; Celli, B.R.; Chen, R.; Decramer, M.; Fabbri, L.M.; et al. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease 2017 Report. GOLD Executive Summary. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 557–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.T.; Green, J.; Wang, W.F.; Yang, Y.J.; Shiao, G.M.; King, S.C. Measurements of components of resistance to breathing. Chest 1989, 96, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingenito, E.P.; Evans, R.B.; Loring, S.H.; Kaczka, D.W.; Rodenhouse, J.D.; Body, S.C.; Sugarbaker, D.J.; Mentzer, S.J.; DeCamp, M.M.; Reilly, J.J., Jr. Relation between preoperative inspiratory lung resistance and the outcome of lung-volume-reduction surgery for emphysema. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, J.C.; Macklem, P.T.; Thurlbeck, W.M. Site and nature of airway obstruction in chronic obstructive lung disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1968, 278, 1355–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, M.; Sekizawa, K.; Ohrui, T.; Sasaki, H.; Takishima, T. Site of airway obstruction in pulmonary disease: Direct measurement of intrabronchial pressure. J. Appl. Physiol. 1992, 72, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosken, C.H.; Wiggs, B.R.; Pare, P.D.; Hogg, J.C. Small airway dimensions in smokers with obstruction to airflow. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1990, 142, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, J.C.; Chu, F.; Utokaparch, S.; Woods, R.; Elliott, W.M.; Buzatu, L.; Cherniack, R.M.; Rogers, R.M.; Sciurba, F.C.; Coxson, H.O.; et al. The nature of small-airway obstruction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2645–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, D.E.; Laveneziana, P. Dyspnea and activity limitation in COPD: Mechanical factors. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2007, 4, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, L.K.; Schwartzstein, R.M. Mechanisms of dyspnea in chronic lung disease. Curr. Opin. Support. Palliat. Care 2007, 1, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weibel, E.R. Morphometry of the human lung: The state of the art after two decades. Bull. Eur. Physiopathol. Respir. 1979, 15, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wiggs, B.R.; Moreno, R.; Hogg, J.C.; Hilliam, C.; Pare, P.D. A model of the mechanics of airway narrowing. J. Appl.Physiol. 1990, 69, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuba, K.; Thurlbeck, W.M. The number and dimensions of small airways in emphysematous lungs. Am. J. Pathol. 1972, 67, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thurlbeck, W.M.; Muller, N.L. Emphysema: Definition, imaging, and quantification. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1994, 163, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The definition of emphysema. Report of a National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Division of Lung Diseases workshop. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1985, 132, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mead, J.; Turner, J.M.; Macklem, P.T.; Little, J.B. Significance of the relationship between lung recoil and maximum expiratory flow. J. Appl. Physiol. 1967, 22, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.D.; Eidelman, D.H.; Izquierdo, J.L.; Ghezzo, H.; Saetta, M.P.; Cosio, M.G. Centrilobular and panlobular emphysema in smokers. Two distinct morphologic and functional entities. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1991, 144, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heppleston, A.G.; Leopo Ld, J.G. Chronic pulmonary emphysema: Anatomy and pathogenesis. Am. J. Med. 1961, 31, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heard, B.E. Further observations on the pathology of pulmonary emphysema in chronic bronchitics. Thorax 1959, 14, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogg, J.C.; Wright, J.L.; Wiggs, B.R.; Coxson, H.O.; Opazo Saez, A.; Pare, P.D. Lung structure and function in cigarette smokers. Thorax 1994, 49, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thulborn, S.J.; Mistry, V.; Brightling, C.E.; Moffitt, K.L.; Ribeiro, D.; Bafadhel, M. Neutrophil elastase as a biomarker for bacterial infection in COPD. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, K.C.; De, S.; Mishra, P.K. Role of Proteases in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, V.; Criner, G.J. Chronic bronchitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, V.; Han, M.K.; Vance, G.B.; Make, B.J.; Newell, J.D.; Hokanson, J.E.; Hersh, C.P.; Stinson, D.; Silverman, E.K.; Criner, G.J.; et al. The chronic bronchitic phenotype of COPD: An analysis of the COPDGene Study. Chest 2011, 140, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oca, M.M.; Halbert, R.J.; Lopez, M.V.; Perez-Padilla, R.; Talamo, C.; Moreno, D.; Muino, A.; Jardim, J.R.; Valdivia, G.; Pertuze, J.; et al. The chronic bronchitis phenotype in subjects with and without COPD: The PLATINO study. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullen, J.B.; Wright, J.L.; Wiggs, B.R.; Pare, P.D.; Hogg, J.C. Reassessment of inflammation of airways in chronic bronchitis. Br. Med. J. (Clin. Res. Ed.) 1985, 291, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.G.; Minty, B.D.; Lawler, P.; Hulands, G.; Crawley, J.C.; Veall, N. Increased alveolar epithelial permeability in cigarette smokers. Lancet 1980, 1, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestbo, J.; Prescott, E.; Lange, P. Association of chronic mucus hypersecretion with FEV1 decline and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease morbidity. Copenhagen City Heart Study Group. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 153, 1530–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgel, P.R.; Nadel, J.A. Roles of epidermal growth factor receptor activation in epithelial cell repair and mucin production in airway epithelium. Thorax 2004, 59, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgel, P.R.; Escudier, E.; Coste, A.; Dao-Pick, T.; Ueki, I.F.; Takeyama, K.; Shim, J.J.; Murr, A.H.; Nadel, J.A. Relation of epidermal growth factor receptor expression to goblet cell hyperplasia in nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 106, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saetta, M.; Turato, G.; Facchini, F.M.; Corbino, L.; Lucchini, R.E.; Casoni, G.; Maestrelli, P.; Mapp, C.E.; Ciaccia, A.; Fabbri, L.M. Inflammatory cells in the bronchial glands of smokers with chronic bronchitis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 1633–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanner, R.E.; Anthonisen, N.R.; Connett, J.E.; Lung Health Study Research, G. Lower respiratory illnesses promote FEV(1) decline in current smokers but not ex-smokers with mild chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Results from the lung health study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crystal, R.G. Airway basal cells. The “smoking gun” of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerbach, O.; Forman, J.B.; Gere, J.B.; Kassouny, D.Y.; Muehsam, G.E.; Petrick, T.G.; Smolin, H.J.; Stout, A.P. Changes in the bronchial epithelium in relation to smoking and cancer of the lung; a report of progress. N. Engl. J. Med. 1957, 256, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Roisin, R.; Drakulovic, M.; Rodriguez, D.A.; Roca, J.; Barbera, J.A.; Wagner, P.D. Ventilation-perfusion imbalance and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease staging severity. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 1902–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, I.H.; Bye, P.T. Gas exchange in disease: Asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cystic fibrosis, and interstitial lung disease. Compr. Physiol. 2011, 1, 663–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbera, J.A.; Roca, J.; Ferrer, A.; Felez, M.A.; Diaz, O.; Roger, N.; Rodriguez-Roisin, R. Mechanisms of worsening gas exchange during acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur. Respir. J. 1997, 10, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hikisz, P.; Jacenik, D. The Tobacco Smoke Component, Acrolein, as a Major Culprit in Lung Diseases and Respiratory Cancers: Molecular Mechanisms of Acrolein Cytotoxic Activity. Cells 2023, 12, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horinouchi, T.; Higashi, T.; Mazaki, Y.; Miwa, S. Carbonyl Compounds in the Gas Phase of Cigarette Mainstream Smoke and Their Pharmacological Properties. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 39, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caliri, A.W.; Tommasi, S.; Besaratinia, A. Relationships among smoking, oxidative stress, inflammation, macromolecular damage, and cancer. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2021, 787, 108365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Strate, B.W.; Postma, D.S.; Brandsma, C.A.; Melgert, B.N.; Luinge, M.A.; Geerlings, M.; Hylkema, M.N.; van den Berg, A.; Timens, W.; Kerstjens, H.A. Cigarette smoke-induced emphysema: A role for the B cell? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Meza, H.; Vilchis-Landeros, M.M.; Vazquez-Carrada, M.; Uribe-Ramirez, D.; Matuz-Mares, D. Cellular Compartmentalization, Glutathione Transport and Its Relevance in Some Pathologies. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, I.; MacNee, W. Oxidative stress and regulation of glutathione in lung inflammation. Eur. Respir. J. 2000, 16, 534–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, N.S.; Min, E.; Gauthier, S.; Martin, R.J.; Day, B.J. Lung glutathione adaptive responses to cigarette smoke exposure. Respir. Res. 2011, 12, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. Oxidative Stress in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonga, K.O.; Berend, N.; Thamrin, C.; Farah, C.S.; Jetmalani, K.; Chapman, D.G.; King, G.G. Lung elastic recoil and ventilation heterogeneity of diffusion-dependent airways in older people with asthma and fixed airflow obstruction. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papandrinopoulou, D.; Tzouda, V.; Tsoukalas, G. Lung compliance and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pulm. Med. 2012, 2012, 542769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, D.J.; Stone, P.J.; Sparrow, D.; Gale, M.E.; Weiss, S.T.; Snider, G.L.; O’Connor, G.T. Urinary desmosine excretion in smokers with and without rapid decline of lung function: The Normative Aging Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 154, 1290–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorenza, D.; Viglio, S.; Lupi, A.; Baccheschi, J.; Tinelli, C.; Trisolini, R.; Iadarola, R.; Luisetti, M.; Snider, G.L. Urinary desmosine excretion in acute exacerbations of COPD: A preliminary report. Respir. Med. 2002, 96, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, S.D.; Goldstein, N.M.; Houghton, A.M.; Kobayashi, D.K.; Kelley, D.; Belaaouaj, A. Neutrophil elastase contributes to cigarette smoke-induced emphysema in mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 2329–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. Alveolar macrophages as orchestrators of COPD. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2004, 1, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crystal, R.G. Alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency, emphysema, and liver disease. Genetic basis and strategies for therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 85, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, D.; Oliveira, M.J.; Guimaraes, M.; Lima, R.; Gomes, S.; Seixas, S. Alpha-1-antitrypsin (SERPINA1) mutation spectrum: Three novel variants and haplotype characterization of rare deficiency alleles identified in Portugal. Respir. Med. 2016, 116, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, K.R.; Chorostowska-Wynimko, J.; Koczulla, A.R.; Ferrarotti, I.; McElvaney, N.G. Alpha 1 antitrypsin to treat lung disease in alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency: Recent developments and clinical implications. Int. J. Chron. Obs. Pulmon. Dis. 2018, 13, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finlay, G.A.; O’Driscoll, L.R.; Russell, K.J.; D’Arcy, E.M.; Masterson, J.B.; FitzGerald, M.X.; O’Connor, C.M. Matrix metalloproteinase expression and production by alveolar macrophages in emphysema. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Kim, H.; Liu, X.; Sugiura, H.; Kohyama, T.; Fang, Q.; Wen, F.Q.; Abe, S.; Wang, X.; Atkinson, J.J.; et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 activates TGF-beta and stimulates fibroblast contraction of collagen gels. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L1006–L1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, J.J.; Lutey, B.A.; Suzuki, Y.; Toennies, H.M.; Kelley, D.G.; Kobayashi, D.K.; Ijem, W.G.; Deslee, G.; Moore, C.H.; Jacobs, M.E.; et al. The role of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in cigarette smoke-induced emphysema. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, J.M.; Parker, M.M.; Oster, R.A.; Bowler, R.P.; Dransfield, M.T.; Bhatt, S.P.; Cho, M.H.; Kim, V.; Curtis, J.L.; Martinez, F.J.; et al. Elevated circulating MMP-9 is linked to increased COPD exacerbation risk in SPIROMICS and COPDGene. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e123614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, R.E.; Culpitt, S.V.; DeMatos, C.; Donnelly, L.; Smith, M.; Wiggins, J.; Barnes, P.J. Release and activity of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 by alveolar macrophages from patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2002, 26, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hautamaki, R.D.; Kobayashi, D.K.; Senior, R.M.; Shapiro, S.D. Requirement for macrophage elastase for cigarette smoke-induced emphysema in mice. Science 1997, 277, 2002–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J.; Celli, B.R. Systemic manifestations and comorbidities of COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 33, 1165–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, W.R.; Hurst, J.R.; Wilkinson, T.M.; Sapsford, R.J.; Mullerova, H.; Donaldson, G.C.; Wedzicha, J.A. Inflammatory changes, recovery and recurrence at COPD exacerbation. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 29, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, M.; Vestbo, J.; Lange, P.; Bojesen, S.E.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Nordestgaard, B.G. C-reactive protein as a predictor of prognosis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 175, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozinovski, S.; Hutchinson, A.; Thompson, M.; Macgregor, L.; Black, J.; Giannakis, E.; Karlsson, A.S.; Silvestrini, R.; Smallwood, D.; Vlahos, R.; et al. Serum amyloid a is a biomarker of acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Shepard, L.W.; Chen, J.; Pan, Z.K.; Ye, R.D. Serum amyloid A is an endogenous ligand that differentially induces IL-12 and IL-23. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 4072–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, M.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Vestbo, J.; Lange, P.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Elevated plasma fibrinogen associated with reduced pulmonary function and increased risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 1008–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. Inflammatory mechanisms in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of asthma and COPD. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 1541–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keatings, V.M.; Collins, P.D.; Scott, D.M.; Barnes, P.J. Differences in interleukin-8 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in induced sputum from patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 153, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genschmer, K.R.; Russell, D.W.; Lal, C.; Szul, T.; Bratcher, P.E.; Noerager, B.D.; Abdul Roda, M.; Xu, X.; Rezonzew, G.; Viera, L.; et al. Activated PMN Exosomes: Pathogenic Entities Causing Matrix Destruction and Disease in the Lung. Cell 2019, 176, 113–126.e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanino, M.; Betsuyaku, T.; Takeyabu, K.; Tanino, Y.; Yamaguchi, E.; Miyamoto, K.; Nishimura, M. Increased levels of interleukin-8 in BAL fluid from smokers susceptible to pulmonary emphysema. Thorax 2002, 57, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparrow, D.; Glynn, R.J.; Cohen, M.; Weiss, S.T. The relationship of the peripheral leukocyte count and cigarette smoking to pulmonary function among adult men. Chest 1984, 86, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussell, T.; Bell, T.J. Alveolar macrophages: Plasticity in a tissue-specific context. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, C.; Xiong, G.; Ye, X.; Li, L.; Fang, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, W.; Du, X. The role of lung macrophages in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir. Med. 2022, 205, 107035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Chun, W.; Lee, H.J.; Min, J.H.; Kim, S.M.; Seo, J.Y.; Ahn, K.S.; Oh, S.R. The Role of Macrophages in the Development of Acute and Chronic Inflammatory Lung Diseases. Cells 2021, 10, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.J.; Allen, J.E.; Biswas, S.K.; Fisher, E.A.; Gilroy, D.W.; Goerdt, S.; Gordon, S.; Hamilton, J.A.; Ivashkiv, L.B.; Lawrence, T.; et al. Macrophage activation and polarization: Nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity 2014, 41, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, A.J.; Mathie, S.A.; Gregory, L.G.; Lloyd, C.M. Pulmonary macrophages: Key players in the innate defence of the airways. Thorax 2015, 70, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginhoux, F.; Guilliams, M. Tissue-Resident Macrophage Ontogeny and Homeostasis. Immunity 2016, 44, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeffel, G.; Chen, J.; Lavin, Y.; Low, D.; Almeida, F.F.; See, P.; Beaudin, A.E.; Lum, J.; Low, I.; Forsberg, E.C.; et al. C-Myb(+) erythro-myeloid progenitor-derived fetal monocytes give rise to adult tissue-resident macrophages. Immunity 2015, 42, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.J. Macrophage Polarization. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 541–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, F.O.; Gordon, S. The M1 and M2 paradigm of macrophage activation: Time for reassessment. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleetwood, A.J.; Dinh, H.; Cook, A.D.; Hertzog, P.J.; Hamilton, J.A. GM-CSF- and M-CSF-dependent macrophage phenotypes display differential dependence on type I interferon signaling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Sica, A.; Sozzani, S.; Allavena, P.; Vecchi, A.; Locati, M. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Schmidt, S.V.; Sander, J.; Draffehn, A.; Krebs, W.; Quester, I.; De Nardo, D.; Gohel, T.D.; Emde, M.; Schmidleithner, L.; et al. Transcriptome-based network analysis reveals a spectrum model of human macrophage activation. Immunity 2014, 40, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finicelli, M.; Digilio, F.A.; Galderisi, U.; Peluso, G. The Emerging Role of Macrophages in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: The Potential Impact of Oxidative Stress and Extracellular Vesicle on Macrophage Polarization and Function. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedoret, D.; Wallemacq, H.; Marichal, T.; Desmet, C.; Quesada Calvo, F.; Henry, E.; Closset, R.; Dewals, B.; Thielen, C.; Gustin, P.; et al. Lung interstitial macrophages alter dendritic cell functions to prevent airway allergy in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 3723–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharat, A.; Bhorade, S.M.; Morales-Nebreda, L.; McQuattie-Pimentel, A.C.; Soberanes, S.; Ridge, K.; DeCamp, M.M.; Mestan, K.K.; Perlman, H.; Budinger, G.R.; et al. Flow Cytometry Reveals Similarities between Lung Macrophages in Humans and Mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 54, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, Y.; Berclaz, P.Y.; Chroneos, Z.C.; Yoshida, M.; Whitsett, J.A.; Trapnell, B.C. GM-CSF regulates alveolar macrophage differentiation and innate immunity in the lung through PU.1. Immunity 2001, 15, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlahos, R.; Bozinovski, S. Role of alveolar macrophages in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, E.D.; Ramberg, R.E.; Sale, G.E.; Sparkes, R.S.; Golde, D.W. Direct evidence for a bone marrow origin of the alveolar macrophage in man. Science 1976, 192, 1016–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatel, C.; Radermecker, C.; Fievez, L.; Paulissen, G.; Chakarov, S.; Fernandes, C.; Olivier, S.; Toussaint, M.; Pirottin, D.; Xiao, X.; et al. Exposure to Bacterial CpG DNA Protects from Airway Allergic Inflammation by Expanding Regulatory Lung Interstitial Macrophages. Immunity 2017, 46, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.Y.; Krasnow, M.A. Developmental origin of lung macrophage diversity. Development 2016, 143, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evren, E.; Ringqvist, E.; Tripathi, K.P.; Sleiers, N.; Rives, I.C.; Alisjahbana, A.; Gao, Y.; Sarhan, D.; Halle, T.; Sorini, C.; et al. Distinct developmental pathways from blood monocytes generate human lung macrophage diversity. Immunity 2021, 54, 259–275.e257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, A.J.; Powell, J.E.; O’Sullivan, B.J.; Ogger, P.P.; Hoffland, A.; Cook, J.; Bonner, K.L.; Hewitt, R.J.; Wolf, S.; Ghai, P.; et al. Dynamics of human monocytes and airway macrophages during healthy aging and after transplant. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20191236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguiluz-Gracia, I.; Schultz, H.H.; Sikkeland, L.I.; Danilova, E.; Holm, A.M.; Pronk, C.J.; Agace, W.W.; Iversen, M.; Andersen, C.; Jahnsen, F.L.; et al. Long-term persistence of human donor alveolar macrophages in lung transplant recipients. Thorax 2016, 71, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, D.K.; Zhou, F.; Xu, M.; Huang, J.; Tsuji, M.; Hachem, R.; Mohanakumar, T. Long-Term Persistence of Donor Alveolar Macrophages in Human Lung Transplant Recipients That Influences Donor-Specific Immune Responses. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 2300–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van oud Alblas, A.B.; van Furth, R. Origin, Kinetics, and characteristics of pulmonary macrophages in the normal steady state. J. Exp. Med. 1979, 149, 1504–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hume, P.S.; Gibbings, S.L.; Jakubzick, C.V.; Tuder, R.M.; Curran-Everett, D.; Henson, P.M.; Smith, B.J.; Janssen, W.J. Localization of Macrophages in the Human Lung via Design-based Stereology. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, D.G.; Huang, X.; Kaminski, N.; Wang, Y.; Shapiro, S.D.; Dolganov, G.; Glick, A.; Sheppard, D. Loss of integrin alpha(v)beta6-mediated TGF-beta activation causes Mmp12-dependent emphysema. Nature 2003, 422, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesci, A.; Balbi, B.; Majori, M.; Cacciani, G.; Bertacco, S.; Alciato, P.; Donner, C.F. Inflammatory cells and mediators in bronchial lavage of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur. Respir. J. 1998, 12, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retamales, I.; Elliott, W.M.; Meshi, B.; Coxson, H.O.; Pare, P.D.; Sciurba, F.C.; Rogers, R.M.; Hayashi, S.; Hogg, J.C. Amplification of inflammation in emphysema and its association with latent adenoviral infection. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, T.; Abboud, R.T.; Wallace, A.M.; English, J.C.; Coxson, H.O.; Finley, R.J.; Shumansky, K.; Pare, P.D.; Sandford, A.J. Alveolar macrophage proteinase/antiproteinase expression in lung function and emphysema. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akata, K.; van Eeden, S.F. Lung Macrophage Functional Properties in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapellos, T.S.; Bassler, K.; Aschenbrenner, A.C.; Fujii, W.; Schultze, J.L. Dysregulated Functions of Lung Macrophage Populations in COPD. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 2349045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mautino, G.; Oliver, N.; Chanez, P.; Bousquet, J.; Capony, F. Increased release of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and by alveolar macrophages of asthmatics. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1997, 17, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Roche, N.; Oliver, B.G.; Mattos, W.; Barnes, P.J.; Chung, K.F. Balance of matrix metalloprotease-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloprotease-1 from alveolar macrophages in cigarette smokers. Regulation by interleukin-10. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 1355–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortaz, E.; Adcock, I.M.; Tabarsi, P.; Masjedi, M.R.; Mansouri, D.; Velayati, A.A.; Casanova, J.L.; Barnes, P.J. Interaction of Pattern Recognition Receptors with Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. J. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 35, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.B.; Irving, G.R.; Lawson, R.A.; Lee, M.E.; Read, R.C. Intracellular trafficking and killing of Streptococcus pneumoniae by human alveolar macrophages are influenced by opsonins. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 2286–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laza-Stanca, V.; Stanciu, L.A.; Message, S.D.; Edwards, M.R.; Gern, J.E.; Johnston, S.L. Rhinovirus replication in human macrophages induces NF-kappaB-dependent tumor necrosis factor alpha production. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 8248–8258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walton, E.L. Microbes are off the menu: Defective macrophage phagocytosis in COPD. Biomed. J. 2017, 40, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papi, A.; Bellettato, C.M.; Braccioni, F.; Romagnoli, M.; Casolari, P.; Caramori, G.; Fabbri, L.M.; Johnston, S.L. Infections and airway inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease severe exacerbations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, I.S.; Seemungal, T.A.; Wilks, M.; Lloyd-Owen, S.J.; Donaldson, G.C.; Wedzicha, J.A. Relationship between bacterial colonisation and the frequency, character, and severity of COPD exacerbations. Thorax 2002, 57, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Belchamber, K.B.R.; Fenwick, P.S.; Chana, K.; Donaldson, G.; Wedzicha, J.A.; Barnes, P.J.; Donnelly, L.E.; COPDMAP Consortium. Defective monocyte-derived macrophage phagocytosis is associated with exacerbation frequency in COPD. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, H.B.; Jersmann, H.; Truong, T.T.; Hamon, R.; Roscioli, E.; Ween, M.; Pitman, M.R.; Pitson, S.M.; Hodge, G.; Reynolds, P.N.; et al. Disrupted epithelial/macrophage crosstalk via Spinster homologue 2-mediated S1P signaling may drive defective macrophage phagocytic function in COPD. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrot, P.; Prevel, R.; Berger, P.; Dupin, I. Chemokines in COPD: From Implication to Therapeutic Use. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wortham, B.W.; Eppert, B.L.; Flury, J.L.; Garcia, S.M.; Donica, W.R.; Osterburg, A.; Joyce-Shaikh, B.; Cua, D.J.; Borchers, M.T. Cutting Edge: CLEC5A Mediates Macrophage Function and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Pathologies. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 3227–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, T.Y.W.; Nguyen, N.; Peh, H.Y.; Shanmugasundaram, M.; Chandna, R.; Tee, J.H.; Ong, C.B.; Hossain, M.Z.; Venugopal, S.; Zhang, T.; et al. ISM1 protects lung homeostasis via cell-surface GRP78-mediated alveolar macrophage apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2019161119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Ni, H.; Wang, H.; Gu, H. NLRP3 inflammasome is essential for the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 13209–13216. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Lv, C.; Wang, S.; Ying, H.; Weng, Y.; Yu, W. NLRP3 Inflammasome Involves in the Acute Exacerbation of Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Inflammation 2018, 41, 1321–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, E.M.; Sadiku, P.; Coelho, P.; Watts, E.R.; Zhang, A.; Howden, A.J.M.; Sanchez-Garcia, M.A.; Bewley, M.; Cole, J.; McHugh, B.J.; et al. NRF2 Activation Reprograms Defects in Oxidative Metabolism to Restore Macrophage Function in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 998–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bewley, M.A.; Preston, J.A.; Mohasin, M.; Marriott, H.M.; Budd, R.C.; Swales, J.; Collini, P.; Greaves, D.R.; Craig, R.W.; Brightling, C.E.; et al. Impaired Mitochondrial Microbicidal Responses in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Macrophages. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eapen, M.S.; Hansbro, P.M.; McAlinden, K.; Kim, R.Y.; Ward, C.; Hackett, T.L.; Walters, E.H.; Sohal, S.S. Abnormal M1/M2 macrophage phenotype profiles in the small airway wall and lumen in smokers and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takiguchi, H.; Yang, C.X.; Yang, C.W.T.; Sahin, B.; Whalen, B.A.; Milne, S.; Akata, K.; Yamasaki, K.; Yang, J.S.W.; Cheung, C.Y.; et al. Macrophages with reduced expressions of classical M1 and M2 surface markers in human bronchoalveolar lavage fluid exhibit pro-inflammatory gene signatures. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akata, K.; Leung, J.M.; Yamasaki, K.; Leitao Filho, F.S.; Yang, J.; Xi Yang, C.; Takiguchi, H.; Shaipanich, T.; Sahin, B.; Whalen, B.A.; et al. Altered Polarization and Impaired Phagocytic Activity of Lung Macrophages in People with Human Immunodeficiency Virus and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 225, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Taneja, V.; Vassallo, R. Cigarette smoking and inflammation: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. J. Dent. Res. 2012, 91, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, K.; Sarir, H.; Mortaz, E.; Smit, J.J.; Hosseini, H.; De Kimpe, S.J.; Nijkamp, F.P.; Folkerts, G. Toll-like receptor-4 mediates cigarette smoke-induced cytokine production by human macrophages. Respir. Res. 2006, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.R.; Chida, A.S.; Bauter, M.R.; Shafiq, N.; Seweryniak, K.; Maggirwar, S.B.; Kilty, I.; Rahman, I. Cigarette smoke induces proinflammatory cytokine release by activation of NF-kappaB and posttranslational modifications of histone deacetylase in macrophages. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2006, 291, L46–L57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Cowan, M.J.; Hasday, J.D.; Vogel, S.N.; Medvedev, A.E. Tobacco smoking inhibits expression of proinflammatory cytokines and activation of IL-1R-associated kinase, p38, and NF-kappaB in alveolar macrophages stimulated with TLR2 and TLR4 agonists. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 6097–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, N.K.; Murphy, W.J.; Filla, M.B.; Crespo, A.J.; Latham, H.A.; O’Brien-Ladner, A. Down modulation of IFN-gamma signaling in alveolar macrophages isolated from smokers. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 237, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Fu, X.; Shi, H.; Chen, G.; Dong, P.; Zhang, W. Induction of murine macrophage M2 polarization by cigarette smoke extract via the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaykhiev, R.; Krause, A.; Salit, J.; Strulovici-Barel, Y.; Harvey, B.G.; O’Connor, T.P.; Crystal, R.G. Smoking-dependent reprogramming of alveolar macrophage polarization: Implication for pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 2867–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Zyl-Smit, R.N.; Binder, A.; Meldau, R.; Semple, P.L.; Evans, A.; Smith, P.; Bateman, E.D.; Dheda, K. Cigarette smoke impairs cytokine responses and BCG containment in alveolar macrophages. Thorax 2014, 69, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, M.; Nakata, H.; Pinkerton, K. Effect of cigarette smoking on M1/M2 type Alveolar Macrophage (AM) and the restoration of AM by smoking cessation. J. Allergy Clin. Immun. 2021, 147, Ab80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traves, S.L.; Culpitt, S.V.; Russell, R.E.; Barnes, P.J.; Donnelly, L.E. Increased levels of the chemokines GROalpha and MCP-1 in sputum samples from patients with COPD. Thorax 2002, 57, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Di, T.; Wu, Y.; Bian, T. NCOA4-Mediated Ferroptosis in Bronchial Epithelial Cells Promotes Macrophage M2 Polarization in COPD Emphysema. Int. J. Chron. Obs. Pulmon. Dis. 2022, 17, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, W.; Kapellos, T.S.; Bassler, K.; Handler, K.; Holsten, L.; Knoll, R.; Warnat-Herresthal, S.; Oestreich, M.; Hinkley, E.R.; Hasenauer, J.; et al. Alveolar macrophage transcriptomic profiling in COPD shows major lipid metabolism changes. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 00915-2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi, A.K.; Plumb, J.; Gaskell, R.; Mason, S.; Broome, C.S.; Booth, G.; Catley, M.; Vestbo, J.; Singh, D. COPD monocytes demonstrate impaired migratory ability. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Tian, R.; Zhang, X.; Yao, Q.; Chen, Q.; Liu, B.; Liao, L.; Gong, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, D. PPARgamma inhibits small airway remodeling through mediating the polarization homeostasis of alveolar macrophages in COPD. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 250, 109293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.Y.; Kim, G.D.; Choi, D.W.; Shin, D.U.; Eom, J.E.; Kim, S.Y.; Chai, O.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Shin, H.S. Epilobiumpyrricholophum Extract Suppresses Porcine Pancreatic Elastase and Cigarette Smoke Extract-Induced Inflammatory response in a Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Model. Foods 2021, 10, 2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Lin, Z.; Liang, W.; Qin, L.; Ding, J.; Chen, S.; Zhou, L. Isorhamnetin Alleviates Airway Inflammation by Regulating the Nrf2/Keap1 Pathway in a Mouse Model of COPD. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 860362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akata, K.; Yamasaki, K.; Leitao Filho, F.S.; Yang, C.X.; Takiguchi, H.; Sahin, B.; Whalen, B.A.; Yang, C.W.T.; Leung, J.M.; Sin, D.D.; et al. Abundance of Non-Polarized Lung Macrophages with Poor Phagocytic Function in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Biomedicines 2020, 8, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, W.; Wu, Y.; Bian, T. MicroRNA Let-7 Induces M2 Macrophage Polarization in COPD Emphysema Through the IL-6/STAT3 Pathway. Int. J. Chron. Obs. Pulmon. Dis. 2023, 18, 575–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzan, E.; Turato, G.; Tine, M.; Radu, C.M.; Balestro, E.; Rigobello, C.; Biondini, D.; Schiavon, M.; Lunardi, F.; Baraldo, S.; et al. Dual polarization of human alveolar macrophages progressively increases with smoking and COPD severity. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaku, Y.; Imaoka, H.; Morimatsu, Y.; Komohara, Y.; Ohnishi, K.; Oda, H.; Takenaka, S.; Matsuoka, M.; Kawayama, T.; Takeya, M.; et al. Overexpression of CD163, CD204 and CD206 on alveolar macrophages in the lungs of patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunz, L.I.; Lapperre, T.S.; Snoeck-Stroband, J.B.; Budulac, S.E.; Timens, W.; van Wijngaarden, S.; Schrumpf, J.A.; Rabe, K.F.; Postma, D.S.; Sterk, P.J.; et al. Smoking status and anti-inflammatory macrophages in bronchoalveolar lavage and induced sputum in COPD. Respir. Res. 2011, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Pang, N.; Li, Z.; Xu, D.; Jing, J.; Li, F.; Ding, J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, M. The Activation of M1 Macrophages is Associated with the JNK-m6A-p38 Axis in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int. J. Chron. Obs. Pulmon. Dis. 2023, 18, 2195–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, P.T.; MacDonald, M.; Bardin, P.G. Bacteria in COPD; their potential role and treatment. Transl. Respir. Med. 2013, 1, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, S.; Reynolds, P.N. Low-dose azithromycin improves phagocytosis of bacteria by both alveolar and monocyte-derived macrophages in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease subjects. Respirology 2012, 17, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bewley, M.A.; Belchamber, K.B.; Chana, K.K.; Budd, R.C.; Donaldson, G.; Wedzicha, J.A.; Brightling, C.E.; Kilty, I.; Donnelly, L.E.; Barnes, P.J.; et al. Differential Effects of p38, MAPK, PI3K or Rho Kinase Inhibitors on Bacterial Phagocytosis and Efferocytosis by Macrophages in COPD. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenson, C.S.; Kruzel, R.L.; Eberhardt, E.; Sethi, S. Phagocytic dysfunction of human alveolar macrophages and severity of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 2036–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnawi, J.; Tran, H.; Jersmann, H.; Pitson, S.; Roscioli, E.; Hodge, G.; Meech, R.; Haberberger, R.; Hodge, S. Potential Link between the Sphingosine-1-Phosphate (S1P) System and Defective Alveolar Macrophage Phagocytic Function in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.E.; Finney-Hayward, T.K.; Quint, J.K.; Thomas, C.M.; Tudhope, S.J.; Wedzicha, J.A.; Barnes, P.J.; Donnelly, L.E. Defective macrophage phagocytosis of bacteria in COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 35, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltboli, O.; Bafadhel, M.; Hollins, F.; Wright, A.; Hargadon, B.; Kulkarni, N.; Brightling, C. COPD exacerbation severity and frequency is associated with impaired macrophage efferocytosis of eosinophils. BMC Pulm. Med. 2014, 14, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, S.; Hodge, G.; Ahern, J.; Jersmann, H.; Holmes, M.; Reynolds, P.N. Smoking alters alveolar macrophage recognition and phagocytic ability: Implications in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanno, A.; Fujino, N.; Yamada, M.; Sugiura, H.; Hirano, T.; Tanaka, R.; Sano, H.; Suzuki, S.; Okada, Y.; Ichinose, M. Decreased expression of a phagocytic receptor Siglec-1 on alveolar macrophages in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culpitt, S.V.; Rogers, D.F.; Shah, P.; De Matos, C.; Russell, R.E.; Donnelly, L.E.; Barnes, P.J. Impaired inhibition by dexamethasone of cytokine release by alveolar macrophages from patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knobloch, J.; Hag, H.; Jungck, D.; Urban, K.; Koch, A. Resveratrol impairs the release of steroid-resistant cytokines from bacterial endotoxin-exposed alveolar macrophages in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 109, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons, A.R.; Sauleda, J.; Noguera, A.; Pons, J.; Barcelo, B.; Fuster, A.; Agusti, A.G. Decreased macrophage release of TGF-beta and TIMP-1 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higham, A.; Booth, G.; Lea, S.; Southworth, T.; Plumb, J.; Singh, D. The effects of corticosteroids on COPD lung macrophages: A pooled analysis. Respir. Res. 2015, 16, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendrasozhan, S.; Yang, S.R.; Kinnula, V.L.; Rahman, I. SIRT1, an antiinflammatory and antiaging protein, is decreased in lungs of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauler, M.; McDonough, J.E.; Adams, T.S.; Kothapalli, N.; Barnthaler, T.; Werder, R.B.; Schupp, J.C.; Nouws, J.; Robertson, M.J.; Coarfa, C.; et al. Characterization of the COPD alveolar niche using single-cell RNA sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Summer, R.; Chen, Z.; Tian, Y.; Ma, J.; Cui, J.; Hao, X.; Guo, L.; Xu, H.; Wang, H.; et al. Lipid Uptake by Alveolar Macrophages Drives Fibrotic Responses to Silica Dust. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Williams, K.J.; McCarthy, C.; Bridges, J.P.; Redente, E.F.; de Aguiar Vallim, T.Q.; Barrington, R.A.; Wang, T.; Tarling, E.J. Alveolar macrophage lipid burden correlates with clinical improvement in patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. J. Lipid Res. 2024, 65, 100496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedard, M.; van der Niet, S.; Bernard, E.M.; Babunovic, G.; Cheng, T.Y.; Aylan, B.; Grootemaat, A.E.; Raman, S.; Botella, L.; Ishikawa, E.; et al. A terpene nucleoside from M. tuberculosis induces lysosomal lipid storage in foamy macrophages. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e161944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, M.H.; Chen, P.C.; Hsu, H.Y.; Liu, J.C.; Ho, Y.S.; Lin, Y.J.; Kuo, C.W.; Kuo, W.S.; Kao, H.F.; Wang, S.D.; et al. Surfactant protein D inhibits lipid-laden foamy macrophages and lung inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2023, 20, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassler, K.; Fujii, W.; Kapellos, T.S.; Dudkin, E.; Reusch, N.; Horne, A.; Reiz, B.; Luecken, M.D.; Osei-Sarpong, C.; Warnat-Herresthal, S.; et al. Alveolar macrophages in early stage COPD show functional deviations with properties of impaired immune activation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 917232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ween, M.P.; White, J.B.; Tran, H.B.; Mukaro, V.; Jones, C.; Macowan, M.; Hodge, G.; Trim, P.J.; Snel, M.F.; Hodge, S.J. The role of oxidised self-lipids and alveolar macrophage CD1b expression in COPD. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Zhang, D.; Yin, Y.; Kang, J.; Zheng, R. Salidroside ameliorated the pulmonary inflammation induced by cigarette smoke via mitigating M1 macrophage polarization by JNK/c-Jun. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 4251–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.C.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, C.; Zhu, Y.N.; Ye, Y.M.; Sun, Y.K.; Xiang, S.Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.B.; Zhang, X.F. Hydrogen regulates the M1/M2 polarization of alveolar macrophages in a rat model of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Exp. Lung Res. 2021, 47, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; Feng, X.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Zhao, Z. The key role of macrophage depolarization in the treatment of COPD with ergosterol both in vitro and in vivo. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 79, 106086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Yin, Y.; Zheng, R.; Kang, J. Rosiglitazone ameliorated airway inflammation induced by cigarette smoke via inhibiting the M1 macrophage polarization by activating PPARgamma and RXRalpha. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 97, 107809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X. Fine particulate matter exposure promotes M2 macrophage polarization through inhibiting histone deacetylase 2 in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Xie, L.; Sun, S. The inhibitor miR-21 regulates macrophage polarization in an experimental model of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Tob. Induc. Dis. 2021, 19, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.P.; Niu, H.; Wang, H.; Lin, J.; Yao, J.J. Knockdown of RTEL1 Alleviates Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease by Modulating M1, M2 Macrophage Polarization and Inflammation. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2024, 21, 2316607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff, J.W.; Powers, L.S.; Dickson, A.M.; Kim, J.; Reisetter, A.C.; Hassan, I.H.; Kremens, K.; Gross, T.J.; Wilson, M.E.; Monick, M.M. Cigarette smoking decreases global microRNA expression in human alveolar macrophages. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, Z.; Kong, L.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wan, Y. miRNA-486-5p Promotes COPD Progression by Targeting HAT1 to Regulate the TLR4-Triggered Inflammatory Response of Alveolar Macrophages. Int. J. Chron. Obs. Pulmon. Dis. 2020, 15, 2991–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Qin, Y.; Cai, Z.; Tian, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, P. Effective-components combination improves airway remodeling in COPD rats by suppressing M2 macrophage polarization via the inhibition of mTORC2 activity. Phytomedicine 2021, 92, 153759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, S.; Hodge, G.; Jersmann, H.; Matthews, G.; Ahern, J.; Holmes, M.; Reynolds, P.N. Azithromycin improves macrophage phagocytic function and expression of mannose receptor in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, S.; Tran, H.B.; Hamon, R.; Roscioli, E.; Hodge, G.; Jersmann, H.; Ween, M.; Reynolds, P.N.; Yeung, A.; Treiberg, J.; et al. Nonantibiotic macrolides restore airway macrophage phagocytic function with potential anti-inflammatory effects in chronic lung diseases. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2017, 312, L678–L687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higham, A.; Scott, T.; Li, J.; Gaskell, R.; Dikwa, A.B.; Shah, R.; Montero-Fernandez, M.A.; Lea, S.; Singh, D. Effects of corticosteroids on COPD lung macrophage phenotype and function. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porpodis, K.; Domvri, K.; Zarogoulidis, P.; Petridis, D.; Tsirgogianni, K.; Papaioannou, A.; Hatzizisi, O.; Kioumis, I.; Liaka, A.; Kikidaki, V.; et al. Roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, induces phagocytic activity in Greek COPD patients. Int. J. Chron. Obs. Pulmon. Dis. 2015, 10, 1123–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zeng, X.; Shu, J.; Bao, H.; Liu, X. MiR-155 enhances phagocytosis of alveolar macrophages through the mTORC2/RhoA pathway. Medicine 2023, 102, e34592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, C.J.; Thimmulappa, R.K.; Sethi, S.; Kong, X.; Yarmus, L.; Brown, R.H.; Feller-Kopman, D.; Wise, R.; Biswal, S. Targeting Nrf2 signaling improves bacterial clearance by alveolar macrophages in patients with COPD and in a mouse model. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 78ra32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bewley, M.A.; Budd, R.C.; Ryan, E.; Cole, J.; Collini, P.; Marshall, J.; Kolsum, U.; Beech, G.; Emes, R.D.; Tcherniaeva, I.; et al. Opsonic Phagocytosis in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Is Enhanced by Nrf2 Agonists. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lea, S.; Metryka, A.; Li, J.; Higham, A.; Bridgewood, C.; Villetti, G.; Civelli, M.; Facchinetti, F.; Singh, D. The modulatory effects of the PDE4 inhibitors CHF6001 and roflumilast in alveolar macrophages and lung tissue from COPD patients. Cytokine 2019, 123, 154739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culpitt, S.V.; Rogers, D.F.; Fenwick, P.S.; Shah, P.; De Matos, C.; Russell, R.E.; Barnes, P.J.; Donnelly, L.E. Inhibition by red wine extract, resveratrol, of cytokine release by alveolar macrophages in COPD. Thorax 2003, 58, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.Y.; Qiang, L.X.; Wang, B.C.; Zhang, Y.P.; Li, Z.H.; Li, X.S.; Jin, L.L.; Jin, S.D. Complex Evaluation of Surfactant Protein A and D as Biomarkers for the Severity of COPD. Int. J. Chron. Obs. Pulmon. Dis. 2022, 17, 1537–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Han, Y.; Almuntashiri, S.; Dutta, S.; Wang, X.; Owen, C.A.; Zhang, D. Dysregulation of miR-103a Mediates Cigarette Smoking-induced Lipid-laden Macrophage Formation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2022, 67, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| M1 | M2 | DP | DN | Source | Method | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marker | CD40+CD163− | CD40−CD163+ | CD40+CD163+ | CD40−CD163− | BALF | Flow cytometry | [155] |
| COPD (vs. NC) | NS | NS | Decreased | Increased | |||
| Marker | CD40+CD163− | CD40−CD163+ | CD40+CD163+ | CD40−CD163− | BALF | Flow cytometry | [137] |
| COPD (vs. NC) | NS | NS | Decreased | Increased | |||
| Marker | CD86+ | CD206+ | BALF | Flow cytometry | [152] | ||
| COPD (vs. NC) | Increased | Increased | No detection | No detection | |||
| Marker | iNOS+ | CD206+ | Lung tissues | IHC | [149,156] | ||
| COPD (vs. NC) | Decreased | Increased | No detection | No detection | |||
| Marker | iNOS+ | CD206+ | iNOS+CD206+ | iNOS−CD206− | Lung tissues | IHC | [157] |
| COPD (vs. NC) | Increased | Increased | Increased | Decreased | |||
| Marker | CD163+, CD204+, or CD206+ | Lung tissues | IHC | [158] | |||
| COPD (vs. NC) | No detect | Increased | No detection | No detection |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, G.-D.; Lim, E.Y.; Shin, H.S. Macrophage Polarization and Functions in Pathogenesis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115631
Kim G-D, Lim EY, Shin HS. Macrophage Polarization and Functions in Pathogenesis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(11):5631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115631
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Gun-Dong, Eun Yeong Lim, and Hee Soon Shin. 2024. "Macrophage Polarization and Functions in Pathogenesis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 11: 5631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115631
APA StyleKim, G.-D., Lim, E. Y., & Shin, H. S. (2024). Macrophage Polarization and Functions in Pathogenesis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(11), 5631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115631






