Clinical Applications of Adipose-Derived Stem Cell (ADSC) Exosomes in Tissue Regeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Characterization and Isolation Methods of the Multipotent ADSCs
3. Functional Characteristics of ADSCs Based on Their Origin
4. Isolation Methods of ADSC-Exosomes
5. Bioactive Cargos of ADSC-Exos and Factors Affecting Their Production
6. Clinical Applications of ADSC-Exosomes
6.1. ADSC-Exos in Wound Healing
6.2. Musculoskeletal Regeneration through ADSC-Exos
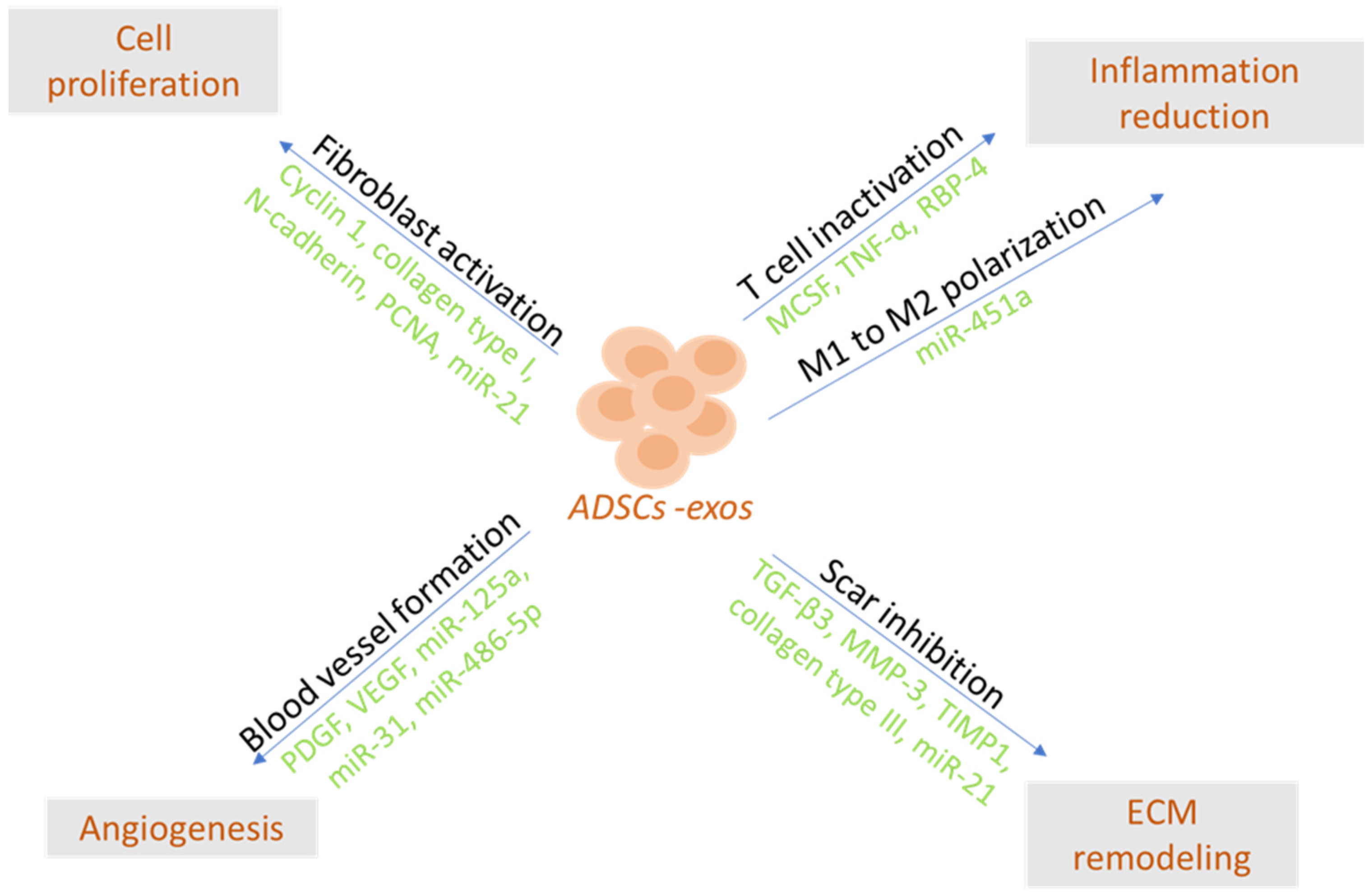
6.3. ADSC-Exos in Dermatology and Plastic Surgery
7. ADSC-Exo Applications in Tissue Engineering
7.1. Scaffolds and In Vitro Tissue Engineering Approaches
7.2. In Vivo Tissue Engineering Approaches
8. Clinical Trials and Current Legislation Status of Exosomes for Clinical Purposes
9. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zuk, P.A.; Zhu, M.; Ashjian, P.; De Ugarte, D.A.; Huang, J.I.; Mizuno, H.; Alfonso, Z.C.; Fraser, J.K.; Benhaim, P.; Hedrick, M.H. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 4279–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocucci, E.; Meldolesi, J. Ectosomes and exosomes: Shedding the confusion between extracellular vesicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.; Krause, D.; Deans, R.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.; Horwitz, E. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Lee, J.; Kwon, Y.; Park, K.S.; Jeong, J.H.; Choi, S.J.; Bang, S.I.; Chang, J.W.; Lee, C. Comparative Proteomic Analysis of the Mesenchymal Stem Cells Secretome from Adipose, Bone Marrow, Placenta and Wharton’s Jelly. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mildmay-White, A.; Khan, W. Cell Surface Markers on Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: A Systematic Review. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 12, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Khan, D.; Delling, J.; Tobiasch, E. Mechanisms underlying the osteo- and adipo-differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 793823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindroos, B.; Suuronen, R.; Miettinen, S. The potential of adipose stem cells in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2011, 7, 269–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, M.E.; Widgerow, A.D.; Evans, G.R. Stem cell research in tissue engineering and translational medicine. In Tissue Engineering; Chandra, P.S., Thomas, C., Vinoy, T., Finosh, G.T., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 157–172. [Google Scholar]
- Oedayrajsingh-Varma, M.J.; van Ham, S.M.; Knippenberg, M.; Helder, M.N.; Klein-Nulend, J.; Schouten, T.E.; Ritt, M.J.; van Milligen, F.J. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell yield and growth characteristics are affected by the tissue-harvesting procedure. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreml, S.; Babilas, P.; Fruth, S.; Orsó, E.; Schmitz, G.; Mueller, M.B.; Nerlich, M.; Prantl, L. Harvesting human adipose tissue-derived adult stem cells: Resection versus liposuction. Cytotherapy 2009, 11, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyyanki, T.; Hubenak, J.; Liu, J.; Chang, E.I.; Beahm, E.K.; Zhang, Q. Harvesting technique affects adipose-derived stem cell yield. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2015, 35, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenis, R.; Lazzaro, L.; Calabrese, S.; Mangoni, D.; Gallelli, A.; Bourkoula, E.; Manini, I.; Bergamin, N.; Toffoletto, B.; Beltrami, C.A.; et al. Adipose tissue derived stem cells: In vitro and in vivo analysis of a standard and three commercially available cell-assisted lipotransfer techniques. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, P.P.; Gimble, J.M.; Dias, I.R.; Gomes, M.E.; Reis, R.L. Xenofree enzymatic products for the isolation of human adipose-derived stromal/stem cells. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2013, 19, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiryaki, T.; Cohen, S.R.; Canikyan Turkay, S.; Kocak, P.; Sterodimas, A.; Schlaudraff, K.U.; Akgün Demir, I.; Agovino, A.; Kul, Y. Hybrid Stromal Vascular Fraction (Hybrid-SVF): A New Paradigm in Mechanical Regenerative Cell Processing. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2022, 10, e4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.-H.; Kuo, T.-L.; Kuo, K.-K.; Hsiao, C.-C. Human adipose-derived stem cells: Isolation, characterization and current application in regeneration medicine. Genom. Med. Biomark. Health Sci. 2011, 3, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suga, H.; Matsumoto, D.; Eto, H.; Inoue, K.; Aoi, N.; Kato, H.; Araki, J.; Yoshimura, K. Functional implications of CD34 expression in human adipose–derived stem/progenitor cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2009, 18, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourin, P.; Bunnell, B.A.; Castilla, L.; Dominici, M.; Katz, A.J.; March, K.L.; Redl, H.; Rubin, J.P.; Yoshimura, K.; Gimble, J.M. Stromal cells from the adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction and culture expanded adipose tissue-derived stromal/stem cells: A joint statement of the International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science (IFATS) and the International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT). Cytotherapy 2013, 15, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Liang, X.; Bae, J.; Huang, X.; Li, Q. Efficacy and Safety of Cell-Assisted Lipotransfer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 137, 44e–57e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanata, F.; Bowles, A.; Frazier, T.; Curley, J.L.; Bunnell, B.A.; Wu, X.; Wade, J.; Devireddy, R.; Gimble, J.M.; Ferreira, L.M. Effect of cryopreservation on human adipose tissue and isolated stromal vascular fraction cells. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 141, 232e–243e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, R.; Wang, Z.; Samanipour, R.; Koo, K.I.; Kim, K. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine Applications. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 6737345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, K.; Zvonic, S.; Garrett, S.; Mitchell, J.B.; Floyd, Z.E.; Hammill, L.; Kloster, A.; Di Halvorsen, Y.; Ting, J.P.; Storms, R.W.; et al. The immunogenicity of human adipose-derived cells: Temporal changes in vitro. Stem Cells 2006, 24, 1246–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohan, P.; Treacy, O.; Griffin, M.D.; Ritter, T.; Ryan, A.E. Anti-donor immune responses elicited by allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells and their extracellular vesicles: Are we still learning? Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohan, P.; Coleman, C.M.; Murphy, J.; Griffin, M.D.; Ritter, T.; Ryan, A.E. Changes in immunological profile of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells after differentiation: Should we be concerned? Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2014, 5, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrikoski, M.; Sivula, J.; Huhtala, H.; Helminen, M.; Salo, F.; Mannerström, B.; Miettinen, S. Different culture conditions modulate the immunological properties of adipose stem cells. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2014, 3, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritter, A.; Friemel, A.; Fornoff, F.; Adjan, M.; Solbach, C.; Yuan, J.; Louwen, F. Characterization of adipose-derived stem cells from subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissues and their function in breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 34475–34493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritter, A.; Friemel, A.; Roth, S.; Kreis, N.N.; Hoock, S.C.; Safdar, B.K.; Fischer, K.; Möllmann, C.; Solbach, C.; Louwen, F.; et al. Subcutaneous and visceral adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Commonality and diversity. Cells 2019, 8, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raajendiran, A.; Ooi, G.; Bayliss, J.; O’Brien, P.E.; Schittenhelm, R.B.; Clark, A.K.; Taylor, R.A.; Rodeheffer, M.S.; Burton, P.R.; Watt, M.J. Identification of metabolically distinct adipocyte progenitor cells in human adipose tissues. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 1528–1540.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, W.K.; Tan, C.S.; Chan, K.L.; Goesantoso, G.G.; Chan, X.H.; Chan, E.; Yin, J.; Yeo, C.R.; Khoo, C.M.; So, J.B.; et al. Identification of specific cell-surface markers of adipose-derived stem cells from subcutaneous and visceral fat depots. Stem Cell Rep. 2014, 2, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, H.; Song, P.; Wang, D.; Yin, J.; Zhao, W.; Xie, Z.; Wang, F.; et al. CD90 serves as a differential modulator of subcutaneous and visceral adipose-derived stem cells by regulating AKT activation that influences adipose tissue and metabolic homeostasis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, R.; Rodeheffe, M.S.; Rosen, C.J.; Horowitz, M.C. Adipose tissue-residing progenitors (adipocyte lineage progenitors and adipose-derived stem cells (ADSC)). Curr. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 1, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.M.; Sanchez-Gurmaches, J.; Guertin, D.A. Brown adipose tissue development and metabolism. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2019, 251, 3–36. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji, T.; Ikado, K.; Koizumi, H.; Uchiyama, S.; Kajimoto, K. Difference in intracellular temperature rise between matured and precursor brown adipocytes in response to uncoupler and β-adrenergic agonist stimuli. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, S.Y.; Desai, A.; Yang, Z.; Sharma, A.; DeSouza, T.; Genga, R.M.J.; Kucukural, A.; Lifshitz, L.M.; Nielsen, S.; Scheele, C.; et al. Diverse repertoire of human adipocyte subtypes develops from transcriptionally distinct mesenchymal progenitor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 17970–17979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Kissig, M.; Rajakumari, S.; Huang, L.; Lim, H.W.; Won, K.J.; Seale, P. Ebf2 is a selective marker of brown and beige adipogenic precursor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14466–14471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, F.J.; Holt, D.J.; Vargas, V.; Yockman, J.; Boudina, S.; Atkinson, D.; Grainger, D.W.; Revelo, M.P.; Sherman, W.; Bull, D.A.; et al. Metabolically active human brown adipose tissue derived stem cells. Stem Cells 2013, 32, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, W.; Zhao, C.; Lv, W.; Yi, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, M. Exosomes From Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: The Emerging Roles and Applications in Tissue Regeneration of Plastic and Cosmetic Surgery. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 574223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazini, L.; Ezzoubi, M.; Malka, G. Overview of current adipose-derived stem cell (ADSCs) processing involved in therapeutic advancements: Flow chart and regulation updates before and after COVID-19. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter-Ovanesyan, D.; Norman, M.; Lazarovits, R.; Trieu, W.; Lee, J.H.; Church, G.M.; Walt, D.R. Framework for rapid comparison of extracellular vesicle isolation methods. eLife 2021, 10, e70725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, N.; Nishimura, H.; Matsumoto, A.; Asano, R.; Muranaka, K.; Fujita, M.; Takeda, M.; Hashimoto, H.; Takeda-Morishita, M. Comparative study of commercial protocols for high recovery of high-purity mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicle isolation and their efficient labeling with fluorescent dyes. Nanomedicine 2021, 35, 102396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmer, A.; Kajau, H.; Margolis, E.; Tutrone, R.; Grimm, T.; Trottmann, M.; Stief, C.; Stoll, G.; Fischer, C.A.; Flinspach, C.; et al. Validation of a CE-IVD, urine exosomal RNA expression assay for risk assessment of prostate cancer prior to biopsy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam, S.E.; Elsadek, N.E.; Abu-Lila, A.S.; Takata, H.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Ando, H.; Ishima, Y.; Ishida, T. Anti-PEG IgM production and accelerated blood clearance phenomenon after the administration of PEGylated exosomes in mice. J. Control. Release 2021, 334, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wu, C.; Lin, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, W.; Wang, T.; Cui, Y. Establishment of a simplified dichotomic size-exclusion chromatography for isolating extracellular vesicles toward clinical applications. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Li, A.; Hu, J.; Feng, L.; Liu, L.; Shen, Z. Recent developments in isolating methods for exosomes. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 10, 1100892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bathini, S.; Pakkiriswami, S.; Ouellette, R.J.; Ghosh, A.; Packirisamy, M. Magnetic particle based liquid biopsy chip for isolation of extracellular vesicles and characterization by gene amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 194, 113585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.Y.; Kumar, R.; Zhong, C.; Gorji, S.; Paniushkina, L.; Masood, R.; Wittel, U.A.; Fuchs, H.; Nazarenko, I.; Hirtz, M. Rapid Capture of Cancer Extracellular Vesicles by Lipid Patch Microarrays. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2008493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Shang, Q.; Pan, Z.; Bai, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q. Exosomes From Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Attenuate Adipose Inflammation and Obesity Through Polarizing M2 Macrophages and Beiging in White Adipose Tissue. Diabetes 2018, 67, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Q.; Bai, Y.; Wang, G.; Song, Q.; Guo, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q. Delivery of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Attenuates Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Obese Mice Through Remodeling Macrophage Phenotypes. Stem Cells Dev. 2015, 24, 2052–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julier, Z.; Park, A.J.; Briquez, P.S.; Martino, M.M. Promoting tissue regeneration by modulating the immune system. Acta Biomater. 2017, 53, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Kikuiri, T.; Akiyama, K.; Chen, C.; Xu, X.; Yang, R.; Chen, W.; Wang, S.; Shi, S. Mesenchymal stem cell-based tissue regeneration is governed by recipient T lymphocytes via IFN-γ and TNF-α. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1594–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, J.D.; Whartenby, K.A. Mesenchymal stem cells: Emerging mechanisms of immunomodulation and therapy. World J. Stem Cells 2014, 6, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croitoru-Lamoury, J.; Lamoury, F.M.; Caristo, M.; Suzuki, K.; Walker, D.; Takikawa, O.; Taylor, R.; Brew, B.J. Interferon-γ regulates the proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via activation of indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase (IDO). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenis, R.; Cifù, A.; Quaglia, S.; Pistis, C.; Moretti, M.; Vicario, A.; Parodi, P.C.; Fabris, M.; Niazi, K.R.; Soon-Shiong, P.; et al. Pro inflammatory stimuli enhance the immunosuppressive functions of adipose mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, E.M.; Seo, B.R.; Califano, J.P.; Andresen Eguiluz, R.C.; Lee, J.S.; Yoon, C.J.; Tims, D.T.; Wang, J.X.; Cheng, L.; Mohanan, S.; et al. Implanted adipose progenitor cells as physicochemical regulators of breast cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9786–9791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skouras, P.; Gargalionis, A.N.; Piperi, C. Exosomes as Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Tools in Gliomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiller, K.L.; Koh, T.J. Macrophage-based therapeutic strategies in regenerative medicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 122, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, M.; Yu, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Paul, C.; Millard, R.W.; Xiao, D.S.; Ashraf, M.; Xu, M. Mesenchymal stem cells release exosomes that transfer miRNAs to endothelial cells and promote angiogenesis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 45200–45212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Wen, H.; Huang, J.; Liao, P.; Liao, H.; Tu, J.; Zeng, Y. Extracellular vesicle-enclosed miR-486-5p mediates wound healing with adipose-derived stem cells by promoting angiogenesis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 9590–9604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Han, Q.; Zhao, R.C. Exosomes secreted by mesenchymal stem cells promote endothelial cell angiogenesis by transferring miR-125a. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 2182–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, T.; Jones, T.M.; Naddell, C.; Bacanamwo, M.; Calvert, J.W.; Thompson, W.E.; Bond, V.C.; Chen, Y.E.; Liu, D. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Induce Angiogenesis via Microvesicle Transport of miRNA-31. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, D.R.; Wang, C.; Patel, R.; Trujillo, A.; Patel, N.A.; Prather, J.; Gould, L.J.; Wu, M.H. Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Conditioned Media and Exosomes Containing MALAT1 Promote Human Dermal Fibroblast Migration and Ischemic Wound Healing. Adv. Wound Care 2018, 7, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhu, C.; Jia, J.; Hao, X.Y.; Yu, X.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Shu, M.G. ADSC-Exos containing MALAT1 promotes wound healing by targeting miR-124 through activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20192549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yi, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Nie, J. Effects of adipose-derived stem cell released exosomes on wound healing in diabetic mice. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi 2020, 34, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xie, X.; Lian, W.; Shi, R.; Han, S.; Zhang, H.; Lu, L.; Li, M. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells overexpressing Nrf2 accelerate cutaneous wound healing by promoting vascularization in a diabetic foot ulcer rat model. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhamodharan, U.; Karan, A.; Sireesh, D.; Vaishnavi, A.; Somasundar, A.; Rajesh, K.; Ramkumar, K.M. Tissue-specific role of Nrf2 in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers during hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 138, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.W.; Seo, M.K.; Woo, E.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Park, E.J.; Kim, S. Exosomes from human adipose-derived stem cells promote proliferation and migration of skin fibroblasts. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 1170–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, L.; Zhou, X.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, C.; Shehada, H.M.A.; Hu, B.; Song, J.; Chen, L. Exosomes secreted by human adipose mesenchymal stem cells promote scarless cutaneous repair by regulating extracellular matrix remodeling. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Bai, X.; Zhao, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Luo, L.; Han, F.; Zhang, J.; et al. Cell-free therapy based on adipose tissue stem cell-derived exosomes promotes wound healing via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 370, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Luo, L.; Bai, X.; Shen, K.; Liu, K.; Wang, J.; Hu, D. Highly-expressed micoRNA-21 in adipose derived stem cell exosomes can enhance the migration and proliferation of the HaCaT cells by increasing the MMP-9 expression through the PI3K/AKT pathway. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 681, 108259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, D.H.; Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, H.P.; Nguyen, X.H.; Do, P.T.X.; Dang, V.D.; Dam, P.T.M.; Bui, H.T.H.; Trinh, M.Q.; Vu, D.M.; et al. Differential Wound Healing Capacity of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Originated from Bone Marrow, Adipose Tissue and Umbilical Cord Under Serum- and Xeno-Free Conditions. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, A.M.; Patton, J.G. Argonautes in Extracellular Vesicles: Artifact or Selected Cargo? Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.; Mellows, B.; Sheard, J.; Antonioli, M.; Kretz, O.; Chambers, D.; Zeuner, M.T.; Tomkins, J.E.; Denecke, B.; Musante, L.; et al. Secretome of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes skeletal muscle regeneration through synergistic action of extracellular vesicle cargo and soluble proteins. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fordham, J.B.; Naqvi, A.R.; Nares, S. miR-24 regulates macrophage polarization and plasticity. J. Clin. Cell. Immunol. 2015, 6, 362–369. [Google Scholar]
- Semaan, N.; Frenzel, L.; Alsaleh, G.; Suffert, G.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Sibilia, J.; Pfeffer, S.; Wachsmann, D. miR-346 controls release of TNF-α protein and stability of its mRNA in rheumatoid arthritis via tristetraprolin stabilization. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Chen, J.Y.; Peng, W.M.; Yuan, B.; Bi, Q.; Xu, Y.J. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells promote chondrogenesis and suppress inflammation by upregulating miR-145 and miR-221. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 1881–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Guo, S.; Tong, S.; Sun, X. Exosomal miR-130a-3p regulates osteogenic differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived stem cells through mediating SIRT7/Wnt/β-catenin axis. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Liu, Y.; Qin, H.; Tong, S.; Sun, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Cui, M.; Guo, S. Osteogenically-induced exosomes stimulate osteogenesis of human adipose-derived stem cells. Cell Tissue Bank. 2021, 22, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, T.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J. Progenitor cell-derived exosomes endowed with VEGF plasmids enhance osteogenic induction and vascular remodeling in large segmental bone defects. Theranostics 2021, 11, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, A.; Xue, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, M.; Jiang, Y. Kartogenin Induced Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Exosomes Enhance the Chondrogenic Differentiation Ability of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 6943630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruijing, C.; Taojin, F.; Shi, C.; Ming, C.; Yi, L.; Zihui, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yin, P.; Zhang, L.; Tang, P. Evaluating the defect targeting effects and osteogenesis promoting capacity of exosomes from 2D- and 3D-cultured human adipose-derived stem cells. Nano Today 2023, 49, 101789. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X.W.; Liu, Z.Y.; Ma, N.F.; Jiang, W.K.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, B.; Guan, W.G.; Yan, J.J.; Yang, M. Exosomes from Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Alleviate Dexamethasone-Induced Bone Loss by Regulating the Nrf2/HO-1 Axis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2023, 2023, 3602962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, M.; Dai, M.; Chen, C.; Tang, Q.; Jing, W.; Wang, H.; Tian, W. miR-450a-5p within rat adipose tissue exosome-like vesicles promotes adipogenic differentiation by targeting WISP2. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ren, S.; Duscher, D.; Kang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Yuan, M.; Guo, G.; Xiong, H.; Zhan, P.; et al. Exosomes from human adipose-derived stem cells promote sciatic nerve regeneration via optimizing Schwann cell function. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 23097–23110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, C.; Wang, J.; Gan, W.; Qin, X.; Yang, R.; Chen, X. Therapeutic potential of exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells in chronic wound healing. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 1030288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Sicco, C.; Reverberi, D.; Balbi, C.; Ulivi, V.; Principi, E.; Pascucci, L.; Becherini, P.; Bosco, M.C.; Varesio, L.; Franzin, C.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Mediators of Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Endorsement of Macrophage Polarization. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Zhao, J.; Nie, F.; Qin, Z.; Xue, H.; Wang, G.; Li, D. Exosomes from Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs) Overexpressing miR-21 Promote Vascularization of Endothelial Cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Miyaki, S.; Ishitobi, H.; Matsuyama, S.; Nakasa, T.; Kamei, N.; Matsuyama, S.; Nakasa, T.; Kamei, N.; Akimoto, T.; et al. Mesenchymal-stem-cell-derived exosomes accelerate skeletal muscle regeneration. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazaeli, H.; Kalhor, N.; Naserpour, L.; Davoodi, F.; Sheykhhasan, M.; Hosseini, S.K.E.; Rabiei, M.; Sheikholeslami, A. A Comparative Study on the Effect of Exosomes Secreted by Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Adipose and Bone Marrow Tissues in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis- Induced Mouse Model. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 9688138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ngo, H.T.T.; Hwang, E.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Yi, T.H. Conditioned Medium from Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Culture Prevents UVB-Induced Skin Aging in Human Keratinocytes and Dermal Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.J.; Zhou, Z.H.; Li, Z.P.; Liao, S.M.; Wu, Z.Y.; Huang, H.H.; Shi, Y.C. The effect of inhibiting exosomes derived from adipose-derived stem cells via the TGF-β1/Smad pathway on the fibrosis of keloid fibroblasts. Gland Surg. 2021, 10, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.S.; Kim, J.O.; Ha, D.H.; Yi, Y.W. Exosomes derived from human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate atopic dermatitis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, Q.; Wu, S.; Yuan, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhu, N. Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Exosomes Promoted Hair Regeneration. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2021, 18, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, P.; Cervelli, V.; De Fazio, D.; Calabrese, C.; Scioli, M.G.; Orlandi, A. Mechanical and Enzymatic Digestion of Autologous Fat Grafting (A-FG): Fat Volume Maintenance and AD-SVFs Amount in Comparison. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2023, 47, 2051–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, S.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Q.; Xiao, P.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z. Extracellular Vesicles from Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells for the Improvement of Angiogenesis and Fat-Grafting Application. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 144, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.D.; Bai, Y.; Yan, X.L.; Ren, J.; Zeng, Q.; Li, X.D.; Pei, X.T.; Han, Y. Co-transplantation of exosomes derived from hypoxia-preconditioned adipose mesenchymal stem cells promotes neovascularization and graft survival in fat grafting. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 497, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Ren, J.; Bai, Y.; Pei, X.; Han, Y. Corrigendum to “Exosomes from hypoxia-treated human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhance angiogenesis through VEGF/VEGF-R” [Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 109 April (2019) 59–68]. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 126, 105805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, H.; Millard, D.R. The Principles and Art of Plastic Surgery; Little Brown and Company: Boston, MA, USA, 1957; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Cormack, G.C.; Lamberty, B.G. A classification of fascio-cutaneous flaps according to their patterns of vascularisation. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1984, 37, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Han, Y.D.; Yan, X.L.; Ren, J.; Zeng, Q.; Li, X.D.; Pei, X.T.; Han, Y. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes stimulated by hydrogen peroxide enhanced skin flap recovery in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 500, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, C.M.; Liu, C.W.; Liang, C.J.; Yen, Y.H.; Chen, S.H.; Jiang-Shieh, Y.F.; Chien, C.L.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, Y.L. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Protect Skin Flaps against Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via IL-6 Expression. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.C.; Grahovac, T.; Oh, S.J.; Ieraci, M.; Rubin, J.P.; Marra, K.G. Evaluation of a multi-layer adipose-derived stem cell sheet in a full-thickness wound healing model. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 5243–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Khan, G.; Park, E.S. Validation of the optimal scaffold pore size of nasal implants using the 3-dimensional culture technique. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2020, 47, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafei, S.; Khanmohammadi, M.; Heidari, R.; Ghanbari, H.; Taghdiri Nooshabadi, V.; Farzamfar, S.; Akbariqomi, M.; Sanikhani, N.S.; Absalan, M.; Tavoosidana, G. Exosome loaded alginate hydrogel promotes tissue regeneration in full-thickness skin wounds: An in vivo study. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2020, 108, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Shen, K.; Wang, K.J.; Tian, C.; Hu, D. Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Promote Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts Embedded in Collagen/Platelet-Rich Plasma Scaffold and Accelerate Wound Healing. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2303642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassling, V.; Douglas, T.; Warnke, P.H.; Açil, Y.; Wiltfang, J.; Becker, S.T. Platelet-rich fibrin membranes as scaffolds for periosteal tissue engineering. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2010, 21, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Wu, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, D.; Lang, X.; Wang, X. A tailored bioactive 3D porous poly(lactic-acid)-exosome scaffold with osteo-immunomodulatory and osteogenic differentiation properties. J. Biol. Eng. 2022, 16, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Lee, S.; Kim, M.; Jeong, Y.; Lee, S. Exosome-coated silk fibroin 3D-scaffold for inducing osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 127080. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Lv, L.; Zhang, X.; Jia, L.; Zhou, Y. Exosomes derived from miR-375-overexpressing human adipose mesenchymal stem cells promote bone regeneration. Cell Prolif. 2019, 52, e12669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, X.; Wu, G.; Zhou, Y. Tissue-Engineered Bone Immobilized with Human Adipose Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes Promotes Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5240–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, J.; Chiang, C.L.; Pan, J.; Wang, X.; Kwak, K.J.; Li, H.; Zhao, R.; Rima, X.Y.; et al. Exosomal mRNAs for Angiogenic-Osteogenic Coupled Bone Repair. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2302622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, D.; Wang, H.; Chen, K.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Ji, P. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells regulate M1/M2 macrophage phenotypic polarization to promote bone healing via miR-451a/MIF. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Yang, R.; Sun, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wang, B.; Cai, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhuang, C.; et al. Adipose stem cells-derived exosomes modified gelatin sponge promotes bone regeneration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1096390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Tao, M.; Xie, Z.; Xia, C.; Gu, C.; Chen, J.; Qiu, P.; Mei, S.; et al. Desktop-stereolithography 3D printing of a radially oriented extracellular matrix/mesenchymal stem cell exosome bioink for osteochondral defect regeneration. Theranostics 2019, 9, 2439–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Hao, Y.; Wang, F.; Hou, W.; Chen, H.; Luo, Y. Mesenchymal stromal exosome-functionalized scaffolds induce innate and adaptive immunomodulatory responses toward tissue repair. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Li, M.; Crawford, R.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, Y. Exosome-integrated titanium oxide nanotubes for targeted bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2019, 86, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallock, G.G. Simplified nomenclature for compound flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2000, 105, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Houseman, N.D.; Taylor, G.I.; Pan, W.R. The angiosomes of the head and neck: Anatomic study and clinical applications. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2000, 105, 2287–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.T. Vascular implantation into skin flap: Experimental study and clinical application: A preliminary report. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1981, 68, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pribaz, J.J.; Fine, N.A. Prelamination: Defining the prefabricated flap-a case report and review. Microsurgery 1994, 15, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouniavski, E.; Egozi, D.; Wolf, Y. Techniques and Innovations in Flap Engineering: A Review. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2022, 10, e4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisawa, D.; Sekine, H.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, H.; Shimizu, T. Ex Vivo Prefabricated Rat Skin Flap Using Cell Sheets and an Arteriovenous Vascular Bundle. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2015, 3, e424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiklin, I.L.; Shabunin, A.V.; Kolsanov, A.V.; Volova, L.T. In Vivo Bone Tissue Engineering Strategies: Advances and Prospects. Polymers 2022, 14, 3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Liu, Z.; Wu, M.; Sun, M.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Y. Comparison of Proangiogenic Effects of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells and Foreskin Fibroblast Exosomes on Artificial Dermis Prefabricated Flaps. Stem Cells Int. 2020, 2020, 5293850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, B.; Bayramiçli, M.; Ercan, F.; Şirinoğlu, H.; Turan, P.; Numanoğlu, A. Comparison of bone prefabrication with vascularized periosteal flaps, hydroxyapatite, and bioactive glass in rats. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2015, 31, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aliyev, A.; Ekin, Ö.; Bitik, O.; Korkusuz, P.; Yersal, N.C.; Çelik, H.H.; Tunçbilek, G. Erratum to: A Novel Method of Neo-osseous Flap Prefabrication: Induction of Free Calvarial Periosteum with Bioactive Glass. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2018, 34, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernice, N.A.; Ann Askinas, C.; Shih, S.; Corpuz, G.S.; Shin, J.; Bonassar, L.J.; Spector, J.A. The Better to Ear You With: Bioengineering Full-scale Auricles Using 3D-printed External Scaffolds and Decellularized Cartilage Xenograft. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2022, 10, 33–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.G.; Park, S.A.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, J.S.; Cho, H.; Lee, S.J.; Kwon, Y.W.; Kwon, S.K. Transplantation of a 3D-printed tracheal graft combined with iPS cell-derived MSCs and chondrocytes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulco, I.; Miot, S.; Haug, M.D.; Barbero, A.; Wixmerten, A.; Feliciano, S.; Wolf, F.; Jundt, G.; Marsano, A.; Farhadi, J.; et al. Engineered autologous cartilage tissue for nasal reconstruction after tumor resection: An observational first-in-human trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.; Zaitseva, T.S.; Zhou, A.; Rochlin, D.; Sue, G.; Deptula, P.; Tabada, P.; Wan, D.; Loening, A.; Paukshto, M.; et al. Lymphatic regeneration after implantation of aligned nanofibrillar collagen scaffolds: Preliminary preclinical and clinical results. J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 125, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.Y.; Tinhofer, I.E.; Nguyen, D.; Cheng, M.H. Enhancing lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic drainage to vascularized lymph nodes with nanofibrillar collagen scaffolds. J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 126, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Yang, J.; Wang, R.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, X.; Qiu, S.; Weng, R.; Wu, Z.; Tang, C.; et al. Delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGFC) via engineered exosomes improves lymphedema. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.H.; Yang, S.H.; Lee, J.; Park, B.C.; Park, K.Y.; Jung, J.Y.; Bae, Y.; Park, G.H. Combination Treatment with Human Adipose Tissue Stem Cell-derived Exosomes and Fractional CO2 Laser for Acne Scars: A 12-week Prospective, Double-blind, Randomized, Split-face Study. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 2020, 100, adv00310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Shi, M.M.; Monsel, A.; Dai, C.X.; Dong, X.; Shen, H.; Li, S.K.; Chang, J.; Xu, C.L.; Li, P.; et al. Nebulized exosomes derived from allogenic adipose tissue mesenchymal stromal cells in patients with severe COVID-19: A pilot study. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Song, Q.; Dai, C.; Cui, S.; Tang, R.; Li, S.; Chang, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; et al. Clinical safety and efficacy of allogenic human adipose mesenchymal stromal cells-derived exosomes in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease: A phase I/II clinical trial. Gen. Psychiatr. 2023, 36, e101143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaie, J.; Feghhi, M.; Etemadi, T. A review on exosomes application in clinical trials: Perspective, questions, and challenges. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skouras, P.; Markouli, M.; Kalamatianos, T.; Stranjalis, G.; Korkolopoulou, P.; Piperi, C. Advances on Liquid Biopsy Analysis for Glioma Diagnosis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|
| Liposuction with a vacuum machine |
|
|
| Liposuction with vacuum syringe—Coleman Technique |
|
|
| Surgical resection |
|
|
| Origin of Exosomes | Cargo | Target Cells | Mechanism of Action | Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADSC-EVs | miR-486-5p | HDF and HMECs | Neoangiogenesis | Improved healing | [57] |
| ADSC-exos | miR-125a, miR-31 | HUVECs | The enhancement of pro-angiogenic activity by targeting FIH1 in endothelial cells | Angiogenesis | [58,59] |
| ADSC-exos | lncRNA MALAT1 | HDF/HaCaT | HDF proliferation and migration, Wnt/β-catenin activation through miR-124 binding, and the inhibition of oxidative stress | Improved healing | [60,61] |
| ADSC-exos | - | EPCs | Nrf2 expression and the inhibition of oxidative stress | Neoangiogenesis/improved healing in the hyperglycemic state | [62] |
| ADSC-exos | - | HDF | Increase in TGF-β3, collagen III, and MMP-3 through the ERK/MAPK pathway | Improved healing | [65] |
| ADSC-exos | miR-21 | HaCaT | The activation of keratinocyte proliferation and induction of MMP-9 | Improved healing in tissue deficits | [67,68] |
| ADSC-exos | CD9, CD63, AGO2 (as surface molecules) | HDF | The expression of VEGF-A, FGF-2, HGF, and PDGF-BB, and the conversion of fibroblasts to myofibroblasts | Improved healing | [69] |
| ADSC-EVs | miR-23a, miR-23b, miR-let7, miR-24, miR-125b miR-16 | Macrophages | Proangiogenesis, M2 macrophage polarity, and the downregulation of MYD88/NF-κB, IL-6/TNF-α, and IKK-α | Muscle regeneration | [72,73] |
| ADSC-exos | miR-145, miR-221 | Periosteal cells and ADSCs | Guiding cells to differentiate, KGN-induced ADSC-exos promote ADSCs into chondrocytes | Chondrogenesis | [74,78] |
| ADSC-exos | miR-130a-3p | ADSCs | Increase in Runx2 and ALP and the osteogenic differentiation of ADSCs via SIRT7/Wnt/β-catenin | Osteogenesis | [75,76] |
| AT-EVs | miR-450a-5p | ADSCs | The differentiation of ADSCs to mature adipose tissue through WISP2 inhibition | Lipogenesis | [81] |
| ADSC-exos | - | Schwann cells | The overexpression of Ccnd1, Ccna2, Rac1, Cthrc1, and MMP-9 | Neural regeneration | [82] |
| ADSC-exos | miR-21 | HUVECs | The promotion of endothelial cells towards angiogenesis | Angiogenesis | [85] |
| MSC-exos | miR-1, miR-133, miR-206, miR-494 | Muscle cells | Increase in VEGF and IL-6 | Muscle regeneration and angiogenesis | [86] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papadopoulos, K.S.; Piperi, C.; Korkolopoulou, P. Clinical Applications of Adipose-Derived Stem Cell (ADSC) Exosomes in Tissue Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115916
Papadopoulos KS, Piperi C, Korkolopoulou P. Clinical Applications of Adipose-Derived Stem Cell (ADSC) Exosomes in Tissue Regeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(11):5916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115916
Chicago/Turabian StylePapadopoulos, Konstantinos S., Christina Piperi, and Penelope Korkolopoulou. 2024. "Clinical Applications of Adipose-Derived Stem Cell (ADSC) Exosomes in Tissue Regeneration" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 11: 5916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115916
APA StylePapadopoulos, K. S., Piperi, C., & Korkolopoulou, P. (2024). Clinical Applications of Adipose-Derived Stem Cell (ADSC) Exosomes in Tissue Regeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(11), 5916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115916







