T Cell Homeostasis Disturbances in a Cohort of Long-Term Elite Controllers of HIV Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of the Study Groups
2.2. Unsupervised Multidimensional Analysis of Flow Cytometry Data Yielded Several CD4 and CD8 T Cell Clusters That Differentiated the Study Groups
2.3. Uncontrolled Viral Replication Is Associated with a Deep Perturbation of CD4 and CD8 T Cell Homeostasis
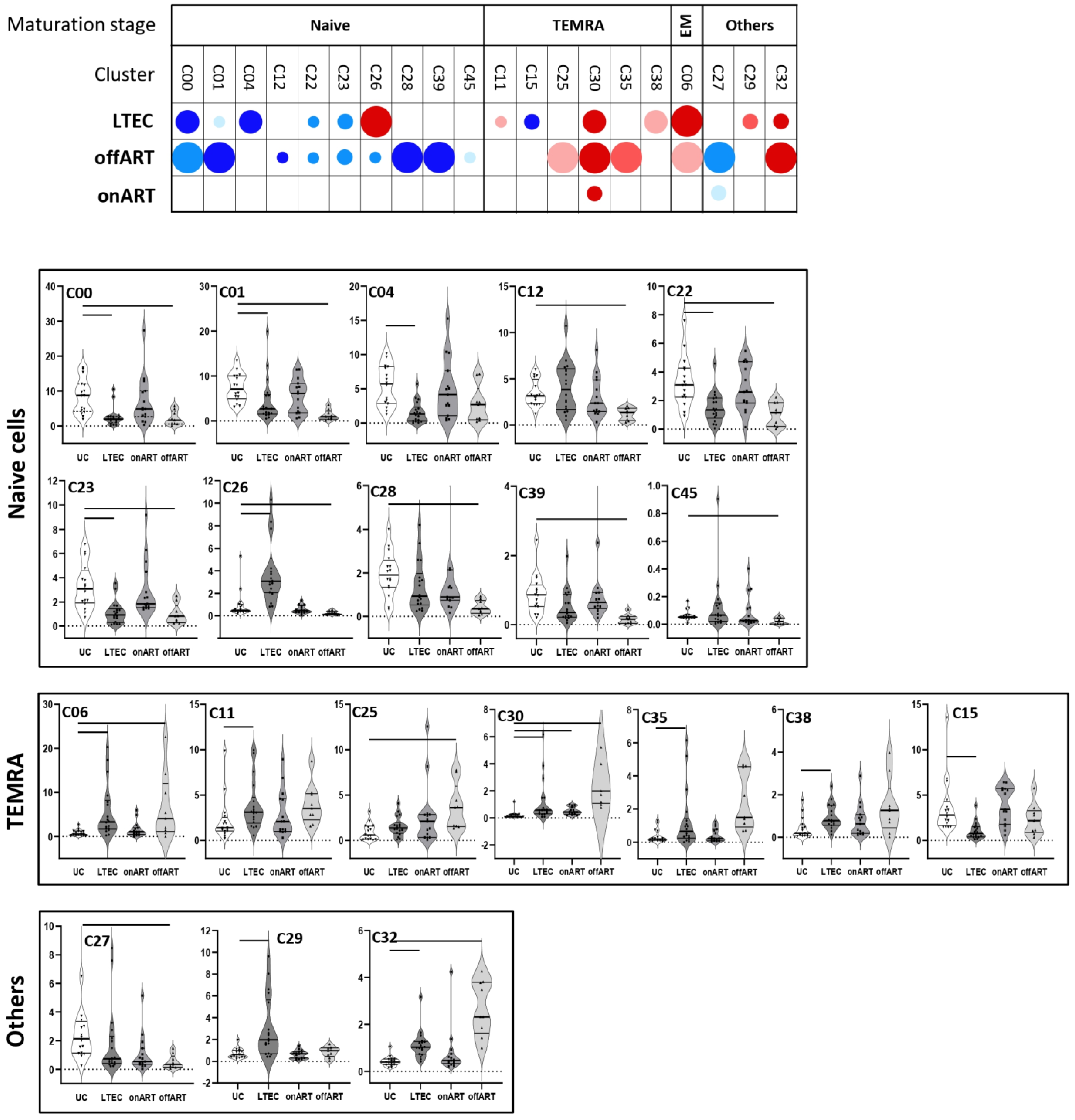
2.4. The Majority of T Cell Homeostasis Disturbances Are Restored with Long-Term ART
2.5. PLWH with Spontaneous Control of HIV Replication Show a Deep Perturbation of CD4 and CD8 T Cell Clusters
2.6. A Specific Profile of CD4 and CD8 T Cell Clusters Associated with the Spontaneous Control of HIV Replication
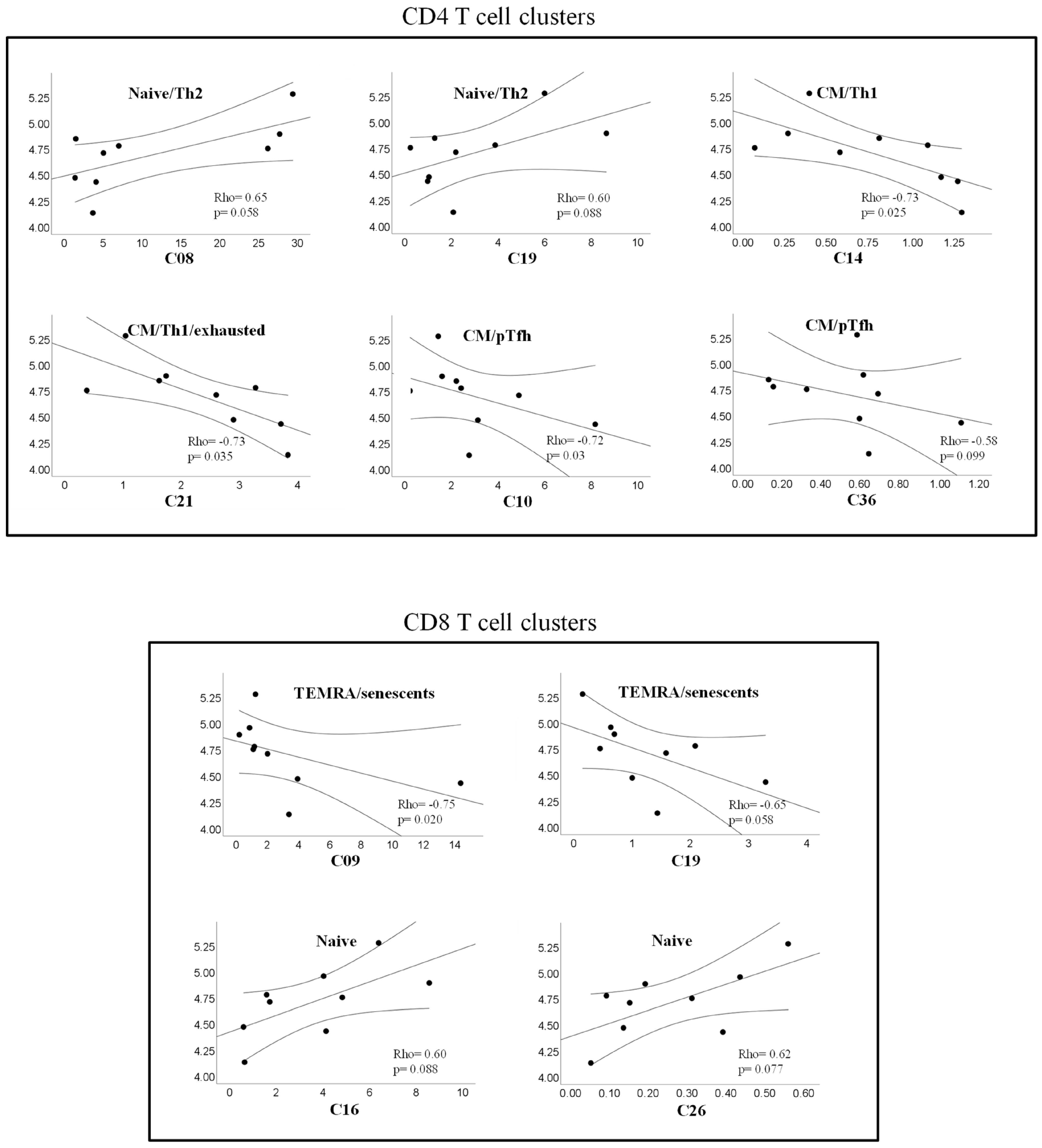
2.7. Correlations between T Cell Clusters and Inmmuno-Virological Parameters
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Participants
4.2. Cell Samples
4.3. Multiparameter Flow Cytometry
4.4. Preparation of Flow Cytometry Data for Unsupervised Multidimensional Analysis
4.5. Unsupervised Analysis of Flow Cytometry Data
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Autran, B.; Descours, B.; Avettand-Fenoel, V.; Rouzioux, C. Elite controllers as a model of functional cure. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2011, 6, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeks, S.G.; Lewin, S.R.; Ross, A.L.; Ananworanich, J.; Benkirane, M.; Cannon, P.; Chomont, N.; Douek, D.; Lifson, J.D.; Lo, Y.R.; et al. International AIDS Society global scientific strategy: Towards an HIV cure 2016. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwaa, A.K.; Blankson, J.N. Immune responses in controllers of HIV. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 42, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betts, M.R.; Nason, M.C.; West, S.M.; De Rosa, S.C.; Migueles, S.A.; Abraham, J.; Lederman, M.M.; Benito, J.M.; Goepfert, P.A.; Connors, M.; et al. HIV nonprogressors preferentially maintain highly functional HIV-specific CD8+ T cells. Blood 2006, 107, 4781–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndhlovu, Z.M.; Stampouloglou, E.; Cesa, K.; Mavrothalassitis, O.; Alvino, D.M.; Li, J.Z.; Wilton, S.; Karel, D.; Piechocka-Trocha, A.; Chen, H.; et al. The Breadth of Expandable Memory CD8+ T Cells Inversely Correlates with Residual Viral Loads in HIV Elite Controllers. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 10735–10747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migueles, S.A.; Osborne, C.M.; Royce, C.; Compton, A.A.; Joshi, R.P.; Weeks, K.A.; Rood, J.E.; Berkley, A.M.; Sacha, J.B.; Cogliano-Shutta, N.A.; et al. Lytic granule loading of CD8+ T cells is required for HIV-infected cell elimination associated with immune control. Immunity 2008, 29, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mothe, B.; Llano, A.; Ibarrondo, J.; Zamarreño, J.; Schiaulini, M.; Miranda, C.; Ruiz-Riol, M.; Berger, C.T.; Herrero, M.J.; Palou, E.; et al. CTL responses of high functional avidity and broad variant cross-reactivity are associated with HIV control. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiepiela, P.; Ngumbela, K.; Thobakgale, C.; Ramduth, D.; Honeyborne, I.; Moodley, E.; Reddy, S.; de Pierres, C.; Mncube, Z.; Mkhwanazi, N.; et al. CD8+ T-cell responses to different HIV proteins have discordant associations with viral load. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete-Muñoz, M.A.; Restrepo, C.; Benito, J.M.; Rallón, N. Elite controllers: A heterogeneous group of HIV-infected patients. Virulence 2020, 11, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, A.; Perez, I.; Ruiz-Mateos, E.; Benito, J.M.; Leal, M.; Lopez-Galindez, C.; Rallon, N.; Alcami, J.; Lopez-Aldeguer, J.; Viciana, P.; et al. Rate and predictors of progression in elite and viremic HIV-1 controllers. AIDS 2016, 30, 1209–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabar, S.; Selinger-Leneman, H.; Abgrall, S.; Pialoux, G.; Weiss, L.; Costagliola, D. Prevalence and comparative characteristics of long-term nonprogressors and HIV controller patients in the French Hospital Database on HIV. AIDS 2009, 23, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernas, M.; Tarancón-Diez, L.; Rodríguez-Gallego, E.; Gómez, J.; Prado, J.G.; Casado, C.; Dominguez-Molina, B.; Olivares, I.; Coiras, M.; León, A.; et al. Factors leading to the loss of natural elite control of HIV-1 infection. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01805–e01817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Gallego, E.; Tarancón-Diez, L.; García, F.; Del Romero, J.; Benito, J.; Alba, V.; Herrero, P.; Rull, A.; Dominguez-Molina, B.; Martinez-Madrid, O.; et al. Proteomic Profile Associated with Loss of Spontaneous HIV-1 Elite Control. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 291, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benito, J.M.; Ortiz, M.C.; León, A.; Sarabia, L.A.; Ligos, J.M.; Montoya, M.; Garcia, M.; Ruiz-Mateos, E.; Palacios, R.; Cabello, A.; et al. Class-modeling analysis reveals T-cell homeostasis disturbances involved in loss of immune control in elite controllers. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenwick, C.; Joo, V.; Jacquier, P.; Noto, A.; Banga, R.; Perreau, M.; Pantaleo, G. T-cell exhaustion in HIV infection. Immunol. Rev. 2019, 292, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douek, D.C. Disrupting T-cell homeostasis: How HIV-1 infection causes disease. AIDS Rev. 2003, 5, 172–177. [Google Scholar]
- Soukas, C. Immunosenescence and aging in HIV. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2014, 9, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakhour, R.; Tran, D.Q.; Heresi, G.P.; Degaffe, G.; Bell, C.S.; Donnachie, E.; Zhang, W.; Pérez, N.; Benjamins, L.J.; Del Bianco, G.; et al. CD31 Expression on CD4+ Cells: A Simple Method for Quantitation of Recent Thymus Emigrant CD4 Cells. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 95, 970–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, R.; Mackall, C. Thymic function in HIV infection. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2005, 2, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, N.; Kaufmann, D.; Lahey, T.; Rosenberg, E.S.; Wucherpfennig, K.W. Expansion and Contraction of HIV-Specific CD4 T Cells with Short Bursts of Viremia, but Physical Loss of the Majority of These Cells with Sustained Viral Replication. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 6948–6958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollet, L.; Li, T.S.; Samri, A.; Tournay, C.; Tubiana, R.; Calvez, V.; Debré, P.; Katlama, C.; Autran, B.; RESTIM and COMET Study Groups. Dynamics of HIV-Specific CD81 T Lymphocytes with Changes in Viral Load. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 1692–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianella, S.; Letendre, S. Cytomegalovirus and HIV: A Dangerous Pas de Deux. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214, S67–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, A.F.; Luo, X.; Neidleman, J.; Hoh, R.; Vohra, P.; Thomas, R.; Shin, M.G.; Lee, M.J.; Blish, C.A.; Deeks, S.G.; et al. Deep Phenotypic Analysis of Blood and Lymphoid T and NK Cells From HIV+ Controllers and ART-Suppressed Individuals. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 803417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Mateos, E.; Ferrando-Martinez, S.; Machmach, K.; Viciana, P.; Pacheco, Y.M.; Nogales, N.; Genebat, M.; Leal, M. High Levels of CD57+ CD28− T-Cells, Low T-Cell Proliferation and Preferential Expansion of Terminally Differentiated CD4+ T-Cells in HIV Elite Controllers. Curr. HIV Res. 2010, 8, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Al-Mozainia, M.; Buzon, M.J.; Beamon, J.; Ferrando-Martinez, S.; Ruiz-Mateos, E.; Rosenberg, E.S.; Pereyra, F.; Yu, X.G.; Lichterfeld, M. CD4 T-cell regeneration in HIV-1 elite controllers. AIDS 2012, 26, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, A.; Sterrett, S.; Erdmann, N.; Westfall, A.O.; Dionne-Odom, J.; Overton, E.T.; Goepfert, P.A. Normal T-cell activation in elite controllers with preserved CD4+ T-cell counts. AIDS 2015, 29, 2245–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, M.; Soriano, V.; Peris-Pertusa, A.; Rallón, N.; Restrepo, C.; Benito, J.M. Elite controllers display higher activation on central memory CD8 T cells than HIV patients successfully on HAART. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2011, 27, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamya, P.; Tsoukas, C.M.; Boulet, S.; Routy, J.P.; Thomas, R.; Côté, P.; Boulassel, M.R.; Lessard, B.; Kaul, R.; Ostrowski, M.; et al. T cell Activation does not drive CD4 decline in longitudinally followed HIV-infected Elite Controllers. AIDS Res. Ther. 2011, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caetano, D.G.; de Paula, H.H.S.; Bello, G.; Hoagland, B.; Villela, L.M.; Grinsztejn, B.; Veloso, V.G.; Morgado, M.G.; Guimarães, M.L.; Côrtes, F.H. HIV-1 elite controllers present a high frequency of activated regulatory T and Th17 cells. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, L.; Benfield, T.; Mens, H.; Clausen, L.N.; Katzenstein, T.L.; Fomsgaard, A.; Karlsson, I. Low Level of Regulatory T Cells and Maintenance of Balance Between Regulatory T Cells and TH17 Cells in HIV-1–Infected Elite Controllers. J. Acquir. Immun. Defic. Syndr. 2011, 57, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landay, A.; Golub, E.T.; Desai, S.; Zhang, J.; Winkelman, V.; Anastos, K.; Durkin, H.; Young, M.; Villacres, M.C.; Greenblatt, R.M.; et al. HIV RNA levels in plasma and cervical-vaginal lavage fluid in elite controllers and HAART recipients. AIDS 2014, 28, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinoso, J.B.; Kim, S.Y.; Siliciano, R.F.; Blankson, J.N. A Comparison of Viral Loads between HIV-1–Infected Elite Suppressors and Individuals Who Receive Suppressive Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatano, H.; Delwart, E.L.; Norris, P.J.; Lee, T.H.; Dunn-Williams, J.; Hunt, P.W.; Hoh, R.; Stramer, S.L.; Linnen, J.M.; McCune, J.M.; et al. Evidence for Persistent Low-Level Viremia in Individuals Who Control Human Immunodeficiency Virus in the Absence of Antiretroviral Therapy. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedaghat, A.R.; Rastegar, D.A.; O’Connell, K.A.; Dinoso, J.B.; Wilke, C.O.; Blankson, J.N. T Cell Dynamics and the Response to HAART in a Cohort of HIV-1–Infected Elite Suppressors. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 1763–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Z.; Segal, F.P.; Bosch, R.J.; Lalama, C.M.; Roberts-Toler, C.; Delagreverie, H.; Getz, R.; Garcia-Broncano, P.; Kinslow, J.; Tressler, R.; et al. Antiretroviral Therapy Reduces T-cell Activation and Immune Exhaustion Markers in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Controllers. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 1636–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellino, F.; Germain, R.N. Cooperation between CD4+ and CD8+ T cells: When, where, and how. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 24, 519–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, T.J.; Mackall, C.L. The many faces of IL-7, from thymopoiesis to peripheral T cell maintenance. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 6571–6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Carretero, D.; Ligos, J.M.; Martínez-López, M.; Sancho, D.; Montoya, M.C. Flow Cytometry Data Preparation Guidelines for Improved Automated Phenotypic Analysis. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 3319–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gassen, S.; Gaudilliere, B.; Angst, M.S.; Saeys, Y.; Aghaeepour, N. CytoNorm: A Normalization Algorithm for Cytometry Data. Cytom. A 2020, 97, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Hao, S.; Andersen-Nissen, E.; Mauck, W.M., III; Zheng, S.; Butler, A.; Satija, R. Integrated analysis of multimodal single-cell data. Cell 2021, 184, 3573–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltman, L.; Van Eck, N.J. A smart local moving algorithm for large-scale modularity-based community detection. Eur. Phys. J. B 2013, 86, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linderman, G.C.; Rachh, M.; Hoskins, J.G.; Steinerberger, S.; Kluger, Y. Fast interpolation-based t-SNE for improved visualization of single-cell RNA-seq data. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emu, B.; Moretto, W.J.; Hoh, R.; Krone, M.; Martin, J.N.; Nixon, D.F.; Deeks, S.G.; McCune, J.M. Composition and function of T cell subpopulations are slow to change despite effective antiretroviral treatment of HIV disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 21, e85613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahnke, Y.D.; Brodie, T.M.; Sallusto, F.; Roederer, M.; Lugli, E. The who’s who of T-cell differentiation: Human memory T-cell subsets. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 2797–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, S.; Thiel, A. Life after the thymus: CD31+ and CD31- human naive CD4+ T-cell subsets. Blood 2009, 113, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Cumberland, W.G.; Hultin, L.E.; Prince, H.E.; Detels, R.; Giorgi, J.V. Elevated CD38 antigen expression on CD8+ T cells is a stronger marker for the risk of chronic HIV disease progression to AIDS and death in the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study than CD4+ cell count, soluble immune activation markers, or combinations of HLA-DR and CD38 expression. J. Acquir. Immune. Defic. Syndr. Hum. Retrovirol. 1997, 16, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paiardini, M.; Müller-Trutwin, M. HIV-associated chronic immune activation. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 254, 78–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pangrazzi, P.; Reidla, J.; Carmona-Arana, J.A.; Naismith, E.; Miggitsch, C.; Meryk, A.; Keller, M.; Krause, A.A.N.; Melzer, F.L.; Trieb, K.; et al. CD28 and CD57 define four populations with distinct phenotypic properties within human CD8+ T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 50, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strioga, M.; Pasukoniene, V.; Characiejus, D. CD8+ CD28- and CD8+ CD57+ T cells and their role in health and disease. Immunology 2011, 134, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hove-Skovsgaard, M.; Zhao, Z.; Tingstedt, J.L.; Hartling, H.J.; Thudium, R.F.; Benfield, T.; Afzal, S.; Nordestgaard, B.; Ullum, H.; Gerstoft, J.; et al. Impact of Age and HIV Status on Immune Activation, Senescence and Apoptosis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 583569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, A.M.; Angel, J.B. The influence of HIV on CD127 expression and its potential implications for IL-7 therapy. Semin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunham, R.M.; Cervasi, B.; Brenchley, J.M.; Albrecht, H.; Weintrob, A.; Sumpter, B.; Engram, J.; Gordon, S.; Klatt, N.R.; Frank, I.; et al. CD127 and CD25 expression defines CD4+ T cell subsets that are differentially depleted during HIV infection. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 5582–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouas, R.; Merimi, M.; Najar, M.; El Zein, N.; Fayyad-Kazan, M.; Berehab, M.; Agha, D.; Bron, D.; Burny, A.; Rachidi, W.; et al. Human CD8+ CD25 + CD127 low regulatory T cells: microRNA signature and impact on TGF-β and IL-10 expression. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 17459–17472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenaka, M.V.; Robson, S.; Quintana, F.J. Regulation of the T Cell Response by CD39. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groom, J.R.; Luster, A.D. CXCR3 in T cell function. Exp. Cell. Res. 2011, 317, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira-Mattos, S.M.; Narendran, G.; Akrami, K.; Fukutani, K.F.; Anbalagan, S.; Nayak, K.; Subramanyam, S.; Subramani, R.; Vinhaes, C.L.; Oliveira-de Souza, D.; et al. Differential expression of CXCR3 and CCR6 on CD4+ T-lymphocytes with distinct memory phenotypes characterizes tuberculosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory síndrome. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.Y.S.; Körner, H. CCR6/CCL20 chemokine axis in human immunodeficiency virus immunity and pathogenesis. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinuesa, C.G.; Linterman, M.A.; Yu, D.; MacLennan, I.C.M. Follicular Helper T Cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 34, 335–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | LTEC (n = 22) | onART (n = 15) | offART (n = 10) | UC (n = 20) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 44 [35–49] | 44 [42–49] | 43 [36–49] | 43 [36–49] | 0.266 |
| Sex (% of males) | 59 * | 80 | 100 | 50 * | 0.025 |
| Years since HIV diagnosis | 15 * [6–20] | 12 [5–15] | 5 [3–9] | NA | 0.027 |
| Years as EC | 13 [7–16] | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Years on ART | NA | 6 [3–9] | NA | NA | NA |
| Plasma HIV load (copies/mL) | 50 | 50 | 57,937 [28,817–80,676] | NA | NA |
| CD4 count (cells/μL) | 837 [603–1210] | 820 [599–1127] | 625 [518–920] | NA | 0.200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benito, J.M.; Jiménez-Carretero, D.; Restrepo, C.; Ligos, J.M.; Valentín-Quiroga, J.; Mahillo, I.; Cabello, A.; López-Collazo, E.; Sánchez-Cabo, F.; Górgolas, M.; et al. T Cell Homeostasis Disturbances in a Cohort of Long-Term Elite Controllers of HIV Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5937. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115937
Benito JM, Jiménez-Carretero D, Restrepo C, Ligos JM, Valentín-Quiroga J, Mahillo I, Cabello A, López-Collazo E, Sánchez-Cabo F, Górgolas M, et al. T Cell Homeostasis Disturbances in a Cohort of Long-Term Elite Controllers of HIV Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(11):5937. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115937
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenito, José M., Daniel Jiménez-Carretero, Clara Restrepo, José M. Ligos, Jaime Valentín-Quiroga, Ignacio Mahillo, Alfonso Cabello, Eduardo López-Collazo, Fátima Sánchez-Cabo, Miguel Górgolas, and et al. 2024. "T Cell Homeostasis Disturbances in a Cohort of Long-Term Elite Controllers of HIV Infection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 11: 5937. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115937
APA StyleBenito, J. M., Jiménez-Carretero, D., Restrepo, C., Ligos, J. M., Valentín-Quiroga, J., Mahillo, I., Cabello, A., López-Collazo, E., Sánchez-Cabo, F., Górgolas, M., Estrada, V., & Rallón, N., on behalf of the ECRIS Integrated in the Spanish AIDS Research Network. (2024). T Cell Homeostasis Disturbances in a Cohort of Long-Term Elite Controllers of HIV Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(11), 5937. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115937







