Molecular Docking Studies of Ortho-Substituted Phenols to Tyrosinase Helps Discern If a Molecule Can Be an Enzyme Substrate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
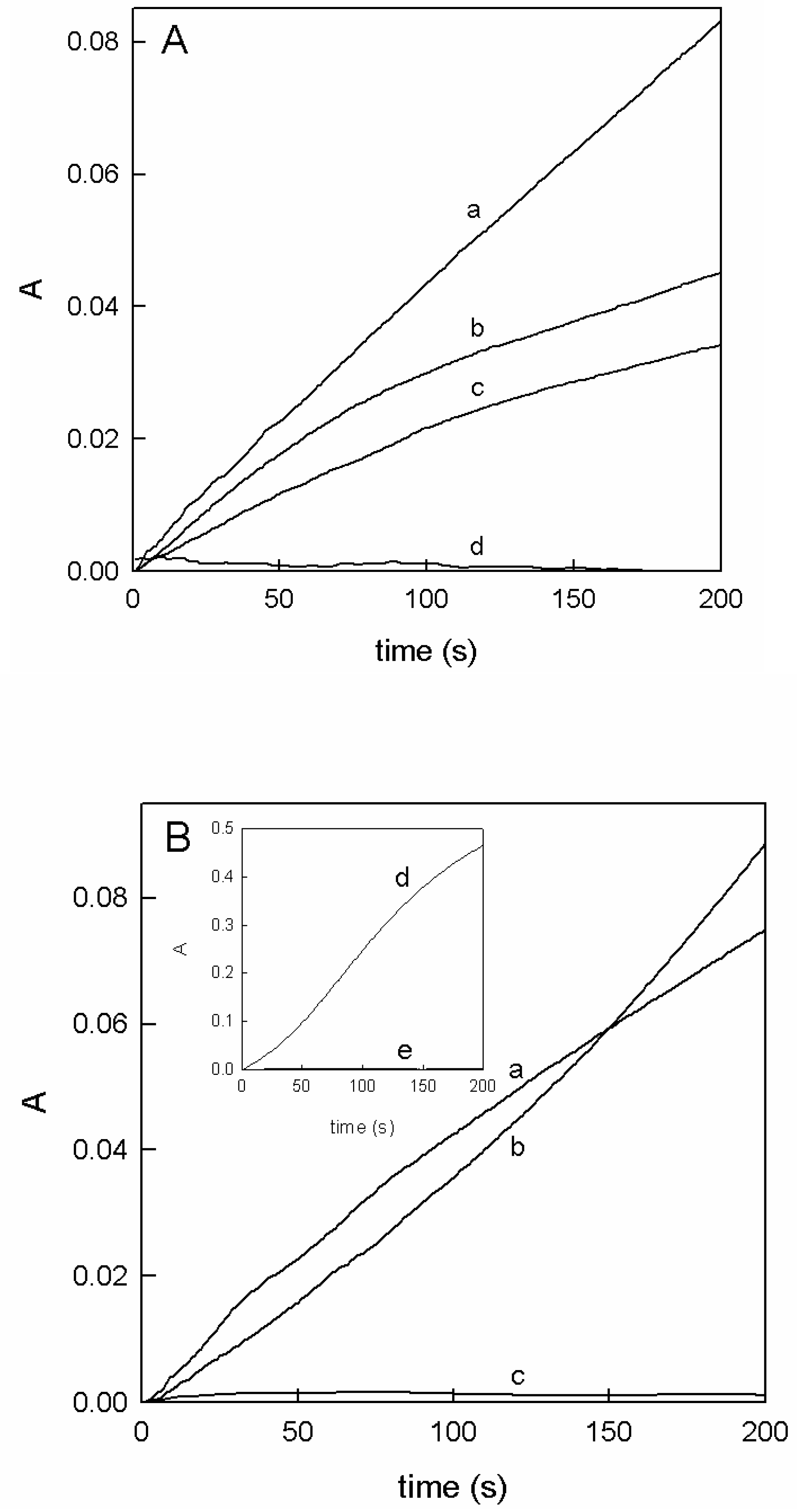
2.1. The Apparent Inhibition in the Action of Tyrosinase on L-Dopa in the Presence of Ortho-Substituted Phenols
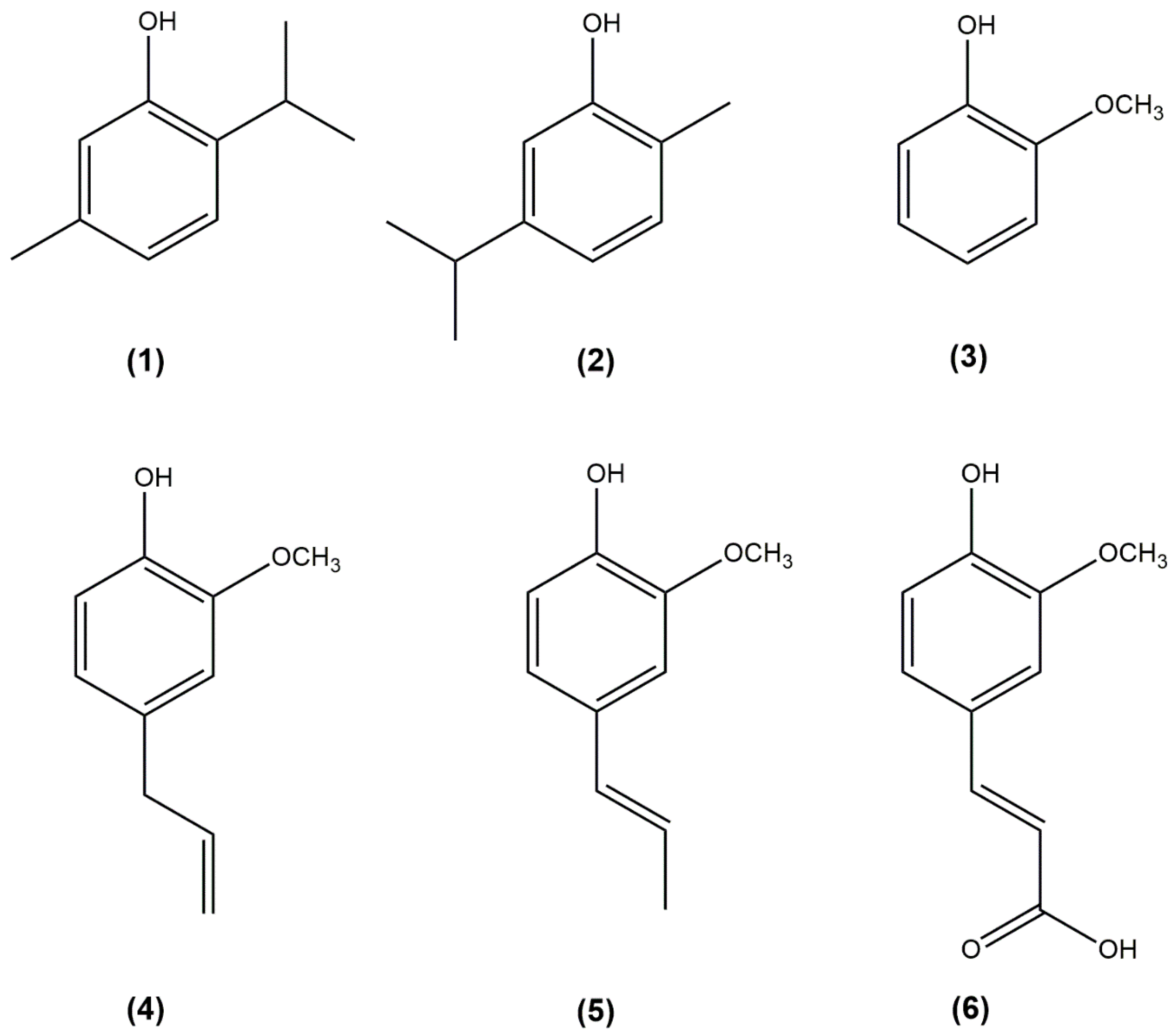
2.2. Characterization of Ortho-Substituted Phenols as Tyrosinase Substrates
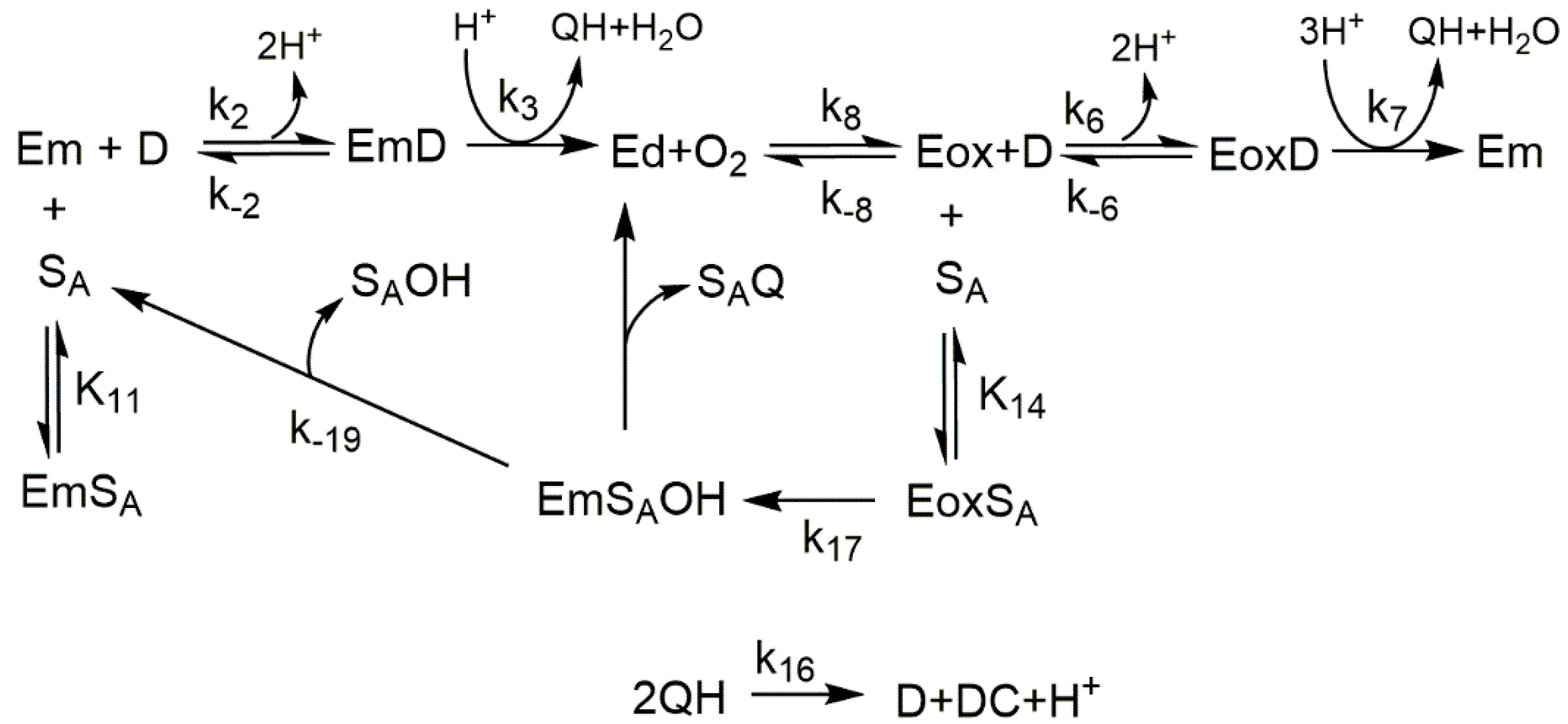
- Achieve the transition from Em to Eoxy by adding hydrogen peroxide according to Em + H2O2 ⇄ Eoxy (Scheme 1). Hydrogen peroxide causes the transformation of the met-tyrosinase form (inactive on monophenols) to the oxy-tyrosinase form (active on monophenols).
- Study the action of tyrosinase on monophenols such as thymol and carvacrol in the presence of their corresponding o-diphenol: 3-isopropyl-6-methylcatechol or 3-methoxycatechol in the case of guaiacol. In these cases, it is the added o-diphenol that causes the transition from met-tyrosinase to oxy-tyrosinase, according to Em + D⇄ EmD → Q + Ed + O2 ⇄ Eox. The kinetic parameters described in Table 1 are obtained [26].
- Study the action of tyrosinase on o-substituted monophenol in the presence of an o-diphenol such as L-dopa.
- 4.
- To study the action of tyrosinase on o-subtitled monophenols in the presence of catechol, the mechanism is similar to cases 1, 2, and 4. The FA was studied under this experimental approach by measuring the increase in absorbance at λ = 480 nm; thus, the kinetic parameters shown in Table 1 were determined [13].
- 5.
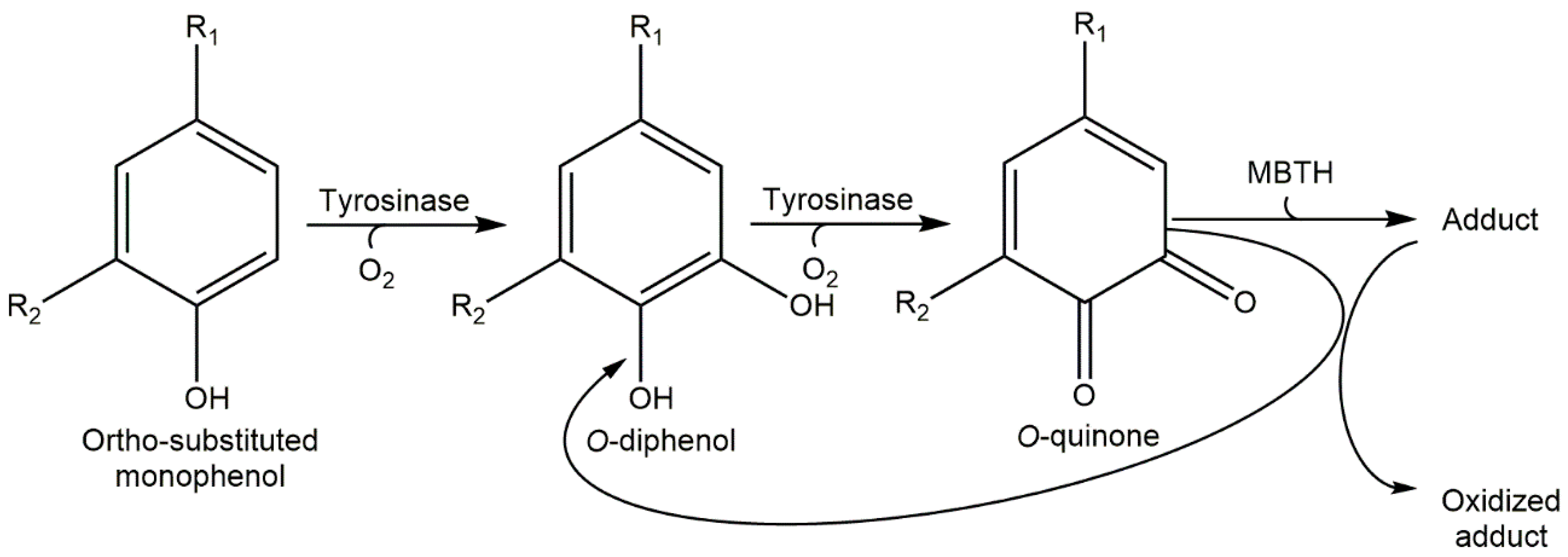
- Study the action of the enzyme on ortho-substituted phenol in the presence of hydrogen peroxide (Scheme 1), or a nucleophile like MBTH and the nucleophile MBTH in order to increase the spectrophotometric signal, since the adducts that originate from the attack of MBTH on o-quinone have a very high molar absorptivity coefficient (Scheme 2) [27]. Under this approach, FA was studied [27], thus characterizing the value (see Table 1).
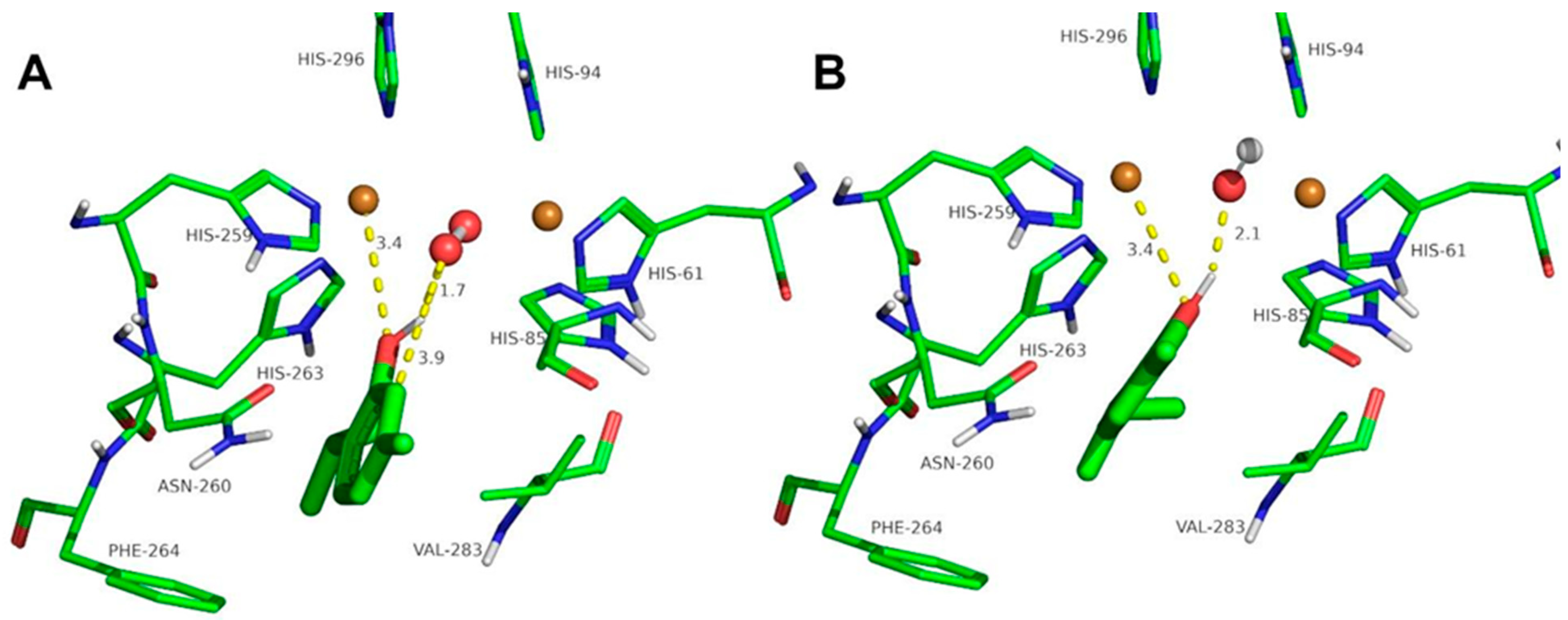
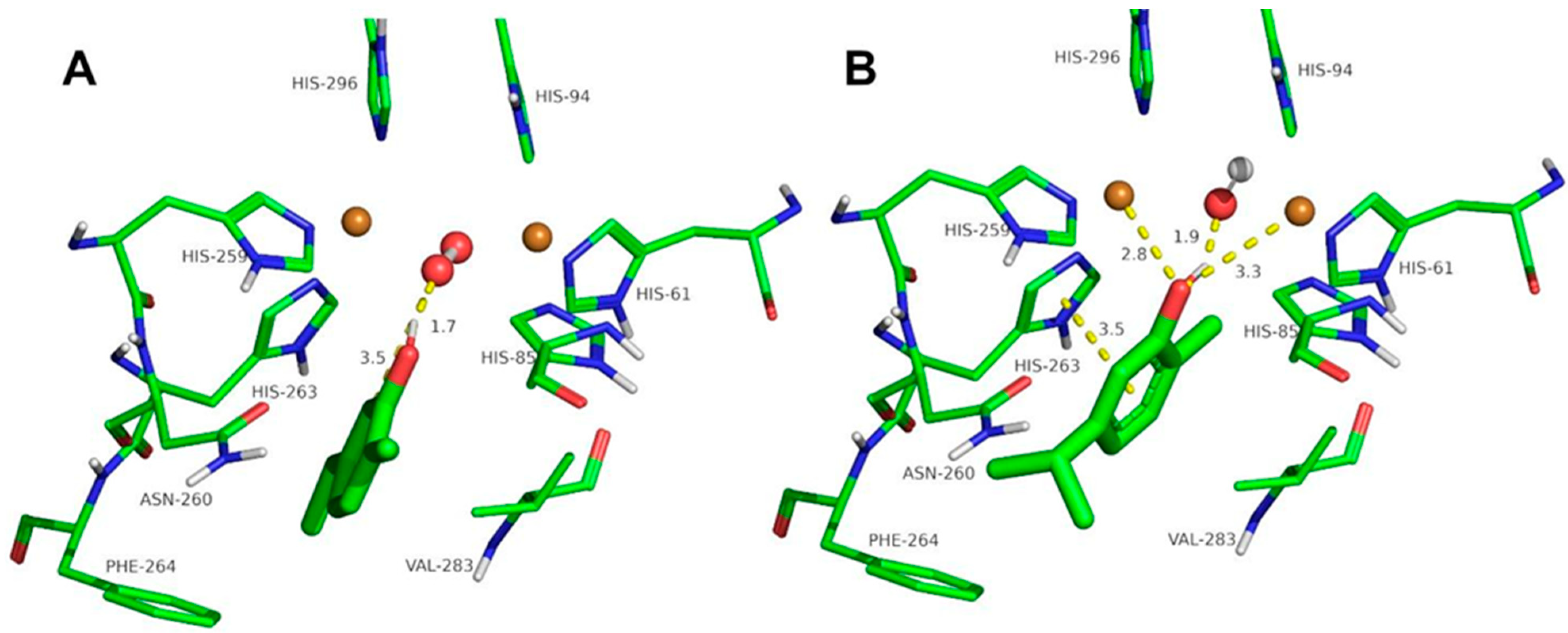
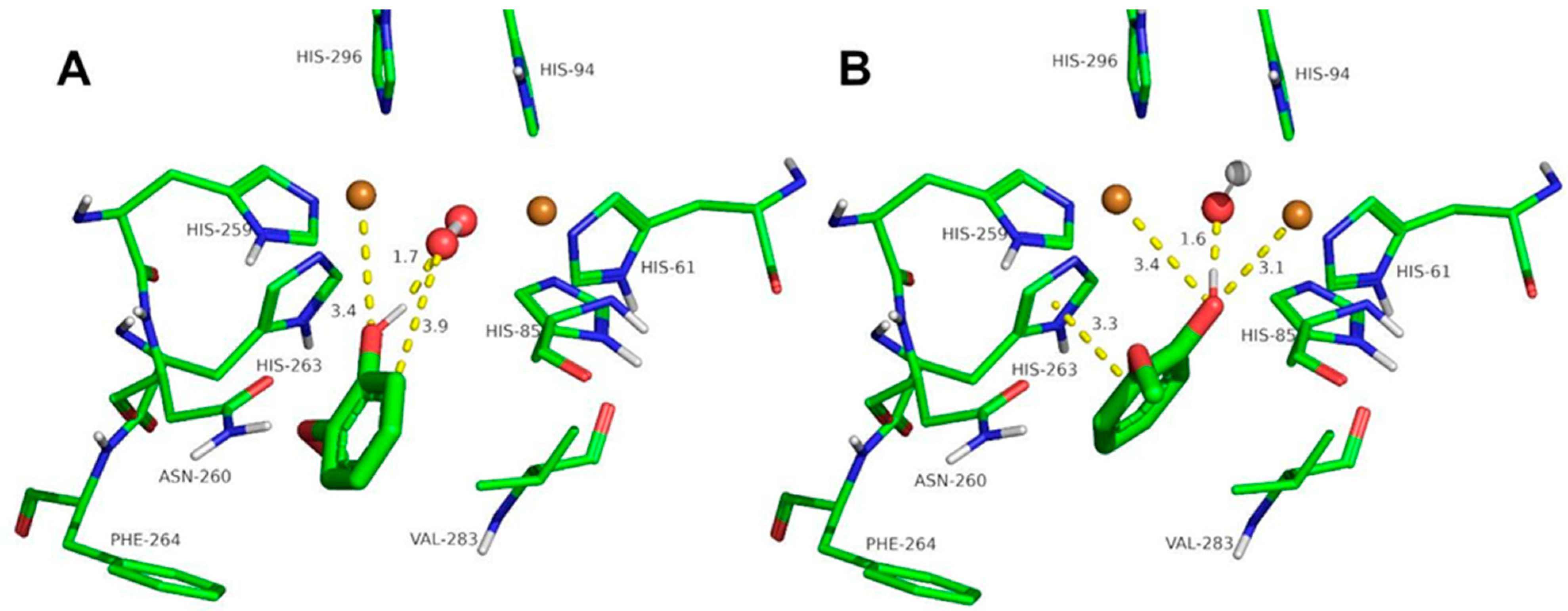
2.3. Docking Studies of the Compounds Described in This Work to Tyrosinase
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Enzyme Source
3.2. Reagents
3.3. Spectrophotometric Assays
3.4. Computational Simulation of Interaction between Ortho-Substituted Phenols to Met-Tyrosinase and Oxy-Tyrosinase
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sánchez-Ferrer, Á.; Rodríguez-López, J.N.; García-Cánovas, F.; García-Carmona, F. Tyrosinase: A comprehensive review of its mechanism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1995, 1247, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, E.I.; Sundaram, U.M.; Machonkin, T.E. Multicopper oxidases and oxygenases. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 2563–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, F.G.; Muñoz, J.L.; Varón, R.; López, J.N.R.; Cánovas, F.G.; Tudela, J. An approximate analytical solution to the lag period of monophenolase activity of tyrosinase. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Molina, M.d.M.; Muñoz Muñoz, J.L.; Martinez Ortiz, F.; Martinez, J.R.; García Ruiz, P.A.; Rodriguez López, J.N.; García Cánovas, F. Tyrosinase-catalyzed hydroxylation of hydroquinone, a depigmenting agent, to hydroxyhydroquinone: A kinetic study. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 3360–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Ruiz, C.V.; Ballesta de los Santos, M.; Berna, J.; Fenoll, J.; Garcia-Ruiz, P.A.; Tudela, J.; Garcia-Canovas, F. Kinetic characterization of oxyresveratrol as a tyrosinase substrate. IUBMB Life 2015, 67, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Ruiz, C.V.; Berna, J.; Rodriguez-Lopez, J.N.; Tomas, V.; Garcia-Canovas, F. Tyrosinase-Catalyzed Hydroxylation of 4-Hexylresorcinol, an Antibrowning and Depigmenting Agent: A Kinetic Study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7032–7040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Jimenez, A.; García-Molina, F.; Teruel-Puche, J.A.; Saura-Sanmartin, A.; Garcia-Ruiz, P.A.; Ortiz-Lopez, A.; Rodríguez-López, J.N.; Garcia-Canovas, F.; Munoz-Munoz, J. Catalysis and inhibition of tyrosinase in the presence of cinnamic acid and some of its derivatives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Jimenez, A.; Teruel-Puche, J.A.; Ortiz-Ruiz, C.V.; Berna, J.; Tudela, J.; Garcia-Canovas, F. 4-n-butylresorcinol, a depigmenting agent used in cosmetics, reacts with tyrosinase. IUBMB Life 2016, 68, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Jimenez, A.; Teruel-Puche, J.A.; Berna, J.; Rodriguez-Lopez, J.N.; Tudela, J.; Garcia-Ruiz, P.A.; Garcia-Canovas, F. Characterization of the action of tyrosinase on resorcinols. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 4434–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Molina, M.d.M.; Berna, J.; Muñoz-Muñoz, J.L.; García-Ruiz, P.A.; Moreno, M.G.; Martinez, J.R.; Garcia-Canovas, F. Action of tyrosinase on hydroquinone in the presence of catalytic amounts of o-diphenol. A kinetic study. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2014, 112, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Muñoz, J.L.; García-Molina, F.; Varón, R.; Tudela, J.; García-Cánovas, F.; Rodríguez-López, J.N. Generation of hydrogen peroxide in the melanin biosynthesis pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Proteins Proteom. 2009, 1794, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary of the Sea GARCÍA-MOLINA; Muñoz-Muñoz, J.L.; Berna, J.; Rodríguez-López, J.N.; Varón, R.; García-Cánovas, F. Hydrogen Peroxide Helps in the Identification of Monophenols as Possible Substrates of Tyrosinase. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 2383–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, L.R.; Paul, B. Diphenol Activation of the Monophenolase and Diphenolase Activities of Field Bean (Dolichos lablab) Polyphenol Oxidase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1608–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, E. Antioxidant potential of ferulic acid. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1992, 13, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosazza, J.P.N.; Huang, Z.; Dostal, L.; Volm, T.; Rousseau, B. Review: Biocatalytic transformations of ferulic acid: An abundant aromatic natural product. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1995, 15, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanski, J.; Aksenova, M.; Stoyanova, A.; Butterfield, D.A. Ferulic acid antioxidant protection against hydroxyl and peroxyl radical oxidation in synaptosomal and neuronal cell culture systems in vitro: Structure-activity studies. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2002, 13, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.Z.; Cheng, J.A.; Yang, Z.R. Inhibitory effect of ferulic acid on oxidation of L-DOPA catalyzed by mushroom tyrosinase. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2005, 13, 771–775. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, S.; Yin, M.; Yun, Z. Kinetics of inhibitory effect of isoferulic acid on mushroom tyrosinase. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013, 64, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Satooka, H.; Kubo, I. Effects of Thymol on Mushroom Tyrosinase-Catalyzed Melanin Formation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 8908–8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojazadeh, T.; Zolghadr, L.; Gharaghani, S.; JafarKhani, S.; Molaabasi, F.; Piri, H.; Gheibi, N. New insights into the inhibitory effect of phenol carboxylic acid antioxidants on mushroom tyrosinase by molecular dynamic studies and experimental assessment. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 13404–13414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Molina, P.; Garcia-Molina, F.; Teruel-Puche, J.A.; Rodriguez-Lopez, J.N.; Garcia-Canovas, F.; Muñoz-Muñoz, J.L. The relationship between the IC50 values and the apparent inhibition constant in the study of inhibitors of tyrosinase diphenolase activity helps confirm the mechanism of inhibition. Molecules 2022, 27, 3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alifah, L.H.N.; Jatmika, C.; Hayun, H. Exploration of Ferulic Acid and Its Derivatives as Potent Anti-Tyrosinase: A Systematic Review. Egypt. J. Chem. 2024, 67, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Ruiz, C.V.; Garcia-Molina, M.d.M.; Serrano, J.T.; Tomas-Martinez, V.; Garcia-Canovas, F. Discrimination between Alternative Substrates and Inhibitors of Tyrosinase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 2162–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros, J.; Rodríguez-López, J.; García-Cánovas, F. Tyrosinase: Kinetic analysis of the transient phase and the steady state. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1994, 1204, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenoll, L.G.; Rodríguez-López, J.N.; García-Sevilla, F.; García-Ruiz, P.A.; Varón, R.; García-Cánovas, F.; Tudela, J. Analysis and interpretation of the action mechanism of mushroom tyrosinase on monophenols and diphenols generating highly unstable o-quinones. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 2001, 1548, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Molina, M.d.M.; Muñoz-Muñoz, J.L.; Garcia-Molina, F.; García-Ruiz, P.A.; Garcia-Canovas, F. Action of Tyrosinase on Ortho-Substituted Phenols: Possible Influence on Browning and Melanogenesis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 6447–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morosanova, M.; Fedorov, A.; Morosanova, E. Crude Plant Extracts Mediated Polyphenol Oxidation Reactions in Presence of 3-Methyl-2-Benzothiazolinone Hydrazone for Determination of Total Polyphenol Content in Beverages. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2018, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-López, J.N.; Fenoll, L.; García-Ruiz, P.A.; Varón, R.; Tudela, J.; Thorneley, R.N.F.; García-Cánovas, F. Stopped-flow and steady-state study of the diphenolase activity of mushroom tyrosinase. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 10497–10506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Molina, F.; Muñoz-Muñoz, J.L.; Varón, R.; Rodríguez-López, J.N.; García-Cánovas, F.; Tudela, J. A review on spectrophotometric methods for measuring the monophenolase and diphenolase activities of tyrosinase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 9739–9749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Thiessen, P.A.; Bolton, E.E.; Chen, J.; Fu, G.; Gindulyte, A.; Han, L.; He, J.; He, S.; Shoemaker, B.A.; et al. PubChem substance and compound databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D1202–D1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismaya, W.T.; Rozeboom, H.J.; Weijn, A.; Mes, J.J.; Fusetti, F.; Wichers, H.J.; Dijkstra, B.W. Crystal structure of Agaricus bisporus mushroom tyrosinase: Identity of the tetramer subunits and interaction with tropolone. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 5477–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maria-Solano, M.A.; Ortiz-Ruiz, C.V.; Muñoz-Muñoz, J.L.; Teruel-Puche, J.A.; Berna, J.; Garcia-Ruiz, P.A.; Garcia-Canovas, F. Further insight into the pH effect on the catalysis of mushroom tyrosinase. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2016, 125, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanner, M.F. Python: A programming language for software integration and development. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 1999, 17, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and autoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huey, R.; Morris, G.M.; Olson, A.J.; Goodsell, D.S. A semiempirical free energy force field with charge-based desolvation. J. Comput. Chem. 2007, 28, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Molina, P.; García-Molina, F.; Teruel-Puche, J.A.; Rodríguez-López, J.N.; García-Cánovas, F.; Muñoz-Muñoz, J.L. Considerations about the kinetic mechanism of tyrosinase in its action on monophenols: A review. Mol. Catal. 2022, 518, 112072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger, L. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.3; DeLano Scientific LLC.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Espín, J.C.; Varón, R.; Fenoll, L.G.; Gilabert, M.A.; García-Ruíz, P.A.; Tudela, J.; García-Cánovas, F. Kinetic characterization of the substrate specificity and mechanism of mushroom tyrosinase. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

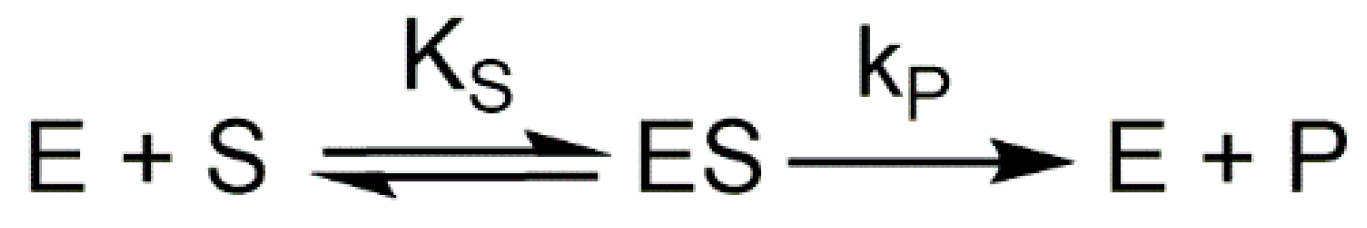




| Substrate | Enzyme | kcat (S−1) | KM (mM) | kcat/KM (M−1 S−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thymol | Mushroom (Agaricus Bisporus) | 161 4 | [26] | ||
| Carvacrol | Mushroom (Agaricus Bisporus) | 95 7 | [26] | ||
| Guaiacol | Mushroom (Agaricus Bisporus) | 5.40 0.14 | 4.65 0.39 | 1160 101 | [26] |
| Ferulic acid | Field Bean (Dolichos lablab) | 0.09 | [13] | ||
| Ferulic acid | Grean Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) extract | 0.23 | [27] |
| Ligand | Oxy Form | Met Form | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kd | d(O2-HO) | d(O2-oC) | d(Cu-OH) | d(π-π) | Kd | d(OH-OH) | d(Cu-OH) | d(π-π) | |
| Ferulic acid | 7.8 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 3.3 | - | 4.8 | 2.1 | 2.6 | - |
| Thymol | 0.61 | 1.7 | 3.9 | 3.4 | - | 0.92 | 2.1 | 3.4 | - |
| Carvacrol | 0.9 | 1.7 | 3.5 | - | - | 0.84 | 1.9 | 2.8 | 3.5 |
| Guaiacol | 7.3 | 1.7 | 3.9 | 3.4 | - | 2.2 | 1.6 | 3.1 | 3.3 |
| Eugenol | 3.9 | 1,7 | 3.8 | 3.4 | - | 0.63 | 1.6 | 2.5 | 3.6 |
| Isoeugenol | 3 | 1.8 | 3,6 | 3.4 | - | 2.4 | 1.9 | 2.8 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montenegro, M.F.; Teruel, J.A.; García-Molina, P.; Tudela, J.; Rodríguez-López, J.N.; García-Cánovas, F.; García-Molina, F. Molecular Docking Studies of Ortho-Substituted Phenols to Tyrosinase Helps Discern If a Molecule Can Be an Enzyme Substrate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6891. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136891
Montenegro MF, Teruel JA, García-Molina P, Tudela J, Rodríguez-López JN, García-Cánovas F, García-Molina F. Molecular Docking Studies of Ortho-Substituted Phenols to Tyrosinase Helps Discern If a Molecule Can Be an Enzyme Substrate. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(13):6891. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136891
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontenegro, María F., José A. Teruel, Pablo García-Molina, José Tudela, José Neptuno Rodríguez-López, Francisco García-Cánovas, and Francisco García-Molina. 2024. "Molecular Docking Studies of Ortho-Substituted Phenols to Tyrosinase Helps Discern If a Molecule Can Be an Enzyme Substrate" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 13: 6891. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136891
APA StyleMontenegro, M. F., Teruel, J. A., García-Molina, P., Tudela, J., Rodríguez-López, J. N., García-Cánovas, F., & García-Molina, F. (2024). Molecular Docking Studies of Ortho-Substituted Phenols to Tyrosinase Helps Discern If a Molecule Can Be an Enzyme Substrate. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(13), 6891. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136891






