Exercise Rescues Obesogenic-Related Genes in the Female Hypothalamic Arcuate Nucleus: A Potential Role of miR-211 Modulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
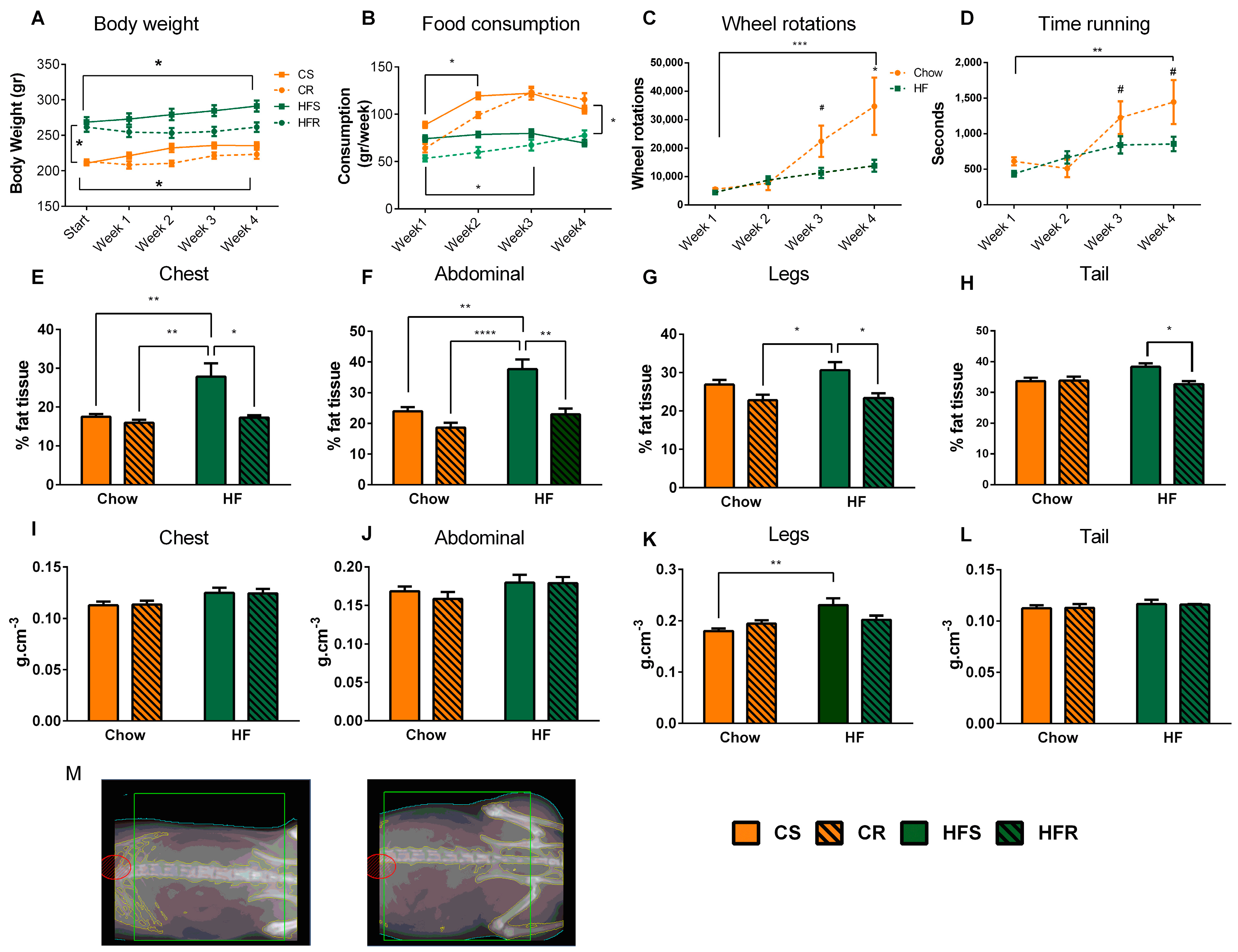
2.1. Voluntary Exercise Reduces Weight Gain and Body Fat in Diet-Induced Obese Rats
2.2. Voluntary Physical Activity, on the Background of HFD Affects the Expression of Functional Gene Families in the ARC
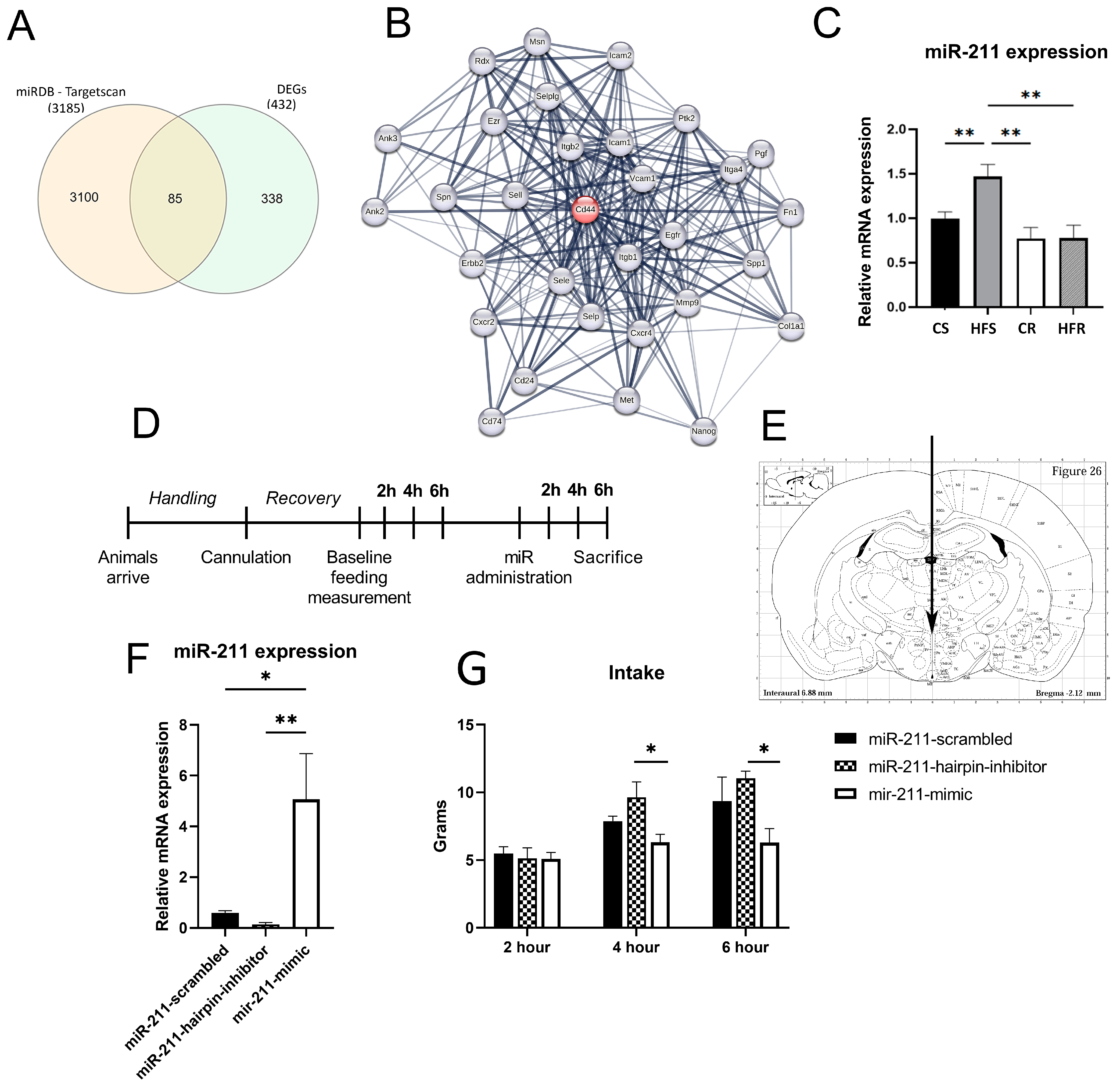
2.3. miR-211 Modulates Feeding Behavior
2.4. miR-211 Is Involved in Inflammation and Cell Cycle Regulation
3. Discussion
3.1. Voluntary Exercise Reduces Weight Gain and Body Fat in Diet-Induced Obese Rats
3.2. Voluntary Physical Activity, on the Background of HFD-DIO Affects the Expression of Functional Gene Families in the ARC
3.3. miR-211 Modulates Feeding Behavior and Is Involved in Inflammation Processes in the ARC
3.4. Voluntary vs. Obligatory Exercise in DIO Rats
4. Limitations, Future Directions, and Conclusions
5. Material and Methods
5.1. Animals
5.2. Voluntary Wheel Running after Diet-Induced Obesity
5.3. Intracerebroventricular Administration miR-211
5.3.1. Surgery and Cannula Implantation
5.3.2. Feeding Assessment
5.3.3. Pharmacological Compounds
5.4. Tissue Collection
5.4.1. Sacrifice
5.4.2. Neural Tissue Extraction
5.5. DEXA
5.6. Total RNA Extraction
5.6.1. Micro-RNA Quantification
5.6.2. RNA-Seq
5.6.3. RNA-Seq Analysis
5.7. Luciferase Assay
5.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Priest, C.; Tontonoz, P. Inter-organ cross-talk in metabolic syndrome. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jais, A.; Brüning, J.C. Arcuate Nucleus-Dependent Regulation of Metabolism-Pathways to Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus. Endocr. Rev. 2022, 43, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, T.L.; Sarman, B.; García-Cáceres, C.; Enriori, P.J.; Sotonyi, P.; Shanabrough, M.; Borok, E.; Argente, J.; Chowen, J.A.; Perez-Tilve, D.; et al. Synaptic input organization of the melanocortin system predicts diet-induced hypothalamic reactive gliosis and obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14875–14880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNay, D.E.G.; Briançon, N.; Kokoeva, M.V.; Maratos-Flier, E.; Flier, J.S. Remodeling of the arcuate nucleus energy-balance circuit is inhibited in obese mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Suk, K.; Yu, R.; Kim, M.S. Cellular Contributors to Hypothalamic Inflammation in Obesity. Mol. Cells 2020, 43, 431–437. [Google Scholar]
- Petridou, A.; Siopi, A.; Mougios, V. Exercise in the management of obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Liegro, C.M.; Schiera, G.; Proia, P.; Di Liegro, I. Physical Activity and Brain Health. Genes 2019, 10, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.E.; Király, M.A.; Atkinson, D.J.; D’Souza, A.M.; Vranic, M.; Riddell, M.C. Regular exercise prevents the development of hyperglucocorticoidemia via adaptations in the brain and adrenal glands in male Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 299, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, J.; Maggi, R.; Tromm, C.; Silva, L.; Luciano, T.; Marques, S.; Lira, F.; De Souza, C.; Pinho, R.A. Exercise training performed simultaneously to a high-fat diet reduces the degree of insulin resistance and improves adipoR1-2/APPL1 protein levels in mice. Lipids Health Dis. 2012, 11, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, R.L.; Jeon, J.Y.; Liu, F.-F.; Maratos-Flier, E. Voluntary exercise improves insulin sensitivity and adipose tissue inflammation in diet-induced obese mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 295, E586–E594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stranahan, A.M.; Lee, K.; Mattson, M.P. Central mechanisms of HPA axis regulation by voluntary exercise. Neuromolecular Med. 2008, 10, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKay, H.; Scott, C.A.; Duryea, J.D.; Baker, M.S.; Laritsky, E.; Elson, A.E.; Garland, T., Jr.; Fiorotto, M.L.; Chen, R.; Li, Y.; et al. DNA methylation in AgRP neurons regulates voluntary exercise behavior in mice. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, B.T.; Do, K.; Matsubara, T.; Wert, D.W.; Avery, M.J.; Langdon, E.M.; Zheng, D.; Huang, H. Voluntary exercise improves hypothalamic and metabolic function in obese mice. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 229, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobbo, V.C.; Engel, D.F.; Jara, C.P.; Mendes, N.F.; Haddad-Tovolli, R.; Prado, T.P.; Sidarta-Oliveira, D.; Morari, J.; Velloso, L.A.; Araujo, E.P. Interleukin-6 actions in the hypothalamus protects against obesity and is involved in the regulation of neurogenesis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.R.R.; Micheletti, T.O.; Katashima, C.K.; Lenhare, L.; Morari, J.; Moura-Assis, A.; de Lima-Júnior, J.C.; Camargo, J.A.; Passos, G.R.; Gaspar, R.S.; et al. Exercise activates the hypothalamic S1PR1–STAT3 axis through the central action of interleukin 6 in mice. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 9426–9436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, A.; Kisliouk, T.; Tabachnik, T.; Meiri, N.; Weller, A. Overweight and CpG methylation of the Pomc promoter in offspring of high-fat-diet-fed dams are not “reprogrammed” by regular chow diet in rats. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 4148–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapps, K.; Kisliouk, T.; Marco, A.; Weller, A.; Meiri, N. Dieting reverses histone methylation and hypothalamic AgRP regulation in obese rats. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabachnik, T.; Kisliouk, T.; Marco, A.; Meiri, N.; Weller, A. Thyroid hormone-dependent epigenetic regulation of melanocortin 4 receptor levels in female offspring of obese rats. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkholt, P.; Rigbolt, K.T.G.; Falkenhahn, M.; Hübschle, T.; Schwahn, U.; Fernandez-Cachon, M.L.; Schmidt, T.; Theis, S.; Hansen, H.H.; Hay-Schmidt, A.; et al. Global transcriptome analysis of rat hypothalamic arcuate nucleus demonstrates reversal of hypothalamic gliosis following surgically and diet induced weight loss. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, L.; Rabasa Lhoret, R.; Faraj, M.; Lavoie, M.-E.; Mill, J.; Perusse, L.; Vohl, M.-C. Differential epigenomic and transcriptomic responses in subcutaneous adipose tissue between low and high responders to caloric restriction. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, C.; Khaled, M.; Iliopoulos, D.; Janas, M.M.; Schubert, S.; Pinner, S.; Chen, P.H.; Li, S.; Fletcher, A.L.; Yokoyama, S.; et al. Intronic miR-211 assumes the tumor suppressive function of its host gene in melanoma. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.K.; Lin, C.H.; Kuo, Y.L.; Ger, L.P.; Cheng, H.C.; Yao, Y.C.; Hsiao, M.; Lu, P.J. MiR-211 determines brain metastasis specificity through SOX11/NGN2 axis in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncogene 2021, 40, 1737–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gan, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, D. LPS-induced downregulation of microRNA-204/211 upregulates and stabilizes Angiopoietin-1 mRNA in EA.hy926 endothelial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 6081–6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Wu, Q.; Ye, X.; Luo, H.; Yan, D.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, H.; Diao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wan, J. Role of miR-211 in Neuronal Differentiation and Viability: Implications to Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, T.; Nonaka, W.; Iwama, H.; Kobara, H.; Deguchi, K.; Masugata, H.; Touge, T.; Miyamoto, O.; Nakamura, T.; Itano, T.; et al. Light exercise without lactate elevation induces ischemic tolerance through the modulation of microRNA in the gerbil hippocampus. Brain Res. 2020, 1732, 146710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie, M.; Itoh, J.; Matsuzawa, A.; Ikawa, M.; Kiyonarim, H.; Kihara, M.; Suzuki, T.; Hiraoka, Y.; Ishino, F.; Kaneko-Ishino, T. Retrovirus-derived RTL5 and RTL6 genes are novel constituents of the innate immune system in the eutherian brain. Development 2022, 2149, dev200976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micevych, P.E.; Go, V.L.; Yaksh, T.L.; Finkelstein, J. In vitro, release of cholecystokinin from hypothalamus and frontal cortex of Sprague-Dawley, Zucker lean (Fa/-) and obese (fa/fa) rats. Peptides 1984, 5, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Hokazono, C.; Tokizawa, K.; Marui, S.; Iwata, M.; Lira, V.A.; Suzuki, K.; Miura, S.; Nagashima, K.; Okutsu, M. Muscle-derived SDF-1α/CXCL12 modulates endothelial cell proliferation but not exercise training-induced angiogenesis. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2019, 317, R770–R779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppo, M.; Bandinelli, M.; Chiostri, M.; Modesti, P.A.; Poggesi, L.; Boddi, M. T Cell-based RAS Activity and Insulin Levels in Obese Subjects with Low Grade Inflammation. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 363, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Karin, M.; Bai, H.; Cai, D. Hypothalamic IKKβ/NF-κB and ER stress link overnutrition to energy imbalance and obesity. Cell 2008, 135, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Li, M.; Tan, X.; Xiang, P.; Wang, H.; Luo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, Z.; Xia, H.; et al. miR-211-5p alleviates focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by down-regulating the expression of COX2. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 113983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Chen, N.; Yin, B.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, T.; Guo, S.; Deng, G. MicroRNA-211 regulates the expression of TAB1 and inhibits the NF-κB signaling pathway in lipopolysaccharide-induced endometritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aili, D.; Wu, T.; Gu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, W. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 suppresses the progression of osteoarthritis by mediating the miR-211-5p/TCF4 axis in vitro. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, J.E.; Blair, S.N.; Jakicic, J.M.; Manore, M.M.; Rankin, J.W.; Smith, B.K. Appropriate physical activity intervention strategies for weight loss and prevention of weight regain for adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foright, R.M.; Johnson, G.C.; Kahn, D.; Charleston, C.A.; Presby, D.M.; Bouchet, C.A.; Wellberg, E.A.; Sherk, V.D.; Jackman, M.R.; Greenwood, B.N.; et al. Compensatory eating behaviors in male and female rats in response to exercise training. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2020, 319, R171–R183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savvidis, C.; Tournis, S.; Dede, A.D. Obesity and bone metabolism. Hormones 2018, 17, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, N.; Kim, K. Effects of aerobic and resistance exercise on myokines in high fat diet-induced middle-aged obese rats. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2685–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.; Bouter, L.M.; McQuillan, G.M.; Wener, M.H.; Harris, T.B. Low-grade systemic inflammation in overweight children. Pediatrics 2001, 107, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merk, M.; Zierow, S.; Leng, L.; Das, R.; Du, X.; Schulte, W.; Fan, J.; Lue, H.; Chen, Y.; Xiong, H.; et al. The D-dopachrome tautomerase (DDT) gene product is a cytokine and functional homolog of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E577–E585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaler, J.P.; Yi, C.X.; Schur, E.A.; Guyenet, S.J.; Hwang, B.H.; Dietrich, M.O.; Zhao, X.; Sarruf, D.A.; Izgur, V.; Maravilla, K.R.; et al. Obesity is associated with hypothalamic injury in rodents and humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, J.C.; Coope, A.; Morari, J.; Cintra, D.E.; Roman, E.A. High-Fat Diet Induces apoptosis of hypothalamic neurons. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, 5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, S.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, S.; Price, R.L.; Singh, U.P. Adipocyte, Immune Cells, and miRNA Crosstalk: A Novel Regulator of Metabolic Dysfunction and Obesity. Cells 2021, 10, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, A.; Gomes, J.; Roque, F.; Fernandes, T.; de Oliveira, E.M. MicroRNAs in Obesity-Associated Disorders: The Role of Exercise Training. Obes. Facts 2022, 15, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falzone, L.; Grimaldi, M.; Celentano, E.; Augustin, L.S.A.; Libra, M. Identification of Modulated MicroRNAs Associated with Breast Cancer, Diet, and Physical Activity. Cancers 2020, 12, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, B.D.; Arem, H.; Hubal, M.J.; Cartmel, B.; Li, F.; Harrigan, M.; Sanft, T.; Cheng, C.J.; Pusztai, L.; Irwin, M.L. Exercise and weight loss interventions and miRNA expression in women with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 170, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, N.L.; Fernández-Tussy, P.; Varela, L.; Cardelo, M.P.; Shanabrough, M.; Aryal, B.; de Cabo, R.; Suárez, Y.; Horvath, T.L.; Fernández-Hernando, C. microRNA-33 controls hunger signaling in hypothalamic AgRP neurons. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leasure, J.L.; Jones, M. Forced and voluntary exercise differentially affect brain and behavior. Neuroscience 2008, 156, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlard, P.A.; Cotman, C.W. Voluntary exercise protects against stress-induced decreases in brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein expression. Neuroscience 2004, 124, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, I.; Chatterjee, A. Recent Advances in miRNA Delivery Systems. Methods Protoc. 2021, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C.; Pennisi, M.; Topple, A. Bregma, lambda and the interaural midpoint in stereotaxic surgery with rats of different sex, strain and weight. J. Neurosci. Methods 1985, 13, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazut, N.; Rapps, K.; Weller, A.; Susswein, A.J. Nitric oxide and l-arginine have mixed effects on mammalian feeding in condition of a high motivation to feed. Appetite 2021, 158, 105011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaitin, D.A.; Kenigsberg, E.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Elefant, N.; Paul, F.; Zaretsky, I.; Mildner, A.; Cohen, N.; Jung, S.; Tanay, A.; et al. Massively parallel single-cell RNA-seq for marker-free decomposition of tissues into cell types. Science 2014, 343, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keren-Shaul, H.; Kenigsberg, E.; Jaitin, D.A.; David, E.; Paul, F.; Tanay, A.; Amit, I. MARS-seq2.0: An experimental and analytical pipeline for indexed sorting combined with single-cell RNA sequencing. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 1841–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinz, S.; Benner, C.; Spann, N.; Bertolino, E.; Lin, Y.C.; Laslo, P.; Cheng, J.X.; Murre, C.; Singh, H.; Glass, C.K. Simple combinations of lineage-determining transcription factors prime cis-regulatory elements required for macrophage and B cell identities. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.Y.; Tan, C.M.; Kou, Y.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Meirelles, G.V.; Clark, N.R.; Ma’ayan, A. Enrichr: Interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W90–W97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Bailey, A.; Kuleshov, M.V.; Clarke, D.J.B.; Evangelista, J.E.; Jenkins, S.L.; Lachmann, A.; Wojciechowicz, M.L.; Kropiwnicki, E.; Jagodnik, K.M.; et al. Gene set knowledge discovery with Enrichr. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisliouk, T.; Yosefi, S.; Meiri, N. MiR-138 inhibits EZH2 methyltransferase expression and methylation of histone H3 at lysine 27, and affects thermotolerance acquisition. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 33, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marco, A.; Kisliouk, T.; Weller, A.; Meiri, N. High fat diet induces hypermethylation of the hypothalamic Pomc promoter and obesity in post-weaning rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38, 2844–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rapps, K.; Marco, A.; Pe’er-Nissan, H.; Kisliouk, T.; Stemp, G.; Yadid, G.; Weller, A.; Meiri, N. Exercise Rescues Obesogenic-Related Genes in the Female Hypothalamic Arcuate Nucleus: A Potential Role of miR-211 Modulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7188. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137188
Rapps K, Marco A, Pe’er-Nissan H, Kisliouk T, Stemp G, Yadid G, Weller A, Meiri N. Exercise Rescues Obesogenic-Related Genes in the Female Hypothalamic Arcuate Nucleus: A Potential Role of miR-211 Modulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(13):7188. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137188
Chicago/Turabian StyleRapps, Kayla, Asaf Marco, Hilla Pe’er-Nissan, Tatiana Kisliouk, Gabrielle Stemp, Gal Yadid, Aron Weller, and Noam Meiri. 2024. "Exercise Rescues Obesogenic-Related Genes in the Female Hypothalamic Arcuate Nucleus: A Potential Role of miR-211 Modulation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 13: 7188. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137188
APA StyleRapps, K., Marco, A., Pe’er-Nissan, H., Kisliouk, T., Stemp, G., Yadid, G., Weller, A., & Meiri, N. (2024). Exercise Rescues Obesogenic-Related Genes in the Female Hypothalamic Arcuate Nucleus: A Potential Role of miR-211 Modulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(13), 7188. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137188






