Protective Effect of Arzanol against H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress Damage in Differentiated and Undifferentiated SH-SY5Y Cells
Abstract
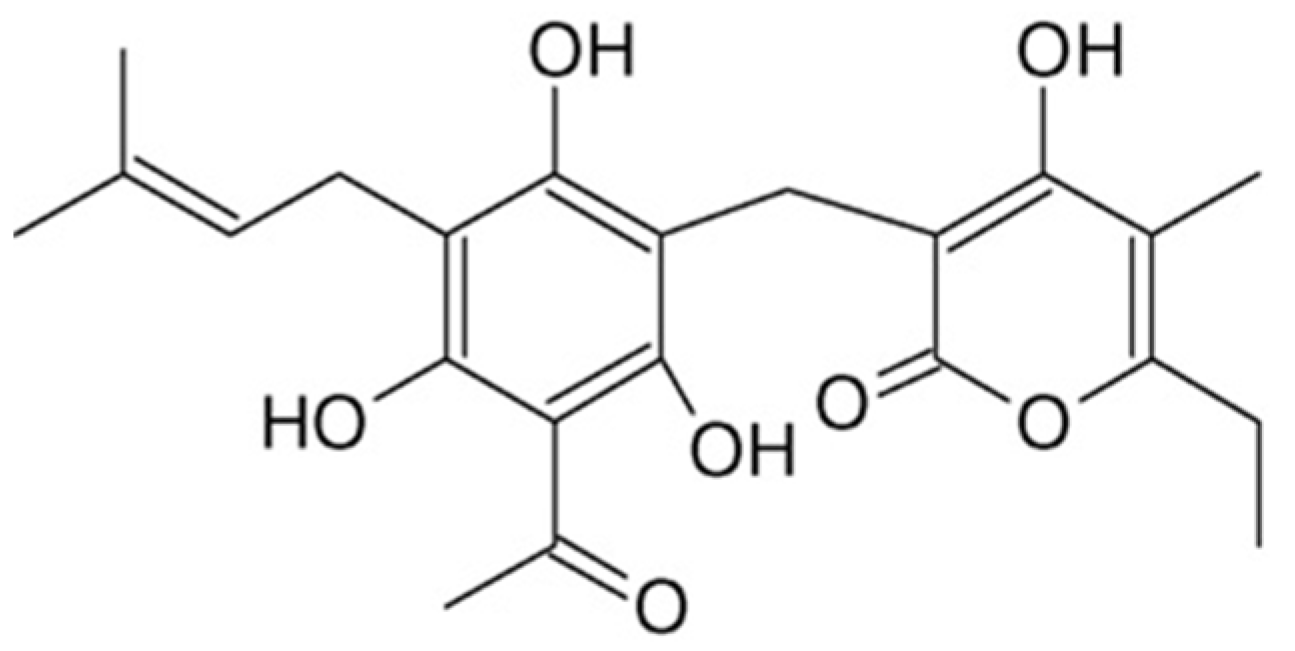
:1. Introduction
2. Results
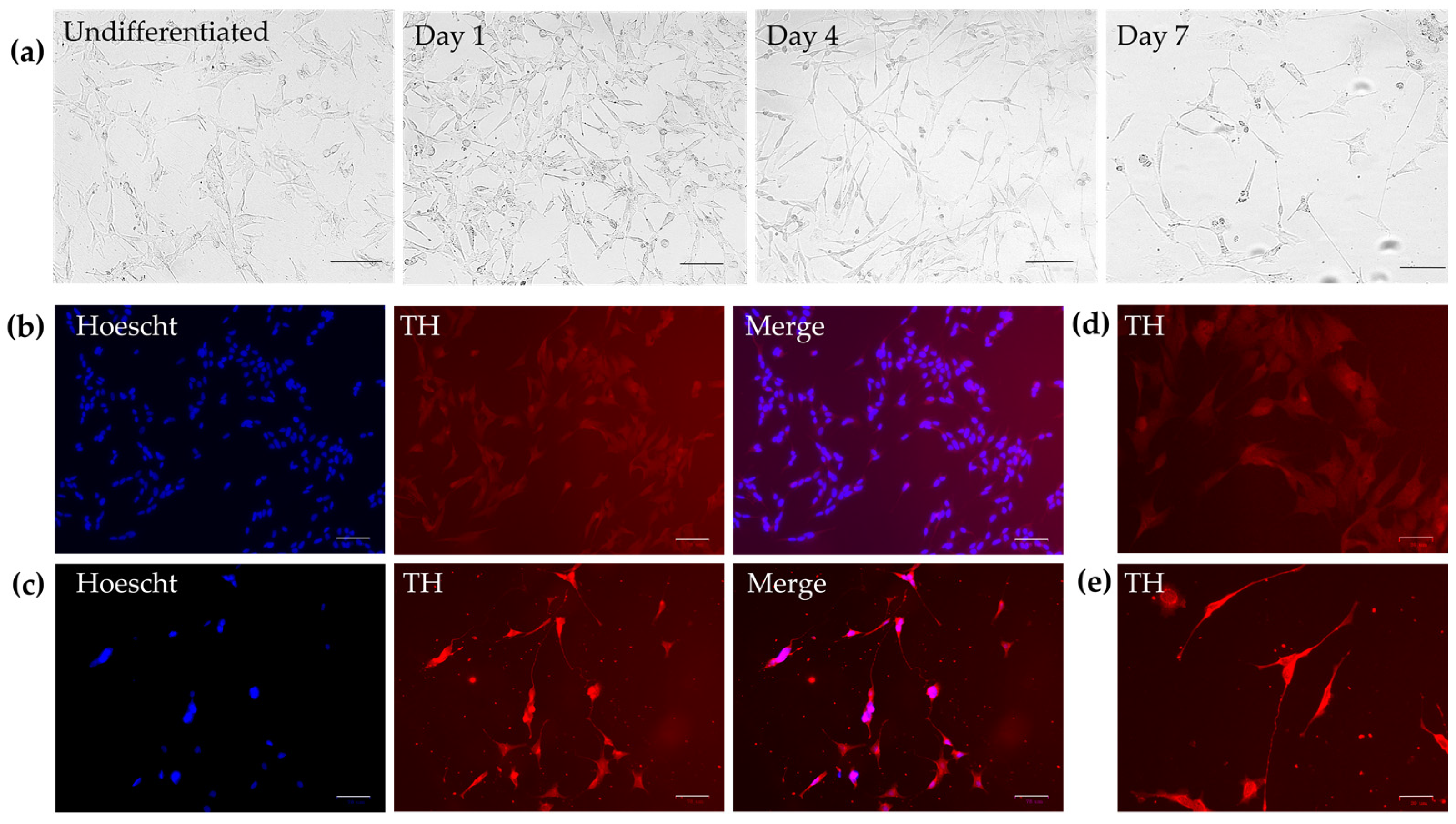
2.1. Cell Differentiation
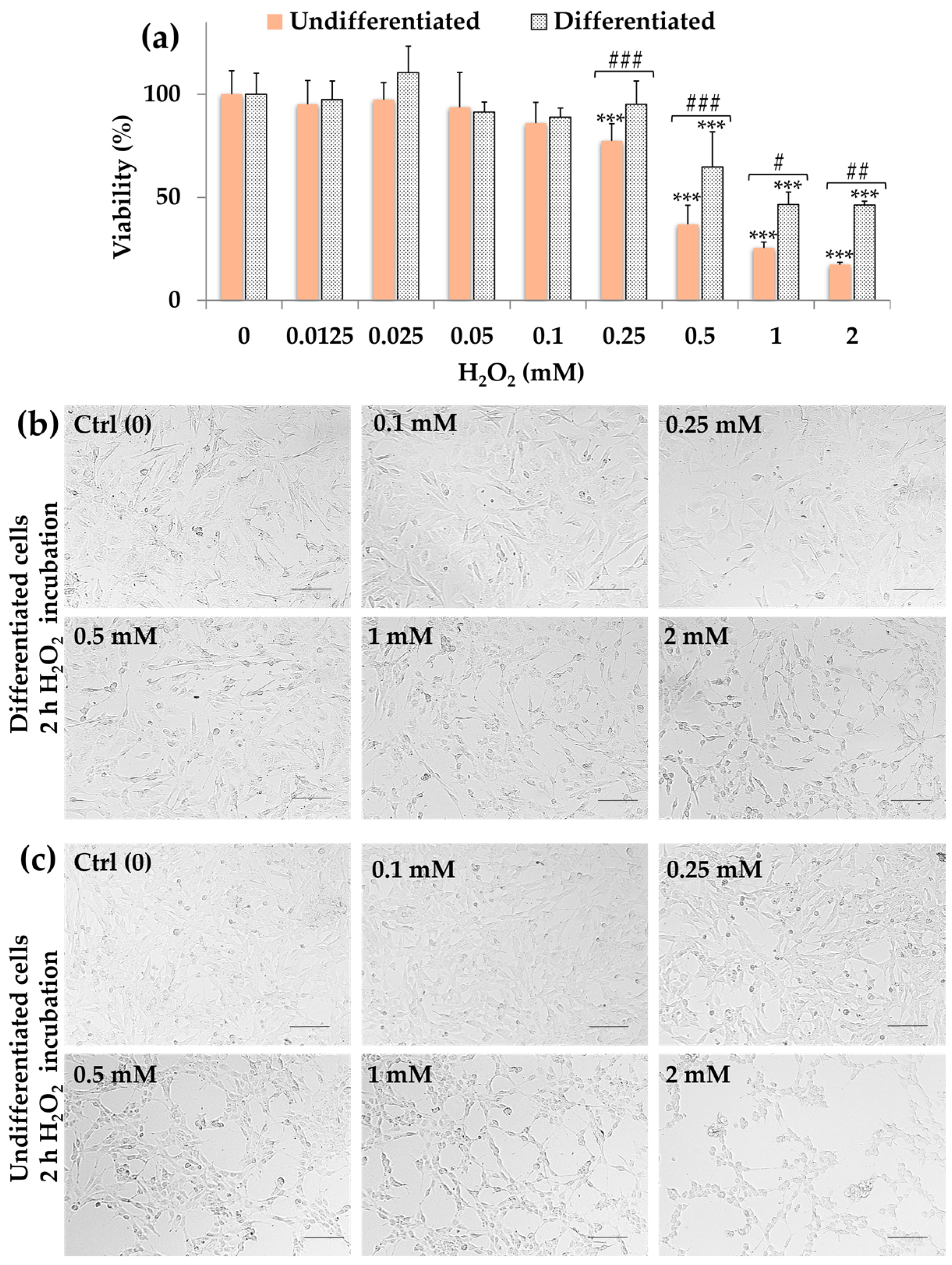
2.2. Effect of H2O2 on SH-SY5Y Cell Viability (MTT Assay)
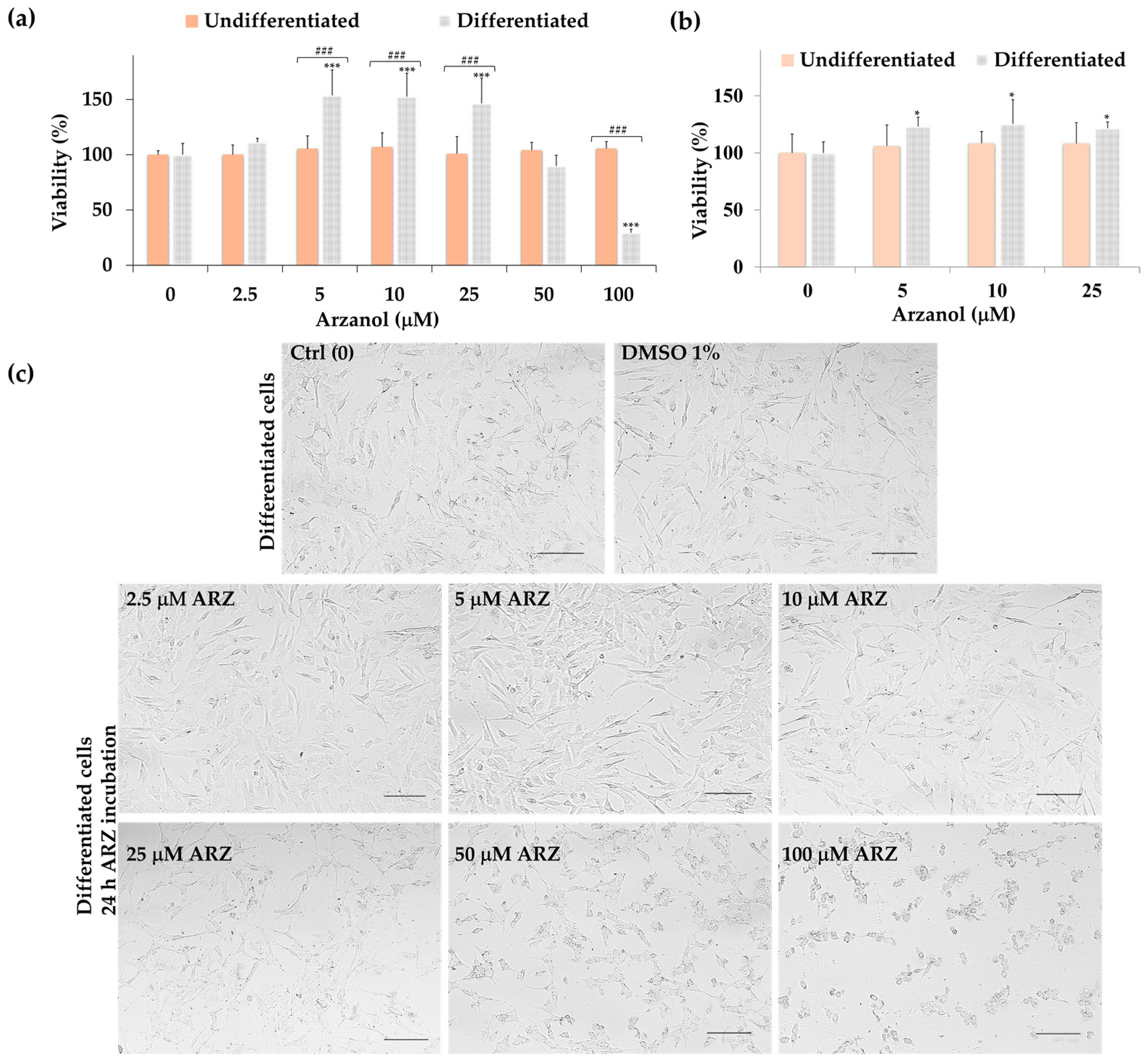
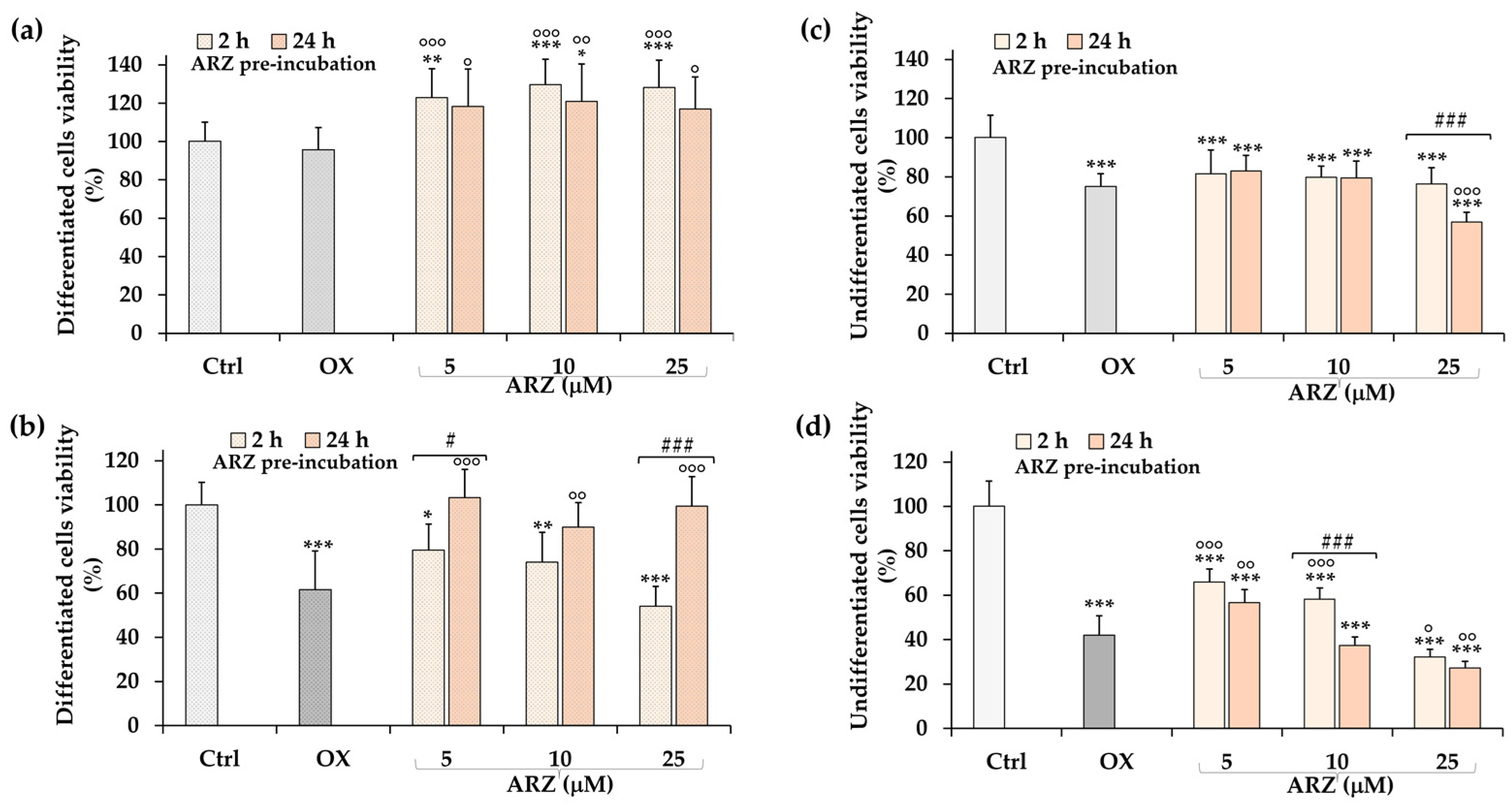
2.3. Effect of Arzanol on SH-SY5Y Cell Viability (MTT Assay)
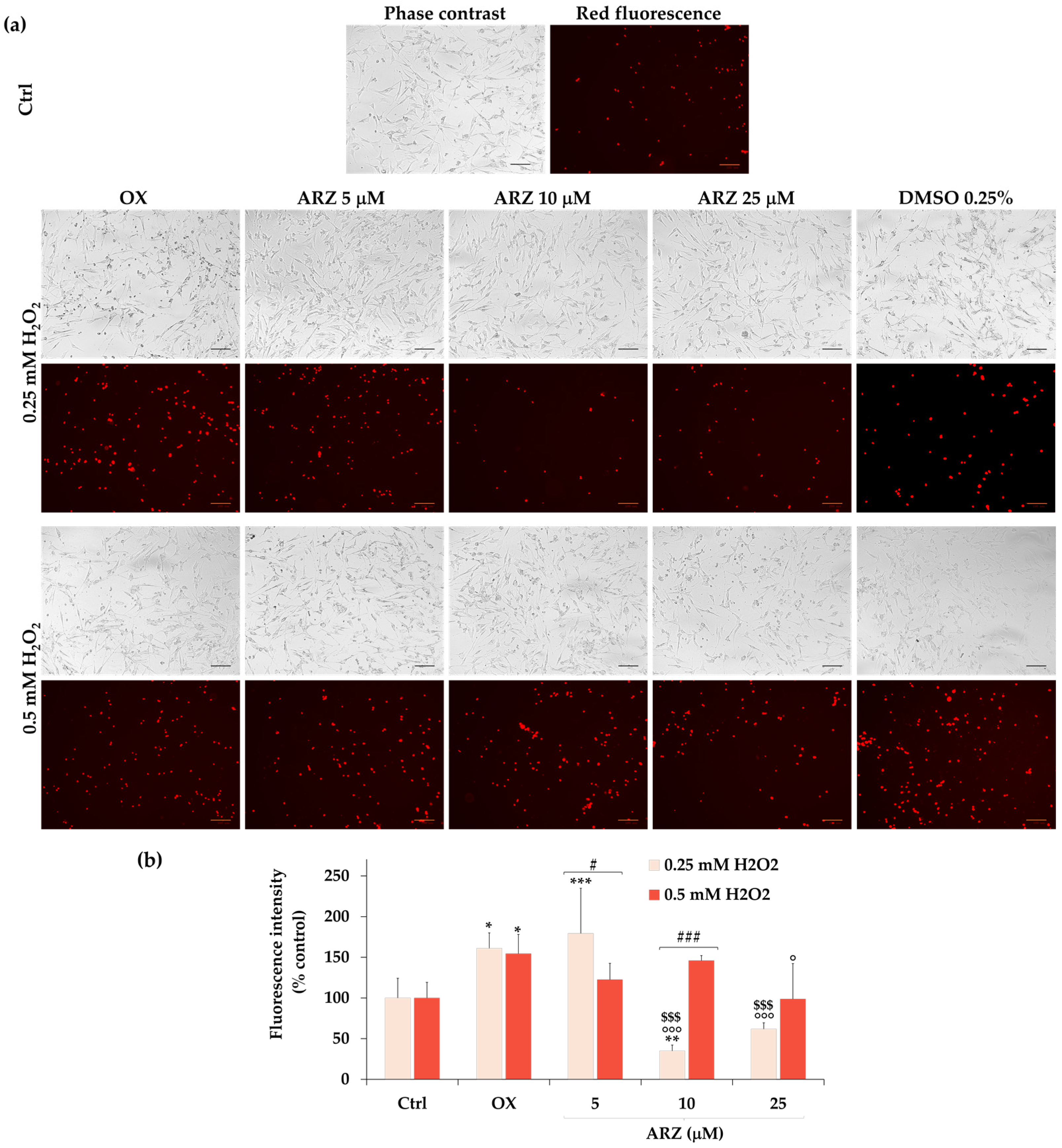
2.4. Protective Role of Arzanol against H2O2 Cytotoxicity
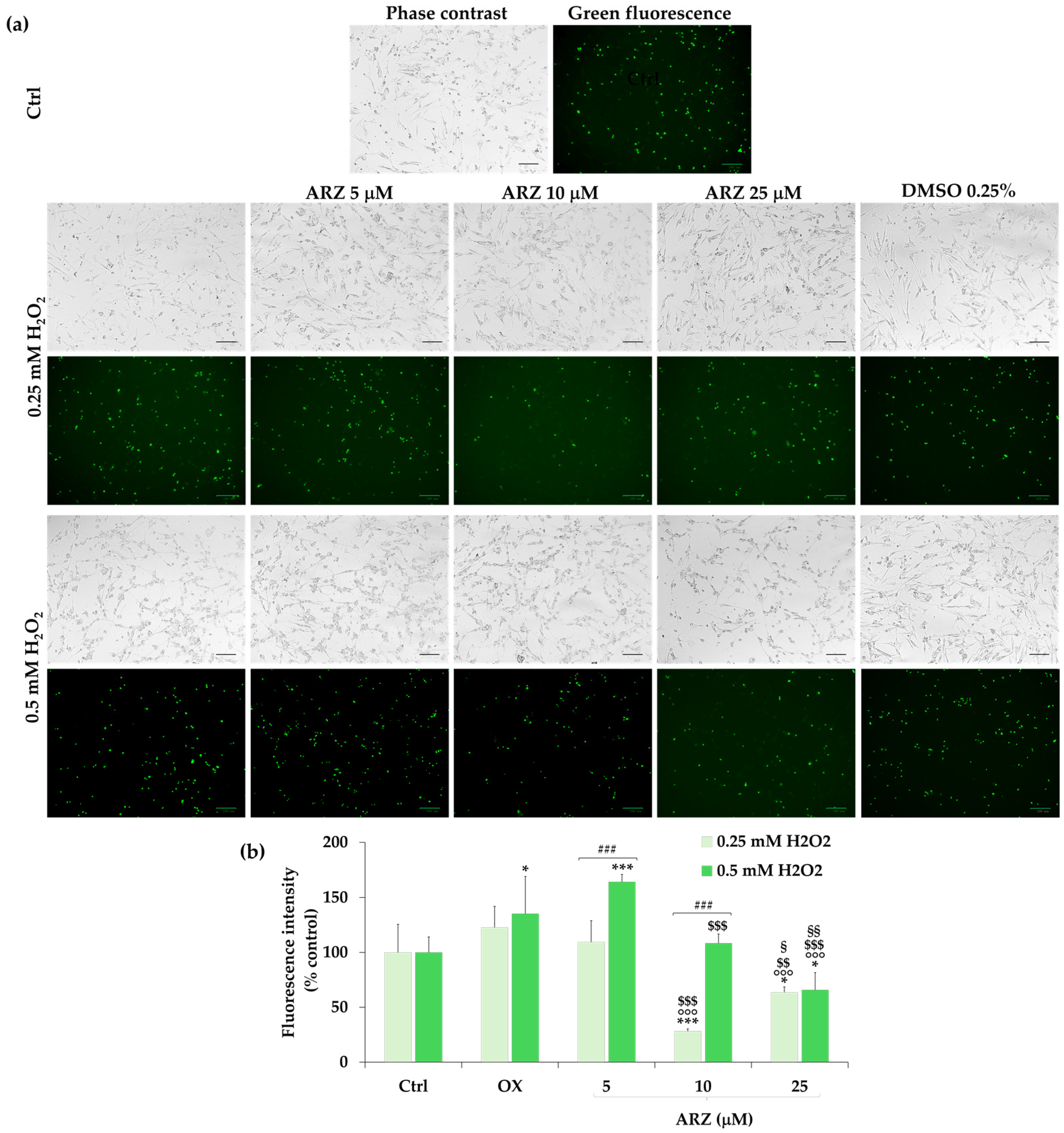
2.5. Protective Role of Arzanol against H2O2-Induced ROS Generation
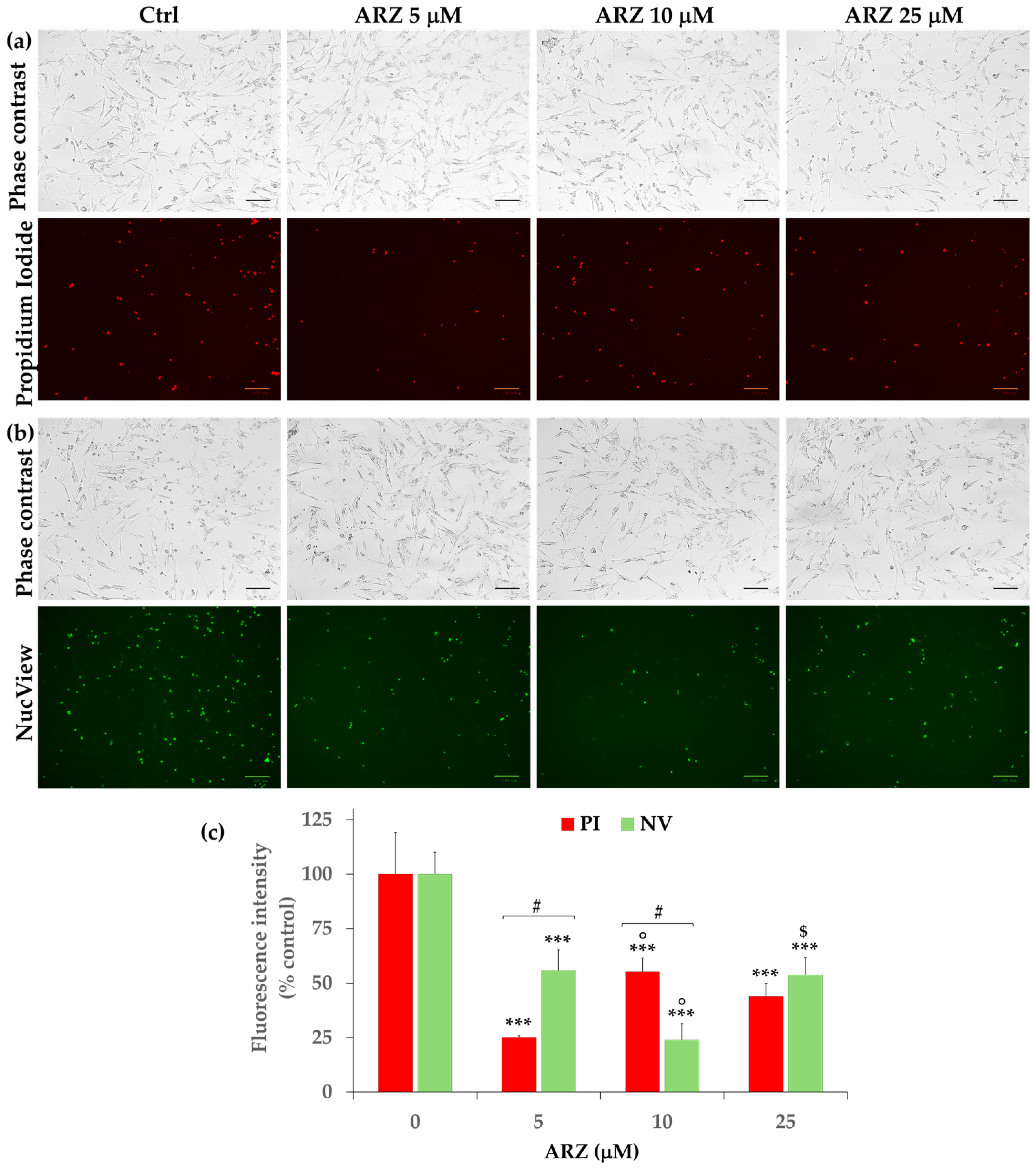
2.6. Protective Effect of Arzanol against Apoptosis
2.7. In Silico Evaluation of Physicochemical and Pharmacokinetic Properties of Arzanol
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Arzanol Extraction and Isolation
4.3. SH-SY5Y Cell Culture
4.4. Neuronal Differentiation Induction
4.5. Immunofluorescence
4.6. Cell Viability (MTT Assay)
4.6.1. Effect of H2O2 and Arzanol on Cell Viability
4.6.2. Protective Effect of Arzanol against H2O2-Induced Neuronal Cytotoxicity
4.7. H2O2-Induced ROS Generation
4.8. Propidium Iodide and NucView Apoptosis Assays
4.9. In Silico Evaluation of the Physicochemical and Pharmacokinetic Properties of Arzanol
4.10. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scarian, E.; Viola, C.; Dragoni, F.; Di Gerlando, R.; Rizzo, B.; Diamanti, L.; Gagliardi, S.; Bordoni, M.; Pansarasa, O. New insights into oxidative stress and inflammatory response in neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayne, K.; White, J.A.; McMurran, C.E.; Rivera, F.J.; de la Fuente, A.G. Aging and neurodegenerative disease: Is the adaptive immune system a friend or foe? Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 572090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; O, W.; Li, W.; Jiang, Z.-G.; Ghanbari, H.A. Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 24438–24475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olufunmilayo, E.O.; Gerke-Duncan, M.B.; Holsinger, R.M.D. Oxidative stress and antioxidants in neurodegenerative disorders. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Kukreti, S. Oxidative stress: A key modulator in neurodegenerative diseases. Molecules 2019, 24, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lushchak, V.I.; Storey, K.B. Oxidative stress concept updated: Definitions, classifications, and regulatory pathways implicated. EXCLI J. 2021, 20, 956–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H. Hydrogen peroxide as a central redox signaling molecule in physiological oxidative stress: Oxidative eustress. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H. Oxidative stress: Concept and some practical aspects. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Fang, J.; Li, S.; Gaur, U.; Xing, X.; Wang, H.; Zheng, W. Artemisinin attenuated hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced oxidative injury in SH-SY5Y and hippocampal neurons via the activation of AMPK Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, T.; Melo, E.P.; Chambers, J.E.; Avezov, E. Intracellular sources of ROS/H2O2 in health and neurodegeneration: Spotlight on endoplasmic reticulum. Cells 2021, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, M.; Futerman, A.H. The brain lipidome in neurodegenerative lysosomal storage disorders. Biochem. Biophys. Commun. 2018, 504, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, A.H.; Dar, K.B.; Anees, S.; Zargar, M.A.; Masood, A.; Sofi, M.A.; Ganie, S.A. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegenerative diseases; a mechanistic insight. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 74, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.J.; Lv, C.H.; Chen, Z.; Shi, M.; Zeng, C.X.; Hou, D.X.; Qin, S. The regulatory effect of phytochemicals on chronic diseases by targeting Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingappa, S.; Shivakumar, M.S.; Manivasagam, T.; Somasundaram, S.T.; Seedevi, P. Neuroprotective effect of Epalrestat on hydrogen peroxide-induced neurodegeneration in SH-SY5Y cellular model. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen-Thi, P.T.; Vo, T.K.; Pham, T.H.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Van Vo, G. Natural flavonoids as potential therapeutics in the management of Alzheimer’s disease: A review. 3 Biotech. 2024, 14, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Paolo, M.; Papi, L.; Gori, F.; Turillazzi, E. Natural products in neurodegenerative diseases: A great promise but an ethical challenge. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, P.; Gogia, N.; Singh, A. Exploring the efficacy of natural products in alleviating Alzheimer’s disease. Neural. Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, R.; Ji, E.; Kim, S.Y. Phytochemicals that regulate neurodegenerative disease by targeting neurotrophins: A comprehensive review. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 814068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Jahan, S.; Alshahrani, S.; Alshehri, B.M.; Sameer, A.S.; Arafah, A.; Ahmad, A.; Rehman, M.U. Phytotherapeutic agents for neurodegenerative disorders: A neuropharmacological review. Phytomedicine 2021, 581–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornano, L.; Venditti, A.; Sanna, C.; Ballero, M.; Maggi, F.; Lupidi, G.; Bianco, A. Chemical composition and biological activity of the essential oil from Helichrysum microphyllum Cambess. ssp. Tyrrhenicum Bacch., Brullo e Giusso growing in La Maddalena Archipelago, Sardinia. J. Oleo Sci. 2015, 64, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appendino, G.; Ottino, M.; Marquez, N.; Bianchi, F.; Giana, A.; Ballero, M.; Sterner, O.; Fiebich, B.L.; Munoz, E. Arzanol, an antiinflammatory and anti-HIV-1 phloroglucinol alpha-pyrone from Helichrysum italicum ssp. microphyllum. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, J.; Koeberle, A.; Dehm, F.; Pollastro, F.; Appendino, G.; Northoff, H.; Rossi, A.; Sautebin, L.; Werz, O. Arzanol, a prenylated heterodimeric phloroglucinyl pyrone, inhibits eicosanoid biosynthesis and exhibits anti-inflammatory efficacy in vivo. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 81, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deitersen, J.; Berning, L.; Stuhldreier, F.; Ceccacci, S.; Schlütermann, D.; Friedrich, A.; Wu, W.; Sun, Y.; Böhler, P.; Berleth, N.; et al. High-throughput screening for natural compound-based autophagy modulators reveals novel chemotherapeutic mode of action for arzanol. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Gaudio, F.; Pollastro, F.; Mozzicafreddo, M.; Riccio, R.; Minassi, A.; Monti, M.C. Chemoproteomic fishing identifies arzanol as a positive modulator of brain glycogen phosphorylase. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 12863–12866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mammino, L. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding and conformational preferences of arzanol-An antioxidant acylphloroglucinol. Molecules 2017, 22, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, A.; Deiana, M.; Atzeri, A.; Corona, G.; Incani, A.; Melis, M.P.; Appendino, G.; Dessì, M.A. Evaluation of the antioxidant and cytotoxic activity of arzanol, a prenylated alpha-pyrone-phloroglucinol etherodimer from Helichrysum italicum subsp. microphyllum. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2007, 165, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, A.; Atzeri, A.; Nieddu, M.; Appendino, G. New insights into the antioxidant activity and cytotoxicity of arzanol and effect of methylation on its biological properties. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2017, 205, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kothavade, P.S.; Nagmoti, D.M.; Bulani, V.D.; Juvekar, A.R. Arzanol, a potent mPGES-1 inhibitor: Novel anti-inflammatory agent. ScientificWorldJournal 2013, 2013, 986429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, A.; Pollastro, F.; Atzeri, A.; Appendino, G.; Melis, M.P.; Deiana, M.; Incani, A.; Loru, D.; Dessì, M.A. Protective role of arzanol against lipid peroxidation in biological systems. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2011, 164, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piras, F.; Sogos, V.; Pollastro, F.; Appendino, G.; Rosa, A. Arzanol, a natural phloroglucinol α-pyrone, protects HaCaT keratinocytes against H2O2-induced oxidative stress, counteracting cytotoxicity, reactive oxygen species generation, apoptosis, and mitochondrial depolarization. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2024, 44, 720–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgonetti, V.; Caroli, C.; Governa, P.; Virginia, B.; Pollastro, F.; Franchini, S.; Manetti, F.; Les, F.; López, V.; Pellati, F.; et al. Helichrysum stoechas (L.) Moench reduces body weight gain and modulates mood disorders via inhibition of silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1) by arzanol. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 4304–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Q.Q.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, E.J. Protective effects and mechanisms of pectolinarin against H2O2-induced oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y neuronal cells. Molecules 2023, 28, 5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenzen, S.; Lushchak, V.I.; Scholz, F. The pro-radical hydrogen peroxide as a stable hydroxyl radical distributor: Lessons from pancreatic beta cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2022, 96, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.; Lee, H.; Noh, J.S.; Jin, C.Y.; Kim, G.Y.; Hyun, J.W.; Leem, S.H.; Choi, Y.H. Hemistepsin A protects human keratinocytes against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress through activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 691, 108512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Mao, X. Chitopentaose protects HaCaT cells against H2O2-induced oxidative damage through modulating MAPKs and Nrf2/ARE signaling pathways. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 72, 104086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedler, J.L.; Helson, L.; Spengler, B.A. Morphology and growth, tumorigenicity, and cytogenetics of human neuroblastoma cells in continuous culture. Cancer Res. 1973, 33, 2643–2652. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Suarez, L.; Awabdh, S.A.; Coumoul, X.; Chauvet, C. The SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell line, a relevant in vitro cell model for investigating neurotoxicology in human: Focus on organic pollutants. Neurotoxicology 2022, 92, 131–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, J.I.; Köglsberger, S.; Trefois, C.; Boyd, O.; Baumuratov, A.S.; Buck, L.; Balling, R.; Antony, P.M. Characterization of differentiated SH-SY5Y as neuronal screening model reveals increased oxidative vulnerability. J. Biomol. Screen. 2016, 21, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Carballo, G.; Moreno, L.; Masiá, S.; Pérez, P.; Barettino, D. Activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway by retinoic acid is required for neural differentiation of SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25297–25304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogos, V.; Caria, P.; Porcedda, C.; Mostallino, R.; Piras, F.; Miliano, C.; De Luca, M.A.; Castelli, M.P. Human neuronal cell lines as an in vitro toxicological tool for the evaluation of novel psychoactive substances. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, Y.T.; Lau, W.K.; Yu, M.S.; Lai, C.S.; Yeung, S.C.; So, K.F.; Chang, R.C. Effects of all-trans-retinoic acid on human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma as in vitro model in neurotoxicity research. Neurotoxicology 2009, 30, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinicola, S.; Mariggiò, M.A.; Morabito, C.; Guarnieri, S.; Cucina, A.; Pasqualato, A.; D’Anselmi, F.; Proietti, S.; Coluccia, P.; Bizzarri, M. Grape seed extract triggers apoptosis in Caco-2 human colon cancer cells through reactive oxygen species and calcium increase: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase involvement. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meenambal, R.; Kruk, T.; Gurgul, J.; Warszyński, P.; Jantas, D. Neuroprotective effects of polyacrylic acid (PAA) conjugated cerium oxide against hydrogen peroxide- and 6-OHDA-induced SH-SY5Y cell damage. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PubChem-NIH. 2023. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- SwissADME. Available online: http://swissadme.ch/index.php (accessed on 27 May 2024).
- pkCSM-Pharmacokinetics. Available online: https://biosig.lab.uq.edu.au/pkcsm/prediction (accessed on 24 May 2024).
- Chen, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, H.; An, J. Neuroprotective effects of natural compounds on neurotoxin-induced oxidative stress and cell apoptosis. Nutr. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 1078–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tie, F.; Fu, Y.; Hu, N.; Wang, H. Silibinin protects against H2O2-induced oxidative damage in SH-SY5Y cells by improving mitochondrial function. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.M.; Yang, C.Q.; Cheng, B.H.; Chen, J.; Bai, B. Orexin-A protects SH-SY5Y cells against H2O2-induced oxidative damage via the PI3K/MEK1/2/ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2018, 32, 2058738418785739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschelli, S.; Lanuti, P.; Ferrone, A.; Gatta, D.M.P.; Speranza, L.; Pesce, M.; Grilli, A.; Cacciatore, I.; Ricciotti, E.; Di Stefano, A.; et al. Modulation of apoptotic cell death and neuroprotective effects of glutathione-L-dopa codrug against H2O2-induced cellular toxicity. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Aranguren, L.; Marwah, M.K.; Nadeem, S. Neuroprotective effects of mitochondrial-targeted hydrogen sulphide donor, AP39 on H2O2-induced oxidative stress in human neuroblastoma SHSY5Y cell line. Adv. Redox Res. 2021, 3, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafaru, M.S.; Nordin, N.; Rosli, R.; Shaari, K.; Bako, H.Y.; Noor, N.M.; Abdull Razis, A.F. Prospective role of mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in mediating GMG-ITC to reduce cytotoxicity in H2O2-induced oxidative stress in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 119, 109445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunzler, A.; Zeidán-Chuliá, F.; Gasparotto, J.; Girardi, C.S.; Klafke, K.; Petiz, L.L.; Bortolin, R.C.; Rostirolla, D.C.; Zanotto-Filho, A.; de Bittencourt Pasquali, M.A.; et al. Changes in cell cycle and up-regulation of neuronal markers during SH-SY5Y neurodifferentiation by retinoic acid are mediated by reactive species production and oxidative stress. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 6903–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Liu, J.; Fu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; He, D.; Ran, X.; Yan, X.; Du, J.; Meng, T.; et al. α-Cyperone attenuates H2O2-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells via activation of Nrf2. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, S.; Krishnaswamy, S.; Devashya, V.; Sethuraman, S.; Krishnan, U.M. Influence of membrane lipid composition on flavonoid-membrane interactions: Implications on their biological activity. Prog. Lipid Res. 2015, 58, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlazzo, N.; Cirmi, S.; Maugeri, A.; Russo, C.; Lombardo, G.E.; Gangemi, S.; Calapai, G.; Mollace, V.; Navarra, M. Neuroprotective effect of bergamot juice in 6-OHDA-induced SH-SY5Y cell death, an in vitro model of Parkinson’s disease. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, H.R.; Yun, J.M. Neuroprotective effects of hesperetin on H2O2-induced damage in neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2023, 17, 899–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Martínez, J.D.; Valdés, A.; Gallego, R.; Suárez-Montenegro, Z.J.; Alarcón, M.; Ibañez, E.; Alvarez-Rivera, G.; Cifuentes, A. Blood-brain barrier permeability study of potential neuroprotective compounds recovered from plants and agri-food by-908 products. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 924596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Villa, F.X.; Durán-Iturbide, N.A.; Ávila-Zárraga, J.G. Synthesis, molecular docking, and in silico ADME/Tox profiling studies of new 1-aryl-5-(3-azidopropyl)indol-4-ones: Potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 106, 104497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavelescu, L.A. On reactive oxygen species measurement in living systems. J. Med. Life 2015, 8, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, D.E.; Blundell, T.L.; Ascher, D.B. pkCSM: Predicting small-molecule pharmacokinetic and toxicity properties using graph-based signatures. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4066–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piras, F.; Sogos, V.; Pollastro, F.; Rosa, A. Protective Effect of Arzanol against H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress Damage in Differentiated and Undifferentiated SH-SY5Y Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137386
Piras F, Sogos V, Pollastro F, Rosa A. Protective Effect of Arzanol against H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress Damage in Differentiated and Undifferentiated SH-SY5Y Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(13):7386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137386
Chicago/Turabian StylePiras, Franca, Valeria Sogos, Federica Pollastro, and Antonella Rosa. 2024. "Protective Effect of Arzanol against H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress Damage in Differentiated and Undifferentiated SH-SY5Y Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 13: 7386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137386
APA StylePiras, F., Sogos, V., Pollastro, F., & Rosa, A. (2024). Protective Effect of Arzanol against H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress Damage in Differentiated and Undifferentiated SH-SY5Y Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(13), 7386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137386







