Associations between Diabetes Mellitus and Selected Cancers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Diabetes Mellitus and Cancer
2.1. Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Cancer
2.2. Type 3c Diabetes Mellitus and Cancer
2.3. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Cancer
2.4. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cancer
2.4.1. Pancreatic Cancer
2.4.2. Primary Liver Cancer
2.4.3. Esophageal Carcinoma
2.4.4. Gastric Cancer
2.4.5. Oral Cancer
2.4.6. Colorectal Cancer
2.4.7. Kidney Cancer
2.4.8. Urothelial Cancer
2.4.9. Thyroid Cancer
2.4.10. Hematologic Malignancies
2.4.11. Lung Cancer
2.4.12. Breast Cancer
2.4.13. Endometrial Cancer
2.4.14. Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
2.4.15. Cervical Cancer
2.4.16. Prostate Cancer
2.4.17. Testicular Cancer
2.4.18. Melanoma
2.5. Mortality of Patients with T2DM and Cancer
2.6. Association of Specific Cancer with T2DM
3. Underlying Mechanisms of Associations between Diabetes Mellitus and Cancer
3.1. Insulin Resistance and Hyperinsulinemia
3.2. Hyperglycemia
3.3. Obesity
3.4. Age
3.5. Inflammatory Cytokines
3.6. Advanced Glycation End Products
3.7. Other Mechanisms Involved in Associations between Diabetes Mellitus and Cancer
4. Anticancer Therapies Which May Cause Hyperglycemia and Insulin Resistance
4.1. Immunotherapy
4.2. Targeted Therapy
4.2.1. Inhibitors of PI3K/mTOR Pathway
4.2.2. Inhibitors of IGF-1R
4.2.3. Inhibitors of EGFR
4.2.4. Inhibitors of BCR-ABL Multi-Targeted Tyrosine-Kinase
4.2.5. Glucocorticoids
4.2.6. Hormonal Therapies
4.2.7. Other Compounds
4.2.8. Chemotherapy
5. Hypoglycemic Therapies Which May Be Associated with Cancer Risk
5.1. Biguanide Derivatives
5.2. Thiazolidinediones
5.3. Sulfonylureas
5.4. Sodium-Glucose Transporter-2 Inhibitors
5.5. α-Glucosidase Inhibitors
5.6. Incretin-Based Drugs
5.7. Insulin and Insulin Analog
6. Future Direction and Perspective
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Furukawa, S.; Fujita, T.; Shimabukuro, M.; Iwaki, M.; Yamada, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Makayama, O.; Makishima, Y.; Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Health Estimates 2020: Deaths by Cause, Age, Sex, by Country and by Region. 2000–2019; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Hu, F.B. The global implications of diabetes and cancer. Lancet 2014, 383, 1947–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ren, Z.H.; Qiang, H.; Wu, J.; Shen, M.; Zhang, L.; Lyn, J. Trends in the incidence of diabetes mellitus: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017 and implication for diabetes mellitus prevention. BMC Publ. Health 2020, 20, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.F.; Andersen, D.K. Diabetes and pancreatic cancer. Endocrinol. Relat. Cancer 2012, 19, F9–F26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidis, M.; Moraitou, D.; Tata, D.A.; Kalinderi, K.; Papamitsou, T.; Papaliagkas, V. Alzheimer’s disease as type 3 diabetes: Common pathophysiological mechanisms between Alzheimer’s disease and type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson-Stuttard, J.; Papadimitriou, N.; Markozonnes, G.; Civfidini, S.; Kakourou, A.; Gill, D.; Rizos, E.C.; Monori, G.; Ward, H.A.; Kyrgiou, M.; et al. Type 2 diabetes and cancer: An umbrella review of observational and Mendelian randomized studies. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2021, 30, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milluzzo, A.; Vigneri, P.; Martorana, F.; Vigneri, R.; Sciacca, L. Type 2 diabetes and cancer: Problems and suggestions for best patient management. Explor. Med. 2020, 1, 184–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.M.M.; Chua, Z.J.Y.; Tan, J.C.; Yang, Y.; Liao, Z.; Zhao, Y. From pre-diabetes to diabetes: Diagnosis, treatment and translational research. Medicina 2019, 55, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, E.W.; Zhuo, X.; Cheng, Y.J.; Albright, A.L.; Narayan, K.M.; Thompson, T.J. Trends in lifetime risk and years of life lost due to diabetes in the USA, 1985–2011: A modeling study. Lancet Diabet. Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, K.H.; Jeong, J.-W.; Ku, B.J. The association between type 2 diabetes mellitus and women cancer: The epidemiological evidence and putative mechanisms. BioMed Res. Intern. 2015, 2015, 920618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, I.; Athar, M.T.; Islam, M. Type 2 diabetes, obesity, and cancer share some common and critical pathways. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 600824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-S.; Scherer, P.E. Obesity, diabetes, and increased cancer progression. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magruder, J.T.; Elahi, D.; Andersen, D.K. Diabetes and pancreatic cancer: Chicken or egg? Pancreas 2011, 40, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, K.K. The diabetes-cancer link. Diabetes Spectr. 2014, 27, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsilidis, K.K.; Kasimis, J.C.; Lopez, D.S.; Ntzani, E.E.; Joannidis, J.P.A. Type 2 diabetes and cancer: Umbrella review of meta-analysis of observational studies. BMJ 2015, 350, 7607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, J.; Mimura, M.; Gotyo, N.; Watanabe, T. The development of fulminant type 1 diabetes during chemotherapy for rectal cancer. Intern. Med. 2015, 54, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yanase, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Yasui, T.; Kakimoto, M.O.Y. Fulminant type 1 diabetes mellitus onset during postoperative chemotherapy for breast cancer. Tonyobyo 2010, 53, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Uto, H.; Matsuoka, H.; Murata, M.; Okamoto, T.; Miyata, Y.; Hori, T.; Ido, A.; Hirono, S.; Hayashi, K.; Tsubouchi, H. A case of chronic hepatitis C developing insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus associated with various autoantibodies during interferon therapy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2000, 49, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, J.; Simoni, Y.; Furio, L.; Beaudoin, L.; Agerberth, B.; Barrat, F.; Lehuen, A. Crosstalk between neutrophils, B-1a cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells initiates autoimmune diabetes. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Raalte, D.H.; Ouwens, D.M.; Diamant, M. Novel insights into glucocorticoid-mediated diabetogenic effects: Towards expansion of therapeutic options? Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 39, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellati, M.; Eaton, K.D.; Brooks-Worrell, B.M.; Hagopian, W.A.; Martins, R.; Palmer, J.P.; Palmer, J.P. Anti-PD-1 and anti-PDL-1 monoclonal antibodies causing type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, e137–e138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, R.K.; Ahmed, S.; Le, D.; Yadav, S. Diabetes and cancer: Risk, challenges, management and outcomes. Cancers 2021, 13, 5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlstad, O.; Starup-Linde, J.; Vestergaard, P.; Hjellvik, V.; Bazelier, M.T.; Schmidt, M.K.; Andersen, M.; Auvinen, A.; Haukka, J.; Furu, K.; et al. Use of insulin and insulin analogs and the risk of cancer—Systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Curr. Drug. Saf. 2013, 8, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elashoff, M.; Matveyenko, A.V.; Gier, B.; Elashoff, R.; Butler, P.C. Pancreatitis, pancreatic and thyroid cancer with glucagon-like peptide-1 based therapies. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Dai, Q.; Shi, W.; Zhai, S.; Song, Y.; Han, J. SGLT2 inhibitors and risk of cancer in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1862–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monami, M.; Lamanna, C.; Balzi, D.; Marchionni, N.; Mannucci, E. Sulphonylureas and cancer: A case-control study. Acta Diabetol. 2009, 46, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanjan, M.J.; Mohammed, M.; Prashantha Kumar, B.R.; Chandrasekar, M.J.N. Thiazolidinediones as antidiabetic agents: A critical review. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 77, 548–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Mushashi, F.; Son, S.; Bhatti, P.; Dummer, T.; Murphy, R.A. Diabetes medication and cancer risk associations: A systematic review and meta-analysis of evidence over the past 10 years. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Liao, Z. Diabetes and cancer: Epidemiological and biological links. World J. Diabetes 2020, 11, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.W.; Ahn, E.; Kim, H.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.A.; Yun, Y.H. Non-cancer mortality among long-term survivors of adult cancer in Korea. National cancer registry study. Cancer Causes Control. 2010, 216, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noto, H.; Tsujimoto, T.; Sasazuki, T.; Noda, M. Significantly increased risk of cancer in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocr. Pract. 2011, 17, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arreskov, A.B.; Olsen, M.Å.; Pouplier, S.S.; Siersma, V.; Andersen, C.L.; Friss, S.; de Fine Olivarius, N. The impact of cancer on diabetes outcome. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2019, 19, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolde, H.F.; Molla, M.D.; Aragie, H.; Adugna, D.G.; Teferi, E.T.; Melese, E.B.; Assefa, Y.A.; Kifle, H.; Worku, Y.B.; Belay, D.G.; et al. High burden of diabetes and prediabetes among cancer patients at University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, S.L.; Rojna, M. Diabetes and risk of cancer. Int. Sch. Res. Nat. 2013, 2013, 583786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwangbo, Y.; Kang, D.; Kang, M.; Kim, S.; Lee, E.K.; Kim, Y.A.; Chang, Y.J.; Choi, K.S.; Jung, S.Y.; Woo, E.K.; et al. Incidence of diabetes after cancer development: A Korean national cohort study. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zendehdel, K.; Nyrén, O.; Östenson, C.G.; Adami, H.O.; Ekbam, A.; Ye, W. Cancer incidence in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: A population-based cohort study in Sweden. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 1797–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.-H. The relationship between diabetes mellitus and gastric cancer and the potential benefits of metformin: An extensive review of the literature. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liu, C.; Pan, J.; Yang, J. Relationship between diabetes and risk of gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort study. Diab. Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 187, 109866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardefeldt, P.; Edirimanne, S.; Eslick, G.D. Diabetes increases the risk of breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2012, 19, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, J.L.; Shaw, J.E.; Peeters, A.; Cartensen, B.; Magliano, D.J. Cancer risk among people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: Disentangling true associations, detection bias and reverse causation. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menini, S.; Iacobini, C.; Vitale, M.; Pesce, C.; Pugliese, G. Diabetes and pancreatic cancer—A dangerous liaison relying on carbonyl stress. Cancers 2021, 13, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, X.; Ji, J.; Li, X.; Sundquist, J.; Sundquist, K.; Hemminki, K. Cancer risk among patients hospitalized for Type 1 diabetes mellitus: A population-based cohort study in Sweden. Diabet. Med. 2010, 27, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, T.; Zhang, L.; Ma, X.; Zhou, J.; Shen, J. Diabetes mellitus and incidence and mortality of gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2012, 120, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemkens, L.G.; Grouver, U.; Bender, R.; Günster, C.; Gutschmidt, S.; Selke, G.W.; Sawicki, P.T. Risk of malignancies in patients with diabetes treated with human insulin or insulin analogues: A cohort study. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 1732–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahaly, G.J.; Hansen, M.P. Type 1 diabetes associated immunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazmamoun, H.; Rafeey, M.; Nikpourl, M.; Ghergherehchi, R. Helicobacter pylori infection in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus: A case-control study. J. Res. Health Sci. 2016, 16, 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- Carstensen, B.; Read, S.H.; Friis, S.; Sund, R.; Keskimaki, T.; Svensson, A.M.; Ljung, R.; Wild, S.H.; Kerssens, J.J.; Harding, J.L.; et al. Cancer incidence in persons with type 1 diabetes: A five-country study of 9.000 cancers in type 1 diabetes individuals. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Qu, S. The relationship between diabetes mellitus and cancers and its underlying mechanisms. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 800995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sona, M.F.; Myung, S.K.; Park, K.; Jargalsaikhan, G. Type 1 diabetes mellitus and risk of cancer: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 48, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, A.J.; Laing, S.P.; Qiao, Z.; Slater, S.D.; Burden, A.C.; Botha, J.L.; Waugh, N.R.; Morris, A.D.; Gatling, W.; Gale, E.A.; et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in patients with insulin-treated diabetes: A UK cohort study. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 2070–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallhager, E.J.; LeRoith, D. Obesity and diabetes: The increased risk of cancer and cancer-related mortality. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 727–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes–2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, S15–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandharkar, S.A.; Mathew, J.; Petrow, M.S. Prevalence of diabetes associated with diseases of the exocrine pancreas: A population based study. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewald, N.; Kaufmann, C.; Raspe, A.; Kloer, H.U.; Bretzel, R.G.; Hardt, P.D. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus secondary to pancreatic diseases (Type 3c). Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2012, 28, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Andersen, D.K. Pancreatogenic diabetes: Special considerations for management. Pancreatology 2011, 11, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganda, O.P. Secondary forms of diabetes. In Joslin’s Diabetes Mellitus, 14th ed.; Kahn, C.R., Weir, G.C., King, G.L., Jacobson, A.M., Moses, A.C., Smith, R.J., Eds.; Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005; pp. 477–492. [Google Scholar]
- Lowenfels, A.B.; Maissonneuve, P.; Cavallini, G.; Ammann, R.W.; Lankisch, P.G.; Andersen, J.R.; Dimagno, E.P.; Andren-Sandberg, A.; Domellof, L.; International Pancreatitis Study Group. Pancreatitis and the risk of pancreatic. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisonneuve, P.; Lowenfels, A.B.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, H.B.; Ghadirian, P.; Baghurst, P.A.; Zatonski, W.A.; Miller, A.B.; Duelle, E.J.; Boffetta, P.; Boyle, P. Past medical history and pancreatic cancer risk: A results from a multicenter case-control study. Annals Epidemiol. 2010, 20, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.F.; Lai, S.W.; Li, C.I.; Chen, W.C. Diabetes mellitus correlates with increased risk of pancreatic cancer: A population-based cohort study in Taiwan. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Bakare, A.; Taylor, R.; Gill, G.V.; Alberti, K.G. Tropical or malnutrition-related diabetes: A real syndrome? Lancet 1986, 1, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardt, P.D.; Kloer, H.U.; Brendel, M.D.; Bretzel, R.G. Is pancreatic (Type 3c) diabetes underdiagnosed and misdiagnosed? Diabetes Care 2008, 31 (Suppl. S2), S165–S169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malka, D.; Hammel, P.; Sauvanet, A.; Rufat, P.; O’Toole, D.; Bardet, P.; Belghiti, J.; Bernades, P.; Ruszniewski, P.; Lévy, P. Risk factors for diabetes mellitus in chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Tian, H.; Shen, Y.; Tuomilehto, J.; Yu, Z.; Yang, X.; Hu, G.; et al. β-cell function or insulin resistance was associated with the risk of type 2 diabetes among women with or without obesity and a history of gestational diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellamy, L.; Casas, J.-P.; Hingorani, A.D.; Williams, D. Type 2 diabetes mellitus after gestational diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2009, 373, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, R.; Rahne, E.; Dasgupta, K. Gestational diabetes mellitus and risk of incident primary cancer: A population-based retrospective cohort study. J. Diabetes 2020, 12, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.S.; Lin, J.R.; Cheng, B.H.; Ho, C.; Lin, Y.H.; Shen, C.H.; Tsai, M.H. Incidence and relative risk for developing cancers in women with gestational diabetes mellitus: A nationwide cohort study in Taiwan. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e024583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.T.; Cho, G.J.; Kim, E.H. Evaluation of the association between gestational diabetes mellitus at the first pregnancy and cancer within 10 years postpartum using National Health Insurance data in South Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejaimal, S.A.; Wu, C.F.; Lowe, J.; Feig, D.S.; Shah, B.R.; Lipscombe, L.L. Short-term risk of cancer among women with previous gestational diabetes: A population-based study. Diabet. Med. 2016, 33, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.-W.; Zhang, D.-L.; Wang, Z.-H.; Lv, C.-Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, H. Different types of diabetes mellitus and risk of thyroid cancer: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 971213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollison, D.E.; Giuliano, A.R.; Sellers, T.A.; Laronga, C.; Sweeney, C.; Risendal, B.; Baumgartner, K.B.; Byers, T.; Slattery, M.L. Population-based canse-control study of diabetes and breast cancer risk in Hispanic and non-Hispanic White women living in US southwestern states. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 167, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sella, T.; Chodick, G.; Barchana, M.; Haymann, A.D.; Poroth, A.; Kokia, E.; Shalev, V. Gestational diabetes and risk of incidence primary cancer: A large historical cohort study in Israel. Cancer Causes Control 2011, 22, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, R.; Weiss, H.A.; Hoover, R.; Potischman, N.A.; Swanson, C.; Brogan, D.; Coates, R.J.; Gammon, M.D.; Malone, K.E.; Daling, J.R.; et al. Pregnancy characteristic and maternal risk of breast cancer. Epidemiology 1998, 9, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, D.A.; Smith, G.D.; Ebrahim, S. Hyperinsulinemia and increased risk of breast cancer: Findings from the British Women’s Heart and Healthy Study. Cancer Causes Control 2004, 15, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, M.C.; Terry, M.B.; Kleinhaus, K.; Deutsch, L.; Yanetz, R.; Tiram, E.; Calderon-Margalit, R.; Friedlander, Y.; Paltiel, O.; Harlap, S. Gestational diabetes and the risk of breast cancer among women in Jerusalem perinatal study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 108, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchison, E.A.; Gridley, G.; Carreon, J.D.; Leitzmann, M.F.; McGlynn, K.A. Risk of cancer in a large cohort of U.S. Veterans with diabetes. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian Gang, P.; Mo, L.; Lu, Y.; Rungi, L.; Xing, Z. Diabetes mellitus and the risk of prostate cancer: An update and cumulative meta-analysis. Endocr. Res. 2015, 40, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao Kondapally Seshasai, S.; Kaptoge, S.; Thompson, A.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Gao, P.; Sarwar, N.; Whincup, P.H.; Mukamal, K.J.; Gillum, V.; Holme, I.; et al. Diabetes mellitus, fasting glucose, and risk of case-specific death. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 829–841. [Google Scholar]
- Barone, B.B.; Yeh, H.C.; Snyder, C.F.; Peairs, K.S.; Stein, K.B.; Derr, C.F.; Wolff, A.C.; Brancati, F.L. Long-term all-cause mortality in cancer patients with preexisting diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2008, 300, 2754–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, P.T.; Newton, C.C.; Patel, A.V.; Jacobs, E.J.; Gapstur, S.M. Diabetes and cause-specific mortality in a prospective cohort study of one million U.S. adults. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1835–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, F.; Saito, E.; Lin, Y.; Song, M.; Luu, H.N.; Gupta, P.C.; Sawada, N.; Tamakoshi, A.; Shu, X.-O.; et al. Association between type 2 diabetes and risk of cancer mortality: A pooled analysis of over 771,000 individuals in the Asia cohort consortium. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlin, N.J.; Amin, S.B.; Buras, M.R.; Kosiorek, H.E.; Verona, P.M.; Cook, C.B. Patient outcomes from lung cancer and diabetes mellitus: A matched case-control study. Future Sci. OA 2018, 4, FSO248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonagiri, P.R.; Shubrook, J.H. Review of associations between type 2 diabetes and cancer. Clin. Diabet. J. 2020, 38, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, A.; Berlin, J.; Chari, S.; Kindler, H.; Matrisian, L.; Mayoral, A.; Mills, J.; Nissen, N.; Picozzi, V.; Zelada-Arenas, F. Management of patients with pancreatic cancer using the “Right Track” Model. Oncologist 2023, 28, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bian, X.; Wei, S.; He, M.; Yang, Y. The relationship between pancreatic cancer and type 2 diabetes: Cause and consequence. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 8257–8268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwi, S.O.; Oberg, A.L.; Shivappa, N.; Bamlet, W.R.; Chaffee, K.G.; Steck, S.E.; Hébert, J.R.; Petersen, G.M. Pancreatic cancer: Associations of inflammatory, potential of diet, cigarette smoking and long-standing diabetes. Carcinogenesis 2016, 37, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munigala, S.; Singh, A.; Gelrud, A.; Agarwal, B. Predictors for pancreatic cancer diagnosis following new-onset diabetes mellitus. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2015, 6, e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Hao, L.; Li, Z.; Sun, S. Long-term diabetes mellitus is associated with an increased risk of pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, S.T.; Leibson, C.L.; Rabe, K.G.; Ransom, J.; de Andrade, M.; Petersen, G.M. Probability of pancreatic cancer following diabetes: A population-based study. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Tang, H.; Hassan, M.M.; Holly, E.A.; Bracci, P.M.; Silverman, D.T. Diabetes and risk of pancreatic cancer: A pooled analysis of three large case-control studies. Cancer Cause Control 2011, 22, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosetti, C.; Rosato, V.; Li, D.; Silverman, D.; Petersen, G.M.; Bracci, P.M.; Neale, R.E.; Muscat, J.; Anderson, K.; Gallinger, S.; et al. Diabetes, antidiabetic medications, and pancreatic cancer risk: An analysis from the International Pancreatic Cancer Case-Control Consortium. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 2065–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batabyal, P.; Vander Hoorn, S.; Christophi, C.; Nikfarjam, M. Association of diabetes mellitus and pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A meta-analysis of 88 studies. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 2453–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben, Q.; Xu, M.; Ning, X.; Liu, J.; Hong, S.; Huang, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z. Diabetes mellitus and risk of pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 1928–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setiawan, V.W.; Stram, D.O.; Porcel, J.; Chari, S.T.; Maskarinec, G.; Le Marchand, L.; Wilkens, L.R.; Haiman, C.A.; Pandol, S.J.; Monroe, K.R. Pancreatic cancer following incident diabetes in African Americans and Latinos. The multiethnic cohort. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019, 111, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Vittinghoff, E.; Bertenthal, D.; Corley, D.; Shen, H.; Walter, L.C.; McQuid, K. New-onset diabetes and pancreatic cancer. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniraj, T.; Chari, S.T. Diabetes and pancreatic cancer. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2012, 58, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, D. Diabetes and pancreatic cancer. Mol. Carcinog. 2012, 51, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ose, D.J.; Viskochil, R.; Holowatyj, A.N.; Larson, M.; Wilson, D.; Dunson, W.A., Jr.; Desmukh, V.G.; Butcher, J.R.; Taylor, B.R.; Svoboda, K.; et al. Understanding the prevalence of prediabetes and diabetes in patients with cancer in clinical practice: A real-world cohort study. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2021, 19, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, M.; Adinolfi, V.; Morviducci, L.; Acquati, S.; Tuveri, E.; Ferrari, P.; Zatelli, M.C.; Faggiano, A.; Argentiero, A.; Natalicchio, A.; et al. Early prediction of pancreatic cancer from new-onset diabetes: An Associazione Italiana Oncologica Medica (AIOM)/Associazione Medici Diabetologi (AMD)/Societa Italiana Endocrinologia (SIE)/Societa Italiana Farmacologia (SIF) multidisciplinary consensus position paper. ESMO Open Cancer Horiz. 2021, 6, 100155. [Google Scholar]
- Pannala, R.; Leirness, J.B.; Bamlet, W.R.; Basu, A.; Petersen, G.M.; Chari, S.T. Prevalence and clinical profile of pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes mellitus. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.-A.; Park, H.Y.; Yong, H.; Hyuck, L.K.; Taek, L.K.; Kyun, L.J.; Cheol, B.J.; Won, K.K. New-onset diabetes patients need pancreatic cancer screening? J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 46, e58–e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, Z.J.; Tsilimigras, D.I.; Ruff, S.M.; Mohseni, A.; Kamel, I.R.; Cloyd, J.M.; Pawlik, T.M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. A review. JAMA Surg. 2023, 158, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosetti, C.; Turati, F.; La Vecchia, C. Hepatocellular carcinoma epidemiology. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 28, 753–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainwright, P.; Scorletti, E.; Byrne, C.D. Type 2 diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma: Risk factors and pathogenesis. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2017, 17, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, M.-S.; Hsieh, M.-S.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Chen, T.H.-H. Type 2 diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma: A cohort study in high prevalence are hepatitis virus infection. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Targher, G. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: Spotlight on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneri, P.; Frasca, F.; Sciacca, L.; Pandini, G.; Vigneri, R. Diabetes and cancer. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2009, 16, 1103–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurney, J.; Stanley, J.; Teng, A.; Krebs, J.; Koea, J.; Lao, C.; Lawrenson, R.; Meredith, I.; Sika-Paotonu, D.; Sarfati, D. Cancer and diabetes co-occurrence: A national study with 44 million person-years of follow-up. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Das, B.; Gadad, P.C. Impact of diabetes on the increased risk of hepatic cancer: An updated review of biological aspects. Diabet. Epidemiol. Manag. 2021, 4, 100025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.D.; Stengel, J.; Asike, M.I.; Torres, D.M.; Shaw, J.; Contreras, M.; Landt, C.L.; Harrison, S.A. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis among a largely middle-aged population utilizing ultrasound and liver biopsy: A prospective study. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, G.; Baranova, A.; Younossi, Z.M. Systematic review: The epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adults. Aliment. Pharmacol. Therap. 2011, 34, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzero, J.S.; Fontana, R.J.; Su, G.L.; Conjeevaram, H.S.; Emick, D.M.; Lok, A.S. NAFLD may be a common under lying liver disease in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. Hepatology 2002, 36, 1349–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. 2005, 70 (Suppl. S3), 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Duseja, A.; Nanda, M.; Das, A.; Das, R.; Bhansali, A.; Chawla, Y. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia in patients with cryptogenic liver cirrhosis. Trop. Gastroenterol. 2004, 25, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Baffy, G.; Brunt, E.M.; Caldwell, S.H. Hepatocellular carcinoma in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An emerging menace. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takuma, Y.; Nouso, K. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis-associated hepatocellular carcinoma: Our case series and literature reviews. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 1436–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertle, J.; Dechȇne, A.; Sowa, I.-P.; Penndorf, V.; Herzer, K.; Kaiser, G.; Schlaak, J.F.; Gerken, G.; Syn, W.-K.; Canbay, A. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease progress to hepatocellular carcinoma in the absence cirrhosis. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 10, 2436–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Jin, G.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, C.; Liu, R.; Hu, X. Diabetes mellitus and increased risk of cholangiocarcinoma: A meta-analysis. Europ. J. Canc. Prev. 2012, 21, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddinger, S.B.; Haas, J.T.; Yu, B.B.; Bezy, O.; Jing, E.; Zhang, W.; Unterman, T.G.; Carey, M.C.; Kahn, C.R. Hepatic insulin resistance directly promotes formation of cholesterol gallstones. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar Then, E.; Lopez, M.; Saleem, S.; Gayam, V.; Sunkara, T.; Culliford, A.; Gaduputi, V. Esophageal cancer: An update surveillance epidemiology and end results database analysis. World J. Oncol. 2020, 11, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Ren, H.; Ben, Q.; Cai, Q.; Zhu, W.; Li, Z. Risk of esophageal cancer in diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of observational study. Cancer Causes Control 2012, 23, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.; Kim, K.-W. Diabetes and cancer: Cancer should be screened in routine diabetes assessment. Diabet. Metab. J. 2019, 43, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-L.; Tan, Y.-T.; Epplein, M.; Li, H.-L.; Gao, J.; Gao, Y.T.; Zheng, W.; Shu, X.-Q.; Xiang, Y.B. Population-based cohort studies of type 2 diabetes and stomach cancer risk in Chinese men and women. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.J.; Lee, H.; Min, Y.W.; Min, B.H.; Lee, J.H.; Son, H.J.; Rhee, P.L.; Baek, S.Y.; Jung, S.H.; Kim, J.J. Diabetic biomarkers and the risk of proximal or distal gastric cancer. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 1705–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodick, G.; Heymann, A.D.; Rosenmann, L.; Green, M.S.; Flash, S.; Porth, A.; Kokia, E.; Shalev, V. Diabetes and risk of incident cancer: A large population-based cohort study in Israel. Cancer Causes Control 2010, 21, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Chlebowski, R.; Liu, S.; McGlynn, K.A.; Parekh, N.; White, D.L.; Margolis, K.L. Diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for gastrointestinal cancer among postmenopausal women. Cancer Causes Control 2013, 24, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Rutegård, M.; Santoni, G.; Wallner, B.; Johansson, I.; Sund, M.; Xie, S.H.; Lagergren, J. Prediabetes and diabetes in relation to risk of gastric adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosetti, C.; Rosato, V.; Polesel, J.; Levi, F.; Talamini, R.; Montella, M.; Negri, E.; Tavani, A.; Zucchetto, A.; Franceschi, S.; et al. Diabetes mellitus and cancer risk in network of case-control studies. Nutr. Cancer 2012, 64, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romon, I.; Rey, G.; Mandereau-Bruno, L.; Weill, A.; Jougla, E.; Eschwege, E.; Simon, D.; Druet, C.; Fagot-Campagna, A. The excess mortality related to cardiovascular diseases and cancer among adults pharmacologically treated for diabetes—The 2001-2006 ENTRED cohort. Diabet. Med. 2014, 31, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, R.G.P.J.; Peeters, P.J.H.L.; Burden, A.M.; de Bruin, M.L.; Haak, H.R.; Masclee, A.A.M.; de Vries, F.; Janssen-Heijnen, M.L.G. Gastrointestinal cancer incidence in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Results from a large population-based cohort study in the U.K. Cancer Epidemiol. 2018, 54, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, W.; Mu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Chen, L.; Shi, L.; Li, Q.; Wan, Q.; et al. Cohort profile: Risk evaluation of cancers in Chinese diabetic individuals: A longitudinal (REACTION) study. J. Diabet. 2014, 6, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idilbi, N.M.; Barchana, M.; Milman, U.; Carel, R.S. Incidence of cancer among diabetic and non-diabetic adult Israeli Arabs. Isr. Med. Assoc. 2013, 15, 342–347. [Google Scholar]
- Sieri, S.; Agnoli, C.; Pala, V.; Grioni, S.; Brighenti, F.; Pellegrini, N.; Masala, G.; Palli, D.; Mattiello, A.; Panico, S.; et al. Dietary glycemic index, glycemic load, and cancer risk: Results from the EPIC-Italy study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remschmidt, B.; Pau, M.; Gaessler, J.; Zemann, W.; Jakse, N.; Payer, M.; Végh, D. Diabetes mellitus and oral cancer: A retrospective study from Austria. Anticancer Res. 2022, 42, 1899–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.; Al-Maweri, S.A.; Saini, D.; Ismail, N.M.; Ismail, A.R. Oral mucosal lesions in non-oral habit diabetic patients and association of diabetes mellitus with oral precancerous lesions. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2010, 89, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Garcia, P.; Roca-Rodriguez, M.D.M.; Aguilar-Diosdado, M.; Gonzalez-Moles, M.A. Diabetes mellitus and oral cancer/oral potentially malignant disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 404–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantsiyants, E.M.; Surikova, E.I.; Kaplieva, I.V.; Bandovkina, V.A.; Neskubina, I.V.; Sheiko, E.A.; Morozova, M.I.; Kotieva, I.M. Diabetes mellitus and cancer: A system of insulin-like growth factors. Probl. Ecdocrinol. 2021, 67, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, D.; Atkin, W.; Lenz, H.J.; Lynch, H.T.; Minsky, B.; Nordlinger, B.; Starling, N. Colorectal cancer. Lancet 2010, 375, 1030–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzirik, D.L.; Pasquali, L.; Cnop, M. Pancreatic β-cells in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: Different pathways to failure. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miłek, T.; Forysiński, K.; Myrcha, P.; Ciostek, P. Diabetes association of polyps and colon cancer. Pol. Przegl. Chir. 2019, 91, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amshoff, Y.; Maskarinec, G.; Svetsov, Y.B.; Raquinio, P.H.; Grandinetti, A.; Setiowan, V.W.; Haiman, C.A.; Le Marchand, L. Type 2 diabetes and colorectal cancer survival. The multiethnic cohort. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbach, M.; Mehmert, H.; Schnell, O. Diabetes and the risk for colorectal cancer. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2012, 26, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, P.T.; Deka, A.; Jacobs, E.J.; Newton, C.C.; Hildebrand, J.S.; McCullough, M.L.; Limburg, P.J.; Gapstur, S.M. Perspective study reveals associations between colorectal cancer and type 2 diabetes mellitus or insulin use in men. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.C.; Giovannucci, E.; Wolk, A. Diabetes and colorectal cancer incidence in the cohort of Swedish men. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 1805–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lawler, T.; Zoe, L.; Walts, B.A.; Steinwandel, M.; Lipworth, L.; Murff, H.J.; Zheng, W.; Andersen, S.W. Type 2 diabetes and colorectal cancer risk. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2343333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, P.J.H.L.; Bazelier, M.T.; Leufkens, H.G.M.; de Vries, F.; De Bruin, M.L. The risk of colorectal cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes: Associations with treatment stage and obesity. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kort, S.; Masclee, A.A.M.; Sanduleanu, S.; Weijenberg, M.P.; van Herk-Sukel, M.P.P.; Oldenhof, N.J.J.; van den Bergh, J.P.W.; Haak, H.R.; Janssen-Heijnen, M.L. Higher risk of colorectal cancer in patients with newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus before the age of colorectal cancer screening initiation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.T.; Bellows, C.F.; Hoffman, A.E.; Kelly, T.N.; Gagliardi, S. Diabetes mellitus and colorectal cancer prognosis: A meta-analysis. Dis. Colon Rectum. 2013, 56, 1304–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Wu, X.; Wu, B.; Pei, D.; Zhang, L.; Wei, L. The relationship between diabetes and colorectal cancer prognosis: A meta-analysis based on the cohort studies. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, I.; Caberto, C.P.; Lum-Jones, A.; Seifried, A.; Wilkens, L.R.; Schumacher, F.R.; Monroe, K.R.; Lim, U.; Tiirikainen, M.; Kolonel, L.N.; et al. Type 2 diabetes risk variants and colorectal cancer risk: The Multiethnic Cohort and PAGE studies. Gut 2011, 60, 1703–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Khan, U.; Fallah, M.; Sundquist, K.; Sundquist, J.; Brenner, H.; Kharazmi, E. Risk of colorectal cancer in patients with diabetes mellitus: A Swedish nationwide cohort study. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Gui, Z.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Shen, L. Diabetes mellitus and the incidence of colorectal cancer: An update systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 1576–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoen, R.E.; Weissfeld, J.L.; Kuller, L.H.; Thaete, F.L.; Evans, R.W.; Hayes, R.B.; Rosen, C.J. Insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin are associated with the presence and advancement of adenomatous polyps. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 464–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddi, R.; Karki, A.; Shah, A.; DeBari, V.A.; DePasquale, J.R. Association of type 2 diabetes and colon cancer adenomas. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2012, 43, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidiqui, A.A.; Maddur, H.; Naik, S.; Cryer, B. The association of elevated HbA1c on the behavior of adenomatous polyps in patients with type-II diabetes mellitus. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 53, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, A.; Yamaji, T.; Sawada, N.; Momozawa, Y.; Kamatani, Y.; Kubo, M.; Shimazu, T.; Inoue, M.; Noda, M.; Tsunage, S.; et al. Diabetes and cancer risk. A Mendelian randomized study. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.C.; Wolk, A. Diabetes mellitus and incidence of kidney cancer: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, P. End stage and chronic kidney disease associations with renal cancer. Front. Oncol. 2012, 2, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyram, R.; Kansara, A.; Banerji, A.; Loney-Hutchinson, L. Chronic kidney disease and diabetes. Maturitas 2012, 71, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijol, V.; Mendez, G.P.; Hurwitz, S.; Rennke, H.G.; Nosé, V. Evaluation of the nonneoplastic pathology in tumor nephroctomy specimens: Predicting the risk of progressive renal failure. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2006, 30, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsib, S.M.; Pei, Y. The non-neoplastic kidney in tumor nephrectomy specimens: What can it show and what is important? Adv. Ant. Pathol. 2010, 174, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.L.; Prohoda, T.J.; Luna, M.; Werner, S.A. Diabetes and risk of renal cell carcinoma. J. Cancer 2012, 3, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, E.C.; Kim, Y.J.; Hwang, I.S.; Hwang, J.E.; Jung, S.I.I.; Kwon, D.D.; Park, K.; Ryu, S.B. Impact of diabetes mellitus in patients with non-muscle invasive bladder carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study. J. Urol. 2011, 11, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mosalamy, H.; Salmon, T.M.; Ashmawey, A.M.; Osama, N. Role of chronic E. coli infection in the process of bladder cancer—An experimental study. Inf. Agents Cancer 2012, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wu, J.; Mao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Xu, X.; Lin, Y.; Chen, H.; Zheng, X.; Qin, J.; et al. Diabetes mellitus and risk of bladder cancer: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, X.; Shen, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhong, S.; Xu, C. Risk of bladder cancer in patients with diabetes mellitus: An updated meta-analysis of 36 observational studies. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Z.; Zhong, S.; Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Xu, C. Diabetes mellitus and risk of bladder cancer: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turati, F.; Polesel, J.; Di Maso, M.; Montella, M.; Libra, M.; Grimaldi, M.; Tavani, A.; Serraino, D.; La Vecchia, C.; Bosetti, C. Diabetes mellitus and the risk of bladder cancer: An Italian case-cancer study. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prizment, A.E.; Anderson, K.E.; Yuan, J.M.; Folsom, A.R. Diabetes and risk of bladder cancer among postmenopausal women in the Iowa Women’s Health Study. Cancer Causes Control 2013, 24, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Huo, R.; Chen, X.; Xu, X. Diabetes mellitus and the risk of bladder cancer: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis of cohort-studies. Medicine 2017, 96, e8588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, M.E.; Zeegers, M.P.; Bazelier, M.T.; De Bruin, M.I.; Buntinx, F.; de Vries, F. Risk of bladder cancer in patients with diabetes: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e007470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Filho, A.; Lortet-Tiulent, J.; Bray, F.; Cao, B.; Franceschi, S.; Vaccarella, S.; Dal Maso, L. Thyroid cancer incidence trends by histology in 25 countries: A population-based study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, F.; Shang, Y.; Ping, Z.; Liu, L. Thyroid cancer: Incidence and mortality trends in China, 2005-2015. Endocrine 2020, 68, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, K.; Zheng, R.; Zeng, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, R.; Wei, W. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2015. J. Natl. Cancer Cent. 2021, 1, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.-W.; Park, S.; Kong, H.-J.; Won, Y.-Y.; Boo, Y.K.; Shin, H.-R.; Park, E.-O.; Lee, J.-S. Cancer Statistics in Korea: Incidence, Mortality and Survival. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2010, 25, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Brito, J.P.; Vaccarella, S. Long-term declines of thyroid cancer mortality: An international Age-Period-Cohort analysis. Thyroid 2020, 30, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ron, E. A population-based case-control study of thyroid cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1987, 79, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Hirohata, T. Radiation Carcinogenesis. Semin. Oncol. 1976, 3, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, Y.; Ma, S.-H.; Hwang, Y.; Horn-Ross, P.L.; Hsing, A.; Lee, K.-E.; Park, Y.J.; Park, D.-J.; Yoo, K.-Y.; Park, S.K. Diabetes mellitus and risk of thyroid cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Zhang, J.; Zou, G.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Xu, J. Diabetes mellitus and thyroid cancers: Risky correlation, underlying mechanisms and clinical prevention. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2024, 17, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, J.J.; Mull, N.; Reagan, J.L.; Nemr, S.; Mitri, J. Increased incidence of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, leukemia, and diabetes mellitus type 2: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Blood 2012, 119, 4845–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.E.; Gallo, V.; Linseisen, J.; Kaaks, R.; Rohrmann, S.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Tjønneland, A.; Johnsen, H.E.; Overvad, K.; Bergmann, M.M. Diabetes and the risk of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and multiple myeloma in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. Haematologica 2008, 93, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Wang, Z.; Qian, L.; Wang, S.; Cao, H.; Wang, H. HRCT features distinguishing minimally invasive adenocarcinoma from invasive adenocarcinomas appearing as mixed ground-glass nodules. Transl. Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Joh, H.-K.; Choi, S.; Park, S.M. Type 2 diabetes mellitus does not increase the risk of lung cancer among never-smokers: A nationwide cohort study. Transl. Lung Cancer 2019, 8, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vona-Davis, L.; Howard-McNatt, M.; Rose, D.P. Adiposity, type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome in breast cancer. Obes. Rev. 2007, 8, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, P.; Boniol, M.; Koechlin, A.; Robertson, C.; Valentini, F.; Coppens, K.; Fairley, L.L.; Boniol, M.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Diabetes and breast cancer risk: A meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 1608–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alokail, M.S.; Al-Daghri, N.M.; Al-Attas, O.S.; Hussain, T. Combined effect of obesity and type 2 diabetes contribute to increased breast cancer risk in premenopausal women. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2009, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.H.; Yu, M.C.; Tseng, C.C.; Stanczyk, F.Z.; Pike, M.C. Diabetes and risk of breast cancer in Asian-American women. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Li, J.; Wei, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Sun, S. Association between diabetes mellitus and breast cancer risk: A meta-analysis of the literature. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Res. 2011, 12, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Lipscombe, L.L.; Fischer, H.D.; Austin, P.C.; Fu, L.; Jaakkimainen, R.L.; Grinsburg, O.; Rochon, P.A.; Narod, S.; Paszt, L. The association between diabetes and breast cancer stage at diagnosis: A population based study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 150, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, F.; Wang, J.; Nierenberg, J.L.; Van Blarigan, E.L.; Kenfield, S.A.; Chan, J.M.; Schmajuk, G.; Huang, C.-Y.; Graft, R.R. Diabetes mellitus and risk of breast cancer: A large-scale, prospective, population-based study. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 129, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.-M.M.; Bookwalter, D.B.; O’Brien, K.M.; Jackson, C.L.; Weinberg, C.R.; Sandler, D.P. A prospective study of type 2 diabetes, metformin use, and risk of breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, N.; Preti, E.; Landoni, F.; Carinelli, S.; Colombo, A.; Marini, C.; Sessa, C.; ESMO Guidelines Working Group. Endometrial cancer: ESMO clinical practical guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, vi33–vi38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cristofano, A.; Ellenson, L.H. Endometrial carcinoma. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2007, 2, 57–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friberg, E.; Orsini, N.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Wolk, A. Diabetes mellitus and risk of endometrial cancer: A meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vainio, H.; Kaaks, R.; Bianchini, F. Weight control and physical activity in cancer prevention: International evaluation of the evidence. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2002, 11, S94–S100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schouten, L.J.; Goldbohn, R.A.; van den Brandt, P.A. Anthropometry, physical activity, and endometrial cancer risk: Results from the Netherlands Cohort Study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2004, 96, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltzman, B.S.; Doherty, J.A.; Hill, D.A.; Bersford, S.A.; Voight, L.F.; Chen, C.; Weiss, N.S. Diabetes and endometrial cancer: An evolution of the modifying effects of other risk factors. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 167, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-F.; Liu, M.D.; Chen, P.; Chen, L.-H.; Chang, Y.-H.; Wen, P.C.; Li, C.-Y. Risks of breast and endometrial cancer in women with diabetes: A population based cohort study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Su, P.Y.; Hao, J.H.; Sun, Y.H. The role of preexisting diabetes mellitus on incidence and mortality of endometrial cancer: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2013, 23, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindermann, K.; Cvancarova, M.; Eskild, A. Body mass index, diabetes and survival after diagnosis of endometrial cancer: A report from the HUNT-Survey. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 37, 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Folsom, A.R.; Anderson, K.E.; Sweeney, C.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr. Diabetes as a risk factor for death following endometrial cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2004, 94, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, C.J.; Poole, C.D.; Jemkons-Jones, S.; Gale, E.A.M.; Johnson, J.A.; Morgan, C.L. Mortality after incident cancer in people with and without type 2 diabetes: Impact of metformin on survival. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Zhang, D.; Mungo, C.; Tompkins, D.A.; Zeidan, A.M. Is diabetes mellitus associated with increased incidence and disease-specific mortality in endometrial cancer? A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 135, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasi, E.; Capoccia, D.; Granato, T.; Silecchia, G.; Rizzello, M.; Porpora, M.G.; Frati, L.; Angeloni, A.; Leonetti, F. Implementing the risk of ovarian malignancy algorithm adding obesity as a predictive factor. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 6425–6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasi, E.; Filardi, T.; Tartaglione, S.; Lenzi, A.; Angeloni, A.; Morano, S. Linking type 2 diabetes and gynecological cancer: An introductory overview. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 56, 1413–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurman, R.J.; Shih, I.-M. The origin and pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer: A proposed unifying theory. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piek, J.M.; Verheijnen, R.H.; Kenemans, P.; Massuger, L.F.; Bulten, H.; van Diest, P.J. BRCA1/2-related ovarian cancers are of tubal origin: A hypothesis. Gynecol. Oncol. 2003, 90, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gapstur, S.M.; Patel, A.V.; Diver, W.R.; Hildebrand, J.S.; Gaudet, M.M.; Jacobs, E.J.; Campbell, P.T. Type II diabetes mellitus and the incidence of epithelial ovarian cancer in the cancer prevention study-II nutrition cohort. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2012, 21, 2000–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Jeon, I.; Kim, J.W.; Song, Y.S.; Yoon, J.M.; Park, S.M. Diabetes mellitus and ovarian cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2013, 23, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.M.; Erickson, B.K.; Matin, T.; McGwin, G., Jr.; Martin, J.Y.; Daily, L.B.; Pasko, D.; Haygood, C.W.; Fauci, J.M.; Leath, C.A. Diabetes mellitus and ovarian cancer: More complex than just increasing risk. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 135, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.Y.; Lin, Z.Z.; Kuo, R.; Shau, W.Y.; Lai, C.L.; Yang, Y.Y.; Shao, Y.Y.; Hsu, C.; Cheng, W.-F.; Cheng, A.-L.; et al. The prognostic impact of type 2 diabetes mellitus on early cervical cancer in Asia. Oncologist 2015, 20, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jlamset, I.; Hanprasertpong, J. Impact of diabetes mellitus on oncological outcomes after radical hysterectomy for early stage cervical cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 27, e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onitilo, A.A.; Berg, R.L.; Engel, J.M.; Stankowski, R.V.; Glurich, I.; Williams, G.M.; Doi, S.A. Prostate cancer risk in pre-diabetic men: A matched cohort study. Clin. Med. Res. 2013, 11, 2010209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bansal, D.; Bhansali, A.; Kapil, G.; Undela, K.; Tiwari, P. Type 2 diabetes and risk of prostate cancer: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2013, 16, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Giovannucci, E.; Jeon, J.Y. Diabetes and mortality in patients with prostate cancer: A meta-analysis. Springerplus 2016, 5, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häggström, C.; Van Hemelrijck, M.; Garmo, H.; Robinson, D.; Stattin, P.; Rowley, M.; Coolen, A.C.C.; Holmberg, L. Heterogenity in risk of prostate cancer. A Swedish population-based cohort study of competing risks and Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 1868–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szablewski, L. Insulin resistance: The increased risk of cancers. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 998–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szablewski, L. Changes in cells associated with insulin resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, B.D.; Goncalves, M.D.; Cantley, L.C. Insulin-PI3K signaling: An evolutionarily insulated metabolic driver of cancer. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbois-Mouthon, C.; Cadoret, A.; Blivet-Van Eggelpoel, M.J.; Bertrand, F.; Cherqui, G.; Perret, C.; Capeau, J. Insulin and IGF-1 stimulate the β-catenin pathway through two signalling cascade involving GSK-3β inhibition and Ras activation. Oncogene 2001, 20, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easwaran, V.; Lee, S.H.; Inge, L.; Guo, L.; Goldbeck, C.; Garrett, E.; Wiesmann, M.; Garcia, P.D.; Fuller, J.H.; Chan, V.; et al. Beta-catenin regulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression in colon cancer. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 3145–3153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.S.; Rogol, A.D.; Rosenfeld, R.G. The history of the insulin-like growth factor system. Horm. Res. Pediatr. 2021, 95, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; Cantley, L.C.; Thompson, C.B. Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 2009, 324, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, R.; Yamagishi, S. AGE-RAGE system and carcinogenesis. Cur. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Kartsonaki, C.; Guo, Y.; Bragg, F.; Yang, L.; Bian, Z.; Chen, Y.; Iona, A.; Millwood, I.Y.; Lv, J.; et al. Diabetes, plasma glucose and incidence of pancreatic cancer: A prospective study of 0.5 million Chinese adults and a meta-analysis of 22 cohort studies. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannucci, E.; Harlan, D.M.; Archer, M.C.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Gapstur, S.M. Diabetes and cancer. A consensus report. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1674–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, C.R.; Wang, G.; Lee, K.Y. Altered adipose tissue and adipocyte function in the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3990–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalia, A.Z.; Dasari, S.; Johnson, M.L.; Robinson, M.M.; Konopka, A.R.; Distelmaier, K.; Port, J.D.; Glavin, M.T.; Esponda, R.R.; Nair, K.S.; et al. Predictors of whole-body insulin sensitivity across ages and adiposity in adult humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calle, E.E.; Thun, M.J.; Petrelli, J.M.; Rodriguez, C.; Heath, C.W., Jr. Body-mass index and mortality in a prospective cohort of US adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calle, E.E.; Rodriguez, C.; Walker-Thumond, K.; Thun, M.J. Overweight, obesity and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of US adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, T.D.; Stroup, A.M.; Gress, R.R.; Adams, K.F.; Calle, E.E.; Smith, S.C.; Halverson, R.C.; Simper, S.C.; Hopkins, P.N.; Hunt, S.C. Cancer incidence and mortality after gastric bypass surgery. Obesity 2009, 17, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christou, N.V.; Liberman, M.; Sampalis, F.; Sampalis, J.S. Bariatric surgery reduces cancer risk in morbidity obese patients. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2008, 4, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byers, T.; Sedjo, R.L. Body fatness as a cause of cancer: Epidemiologic clues to biologic mechanisms. Endocrinol. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, R125–R134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, A.E.; Galasso, R.; Matveyenko, A.; Riza, R.A.; Dry, S.; Butler, P.C. Pancreatic duct replication is increased with obesity and type 2 diabetes in humans. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, J.H.; Rutkowski, J.M.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin, leptin, and fatty acids in the maintenance of metabolic homeostasis through adipose tissue crosstalk. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 770–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, S.; Shearer, R.F.; Lee, L.S.; van Geldermalsen, M.; Schreuder, M.; Shtein, H.C.; Cairns, R.; Thomas, K.C.; Fazakerley, D.J.; Grewal, T.; et al. Adipocyte lipolysis links obesity to breast cancer growth: Adipocyte-derived fatty acids drive breast cancer cell proliferation and migration. Cancer Metab. 2017, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehr, S.; Hartwig, S.; Sell, H. Adipokines: A treasure trove for the discovery of biomarkers for metabolic disorders. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2012, 6, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guaita-Esteruelas, S.; Bosquet, A.; Saavedra, P.; Gumà, J.; Girona, J.; Lam, E.W.; Amillano, K.; Borriàs, J.; Masana, L. Exogenous FABP4 increases breast cancer cell proliferation and activates the expression of fatty acid transport proteins. Mol. Carcinog. 2017, 56, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.B.; Xu, H.; Zhu, W.H.; Bai, P.D.; Hu, J.M.; Yang, T.; Jiang, H.-W.; Ding, Q. High-fat diet-induced adipokine and cytokine alterations promote the progression of cancer in vivo and in vitro. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Sun, Z.; Li, O.; Guo, C.; Yi, W.; Tan, Z.; Jiang, B. Leptin stimulates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and pro-angiogenic capability of cholangiocarcinoma cells through the miR-122/PKM2 axis. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 55, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Lai, H.Y.; Zhang, F.; Shen, W.J.; Chu, P.Y.; Liang, H.Y.; Liu, Y.-B.; Wang, J.-M. MCL1 participates in leptin-promoted mitochondrial fusion and contributes to drug resistance in gallbladder cancer. JCI Insight 2021, 6, 135438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, S.; Siddharth, S.; Sharma, D. Adiponectin, obesity and cancer: Clash of the bigwigs in health and disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, A.H.; Combs, T.P.; Scherer, P.E. ACR30/adiponectin: An adipokine regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 13, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, Y.; Funahashi, T.; Kihara, S.; Taguchi, T.; Tamaki, Y.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Noguchi, S. Association of serum adiponectin levels with breast cancer risk. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 5699–5704. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ray, A.; Clearly, M.P. The potential role of leptin in tumor invasion and metastasis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017, 38, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Wei, F.; Lian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, J.; Cao, K.; et al. Role of tumor microenvironment in tumorigenesis. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferruzzi, J.; Sun, M.; Gkousioudi, A.; Pilvar, A.; Robler, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zaman, M.H. Compressive remodeling alters fluid transport properties of collagen networks—Implications for tumor growth. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muz, B.; de la Puente, P.; Azab, F.; Azab, A.K. The role of hypoxia in cancer progression, angiogenesis, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Hypoxia 2015, 3, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Yang, F.; Shao, C.; Wei, K.; Xie, M.; Shen, H.; Shu, Y. Role of hypoxia in cancer therapy by regulating the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Hsu, J.L.; Li, Y.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Huang, M.C. Cancer cell metabolism bolsters immunotherapy resistance by promoting an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.; Yu, X.; Zhang, W.; Han, L.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Yuan, Y. Regulating the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment to enhance breast cancer immunotherapy using pH-responsive hybrid membrane-coated nanoparticles. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzo, A.J.; Fuller, A.M.; Makowski, L. Contribution of adipose tissue to development of cancer. Comp. Physiol. 2017, 8, 237–282. [Google Scholar]
- Berraondo, S.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Ochoa, M.C.; Etxeberria, I.; Aznar, M.A.; Pérez-Gracia, J.L.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Ponz-Sarvise, M.; Castañón, E.; Melero, I. Cytokines in clinical cancer immunotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotgia, F.; Martinez-Outschoorn, U.E.; Lisanti, M.P. Mitochondrial oxidative stress drives tumor progression and metastatic: Should we use antioxidants as a key component of cancer treatment and prevention. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.; Jemal, A.; Ward, E.M.; Center, M.M.; Hao, Y.; Siegel, R.L.; Thun, M.J. Global Cancer Facts & Figures 2007; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Krentz, A.J.; Viljoen, A.; Sinclair, A. Insulin resistance: A risk marker for disease and disability in the older person. Diabetes Med. 2013, 30, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowell, B.B.; Shulman, G.I. Mitochondrial dysfunction and type 2 diabetes. Science 2005, 307, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, K.F.; Befroy, D.; Dufour, S.; Dziura, J.; Ariyan, C.; Rothman, D.L. Mitochondrial dysfunction in the elderly: Possible role in insulin resistance. Science 2003, 300, 1140–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkwil, F.; Mantovani, A. Inflammation and cancer: Back to Virchov? Lancet 2001, 357, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.W.; Karin, M.A. Cytokine-mediated link between innate immunity, inflammation and cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Pardoll, D.; Jove, R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: A leading role for STAT3. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquivel-Velázquez, M.; Ostoa-Saloma, P.; Palacios-Arreola, M.I.; Nava-Castro, K.E.; Castro, J.L.; Morales-Montor, J. The role of cytokines in breast cancer development and progression. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015, 35, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baynes, J.W.; Thorpe, S.R. Role of oxidative stress in diabetic complications: A new perspective on an old paradigm. Diabetes 1999, 48, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelen, L.; Lund, S.S.; Ferreira, I.; Tarnow, L.; Parving, H.H.; Gram, J.; Winther, K.; Pedersen, O.; Teerlink, T.; Barto, R.; et al. Improved glycemic control induced by both metformin and repaglinide is associated with a reduction in blood levels of 3-deoxyglucosone in nonobese patients with type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 164, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucala, R.; Mahita, Z.; Koschinsky, T.; Cerami, A.; Vlassara, H. Lipid advanced glycosylation: Pathway for lipid oxidation in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 6434–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassara, H. Advanced glycation in health and disease. Role of the modern environment. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1043, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Khan, H.; Siddiqui, Z.; Khan, M.Y.; Rehman, S.; Shahab, U.; Godovikova, T.; Silnikov, V.; Moinuddin. AGEs, RAGEs and s-RAGE; friend or foe for cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 49, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soman, S.; Raju, R.; Sandhya, V.K.; Advani, J.; Khan, A.A.; Harsha, H.C.; Prasad, T.S.; Sudhakaran, P.R.; Pandey, A.; Adishesha, P.K. A multicellular signal transduction network of AGE/RAGE signaling. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2013, 7, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldini, G.; Dalle-Done, I.; Facino, R.M.; Milzani, A.; Carini, M. Intervention strategies to inhibit protein carbonylation by lipoxydation-derived reactive carbonyls. Med. Res. Rev. 2007, 27, 817–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, S.; Khan, S.; Almatroudi, A.; Khan, A.A.; Alsahli, M.A.; Almatroodi, S.A.; Rahmani, A.H. A review on mechanism of inhibition of advancer glycation end products formation by plant derived polyphenolic compounds. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 787–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Schofour, J.; Wang, D.D.; Dhana, K.; Pan, A.; Liu, X.; Shin, H.J.; Liu, G.; Shin, H.J.; Sun, Q.; et al. Healthy lifestyle and life expectancy free of cancer, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes: Prospective cohort study. BMJ 2020, 368, 16669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czyzyk, A.; Szczepanik, Z. Diabetes mellitus and cancer. Europ. J. Intern. Med. 2000, 11, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.J.X.; Loh, K.; Yap, Y.-S. PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors in breast cancer. Cancer Biol. Med. 2015, 12, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- André, F.; Ciruelos, E.; Rubovszky, G.; Campone, M.; Loibl, S.; Rugo, H.S.; Iwata, H.; Conte, P.; Mayer, I.A.; Kaufman, B.; et al. Alpelisib for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1929–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellmunt, J.; Szczylik, C.; Feingold, J.; Strahs, A.; Berbenblit, A. Temisirolimus safety profile and management of toxic effects in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma and poor prognosis. Annu. Oncol. 2008, 19, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinert, M.; Sylow, L.; Fazakerly, D.J.; Krycer, J.R.; Thomas, K.C.; Oxbøll, A.J.; Jordy, A.B.; Jensen, T.E.; Yang, G.; Schjerling, P.; et al. Acute mTOR inhibition induces insulin resistance and alters substrate utilization in vivo. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Veeken, J.; Oliveira, S.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Storm, G.; van Bergen En Henegouwen, P.M.; Roovers, R.C. Crosstalk between epidermal growth factor receptor and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor signaling. Implications for cancer therapy. Cancer Drug Targets 2009, 9, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollack, M. The insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptor family in neoplasia. An update. Nat. Rep. Cancer 2012, 12, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haluska, P.; Shaw, H.M.; Batzel, G.N.; Yin, D.; Molina, J.R.; Molife, L.R.; Yap, T.A.; Roberts, M.L.; Sharma, A.; Gualberto, A.; et al. Phase I dose escalation study of the anti- insulin-like growth factor I receptor monoclonal antibody CP-751,871 in patients with refractory solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 5834–5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacy, M.Q.; Alsima, M.; Fonseca, R.; Paccagnella, M.L.; Melvin, C.L.; Yin, D.; Sharma, A.; Enriquez Sarano, M.; Pollak, M.; Jagannath, S.; et al. Phase I, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics study of the anti-insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor monoclonal antibody CP-751,871 in patients with multiple myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3196–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Rincon, J.P.; Iida, K.; Gaylinn, B.D.; McCurdy, C.E.; Leitner, J.W.; Barbour, L.A.; Kopchick, J.J.; Friedman, J.E.; Draznin, B.; Thorner, M.O. Growth hormone regulates of p85α expression and phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity in adipose tissue: Mechanism for growth hormone-mediated insulin resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1638–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scartuzzi, M.; Bianconi, M.; Maccaroni, E.; Giampieri, R.; Berardi, R.; Cascinu, S. Dalotuzumab, a recombinant humanized mAb targeted against IGFR1 for the treatment of cancer. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2010, 12, 361–371. [Google Scholar]
- Sclafani, F.; Kim, T.Y.; Cunningham, D.; Tabernero, J.; Schmoll, H.J.; Roh, J.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, Y.S.; Guren, T.K.; Hawkes, E.; et al. A randomized phase II/III study of Dalotuzumab in combination with cetuximab and irinotecan in chemorefractory, KRASWild-Type metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, djv258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassnacht, M.; Berruti, A.; Boudin, E.; Demeure, M.J.; Gilbert, J.; Haak, H.; Kroiss, M.; Quinn, D.I.; Hesseltine, E.; Ronchi, C.L.; et al. Linsitinib (OSI-906) versus placebo for patients with locally advanced or metastatic adrenocortical carcinoma: A double-blind, randomized, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, L.; Wadlow, R.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Wolpin, B.M.; Abrams, T.A.; McCleary, N.J.; Sheehan, S.; Sundaram, E.; Karol, M.D.; Chen, J.; et al. A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of ganetespib (STA-9090) in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Investig. New Drugs 2015, 33, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, R.N.; Fennell, D.A.; Kovcin, V.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Ramlau, R.; Kowalski, D.; Schenker, M.; Yalcin, I.; Teofilovci, F.; Vukovic, V.M. Randomized phase III study of ganetespib, a heat shock protein 90 inhibitor with docetaxel versus docetaxel in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (GALAXY-2). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Kim, D.W.; Mehra, R.; Tan, D.S.; Felip, E.; Chow, L.Q.; Camidge, D.R.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Sharma, S.; De Pas, T.; et al. Certinib in ALK-Rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassonville, O.; Bozec, A.; Fischel, J.L.; Milano, G. EGFR targeting therapies monoclonal antibodies versus tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Similarities and differences. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2007, 62, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.J.; Johnson, D.E.; Grandis, J.R. EGFR-targeted therapies in the post-genomic era. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017, 36, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequist, L.V.; Soria, J.-C.; Goldman, J.W.; Wakelee, H.A.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Varga, A.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.; Solomon, B.J.; Oxnard, G.R.; Dziadziuszko, R.; et al. Rociletinib in EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1700–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liu, J.; Huang, X.; Jiang, Q. Adverse effects of dasatinib on glucose-lipid metabolism in patients with chronic leukemia in the chronic phase. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saglio, G.; Kim, D.-W.; Issaragrisil, S.; Le Coutre, P.; Etienne, G.; Lobo, C.; Pasquini, R.; Clark, R.E.; Hochhaus, A.; Hughes, T.; et al. Nilotinib versus imatinib for newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racil, Z.; Razga, F.; Drapalova, J.; Buresova, L.; Zackova, D.; Palackova, M.; Semerad, L.; Malaskova, L.; Haluzik, M.; Meyer, J. Mechanism of impaired glucose metabolism during nilotinib therapy in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia. Hematology 2013, 98, e124–e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, N.; Miller, A.V.; Hicks, M.A.; Marking, C.B.; Harada, H. Glucocorticoid-mediated BIM induction and apoptosis are regulated by Runx2 and C-Jun in leukemia cells. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maustin, K.M.; Darling, T.V.; Janelsins, M.C.; Jean-Pierre, P.; Roscoe, J.A.; Morrow, G.R. Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. US Oncol. 2008, 4, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen, O.; Aass, N.; Kaasa, S.; Dale, O. Do corticosteroids provide analgesic effects in cancer patients? A systematic literature review. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2013, 46, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, S.Y. Corticosteroids in the treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2012, 10, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haywood, A.; Good, P.; Khan, S.; Leupp, A.; Jenkins-Marsh, S.; Rickett, K.; Hardy, J.R. Corticosteroids for the management of cancer related-related pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2021, CD010756. [Google Scholar]
- Shlomai, G.; Nell, B.; LeRoith, D.; Gallhager, E.J. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and cancer: The role of pharmacotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4261–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamood, R.; Hamood, H.; Merhasin, I.; Keinan-Boker, L. Diabetes after hormone therapy in breast cancer survivors: A case-cohort study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2061–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeletti, S.; Corleto, V.D.; Schillaci, O.; Marignani, M.; Annibale, B.; Moretti, A.; Silecchia, G.; Scopinaro, F.; Basso, N.; Bordi, C.; et al. Use of somatostatin analogue ocreotide to localize and manage somatostatin-producing tumours. Gut 1998, 42, 792–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caplin, M.E.; Pavel, M.; Ćwikła, J.B.; Phan, A.T.; Raderer, M.; Sedláčková, E.; Cadiot, G.; Wolin, E.M.; Capdevila, J.; Wall, L.; et al. Lanreotide in metastatic enteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinke, A.; Müller, H.-H.; Schade-Brittinger, C.; Klose, K.J.; Barth, P.; Wied, M.; Mayer, C.; Aminossadati, B.; Pape, U.F.; Bläker, M.; et al. Placebo-controlled, double blind, prospective, randomized study on the effect of Octreotide LAR in the control of tumor growth in patients with metastatic neuroendocrine mid gut tumors. A report from PROMID Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4656–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.H.; Shafiq, J. Diabetic ketoacidosis following PEG-asparaginase therapy. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. Case Rep. 2018, 2018, 18–0064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, Y.; Nakamura, A.; Takihata, M.; Inoue, Y.; Yahagi, S.; Tajima, K.; Tsuchiya, H.; Takano, T.; Yamakawa, T.; Yoshida, M.; et al. Safety and tolerability of diazoxide in Japanese patients with hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. Endocrinol. J. 2016, 63, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Biernacka, K.M.; Holly, J.M.P.; Jarrett, C.; Morrison, A.A.; Morgan, A.; Winters, Z.E.; Foulstone, E.J.; Shield, J.P.; Perks, C.M. Hyperglycemia confers resistance to chemotherapy on breast cancer cells: The role of fatty acid synthase. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2010, 17, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turturro, F.; Von Burton, G.; Friday, E. Hyperglycemia-induced thioredoxin-interacting protein expression in breast cancer-derived cells and regulates paclitaxel IC50. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 3724–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.P.; Yuan, X.L.; Li, M.; Fang, J.; Xie, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Y.-M.; Luo, M.; Lin, M.; Ye, D.-W. Secondary diabetes associated with 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy regimens in non-diabetic patients with colorectal cancer: Results from a single-centre cohort study. Color. Dis. 2013, 15, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariaans, G.; de Jong, S.; Gietema, J.A.; Lefrandt, J.D.; de Vries, E.G.E.; Jalving, M. Cancer-drug induced insulin resistance: Innocent bystander or unusual suspect. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2015, 41, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viollet, B.; Guigas, B.; Sanz Garcia, N.; Leclerc, J.; Foretz, M.; Andreeli, F. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin: An overview. Clin. Sci. 2020, 122, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.M.; Donnelly, L.A.; Emslie-Smith, A.M.; Alessi, D.R.; Morris, A.D. Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in diabetic patients. BMJ 2005, 330, 1304–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franciosi, M.; Lucisano, G.; Lapice, E.; Sreippoli, G.F.; Pellegrini, F.; Nicolucci, A. Metformin therapy and risk of cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes: Systematic review. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, H.; Tan, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, S. Association of metformin use with cancer incidence and mortality: A meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatude, A.; Nigam, M.; Kunwar Singh, R.; Shikhar Panwar, A.; Lasisi, A.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Jyoti Kumar, V.; Prakash Mishra, A.; Sarifi-Rads, J. Cancer and diabetes: The interlinking metabolic pathways and repurposing actions of antidiabetic drugs. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vissers, P.A.J.; Cardwell, C.R.; van de Poll-Franse, L.V.; Young, I.S.; Pouwer, F.; Murray, L.J. The association between glucose-lowering drug use and mortality among breast cancer patients with type 2 diabetes. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 150, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.H. Diabetes, metformin use, and colon cancer: A population-based cohort study in Taiwan. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 167, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.H. Metformin reduces gastric cancer risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Aging 2016, 8, 1636–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.S.; Sun, H.J.; Whang, Y.M.; Park, Y.J.; Park, D.J.; Cho, S.W. Metformin reduces thyroid cancer growth in the metastatic niche bone by inhibiting osteoblastic RANKL productions. Thyroid 2021, 31, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klubo-Gwiezdzinska, J.; Costello, J.; Patel, A.; Bauer, A.; Jensen, K.; Mete, M.; Burman, K.D.; Wartofsky, L.; Vasko, V. Treatment with metformin is associated with higher remission rate in diabetic patients with thyroid cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 3269–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.Y.; Kang, M.J.; Kim, S.K.; Jung, J.H.; Hahn, J.R.; Kim, T.H.; Nam, J.Y.; Lee, B.-W.; Lee, Y.-H.; Chung, J.H.; et al. Protective effect of metformin against thyroid cancer development: A population-based study in Korea. Thyroid 2018, 28, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian-Yu, E.; Graber, J.M.; Lu, S.-E.; Lin, Y.; Lu-Yao, G.; Tan, X.-L. Effect of metformin and statin use on survival in pancreatic cancer patients: A systemic literature review and meta-analysis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 2595–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.-K.; Su, T.-T.; Si, J.-M.; Sun, L.-M. Metformin is associated with slightly reduced risk of colorectal cancer and moderate survival benefits in diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2016, 95, e2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S. Association between metformin therapy and breast cancer incidence and mortality: Evidence from a meta-analysis. J. Breast Cancer 2015, 18, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.Y.; Martinez-Outschoorn, U.E.; Schilder, R.J.; Kim, C.H.; Richard, S.D.; Rosenblum, N.G.; Johnson, J.M. Metformin as a therapeutic target in endometrial cancer. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Hu, H.; Ye, S.; Wang, H.; Cui, R.; Yi, L. The effect of metformin therapy on incidence and prognosis in prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, R.J.; Ali, R.; Bankhead, C.R.; Bethel, M.A.; Cairns, B.J.; Camisasca, R.P.; Crowe, F.L.; Farmer, A.J.; Harrison, S.; Hirst, J.A.; et al. Cancer outcome and all-cause mortality in adults allocated to metformin: Systematic review and collaborative meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 2593–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzewoski, J.; Drozdowska, A.; Sliwinska, A. Do we have enough data to confirm the link between antidiabetic drug use and cancer development? Pol. Arch. Med. Wewn. 2011, 121, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneri, R.; Sciacca, L.; Vigneri, P. Rethinking the relationship between insulin and cancer. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Yi, Y.; Liu, X.; Keller, E.T.; Qian, C.N.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y. Metformin targets multiple signaling pathways in cancer. Chin. J. Cancer 2017, 36, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Saenz, M.; Lobaton-Ginsberg, M.; Ferreira-Hermosillo, A. Metformin in differentiated thyroid cancer: Molecular pathways and its clinical implications. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Cui, H.; Kang, L.; Zhang, X.; Jin, Z.; Lu, L.; Fan, Z. Metformin inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth, migration, and EMT through the mTOR pathway. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 6295–6304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.; Daley, B.; Klubo-Gwiezdzinska, J. The role of an anti-diabetic drug metformin in the treatment of endocrine tumors. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2019, 63, R17–R35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retnakaran, R.; Zinman, B. Thiazolidinediones and clinical outcomes in type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2009, 373, 2088–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarelli, F.; Di Marzio, D. Peroxisome proliferator-activated recepto-gamma agonists and diabetes: Current evidence and future perspectives. Vasc. Health Ris. Manag. 2008, 4, 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- Rangwala, S.M.; Lazar, M.A. Peroxisome proliferator-associated receptor gamma in diabetes and metabolism. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 25, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanquicett, C.; Roman, J.; Hart, C.M. Thiazolidinediones as anti-cancer agents. Cancer Ther. 2008, 6, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Monami, M.; Lamanna, A.; Marchionni, N.; Mannucci, F. Rosiglitazone and risk of cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karo, C.; Barrett, S.; Qizilbash, N. Cancer risk in thiazolidinedione users compared to other anti-diabetic agents. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2007, 16, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, R.; Lin, L.; Cheng, D.; Xu, Y.; Xu, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bi, Y.; Li, D.; Lu, J. Thiazolidinedione therapy and breast cancer risk in diabetic women: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2018, 34, e2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dormandy, J.A.; Charbonnel, B.; Eckland, D.J.; Erdmann, E.; Massi-Benedetti, M.; Moules, I.K.; Skene, A.M.; Tan, M.H.; Lefebvre, P.J.; Murray, G.D.; et al. Secondary prevention of macrovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes in the PROactive Study (PROspective Pioglitazone Clinical Trial in Macrovasculature Events): A randomized controlled trial. Lancet 2005, 366, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Lei, C. PPARgamma activation serves as therapeutic strategy against bladder cancer via inhibiting PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamichane, S.; Dahal Lamichane, B.; Kwon, S.M. Pivotal roles of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) and their signal cascade for cellular and whole-body energy homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, L.; Wang, F.; Xia, X. The administration of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha/gamma agonist TZD18 inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in human gastric cancer cell lines. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2019, 15, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazzone, P.J.; Rai, H.; Beukemann, M.; Xu, M.; Jain, A.; Sasidhar, M. The effect of metformin and thiazolidinedione use on lung cancer in diabetes. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monami, M.; Dicembrini, I.; Manucci, E. Thiazolidinediones and cancer: Results of a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Acta Diabetol. 2014, 51, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhu, J.; Prokop, L.J.; Murad, M.H. Pharmacologic therapy of diabetes and overall cancer risk and mortality. A meta-analysis of 265 studies. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.H. Rosiglitazone may reduce thyroid cancer risk in patients with type 2 diabetes. Ann. Med. 2013, 45, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.Y.; Wang, J.J.; Lee, H.C.; Chi, C.W.; Lee, C.H.; Hsu, Y.C. Combination of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and retinoid X receptor agonists induces sodium/iodide symporter expression and inhibits cell growth of human thyroid cancer cells. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2020, 83, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.Q.; Hab, J.S.; Ha, J.; Baek, H.S.; Lim, D.J. Lobeglitazone, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonist, inhibits papillary thyroid cancer cell migration and invasion by suppressing p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 36, 1095–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsubaki, M.; Takeda, T.; Tomonari, Y.; Kawashima, K.; Itoh, T.; Imano, M.; Satou, T.; Nishida, S. Pioglitazone inhibits cancer cell growth through STAT3 inhibition and enhanced AIF expression via a PPARgamma-independent pathway. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 3638–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyles, B.E.; Akinyeke, T.O.; Moss, P.E.; Stewart, L.V. Thiazolidinediones regulate expression of cell cycle proteins in human prostate cancer cells via PPARγ-dependent and PPARγ-independent pathways. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosetti, C.; Rosato, V.; Buniato, D.; Zambon, A.; La Vecchia, C.; Corrao, G. Cancer risk for patients using thiazolidinediones for type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. Oncologist 2013, 18, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colmers, I.N.; Bowker, S.L.; Majumdar, S.R.; Johnson, J.A. Use of thiazolidinediones and the risk of bladder cancer among people with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. Can. Med. Associat. J. 2012, 184, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.D.; Habel, L.A.; Quesenberry, C.P.; Strom, B.L.; Peng, T.; Hedderson, M.M.; Ehrlich, S.F.; Mamtani, R.; Bilker, W.; Vaughn, D.J.; et al. Pioglitazone use and risk of bladder cancer and other common cancers in persons with diabetes. JAMA 2015, 314, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sola, D.; Rossi, L.; Schianca, G.P.C.; Maffioli, P.; Bigliocca, M.; Mella, R.; Corliano, F.; Fra, G.P.; Bartoli, E.; Derosa, G. State of the art paper Sulfonylureas and their use in clinical practice. Arch. Med. Sci. 2015, 4, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, M.; Mizuno, C.; Chittiboyina, A.; Kurtz, T.; Pershadsingh, H. Type 2 diabetes and oral antihyperglycemic drugs. Curr. Med. 2008, 15, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowker, S.L.; Majumdar, S.R.; Veugelers, P.; Johnson, J.A. Increased cancer-related mortality for patients with type 2 diabetes who use sulfonylureas or insulin. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chubak, J.; Boudreau, D.M.; Barlow, W.E.; Weiss, N.S.; Li, C.I. Diabetes treatments and risks of adverse breast cancer outcomes among early-stage breast cancer patients: A SEER-Medicare analysis. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 6033–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Du, L.; Li, L.; Ma, J.; Geng, X.; Yao, X.; Liu, G.; Sun, X. Cancer risk of sulfonylureas in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. J. Diabetes 2017, 9, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, B.; Aronis, K.N.; Vamvini, M.T.; Shields, K.; Mantzoros, C.S. Metformin and sulfonylureas in relation to cancer risk in type II diabetes patients: A meta-analysis using primary data of published studies. Metabolism 2013, 62, 922–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasello, G.; Urso, L.; Conte, P.; Favaretto, A. Effects of sulfonylureas on tumor growth: A review of the literature. Oncologist 2013, 18, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cignarelli, A.; Genchi, V.A.; Caruso, I.; Natalicchio, A.; Perrini, S.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F. Diabetes and cancer: Pathophysiological fundamentals of a “dangerous affair”. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 143, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Sun, G.; Li, M.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Qian, X.; Li, P.; Xu, L.; Huang, W.; Wang, X. Glibenclamide targets sulfonylurea receptor 1 to inhibit p70S6K activity and upregulate KLF4 expression to suppress non-small cell lung carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 2085–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Duan, L.; Hu, G. Glibendamide exerts an anti-tumor activity through reactive oxygen species-c-jun (NH2)-terminal kinase pathway in human gastric cancer cell line MGC-803. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicembrini, I.; Nreu, B.; Mannucci, E.; Monami, M. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors and cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes. Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 1871–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, A.M.Y. SGLT2 inhibitors and cancer: Why further evidence is required. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 2536–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ptaszynska, A.; Cohen, S.M.; Messing, E.M.; Reilly, T.P.; Johnsson, E.; Johnsson, K. Assessing bladder cancer risk in type 2 diabetes clinical trials: The dapaglioflozin drug development program as a “Case Study”. Diabetes Ther. 2015, 6, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, A.R.; Rodrigues, M.R.; Li, Z.; Leitner, B.P.; Perry, R.J. SGLT2 inhibition slows tumor growth in mice by reversing hyperinsulinemia. Cancer Metab. 2019, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jojima, T.; Wakamatsu, S.; Kase, M.; Iijima, Y.; Maejima, Y.; Shimomura, K.; Kogai, T.; Tomaru, T.; Usui, I.; Aso, Y. The SGLT2 inhibitor canagliflozin prevents carcinogenesis in a mouse model of diabetes and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-related hepatocarcinogenesis: Association with SGLT2 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaji, K.; Nishimura, N.; Seki, K.; Sato, S.; Saikawa, S.; Nakanishi, K.; Furukawa, M.; Kawaratani, H.; Kitade, M.; Moriya, K.; et al. Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor canagliflozin attenuates liver cancer growth and angiogenic activity by inhibiting glucose uptake. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 1712–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, M.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Chen, L.J.; Chu, P.Y.; Hiseh, F.S.; Tsai, M.H.; Shih, C.T.; Chao, T.-I.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chen, K.-F. Canagliflozin inhibits growth of hepatocellular carcinoma via blocking glucose-influx-induced β-catenin activation. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scafoglio, C.; Hirayama, B.A.; Kepe, V.; Liu, J.; Ghezzi, C.; Satyamurthy, N.; Moatamed, N.; Huang, J.; Koepsel, H.; Barrio, J.R.; et al. Functional expression of sodium-glucose transporters in cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E4111–E4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, S.; Lee, J.; George, J.T.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Zinman, B. Bladder cancer in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 2534–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villani, L.A.; Smith, B.K.; Marcinko, K.; Ford, R.J.; Broadfield, L.A.; Green, A.E.; Houde, V.P.; Muti, P.; Tsakinidis, T.; Steinberg, G.R. The diabetes medication Canagliflozin reduces cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting mitochondrial complex-I supported respiration. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauhtaq, A.; Azam, U.; Mehreen, S.; Naseer, M.M. Synthetic alpha-glucosidase inhibitors as promising anti-diabetic agents: Recent developments and future challenges. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 249, 115119. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Z.T.; Liu, L.; Cheng, M.Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, W.J.; Xu, B. The effects of 6 common antidiabetic drugs on anti-PD1 immune checkpoint inhibitor in tumor treatment. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 2651790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.W.; Liao, K.F.; Chen, P.C.; Tsai, P.Y.; Hsieh, D.P.; Chen, C.C. Antidiabetic drugs correlate with decreased risk of lung cancer: A population-based observation in Taiwan. Clin. Lung Cancer 2012, 13, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.H.; Tsan, Y.T.; Chan, W.C.; Sheu, W.H.; Chen, P.C. Use of an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor and the risk of colorectal cancer in patients with diabetes: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 2068–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Kuang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, H.; Guan, H. Effect of type 2 diabetes and antihyperglycemic drug therapy on signs of tumor invasion in papillary thyroid cancer. Endocrine 2020, 69, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjerre Knudsen, L.; Madsen, L.W.; Andersen, S.; Almholt, K.; de Boer, A.S.; Drucker, D.J.; Gotfredsen, C.; Egerod, F.L.; Hegelund, A.C.; Jacobsen, H.; et al. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonists activate rodent thyroid C-cells causing calcitonin release and C-cell proliferation. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 1473–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Kaelber, D.C.; Xu, R.; Berger, N.A. GLP-1 receptor agonists and colorectal cancer risk in drug naïve patients with type 2 diabetes, with and without overweight/obesity. JAMA Oncol. 2023, 7, E1–E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carstensen, B.; Witte, D.R.; Friss, S. Cancer occurrence in Danish diabetic patients: Duration and insulin effect. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 948–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janghorbani, M.; FDehghani, M.; Salehi-Marzijarami, M. Systemic review and meta-analysis of insulin therapy and risk of cancer. Hormon. Cancer 2012, 3, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.W.; Azoulay, L.; Majdan, A.; Boivin, J.F.; Pollak, M.; Suissa, S. Long-term use of long-acting analogs and breast cancer incidence in women with type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3647–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.T.; Naigamwalla, D.; Oprescu, A.I.; Lam, L.; McKeown-Eyssen, G.; Bruce, W.R.; Giacca, A. Hyperinsulinemia, but not other factors associated with insulin resistance, acutely enhances colorectal epithelial proliferation in vivo. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 1830–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, D.; Simon, M.; Yehezkel, E.; Laron, Z.; Werner, H. Insulin analogues display IGF-1-like mitogenic and anti-apoptotic activities in culture cancer cells. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2009, 25, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Grisouard, J.; Ehemann, V.; Hermani, A.; Enzmann, H.; Mayer, D. Analysis of signaling pathways related to cell proliferation stimulated by insulin analogs in human mammary epithelial cell lines. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2009, 16, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.W.; Filion, K.B.; Azoulay, L.; Doll, M.K.; Suissa, S. Effect of long-acting insulin analogs on the risk of cancer: A systematic review of observational studies. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciacca, L.; Le Moli, R.; Vigneri, R. Insulin analogs and cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ORIGIN Trial Investigators; Gerstein, H.C.; Bosch, J.; Dagenais, G.R.; Diaz, R.; Jung, H.; Maggioni, A.P.; Pogue, J.; Probstfield, J.; Ramachandran, A.; et al. Basal insulin and cardiovascular and other outcomes in dysglycemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 2, 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- ORIGIN Trial Investigators. Cardiovascular and other outcomes postintervention with insulin glargine and omega-3 fatty acids (ORIGINALE). Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starup-Linde, J.; Karlstad, O.; Eriksen, S.A.; Vestergaard, P.; Bronsveld, H.K.; de Vries, F.; Andersen, M.; Auvinen, A.; Haukka, J.; Hjellevik, V.; et al. CARING (Cancer Risk and Insulin analoGues): The association of diabetes mellitus and cancer risk with focus on possible determinants. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr. Drug Saf. 2013, 8, 296–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfeld, M.R.; Muller, G.; Tschank, G.; Seipke, G.; Habermann, P.; Kurrle, R.; Tennagels, N. In vitro metabolic and mitogenic signaling of insulin glargine and its metabolites. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, C.J.; Poole, C.D.; Gale, E.A. The influence of glucose-lowering therapies on cancer risk in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 1766–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsilidis, K.K.; Capothanassi, D.; Allen, N.E.; Rizos, E.C.; Lopez, D.S.; van Veldhoven, K.; Sacerdote, C.; Ashby, D.; Vineis, P.; Tzoulaki, I.; et al. Metformin does not affect cancer risk: A cohort study in the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink analyzed like an intention-to-treat trial. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2522–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padma, V.V. An overview of targeted cancer therapy. BioMedicine 2015, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariff, A.L.; Syed, S.; Shelby, R.; Force, J.; Clarke, J.M.; D’Alessio, D.; Corsino, L. Novel cancer therapies and their associations with diabetes. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2019, 62, R187–R199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popova, P.V.; Klyushina, A.A.; Vasilyeva, L.B.; Tchachuk, A.S.; Vasukova, E.A.; Anopova, A.; Pustozerov, E.A.; Gorelova, I.V.; Kravchuk, E.N.; Pervunina, T.M.; et al. Association of common genetic risk variants with gestational diabetes mellitus and their role in GDM prediction. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 628582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
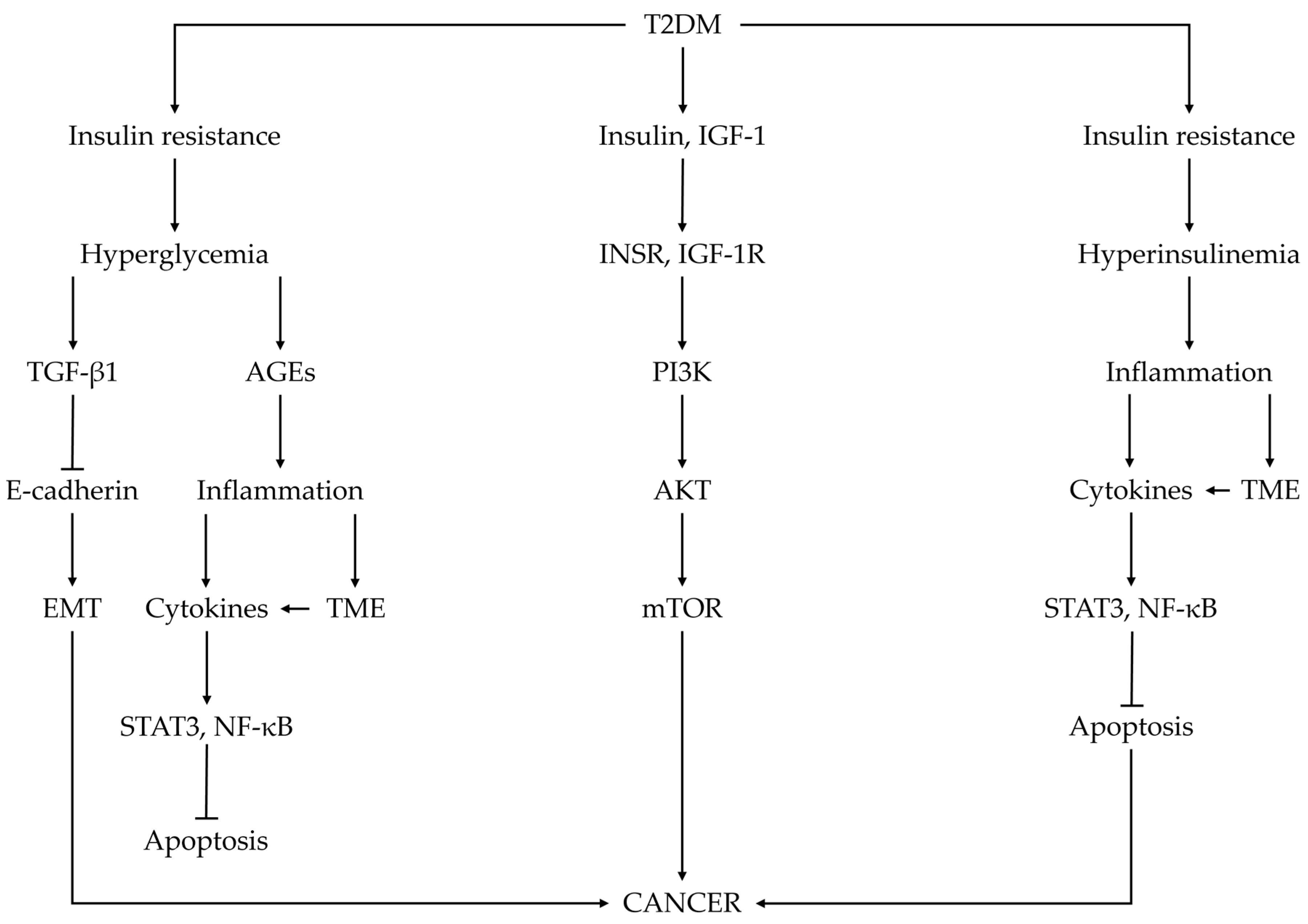
| Cancer Type | Random Effects (95% CI) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Oral | 1.41 (1.16–1.72) | [8] |
| Gastric | 1.28 (0.93–1.76); 1.29 (1.04–1.59) | [8,124] |
| Colorectal | 1.20 (1.03–1.40); 1.20 (1.03–1.40); 1.12 (1.01–1.24) | [8,124,150] |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | 2.43 (1.67–3.55); 2.43 (1.67–3.55); | [8,124] |
| Gallbladder | 1.30 (1.07–1.59) | [8] |
| Breast | 1.24 (0.95–1.62); 1.24 (0.95–1.62); 1.57 (1.23–2.01) | [8,124,193] |
| Endometrial | 1.32 (1.13–1.55); 1.23 (0.78–1.93); | [8,124] |
| Kidney | 1.16 (1.01–1.33) | [124] |
| Cancer mortality in women | ||
| Gastric | 1.24 (0.95–1.63) | [53] |
| Colon | 1.18 (1.04–1.33) | [53] |
| Liver or intrahepatic bile duct | 1.40 (1.05–1.86) | [53] |
| Pancreas | 1.31 (1.14–1.51) | [53] |
| Breast | 1.16 (1.03–1.29) | [53] |
| Endometrial | 1.33 (1.08–1.65) | [53] |
| Cervix | 1.47 (1.19–3.03) | [53] |
| Kidney and urinary organs | 1.15 (0.88–1.52) | [53] |
| Cancer mortality in men | ||
| Oral cavity and pharynx | 1.44 (1.07–1.94) | [53] |
| Colon | 1.15 (1.03–1.29) | [53] |
| Liver or intrahepatic bile duct | 2.26 (1.89–2.70) | [53] |
| Pancreas | 1.40 (1.23–1.59) | [53] |
| Bladder | 1.22 (1.01–1.47) | [53] |
| Breast | 4.20 (2.20–8.04) | [53] |
| Prostate | 0.88 (0.79–0.97) | [53] |
| Cancer Type | Risk Estimates (95% CI) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Liver | SRR = 2.01 (1.61–2.51) | [36] |
| Pancreas | RR = 1.94 (1.66–2.27) | [95] |
| Colorectal | RR = 1.26 (1.20–1.31) | [154] |
| Esophagus | SSR = 1.30 (1.12–1.50) | [123] |
| Kidney | RR = 1.42 (1.06–1.91) | [159] |
| Bladder | RR = 1.24 (1.08–1.42); 1.35 (1.17–1.58) | [36,124] |
| Breast | RR = 1.20 (1.12–1.28); 1.25 (1.20–1.29) | [8,192] |
| Endometrial | RR = 1.65 (1.50–1.81); 1.89 (1.46–2.45); 2.22 (1.80–2.74); 2.10 (1.75–2.53); OR = 1.70 (1.2–2.3) | [8,31,198,201,202] |
| Blood | Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma OR = 1.22 (1.07–1.39); Leukemia OR = 1.22 (1.03–1.44); Myeloma OR = 1.22 (0.98–1.53) | [184] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pliszka, M.; Szablewski, L. Associations between Diabetes Mellitus and Selected Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137476
Pliszka M, Szablewski L. Associations between Diabetes Mellitus and Selected Cancers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(13):7476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137476
Chicago/Turabian StylePliszka, Monika, and Leszek Szablewski. 2024. "Associations between Diabetes Mellitus and Selected Cancers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 13: 7476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137476
APA StylePliszka, M., & Szablewski, L. (2024). Associations between Diabetes Mellitus and Selected Cancers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(13), 7476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137476






