Novel Cascade Alpha Satellite HORs in Orangutan Chromosome 13 Assembly: Discovery of the 59mer HOR—The largest Unit in Primates—And the Missing Triplet 45/27/18 HOR in Human T2T-CHM13v2.0 Assembly
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
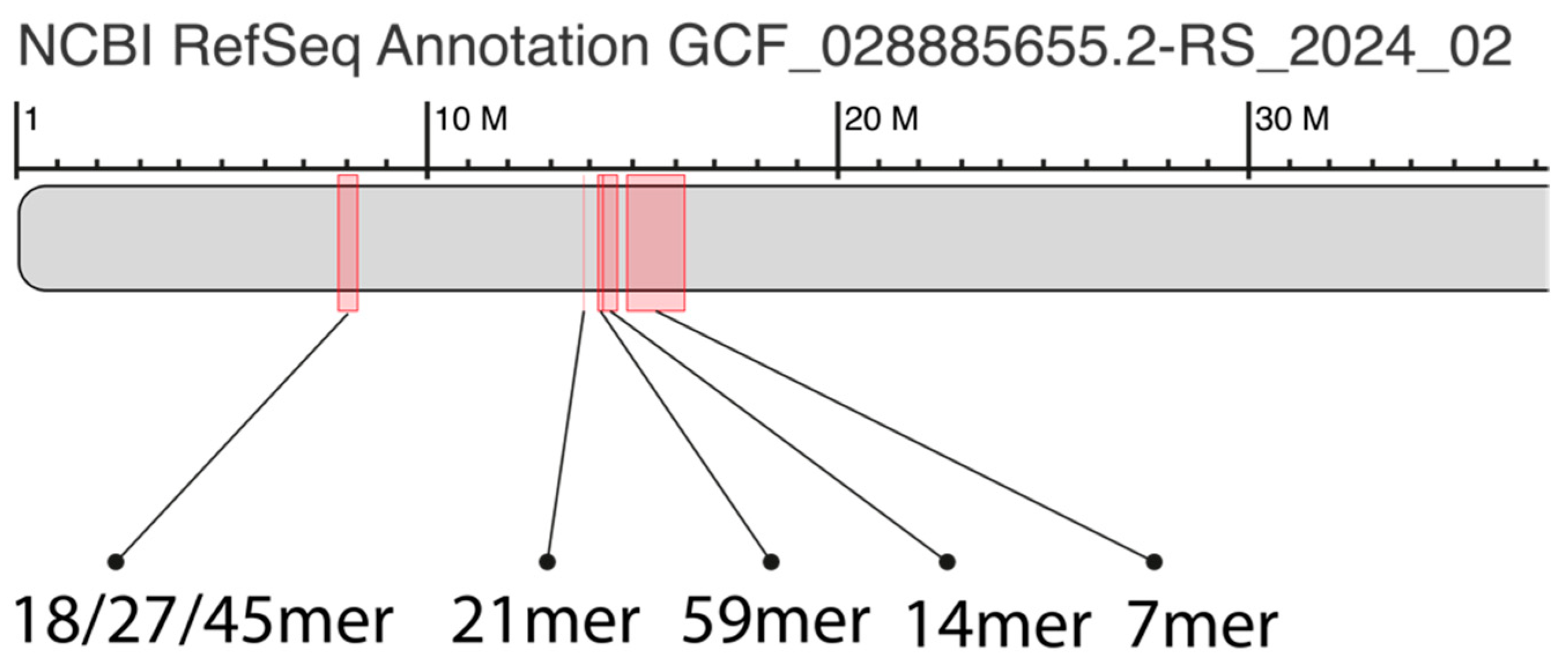
2.1. GRM (Global Repeat Map) Diagram and MD (Monomer Distance) Diagram for Orangutan Chromosome 13
2.2. Novel Orangutan Cascading 59mer HOR—The Largest Alpha Satellite HOR Copy Discovered in Primate Genomes
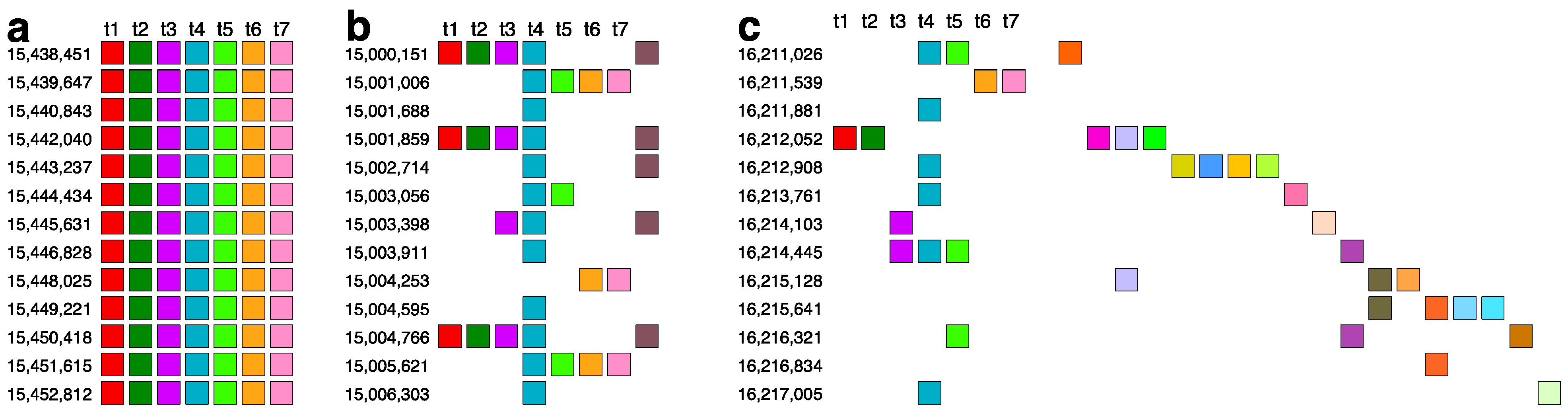
2.3. Aligned Scheme for 7mer HOR Array with 2mer, 4mer, 8mer Subfragments
2.4. Aligned Scheme of Cascading Interspersed 18/27/45mer HOR Array
2.5. Aligned Scheme for Willard’s-Type 14mer HOR Array
2.6. Aligned Scheme for Highly Riddled Willard’s-Type 21mer HOR Array
3. Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nurk, S.; Koren, S.; Rhie, A.; Rautiainen, M.; Bzikadze, A.V.; Mikheenko, A.; Vollger, M.R.; Altemose, N.; Uralsky, L.; Gershman, A.; et al. The complete sequence of a human genome. Science 2022, 376, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miga, K.H. Centromere studies in the era of ‘telomere-to-telomere’ genomics. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 394, 112127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cechova, M.; Miga, K.H. Comprehensive variant discovery in the era of complete human reference genomes. Nat. Methods 2023, 20, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altemose, N.; Logsdon, G.A.; Bzikadze, A.V.; Sidhwani, P.; Langley, S.A.; Caldas, G.V.; Hoyt, S.J.; Uralsky, L.; Ryabov, F.D.; Shew, C.J.; et al. Complete genomic and epigenetic maps of human centromeres. Science 2022, 376, eabl4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altemose, N. A classical revival: Human satellite DNAs enter the genomics era. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 128, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershman, A.; Sauria, M.E.G.; Guitart, X.; Vollger, M.R.; Hook, P.W.; Hoyt, S.J.; Jain, M.; Shumate, A.; Razaghi, R.; Koren, S.; et al. Epigenetic patterns in a complete human genome. Science 2022, 376, eabj5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miga, K.H. The Promises and Challenges of Genomic Studies of Human Centromeres. In Centromeres and Kinetochores; Progress in Molecular and Subcellular Biology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume Voume 56, pp. 285–304. [Google Scholar]
- Miga, K.H.; Alexandrov, I.A. Variation and Evolution of Human Centromeres: A Field Guide and Perspective. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2021, 55, 583–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logsdon, G.A.; Rozanski, A.N.; Ryabov, F.; Potapova, T.; Shepelev, V.A.; Catacchio, C.R.; Porubsky, D.; Mao, Y.; Yoo, D.; Rautiainen, M.; et al. The variation and evolution of complete human centromeres. Nature 2024, 629, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archidiacono, N.; Antonacci, R.; Marzella, R.; Finelli, P.; Lonoce, A.; Rocchi, M. Comparative mapping of human alphoid sequences in great apes using fluorescence in situ hybridization. Genomics 1995, 25, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cechova, M.; Harris, R.S.; Tomaszkiewicz, M.; Arbeithuber, B.; Chiaromonte, F.; Makova, K.D. High Satellite Repeat Turnover in Great Apes Studied with Short- and Long-Read Technologies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 36, 2415–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuelidis, L. Chromosomal localization of complex and simple repeated human DNAs. Chromosoma 1978, 66, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.C.; Manuelidis, L. Sequence definition and organization of a human repeated DNA. J. Mol. Biol. 1980, 142, 363–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willard, H.F. Chromosome-specific organization of human alpha satellite DNA. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1985, 37, 524–532. [Google Scholar]
- Waye, J.S.; Willard, H.F. Structure, organization, and sequence of alpha satellite DNA from human chromosome 17: Evidence for evolution by unequal crossing-over and an ancestral pentamer repeat shared with the human X chromosome. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1986, 6, 3156–3165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Willard, H.F.; Waye, J.S. Chromosome-specific subsets of human alpha satellite DNA: Analysis of sequence divergence within and between chromosomal subsets and evidence for an ancestral pentameric repeat. J. Mol. Evol. 1987, 25, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waye, J.S.; Willard, H.F. Nucleotide sequence heterogeneity of alpha satellite repetitive DNA: A survey of alphoid sequences from different human chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987, 15, 7549–7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, A.L.; Bostock, C.J.; Bak, A.L. Chromosome-specific subfamilies within human alphoid repetitive DNA. J. Mol. Biol. 1986, 187, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willard, H.F. Evolution of alpha satellite. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1991, 1, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, K.H.; Vissel, B.; Nagy, A.; Earle, E.; Kalitsis, P. A survey of the genomic distribution of alpha satellite DNA on all the human chromosomes, and derivation of a new consensus sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991, 19, 1179–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluncic, M.; Paar, V. Direct mapping of symbolic DNA sequence into frequency domain in global repeat map algorithm. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanova, L.Y.; Deriagin, G.V.; Mashkova, T.D.; Tumeneva, I.G.; Mushegian, A.R.; Kisselev, L.L.; Alexandrov, I.A. Evidence for selection in evolution of alpha satellite DNA: The central role of CENP-B/pJ alpha binding region. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 261, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warburton, P.E.; Willard, H.F. Evolution of centromeric alpha satellite DNA: Molecular organisation within and between human primate chromosomes. In Human Genome Evolution; BIOS Scientific Publisher: Oxford, UK, 1996; pp. 121–145. [Google Scholar]
- O’Keefe, C.L.; Matera, A.G. Alpha satellite DNA variant-specific oligoprobes differing by a single base can distinguish chromosome 15 homologs. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, I.; Kazakov, A.; Tumeneva, I.; Shepelev, V.; Yurov, Y. Alpha-satellite DNA of primates: Old and new families. Chromosoma 2001, 110, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schueler, M.G.; Higgins, A.W.; Rudd, M.K.; Gustashaw, K.; Willard, H.F. Genomic and genetic definition of a functional human centromere. Science 2001, 294, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, C.; Eichler, E.E.; Bailey, J.A.; Sahinalp, S.C.; Tuzun, E. The role of unequal crossover in alpha-satellite DNA evolution: A computational analysis. J. Comput. Biol. 2004, 11, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurka, J.; Kapitonov, V.V.; Pavlicek, A.; Klonowski, P.; Kohany, O.; Walichiewicz, J. Repbase Update, a database of eukaryotic repetitive elements. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2005, 110, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudd, M.K.; Wray, G.A.; Willard, H.F. The evolutionary dynamics of alpha-satellite. Genome Res. 2006, 16, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkan, C.; Ventura, M.; Archidiacono, N.; Rocchi, M.; Sahinalp, S.C.; Eichler, E.E. Organization and evolution of primate centromeric DNA from whole-genome shotgun sequence data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2007, 3, 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paar, V.; Gluncic, M.; Rosandic, M.; Basar, I.; Vlahovic, I. Intragene higher order repeats in neuroblastoma breakpoint family genes distinguish humans from chimpanzees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 1877–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, K.E.; Strome, E.D.; Merrett, S.L.; Lee, H.R.; Rudd, M.K.; Willard, H.F. Sequences associated with centromere competency in the human genome. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, S.; Hirai, Y.; Hirai, H.; Koga, A. Higher-order repeat structure in alpha satellite DNA is an attribute of hominoids rather than hominids. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 58, 752–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldrup-Macdonald, M.E.; Sullivan, B.A. The past, present, and future of human centromere genomics. Genes 2014, 5, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miga, K.H.; Newton, Y.; Jain, M.; Altemose, N.; Willard, H.F.; Kent, W.J. Centromere reference models for human chromosomes X and Y satellite arrays. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepelev, V.A.; Uralsky, L.I.; Alexandrov, A.A.; Yurov, Y.B.; Rogaev, E.I.; Alexandrov, I.A. Annotation of suprachromosomal families reveals uncommon types of alpha satellite organization in pericentromeric regions of hg38 human genome assembly. Genom. Data 2015, 5, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, L.L.; Chew, K.; Sullivan, B.A. alpha satellite DNA variation and function of the human centromere. Nucleus 2017, 8, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uralsky, L.I.; Shepelev, V.A.; Alexandrov, A.A.; Yurov, Y.B.; Rogaev, E.I.; Alexandrov, I.A. Classification and monomer-by-monomer annotation dataset of suprachromosomal family 1 alpha satellite higher-order repeats in hg38 human genome assembly. Data Brief 2019, 24, 103708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wlodzimierz, P.; Hong, M.; Henderson, I.R. TRASH: Tandem Repeat Annotation and Structural Hierarchy. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, A.F.A.; Hubley, R.; Green, P. RepeatMasker Open-3.0. 1996–2010. Available online: http://www.repeatmasker.org (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Novak, P.; Neumann, P.; Macas, J. Graph-based clustering and characterization of repetitive sequences in next-generation sequencing data. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunyavskaya, O.; Dvorkina, T.; Bzikadze, A.V.; Alexandrov, I.A.; Pevzner, P.A. Automated annotation of human centromeres with HORmon. Genome Res. 2022, 32, 1137–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bzikadze, A.V.; Pevzner, P.A. Automated assembly of centromeres from ultra-long error-prone reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevim, V.; Bashir, A.; Chin, C.S.; Miga, K.H. Alpha-CENTAURI: Assessing novel centromeric repeat sequence variation with long read sequencing. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 1921–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Yang, X.; Guo, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, B.; Ye, K. HiCAT: A tool for automatic annotation of centromere structure. Genome Biol. 2023, 24, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvorkina, T.; Kunyavskaya, O.; Bzikadze, A.V.; Alexandrov, I.; Pevzner, P.A. CentromereArchitect: Inference and analysis of the architecture of centromeres. Bioinformatics 2021, 37 (Suppl. 1), i196–i204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.W.; Asri, M.; Ebler, J.; Doerr, D.; Haukness, M.; Hickey, G.; Lu, S.; Lucas, J.K.; Monlong, J.; Abel, H.J.; et al. A draft human pangenome reference. Nature 2023, 617, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, D.P.; Hillier, L.W.; Warren, W.C.; Worley, K.C.; Nazareth, L.V.; Muzny, D.M.; Yang, S.P.; Wang, Z.; Chinwalla, A.T.; Minx, P.; et al. Comparative and demographic analysis of orang-utan genomes. Nature 2011, 469, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, A.; Hirai, Y.; Terada, S.; Jahan, I.; Baicharoen, S.; Arsaithamkul, V.; Hirai, H. Evolutionary origin of higher-order repeat structure in alpha-satellite DNA of primate centromeres. DNA Res. 2014, 21, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluncic, M.; Vlahovic, I.; Mrsic, L.; Paar, V. Global Repeat Map (GRM) Application: Finding All DNA Tandem Repeat Units. Algorithms 2022, 15, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluncic, M.; Vlahovic, I.; Rosandic, M.; Paar, V. Tandemly repeated NBPF HOR copies (Olduvai triplets): Possible impact on human brain evolution. Life Sci. Alliance 2023, 6, e202101306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paar, V.; Basar, I.; Rosandic, M.; Gluncic, M. Consensus higher order repeats and frequency of string distributions in human genome. Curr. Genom. 2007, 8, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluncic, M.; Vlahovic, I.; Rosandic, M.; Paar, V. Novel Concept of Alpha Satellite Cascading Higher-Order Repeats (HORs) and Precise Identification of 15mer and 20mer Cascading HORs in Complete T2T-CHM13 Assembly of Human Chromosome 15. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negadi, T. Revealing the genetic code symmetries through computations involving Fibonacci-like sequences and their properties. Computation 2023, 11, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šošić, M.; Šikić, M. Edlib: A C/C ++ library for fast, exact sequence alignment using edit distance. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 1394–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
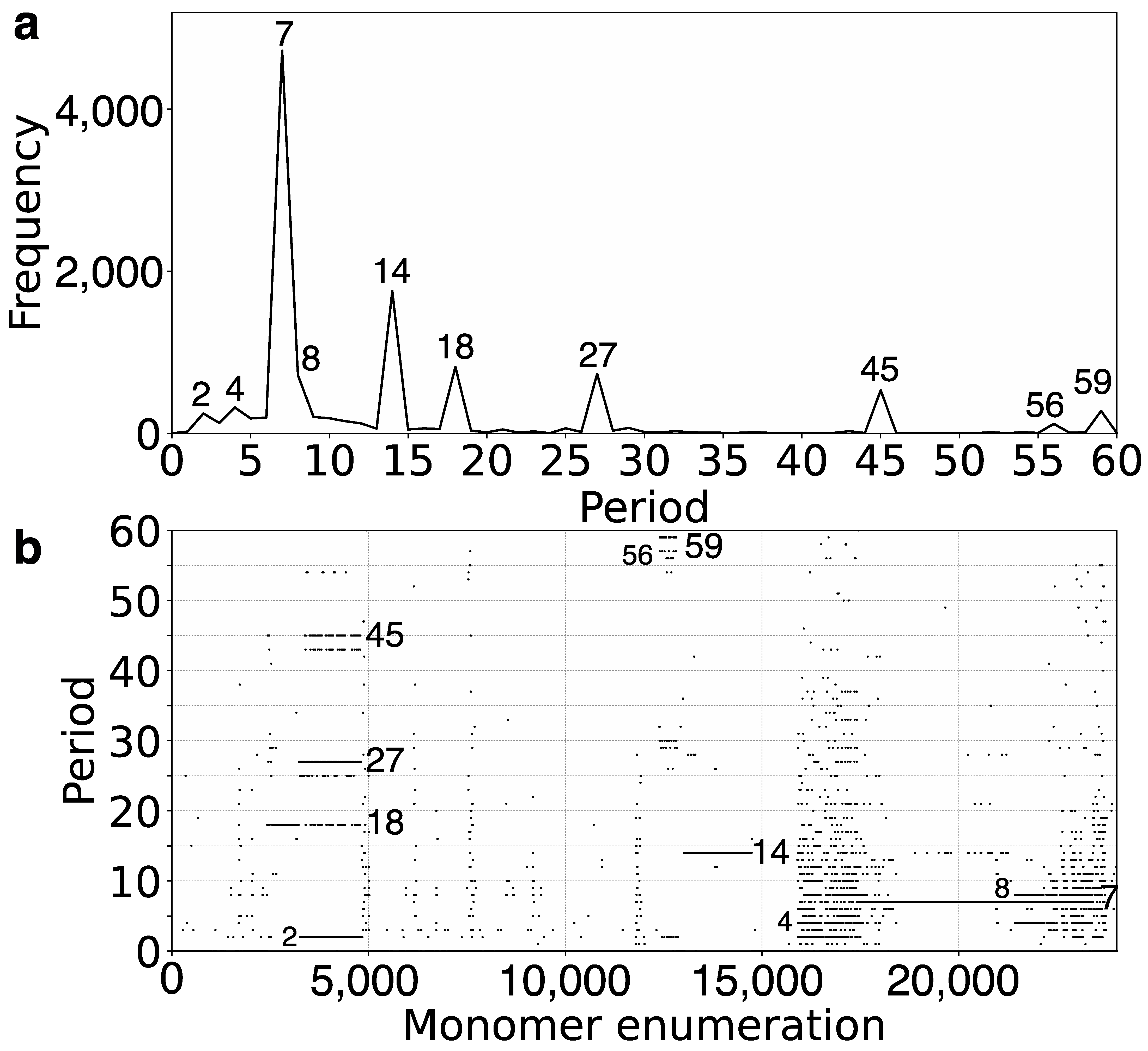
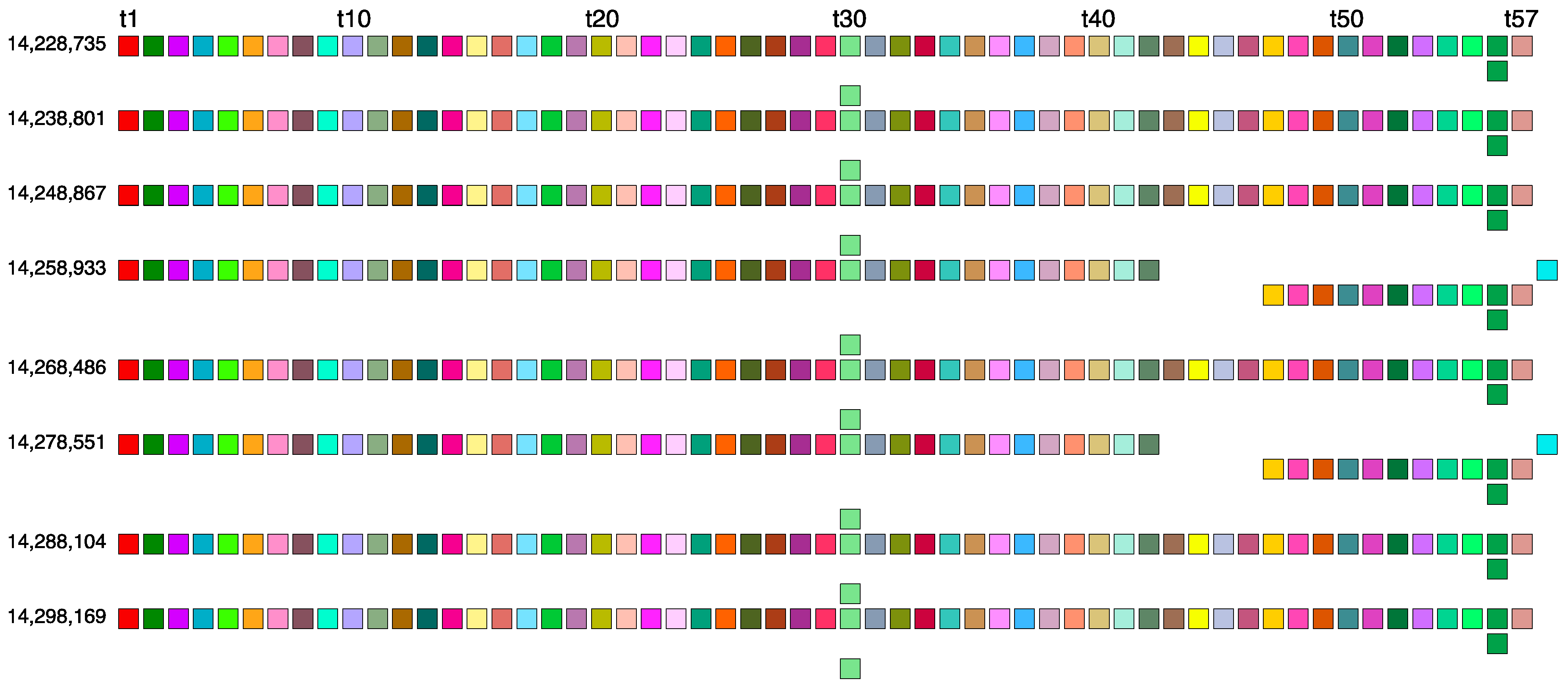
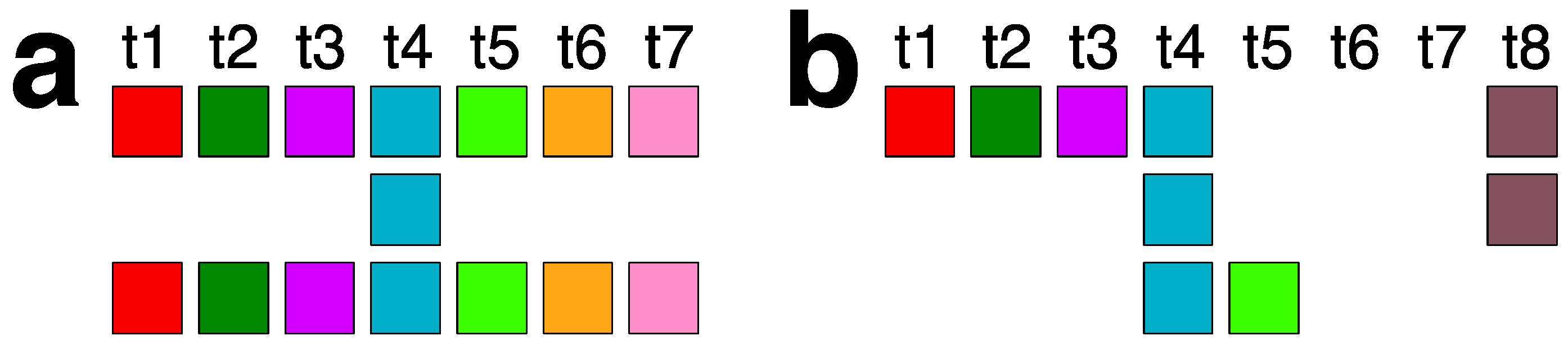

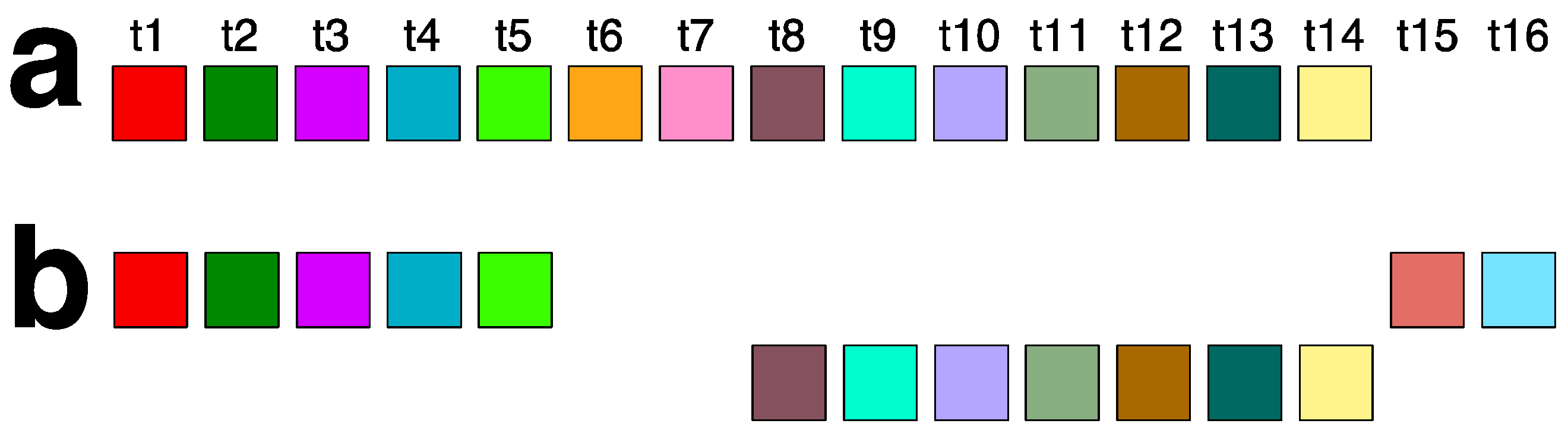
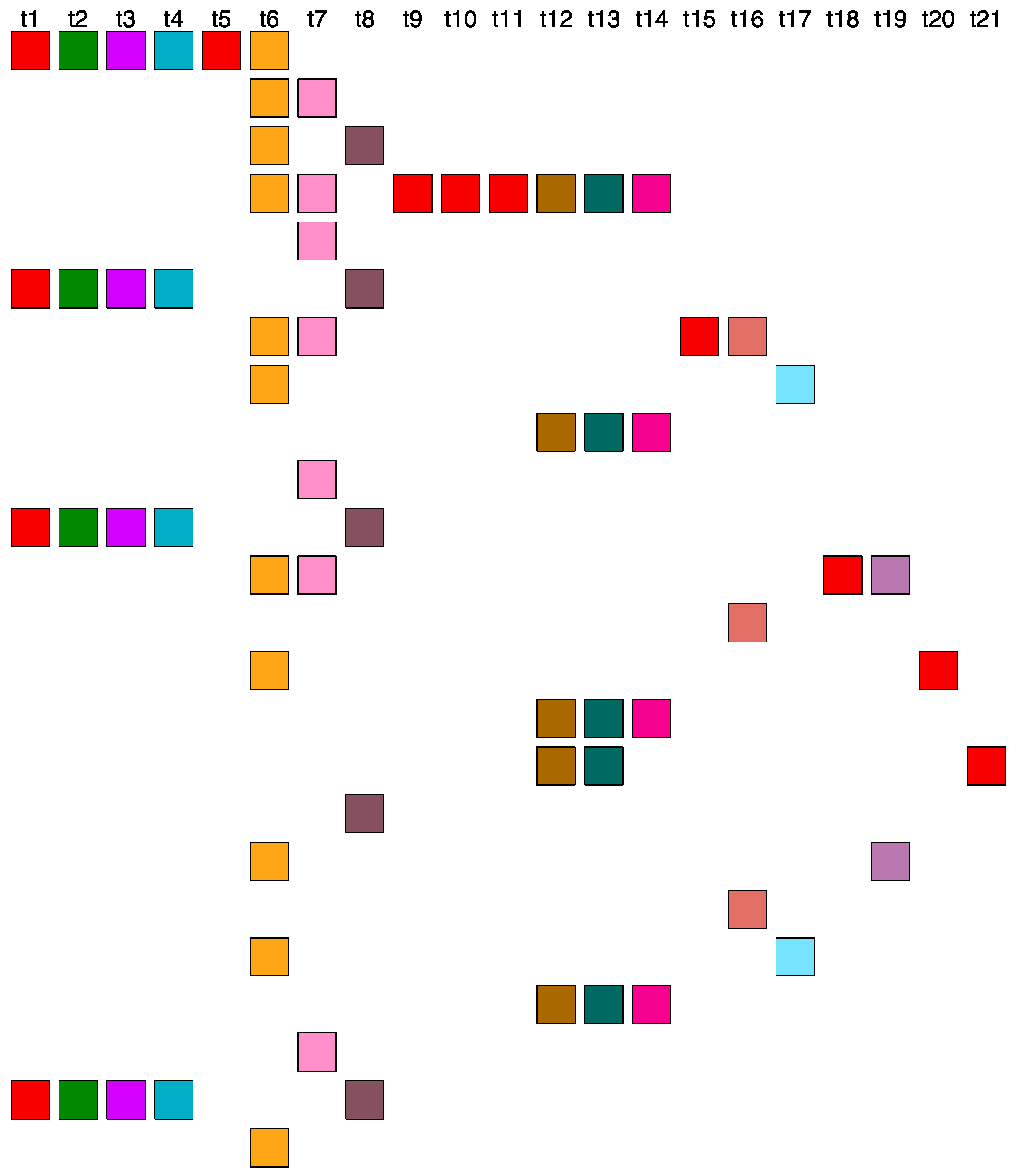

| No. of MD Points | Period | Repeat Pattern |
|---|---|---|
| 4720 | 7 | 7mer HOR |
| 1753 | 14 | 14mer HOR |
| 819 | 18 | interspersed 18/27/45mer HOR |
| 734 | 27 | interspersed 18/27/45mer HOR |
| 718 | 8 | 8mer subfragment in 7mer HOR |
| 530 | 45 | interspersed 14/27/45mer HOR |
| 319 | 4 | 8mer subfragment in 7mer HOR |
| 277 | 59 | 59mer HOR |
| 244 | 2 | 2mer subfragment in 7mer HOR |
| 1 × 18, 1 × 45v, 1 × 45, 1 × 18v, 33 × 18, 5 × 18v, 1 × 18v, 1 × 27, 5 × 27, 1 × 45, 2 × 27, 1 × 18′, 1 × 45, 1 × 18′, |
| 2 × 45, 1 × 18′, 3 × 45, 2 × 27, 1 × 18′, 1 × 45, 1 × 18′, 3 × 45, 2 × 27, 1 × 18′, 5 × 45, 5 × 27, 1 × 45, 1 × 27, 4 × 45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Glunčić, M.; Vlahović, I.; Rosandić, M.; Paar, V. Novel Cascade Alpha Satellite HORs in Orangutan Chromosome 13 Assembly: Discovery of the 59mer HOR—The largest Unit in Primates—And the Missing Triplet 45/27/18 HOR in Human T2T-CHM13v2.0 Assembly. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147596
Glunčić M, Vlahović I, Rosandić M, Paar V. Novel Cascade Alpha Satellite HORs in Orangutan Chromosome 13 Assembly: Discovery of the 59mer HOR—The largest Unit in Primates—And the Missing Triplet 45/27/18 HOR in Human T2T-CHM13v2.0 Assembly. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(14):7596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147596
Chicago/Turabian StyleGlunčić, Matko, Ines Vlahović, Marija Rosandić, and Vladimir Paar. 2024. "Novel Cascade Alpha Satellite HORs in Orangutan Chromosome 13 Assembly: Discovery of the 59mer HOR—The largest Unit in Primates—And the Missing Triplet 45/27/18 HOR in Human T2T-CHM13v2.0 Assembly" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 14: 7596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147596
APA StyleGlunčić, M., Vlahović, I., Rosandić, M., & Paar, V. (2024). Novel Cascade Alpha Satellite HORs in Orangutan Chromosome 13 Assembly: Discovery of the 59mer HOR—The largest Unit in Primates—And the Missing Triplet 45/27/18 HOR in Human T2T-CHM13v2.0 Assembly. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(14), 7596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147596








