Get Spliced: Uniting Alternative Splicing and Arthritis
Abstract
:1. Understanding Alternative Splicing: Principles, Regulation, and Outcomes
Alternative Splicing as a Post-Transcriptional Regulator of Dynamic Cell Responses
2. Alternative Splicing Plays an Important Role in the Immune Response
2.1. Alternative Splicing as a Regulator of Cytokine Expression in Innate Immune Cells
2.2. Alternative Splicing as an Inflammasome Activation Regulator
2.3. Alternative Splicing as a Regulator of Innate Immune Cell Activation
2.4. Alternative Splicing as a Regulator of Cytokine Expression in Adaptive Immune Cells
2.5. Alternative Splicing as a Regulator of T Cell Subset Differentiation
2.6. Alternative Splicing as a Regulator of NFκB Signalling in Adaptive Immune Cells
3. Alternative Splicing in the Scope of Inflammatory Arthritis
3.1. Alternative Splicing of CD44 in Arthritis
3.2. Alternative Splicing of IL-6R in Arthritis
3.3. Alternative Splicing of Survivin in Arthritis
4. The Clinical Relevance of Alternative Splicing in Arthritis
4.1. Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy for the Suppression of Proteins
4.2. Isoform-Specific Targeting with Monoclonal Antibodies
4.3. Utilizing Antagonistic Isoforms to Counter Inflammation
4.4. Challenges, Limitations, and Future Prospects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, B.O.; Xu, Y.-M.; Li, J.; Huang, L.-F.; Lin, J.; Zhang, J.; Min, Q.-H.; Yang, W.-M.; et al. Mechanism of alternative splicing and its regulation. Biomed. Rep. 2015, 3, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaub, A.; Glasmacher, E. Splicing in immune cells-mechanistic insights and emerging topics. Int. Immunol. 2017, 29, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keren, H.; Lev-Maor, G.; Ast, G. Alternative splicing and evolution: Diversification, exon definition and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Manley, J.L. Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation: Insights from molecular and genomics approaches. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, K.W. Consequences of regulated pre-mRNA splicing in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.; Im, S.H. Interleukin and interleukin receptor diversity: Role of alternative splicing. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 29, 77–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, C.M.; Mills, K.H.G. The cells that mediate innate immune memory and their functional significance in inflammatory and infectious diseases. Semin. Immunol. 2016, 28, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, N.M.; Lynch, K.W. Control of alternative splicing in immune responses: Many regulators, many predictions, much still to learn. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 253, 216–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bruin, R.G.; Shiue, L.; Prins, J.; de Boer, H.C.; Singh, A.; Fagg, W.S.; van Gils, J.M.; Duijs, J.M.; Katzman, S.; Kraaijeveld, A.O.; et al. Quaking promotes monocyte differentiation into pro-atherogenic macrophages by controlling pre-mRNA splicing and gene expression. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lorenzini, P.A.; Zhang, F.; Xu, S.; Wong, M.S.M.; Zheng, J.; Roca, X. Alternative splicing analysis in human monocytes and macrophages reveals MBNL1 as major regulator. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 6069–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamo, J.; Suzuki, A.; Ueda, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Nishida, H.; Suzuki, K.; Kaneko, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Ishihama, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; et al. Immune Isoform Atlas: Landscape of alternative splicing in human immune cells. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergun, A.; Doran, G.; Costello, J.C.; Paik, H.H.; Collins, J.J.; Mathis, D.; Benoist, C.; Consortium, I.; Blair, D.A.; Dustin, M.L.; et al. Differential splicing across immune system lineages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14324–14329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberdoerffer, S.; Moita, L.F.; Neems, D.; Freitas, R.P.; Hacohen, N.; Rao, A. Regulation of CD45 alternative splicing by heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein, hnRNPLL. Science 2008, 321, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawes, R.; Petrova, S.; Liu, Z.; Wraith, D.; Beverley, P.C.L.; Tchilian, E.Z. Combinations of CD45 isoforms are crucial for immune function and disease. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 3417–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Dam, G.B.; Zilch, C.F.; Wallace, D.; Wieringa, B.; Beverley, P.C.L.; Poels, L.G.; Screaton, G.R. Regulation of Alternative Splicing of CD45 by Antagonistic Effects of SR Protein Splicing Factors. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 5287–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, K.O.; Scott, H.M.; Torres-Odio, S.; West, A.P.; Patrick, K.L.; Watson, R.O. The Splicing Factor hnRNP M Is a Critical Regulator of Innate Immune Gene Expression in Macrophages. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 1594–1609.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, R.J.; Hammacher, A.; Smith, D.K.; Matthews, J.M.; Ward, L.D. Interleukin-6: Structure-function relationships. Protein Sci. 1997, 6, 929–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoss, F.; Mueller, J.L.; Rojas Ringeling, F.; Rodriguez-Alcazar, J.F.; Brinkschulte, R.; Seifert, G.; Stahl, R.; Broderick, L.; Putnam, C.D.; Kolodner, R.D.; et al. Alternative splicing regulates stochastic NLRP3 activity. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giblin, S.P.; Schwenzer, A.; Midwood, K.S. Alternative splicing controls cell lineage-specific responses to endogenous innate immune triggers within the extracellular matrix. Matrix Biol. 2020, 93, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabas, M.; Elliott, H.; Hoyne, G.F. The Role of Alternative Splicing in the Control of Immune Homeostasis and Cellular Differentiation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Galarza-Munoz, G.; Garcia-Blanco, M.A. Role of RNA Alternative Splicing in T Cell Function and Disease. Genes. 2023, 14, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajaj, E. Alternative splicing of SLAMF6 in human T cells creates a co-stimulatory isoform that counteracts the inhibitory effect of the full-length receptor. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nik Tavakoli, N.; Hambly, B.D.; Sullivan, D.R.; Bao, S. Forkhead box protein 3: Essential immune regulatory role. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 2369–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailer, R.K.; Joly, A.L.; Liu, S.; Elias, S.; Tegner, J.; Andersson, J. IL-1beta promotes Th17 differentiation by inducing alternative splicing of FOXP3. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurchy, A.N.; Gillies, J.; Gizzi, M.C.; Riba, M.; Manuel Garcia-Manteiga, J.; Cittaro, D.; Lazarevic, D.; Nunzio, S.D.; Piras, I.S.; Bulfone, A.; et al. A novel function for FOXP3 in humans: Intrinsic regulation of conventional T cells. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2013, 121, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Lopes, J.E.; Chong, M.M.W.; Ivanov, I.I.; Min, R.; Victora, G.D.; Shen, Y.; Du, J.; Rubtsov, Y.P.; Rudensky, A.Y.; et al. LETTERS TGF-b-induced Foxp3 inhibits T H 17 cell differentiation by antagonizing RORct function Rorc(gt) gfp/+ CD4 Foxp3 Rorc(gt) gfp/gfp CD4 + GFP int Foxp3 + Foxp3-Foxp3 + Foxp3-CD4 CD4 CD4. Nature 2008, 453, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, S.; Chen, S.; Fu, Y.; Spath, S.; Domeier, P.; Hagin, D.; Anover-Sombke, S.; Haouili, M.; et al. FOXP3 exon 2 controls T(reg) stability and autoimmunity. Sci. Immunol. 2022, 7, eabo5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.-C. The noncanonical NF-κB pathway. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, M.; Wilhelmi, I.; Schultz, A.-S.; Preussner, M.; Heyd, F. Activation-induced Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor-associated Factor 3 (Traf3) Alternative Splicing Controls the Noncanonical Nuclear Factor κB Pathway and Chemokine Expression in Human T Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 13651–13660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreuder, M.I.; van den Brand, M.; Hebeda, K.M.; Groenen, P.; van Krieken, J.H.; Scheijen, B. Novel developments in the pathogenesis and diagnosis of extranodal marginal zone lymphoma. J. Hematop. 2017, 10, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, S.; Han, S.; Zheng, Y.; Planelles, V.; Lee, Y. The landscape of alternative splicing in HIV-1 infected CD4 T-cells. BMC Med. Genom. 2020, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Lu, L.; Cai, S.; Chen, J.; Lin, W.; Han, F. Alternative Splicing: A New Cause and Potential Therapeutic Target in Autoimmune Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 713540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takata, A.; Matsumoto, N.; Kato, T. Genome-wide identification of splicing QTLs in the human brain and their enrichment among schizophrenia-associated loci. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Martin, D.; Borsari, B.; Calvo, M.; Reverter, F.; Guigo, R. Identification and analysis of splicing quantitative trait loci across multiple tissues in the human genome. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evsyukova, I.; Somarelli, J.A.; Gregory, S.G.; Garcia-Blanco, M.A. Alternative splicing in multiple sclerosis and other autoimmune diseases. RNA Biol. 2010, 7, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Y.; Leng, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Z. The regulatory role of alternative splicing in inflammatory bowel disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1095267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodde, V.; Floris, M.; Zoroddu, E.; Zarbo, I.R.; Idda, M.L. RNA-binding proteins in autoimmunity: From genetics to molecular biology. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2023, 14, e1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsoula, G.; Steinberg, J.; Tuerlings, M.; Coutinho de Almeida, R.; Southam, L.; Swift, D.; Meulenbelt, I.; Wilkinson, J.M.; Zeggini, E. A molecular map of long non-coding RNA expression, isoform switching and alternative splicing in osteoarthritis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2022, 31, 2090–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Dong, L.; Tao, H.; Dong, Y.; Xiang, W.; Tao, F.; Zhao, Y. RNA-binding proteins potentially regulate the alternative splicing of apoptotic genes during knee osteoarthritis progression. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Huang, D. Alternative Splicing of Pre-mRNA in the Control of Immune Activity. Genes 2021, 12, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundkvist, J.; Kastang, F.; Kobelt, G. The burden of rheumatoid arthritis and access to treatment: Health burden and costs. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2008, 8 (Suppl. S2), S49–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibanez-Costa, A.; Perez-Sanchez, C.; Patino-Trives, A.M.; Luque-Tevar, M.; Font, P.; Arias de la Rosa, I.; Roman-Rodriguez, C.; Abalos-Aguilera, M.C.; Conde, C.; Gonzalez, A.; et al. Splicing machinery is impaired in rheumatoid arthritis, associated with disease activity and modulated by anti-TNF therapy. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshkar Sebban, L.; Ronen, D.; Levartovsky, D.; Elkayam, O.; Caspi, D.; Aamar, S.; Amital, H.; Rubinow, A.; Golan, I.; Naor, D.; et al. The Involvement of CD44 and Its Novel Ligand Galectin-8 in Apoptotic Regulation of Autoimmune Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, S.; Karnad, A.; Freeman, J.W. The biology and role of CD44 in cancer progression: Therapeutic implications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuff, C.A.; Puré, E. A crucial role for CD44 in inflammation. TRENDS Mol. Med. 2001, 7, 213–221. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, P.; Ruffell, B. CD44 and its role in inflammation and inflammatory diseases. Inflamm. Allergy Drug. Targets 2009, 8, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barshishat, M.; Ariel, A.; Cahalon, L.; Chowers, Y.; Lider, O.; Schwartz, B. TNFα and IL-8 regulate the expression and function of CD44 variant proteins in human colon carcinoma cells. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2002, 19, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittl, E.M.; Haberhauer, G.; Ruckser, R.; Selleny, S.; Rech-Weichselbraun, I.; Hinterberger, W.; Bauer, K. Serum levels of soluble CD44 variant isoforms are elevated in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 1997, 16, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naor, D.; Nedvetzki, S. CD44 in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2003, 5, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumertl, T.; Lokau, J.; Rose-John, S.; Garbers, C. Function and proteolytic generation of the soluble interleukin-6 receptor in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2022, 1869, 119143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashizume, M.; Tan, S.L.; Takano, J.; Ohsawa, K.; Hasada, I.; Hanasaki, A.; Ito, I.; Mihara, M.; Nishida, K. Tocilizumab, a humanized anti-IL-6R antibody, as an emerging therapeutic option for rheumatoid arthritis: Molecular and cellular mechanistic insights. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 34, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamas, J.R.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, L.; Tornero-Esteban, P.; Villafuertes, E.; Hoyas, J.; Abasolo, L.; Varade, J.; Alvarez-Lafuente, R.; Urcelay, E.; Fernandez-Gutierrez, B. Alternative splicing and proteolytic rupture contribute to the generation of soluble IL-6 receptors (sIL-6R) in rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine 2013, 61, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkkila, M.; Andersson, K.M.; Amu, S.; Brisslert, M.; Erlandsson, M.C.; Silfversward, S.; Bokarewa, M.I. Suppressed diversity of survivin splicing in active rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2015, 17, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafari, P.; Rafiei, A.; Esmaeili, S.A.; Moonesi, M.; Taghadosi, M. Survivin a pivotal antiapoptotic protein in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 21575–21587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bost, J.P.; Ojansivu, M.; Munson, M.J.; Wesen, E.; Gallud, A.; Gupta, D.; Gustafsson, O.; Saher, O.; Radler, J.; Higgins, S.G.; et al. Novel endosomolytic compounds enable highly potent delivery of antisense oligonucleotides. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Sivanandam, V.; Wong, K.K.M., Jr. Adeno-Associated Virus and Hematopoietic Stem Cells: The Potential of Adeno-Associated Virus Hematopoietic Stem Cells in Genetic Medicines. Hum. Gene Ther. 2020, 31, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.M.; Doss, H.M.; Kim, K.S. Multifaceted Physiological Roles of Adiponectin in Inflammation and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, J.; Ruiz-Tiscar, J.L.; Rodriguez-Sainz, C.; Hernandez, A.; Santamaria, B.; Garcia-Sanchez, F.; Fernandez-Cruz, E. Prevalence of C77G polymorphism in exon 4 of the CD45 gene in the Spanish population. Med. Clin. 2005, 125, 10–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziewicz, M.A.; Tarrant, T.K.; Buckley, B.; Roberts, J.; Fulton, L.; Hansen, H.; Orum, H.; Kole, R.; Sazani, P. An Endogenous TNF-alpha Antagonist Induced by Splice-switching Oligonucleotides Reduces Inflammation in Hepatitis and Arthritis Mouse Models. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, H.; Ishigaki, K. Functional Genetics to Understand the Etiology of Autoimmunity. Genes 2023, 14, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerimov, N.; Hayhurst, J.D.; Peikova, K.; Manning, J.R.; Walter, P.; Kolberg, L.; Samovica, M.; Sakthivel, M.P.; Kuzmin, I.; Trevanion, S.J.; et al. A compendium of uniformly processed human gene expression and splicing quantitative trait loci. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1290–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ner-Gaon, H.; Peleg, R.; Gazit, R.; Reiner-Benaim, A.; Shay, T. Mapping the splicing landscape of the human immune system. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1116392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robak, T.; Gladalska, A.; Stepien, H.; Robak, E. Serum levels of interleukin-6 type cytokines and soluble interleukin-6 receptor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mediat. Inflamm. 1998, 7, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharner, J.; Ma, W.K.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, K.T.; Rigo, F.; Bennett, C.F.; Krainer, A.R. Hybridization-mediated off-target effects of splice-switching antisense oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 802–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Pearson, Z.J.; Boskovic, Z.V.; Wang, J. RNA-Targeting Splicing Modifiers: Drug Development and Screening Assays. Molecules 2021, 26, 2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmers, A.C.; Mekonen, H.E.; Campos, S.; Carpenter, S.; Vollmers, C. Generation of an isoform-level transcriptome atlas of macrophage activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, U.A.; Stephens, J.M. The gp130 receptor cytokine family: Regulators of adipocyte development and function. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolley, C.R.; Chariker, J.H.; Rouchka, E.C.; Ford, E.E.; Hudson, E.A.; Waigel, S.J.; Smith, M.L.; Mitchell, T.C. Reference long-read isoform-aware transcriptomes of 4 human peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets. G3 2022, 12, jkac253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuhara, H.; Yoshida, T.; Sasaki, K.; Obika, S.; Inoue, T. Reduction of Off-Target Effects of Gapmer Antisense Oligonucleotides by Oligonucleotide Extension. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2022, 26, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.A.; Hahm, D.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Sur, B.; Lee, H.M.; Ryu, C.J.; Yang, H.I.; Kim, K.S. Potential therapeutic antibodies targeting specific adiponectin isoforms in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, P.J.; Nowell, M.A.; Horiuchi, S.; McLoughlin, R.M.; Fielding, C.A.; Grau, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Ehrmann, M.; Rose-John, S.; Williams, A.S.; et al. Functional characterization of a soluble gp130 isoform and its therapeutic capacity in an experimental model of inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 1662–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midwood, K.S.; Chiquet, M.; Tucker, R.P.; Orend, G. Tenascin-C at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 4321–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Anastasakis, D.G.; Rodriguez, J.; Palangat, M.; Gudla, P.; Zaki, G.; Tandon, M.; Pegoraro, G.; Chow, C.C.; Hafner, M.; et al. Dynamic imaging of nascent RNA reveals general principles of transcription dynamics and stochastic splice site selection. Cell 2021, 184, 2878–2895.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Donaldson, L.F.; Beazley-Long, N. Alternative RNA splicing: Contribution to pain and potential therapeutic strategy. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 1787–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fan, X.; Tang, L. Aberrant and alternative splicing in skeletal system disease. Gene 2013, 528, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravilli, R.K.; Vikram, S.L.; Kohila, V. The Functional Impact of Alternative Splicing and Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2021, 22, 1014–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Wessel, A.W.; Xu, J.; Reinke, J.G.; Lee, E.; Kim, S.M.; Hsu, A.P.; Zilberman-Rudenko, J.; Cao, S.; Enos, C.; et al. Genetically programmed alternative splicing of NEMO mediates anautoinflammatory disease phenotype. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e128808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Poirier, E.Z.; Buck, M.D.; Chakravarty, P.; Carvalho, J.; Frederico, B.; Cardoso, A.; Healy, L.; Ulferts, R.; Beale, R.; Reis e Sousa, C. An isoform of Dicer protects mammalianstem cells against multiple RNA viruses. Science 2021, 373, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Hou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jia, J.; Wu, J.; Zuo, Z.; Gao, T.; Ren, S.; Bian, Y.; et al. CNC-bZIP protein NFE2L1 regulates osteoclast differentiation in antioxidant-dependent and independent manners. Redox Biol. 2021, 48, 102180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rose, K.W.J.; Taye, N.; Karoulias, S.Z.; Hubmacher, D. Regulation of ADAMTS Proteases. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 701959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Romberger, D.J. Fibronectin. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997, 29, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clanchy, F.I.L.; Borghese, F.; Bystrom, J.; Balog, A.; Penn, H.; Taylor, P.C.; Stone, T.W.; Mageed, R.A.; Williams, R.O. Disease status in human and experimental arthritis, and response to TNF blockade, is associated with MHC class II invariant chain (CD74) isoform expression. J. Autoimmun. 2022, 128, 102810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinhuis, B.; Koenders, M.I.; van de Loo, F.A.; Netea, M.G.; van den Berg, W.B.; Joosten, L.A. Inflammation-dependent secretion and splicing of IL-32(gamma) in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4962–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Baici, A.; Müntener, K.; Willimann, A.; Zwicky, R. Regulation of human cathepsin B by alternative mRNA splicing: Homeostasis, fatal errors and cell death. Biol. Chem. 2006, 387, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shchetynsky, K.; Protsyuk, D.; Ronninger, M.; Diaz-Gallo, L.M.; Klareskog, L.; Padyukov, L. Gene-gene interaction and RNA splicing profiles of MAP2K4 gene in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 158, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muys, B.R.; Anastasakis, D.G.; Claypool, D.; Pongor, L.; Li, X.L.; Grammatikakis, I.; Liu, M.; Wang, X.; Prasanth, K.V.; Aladjem, M.I.; et al. The p53-induced RNA-binding protein ZMAT3 is a splicing regulator that inhibits the splicing of oncogenic CD44 variants in colorectal carcinoma. Genes Dev. 2021, 35, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Santiago, B.; Izquierdo, E.; Rueda, P.; Del Rey, M.J.; Criado, G.; Usategui, A.; Arenzana-Seisdedos, F.; Pablos, J.L. CXCL12γ isoform is expressed on endothelial and dendritic cells in rheumatoid arthritis synovium and regulates T cell activation. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; He, W. UL16 binding proteins. Immunobiology 2004, 209, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobasheri, A.; Matta, C.; Uzielienè, I.; Budd, E.; Martín-Vasallo, P.; Bernotiene, E. The chondrocyte channelome: A narrative review. Jt. Bone Spine 2019, 86, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Borst, D.E.; Horowits, R. Expression and alternative splicing of N-RAP during mouse skeletal muscle development. Cell Motil. Cytoskelet. 2008, 65, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Berardi, S.; Lang, A.; Kostoulas, G.; Hörler, D.; Vilei, E.M.; Baici, A. Alternative messenger RNA splicing and enzyme forms of cathepsin B in human osteoarthritic cartilage and cultured chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Glória, V.G.; Martins de Araújo, M.; Mafalda Santos, A.; Leal, R.; de Almeida, S.F.; Carmo, A.M.; Moreira, A. T cell activation regulates CD6 alternative splicing by transcription dynamics and SRSF1. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondos, S.E.; Geraldo Mendes, G.; Jons, A. Context-dependent HOX transcription factor function in health and disease. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 174, 225–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, D.O.; Gotea, V.; Fedkenheuer, K.; Jaiswal, S.K.; Baugher, C.; Tan, H.; Fedkenheuer, M.; Elnitski, L. Characterization and clustering of kinase isoform expression in metastatic melanoma. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1010065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lin, E.A.; Liu, C.J. The role of ADAMTSs in arthritis. Protein Cell 2010, 1, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Giannopoulou, E.G.; Elemento, O.; Ivashkiv, L.B. Use of RNA sequencing to evaluate rheumatic disease patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jordan, A.R.; Racine, R.R.; Hennig, M.J.; Lokeshwar, V.B. The Role of CD44 in Disease Pathophysiology and Targeted Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gill, R.B.; Day, A.; Barstow, A.; Zaman, G.; Chenu, C.; Dhoot, G.K. Mammalian Sulf1 RNA alternative splicing and its significance to tumour growth regulation. Tumour Biol. 2012, 33, 1669–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkissian, M.; Winne, A.; Lafyatis, R. The mammalian homolog of suppressor-of-white-apricot regulates alternative mRNA splicing of CD45 exon 4 and fibronectin IIICS. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 31106–31114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.H.; Tai, T.S.; Lu, B.; Iannaccone, C.; Cernadas, M.; Weinblatt, M.; Shadick, N.; Miaw, S.C.; Ho, I.C. PTPN22.6, a dominant negative isoform of PTPN22 and potential biomarker of rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Torreggiani, S.; Torcoletti, M.; Campos-Xavier, B.; Baldo, F.; Agostoni, C.; Superti- Furga, A.; Filocamo, G. Progressive pseudorheumatoid dysplasia: A rare childhood disease. Rheumatol. Int. 2019, 39, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porola, P.; Mackiewicz, Z.; Laine, M.; Baretto, G.; Stegaev, V.; Takakubo, Y.; Takagi, M.; Ainola, M.; Konttinen, Y.T. Laminin isoform profiles in salivary glands in Sjögren’s syndrome. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2011, 55, 35–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalaris, A.; Garbers, C.; Rabe, B.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J. The soluble Interleukin 6 receptor: Generation and role in inflammation and cancer. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 90, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardif, G.; Dupuis, M.; Reboul, P.; Geng, C.S.; Pelletier, J.P.; Ranger, P.; Martel-Pelletier, J. Identification and differential expression of human collagenase-3 mRNA species derived from internal deletion, alternative splicing, and different polyadenylation and transcription initiation sites. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2003, 11, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozyrev, S.V.; Alarcon-Riquelme, M.E. The genetics and biology of Irf5-mediated signaling in lupus. Autoimmunity 2007, 40, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S. Interleukin-32 in inflammatory autoimmune diseases. Immune Netw. 2014, 14, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Morand, E.F. Effects of glucocorticoids on inflammation and arthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2007, 19, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Z.; Lin, Z.; Xu, X.H.; Lin, N.; Lu, H.D. The potential roles of circRNAs in osteoarthritis: A coming journey to find a treasure. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Christmas, P.; Ursino, S.R.; Fox, J.W.; Soberman, R.J. Expression of the CYP4F3 gene. tissue-specific splicing and alternative promoters generate high and low K(m) forms of leukotriene B(4) omega-hydroxylase. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 21191–21199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnér, E.S. Focus on mammalian thioredoxin reductases—Important selenoproteins with versatile functions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 495–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, R.N.; Curtis, K.M.; Aenlle, K.K.; Howard, G.A. Hepatocyte growth factor and alternative splice variants-expression, regulation and implications in osteogenesis and bone health and repair. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fan, Y.; Yang, J.; Xie, S.; He, J.; Huang, S.; Chen, J.; Jiang, S.; Yu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, X.; et al. Systematic analysis of inflammation and pain pathways in a mouse model of gout. Mol. Pain 2022, 18, 17448069221097760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Scheller, J.; Garbers, C.; Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6: From basic biology to selective blockade of pro-inflammatory activities. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hersh, E.V.; Lally, E.T.; Moore, P.A. Update on cyclooxygenase inhibitors: Has a third COX isoform entered the fray? Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2005, 21, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Sloane, B.F. Molecular regulation of human cathepsin B: Implication in pathologies. Biol. Chem. 2003, 384, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odhams, C.A.; Cortini, A.; Chen, L.; Roberts, A.L.; Viñuela, A.; Buil, A.; Small, K.S.; Dermitzakis, E.T.; Morris, D.L.; Vyse, T.J.; et al. Mapping eQTLs with RNA-seq reveals novel susceptibility genes, non-coding RNAs and alternative-splicing events in systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 1003–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hashimoto, T.; Yasuda, S.; Koide, H.; Kataoka, H.; Horita, T.; Atsumi, T.; Koike, T. Aberrant splicing of the hRasGRP4 transcript and decreased levels of this signaling protein in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells in a subset of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Baiyasi, A.; Barbosa, J.; Parendo, A.; Lin, X. Pleiotropy of a Stickler syndrome genotype. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 32, NP10–NP12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logsdon, C.D.; Fuentes, M.K.; Huang, E.H.; Arumugam, T. RAGE and RAGE ligands incancer. Curr. Mol. Med. 2007, 7, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, F.J.; Dahal, L.N.; Khanolkar, R.C.; Shankar, S.P.; Barker, R.N. Targeting the alternatively spliced soluble isoform of CTLA-4: Prospects for immunotherapy? Immunotherapy 2014, 6, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, A.K.; Beilstein, K.; Wittmann, S.; Sürün, D.; Saul, M.J.; Schnütgen, F.; Flamand, N.; Capelo, R.; Kahnt, A.S.; Frey, H.; et al. Characterization and cellular localization of human 5-lipoxygenase and its protein isoforms 5-LOΔ13, 5-LOΔ4 and 5-LOp12. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2017, 1862, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Niu, N.; Wada, Y.; Liu, J. The Role of Cdkn1A-Interacting Zinc Finger Protein 1 (CIZ1) in DNA Replication and Pathophysiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Naor, D.; Sionov, R.V.; Ish-Shalom, D. CD44: Structure, function, and association with the malignant process. Adv. Cancer Res. 1997, 71, 241–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nollet, M.; Bachelier, R.; Joshkon, A.; Traboulsi, W.; Mahieux, A.; Moyon, A.; Muller, A.; Somasundaram, I.; Simoncini, S.; Peiretti, F.; et al. Involvement of Multiple Variants of Soluble CD146 in Systemic Sclerosis: Identification of a Novel Profibrotic Factor. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, R.F.; Oliveira, L.; Carmo, A.M. Tuning T Cell Activation: The Function of CD6 At the Immunological Synapse and in T Cell Responses. Curr. Drug Targets 2016, 17, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Targeting interleukin 18 with interleukin 18 binding protein. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2000, 59 (Suppl. S1), i17–i20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cao, X.; Li, P.; Song, X.; Shi, L.; Qin, L.; Chen, D.; Chu, T.; Cheng, Y. PCBP1 isassociated with rheumatoid arthritis by affecting RNA products of genes involved in immune response in Th1 cells. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Barbezier, N.; Tessier, F.J.; Chango, A. Le récepteur des produits de glycation avancée RAGE/AGER: Une vue intégrative pour des applications en clinique [Receptor of advanced glycation endproducts RAGE/AGER: An integrative view for clinical applications]. Ann. Biol. Clin. 2014, 72, 669–680. (In French) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Ladner, U.; Elices, M.J.; Kriegsmann, J.B.; Strahl, D.; Gay, R.E.; Firestein, G.S.; Gay, S. Alternatively spliced CS-1 fibronectin isoform and its receptor VLA-4 in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 24, 1873–1880. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Atsumi, T.; Suzuki, H.; Jiang, J.J.; Okuyama, Y.; Nakagawa, I.; Ota, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Ohki, T.; Katsunuma, K.; Nakajima, K.; et al. Rbm10 regulates inflammation development via alternative splicing of Dnmt3b. Int. Immunol. 2017, 29, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geroldi, D.; Falcone, C.; Emanuele, E. Soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products: From disease marker to potential therapeutic target. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 1971–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.D.; Chao, T.C. Vascular endothelial growth factor in thyroid cancers. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2005, 20, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hull, K.M.; Drewe, E.; Aksentijevich, I.; Singh, H.K.; Wong, K.; McDermott, E.M.; Dean, J.; Powell, R.J.; Kastner, D.L. The TNF receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS): Emerging concepts of an autoinflammatory disorder. Medicine 2002, 81, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittig, B.M.; Stallmach, A.; Zeitz, M.; Günthert, U. Functional involvement of CD44 variant 7 in gut immune response. Pathobiology 2003, 70, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose-John, S.; Waetzig, G.H.; Scheller, J.; Grötzinger, J.; Seegert, D. The IL-6/sIL-6R complex as a novel target for therapeutic approaches. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2007, 11, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Qiao, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, X. Lymphoid-specific tyrosine phosphatase (Lyp): A potential drug target for treatment of autoimmune diseases. Curr. Drug Targets 2014, 15, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebbinghaus, C.; Scheuermann, J.; Neri, D.; Elia, G. Diagnostic and therapeutic applications of recombinant antibodies: Targeting the extra-domain B of fibronectin, a marker of tumor angiogenesis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 1537–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañete, J.D.; Albaladejo, C.; Hernández, M.V.; Laínez, B.; Pinto, J.A.; Ramírez, J.; López- Armada, M.J.; Rodríguez-Cros, J.R.; Engel, P.; Blanco, F.J.; et al. Clinical significance of high levels of soluble tumour necrosis factor-α receptor-2 produced by alternative splicing in rheumatoid arthritis: A longitudinal prospective cohort study. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenol, C.V.; Veit, T.D.; Chies, J.A.; Xavier, R.M. The role of the HLA-G gene and molecule on the clinical expression of rheumatologic diseases. Rev. Bras. Reumatol. 2012, 52, 82–91, (In English, Portuguese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, A.L.; Cuddihy, T.; Haynes, K.; Loo, D.; Morton, C.J.; Oppermann, U.; Leo, P.; Thomas, G.P.; Lê Cao, K.A.; Kenna, T.J.; et al. Genetic Variants in ERAP1 and ERAP2 Associated With Immune-Mediated Diseases Influence Protein Expression and the Isoform Profile. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, B.; Larranaga-Vera, A.; Castro, C.M.; Corciulo, C.; Rabbani, P.; Cronstein, B.N. Adenosine A2A receptor activation reduces chondrocyte senescence. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e22838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulcahy, H.; O’Rourke, K.P.; Adams, C.; Molloy, M.G.; O’Gara, F. LST1 and NCR3 expression in autoimmune inflammation and in response to IFN-gamma, LPS and microbial infection. Immunogenetics 2006, 57, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micheau, O. Cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein: An attractive therapeutic target? Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2003, 7, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Suzuki, A.; Terao, C.; Yamamoto, K. Linking of genetic risk variants to disease-specific gene expression via multi-omics studies in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 49, S49–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.P.; Zhang, Q.B.; Dai, F.; Liao, X.; Dong, Z.R.; Yi, T.; Qing, Y.F. Circular RNAs in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from ankylosing spondylitis. Chin. Med. J. 2021, 134, 2573–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yoon, H.K.; Byun, H.S.; Lee, H.; Jeon, J.; Lee, Y.; Li, Y.; Jin, E.H.; Kim, J.; Hong, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Intron-derived aberrant splicing of A20 transcript in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Błochowiak, K.J.; Trzybulska, D.; Olewicz-Gawlik, A.; Sikora, J.J.; Nowak-Gabryel, M.; Kocięcki, J.; Witmanowski, H.; Sokalski, J. Levels of EGF and VEGF in patients with primary and secondary Sjögren’s syndrome. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 27, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesterovitch, A.B.; Hoffman, M.D.; Simon, M.; Petukhov, P.A.; Tharp, M.D.; Glant, T.T. Mutations in the PSTPIP1 gene and aberrant splicing variants in patients with pyoderma gangrenosum. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 36, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naor, D.; Nedvetzki, S.; Walmsley, M.; Yayon, A.; Turley, E.A.; Golan, I.; Caspi, D.; Sebban, L.E.; Zick, Y.; Garin, T.; et al. CD44 involvement in autoimmune inflammations: The lesson to be learned from CD44-targeting by antibody or from knockout mice. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1110, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Dong, H.; Gong, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, T.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, S.; Zheng, C.; Tian, M.; et al. A Novel missense mutation of COL2A1 gene in a large family with stickler syndrome type I. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 1530–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Etem, E.O.; Koca, S.S.; Erol, D.; Yolbas, S.; Oz, E.; Elyas, H.; Isık, A. Decreased MEFV gene expression in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, H.L.; O’Shea, J.J.; Watford, W.T. STAT5 isoforms: Controversies and clarifications. Biochem. J. 2007, 404, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Peffers, M.J.; Fang, Y.; Cheung, K.; Wei, T.K.; Clegg, P.D.; Birch, H.L. Transcriptome analysis of ageing in uninjured human Achilles tendon. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yoo, S.A.; Leng, L.; Kim, B.J.; Du, X.; Tilstam, P.V.; Kim, K.H.; Kong, J.S.; Yoon, H.J.; Liu, A.; Wang, T.; et al. MIF allele-dependent regulation of the MIF coreceptor CD44 and role in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E7917–E7926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Devauchelle, V.; Essabbani, A.; De Pinieux, G.; Germain, S.; Tourneur, L.; Mistou, S.; Margottin-Goguet, F.; Anract, P.; Migaud, H.; Le Nen, D.; et al. Characterization and functional consequences of underexpression of clusterin in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 6471–6479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Yamaguchi, A.; Tsuchiya, N.; Ikawa, T.; Tamura, N.; Virtala, M.M.; Granfors, K.; Yasaei, P.; Yu, D.T. Induction of alternative splicing of HLA-B27 by bacterialinvasion. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatachalam, K.V. Human 3’-phosphoadenosine 5’-phosphosulfate (PAPS)synthase: Biochemistry, molecular biology and genetic deficiency. IUBMB Life 2003, 55, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaire, R.; Winne, A.; Sarkissian, M.; Lafyatis, R. SF2 and SRp55 regulation of CD45 exon 4 skipping during T cell activation. Eur. J. Immunol. 1999, 29, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulse, R.P.; Drake, R.A.; Bates, D.O.; Donaldson, L.F. The control of alternativesplicing by SRSF1 in myelinated afferents contributes to the development of neuropathic pain. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 96, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Muys, B.R.; Shrestha, R.L.; Anastasakis, D.G.; Pongor, L.; Li, X.L.; Grammatikakis, I.; Polash, A.; Chari, R.; Gorospe, M.; Harris, C.C.; et al. Matrin3 regulates mitotic spindle dynamics by controlling alternative splicing of CDC14B. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rong, J.; Yin, J.; Su, Z. Natural antisense RNAs are involved in the regulation of CD45 expression in autoimmune diseases. Lupus 2015, 24, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, A.H.; Hildyard, J.C.W.; Rushing, S.A.M.; Wells, D.J.; Diez-Leon, M.; Piercy, R.J. Validation of DE50-MD dogs as a model for the brain phenotype of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Dis. Model. Mech. 2022, 15, dmm049291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Qin, Z.; Qin, L.; Feng, X.; Li, Z.; Bian, J. Development of Cdc2-like Kinase 2 Inhibitors: Achievements and Future Directions. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 13191–13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitomi, Y.; Aiba, Y.; Ueno, K.; Nishida, N.; Kawai, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Tsuiji, M.; Iwabuchi, C.; Takada, S.; Miyake, N.; et al. rs2013278 in the multiple immunological-trait susceptibility locus CD28 regulates the production of non-functional splicing isoforms. Hum. Genom. 2022, 16, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ramsay, R.G.; Ciznadija, D.; Vanevski, M.; Mantamadiotis, T. Transcriptional regulation of cyclo-oxygenase expression: Three pillars of control. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2003, 16 (2 Suppl), 59–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aigner, T.; Bartnik, E.; Sohler, F.; Zimmer, R. Functional genomics of osteoarthritis: On the way to evaluate disease hypotheses. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2004, 427, S138–S143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.C.; Roghanian, A.; Brown, D.P.; Chang, C.; Allen, R.L.; Trowsdale, J.; Young, N.T. Alternative mRNA splicing creates transcripts encoding soluble proteins from most LILR genes. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 3195–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, C.H.; Robbins, P.D. The interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and its delivery by gene transfer. Receptor 1994, 4, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.D.; Bae, S.Y.; Hong, J.W.; Azam, T.; Dinarello, C.A.; Her, E.; Choi, W.S.; Kim, B.K.; Lee, C.K.; Yoon, D.Y.; et al. Identification of the most active interleukin-32 isoform. Immunology 2009, 126, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nichols, R.C.; Raben, N.; Boerkoel, C.F.; Plotz, P.H. Human isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase: Sequence of the cDNA, alternative mRNA splicing, and the characteristics of an unusually long C-terminal extension. Gene 1995, 155, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palangat, M.; Anastasakis, D.G.; Fei, D.L.; Lindblad, K.E.; Bradley, R.; Hourigan, C.S.; Hafner, M.; Larson, D.R. The splicing factor U2AF1 contributes to cancer progression through a noncanonical role in translation regulation. Genes Dev. 2019, 33, 482–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ward, F.J.; Dahal, L.N.; Wijesekera, S.K.; Abdul-Jawad, S.K.; Kaewarpai, T.; Xu, H.; Vickers, M.A.; Barker, R.N. The soluble isoform of CTLA-4 as a regulator of T-cell responses. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 1274–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouttenoire, J.; Valcourt, U.; Ronzière, M.C.; Aubert-Foucher, E.; Mallein-Gerin, F.; Herbage, D. Modulation of collagen synthesis in normal and osteoarthritic cartilage. Biorheology 2004, 41, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bottini, N.; Bottini, E.; Gloria-Bottini, F.; Mustelin, T. Low-molecular-weight protein tyrosine phosphatase and human disease: In search of biochemical mechanisms. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2002, 50, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sterenczak, K.A.; Willenbrock, S.; Barann, M.; Klemke, M.; Soller, J.T.; Eberle, N.; Nolte, I.; Bullerdiek, J.; Murua Escobar, H. Cloning, characterisation, and comparative quantitative expression analyses of receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) transcript forms. Gene 2009, 434, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, M.; Yabuuchi, A.; Tanaka, H.; Kawara, T.; Wang, H.; Inoue, K.; Shiozawa, S.; Komai, K. Expression of ASC splice variant found in Japanese patients with palindromic rheumatism is regulated by rs8056505 single nucleotide polymorphism and interleukin-1 beta. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2022. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Dong, H.; Han, J.; Ho, W.T.; Fu, X.; Zhao, Z.J. Identification of a variant form of tyrosine phosphatase LYP. BMC Mol. Biol. 2010, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ichinose, K.; Zhang, Z.; Koga, T.; Juang, Y.T.; Kis-Tóth, K.; Sharpe, A.H.; Kuchroo, V.; Crispín, J.C.; Tsokos, G.C. Brief report: Increased expression of a short splice variant of CTLA-4 exacerbates lupus in MRL/lpr mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Watanabe, H.; Kuroki, K.; Yamada, C.; Saburi, Y.; Maeda, N.; Maenaka, K. Therapeutic effects of soluble human leukocyte antigen G2 isoform in lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice. Hum. Immunol. 2020, 81, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Bello, J.; Vargas-Alarcón, G.; Tovilla-Zárate, C.; Fragoso, J.M. Polimorfismos de un solo nucleótido (SNP): Implicaciones funcionales de los SNP reguladores (rSNP) y de los SNP-ARN estructurales (srSNP) en enfermedades complejas [Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs): Functional implications of regulatory-SNP (rSNP) and structural RNA (srSNPs) in complex diseases]. Gac Med. Mex. 2013, 149, 220–228. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, M.; Miyamoto, Y.; Ikegawa, S. Cloning and characterization of the osteoarthritis-associated gene DVWA. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2011, 29, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hoolwerff, M.; Tuerlings, M.; Wijnen, I.J.L.; Suchiman, H.E.D.; Cats, D.; Mei, H.; Nelissen, R.G.H.H.; van der Linden-van der Zwaag, H.M.J.; Ramos, Y.F.M.; Coutinho de Almeida, R.; et al. Identification and functional characterization of imbalanced osteoarthritis-associated fibronectin splice variants. Rheumatology 2023, 62, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Turner, M.W.; Hamvas, R.M. Mannose-binding lectin: Structure, function, genetics and disease associations. Rev. Immunogenet. 2000, 2, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parker, A.E.; Boutell, J.; Carr, A.; Maciewicz, R.A. Novel cartilage-specific splice variants of fibronectin. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2002, 10, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sztrolovics, R.; Grover, J.; Cs-Szabo, G.; Shi, S.L.; Zhang, Y.; Mort, J.S.; Roughley, P.J. The characterization of versican and its message in human articular cartilage and intervertebral disc. J. Orthop. Res. 2002, 20, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peffers, M.J.; Collins, J.; Fang, Y.; Goljanek-Whysall, K.; Rushton, M.; Loughlin, J.; Proctor, C.; Clegg, P.D. Age-related changes in mesenchymal stem cells identified using a multi-omics approach. Eur. Cell Mater. 2016, 31, 136–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryder, L.R.; Bartels, E.M.; Woetmann, A.; Madsen, H.O.; Odum, N.; Bliddal, H.; Danneskiold-Samsøe, B.; Ribel-Madsen, S.; Ryder, L.P. FoxP3 mRNA splice forms in synovial CD4+ T cells in rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. APMIS 2012, 120, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toussirot, E.; Saas, P.; Deschamps, M.; Pouthier, F.; Perrot, L.; Perruche, S.; Chabod, J.; Tiberghien, P.; Wendling, D. Increased production of soluble CTLA-4 in patients with spondylarthropathies correlates with disease activity. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Bae, S.; Choi, J.; Hong, J.; Ryoo, S.; Jhun, H.; Hong, K.; Kim, E.; Jo, S.; et al. Interleukin-32 gamma specific monoclonal antibody and developing IL-32 specific ELISA. Hybridoma 2010, 29, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seth, P.; Yeowell, H.N. Fox-2 protein regulates the alternative splicing of scleroderma-associated lysyl hydroxylase 2 messenger RNA. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Grisar, J.; Munk, M.; Steiner, C.W.; Amoyo-Minar, L.; Tohidast-Akrad, M.; Zenz, P.; Steiner, G.; Smolen, J.S. Expression patterns of CD44 and CD44 splice variants in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2012, 30, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lamana, A.; Ortiz, A.M.; Alvaro-Gracia, J.M.; Díaz-Sánchez, B.; Novalbos, J.; García- Vicuña, R.; González-Alvaro, I. Characterization of serum interleukin-15 in healthy volunteers and patients with early arthritis to assess its potential use as a biomarker. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2010, 21, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friese, M.A.; Hellwage, J.; Jokiranta, T.S.; Meri, S.; Müller-Quernheim, H.J.; Peter, H.H.; Eibel, H.; Zipfel, P.F. Different regulation of factor H and FHL-1/reconectin by inflammatory mediators and expression of the two proteins in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2000, 121, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jin, P.; Zhang, J.; Sumariwalla, P.F.; Ni, I.; Jorgensen, B.; Crawford, D.; Phillips, S.; Feldmann, M.; Shepard, H.M.; Paleolog, E.M. Novel splice variants derived from the receptor tyrosine kinase superfamily are potential therapeutics for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, R73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zikherman, J.; Weiss, A. Alternative splicing of CD45: The tip of the iceberg. Immunity 2008, 29, 839–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahal, L.N.; Basu, N.; Youssef, H.; Khanolkar, R.C.; Barker, R.N.; Erwig, L.P.; Ward, F.J. Immunoregulatory soluble CTLA-4 modifies effector T-cell responses in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hirata, T.; Usui, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Mimori, T. A novel splice variant of human L-selectin encodes a soluble molecule that is elevated in serum of patients with rheumatic diseases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 462, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salter, D.M.; Godolphin, J.L.; Gourlay, M.S.; Lawson, M.F.; Hughes, D.E.; Dunne, E. Analysis of human articular chondrocyte CD44 isoform expression and function in health and disease. J. Pathol. 1996, 179, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, A.; Kuroki, K.; Okabe, Y.; Kasai, Y.; Matsumoto, N.; Yamada, C.; Takai, T.; Ose, T.; Kon, S.; Matsuda, T.; et al. The immunosuppressive effect of domain- deleted dimer of HLA-G2 isoform in collagen-induced arthritis mice. Hum. Immunol. 2016, 77, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korniejewska, A.; McKnight, A.J.; Johnson, Z.; Watson, M.L.; Ward, S.G. Expression and agonist responsiveness of CXCR3 variants in human T lymphocytes. Immunology 2011, 132, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- De Arras, L.; Laws, R.; Leach, S.M.; Pontis, K.; Freedman, J.H.; Schwartz, D.A.; Alper, S. Comparative genomics RNAi screen identifies Eftud2 as a novel regulator of innate immunity. Genetics 2014, 197, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nascimento, A.; Bruels, C.C.; Donkervoort, S.; Foley, A.R.; Codina, A.; Milisenda, J.C.; Estrella, E.A.; Li, C.; Pijuan, J.; Draper, I.; et al. Variants in DTNA cause a mild, dominantly inherited muscular dystrophy. Acta Neuropathol. 2023, 145, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Yoon, H.K.; Song, S.T.; Park, S.R.; Shim, S.C. Expression of activation- induced cytidine deaminase splicing variants in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Autoimmunity 2017, 50, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.A.; Horiuchi, S.; Topley, N.; Yamamoto, N.; Fuller, G.M. The soluble interleukin 6 receptor: Mechanisms of production and implications in disease. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sender, L.Y.; Gibbert, K.; Suezer, Y.; Radeke, H.H.; Kalinke, U.; Waibler, Z. CD40 ligand-triggered human dendritic cells mount interleukin-23 responses that are further enhanced by danger signals. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aigner, T.; Zien, A.; Hanisch, D.; Zimmer, R. Gene expression in chondrocytes assessed with use of microarrays. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2003, 85 (Suppl. S2), 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Xiao, X.; Li, S.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Q. A novel deep intronic COL2A1 mutation in a family with early-onset high myopia/ocular-only Stickler syndrome. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2020, 40, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lainez, B.; Fernandez-Real, J.M.; Romero, X.; Esplugues, E.; Cañete, J.D.; Ricart, W.; Engel, P. Identification and characterization of a novel spliced variant that encodes human soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor 2. Int. Immunol. 2004, 16, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoonheim, P.J.; Chatzopoulou, A.; Schaaf, M.J. The zebrafish as an in vivo model system for glucocorticoid resistance. Steroids 2010, 75, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badot, V.; Durez, P.; Van den Eynde, B.J.; Nzeusseu-Toukap, A.; Houssiau, F.A.; Lauwerys, B.R. Rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts produce a soluble form of the interleukin-7 receptor in response to pro-inflammatory cytokines. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 2335–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Scanzello, C.R.; Markova, D.Z.; Chee, A.; Xiu, Y.; Adams, S.L.; Anderson, G.; Zgonis, M.; Qin, L.; An, H.S.; Zhang, Y. Fibronectin splice variation in human knee cartilage, meniscus and synovial membrane: Observations in osteoarthritic knee. J. Orthop. Res. 2015, 33, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zwicky, R.; Müntener, K.; Goldring, M.B.; Baici, A. Cathepsin B expression and down-regulation by gene silencing and antisense DNA in human chondrocytes. Biochem. J. 2002, 367 Pt 1, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Feng, D.; Stone, R.C.; Eloranta, M.L.; Sangster-Guity, N.; Nordmark, G.; Sigurdsson, S.; Wang, C.; Alm, G.; Syvänen, A.C.; Rönnblom, L.; et al. Genetic variants and disease- associated factors contribute to enhanced interferon regulatory factor 5 expression in blood cells of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ni Choileain, S.; Weyand, N.J.; Neumann, C.; Thomas, J.; So, M.; Astier, A.L. The dynamic processing of CD46 intracellular domains provides a molecular rheostat for T cell activation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nambiar, M.P.; Enyedy, E.J.; Warke, V.G.; Krishnan, S.; Dennis, G.; Wong, H.K.; Kammer, G.M.; Tsokos, G.C. T cell signaling abnormalities in systemic lupus erythematosus are associated with increased mutations/polymorphisms and splice variants of T cell receptor zeta chain messenger RNA. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 1336–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Marotte, H.; Kwan, K.; Ruth, J.H.; Campbell, P.L.; Rabquer, B.J.; Pakozdi, A.; Koch, A.E. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits IL-6 synthesis and suppresses transsignaling by enhancing soluble gp130 production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14692–14697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bestall, S.M.; Hulse, R.P.; Blackley, Z.; Swift, M.; Ved, N.; Paton, K.; Beazley-Long, N.; Bates, D.O.; Donaldson, L.F. Sensory neuronal sensitisation occurs through HMGB-1-RAGE and TRPV1 in high-glucose conditions. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs215939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bachmann, M.; Hilker, M.; Grölz, D.; Tellmann, G.; Hake, U.; Kater, L.; de Wilde, P.; Tröster, H. Different La/SS-B mRNA isoforms are expressed in salivary gland tissue of patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Autoimmun. 1996, 9, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jéru, I.; Papin, S.; L’hoste, S.; Duquesnoy, P.; Cazeneuve, C.; Camonis, J.; Amselem, S. Interaction of pyrin with 14.3.3 in an isoform-specific and phosphorylation- dependent manner regulates its translocation to the nucleus. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliani, A.L.; Colognesi, D.; Ricco, T.; Roncato, C.; Capece, M.; Amoroso, F.; Wang, Q.G.; De Marchi, E.; Gartland, A.; Di Virgilio, F.; et al. Trophic activity of human P2X7 receptor isoforms A and B in osteosarcoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rafael, M.S.; Cavaco, S.; Viegas, C.S.; Santos, S.; Ramos, A.; Willems, B.A.; Herfs, M.; Theuwissen, E.; Vermeer, C.; Simes, D.C. Insights into the association of Gla-rich protein and osteoarthritis, novel splice variants and γ-carboxylation status. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1636–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousseau, J.C.; Sandell, L.J.; Delmas, P.D.; Garnero, P. Development and clinical application in arthritis of a new immunoassay for serum type IIA procollagen NH2 propeptide. Methods Mol. Med. 2004, 101, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peffers, M.J.; Goljanek-Whysall, K.; Collins, J.; Fang, Y.; Rushton, M.; Loughlin, J.; Proctor, C.; Clegg, P.D. Decoding the Regulatory Landscape of Ageing in Musculoskeletal Engineered Tissues Using Genome-Wide DNA Methylation and RNASeq. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zabeau, L.; Jensen, C.J.; Seeuws, S.; Venken, K.; Verhee, A.; Catteeuw, D.; van Loo, G.; Chen, H.; Walder, K.; Hollis, J.; et al. Leptin’s metabolic and immune functions can be uncoupled at the ligand/receptor interaction level. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schwager, K.; Villa, A.; Rösli, C.; Neri, D.; Rösli-Khabas, M.; Moser, G. A comparative immunofluorescence analysis of three clinical-stage antibodies in head and neck cancer. Head. Neck Oncol. 2011, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Polgár, A.; Brózik, M.; Tóth, S.; Holub, M.; Hegyi, K.; Kádár, A.; Hodinka, L.; Falus, A. Soluble interleukin-6 receptor in plasma and in lymphocyte culture supernatants of healthy individuals and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2000, 6, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Misener, V.L.; Hui, C.; Malapitan, I.A.; Ittel, M.E.; Joyner, A.L.; Jongstra, J. Expression of mouse LSP1/S37 isoforms. S37 is expressed in embryonic mesenchymal cells. J. Cell Sci. 1994, 107 Pt 12, 3591–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriegsmann, J.; Berndt, A.; Hansen, T.; Borsi, L.; Zardi, L.; Bräuer, R.; Petrow, P.K.; Otto, M.; Kirkpatrick, C.J.; Gay, S.; et al. Expression of fibronectin splice variants and oncofetal glycosylated fibronectin in the synovial membranes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2004, 24, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, N.M.; Jin, P.; Raatz, Y.; Sumariwalla, P.F.; Kiriakidis, S.; Shepard, M.; Feldmann, M.; Paleolog, E.M. Regulation of the angiopoietin-Tie ligand-receptor system with a novel splice variant of Tie1 reduces the severity of murine arthritis. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 1828–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madden, J.; Shearman, C.P.; Dunn, R.L.; Dastur, N.D.; Tan, R.M.; Nash, G.B.; Rainger, G.E.; Brunner, A.; Calder, P.C.; Grimble, R.F. Altered monocyte CD44 expression in peripheral arterial disease is corrected by fish oil supplementation. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2009, 19, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebe, H.; Matsumoto, I.; Kawaguchi, H.; Kurata, I.; Tanaka, Y.; Inoue, A.; Kondo, Y.; Tsuboi, H.; Sumida, T. Clinical and functional significance of STEAP4-splice variant in CD14+ monocytes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2018, 191, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, J.; Edberg, J.C.; Gibson, A.W.; Tsao, B.; Kimberly, R.P. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms of T cell receptor zeta chain in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 42, 2601–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Ohya, S.; Yamamura, H.; Giles, W.R.; Imaizumi, Y. A New Splice Variant of Large Conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BK) Channel α Subunit Alters Human Chondrocyte Function. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 24247–24260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Du, M.; Roy, K.M.; Zhong, L.; Shen, Z.; Meyers, H.E.; Nichols, R.C. VEGF gene expression is regulated post-transcriptionally in macrophages. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 732–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friese, M.A.; Hellwage, J.; Jokiranta, T.S.; Meri, S.; Peter, H.H.; Eibel, H.; Zipfel, P.F. FHL-1/reconectin and factor H: Two human complement regulators which are encoded by the same gene are differently expressed and regulated. Mol. Immunol. 1999, 36, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baici, A.; Lang, A.; Zwicky, R.; Müntener, K. Cathepsin B in osteoarthritis: Uncontrolled proteolysis in the wrong place. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 34 (Suppl. S2), 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlFadhli, S.; Nizam, R. Differential expression of alternative splice variants of CTLA4 in Kuwaiti autoimmune disease patients. Gene 2014, 534, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.; Jendro, M.C.; Wadle, A.; Kleber, S.; Stenner, F.; Dinser, R.; Reich, A.; Faccin, E.; Gödde, S.; Dinges, H.; et al. Fibroblast activation protein is expressed by rheumatoid myofibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Horiuchi, S.; Ampofo, W.; Koyanagi, Y.; Yamashita, A.; Waki, M.; Matsumoto, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Yamamoto, N. High-level production of alternatively spliced soluble interleukin-6 receptor in serum of patients with adult T-cell leukaemia/HTLV-I- associated myelopathy. Immunology 1998, 95, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Muller, I.B.; Lin, M.; Lems, W.F.; Ter Wee, M.M.; Wojtuszkiewicz, A.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; Cloos, J.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Jansen, G.; de Jonge, R. Association of altered folylpolyglutamate synthetase pre-mRNA splicing with methotrexate unresponsiveness in early rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chiba, T.; Miyashita, K.; Sugoh, T.; Warita, T.; Inoko, H.; Kimura, M.; Sato, T. IκBL, a novel member of the nuclear IκB family, inhibits inflammatory cytokine expression. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 3577–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulse, R.P.; Beazley-Long, N.; Ved, N.; Bestall, S.M.; Riaz, H.; Singhal, P.; Ballmer Hofer, K.; Harper, S.J.; Bates, D.O.; Donaldson, L.F. Vascular endothelial growth factor-A165b prevents diabetic neuropathic pain and sensory neuronal degeneration. Clin. Sci. 2015, 129, 741–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punwani, D.; Wang, H.; Chan, A.Y.; Cowan, M.J.; Mallott, J.; Sunderam, U.; Mollenauer, M.; Srinivasan, R.; Brenner, S.E.; Mulder, A.; et al. Combined immunodeficiency due to MALT1 mutations, treated by hematopoietic cell transplantation. J. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 35, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lemaire, R.; Prasad, J.; Kashima, T.; Gustafson, J.; Manley, J.L.; Lafyatis, R. Stability of a PKCI-1-related mRNA is controlled by the splicing factor ASF/SF2: A novel function for SR proteins. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Weisbart, R.H.; Chan, G.; Li, E.; Farmani, N.; Heinze, E.; Rubell, A.; Nishimura, R.N.; Colburn, K. BRAF splice variants in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts activate MAPK through CRAF. Mol. Immunol. 2013, 55, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedretti, M.; Rancic, Z.; Soltermann, A.; Herzog, B.A.; Schliemann, C.; Lachat, M.; Neri, D.; Kaufmann, P.A. Comparative immunohistochemical staining of atherosclerotic plaques using F16, F8 and LThree clinical-grade fully human antibodies. Atherosclerosis 2010, 208, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Brophy, R.H.; Tycksen, E.D.; Duan, X.; Nunley, R.M.; Rai, M.F. Distinct expression pattern of periostin splice variants in chondrocytes and ligament progenitor cells. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 8386–8405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Boyle, D.L.; Shi, Y.; Gay, S.; Firestein, G.S. Regulation of CS1 fibronectin expression and function by IL-1 in endothelial cells. Cell. Immunol. 2000, 200, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwager, K.; Kaspar, M.; Bootz, F.; Marcolongo, R.; Paresce, E.; Neri, D.; Trachsel, E. Preclinical characterization of DEKAVIL (F8-IL10), a novel clinical-stage immunocytokine which inhibits the progression of collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kono, M.; Kurita, T.; Yasuda, S.; Kono, M.; Fujieda, Y.; Bohgaki, T.; Katsuyama, T.; Tsokos, G.C.; Moulton, V.R.; Atsumi, T. Decreased Expression of Serine/Arginine-Rich Splicing Factor 1 in T Cells From Patients With Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Accounts for Reduced Expression of RasGRP1 and DNA Methyltransferase 1. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 2046–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlFadhli, S. Overexpression and secretion of the soluble CTLA-4 splice variant in various autoimmune diseases and in cases with overlapping autoimmunity. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2013, 17, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Oparina, N.Y.; Delgado-Vega, A.M.; Martinez-Bueno, M.; Magro-Checa, C.; Fernández, C.; Castro, R.O.; Pons-Estel, B.A.; D’Alfonso, S.; Sebastiani, G.D.; Witte, T.; et al. PXK locus in systemic lupus erythematosus: Fine mapping and functional analysis reveals novel susceptibility gene ABHD6. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, G.; Almeida, M.; Pintacuda, G.; Coker, H.; Bowness, J.S.; Ule, J.; Brockdorff, N. Acute depletion of METTL3 implicates N6-methyladenosine in alternative intron/exon inclusion in the nascent transcriptome. Genome Res. 2021, 31, 1395–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thomas, H.; Beck, K.; Adamczyk, M.; Aeschlimann, P.; Langley, M.; Oita, R.C.; Thiebach, L.; Hils, M.; Aeschlimann, D. Transglutaminase 6: A protein associated with central nervous system development and motor function. Amino Acids 2013, 44, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mamegano, K.; Kuroki, K.; Miyashita, R.; Kusaoi, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Matsuta, K.; Maenaka, K.; Colonna, M.; Ozaki, S.; Hashimoto, H.; et al. Association of LILRA2 (ILT1, LIR7) splice site polymorphism with systemic lupus erythematosus and microscopic polyangiitis. Genes Immun. 2008, 9, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terkeltaub, R.; Lotz, M.; Johnson, K.; Deng, D.; Hashimoto, S.; Goldring, M.B.; Burton, D.; Deftos, L.J. Parathyroid hormone-related proteins is abundant in osteoarthritic cartilage, and the parathyroid hormone-related protein 1-173 isoform is selectively induced by transforming growth factor beta in articular chondrocytes and suppresses generation of extracellular inorganic pyrophosphate. Arthritis Rheum. 1998, 41, 2152–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichenbach, G.; Starzinski-Powitz, A.; Doll, M.; Hrgovic, I.; Valesky, E.M.; Kippenberger, S.; Bernd, A.; Kaufmann, R.; Meissner, M. Ligand activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta suppresses cathepsin B expression in human endothelial cells in a posttranslational manner. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.H.; Tseng, W.; Cui, J.; Costenbader, K.; Ho, I.C. Altered expression of protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 22 isoforms in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wibulswas, A.; Croft, D.; Pitsillides, A.A.; Bacarese-Hamilton, I.; McIntyre, P.; Genot, E.; Kramer, I.M. Influence of epitopes CD44v3 and CD44v6 in the invasive behavior of fibroblast-like synoviocytes derived from rheumatoid arthritic joints. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 2059–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrea, A.; Preisegger, M.A.; Velasco Zamora, J.; Dewey, R.A. The mRNA levels of TGF-β Type II receptor splice variants in monocytes are associated with disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raben, N.; Nichols, R.C.; Martiniuk, F.; Plotz, P.H. A model of mRNA splicing in adult lysosomal storage disease (glycogenosis type II). Hum. Mol. Genet. 1996, 5, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peake, N.J.; Khawaja, K.; Myers, A.; Nowell, M.A.; Jones, S.A.; Rowan, A.D.; Cawston, T.E.; Foster, H.E. Interleukin-6 signalling in juvenile idiopathic arthritis is limited by proteolytically cleaved soluble interleukin-6 receptor. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 1485–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudepierre, P.; Allanore, Y.; Belec, L.; Larget-Piet, B.; Zardi, L.; Chevalier, X. Increased Ed-B fibronectin plasma levels in spondyloarthropathies: Comparison with rheumatoid arthritis patients and a healthy population. Rheumatology 1999, 38, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Gallo, L.M.; Martin, J. PTPN22 splice forms: A new role in rheumatoid arthritis. Genome Med. 2012, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bäckdahl, L.; Ekman, D.; Jagodic, M.; Olsson, T.; Holmdahl, R. Identification of candidate risk gene variations by whole-genome sequence analysis of four rat strains commonly used in inflammation research. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ala-Kokko, L.; Prockop, D.J. Completion of the intron-exon structure of the gene for human type II procollagen (COL2A1): Variations in the nucleotide sequences of the alleles from three chromosomes. Genomics 1990, 8, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojo, S.; Tsutsumi, A.; Goto, D.; Sumida, T. Low expression levels of soluble CD1d gene in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 2524–2528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fattorusso, R.; Pellecchia, M.; Viti, F.; Neri, P.; Neri, D.; Wüthrich, K. NMR structure of the human oncofoetal fibronectin ED-B domain, a specific marker for angiogenesis. Structure 1999, 7, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valas, S.; Rolland, M.; Perrin, C.; Perrin, G.; Mamoun, R.Z. Characterization of a new 5’ splice site within the caprine arthritis encephalitis virus genome: Evidence for a novel auxiliary protein. Retrovirology 2008, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Carsons, S. Extra domain-positive fibronectins in arthritis: Wolf in sheep’s clothing? Rheumatology 2001, 40, 721–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.G.; McBride, O.W.; Wang, M.; Kim, S.Y.; Idler, W.W.; Steinert, P.M. Structure and organization of the human transglutaminase 1 gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 7710–7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickie, L.J.; Aziz, A.M.; Savic, S.; Lucherini, O.M.; Cantarini, L.; Geiler, J.; Wong, C.H.; Coughlan, R.; Lane, T.; Lachmann, H.J.; et al. Involvement of X-box binding protein 1 and reactive oxygen species pathways in the pathogenesis of tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Galdo, F.; Maul, G.G.; Jiménez, S.A.; Artlett, C.M. Expression of allograft inflammatory factor 1 in tissues from patients with systemic sclerosis and in vitro differential expression of its isoforms in response to transforming growth factor beta. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2616–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Zhu, Q.; Jiang, T.; Wang, R.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.; Bai, F.; Ding, Q.; Zhou, X.; et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation patterns in CD4+ T cells from Chinese Han patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2017, 27, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faggian, J.; Fosang, A.J.; Zieba, M.; Wallace, M.J.; Hooper, S.B. Changes in versican and chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans during structural development of the lung. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 293, R784–R792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, R.B.; Day, A.; Barstow, A.; Liu, H.; Zaman, G.; Dhoot, G.K. Sulf2 gene is alternatively spliced in mammalian developing and tumour tissues with functional implications. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 414, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, D.R.; Dall, P.; Davies, D.; Jackson, D.G.; McIntyre, P.; Kramer, I.M. Complex CD44 splicing combinations in synovial fibroblasts from arthritic joints. Eur. J. Immunol. 1997, 27, 1680–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, J.; Langstein, J.; Hofstädter, F.; Schwarz, H. A soluble form of CD137 (ILA/4-1BB), a member of the TNF receptor family, is released by activated lymphocytes and is detectable in sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Immunol. 1998, 28, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, F.; Ellingson, S.M.; Kyogoku, C.; Peterson, E.J.; Gaffney, P.M. Exon 6 variants carried on systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) risk haplotypes modulate IRF5 function. Autoimmunity 2011, 44, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, H.; Reksten, T.R.; Ice, J.A.; Kelly, J.A.; Adrianto, I.; Rasmussen, A.; Wang, S.; He, B.; Grundahl, K.M.; Glenn, S.B.; et al. Identification of a Sjögren’s syndrome susceptibility locus at OAS1 that influences isoform switching, protein expression, and responsiveness to type I interferons. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cutolo, M.; Picasso, M.; Ponassi, M.; Sun, M.Z.; Balza, E. Tenascin and fibronectin distribution in human normal and pathological synovium. J. Rheumatol. 1992, 19, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schaaf, M.J.; Cidlowski, J.A. AUUUA motifs in the 3’UTR of human glucocorticoid receptor alpha and beta mRNA destabilize mRNA and decrease receptor protein expression. Steroids 2002, 67, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerna, I.; Kisand, K.; Suutre, S.; Murde, M.; Tamm, A.; Kumm, J.; Tamm, A. The ADAM12 is upregulated in synovitis and postinflammatory fibrosis of the synovial membrane in patients with early radiographic osteoarthritis. Jt. Bone Spine 2014, 81, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, G.R.; Markova, N.G.; De Laurenzi, V.; Rizzo, W.B.; Compton, J.G. Genomic organization and expression of the human fatty aldehyde dehydrogenase gene (FALDH). Genomics 1997, 39, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukada, Y.; Ichikawa, H.; Chai, Z.; Lai, F.P.; Dunster, K.; Sentry, J.W.; Toh, B.H. Novel variant of p230 trans-Golgi network protein identified by serum from Sjögren’s syndrome patient. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 79, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedvetzki, S.; Walmsley, M.; Alpert, E.; Williams, R.O.; Feldmann, M.; Naor, D. CD44 involvement in experimental collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). J. Autoimmun. 1999, 13, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokuda, S.; Miyazaki, T.; Ito, Y.; Yamasaki, S.; Inoue, H.; Guo, Y.; Kong, W.S.; Kanno, M.; Takasugi, K.; Sugiyama, E.; et al. The proto-oncogene survivin splice variant 2B is induced by PDGF and leads to cell proliferation in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ohkubo, T.; Takei, M.; Mitamura, K.; Horie, T.; Fujiwara, S.; Shimizu, K.; Ryu, J.; Shiraiwa, H.; Sawada, S. Increased soluble CD4 molecules and the role of soluble CD4 production in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2001, 29, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmer, S.; Vater, A.; Licha, K.; Gemeinhardt, I.; Gemeinhardt, O.; Voigt, J.; Ebert, B.; Schnorr, J.; Taupitz, M.; Macdonald, R.; et al. Extra domain B fibronectin as a target for near-infrared fluorescence imaging of rheumatoid arthritis affected joints in vivo. Mol. Imaging 2009, 8, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hikichi, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Takigawa, M. All-trans retinoic acid-induced ADAM28 degrades proteoglycans in human chondrocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 386, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roescher, N.; Vosters, J.L.; Alsaleh, G.; Dreyfus, P.; Jacques, S.; Chiocchia, G.; Sibilia, J.; Tak, P.P.; Chiorini, J.A.; Mariette, X.; et al. Targeting the splicing of mRNA in autoimmune diseases: BAFF inhibition in Sjögren’s syndrome as a proof of concept. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kapsogeorgou, E.K.; Manoussakis, M.N. Salivary gland epithelial cells (SGEC): Carriers of exquisite B7-2 (CD86) costimulatory molecules. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 35, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fay, J.; Varoga, D.; Wruck, C.J.; Kurz, B.; Goldring, M.B.; Pufe, T. Reactive oxygen species induce expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in chondrocytes and human articular cartilage explants. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jiang, H.; Knudson, C.B.; Knudson, W. Antisense inhibition of CD44 tailless splice variant in human articular chondrocytes promotes hyaluronan internalization. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 2599–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolboom, T.C.; Huidekoper, A.L.; Kramer, I.M.; Pieterman, E.; Toes, R.E.; Huizinga, T.W. Correlation between expression of CD44 splice variant v8-v9 and invasiveness of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in an in vitro system. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2004, 22, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peters, J.H.; Carsons, S.; Kalunian, K.; McDougall, S.; Yoshida, M.; Ko, F.; van der Vliet-Hristova, M.; Hahn, T.J. Preferential recognition of a fragment species of osteoarthritic synovial fluid fibronectin by antibodies to the alternatively spliced EIIIA segment. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 2572–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niarakis, A.; Giannopoulou, E.; Ravazoula, P.; Panagiotopoulos, E.; Zarkadis, I.K.; Aletras, A.J. Detection of a latent soluble form of membrane type 1 matrix metalloprotease bound with tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases-2 in periprosthetic tissues and fluids from loose arthroplasty endoprostheses. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 6541–6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirayasu, K.; Ohashi, J.; Kashiwase, K.; Takanashi, M.; Satake, M.; Tokunaga, K.; Yabe, T. Long-term persistence of both functional and non-functional alleles at the leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor A3 (LILRA3) locus suggests balancing selection. Hum. Genet. 2006, 119, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousaf, N.; Low, W.Y.; Onipinla, A.; Mein, C.; Caulfield, M.; Munroe, P.B.; Chernajovsky, Y. Differences between disease-associated endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (ERAP1) isoforms in cellular expression, interactions with tumour necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNF-R1) and regulation by cytokines. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 180, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hasegawa, M.; Nakoshi, Y.; Muraki, M.; Sudo, A.; Kinoshita, N.; Yoshida, T.; Uchida, A. Expression of large tenascin-C splice variants in synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Orthop. Res. 2007, 25, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainwright, S.D.; Bondeson, J.; Hughes, C.E. An alternative spliced transcript of ADAMTS4 is present in human synovium from OA patients. Matrix Biol. 2006, 25, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buyon, J.P.; Tseng, C.E.; Di Donato, F.; Rashbaum, W.; Morris, A.; Chan, E.K. Cardiac expression of 52beta, an alternative transcript of the congenital heart block- associated 52-kd SS-A/Ro autoantigen, is maximal during fetal development. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciore, P.; Frank, C.B.; Hart, D.A. Identification of sex hormone receptors in human and rabbit ligaments of the knee by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction: Evidence that receptors are present in tissue from both male and female subjects. J. Orthop. Res. 1998, 16, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greetham, D.; Ellis, C.D.; Mewar, D.; Fearon, U.; an Ultaigh, S.N.; Veale, D.J.; Guesdon, F.; Wilson, A.G. Functional characterization of NF-kappaB inhibitor-like protein 1 (NFkappaBIL1), a candidate susceptibility gene for rheumatoid arthritis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 16, 3027–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoornaert, K.P.; Vereecke, I.; Dewinter, C.; Rosenberg, T.; Beemer, F.A.; Leroy, J.G.; Bendix, L.; Björck, E.; Bonduelle, M.; Boute, O.; et al. Stickler syndrome caused by COL2A1 mutations: Genotype- phenotype correlation in a series of 100 patients. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 18, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alvarez-Errico, D.; Yamashita, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Odom, S.; Furumoto, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Rivera, J. Functional analysis of Lyn kinase A and B isoforms reveals redundant and distinct roles in Fc epsilon RI-dependent mast cell activation. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 5000–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kalinski, H.; Yaniv, A.; Mashiah, P.; Miki, T.; Tronick, S.R.; Gazit, A. rev-like transcripts of caprine arthritis encephalitis virus. Virology 1991, 183, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derijk, R.H.; Schaaf, M.J.; Turner, G.; Datson, N.A.; Vreugdenhil, E.; Cidlowski, J.; de Kloet, E.R.; Emery, P.; Sternberg, E.M.; Detera-Wadleigh, S.D. A human glucocorticoid receptor gene variant that increases the stability of the glucocorticoid receptor beta-isoform mRNA is associated with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2001, 28, 2383–2388. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shiozawa, K.; Hino, K.; Shiozawa, S. Alternatively spliced EDA-containing fibronectin in synovial fluid as a predictor of rheumatoid joint destruction. Rheumatology 2001, 40, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, B.K.; Murphy, R.; Ray, P.; Ray, A. SAF-2, a splice variant of SAF-1, acts as a negative regulator of transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 46822–46830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaire, R.; Flipo, R.M.; Migaud, H.; Fontaine, C.; Huet, G.; Dacquembronne, E.; Lafyatis, R. Alternative splicing of the 5’ region of cathepsin B pre-messenger RNA in rheumatoid synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 1540–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.H.; Wei, S.; Lamy, T.; Li, Y.; Epling-Burnette, P.K.; Djeu, J.Y.; Loughran, T.P., Jr. Blockade of Fas-dependent apoptosis by soluble Fas in LGL leukemia. Blood 2002, 100, 1449–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugan, J.; Griffiths, E.; Snow, P.; Rosenzweig, H.; Lee, E.; Brown, B.; Carr, D.W.; Rose, C.; Rosenbaum, J.; Davey, M.P. Blau syndrome-associated Nod2 mutation alters expression of full-length NOD2 and limits responses to muramyl dipeptide in knock-in mice. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Maretzky, T.; Le Gall, S.M.; Worpenberg-Pietruk, S.; Eder, J.; Overall, C.M.; Huang, X.Y.; Poghosyan, Z.; Edwards, D.R.; Blobel, C.P. Src stimulates fibroblast growth factor receptor-2 shedding by an ADAM15 splice variant linked to breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4573–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banda, N.K.; Mehta, G.; Kjaer, T.R.; Takahashi, M.; Schaack, J.; Morrison, T.E.; Thiel, S.; Arend, W.P.; Holers, V.M. Essential role for the lectin pathway in collagen antibody- induced arthritis revealed through use of adenovirus programming complement inhibitor MAp44 expression. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 2455–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sarkissian, M.; Lafyatis, R. Transforming growth factor-beta and platelet derived growth factor regulation of fibrillar fibronectin matrix formation by synovial fibroblasts. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 25, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Labat-Robert, J.; Chevalier, X. Fibronectine, vieillissement et pathologies associées [Fibronectin, aging and related pathologies]. C. R. Seances Soc. Biol. Fil. 1991, 185, 121–126. (In French) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wan, B.; Nie, H.; Liu, A.; Feng, G.; He, D.; Xu, R.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, C.; Zhang, J.Z. Aberrant regulation of synovial T cell activation by soluble costimulatory molecules in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 8844–8850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proussakova, O.V.; Rabaya, N.A.; Moshnikova, A.B.; Telegina, E.S.; Turanov, A.; Nanazashvili, M.G.; Beletsky, I.P. Oligomerization of soluble Fas antigen induces its cytotoxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 36236–36241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pufe, T.; Petersen, W.; Tillmann, B.; Mentlein, R. The splice variants VEGF121 and VEGF189 of the angiogenic peptide vascular endothelial growth factor are expressed in osteoarthritic cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainwright, S.D.; Bondeson, J.; Caterson, B.; Hughes, C.E. ADAMTS-4_v1 is a splice variant of ADAMTS-4 that is expressed as a protein in human synovium and cleaves aggrecan at the interglobular domain. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 2866–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Banda, N.K.; Desai, D.; Scheinman, R.I.; Pihl, R.; Sekine, H.; Fujita, T.; Sharma, V.; Hansen, A.G.; Garred, P.; Thiel, S.; et al. Targeting of Liver Mannan-Binding Lectin-Associated Serine Protease-3 with RNA Interference Ameliorates Disease in a Mouse Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunohorizons 2018, 2, 274–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Oda, H.; Beck, D.B.; Kuehn, H.S.; Sampaio Moura, N.; Hoffmann, P.; Ibarra, M.; Stoddard, J.; Tsai, W.L.; Gutierrez-Cruz, G.; Gadina, M.; et al. Second Case of HOIP Deficiency Expands Clinical Features and Defines Inflammatory Transcriptome Regulated by LUBAC. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ryder, L.R.; Ryder, L.P.; Bartels, E.M.; Woetmann, A.; Madsen, H.O.; Ødum, N.; Danneskiold- Samsøe, B.; Ribel-Madsen, S.; Bliddal, H. Differential effects of decoy receptor- and antibody-mediated tumour necrosis factor blockage on FoxP3 expression in responsive arthritis patients. APMIS 2013, 121, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claus, R.; Bittorf, T.; Walzel, H.; Brock, J.; Uhde, R.; Meiske, D.; Schulz, U.; Hobusch, D.; Schumacher, K.; Witt, M.; et al. High concentration of soluble HLA-DR in the synovial fluid: Generation and significance in "rheumatoid-like" inflammatory joint diseases. Cell. Immunol. 2000, 206, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissbach, L.; Tran, K.; Colquhoun, S.A.; Champliaud, M.F.; Towle, C.A. Detection of an interleukin-1 intracellular receptor antagonist mRNA variant. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 244, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seperack, P.K.; Mercer, J.A.; Strobel, M.C.; Copeland, N.G.; Jenkins, N.A. Retroviral sequences located within an intron of the dilute gene alter dilute expression in a tissue-specific manner. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 2326–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Andersson, S.E.; Svensson, M.N.; Erlandsson, M.C.; Dehlin, M.; Andersson, K.M.; Bokarewa, M.I. Activation of Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 signaling enhances survivin expression in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Richards, A.J.; Laidlaw, M.; Meredith, S.P.; Shankar, P.; Poulson, A.V.; Scott, J.D.; Snead, M.P. Missense and silent mutations in COL2A1 result in Stickler syndrome but via different molecular mechanisms. Hum. Mutat. 2007, 28, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolard, J.; Wang, W.Y.; Bevan, H.S.; Qiu, Y.; Morbidelli, L.; Pritchard-Jones, R.O.; Cui, T.G.; Sugiono, M.; Waine, E.; Perrin, R.; et al. VEGF165b, an inhibitory vascular endothelial growth factor splice variant: Mechanism of action, in vivo effect on angiogenesis and endogenous protein expression. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7822–7835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, G.; Goodall, J.C.; Jarvis, L.B.; Hill Gaston, J.S. Characterisation of Foxp3 splice variants in human CD4+ and CD8+ T cells—Identification of Foxp3Δ7 in human regulatory T cells. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 48, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibulswas, A.; Croft, D.; Bacarese-Hamilton, I.; McIntyre, P.; Genot, E.; Kramer, I.M. The CD44v7/8 epitope as a target to restrain proliferation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 2037–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nambiar, M.P.; Enyedy, E.J.; Fisher, C.U.; Krishnan, S.; Warke, V.G.; Gilliland, W.R.; Oglesby, R.J.; Tsokos, G.C. Abnormal expression of various molecular forms and distribution of T cell receptor zeta chain in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksentijevich, I.; Galon, J.; Soares, M.; Mansfield, E.; Hull, K.; Oh, H.H.; Goldbach- Mansky, R.; Dean, J.; Athreya, B.; Reginato, A.J.; et al. The tumor-necrosis-factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome: New mutations in TNFRSF1A, ancestral origins, genotype-phenotype studies, and evidence for further genetic heterogeneity of periodic fevers. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 69, 301–314, Erratum in Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 69, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyashita, K.; Sakashita, E.; Miyamoto, K.; Tokita, M.; Komai, T. Development of the selective adsorbent for EDA containing fibronectin using heparin immobilized cellulose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1998, 22, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elices, M.J.; Tsai, V.; Strahl, D.; Goel, A.S.; Tollefson, V.; Arrhenius, T.; Wayner, E.A.; Gaeta, F.C.; Fikes, J.D.; Firestein, G.S. Expression and functional significance of alternatively spliced CS1 fibronectin in rheumatoid arthritis microvasculature. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pufe, T.; Petersen, W.; Tillmann, B.; Mentlein, R. Splice variants VEGF121 and VEGF165 of the angiogenic peptide vascular endothelial cell growth factor are expressed in the synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2001, 28, 1482–1485. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sherman, J.B.; Raben, N.; Nicastri, C.; Argov, Z.; Nakajima, H.; Adams, E.M.; Eng, C.M.; Cowan, T.M.; Plotz, P.H. Common mutations in the phosphofructokinase-M gene in Ashkenazi Jewish patients with glycogenesis VII--and their population frequency. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1994, 55, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Del Galdo, F.; Jiménez, S.A. T cells expressing allograft inflammatory factor 1 display increased chemotaxis and induce a profibrotic phenotype in normal fibroblasts in vitro. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 3478–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, R.; Ito, K.; Tatewaki, M.; Nagai, M.; Aizawa, S.; Higashihara, M.; Ishida, T.; Inoue, J.; Takizawa, H.; Watanabe, T. A variant CD30 protein lacking extracellular and transmembrane domains is induced in HL-60 by tetradecanoylphorbol acetate and is expressed in alveolar macrophages. Blood 1996, 88, 2422–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, A.; Hu, C.; Kastner, D.L.; Schaner, P.; Reginato, A.M.; Richards, N.; Gumucio, D.L. Lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of multiple alternatively spliced MEFV transcripts in human synovial fibroblasts: A prominent splice isoform lacks the C-terminal domain that is highly mutated in familial Mediterranean fever. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 3679–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, E.K.; Di Donato, F.; Hamel, J.C.; Tseng, C.E.; Buyon, J.P. 52-kD SS-A/Ro: Genomic structure and identification of an alternatively spliced transcript encoding a novel leucine zipper-minus autoantigen expressed in fetal and adult heart. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 182, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kozyrev, S.V.; Lewén, S.; Reddy, P.M.; Pons-Estel, B.; Argentine Collaborative Group; Witte, T.; German Collaborative Group; Junker, P.; Laustrup, H.; Gutiérrez, C.; et al. Structural insertion/deletion variation in IRF5 is associated with a risk haplotype and defines the precise IRF5 isoforms expressed in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hospach, T.; Lohse, P.; Heilbronner, H.; Dannecker, G.E.; Lohse, P. Pseudodominant inheritance of the hyperimmunoglobulinemia D with periodic fever syndrome in a mother and her two monozygotic twins. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 3606–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raben, N.; Sherman, J.; Miller, F.; Mena, H.; Plotz, P. A 5’ splice junction mutation leading to exon deletion in an Ashkenazic Jewish family with phosphofructokinase deficiency (Tarui disease). J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 4963–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, J.R.; Minton, J.A.; Ho, M.L.; Wei, N.; Winkler, J.D. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in synovial fibroblasts is induced by hypoxia and interleukin 1beta. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 24, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bär, K.J.; Natura, G.; Telleria-Diaz, A.; Teschner, P.; Vogel, R.; Vasquez, E.; Schaibl, H.G.; Ebersberger, A. Changes in the effect of spinal prostaglandin E2 during inflammation: Prostaglandin E (EP1-EP4) receptors in spinal nociceptive processing of input from the normal or inflamed knee joint. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tröster, H.; Metzger, T.E.; Semsei, I.; Schwemmle, M.; Winterpacht, A.; Zabel, B.; Bachmann, M. One gene, two transcripts: Isolation of an alternative transcript encoding for the autoantigen La/SS-B from a cDNA library of a patient with primary Sjögrens’ syndrome. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 2059–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hu, S.I.; Klein, M.; Carozza, M.; Rediske, J.; Peppard, J.; Qi, J.S. Identification of a splice variant of neutrophil collagenase (MMP-8). FEBS Lett. 1999, 443, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hino, K.; Maeda, T.; Sekiguchi, K.; Shiozawa, K.; Hirano, H.; Sakashita, E.; Shiozawa, S. Adherence of synovial cells on EDA-containing fibronectin. Arthritis Rheum. 1996, 39, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevchenko, Y.O.; Compton, J.G.; Toro, J.R.; DiGiovanna, J.J.; Bale, S.J. Splice-site mutation in TGM1 in congenital recessive ichthyosis in American families: Molecular, genetic, genealogic, and clinical studies. Hum. Genet. 2000, 106, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hübener, C.; Mincheva, A.; Lichter, P.; Schraven, B.; Bruyns, E. Genomic organization and chromosomal localization of the human gene encoding the T-cell receptor-interacting molecule (TRIM). Immunogenetics 2000, 51, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, H.J.; Ingemann-Hansen, T.; Poulsen, J.H. The epidermal growth factor-like domain of the human cartilage large aggregating proteoglycan, aggrecan: Increased serum concentration in rheumatoid arthritis. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1994, 33, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, K.M.; Kirby, M.Y.; McClain, M.T.; Harley, J.B.; James, J.A. Lupus autoantibodies recognize the product of an alternative open reading frame of SmB/B’. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 285, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, J.J.; Komarow, H.D.; Cheng, J.; Wood, G.; Raben, N.; Liu, P.P.; Kastner, D.L. Targeted disruption of pyrin, the FMF protein, causes heightened sensitivity to endotoxin and a defect in macrophage apoptosis. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feyertag, J.; Haberhauer, G.; Skoumal, M.; Kittl, E.M.; Bauer, K.; Dunky, A. Serumspiegel löslicher CD44-Isoform-Variante 5 von Patienten mit seropositiver Rheumatoid-Arthritis unter Cyclosporin-A-Therapie [Serum soluble CD44 isoform variant 5 level in patients with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis treated with cyclosporin A]. Acta Med. Austriaca 2000, 27, 156–159. (In German) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Phang, D.; Laxer, R.M.; Silverman, E.D.; Pan, S.; Doherty, P.J. Evolution of the T cell receptor beta repertoire from synovial fluid T cells of patients with juvenile onset rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 24, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cole, W.G. Abnormal skeletal growth in Kniest dysplasia caused by type II collagen mutations. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1997, 341, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazit, A.; Mashiah, P.; Kalinski, H.; Gast, A.; Rosin-Abersfeld, R.; Tronick, S.R.; Yaniv, A. Two species of Rev proteins, with distinct N termini, are expressed by caprine arthritis encephalitis virus. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 2674–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nichols, R.C.; Rudolphi, O.; Ek, B.; Exelbert, R.; Plotz, P.H.; Raben, N. Glycogenosis type VII (Tarui disease) in a Swedish family: Two novel mutations in muscle phosphofructokinase gene (PFK-M) resulting in intron retentions. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1996, 59, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hiraoka, M.; Saito, I.; Tsubota, K.; Sugai, S.; Miyasaka, N. Augmented expression of CD44 splice variants in lymphoproliferative disorder of the lacrimal gland in Sjögren’s syndrome. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 1997, 41, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Ladner, U.; Kriegsmann, J.; Strahl, D.; Gay, R.E.; Elices, M.; Gay, S. Messenger-RNA-Expression der alternativ gesplicten CS-1 Fibronektin-Isoformen im Rheumatoid-Arthritis (RA)-Synovium [Messenger RNA expression of alternatively spliced CS-1 fibronectin isoforms in Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovium]. Verh. Dtsch. Ges. Pathol. 1996, 80, 329. (In German) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wei, P.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Integrated Analysis of Transcriptome Changes in Osteoarthritis: Gene Expression, Pathways and Alternative Splicing. Cartilage 2023, 14, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, I.B.; Lin, M.; Jonge, R.; Will, N.; López-Navarro, B.; Laken, C.V.; Struys, E.A.; Oudejans, C.B.M.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Cloos, J.; et al. Methotrexate Provokes Disparate Folate Metabolism Gene Expression and Alternative Splicing in Ex Vivo Monocytes and GM-CSF- and M-CSF-Polarized Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
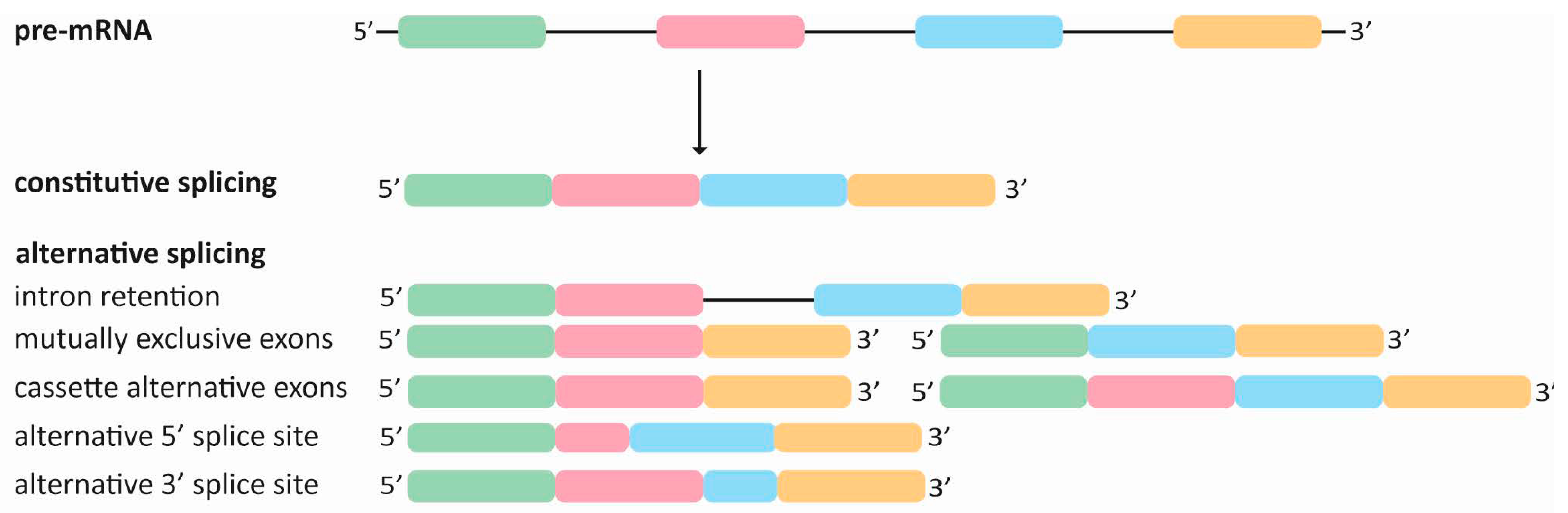
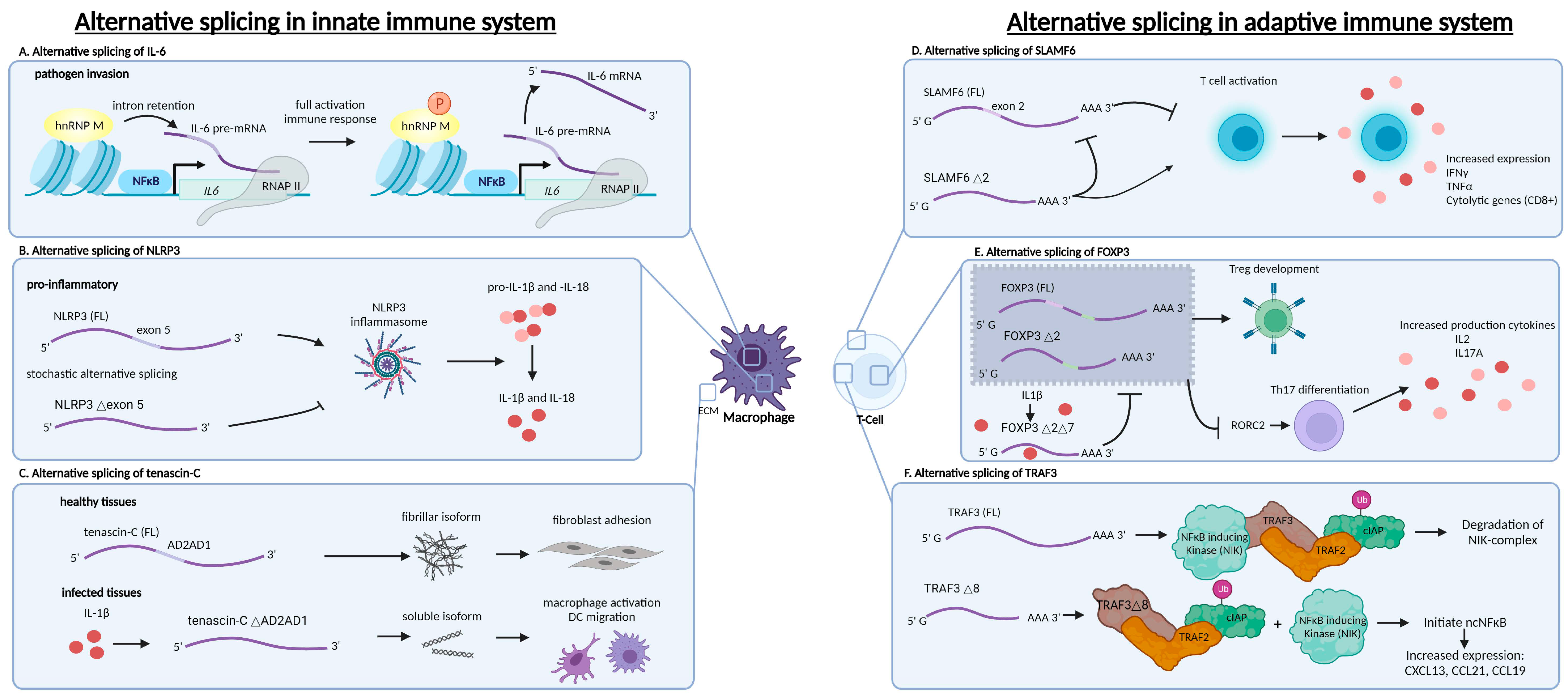
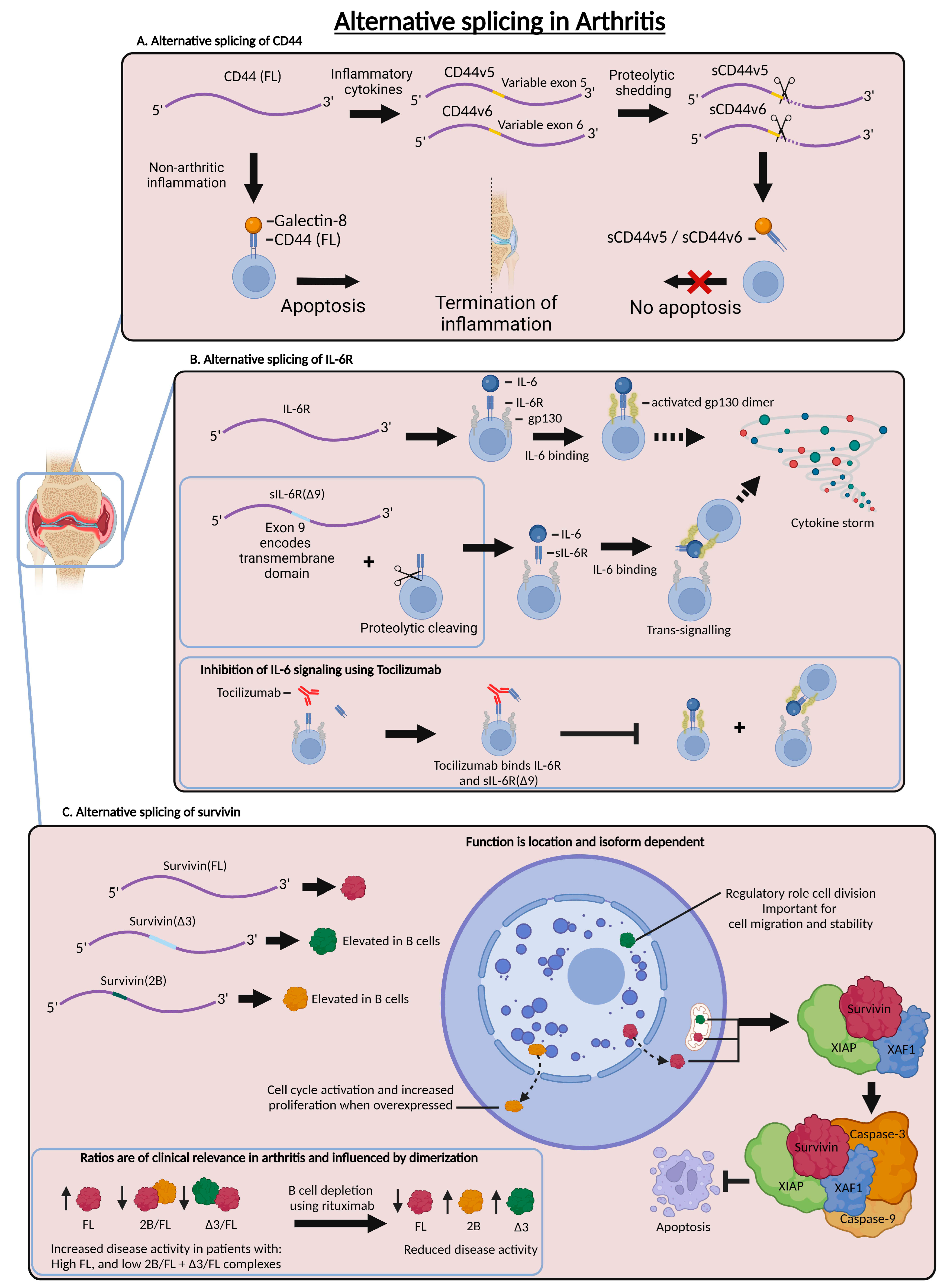
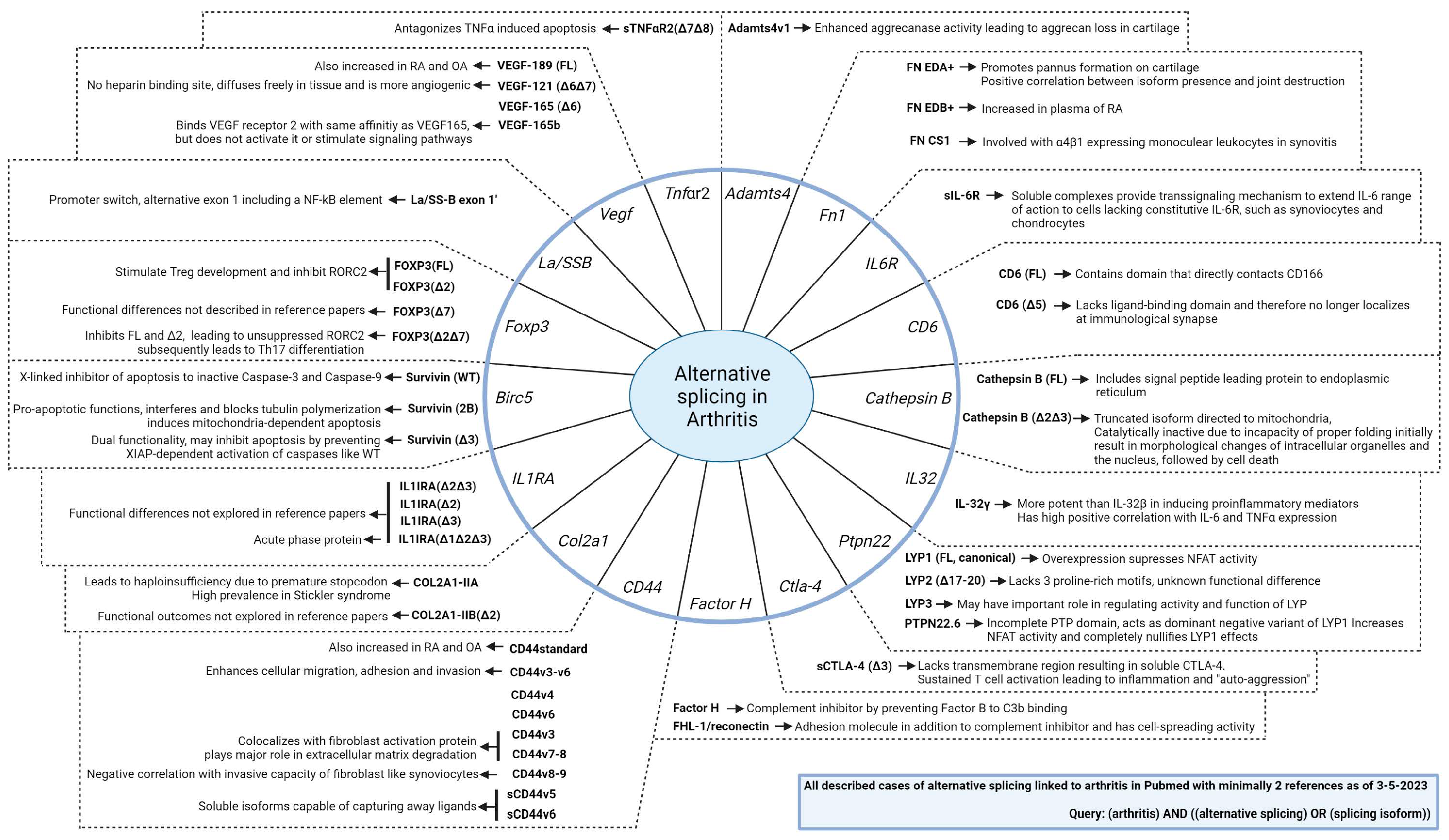
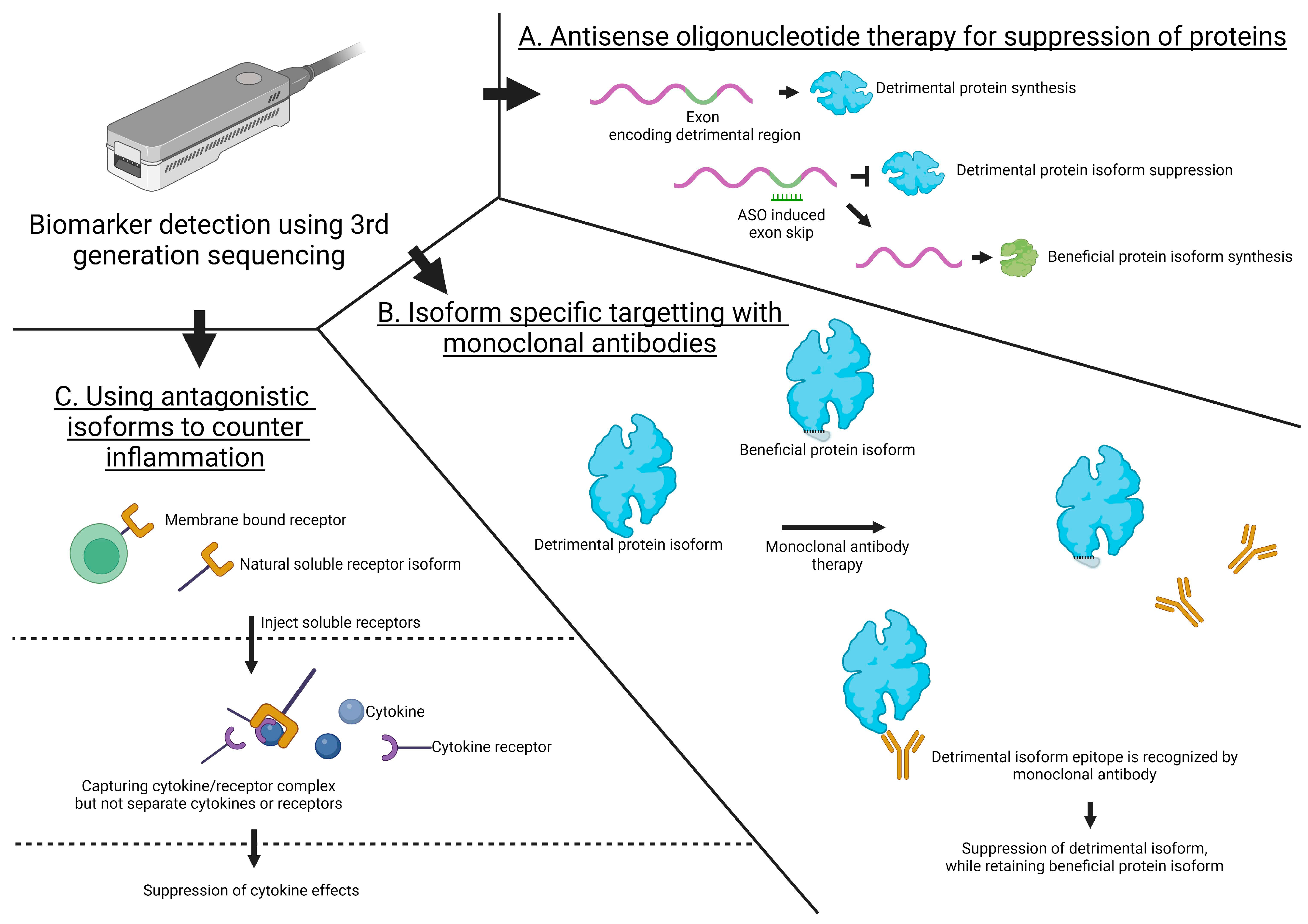
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
van Haaren, M.J.H.; Steller, L.B.; Vastert, S.J.; Calis, J.J.A.; van Loosdregt, J. Get Spliced: Uniting Alternative Splicing and Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158123
van Haaren MJH, Steller LB, Vastert SJ, Calis JJA, van Loosdregt J. Get Spliced: Uniting Alternative Splicing and Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(15):8123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158123
Chicago/Turabian Stylevan Haaren, Maurice J. H., Levina Bertina Steller, Sebastiaan J. Vastert, Jorg J. A. Calis, and Jorg van Loosdregt. 2024. "Get Spliced: Uniting Alternative Splicing and Arthritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 15: 8123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158123
APA Stylevan Haaren, M. J. H., Steller, L. B., Vastert, S. J., Calis, J. J. A., & van Loosdregt, J. (2024). Get Spliced: Uniting Alternative Splicing and Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(15), 8123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158123





