Evaluation of the Ameliorative Potential of 3,5-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-1,3,5-thiadiazinane-2-thione against Scopolamine-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Acute Toxicity Test
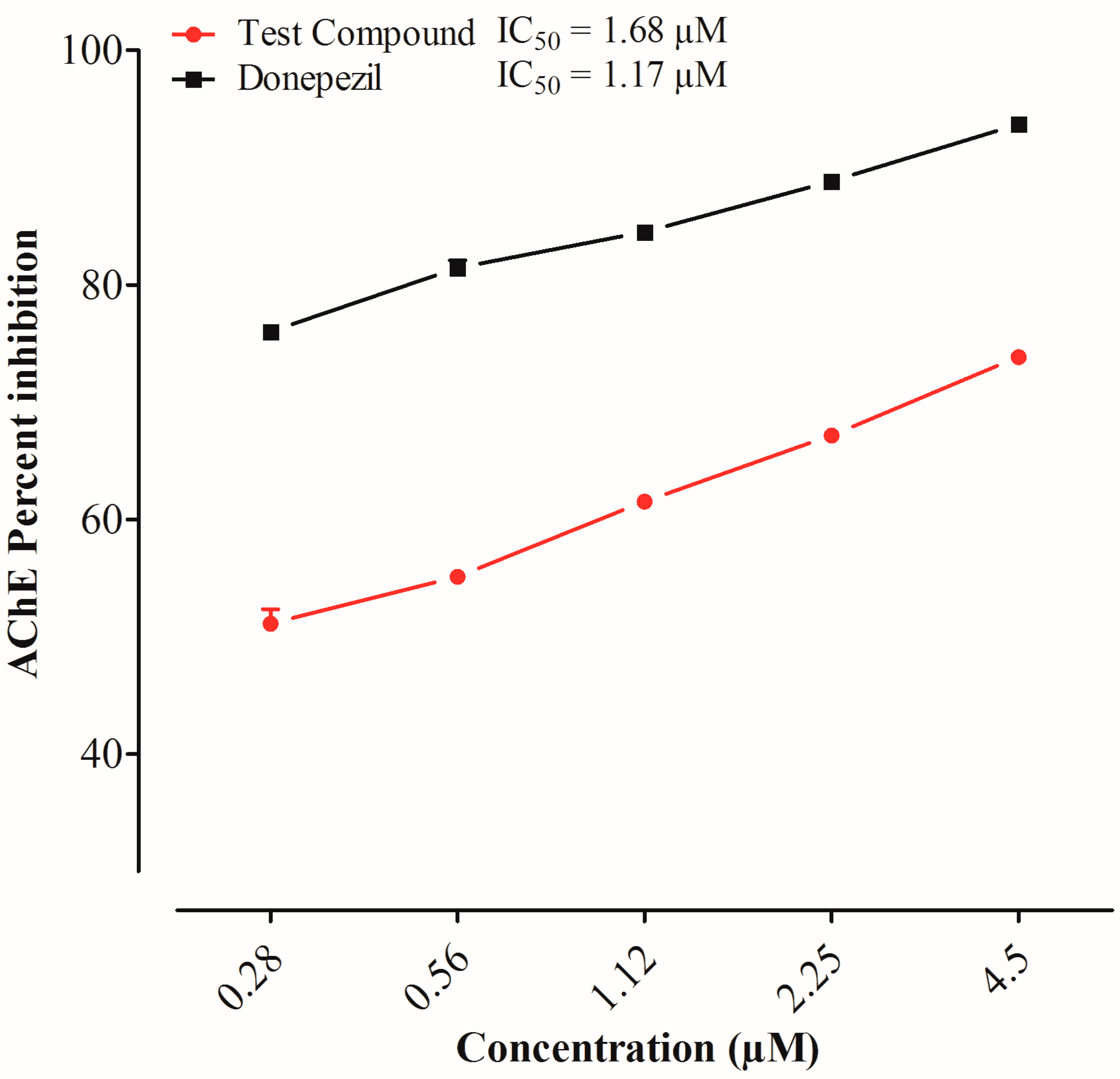
2.2. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition by 3,5-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-1,3,5-thiadiazinane-2-thione
2.3. 1,1-Diphenyl, 2-Picrylhydrazal Free Radical Scavenging Assay
2.4. Results of the Behavioral Studies
2.4.1. Effect of the Test Compound in the Elevated Plus Maze
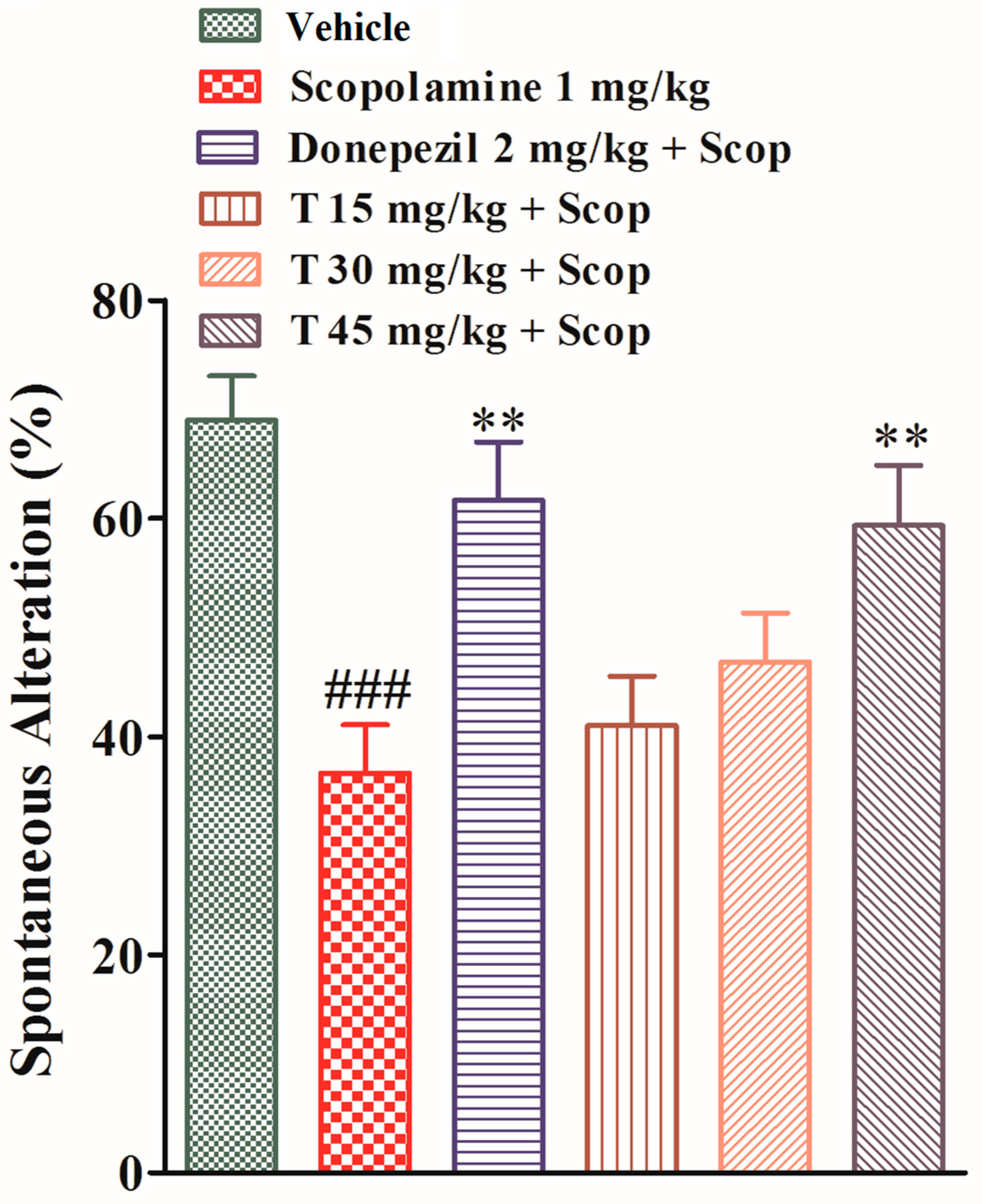
2.4.2. Effect of the Test Compound in the Y-Maze Test
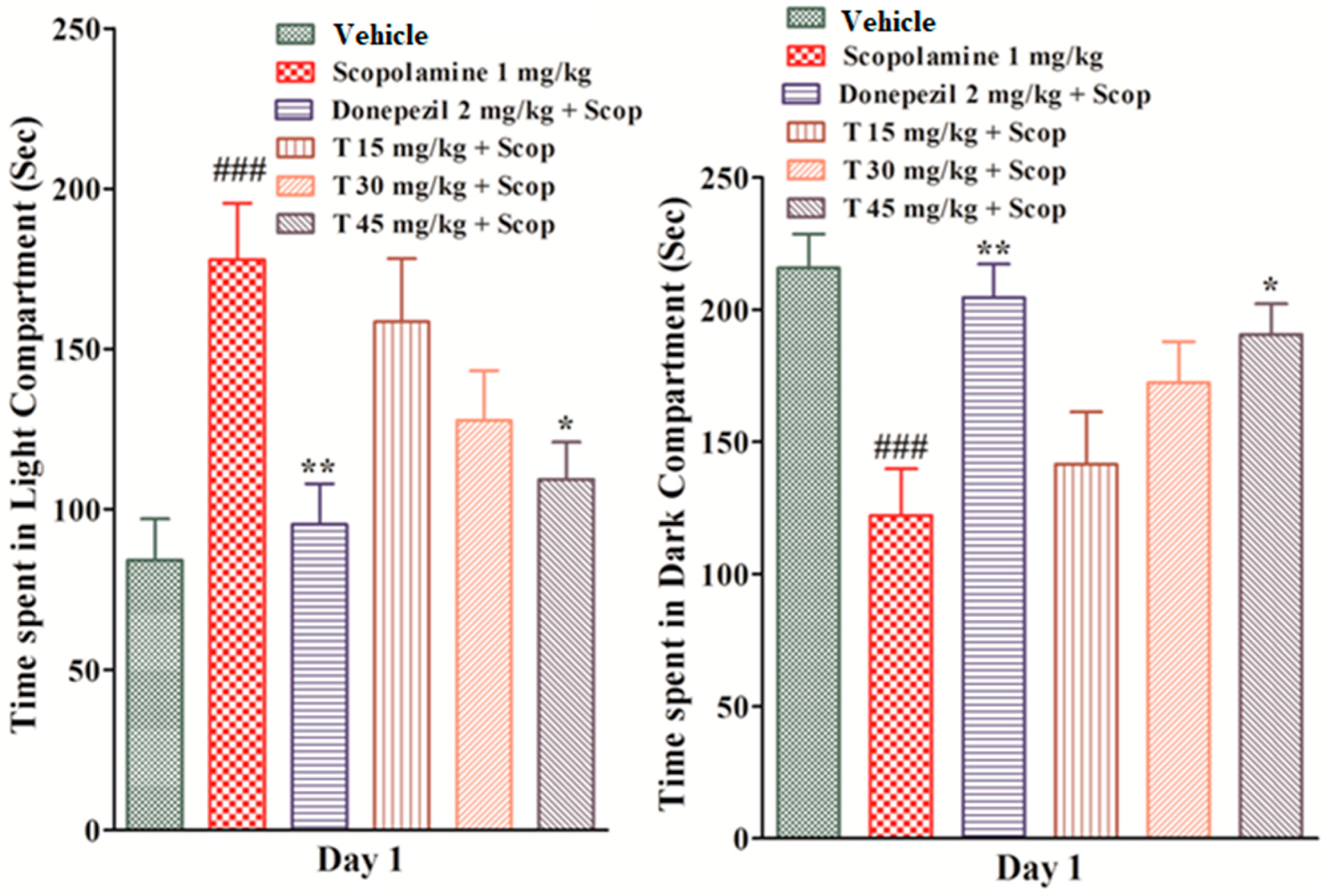
2.4.3. Effect of the Test Compound in the Light and Dark Test
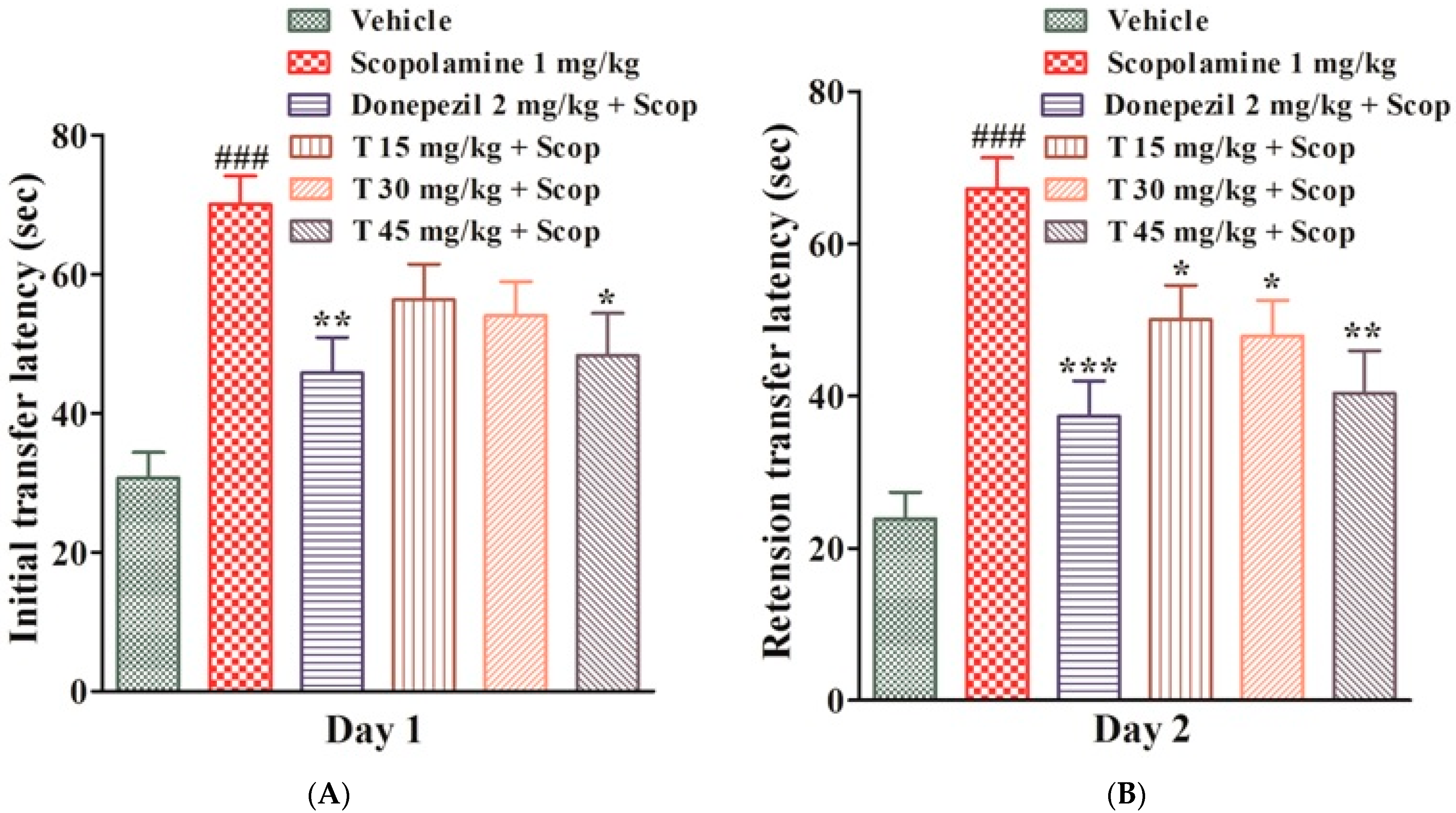
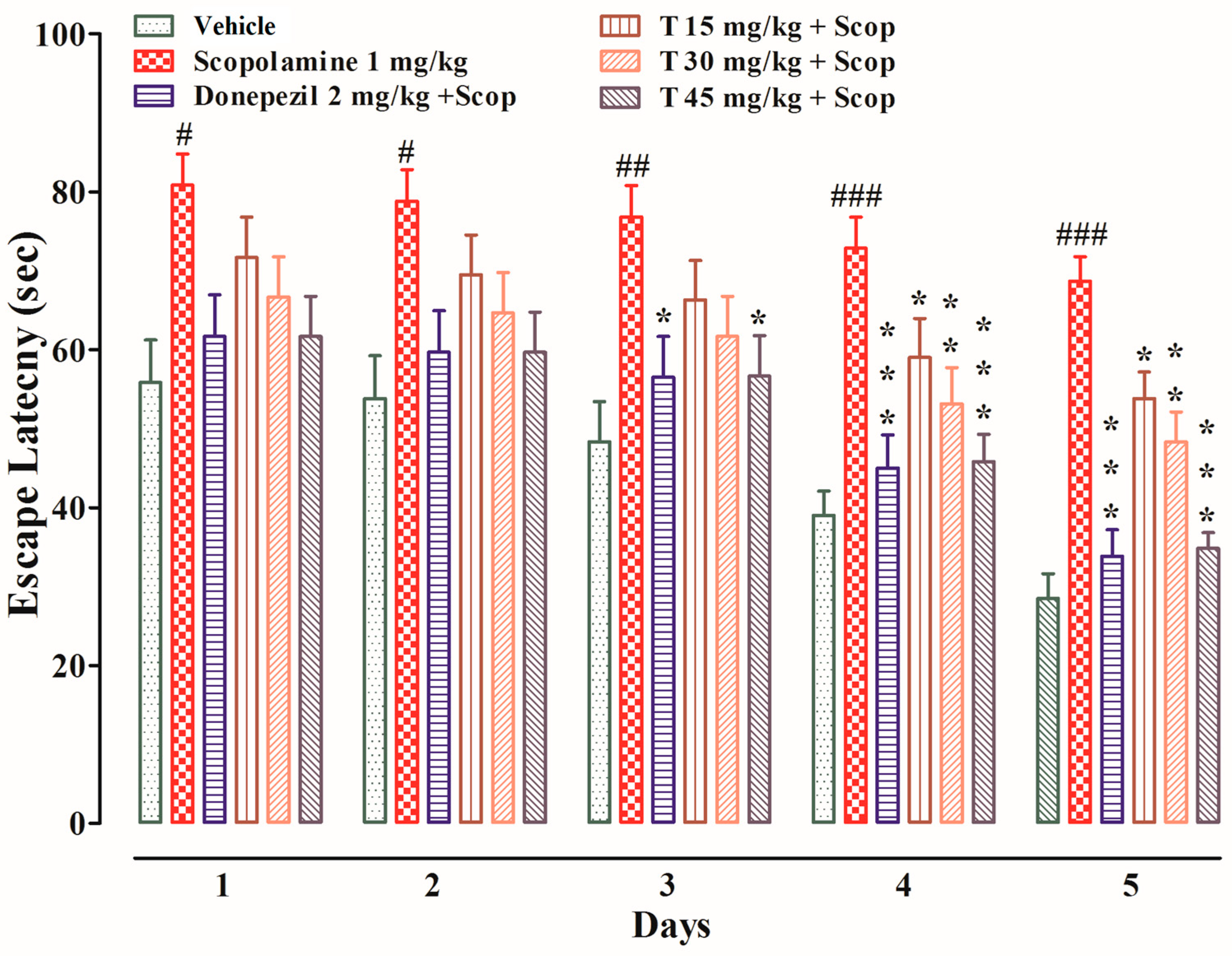
2.4.4. Effect of the Test Compound in the MWM Test
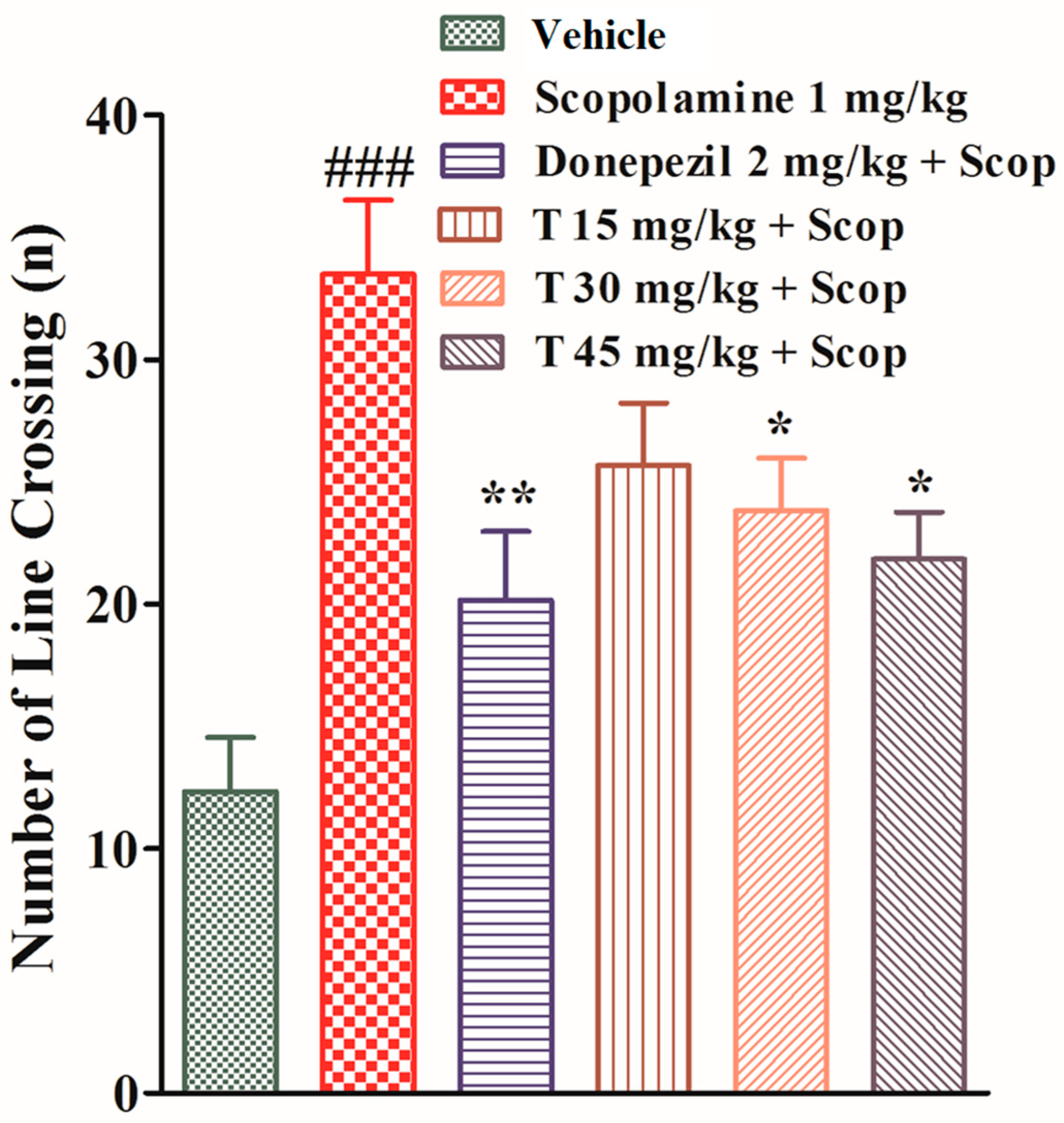
2.4.5. Effect of the Test Compound in the Open Field Test
2.5. Effect of the Test Compound on the Frontal Cortex and Hippocampal Acetylcholinesterase Enzyme
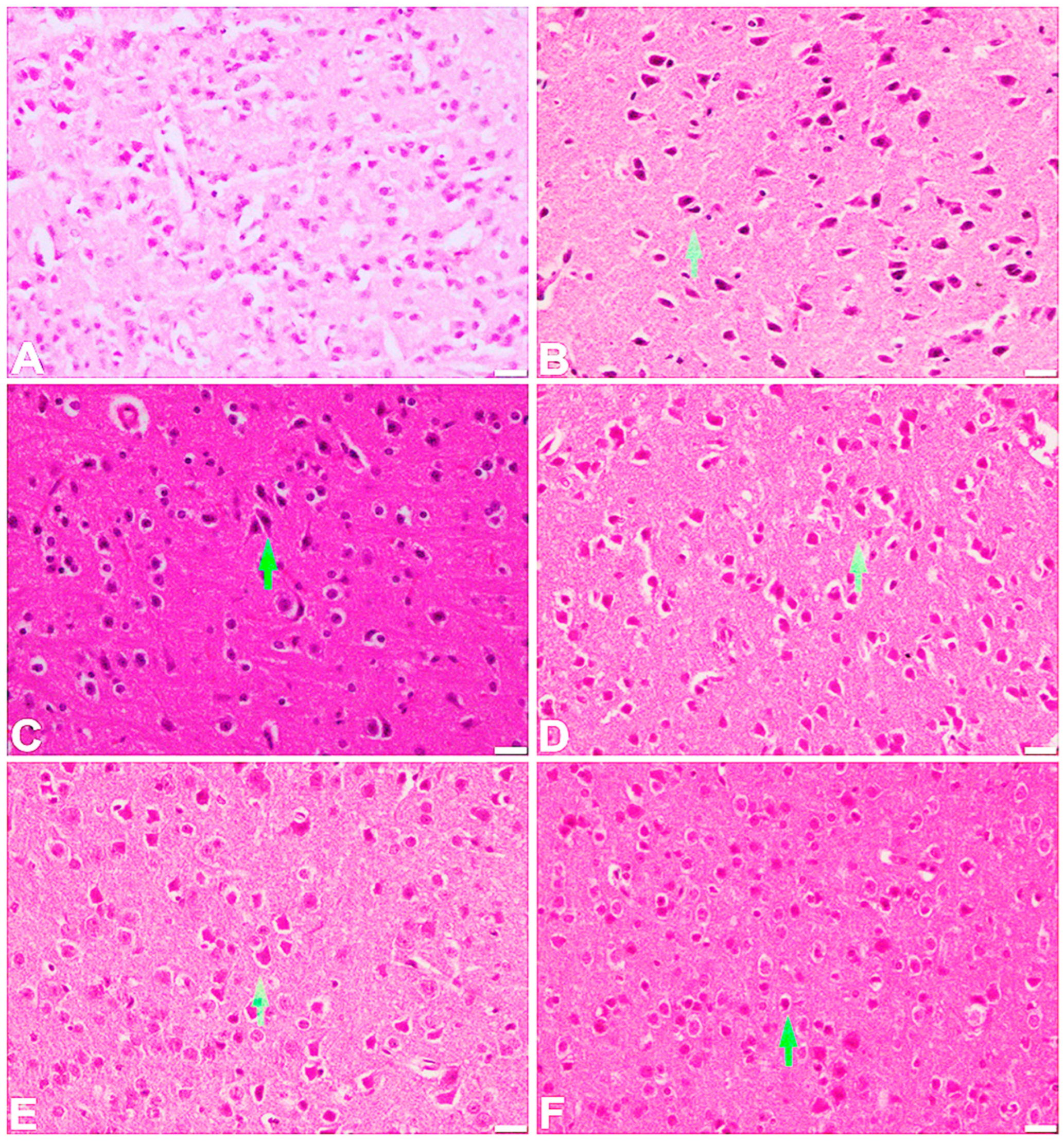
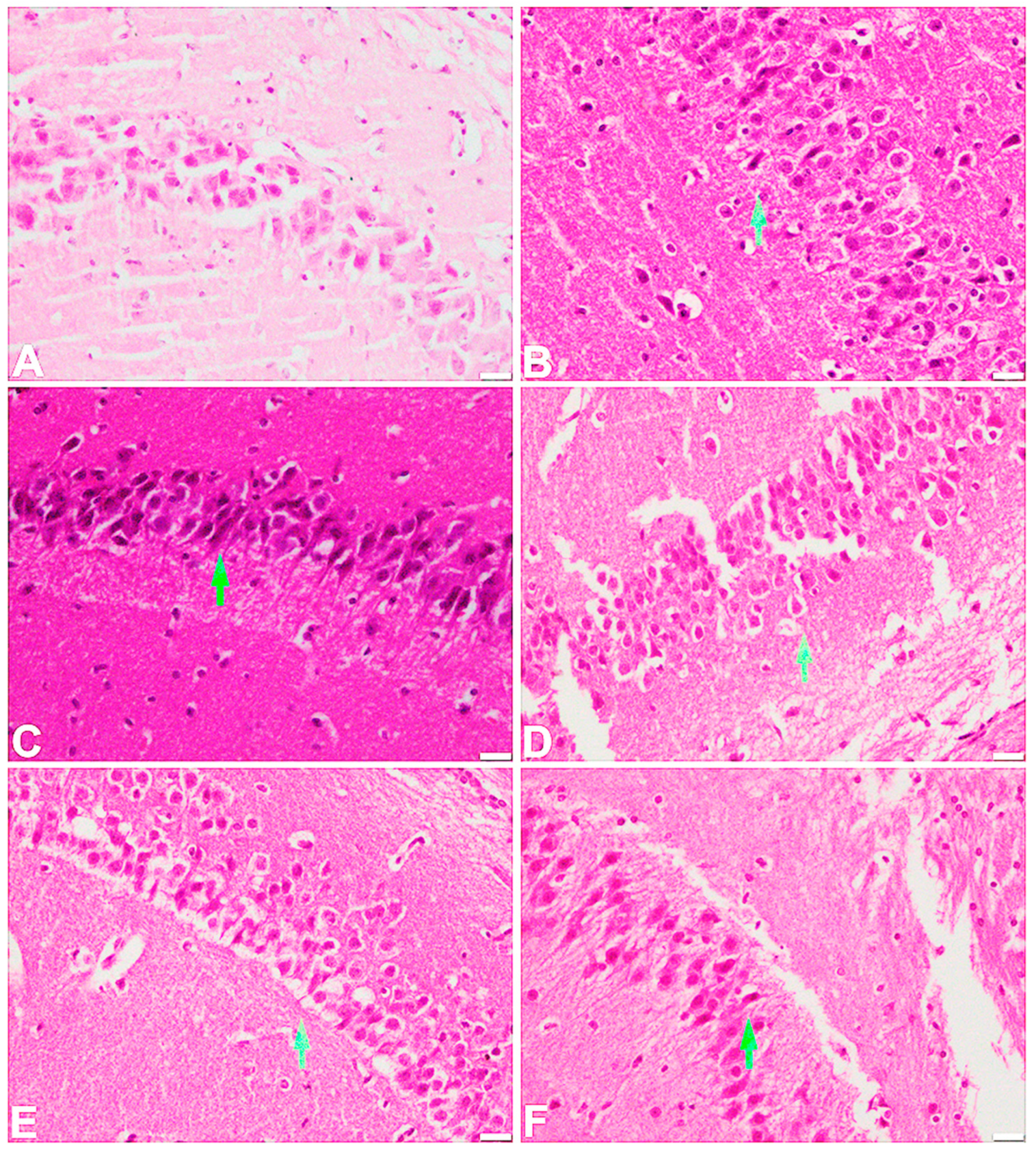
2.6. Effect of the Test Compound on the Histopathological Examination of the Frontal Cortex and Hippocampus
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Biochemical Assays
4.2.1. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Inhibition Assay
4.2.2. 1,1-diphenyl, 2-picrylhydrazal Free Radical Scavenging Assay
4.3. In Vivo Study
4.3.1. Animals
4.3.2. Drug Solubility and Administration Protocol
4.3.3. Acute Toxicity Test
4.3.4. Animal Grouping
4.3.5. Elevated Plus Maze (EPM)
4.3.6. Y-Maze Test
4.3.7. Light and Dark Box Test
4.3.8. Morris Water Maze Test
4.3.9. Open Field Test
4.3.10. Assessment of Acetylcholine Esterase in the Frontal Cortex and Hippocampus
4.3.11. Histopathological Evaluation
4.3.12. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ayaz, M.; Junaid, M.; Ullah, F.; Subhan, F.; Sadiq, A.; Ali, G.; Ovais, M.; Shahid, M.; Ahmad, A.; Wadood, A. Anti-Alzheimer’s studies on β-sitosterol isolated from Polygonum hydropiper L. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, V.; Riju, T.; Venkatesh, S.; Babu, G. Memory enhancing activity of Lawsonia inermis Linn. leaves against scopolamine induced memory impairment in Swiss albino mice. Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med. 2017, 17, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookmeyer, R.; Johnson, E.; Ziegler-Graham, K.; Arrighi, H.M. Forecasting the global burden of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2007, 3, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushtaq, A.; Anwar, R.; Ahmad, M. Lavandula stoechas L. alleviates dementia by preventing oxidative damage of cholinergic neurons in mice brain. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 17, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Patience, A.A.; Sharma, N.; Khurana, N. The present and future of pharmacotherapy of Alzheimer’s disease: A comprehensive review. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 815, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kametani, F.; Hasegawa, M. Reconsideration of amyloid hypothesis and tau hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikova, A.; Perova, N.; Chupakhin, O. Synthesis and properties of functional derivatives of 1,3,4-thiadiazines and condensed systems based on these compounds. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 1991, 27, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboul-Fadl, T.; Hassanin, K. Tetrahydro-2H-1, 3,5-thiadiazine-5-(4-pyridylcarboxamide)-2-thione derivatives as prodrugs for isoniazid; synthesis, investigations and in vitro antituberculous activity. Pharmazie 1999, 54, 244–247. [Google Scholar]
- Bermello, J.C.; Piñeiro, R.P.; Fidalgo, L.M.; Cabrera, H.R.; Navarro, M.S. Thiadiazine derivatives as antiprotozoal new drugs. Open Med. Chem. J. 2011, 5, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertan, M.; Bilgin, A.; Palaska, E.; Yulug, N. Syntheses and antifungal activities of some 3-(2-phenylethyl)-5-substituted-tetrahydro-2H-1, 3,5-thiadiazine-2-thiones. Arzneim. Forsch. 1992, 42, 160–163. [Google Scholar]
- Citron, M. Alzheimer’s disease: Strategies for disease modification. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malekzadeh, S.; Edalatmanesh, M.; Mehrabani, D.; Shariati, M. Drugs Induced Alzheimer’s Disease in Animal Model. Galen Med. J. 2017, 6, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, H.; Nazirolu, M.; Demirci, K.; Övey, İ.S. The protective role of selenium on scopolamine-induced memory impairment, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in aged rats: The involvement of TRPM2 and TRPV1 channels. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akıncıoğlu, H.; Gülçin, İ. Potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Potential drugs for Alzheimer’s disease. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemati, F.; Whishaw, I.Q. The point of entry contributes to the organization of exploratory behavior of rats on an open field: An example of spontaneous episodic memory. Behav. Brain Res. 2007, 182, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calamandrei, G.; Venerosi, A.; Valanzano, A.; Alleva, E. Effects of prenatal AZT+ 3TC treatment on open field behavior and responsiveness to scopolamine in adult mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2000, 67, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasekaran, S.; Perumal, P.; Palayan, M. In-vitro Screening for acetylcholinesterase enzyme inhibition potential and antioxidant activity of extracts of Ipomoea aquatica Forsk: Therapeutic lead for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci 2015, 5, 012–016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, Z.; Ullah, F.; Ayaz, M.; Sadiq, A.; Ahmad, S.; Zeb, A.; Hussain, A.; Imran, M. Anticholinesterse and antioxidant investigations of crude extracts, subsequent fractions, saponins and flavonoids of Atriplex laciniata L.: Potential effectiveness in Alzheimer’s and other neurological disorders. Biol. Res. 2015, 48, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Ullah, F.; Ayaz, M.; Sadiq, A.; Imran, M. Antioxidant and anticholinesterase investigations of Rumex hastatus D. Don: Potential effectiveness in oxidative stress and neurological disorders. Biol. Res. 2015, 48, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Subhan, F.; Islam, N.U.; Shahid, M.; Rahman, F.U.; Sewell, R.D. Gabapentin and its salicylaldehyde derivative alleviate allodynia and hypoalgesia in a cisplatin-induced neuropathic pain model. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 814, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukh, L.; Ali, G.; Ullah, R.; Islam, N.U.; Shahid, M. Efficacy assessment of salicylidene salicylhydrazide in chemotherapy associated peripheral neuropathy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 173481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Ali, G.; Subhan, F.; Khan, A.; Ahsan Halim, S.; Naveed, M.; Kalsoom, S.; Al-Harrasi, A. Attenuation of spatial memory in 5xFAD mice by targeting cholinesterases, oxidative stress and inflammatory signaling using 2-(hydroxyl-(2-nitrophenyl)methyl)cyclopentanone. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 100, 108083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Ali, G.; Khan, A.; Ahmad, S.; Al-Harrasi, A. Cyclopentanone Derivative Attenuates Memory Impairment by Inhibiting Amyloid Plaques Formation in the 5xFAD Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Bi, W.; Fan, K.; Li, T.; Yan, T.; Xiao, F.; He, B.; Bi, K.; Jia, Y. Ameliorating effect of Alpinia oxyphylla—Schisandra chinensis herb pair on cognitive impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, R.; Ali, G.; Baseer, A.; Khan, S.I.; Akram, M.; Khan, S.; Ahmad, N.; Farooq, U.; Nawaz, N.K.; Shaheen, S. Tannic acid inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive impairment in adult mice by targeting multiple pathological features. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 110, 108970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Dong, L.; Lv, J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, B.; Wang, F.; Liu, X. 20 (S)-protopanaxadiol (PPD) alleviates scopolamine-induced memory impairment via regulation of cholinergic and antioxidant systems, and expression of Egr-1, c-Fos and c-Jun in mice. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 279, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, A.; Inam, W.; Khan, S.A.; Mahmood, W.; Abbas, G. β-glucan attenuated scopolamine induced cognitive impairment via hippocampal acetylcholinesterase inhibition in rats. Brain Res. 2016, 1644, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Ali, G.; Rasheed, A.; Subhan, F.; Khan, A.; Halim, S.A.; Al-Harrasi, A. The 7-Hydroxyflavone attenuates chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain by targeting inflammatory pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 107, 108674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Concentration (μg/mL) | %-DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Activity (Mean ± SEM) | IC50 (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test Compound | 1000 | 75 ± 3.0 | 97.75 |
| 500 | 65 ± 2.7 | ||
| 250 | 50 ± 2.9 | ||
| 125 | 41.7 ± 4.2 | ||
| 62.5 | 28.3 ± 4.41 | ||
| Ascorbic Acid | 1000 | 80 ± 3.5 | 67.98 |
| 500 | 71 ± 3.8 | ||
| 250 | 60 ± 3 | ||
| 125 | 51 ± 5 | ||
| 62.5 | 28.3 ± 4.4 |
| Frontal Cortex Region | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. No. | Group | Degeneration Process | Plaques/Fibrosis | ||
| Pyknosis | Karyolysis | Vacuolation | |||
| 1 | Vehicle group | No | No | No | No |
| 2 | Scopolamine | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 3 | Scopolamine + donepezil | No | No | Yes | No |
| 4 | T15 + scopolamine | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 5 | T30 + scopolamine | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| 6 | T45 + scopolamine | No | No | Yes | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shagufta; Ali, G.; Khan, A.; Rasheed, A.; Deeba, F.; Ullah, R.; Shahid, M.; Ali, H.; Khan, R.; Shamezai, N.; et al. Evaluation of the Ameliorative Potential of 3,5-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-1,3,5-thiadiazinane-2-thione against Scopolamine-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25169104
Shagufta, Ali G, Khan A, Rasheed A, Deeba F, Ullah R, Shahid M, Ali H, Khan R, Shamezai N, et al. Evaluation of the Ameliorative Potential of 3,5-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-1,3,5-thiadiazinane-2-thione against Scopolamine-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(16):9104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25169104
Chicago/Turabian StyleShagufta, Gowhar Ali, Adnan Khan, Abdur Rasheed, Farah Deeba, Rahim Ullah, Muhammad Shahid, Haleema Ali, Rasool Khan, Najeebullah Shamezai, and et al. 2024. "Evaluation of the Ameliorative Potential of 3,5-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-1,3,5-thiadiazinane-2-thione against Scopolamine-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 16: 9104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25169104
APA StyleShagufta, Ali, G., Khan, A., Rasheed, A., Deeba, F., Ullah, R., Shahid, M., Ali, H., Khan, R., Shamezai, N., & Sharif, N. (2024). Evaluation of the Ameliorative Potential of 3,5-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-1,3,5-thiadiazinane-2-thione against Scopolamine-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(16), 9104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25169104





