Pitfalls When Determining HNA-1 Genotypes and Finding Novel Alleles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
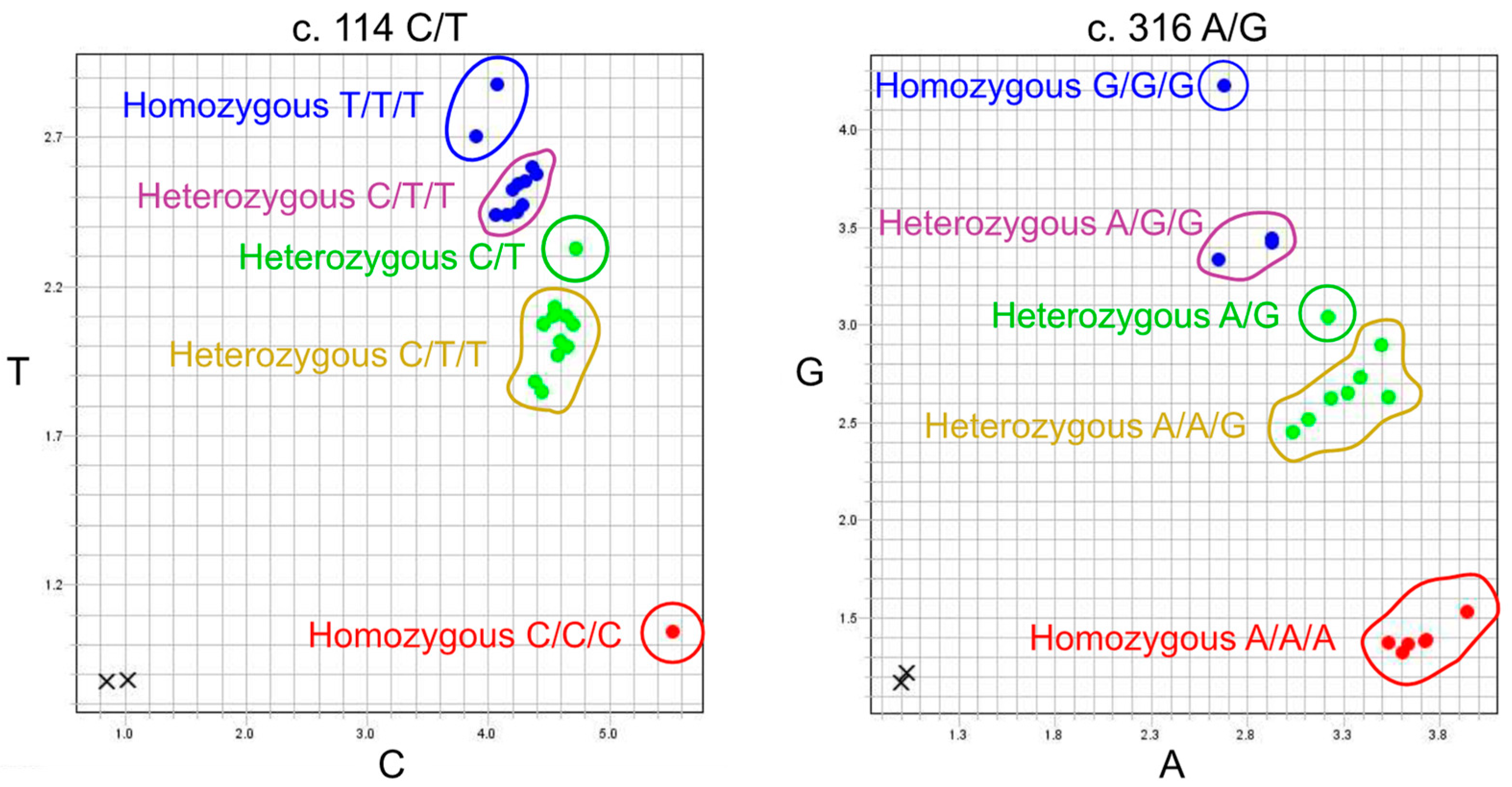
2.1. In-House TaqMan PCR Genotyping Data
2.2. Commercial PCR-SSP Genotyping Dats
2.3. Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification Data
2.4. PCR-SBT Data
2.5. Long-Read Nanopore Sequencing Data
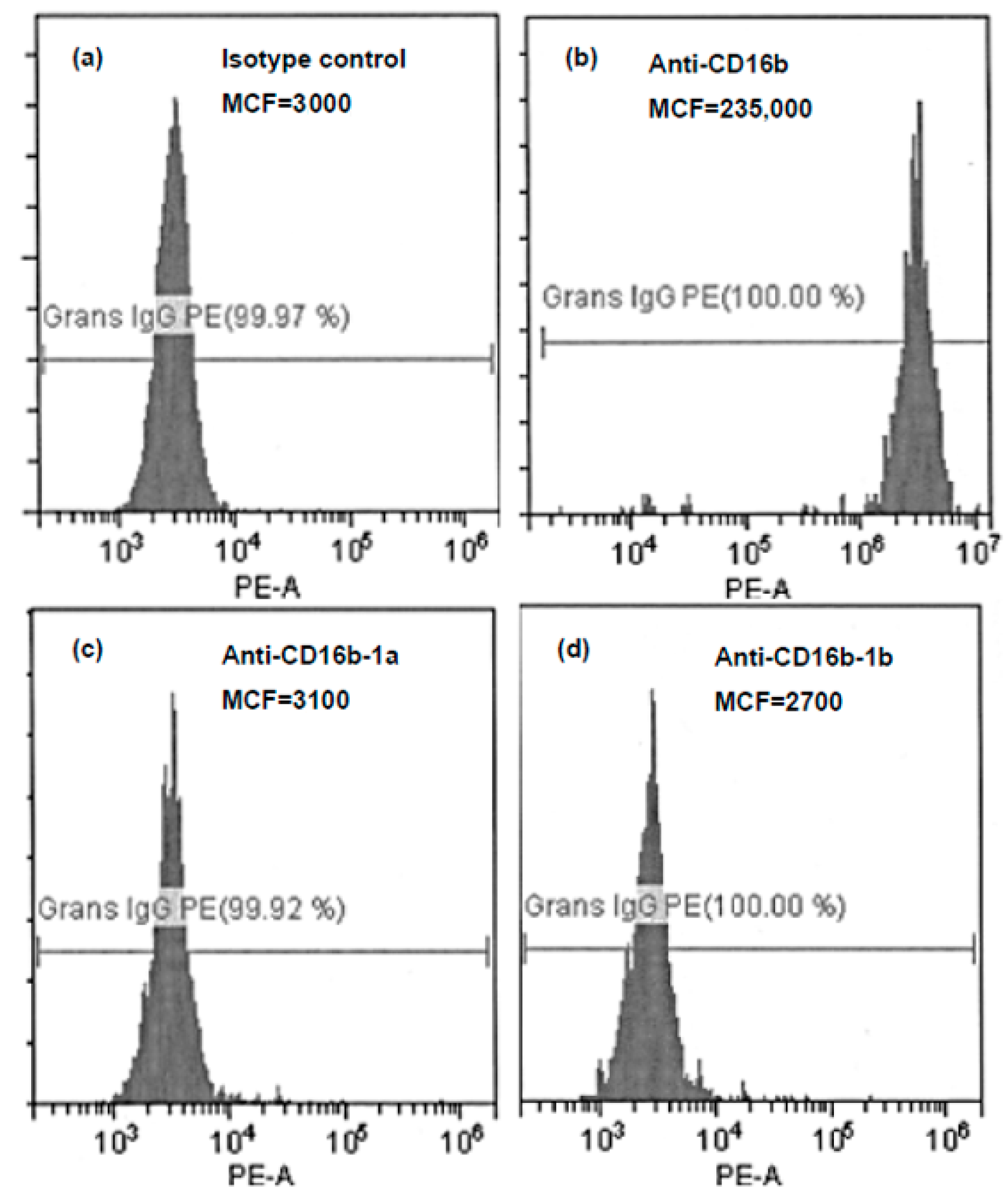
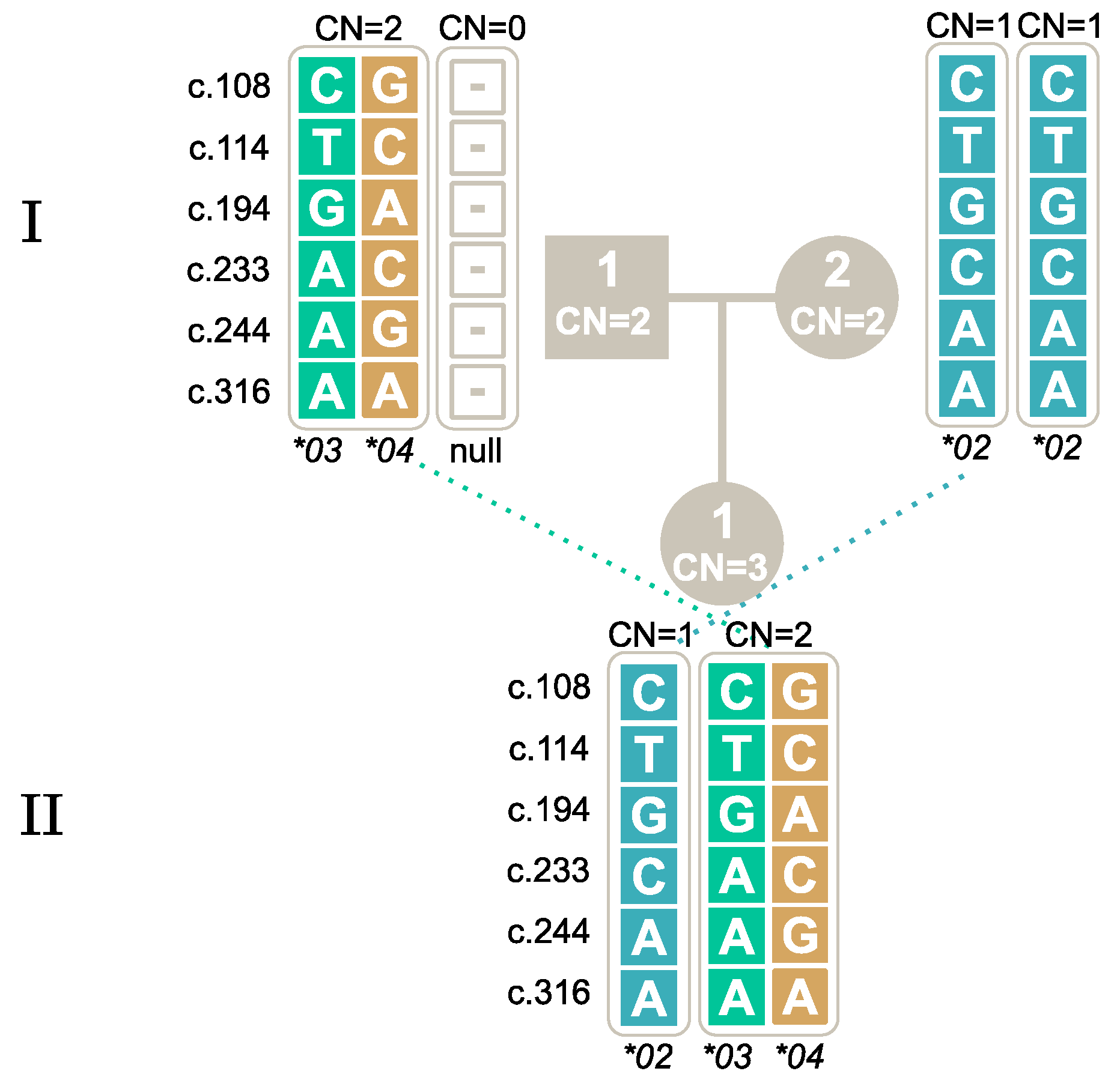
2.6. Novel Alleles
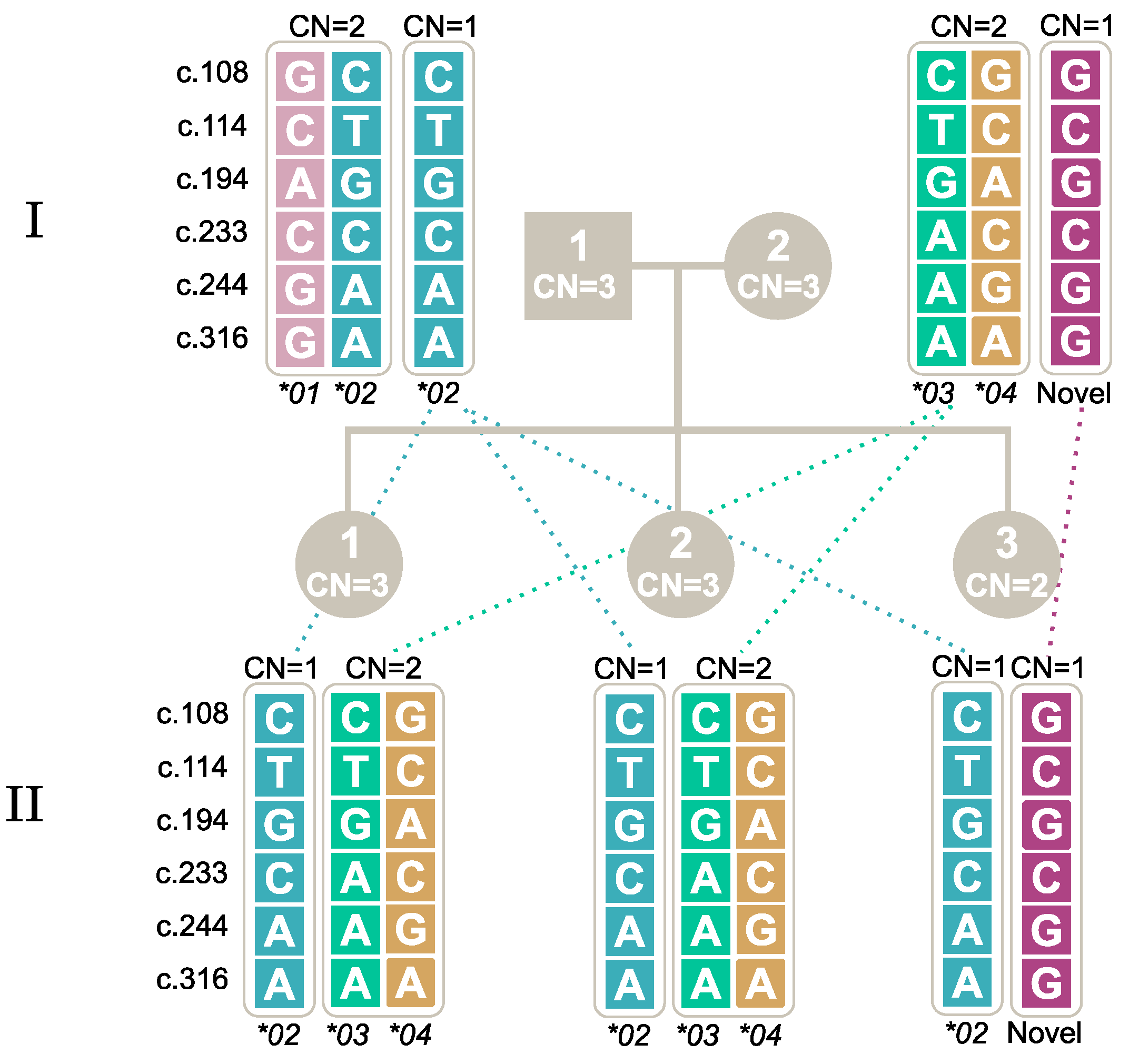
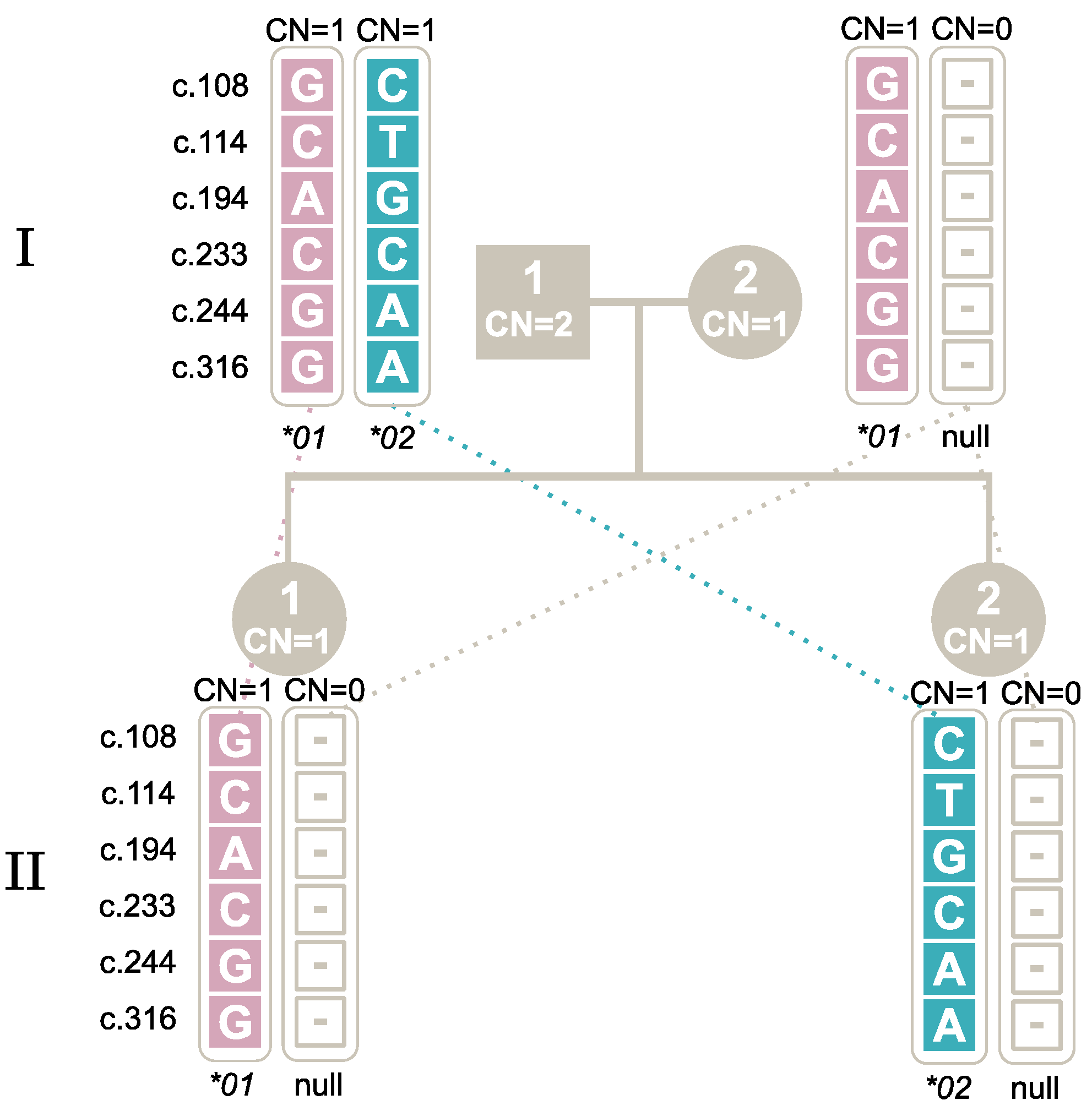
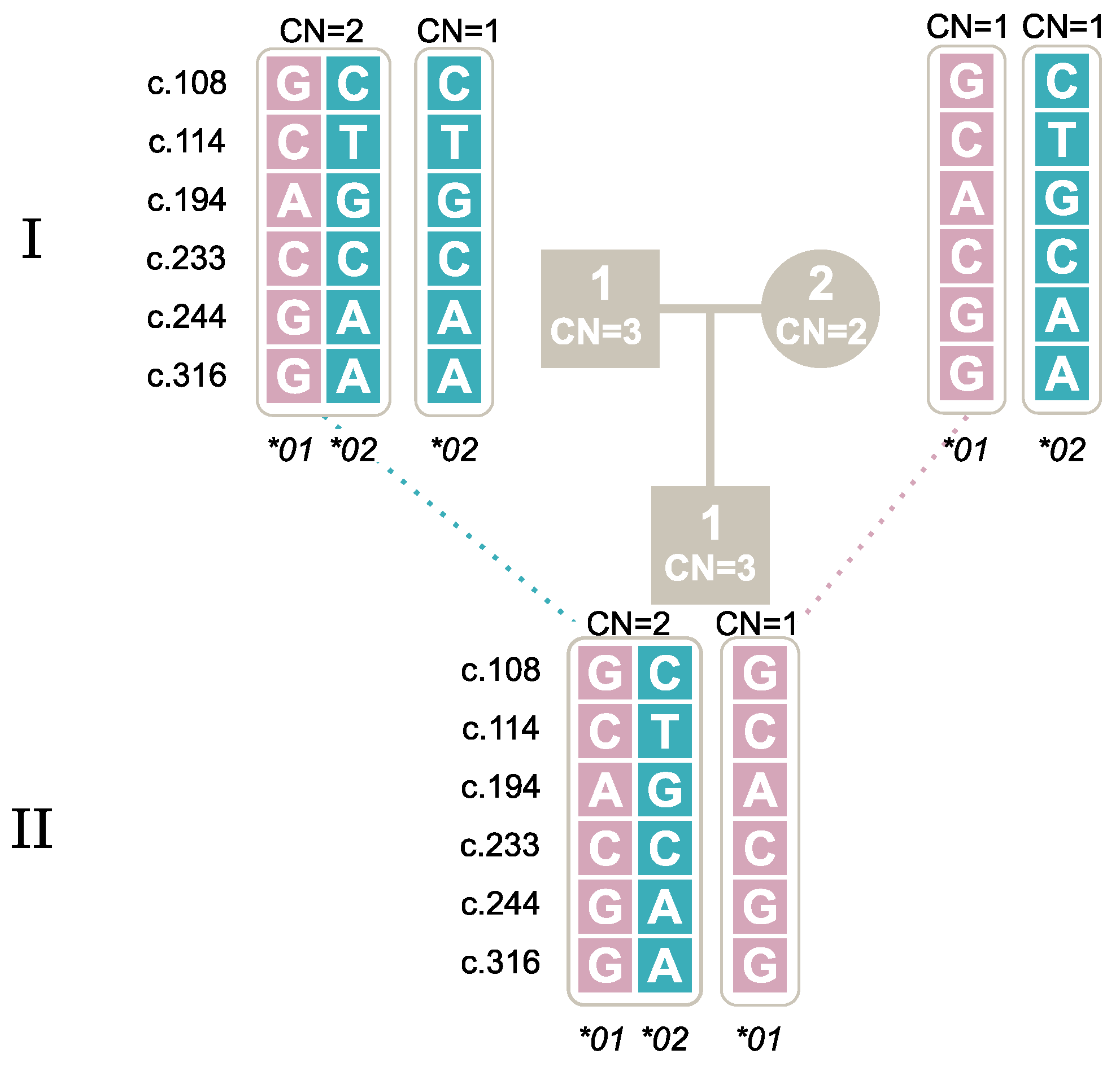
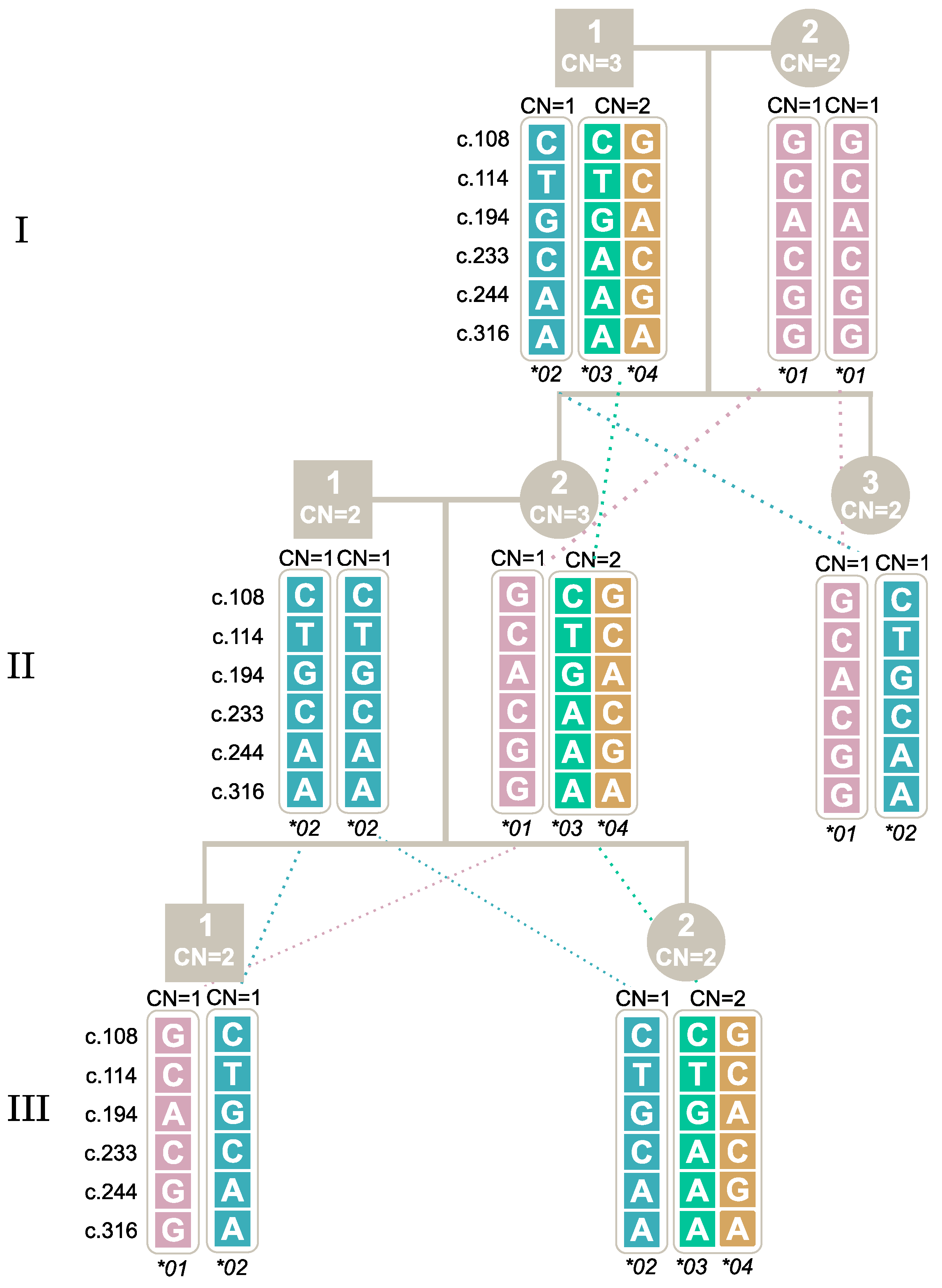
2.7. Segregation of Alleles through Family Studies
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Study Cohort
4.2. Validation Cohort
4.3. In-House TaqMan PCR and Commercial PCR-SSP Testing
4.4. Real-Time qPCR CN Investigation
4.5. Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification Testing
4.6. PCR-SBT Analysis
4.7. Long-Read Nanopore Sequencing
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Bux, J. Human neutrophil alloantigens. Vox Sang. 2008, 94, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koene, H.R.; Haas, M.D.; Kleijer, M.; Roos, D.; Von Dem Borne, A.E.G.K. NA-phenotype-dependent differences in neutrophil FcγRIIIb expression cause differences in plasma levels of soluble FcγRIII. Br. J. Haematol. 1996, 93, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraru, M.; Perez-Portilla, A.; Al-Akioui Sanz, K.; Blazquez-Moreno, A.; Arnaiz-Villena, A.; Reyburn, H.T.; Vilches, C. FCGR Genetic Variation in Two Populations from Ecuador Highlands-Extensive Copy-Number Variation, Distinctive Distribution of Functional Polymorphisms, and a Novel, Locally Common, Chimeric FCGR3B/A (CD16B/A) Gene. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 615645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalezari, P.; Radel, E. Neutrophil-specific antigens: Immunology and clinical significance. Semin. Hematol. 1974, 11, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bux, J. Granulocyte antibody-mediated neutropenias and transfusion reactions. Infusionsther. Transfusionsmed. 1999, 26, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bux, J. Molecular genetics of granulocyte polymorphisms. Vox Sang. 2000, 78 (Suppl. 2), 125–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ravetch, J.V.; Perussia, B. Alternative membrane forms of Fc gamma RIII(CD16) on human natural killer cells and neutrophils. Cell type-specific expression of two genes that differ in single nucleotide substitutions. J. Exp. Med. 1989, 170, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ory, P.A.; Clark, M.R.; Kwoh, E.E.; Clarkson, S.B.; Goldstein, I.M. Sequences of complementary DNAs that encode the NA1 and NA2 forms of Fc receptor III on human neutrophils. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 84, 1688–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flesch, B.K.; Curtis, B.R.; de Haas, M.; Lucas, G.; Sachs, U.J. Update on the nomenclature of human neutrophil antigens and alleles. Transfusion 2016, 56, 1477–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissel, K.; Hofmann, C.; Gittinger, F.S.; Daniels, G.; Bux, J. HNA-1a, HNA-1b, and HNA-1c (NA1, NA2, SH) frequencies in African and American Blacks and in Chinese. Tissue Antigens 2000, 56, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bux, J.; Stein, E.L.; Bierling, P.; Fromont, P.; Clay, M.; Stroncek, D.; Santoso, S. Characterization of a new alloantigen (SH) on the human neutrophil Fc gamma receptor IIIb. Blood 1997, 89, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kløve-Mogensen, K.; Steffensen, R.; Masmas, T.N.; Glenthøj, A.; Jensen, C.F.; Haunstrup, T.M.; Ratcliffe, P.; Höglund, P.; Hasle, H.; Nielsen, K.R. Genetic variations in low-to-medium-affinity Fcγ receptors and autoimmune neutropenia in early childhood in a Danish cohort. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2023, 50, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flesch, B.K.; Reil, A. Molecular Genetics of the Human Neutrophil Antigens. Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2018, 45, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.R.; Koelbaek, M.D.; Varming, K.; Baech, J.; Steffensen, R. Frequencies of HNA-1, HNA-3, HNA-4, and HNA-5 in the Danish and Zambian populations determined using a novel TaqMan real time polymerase chain reaction method. Tissue Antigens 2012, 80, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagelkerke, S.Q.; Tacke, C.E.; Breunis, W.B.; Tanck, M.W.T.; Geissler, J.; Png, E.; Hoang, L.T.; van der Heijden, J.; Naim, A.N.M.; Yeung, R.S.M.; et al. Extensive Ethnic Variation and Linkage Disequilibrium at the FCGR2/3 Locus: Different Genetic Associations Revealed in Kawasaki Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flesch, B.K.; Doose, S.; Siebert, R.; Ntambi, E.; Neppert, J. FCGR3 variants and expression of human neutrophil antigen-1a, -1b, and -1c in the populations of northern Germany and Uganda. Transfusion 2002, 42, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcelijn, L.; de Haas, M. Neonatal Alloimmune Neutropenia. Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2018, 45, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, S.P.; Chong, W.; Lucas, G.; Green, A.; Navarrete, C. Determination of human neutrophil antigen-1, -3, -4 and -5 allele frequencies in English Caucasoid blood donors using a multiplex fluorescent DNA-based assay. Vox Sang. 2013, 105, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Haas, M.; Kleijer, M.; van Zwieten, R.; Roos, D.; von dem Borne, A.E. Neutrophil Fc gamma RIIIb deficiency, nature, and clinical consequences: A study of 21 individuals from 14 families. Blood 1995, 86, 2403–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reil, A.; Flesch, B.; Bux, J. FCGR3B* 04-a novel allele of the human Fc gamma receptor IIIb gene. Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2011, 38, 69. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo, K.; Procter, J.L.; Chanock, S.; Stroncek, D.F. The expression of NA antigens in people with unusual Fcgamma receptor III genotypes. Transfusion 2001, 41, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffensen, R.; Gülen, T.; Varming, K.; Jersild, C. FcgammaRIIIB polymorphism: Evidence that NA1/NA2 and SH are located in two closely linked loci and that the SH allele is linked to the NA1 allele in the Danish population. Transfusion 1999, 39, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, K.; Procter, J.; Stroncek, D. Variations in genes encoding neutrophil antigens NA1 and NA2. Transfusion 2000, 40, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, K.S.; Tong, Y.; Siebert, R.; Marget, M.; Humpe, A.; Neppert, J.; Flesch, B.K. Evidence for gene recombination in FCGR3 gene variants. Vox Sang. 2009, 97, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covas, D.T.; Kashima, S.; Guerreiro, J.F.; Dos Santos, S.E.B.; Zago, M.A. Variation in the FcγR3B gene among distinct Brazilian populations. Tissue Antigens 2005, 65, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzian, C.C.N.; Chiba, A.K.; Santos, V.C.; Silva, N.P.; Bordin, J.O. FCGR3B*03 allele inheritance pattern in Brazilian families and some new variants of gene FCGR3B. Transfusion 2012, 52, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bux, J.; Stein, E.L.; Santoso, S.; Mueller-Eckhardt, C. NA gene frequencies in the German population, determined by polymerase chain reaction with sequence-specific primers. Transfusion 1995, 35, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacHado, L.R.; Hardwick, R.J.; Bowdrey, J.; Bogle, H.; Knowles, T.J.; Sironi, M.; Hollox, E.J. Evolutionary history of copy-number-variable locus for the low-affinity Fcγ receptor: Mutation rate, autoimmune disease, and the legacy of helminth infection. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagelkerke, S.Q.; Tacke, C.E.; Breunis, W.B.; Geissler, J.; Sins, J.W.R.; Appelhof, B.; van den Berg, T.K.; de Boer, M.; Kuijpers, T.W. Nonallelic homologous recombination of the FCGR2/3 locus results in copy number variation and novel chimeric FCGR2 genes with aberrant functional expression. Genes Immun. 2015, 16, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Willcocks, L.C.; Lyons, P.A.; Clatworthy, M.R.; Robinson, J.I.; Yang, W.; Newland, S.A.; Plagnol, V.; McGovern, N.N.; Condliffe, A.M.; Chilvers, E.R.; et al. Copy number of FCGR3B, which is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus, correlates with protein expression and immune complex uptake. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbari, R.; Zuccherato, L.W.; Tischler, G.; Chihota, B.; Ozturk, H.; Saleem, S.; Tarazona-Santos, E.; Machado, L.R.; Hollox, E.J. Understanding the Genomic Structure of Copy-Number Variation of the Low-Affinity Fcγ Receptor Region Allows Confirmation of the Association of FCGR3B Deletion with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Hum. Mutat. 2017, 38, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Guan, W.; Viken, K.; Perlman, D.M.; Bhargava, M. FCGR3A and FCGR3B copy number variations are risk factors for sarcoidosis. Hum. Genet. 2016, 135, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Zhao, D.; Wu, L.; Xu, X.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, J. FCGR3B copy number loss rather than gain is a risk factor for systemic lupus erythematous and lupus nephritis: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 18, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breunis, W.B.; van Mirre, E.; Geissler, J.; Laddach, N.; Wolbink, G.; van der Schoot, E.; de Haas, M.; de Boer, M.; Roos, D.; Kuijpers, T.W. Copy number variation at the FCGR locus includes FCGR3A, FCGR2C and FCGR3B but not FCGR2A and FCGR2B. Hum. Mutat. 2009, 30, E640–E650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang-A-Sjoe, M.W.P.; Nagelkerke, S.Q.; Bultink, I.E.M.; Geissler, J.; Tanck, M.W.T.; Tacke, C.E.; Ellis, J.A.; Zenz, W.; Bijl, M.; Berden, J.H.; et al. Fc-gamma receptor polymorphisms differentially influence susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, K.R.; Bojsen, S.R.; Masmas, T.N.; Fjordside, A.-L.; Baech, J.; Haunstrup, T.M.; Steffensen, R. Association between human leukocyte antigens (HLAs) and human neutrophil antigens (HNAs) and autoimmune neutropenia of infancy in Danish patients. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 32, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, W.Y.; Abadeh, S.; Jefferis, R.; Savage, C.O.; Adu, D. Neutrophil FcgammaRIIIb allelic polymorphism in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-positive systemic vasculitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2000, 119, 574–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, J.E.; Edberg, J.C.; Brogle, N.L.; Kimberly, R.P. Allelic polymorphisms of human Fc gamma receptor IIA and Fc gamma receptor IIIB. Independent mechanisms for differences in human phagocyte function. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 89, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyogoku, C.; Dijstelbloem, H.M.; Tsuchiya, N.; Hatta, Y.; Kato, H.; Yamaguchi, A.; Fukazawa, T.; Jansen, M.D.; Hashimoto, H.; van de Winkel, J.G.J.; et al. Fcgamma receptor gene polymorphisms in Japanese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Contribution of FCGR2B to genetic susceptibility. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 1242–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrnbecher, T.; Foster, C.B.; Zhu, S.; Leitman, S.F.; Goldin, L.R.; Huppi, K.; Chanock, S.J. Variant genotypes of the low-affinity Fcgamma receptors in two control populations and a review of low-affinity Fcgamma receptor polymorphisms in control and disease populations. Blood 1999, 94, 4220–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kløve-Mogensen, K.; Terp, S.K.; Steffensen, R. Comparison of real-time quantitative PCR and two digital PCR platforms to detect copy number variation in FCGR3B. J. Immunol. Methods 2024, 526, 113628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagelkerke, S.Q.; Schmidt, D.E.; de Haas, M.; Kuijpers, T.W. Genetic Variation in Low-To-Medium-Affinity Fcγ Receptors: Functional Consequences, Disease Associations, and Opportunities for Personalized Medicine. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollox, E.J.; Detering, J.-C.; Dehnugara, T. An integrated approach for measuring copy number variation at the FCGR3 (CD16) locus. Hum. Mutat. 2009, 30, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Niederer, H.A.; Willcocks, L.C.; Rayner, T.F.; Yang, W.; Lau, Y.L.; Williams, T.N.; Scott, J.A.G.; Urban, B.C.; Peshu, N.; Dunstan, S.J.; et al. Copy number, linkage disequilibrium and disease association in the FCGR locus. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 3282–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassaunière, R.; Tiemessen, C.T. Variability at the FCGR locus: Characterization in Black South Africans and evidence for ethnic variation in and out of Africa. Genes Immun. 2016, 17, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccherato, L.W.; Schneider, S.; Tarazona-Santos, E.; Hardwick, R.J.; Berg, D.E.; Bogle, H.; Gouveia, M.H.; Machado, L.R.; Machado, M.; Rodrigues-Soares, F.; et al. Population genetics of immune-related multilocus copy number variation in Native Americans. J. R. Soc. Interface 2017, 14, 20170057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffensen, R.; Baech, J.; Nielsen, K.R. Allelic Discrimination by TaqMan-PCR for Genotyping of Human Neutrophil Antigens. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1310, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, N.; Han, Z.; He, J.; Zhu, F.; Lv, H. Genotyping of human neutrophil antigens by polymerase chain reaction sequence-based typing. Blood Transfus. 2014, 12 (Suppl. 1), s292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, T. Human Neutrophil Antigen Allele Assignment Using Next Generation Sequencing; The University of Manchester (United Kingdom): Manchester, UK, 2022; pp. 83–93. Available online: https://research.manchester.ac.uk/en/studentTheses/human-neutrophil-antigen-allele-assignment-using-next-generation- (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Sachs, U.J.; Radke, C.; Bein, G.; Grabowski, C.; Simtong, P.; Bux, J.; Bayat, B.; Reil, A. Primary structure of human neutrophil antigens 1a and 1b. Transfusion 2020, 60, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culliford, S.; Keen, L.; Poles, A.; Lucas, G.; Green, A. Genotyping using PCR-SBT identifies variants in the HNA alleles not detected by PCR-SSP. Tissue Antigens 2012, 79, 477–478. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, F.J.; Amode, M.R.; Aneja, A.; Austine-Orimoloye, O.; Azov, A.G.; Barnes, I.; Becker, A.; Bennett, R.; Berry, A.; Bhai, J.; et al. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D933–D941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| New Nomenclature | c.108 | c.114 | c.194 | c.233 | c.244 | c.316 | STOP CODON | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Old Nomenclature | c.141 | c.147 | c.227 | c.266 | c.277 | c.349 | c.473 | c.505 | c.559 | c.641 | c.733 |
| rs no. | rs200688856 | rs527909462 | rs448740 | rs5030738 | rs147574249 | rs2290834 | rs71632959 | rs71632958 | rs200215055 | rs758550229 | rs374752953 |
| Pos (Hg38) | 161,629,989 | 161,629,983 | 161,629,903 | 161,629,864 | 161,629,853 | 161,629,781 | 161,626,282 | 161,626,250 | 161,626,196 | 161,624,609 | 161,624,517 |
| Exons in FCGR3B | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||||||||
| Amino acid change | Arg36Ser | 38Leu | Asn65Ser | Ala78Asp | Asp82Asn | Val106Ile | Val176Phe | ||||
| FCGR3B*01 | G | C | A | C | G | G | A | C | G | C | T |
| FCGR3B*02 | C | T | G | C | A | A | A | C | G | C | T |
| FCGR3B*03 | C | T | G | A | A | A | A | C | G | C | T |
| FCGR3B*04 (FCGR3B*01 var c.349G) | G | C | A | C | G | A | A | C | G | C | T |
| FCGR3B*05 (FCGR3B*02 var c.244G) | C | T | G | C | G | A | A | C | G | C | T |
| FCGR3B*01 var c.194G | G | C | G | C | G | G | A | C | G | C | T |
| FCGR3B*02 var c.194G | C | T | A | C | A | A | A | C | G | C | T |
| FCGR3A | G | C | G | C | G | A | G | T | T | T | C |
| Method | Type | SNPs Included | CN Included | FCGR3B Specific | Detect Hemizygosity 1 | Type >2 Alleles | Detect Rare Variants | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c.108 | c.114 | c.194 | c.233 | c.244 | c.316 | |||||||
| In-house | TaqMan PCR | x | x | x | x | x | No | No | Yes/no 2 | No | Yes/no 3 | |
| ERY Q | PCR-SSP/Gel | x | x | No | Yes | No | No | No | ||||
| MLPA | Genescan | x | x | x | x | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes/no 3 | ||
| Sanger sequencing | PCR-SBT | Short fragment sequencing of exon 3 (526 bp) | No | No | No | No | No | |||||
| Nanopore sequencing | Target specific amplification | Long-read sequencing (8262 bp) | Yes 4 | Yes | No 5 | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Commercial PCR-SSP 1 | qPCR | In-House TaqMan PCR | MLPA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Father | c.194A(+) c.233C(+) c.233A(-) | CN = 2 | c.114C/T c.194A/G c.233C/C c.244G/A c.316G/A | CN = 2 c.114C/T c.194A/G c.233C/C c.316G/A |
 | ||||
| FCGR3B*01/*02 | FCGR3B*01/*02 | FCGR3B*01/*02 | ||
| Mother | c.194A(+) c.233C(-) c.233A(-) | CN = 1 | c.114C/C c.194A/G c.233C/C c.244G/G c.316G/A | CN = 1 c.114C c.194A c.233C c.316G |
 | ||||
| FCGR3B*01 | FCGR3B*01/*Null 2 | FCGR3B*01/*Null | ||
| Child 1 | c.194A(+) c.233C(-) c.233A(-) | CN = 1 | c.114C/C c.194A/G c.233C/C c.244G/G c.316G/A | CN = 1 c.114C c.194A c.233C c.316G |
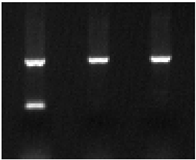 | ||||
| FCGR3B*01 | FCGR3B*01/*Null 2 | FCGR3B*01/*Null | ||
| Child 2 | c.194A(-) c.233C(+) c.233A(-) | CN = 1 | c.114T/C c.194G/G c.233C/C c.244A/G c.316A/A | CN = 1 c.114T c.194G c.233C c.316A |
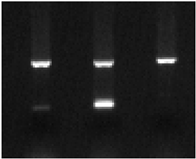 | ||||
| FCGR3B*02 | FCGR3B*02/*Null 2 | FCGR3B*02/*Null |
| Test | Genotype | c.114 | c.194 | c.233 | c.244 | c.316 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | MLPA | FCGR3B*01/*01/*02 | CCT | AAG | CCC | GGA | GGA |
| PCR-SBT | FCGR3B*02/*Null | CT | GG | CC | GA | AA | |
| Sample 2 | MLPA | FCGR3B*01/*02/*02 | CTT | AGG | CCC | GAA | GAA |
| PCR-SBT | FCGR3B*02/*Null | CT | GG | CC | GA | AA | |
| Sample 3 | MLPA/Nanopore | FCGR3B*02/*03/*04 | TTC | GGA | CAC | AAG | AAA |
| PCR-SBT | FCGR3B*04/*Null | CT | GG | CA | AG | AA |
| Sample ID | CN FCGR3B 1 | c.108 | c.114 | c.194 | c.233 | c.244 | c.316 | FCGR3B Alleles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAL_016 | 0 | A: 0% C: 0% G: 0% T: 0% | A: 0% C: 0% G: 0% T: 0% | A: 0% C: 0% G: 0% T: 0% | A: 0% C: 1% G: 0% T: 0% | A: 0% C: 0% G: 0% T: 0% | A: 0% C: 0% G: 0% T: 0% | *Null/*Null |
| BRI_006 | 0 | A: 0% C: 2% G: 0% T: 0% | A: 2% C: 0% G: 2% T: 0% | A: 1% C: 3% G: 0% T: 0% | A: 2% C: 0% G: 2% T: 0% | A: 2% C: 0% G: 1% T: 0% | A: 4% C: 0% G: 0% T: 0% | *Null/*Null |
| BRI_008 | 1 | G: 85% | C: 71% | A: 86% | C: 87% | G: 82% | G: 83% | *01/*Null |
| AAL_001 | 2 | G: 43% C: 51% | T: 55% C: 40% | G: 47% A: 49% | C: 94% | G: 43% A: 53% | G: 44% A: 51% | *01/*02 |
| AAL_011 | 2 | G: 42% C: 52% | T: 58% C: 37% | G: 48% A: 48% | C: 95% | G: 41% A: 54% | G: 43% A: 53% | *01/*02 |
| BRI_001 | 2 | G: 42% C: 51% | T: 57% C: 37% | G: 48% A: 47% | C: 94% | G: 42% A: 53% | G: 43% A: 52% | *01/*02 |
| BRI_004 | 2 | G: 41% C: 50% | T: 56% C: 36% | G: 47% A: 47% | C: 92% | G: 41% A: 52% | G: 42% A: 51% | *01/*02 |
| BRI_005 | 2 | G: 41% C: 50% | T: 56% C: 36% | G: 47% A: 47% | C: 92% | G: 41% A: 52% | G: 42% A: 51% | *01/*02 |
| BRI_003 | 2 | G: 43% C: 50% | T: 56% C: 37% | G: 46% A: 49% | C: 47% A: 47% | G: 42% A: 52% | G: 44% A: 50% | *01/*03 |
| AAL_008 | 2 | C: 92% | T: 93% | G: 91% | C: 49% A: 48% | A: 93% | A: 96% | *02/*03 |
| AAL_005 | 2 | C: 95% | T: 96% | G: 47% A: 52% | C: 97% | A: 98% | A: 97% | *02/*02 var c.194G |
| AAL_004 | 2 | G: 43% C: 50% | T: 56% C: 38% | G: 46% A: 49% | C: 93% | G: 88% | G: 45% A: 50% | *01/*05 2 |
| AAL_009 | 2 | C: 95% | T: 96% | G: 95% | C: 97% | G: 46% A: 52% | A: 97% | *02/*05 2 |
| AAL_010 | 2 | C: 95% | T: 95% | G: 95% | C: 97% | G: 45% A: 53% | A: 97% | *02/*05 2 |
| AAL_007 | 2 | G: 41% C: 51% | T: 57% C: 37% | G: 47% A: 47% | C: 93% | G: 84% | A: 93% | *04/*05 2 |
| AAL_014 | 3 | G: 56% C: 36% | T: 44% C: 49% | G: 33% A: 61% | C: 60% A: 33% | G: 55% A: 39% | G: 28% A: 65% | *01/*03/*04 |
| AAL_002 | 3 | G: 30% C: 65% | T: 68% C: 27% | G: 62% A: 35% | C: 63% A: 32% | G: 29% A: 67% | A: 96% | *02/*03/*04 |
| AAL_006 | 3 | G: 28% C: 65% | T: 68% C: 25% | G: 61% A: 34% | C: 63% A: 31% | G: 28% A: 66% | A: 93% | *02/*03/*04 |
| AAL_012 | 3 | G: 29% C: 62% | T: 65% C: 26% | G: 59% A: 34% | C: 63% A: 30% | G: 29% A: 64% | A: 94% | *02/*03/*04 |
| BRI_002 | 3 | G: 29% C: 64% | T: 67% C: 26% | G: 60% A: 35% | C: 64% A: 30% | G: 29% A: 66% | A: 92% | *02/*03/*04 |
| BRI_009 | 3 | G: 30% C: 64% | T: 67% C: 27% | G: 60% A: 36% | C: 64% A: 31% | G: 30% A: 66% | A: 94% | *02/*03/*04 |
| BRI_010 | 3 | G: 34% C: 61% | T: 66% C: 30% | G: 57% A: 40% | C: 73% A: 24% | G: 34% A: 63% | A: 83% | *02/*03/*04 |
| AAL_015 | 4 | G: 44% C: 50% | T: 56% C: 39% | G: 46% A: 50% | C: 71% A: 24% | G: 43% A: 52% | G: 24% A: 72% | *01/*02/*03/*04 |
| Sample ID | CN FCGR3B 1 | c.108 | c.114 | c.194 | c.197 2 | c.233 | c.244 | c.316 | FCGR3B alleles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAL_003 | 3 | G: 61% C: 33% | T: 39% C: 55% | G: 60% A: 36% | A: 95% | C: 65% A: 30% | G: 30% A: 65% | A: 95% | *03/*04/Novel (GCGCAA 3) |
| AAL_013 | 2 | G: 45% C: 51% | T: 57% C: 40% | G: 95% | A: 95% | C: 97% | A: 97% | A: 97% | *02/Novel (GCGCAA 3) |
| BRI_007 | 1 | G: 83% | C: 70% | G: 83% | C: 79% | C: 85% | G: 80% | A: 85% | *Null/Novel (GCGCGA 3 + novel SNP c.197C) |
| Nucleotide | c.108 | c.114 | c.194 | c.197 1 | c.233 | c.244 | c.316 | STOP CODON | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pos on chr.1 (Hg38) | 161,629,989 | 161,629,983 | 161,629,903 | 161,629,900 | 161,629,864 | 161,629,853 | 161,629,781 | 161,626,282 | 161,626,250 | 161,626,196 | 161,624,609 | 161,624,517 |
| rs no. in FCGR3B | rs200688856 | rs527909462 | rs448740 | rs761007181 | rs5030738 | rs147574249 | rs2290834 | rs71632959 | rs71632958 | rs200215055 | rs758550229 | rs374752953 |
| Exons in FCGR3B | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||||||||
| Amino acid change | Arg36Ser | 38Leu | Asn65Ser | Leu66Arg | Ala78Asp | Asp82Asn | Val106Ile | |||||
| FCGR3B*01 | G | C | A | A | C | G | G | A | C | G | C | T |
| FCGR3B*02 | C | T | G | A | C | A | A | A | C | G | C | T |
| FCGR3B*03 | C | T | G | A | A | A | A | A | C | G | C | T |
| FCGR3B*04 | G | C | A | C | G | A | G | A | C | G | C | T |
| FCGR3B*05 | C | T | G | A | C | G | A | A | C | G | C | T |
| FCGR3B*01 var c. 194G | G | C | G | A | C | G | G | A | C | G | C | T |
| FCGR3B*02 var c. 194A | C | T | A | A | C | A | A | A | C | G | C | T |
| Novel 1 (AAL_003, AAL_013) | G | C | G | A | C | A | A | A | C | G | C | T |
| Novel 2 (BRI_007) | G | C | G | C | C | G | A | A | C | G | C | T |
| FCGR3A | G | C | G | A | C | G | A | G | T | T | T | C |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kløve-Mogensen, K.; Browne, T.; Haunstrup, T.M.; Steffensen, R. Pitfalls When Determining HNA-1 Genotypes and Finding Novel Alleles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25169127
Kløve-Mogensen K, Browne T, Haunstrup TM, Steffensen R. Pitfalls When Determining HNA-1 Genotypes and Finding Novel Alleles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(16):9127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25169127
Chicago/Turabian StyleKløve-Mogensen, Kirstine, Tom Browne, Thure Mors Haunstrup, and Rudi Steffensen. 2024. "Pitfalls When Determining HNA-1 Genotypes and Finding Novel Alleles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 16: 9127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25169127
APA StyleKløve-Mogensen, K., Browne, T., Haunstrup, T. M., & Steffensen, R. (2024). Pitfalls When Determining HNA-1 Genotypes and Finding Novel Alleles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(16), 9127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25169127





