Therapeutic Potential of Momordicine I from Momordica charantia: Cardiovascular Benefits and Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background on Momordica charantia (Bitter Melon)
1.2. Introduction to Momordicine I
2. Chemical Properties and Mechanism of Action
2.1. Chemical Structure and Properties
2.2. Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics
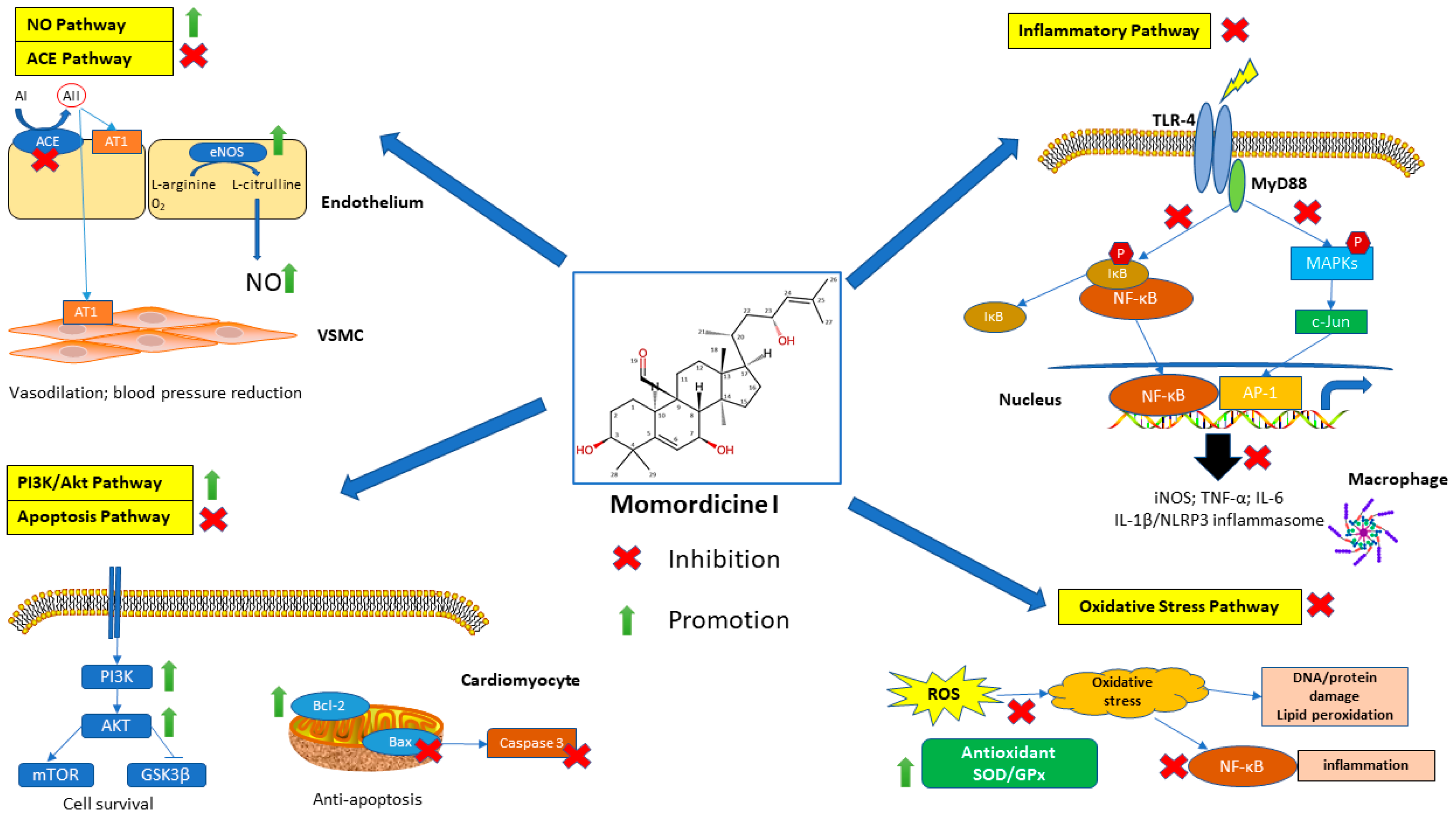
2.3. Mechanisms of Action
3. Cardiovascular Effects of Momordicine I
3.1. Preclinical Studies
3.2. Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Applications
4. Safety and Toxicology
4.1. Toxicological Profile
4.2. Side Effects
4.3. Contraindications and Drug Interactions
5. Conclusions
5.1. Summary of Key Findings
5.2. Future Research and Clinical Directions
5.3. Clinical Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADME | absorption: distribution: metabolism, and excretion |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| CAD | coronary artery disease |
| c-Met | c-mesenchymal–epithelial transition factor |
| DGK-ζ | diacylglycerol kinase-ζ |
| ERK | extracellular signal-related kinase |
| GLP-1 | glucagon-like peptide 1 |
| GLUT4 | stimulation of glucose transporter type 4 |
| GPx | glutathione peroxidase |
| IKK | inhibitor kappa B kinase |
| IL-1β | interleukin-1β |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| iNOS | inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MAPKs | mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-light-chain enhancer of activated B cells |
| Nrf2/HO-1 | nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2/heme oxygenase-1 |
| PLA2G6 | phospholipase A2 group VI |
| PPARγ | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
| SCFAs | short-chain fatty acids |
| Smad2/3 | suppressor of mothers against decapentaplegic 2/3 |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| STAT3 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| TCM | Traditional Chinese Medicine |
| TGF-β1 | transforming growth factor-β1 |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-α |
References
- Zheng, J.; Shang, M.; Dai, G.; Dong, J.; Wang, Y.; Duan, B. Bioactive polysaccharides from Momordica charantia as functional ingredients: A review of their extraction, bioactivities, structural-activity relationships, and application prospects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Qin, D.; Yang, F.; Luo, F.; Lin, Q. Extraction, structures, biological effects and potential mechanisms of Momordica charantia polysaccharides: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 268 Pt 1, 131498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guo, Y.; Sun, J.; Lei, Y.; Guo, M.; Wang, L. Extraction methods, multiple biological activities, and related mechanisms of Momordica charantia polysaccharide: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263 Pt 2, 130473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, A.; Korma, S.A.; Kabir, K.; Kauser, S.; Arif, M.R.; Fatima, H.; Ali, S.; Ali, M.Q.; Yaqub, S.; Shehzad, A.; et al. In vitro and In vivo Determination of Biological Activities of Bitter Gourd (Momordica charantia L.) Peel, Flesh and Seeds. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2024, 79, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Liu, H.; Zhu, C.Y.; Zhang, M.X.; Li, Y.L.; Ling, B.; Wang, G.C. Cucurbitane-type triterpenoids from the leaves of Momordica charantia. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 16, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ChemSpider. Available online: https://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.95601787.html (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Kashyap, H.; Gupta, S.; Bist, R. Impact of Active Antihyperglycemic Components as Herbal Therapy for Preventive Health Care Management of Diabetes. Curr. Mol. Med. 2019, 19, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.Y.; Shih, N.L.; Hao, W.R.; Chen, C.C.; Liu, J.C.; Sung, L.C. Inhibitory Effects of Momordicine I on High-Glucose-Induced Cell Proliferation and Collagen Synthesis in Rat Cardiac Fibroblasts. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 3939714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, M.C.; Lee, Y.J.; Wang, Y.T.; Cheng, S.Y.; Cheng, H.L. Cytotoxic and Anti-Inflammatory Triterpenoids in the Vines and Leaves of Momordica charantia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, S.; Bhartiya, P.; Steele, R.; Brennan, M.; DiPaolo, R.J.; Ray, R.B. Momordicine-I Suppresses Head and Neck Cancer Growth by Reprogrammimg Immunosuppressive Effect of the Tumor-Infiltrating Macrophages and B Lymphocytes. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2024, 23, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Whittaker, P.; Keller, A.C.; Mazzola, E.P.; Pawar, R.S.; White, K.D.; Callahan, J.H.; Kennelly, E.J.; Krynitsky, A.J.; Rader, J.I. Cucurbitane-type triterpenoids from Momordica charantia. Planta Medica 2010, 76, 1758–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, G.-C.; Zhang, M.-X.; Ling, B. The cytotoxicology of momordicins I and II on Spodoptera litura cultured cell line SL-1. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 122, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Pandey, P.; Singh, P.K.; Tripathi, M.; Singh, R.P.; Shukla, S.; Pathak, N.; Singh, R.L. A comprehensive review on phytochemistry, nutritional and pharmacological properties of Momordica charantia. IP Int. J. Compr. Adv. Pharmacol. 2023, 8, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, S.; Steele, R.; Isbell, T.S.; Venkata, K.N.; Rateb, M.E.; Ray, R.B. Momordicine-I, a Bitter Melon Bioactive Metabolite, Displays Anti-Tumor Activity in Head and Neck Cancer Involving c-Met and Downstream Signaling. Cancers 2021, 13, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-B.; Yue, G.; To, M.-H.; Keller, A.; Lau, C.; Kennelly, E. Transport in Caco-2 Cell Monolayers of Antidiabetic Cucurbitane Triterpenoids from Momordica charantia Fruits. Planta Medica 2014, 80, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.T.; Liu, J.Q.; Deng, Y.Y.; Li, H.Z.; Chen, J.C.; Zhang, Z.R.; Zhou, L.; Qiu, M.H. Cucurbitane-type triterpenoids from the stems and leaves of Momordica charantia. Fitoterapia 2014, 95, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.; Chiu, M.H.; Nie, R.L.; Cordell, G.A.; Qiu, S.X. Cucurbitacins and cucurbitane glycosides: Structures and biological activities. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famuyiwa, S.O.; Ahmad, S.; Olufolabo, K.O.; Olanudun, E.A.; Bano, N.; Oguntimehin, S.A.; Adesida, S.A.; Oyelekan, E.I.; Raza, K.; Faloye, K.O. Investigating the multitargeted anti-diabetic potential of cucurbitane-type triterpenoid from Momordica charantia: An LC-MS, docking-based MM\GBSA and MD simulation study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehseen, I.; Haq, T.U.; Ilahi, I.; Khan, A.A.; Attaullah, M.; Zamani, G.Y.; Zaman, S.; Ismail, I. Antidiabetic and hepato-renal protective effects of medicinal plants in STZ induced diabetic rats. Braz. J. Biol. 2022, 84, e260189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Chen, M.; Ahmad, H.; Zheng, X.; Ouyang, Y.; Yang, P.; Yang, Z.; Gao, D.; Tian, Z. Momordica charantia Extract Confers Protection Against Hypertension in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rats. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2022, 77, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udrea, A.M.; Gradisteanu Pircalabioru, G.; Boboc, A.A.; Mares, C.; Dinache, A.; Mernea, M.; Avram, S. Advanced Bioinformatics Tools in the Pharmacokinetic Profiles of Natural and Synthetic Compounds with Anti-Diabetic Activity. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogidigo, J.O.; Iwuchukwu, E.A.; Ibeji, C.U.; Okpalefe, O.; Soliman, M.E.S. Natural phyto, compounds as possible noncovalent inhibitors against SARS-CoV2 protease: Computational approach. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 2284–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.J.; Ye, J.M.; Turner, N.; Hohnen-Behrens, C.; Ke, C.Q.; Tang, C.P.; Chen, T.; Weiss, H.C.; Gesing, E.R.; Rowland, A.; et al. Antidiabetic activities of triterpenoids isolated from bitter melon associated with activation of the AMPK pathway. Chem. Biol. 2008, 15, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Tan, Y.; Guo, P.; Wu, C. The gut microbiota confers the lipid-lowering effect of bitter melon (Momordica charantia L.) In high-fat diet (HFD)-Induced hyperlipidemic mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tossetta, G.; Fantone, S.; Marzioni, D.; Mazzucchelli, R. Role of Natural and Synthetic Compounds in Modulating NRF2/KEAP1 Signaling Pathway in Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Plano, L.M.; Calabrese, G.; Rizzo, M.G.; Oddo, S.; Caccamo, A. The Role of the Transcription Factor Nrf2 in Alzheimer’s Disease: Therapeutic Opportunities. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, Y.; Chou, C.H.; Huang, L.C.; Tsai, C.K. Momordicine I suppresses glioma growth by promoting apoptosis and impairing mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. EXCLI J. 2023, 22, 482–498. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Qiu, Y.; Xie, M.; Ouyang, C.; Ding, X.; Zhang, H.; Dong, W.; Xiong, Y.; Tang, X. Momordicine I alleviates isoproterenol-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through suppression of PLA2G6 and DGK-zeta. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2023, 27, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incalza, M.A.; D’Oria, R.; Natalicchio, A.; Perrini, S.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F. Oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species in endothelial dysfunction associated with cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2018, 100, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ussher, J.R.; Drucker, D.J. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists: Cardiovascular benefits and mechanisms of action. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2023, 20, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.I.; Cheng, S.Y.; Nurlatifah, A.O.; Sung, W.W.; Tu, J.H.; Lee, L.L.; Cheng, H.L. Bitter Melon Extract Yields Multiple Effects on Intestinal Epithelial Cells and Likely Contributes to Anti-diabetic Functions. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.A.; Arumugam, M.; Ponnusamy, N.; Sivaraman, D.; Sertsemariam, W.; Thiruvengadam, M.; Pandiaraj, S.; Rahaman, M.; Devi Rajeswari, V. Anti-diabetic drug discovery using the bioactive compounds of Momordica charantia by molecular docking and molecular dynamics analysis. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Qin, M.; Zhang, B.; Lin, L.; Ma, Q.; Liu, C.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Lai, W.; et al. Comprehensive Metabolomics Identified the Prominent Role of Glycerophospholipid Metabolism in Coronary Artery Disease Progression. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 632950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lii, C.K.; Chen, H.W.; Yun, W.T.; Liu, K.L. Suppressive effects of wild bitter gourd (Momordica charantia Linn. var. abbreviata ser.) fruit extracts on inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 122, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poovitha, S.; Parani, M. In vitro and in vivo α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibiting activities of the protein extracts from two varieties of bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.). BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16 (Suppl. S1), 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, B.S.; Yadav, R.; Yadav, R.B.; Garg, M. Antioxidant activity of various extracts of selected gourd vegetables. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, N.Q.; Lee, D.H.; Oh, J.; Kim, C.S.; Heo, K.S.; Myung, C.S.; Na, M. Inhibition of Proliferation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells by Cucurbitanes from Momordica charantia. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2018–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.S.; Yang, E.; Kim, M.J.; Jeong, D.; Yoon, D.H.; Sung, G.H.; Lee, S.; Yoo, B.C.; Yeo, S.G.; Cho, J.Y. Momordica charantia Inhibits Inflammatory Responses in Murine Macrophages via Suppression of TAK1. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2018, 46, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, A.K.; Kumar, G.S.; Sambaiah, K.; Salimath, P.V. Effect of bitter gourd (Momordica charantia) on glycaemic status in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2005, 60, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klomann, S.D.; Mueller, A.S.; Pallauf, J.; Krawinkel, M.B. Antidiabetic effects of bitter gourd extracts in insulin-resistant db/db mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abas, R.; Othman, F.; Thent, Z.C. Effect of Momordica charantia fruit extract on vascular complication in type 1 diabetic rats. Excli. J. 2015, 14, 179–189. [Google Scholar]
- Yousaf, S.; Hussain, A.; Rehman, S.; Aslam, M.S.; Abbas, Z. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of Lactobacillus fermentum, fruit extracts of Syzygium cumini and Momordica charantia on diabetes induced mice. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 29, 1535–1540. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raish, M. Momordica charantia polysaccharides ameliorate oxidative stress, hyperlipidemia, inflammation, and apoptosis during myocardial infarction by inhibiting the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahwish, M.; Saeed, F.; Nisa, M.U.; Nadeem, M.T. Minerals and phytochemical analysis of bitter melon fruits and its components in some indigenous and exotic cultivars. Biosci. J. 2018, 34, 1622–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.L.; Lin, Y.T.; Kung, H.N.; Hou, Y.C.; Liu, J.J.; Pan, M.H.; Chen, H.L.; Yu, C.H.; Tsai, P.J. A triterpenoid-enriched extract of bitter melon leaves alleviates hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting inflammatory responses in carbon tetrachloride-treated mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 7805–7815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuangchan, A.; Sonthisombat, P.; Seubnukarn, T.; Chanouan, R.; Chotchaisuwat, P.; Sirigulsatien, V.; Ingkaninan, K.; Plianbangchang, P.; Haines, S.T. Hypoglycemic effect of bitter melon compared with metformin in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 134, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.H.; Chen, E.C.; Tsay, H.S.; Huang, C.J. Wild bitter gourd improves metabolic syndrome: A preliminary dietary supplementation trial. Nutr. J. 2012, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trakoon-osot, W.; Sotanaphun, U.; Phanachet, P.; Porasuphatana, S.; Udomsubpayakul, U.; Komindr, S. Pilot study: Hypoglycemic and antiglycation activities of bitter melon (Momordica charantia L.) in type 2 diabetic patients. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 6, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaki, C.S.; Premavalli, K.S. Evaluation of Supplementation of Bittergourd Fermented Beverage to Diabetic Subjects. J. Pharm. Nutr. Sci. 2014, 4, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A.; El-Gengaihi, S.E.; Zikry, E.N. Preliminary clinical trials of karela, Momordica charantia, on non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients. Egypt. Pharm. J. 2015, 14, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Krawinkel, M.B.; Ludwig, C.; Swai, M.E.; Yang, R.Y.; Chun, K.P.; Habicht, S.D. Bitter gourd reduces elevated fasting plasma glucose levels in an intervention study among prediabetics in Tanzania. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 216, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.T.; Li, S.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhao, Y.S.; Daglia, M.; Xiao, X.; Bai, J. Network Pharmacology and Experimental Study of Momordicine I and Momordicine II from Bitter Melon Saponins in Inhibiting Fat Accumulation. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2024, 37, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shih, C.C.; Lin, C.H.; Lin, W.L. Effects of Momordica charantia on insulin resistance and visceral obesity in mice on high-fat diet. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2008, 81, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez-Navarrete, M.; Perez-Rubio, K.G.; Escobedo-Gutierrez, M.J. Role of Fenugreek, Cinnamon, Curcuma longa, Berberine and Momordica charantia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment: A Review. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, F.; Asif, H.M.; Shaheen, G.; Ghauri, A.O.; Rajpoot, S.R.; Tasleem, M.W.; Shamim, T.; Hadi, F.; Noor, R.; Ali, T.; et al. A comprehensive review on medicinal plants possessing antioxidant potential. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2023, 50, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolotti, M.; Mercatelli, D.; Polito, L. Momordica charantia, a Nutraceutical Approach for Inflammatory Related Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minihane, A.M.; Vinoy, S.; Russell, W.R.; Baka, A.; Roche, H.M.; Tuohy, K.M.; Teeling, J.L.; Blaak, E.E.; Fenech, M.; Vauzour, D.; et al. Low-grade inflammation, diet composition and health: Current research evidence and its translation. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedjou, C.G.; Grigsby, J.; Mbemi, A.; Nelson, D.; Mildort, B.; Latinwo, L.; Tchounwou, P.B. The Management of Diabetes Mellitus Using Medicinal Plants and Vitamins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.L.; Kuo, C.Y.; Liao, Y.W.; Lin, C.C. EMCD, a hypoglycemic triterpene isolated from Momordica charantia wild variant, attenuates TNF-α-induced inflammation in FL83B cells in an AMP-activated protein kinase-independent manner. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 689, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobori, M.; Nakayama, H.; Fukushima, K.; Ohnishi-Kameyama, M.; Ono, H.; Fukushima, T.; Akimoto, Y.; Masumoto, S.; Yukizaki, C.; Hoshi, Y.; et al. Bitter gourd suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 4004–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayathry, K.S.; John, J.A. A comprehensive review on bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.) as a gold mine of functional bioactive components for therapeutic foods. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2022, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, R.; Roy, S. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors from plants: A review of their diversity, modes of action, prospects, and concerns in the management of diabetes-centric complications. J. Integr. Med. 2021, 19, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palm, C.L.; Nijholt, K.T.; Bakker, B.M.; Westenbrink, B.D. Short-Chain Fatty Acids in the Metabolism of Heart Failure—Rethinking the Fat Stigma. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 915102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.C.; Chen, C.J.; Lai, Y.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Chiou, W.C.; Lu, H.F.; Chen, Y.F.; Chen, Y.H.; Huang, C. Momordica cochinchinensis Aril Ameliorates Diet-Induced Metabolic Dysfunction and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver by Modulating Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Huang, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, J.; Kim, K.H. Momordica charantia Bioactive Components: Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Benefits Through Gut Health Modulation. J. Med. Food 2024, 27, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Guan, M.; Li, C.; Xu, L.; Zheng, Z.; Li, J.; Xue, Y. Bitter melon (Momordica charantia) attenuates atherosclerosis in apo-E knock-out mice possibly through reducing triglyceride and anti-inflammation. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, J.L.; Shivanagoudra, S.R.; Perera, W.H.; Kim, D.M.; Wu, C.S.; Sun, Y.; Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Patil, B.S. Bitter melon extracts and cucurbitane-type triterpenoid glycosides antagonize lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation via suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 86, 104720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.W.; Chou, C.L.; Lee, K.T.; Shih, C.C.; Huang, T.H.; Sung, L.C. Nattokinase attenuates endothelial inflammation through the activation of SRF and THBS1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 268 Pt 2, 131779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, C. The critical role of signal transducers and activators of transcription-3 in the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Holist. Integr. Pharm. 2023, 4, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, K.; Wang, H.; Kaur, J.; Nalbant, G.; Almaqhawi, A.; Kundakci, B.; Panniyammakal, J.; Heinrich, M.; Lewis, S.A.; Greenfield, S.M.; et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Ayurvedic Medicines in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Management: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 821810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicek, S.S. Momordica charantia L.-Diabetes-Related Bioactivities, Quality Control, and Safety Considerations. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 904643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.C.; Xia, Z.S.; Huang, Y.F.; Peng, Y.; Cao, B.B.; Li, C.Q.; Liang, Y.F.; Zhao, F.H.; Zhang, M.Z.; Chen, Z.M.; et al. Cardiotoxicity induced by Cochinchina momordica seed extract in zebrafish. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 1222–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Jung, J.; Jung, J.H.; Yoon, N.; Kang, S.S.; Roh, G.S.; Hahm, J.R. Hypoglycemic efficacy and safety of Momordica charantia (bitter melon) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 52, 102524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, N.; Akram, M.; Yaniv-Bachrach, Z.; Daniyal, M. Is it safe to consume traditional medicinal plants during pregnancy? Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 1908–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adarmanabadi, S.; Abadi, O.J.K.; Amiri, A.; Tamannaeifar, R.; Balanian, S.; Rasekhjam, M.; Samiazar, M.S.; Hasanpour, S.; Peiravi, S.; Alijanzadeh, D.; et al. Pharmacotherapeutic Potential of Bitter Gourd (Momordica charantia) in Age-related Neurological Diseases. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2024, 23, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, W.Y.; Jadhav, S.; Hsu, P.K.; Kuan, C.M. Evaluation of acute and sub-chronic toxicity of bitter melon seed extract in Wistar rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2022, 9, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogaroglu, Z.G.; Uysal, Y.; Caylali, Z.; Karakoc, G. Antibacterial and phytotoxicological properties assessment of Momordica charantia extract-based ZnO nanoparticles. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 2851–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Moqbel, M.S.; Al-Hizab, F.A. Effect of Momordica charantia on Insulin Immune-Reactive Pancreatic Beta Cells and Blood Glucose Levels in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2022, 68, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsal, O.; Sutcuoglu, O.; Yazici, O. Dangerous interaction of bitter melon (Momordica charantia) with pazopanib: A case of acute pancreatitis. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2022, 28, 486–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelusi, T.I.; Abdul-Hammed, M.; Idris, M.O.; Kehinde, O.Q.; Boyenle, I.D.; Divine, U.C.; Adedotun, I.O.; Folorunsho, A.A.; Kolawole, O.E. Exploring the inhibitory potentials of Momordica charantia bioactive compounds against Keap1-Kelch protein using computational approaches. Silico Pharmacol. 2021, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.W.; Yung, M.M.; Chan, Y.S.; Xuan, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, D.; Zhan, J.B.; Chan, K.K.; Ng, T.B.; Ngan, H.Y. MAP30 protein from Momordica charantia is therapeutic and has synergic activity with cisplatin against ovarian cancer in vivo by altering metabolism and inducing ferroptosis. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 161, 105157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.J.; Chen, S.L.; Chang, Y.T.; Chyuan, J.H.; Hsieh-Li, H.M. Administration of Momordica charantia Enhances the Neuroprotection and Reduces the Side Effects of LiCl in the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuok, C.F.; Hoi, S.O.; Hoi, C.F.; Chan, C.H.; Fong, I.H.; Ngok, C.K.; Meng, L.R.; Fong, P. Synergistic antibacterial effects of herbal extracts and antibiotics on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A computational and experimental study. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

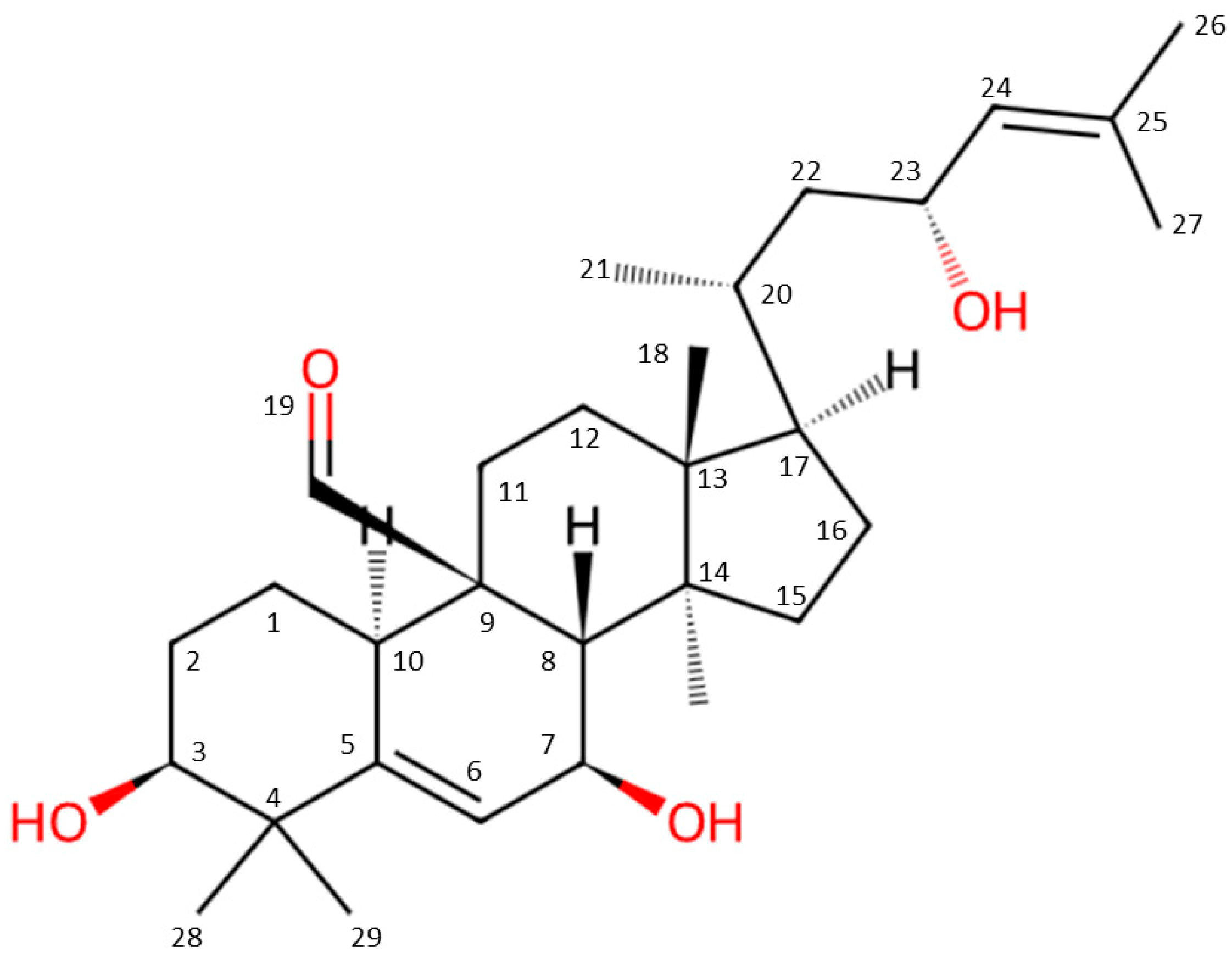

| Title of the Study | Aim/Methods | Summation of Findings | Compounds or Materials Tested | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In vitro studies | ||||
| Suppressive effects of wild bitter gourd (Momordica charantia Linn. var. abbreviate ser.) fruit extracts on inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 macrophages | To examine the anti-inflammatory effect of M. charantia on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. | The ethanol extract of M. charantia reduced LPS-induced inflammatory responses by modulating NF-κB activation. | M. charantia extract | [34] |
| Transport in Caco-2 Cell Monolayers of Antidiabetic Cucurbitane Triterpenoids from Momordica charantia Fruits | To investigate the gastrointestinal transport of a triterpenoid-enriched n-butanol extract of M. charantia by using a Caco-2 monolayer system | The findings demonstrated the transport of cucurbitane triterpenoids in human intestinal epithelial cell monolayers. | cucurbitane triterpenoids | [15] |
| In vitro and in vivo α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibiting activities of the protein extracts from two varieties of bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.) | To examine the inhibitory effect of protein extracts from two varieties of bitter gourd | Protein extracts from two varieties of bitter gourd inhibited α-amylase and α-glucosidase In vitro | M. charantia extract | [35] |
| Antioxidant activity of various extracts of selected gourd vegetables | To evaluate the antioxidative activity of methanolic, ethanolic, and butanolic extracts of selected gourd vegetables. | Extracts of M. charantia revealed significantly higher (p < 0.05) antioxidative activity than did the extracts of other remaining vegetables. | M. charantia extract | [36] |
| Inhibition of Proliferation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells by Cucurbitanes from Momordica charantia | To determine the effects of cucurbitane-type triterpenoids from the fruits of M. charantia on vascular smooth muscle cells | The triterpenoids inhibited the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. | cucurbitane triterpenoids | [37] |
| Inhibitory Effects of Momordicine I on High-Glucose-Induced Cell Proliferation and Collagen Synthesis in Rat Cardiac Fibroblasts | To evaluate the effects of momordicine I (0.3 and 1 μM) pretreatment on rat cardiac fibroblasts cultured in a high-glucose (25 mM) medium | The antifibrotic effect of momordicine I was mediated, at least partially, by the inhibition of the TGF-β1/Smad pathway, reducing fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis through Nrf2 activation. | Momordicine I | [8] |
| Momordica charantia Inhibits Inflammatory Responses in Murine Macrophages via Suppression of TAK1 | To investigate the anti-inflammatory effect of M. charantia on LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. | The methanol extract of M. charantia exerted an anti-inflammatory activity by reducing the action of transforming growth factor β-activated kinase 1, which also affected the activation of NF-κB and AP-1. | M. charantia extract | [38] |
| Momordicine-I, a Bitter Melon Bioactive Metabolite, Displays Anti-Tumor Activity in Head and Neck Cancer Involving c-Met and Downstream Signaling. | To identify momordicine I and evaluate its role in a head and neck cancer (HNC) preclinical mouse model. | Momordicine I inhibited HNC cell growth and c-Met/STAT3 signaling. However, momordicine I had a minimal effect on human normal oral keratinocytes. | Momordicine I | [14] |
| Cytotoxic and Anti-Inflammatory Triterpenoids in the Vines and Leaves of Momordica charantia | To analyze the cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory effects of cucurbitane-type triterpenoid species and the mechanisms underlying these effects. | Momordicine I exerted deleterious effects on cell lines at concentrations greater than 10 or 20 µM. The momordicine I isomer TCD exhibited anti-inflammatory activity in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway and enhancing the expression of Nrf2/HO-1. | Momordicine I | [9] |
| Momordicine I alleviates isoproterenol-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through suppression of PLA2G6 and DGK-ζ | To evaluate the effect of momordicine I, a triterpenoid compound extracted from M. charantia L., on isoproterenol (ISO)-induced hypertrophy in rat H9c2 cardiomyocytes. This study used 12.5 μg/mL of momordicine I. | Momordicine I inhibited ISO-induced upregulation of mRNA levels and protein expression of PLA2G6 and DGK-ζ. Collectively, it alleviated ISO-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. | Momordicine I | [28] |
| In vivo studies | ||||
| Effect of bitter gourd (Momordica charantia) on glycaemic status in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. | To evaluate the effects of bitter gourd powder, incorporated at a 10% level in place of an equivalent amount of corn starch in the AIN-76 basal diet, over a period of 45 days | Improved diabetic status, evidenced by a significant reduction in the glomerular filtration rate | M. charantia | [39] |
| Antidiabetic effects of bitter gourd extracts in insulin-resistant db/db mice | To determine the effects of the whole fruit powder, a lipid fraction, a saponin fraction, or the hydrophilic residue of bitter gourd administered at a daily dosage of 150 mg/kg body weight for 5 weeks | Reduction in glycated Hb levels in all treatment groups. Specifically, the groups treated with saponin and lipid fraction showed decreases in lipid peroxidation in the adipose tissue and protein tyrosine phosphate 1 B activity in skeletal muscles. | M. charantia extract | [40] |
| Effect of Momordica charantia fruit extract on vascular complication in type 1 diabetic rats | To investigate the effects of a fruit extract administered at a rate of 1.5 g/kg of rats for 28 days after induction of diabetes | Improvement in vascular function, evidenced by decreased blood pressure, lipid levels, aortic tissue MDA levels, and increased aortic nitrous oxide levels. | M. charantia extract | [41] |
| In vitro and in vivo α-amylase andα-glucosidase inhibiting activities of the protein extracts from two varieties of bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.) | To determine the effects of protein extracts derived from bitter gourd cultivars and fed to rats at a dosage of 10 mg/kg body weight. Blood samples were drawn after 10, 30, 60, and 120 min of oral administration. | Significant reduction in peak blood glucose levels. | M. charantia extract | [35] |
| Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of Lactobacillus fermentum, fruit extracts of Syzygium cumini and Momordica charantia on diabetes induced mice. | To investigate the effects of the aqueous and ethanol extracts of bitter gourd administered at a rate of 200 mg/kg weight of mice for 3 weeks | Significant reduction in blood glucose levels. | M. charantia extract | [42] |
| Momordica charantia polysaccharides ameliorate oxidative stress, hyperlipidemia, inflammation, and apoptosis during myocardial infarction by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway | To evaluate the effect of the M. charantia extract on endothelial dysfunction in myocardial infarction. | Pretreatment with M. charantia polysaccharides (150 or 300 mg/kg) for 25 days significantly inhibited increases in heart weight, the heart-weight-to-body-weight ratio, and infarction size. This myocardial protective effect is potentially due to the enhancement of the antioxidant defense system through NF-κB pathways and anti-apoptosis through regulation of Bax, caspase-3, and Bcl-2. | M. charantia extract | [43] |
| Minerals and phytochemical analysis of bitter melon fruits and its components in some indigenous and exotic cultivars. | To investigate the effects of administering skin, flesh, and fruit powder from bitter melon at doses of 150 and 300 mg/kg body weight for 56 days | A decrease in the blood glucose level and an increase in the serum insulin level at the dosage of 300 mg. | M. charantia | [44] |
| A triterpenoid-enriched extract of bitter melon leaves alleviates hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting inflammatory responses in carbon tetrachloridetreated (CCl4) mice | To assess the efficacy of a triterpenoid-enriched extract administered at 100 or 150 mg/kg daily via oral gavage, starting one week before and continuing through CCl4 administration | Amelioration of hepatic fibrosis by regulating inflammatory cytokine secretion and α-smooth muscle actin expression in the liver, reducing collagen accumulation. | cucurbitane triterpenoids | [45] |
| Momordicine-I, a Bitter Melon Bioactive Metabolite, Displays Anti-Tumor Activity in Head and Neck Cancer Involving c-Met and Downstream Signaling. | To identify momordicine I and evaluate its role in head and neck cancer preclinical mouse model. | The Cmax values were 18 µM and 0.5 µM after the single 20 mg/kg IP and PO dose, respectively. No adverse events were observed in the IP dosing group. A significant reduction in the expression of c-Met and its downstream molecule c-Myc was observed in the momordicine I- treated group compared with the untreated group. | Momordicine I | [14] |
| Cytotoxic and Anti-Inflammatory Triterpenoids in the Vines and Leaves of Momordica charantia | To analyze the anti-inflammatory effects of cucurbitane-type triterpenoid species | The momordicine I isomer TCD exhibited anti-inflammatory activity. TCD ameliorated ear edema, a sign of ear inflammation, in the mouse model. | Momordicine I | [9] |
| Momordica charantia Extract Confers Protection Against Hypertension in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rats | To determine the antihypertensive effects of M. charantia water extracts | Alleviation of oxidative stress and salt-induced hypertension in Dahl/SS rats | M. charantia extract | [20] |
| Clinical studies | ||||
| Hypoglycemic effect of bitter melon compared with metformin in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients | To assess the effect of bitter melon capsules containing 500 mg of dried fruit pulp with 0.04–0.05 (w/w) of charantin, administered at doses of 500/1000/2000 mg per day and that of with 1000 mg of metformin per day for 4 weeks | Modest hypoglycemic effects were observed, but they were less substantial than those achieved with 100 mg of metformin per day | M. charantia | [46] |
| Wild bitter gourd improves metabolic syndrome: a preliminary dietary supplementation trial | To evaluate the effects of supplementing 42 eligible participants (21 men and 21 women) with a mean age of 45.7 ± 11.4 years (23 to 63 years) with 4.8 g of lyophilized bitter melon powder in capsules daily for 3 months | The incidence rate of metabolic syndrome decreased when compared with baseline. The waist circumference also significantly decreased. | M. charantia | [47] |
| “Pilot study: hypoglycemic and antiglycation activities of bitter melon (Momordica charantia L.) in type 2 diabetic patients | To determine the effects of continuous intake of 6 g/day of M. charantia L. dried-fruit pulp compared with placebo for 16 weeks. | Significant declines in the levels of total advanced glycation end-products in serum after the intervention | M. charantia | [48] |
| Evaluation of supplementation of Bitter gourd fermented beverage to diabetic subjects. | To investigate the effect of a 45 mL daily morning drink of bitter gourd fermented beverage | Significant reductions in the symptoms of diabetes and fasting and post prandial blood sugar levels were observed. | M. charantia | [49] |
| Preliminary clinical trials of karela, Momordica charantia, on non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients. | To test the effect of powdered bitter gourd made into a tablet containing a 20 mg polypeptide, with a dosage of 4 to 6 tablets per day taken half an hour before meals for 8 weeks. | Effective oral adjunct hypoglycemic effect observed with no reportable clinical side effects | M. charantia | [50] |
| Bitter gourd reduces elevated fasting plasma glucose levels in an intervention study among prediabetics in Tanzania | To explore the effects of daily consumption of 2.5 g of bitter gourd powder over a course of 8 weeks, employing a crossover design with an 8-week study period followed by a 4-week washout. | Lowered fasting plasma glucose levels were noted. | M. charantia | [51] |
| In silico study | ||||
| Network Pharmacology and Experimental Study of Momordicine I and Momordicine II from Bitter Melon Saponins in Inhibiting Fat Accumulation | To screen for potential ant-obesity compounds in the bitter melon extract through LC/Q-TOF-MS/MS and network pharmacology and to estimate the lipid-lowering effects of these compounds in vivo based on the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analysis | Triterpenoids in the extract could phosphorylate AMPK/mTOR and subsequently promote GLUT4 translocation to the cell membrane, thereby eliminating hyperglycemia both in vivo and in vitro. Momordicine I was identified as the core component likely responsible for treating obesity according to the compound-target-disease-pathway network. It exerted its lipid reduction capacity through daf-16/FoxO1 and hlh-30/TFEB-mediated lipophagy, consistent with the predicted AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. | Momordicine I | [52] |
| Pathway | Description | Key Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose metabolism | Modulation of glucose metabolism pathways. | Inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase; improves insulin sensitivity; stimulates GLUT-4 translocation; activates the AMPK signaling pathway; increases the expression of PPARγ; and acts as a GLP-1 secretagogue | [7,23,30,31,35] |
| Lipid metabolism | Regulation of lipid metabolism pathways. | Reduces lipid accumulation by inhibiting lipogenic enzymes and lipid peroxidation and increases lipophagy | [40,41,52] |
| Inflammatory | Inhibition of inflammatory mediators and pathways. | Inhibits the NF-κB pathway, reduces TNF-α-induced inflammation, inhibits MAPK phosphorylation, and reduces iNOS and IL-1β/NLRP3 inflammasome expression | [12,34,38,58,59,60] |
| Oxidative stress | Reduction of oxidative stress through the modulation of antioxidant enzymes. | Enhances antioxidant defenses by increasing the activity of superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase or through the NF-κB pathway | [27,36,43,55] |
| Apoptosis | Modulation of apoptosis-related proteins and pathways. | Promotes anti-apoptosis by downregulating Bax/caspase-3 and upregulating Bcl-2 protein expression | [43] |
| Cardiovascular diseases | Protection against cardiovascular-related disorders. | Alleviates cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by suppressing PLA2G6 and DGK-ζ; exerts an antihypertensive effect by inhibiting ACE; inhibits diabetes-associated cardiac fibrosis by increasing SCFA production, activating Nrf2 or inhibiting the TGF-β1/Smad pathway; suppresses the NF-κB-NLRP3 pathway; and downregulates the c-Met/STAT3 pathway | [8,14,24,28,37,62,63,67] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kao, P.-F.; Cheng, C.-H.; Cheng, T.-H.; Liu, J.-C.; Sung, L.-C. Therapeutic Potential of Momordicine I from Momordica charantia: Cardiovascular Benefits and Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910518
Kao P-F, Cheng C-H, Cheng T-H, Liu J-C, Sung L-C. Therapeutic Potential of Momordicine I from Momordica charantia: Cardiovascular Benefits and Mechanisms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(19):10518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910518
Chicago/Turabian StyleKao, Pai-Feng, Chun-Han Cheng, Tzu-Hurng Cheng, Ju-Chi Liu, and Li-Chin Sung. 2024. "Therapeutic Potential of Momordicine I from Momordica charantia: Cardiovascular Benefits and Mechanisms" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 19: 10518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910518
APA StyleKao, P.-F., Cheng, C.-H., Cheng, T.-H., Liu, J.-C., & Sung, L.-C. (2024). Therapeutic Potential of Momordicine I from Momordica charantia: Cardiovascular Benefits and Mechanisms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(19), 10518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910518







