Review of Antimicrobial Properties of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. TiO2 NPs Synthesis Methods
3. Methods for Studying the Physical and Chemical Properties of TiO2 NPs
4. Factors Determining the Magnitude of the TiO2 NPs Antimicrobial Effects
4.1. Target Microorganism
4.2. Morphology of NPs
4.3. Modification of the Composition of NPs
5. Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Action, Photocatalysis and Characteristics of Excitation Light
6. Biocompatibility with Eukaryotic Cells
7. Prospects and Limitations
| No. | Synthesis Method | Composition | Size, nm | Shape | MIC | Microorganism | Medium, Conditions | Effect | Notes | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Species | ||||||||||
| 1 | Laser ablation in water | TiO2 amoxicillin + TiO2 | 11–26 (200 mJ; 10 min) 2–23 (80 mJ, 20 min) | Sph | 400 µg/mL >> >> >> | Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr+ | E. coli, P. aeruginosa P. vulgaris, S. aureus | NA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | Amoxicillin addition significantly increased antibacterial activity. | [75] |
| 2 | Aeromonas hydrophila mediated biosynthesis | TiO2 | 28–54 40.50 (individ.) | Sph | 25 µg/mL 20 µg/mL 30 µg/mL 10 µg/mL 10 µg/mL 15 µg/mL | Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr+ Gr+ Gr+ | A. hydrophila, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, S. pyogenes, S. aureus, E. faecalis | NA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | The antibacterial activity of the synthesized TiO2 NPs was assessed by well diffusion method toward A. hydrophila, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, S. pyogenes, and E. faecalis and showed effective inhibitory activity against S. aureus (33 mm) and S. pyogenes (31 mm). | [95] |
| 3 | Aspergillus flavus mediated biosynthesis | TiO2 | 62–74 | Sph, Oval | 40 µg/mL 40 µg/mL 80 µg/mL 70 µg/mL 45 µg/mL | Gr+ Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr+ | S. aureus, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, K. pneumoniae, B. subtilis | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | Fungus-mediated synthesized TiO2 NPs have proved to be a good novel antibacterial material. | [98] |
| 4 | Sol–gel method | TiO2 | 6(S1)–25.8(S2) 25.8–33(S3) | Sph | 150 µg/mL (S1, S2) 200 µg/mL (S3) 200 µg/mL (S1, S3) 200 µg/mL (S1) 150 µg/mL (S1) 200 µg/mL (S3) 150 µg/mL (S2) | Gr+ Gr+ Gr+ Gr− Gr− Gr− Fungus | S. aureus, S. pneumonia, B. subtilis, P. vulgaris, P. aeruginosa, E. coli, C. albicans | MHA, 12–24 h, 37 ± 1 °C (bacteria) and 27 ± 1 °C (fungus) | BS | The synthesized TiO2 NPs were found to be effective in visible light against S. pneumonia, S. aureus, P. vulgaris, P. aeruginosa, and C. albicans. The powder samples at different calcination temperatures are defined as S1 (400 °C), S2 (600 °C), and S3 (800 °C). | [17] |
| 5 | Commercial TiO2 from Evonik Industries | LDPE-TiO2 | 25 | Sph | 500 µg/mL | Gr− | E. coli | LB, 24 h, 37 °C | BS, FS | The antimicrobial activity of the TiO2 NP-coated films exposed under both types of lighting was found to increase with an increase in the TiO2 NP concentration and the light exposure time. The antimicrobial activity of the films exposed under UV light was higher than that under fluorescent light. | [154] |
| 6 | Microwave-assisted one-step biosynthesis | TiO2 | 20–40 | Sph | 30 µg/mL >> >> >> >> | Gr+ Gr+ Gr− Gr− Gr+ | Bacillus, S. mutans, E. coli, K. pneumonia, C. absonum | NA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | The developed TiO2 NPs demonstrate significant antibacterial activity against bacillus at the concentration of 70 mg/mL. | [155] |
| 7 | Pulsed laser ablation in water | TiO2 | 34 | Sph | 25 µg/mL | Gr− | E. coli | LB, 12 h. (overnight), 37 °C | BS, BC | The best activity was obtained at the highest TiO2 concentration (100 µg/mL) and laser-ablated NPs compared with commercial. | [156] |
| 8 | Magnetic Field-Assisted Laser Ablation in Water | TiO2 | 25–35 | Sph | - | Gr− Gr+ | E. coli, S. aureus | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | The antibacterial effect assay revealed the largest inhibition zone in S. aureus and E. coli, with a more potent effect for TiO2 NPs prepared by a magnetic field when compared with that prepared without the presence of a magnetic field. | [158] |
| 9 | Commercial TiO2 from Jinan Haidebei Bioengineering Co., Ltd. Jinan City, Shandong, China | Chitosan-TiO2 | 30 | Sph | 100 µg/mL | Gr− Gr+ | E. coli, S. aureus | NA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | The chitosan-TiO2 nanocomposite exhibited an inhibitory effect on the growth of E. coli and S. aureus. When the TiO2 NPs concentration was 0.05%, the maximum inhibition zone was found, 11.37 ± 0.76 mm, indicating that, under this concentration, the treatment showed a strong bacteriostasis effect on E. coli. | [67] |
| 10 | Hydrolysis of Titanium Tetrachloride (TiCl4) as precursor | TiO2 | 70–100 | Sph | 5.14 µg/mL 5.35 µg/mL | Fungus Fungus | C. albicans ATCC 10231 (Fluconazole-susceptible) C. albicans ATCC 76615 (Fluconazole-resistant) | YNB, 48 h, 37 °C | FS | Yeast cells of C. albicans, due to their thick cell wall consisting of glucan and chitin, are more resistant than bacteria. It was reported that TiO2 NPs, by producing intracellular reactive oxygen species, induce destructive effects inside the microbial cells, oxidation of intra-cellular Coenzyme A, and peroxidation of the plenty of lipids, which decrease respiratory activity and subsequently cause cell death. | [54] |
| 11 | Sol–gel method | TiO2 | ~100 | Amorph | 1 µg/mL | Gr− | E. coli | MHB, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | The results indicate that in the first 30 min of exposure of the bacteria to the activated amorphous TiO2, the presence of E. coli colonies was significantly reduced, with no presence being detected in the culture. | [157] |
| 12 | Electrochemical method (current density was varied from 10 mA/cm2 to 14 mA/cm2) | TiO2 | 25–30 | Amorph | 50 μL 1 >> | Gr− Gr+ | E. coli, S. aureus | NB, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | TiO2 NPs synthesized at 14 mA/cm2 (15.99 nm) exhibited maximum (19.1 mm) bacterial growth inhibition against S. aureus and (17.0 mm) against E. coli in the form of zone-of-inhibition studies. | [56] |
| 13 | Green synthesis using ginger and garlic crude aqueous extracts (in varying proportions) | TiO2 | 23.38–58.64 | Sph | 10000 µg/mL | Gr+ | S. aureus | MHA, 12 h. (overnight), 37 °C | BS | Garlic-reduced TiO2 NPs at elevated concentration exhibited significantly (p < 0.05) improved antibacterial activity against MDR S. aureus. | [170] |
| 14 | Sonochemical method | TiO2 | 8 | Sph | 6.67 µg/mL 4.32 µg/mL 3.96 µg/mL 2.24 µg/mL 3.46 µg/mL 5.54 µg/mL 21.21 µg/mL 3.79 µg/mL 5.7 µg/mL | Gr− Gr+ Gr+ Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr− | P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, B. aureus, E. aerogenes, E. coli, MRSA, S. marcescens, A. baumannii, S. flexneri | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BC, AV | Results indicated that Gram-positive bacteria were more susceptible compared to Gram-negative bacteria. | [57] |
| 15 | Synthesis using propolis extract | TiO2 | 57.3 ± 4 | Cub, Rect | 16 µg/mL 8 µg/mL 32 µg/mL 32 µg/mL 64 µg/mL 64 µg/mL 128 µg/mL 64 µg/mL | Gr+ Gr+ Fungus Gr− Gr− Gr+ Gr− Gr− | MRSA, S. epidermidis, C. albicans, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa, L. monocytogenes, P. vulgaris, A. baumannii | -(commercial) | BS | The synthesized NPs had higher antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive bacteria than yeast and Gram-negative bacteria, respectively. P. vulgaris was the most resistant strain among the tested microorganisms, while S. epidermidis was the most susceptible microorganism. | [176] |
| 16 | Laser ablation in distilled water (DW) and alcohol | TiO2 | 36 | Circular | 9.45 µg/mL (DW) 4.72 µg/mL (Alc) 18.91 µg/mL(DW) 9.45 µg/mL (Alc) | Gr− Gr+ | E. coli, S. aureus | BHI, 18–24 h, 37 °C | BS | The mechanism of inhibitory activity of TiO2 NPs initiated by laser removal on microorganisms could be by their bond to the cell layer and further infiltration inside or by cooperation with phosphorus-containing mixes like DNA exasperating the replication procedure or, ideally, by their assault on the respiratory chain. | [171] |
| 17 | Hydrothermal method | TiO2 | 10 | Quasi-Sph | 50 µg/mL >> >> >> >> >> | Gr− Gr+ Gr+ Gr− Fungus Fungus | E. coli, S. aureus, B. subtilis, P. aeruginosa, C. albicans, A.niger | MHB, 24 h, 37 °C | BS, Antimicrobial | The green synthesized TiO2 NPs had high antibacterial activity against Gram-positive than Gram-negative bacteria. | [86] |
| 18 | Hydrothermal method | TiO2 | 5–15 | Semisph | 100 µg/mL >> >> | Gr+ Gr− Gr− | MRSA, E. coli, P. aeruginosa | LB, 12 h. (overnight), 37 °C | BS | The smallest nanocrystallite size showed a pronounced inhibitory effect and high reduction in the growth rate of bacteria with increasing the concentrations of TiO2 nanocrystallites for the three strains of bacteria. | [177] |
| 19 | Laser ablation in water | TiO2 | 3–30 | Sph | 400 µg/mL >> | Gr− Gr+ | E. coli, S. aureus | NB, 24 h, 37 °C | BC | The bacterial cell number was dropped in both types of pathogens, and the inhibition was concentration-dependent. | [178] |
| 20 | Sol−gel method | TiO2 | 64.77 ± 0.14 | Sph | <1024 µg/mL | Gr− | 25 isolates P. aeruginosa | MHA, 18 h, 34 °C | BS | It was found that TiO2 NPs showed a significant reduction in biofilm formation (96%) and represented superior antibacterial activity against P. aeruginosa strains in comparison to titanium dioxide powder. | [179] |
| 21 | Sol−gel method | TiO2 | 35 (anatase), 65 (rutile) | Sph | 30 µg/mL 40 µg/mL | Gr− Gr+ | E. coli, S. aureus | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | Antimicrobial activity results showed a strong bactericidal effect against Gram-positive bacteria and demonstrated greater sensitivity to TiO2 NPs at lower concentrations when compared to Gram-negative bacteria. | [180] |
| 22 | Photon-induced method (solar-light photocatalyst anatase TiO2 NPs) | TiO2 | 40–50 (anatase) 50–70 (mixed phase) 95–110 (rutile) 130–160 (rutile) | Sph | 25 µg/mL >> | Gr+ Gr− | S. aureus, E. coli | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BC | Anatase TiO2 NPs (25 nm, 100 μg/mL) demonstrated AB activity against extracellular S. aureus with 80% and E. coli with 82% killing efficacy. | [59] |
| 23 | Green synthesis using mulberry plant extract | Mulberry Plant Extract + TiO2 | 24 (anatase) | Sph | 20 µg/mL >> | Gr+ Gr− | S. aureus, E. coli | MHA, 12 h, 37 °C | BS | The Gr+ bacterial strain is more sensitive due to its weak cell wall membrane. | [181] |
| 24 | Calcination temperature (500 °C, 900 °C) | TiO2 + Geraniol (GER) | 300 ± 100 (anatase) 100(rutile) | Amorph | 1.125 µg/mL 2.05 µg/mL 1.55 µg/mL | Gr+ Gr+ Gr− | S. aureus CCM 4223, MRSA CCM 7110, E. coli CCM 3954 | MHB, 24 h, 37 °C | BC | GER enhances antimicrobial properties due to its high solubility and controlled toxicity. | [182] |
| 25 | Hydrolysis precipitation method with Ti(OBu)4, silver nitrate and ammonia | TiO2 N-TiO2 Ag-N-TiO2 | 19.8 39.2 20.7 | Sph | 5000 µg/mL >> | Gr− Gr+ | E. coli B. Subtilis | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | Both Ag- and N-doped TiO2 show increased antibacterial properties of TiO2 NPs under fluorescent light irradiation | [62] |
| 26 | Biosynthesis by Using Streptomyces sp. HC1 | TiO2 | 30–70 | Sph | <2000 µg/mL >> >> >> >> | Gr+ Gr− Fungus Fungus Gr− | S. aureus ATCC 29213, E. coli ATCC 35218, C. albicans ATCC 10231, A. niger ATCC 6275, P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | MHA (bacteria) SDA (fungus) 37 °C for 24 h | BS | TiO2 NPs showed higher antimicrobial activity against bacteria (12 mm) than against fungi. | [173] |
| 27 | Sol−gel method | TiO2 Mg-doped: 0.014 g/mL 0.028 g/mL 0.042 g/mL | 9.7 7 6.8 6.5 | - | 14,000 µg/mL 14,000 µg/mL 42,000 µg/mL | Gr− Gr+ Gr− | E. coli B. subtilis Pseudomonas | - | BS, Antimicrobial | The 0.14 gm Mg solution doped TiO2 NPs were found to be a good antibiotic compared to others against the E. coli and B. subtilis bacteria. | [135] |
| 28 | Sol–gel electrospinning technique | TiO2 | 200–300 | Rods | 5 µg/mL >> >> >> | Gr+ Gr− Gr− Gr− | S. aureus E. coli S. typhimurium K. pneumonia | NA or TSB, 24 h, 37 °C | BC | The mechanisms by which the UV light-induced photocatalytic activated TiO2 nanorods kill bacteria are suggested to be initial oxidative damage to the cell wall and the cell membrane, followed by damage to the interior DNA molecules, eventually causing death. | [172] |
| 29 | Ionic liquid-assisted hydrothermal method | TiO2 | 35 (TEM) | Sph | 10,000 µg/mL >> >> >> | Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr+ | K. aerogenes E. coli P. desmolyticum S. aureus | NA, 24–36 h, 37 °C | BS | TiO2 nanoparticles exhibited excellent photocatalytic activity for the degradation of methylene blue organic dye. | [183] |
| 30 | Two-step sol−gel method using citric acid and alpha dextrose as double surfactants | TiO2 | 20 | >500 µg/disc >> | Gr+ Gr+ | S. aureus MRSA | NB, 24 h, 30 °C | BS | In the case of nalidixic acid, TiO2 nanoparticle showed a Synergic effect on the antibacterial activity of this antibiotic against the test strain | [160] | |
| 31 | Sol−gel method | TiO2 Nd-TiO2 | 14–10 | Sph | 40 µg/mL >> | Gr− Gr+ | E. coli S. aureas | NA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | Neodymium (Nd) doped TiO2 enhanced the photocatalytic activity. Nd-doped TiO2 NPs showed good antibacterial activity when compared with TiO2 nanoparticles. | [134] |
| 32 | Hydrothermal method | TiO2 | <100 (FE-SEM) | Sph | 100 µg/mL >> >> >> | Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr+ | P. eruginosa (ATCC® 10145), E. coli (ATCC® 33876), K. pneumonia (ATCC® BAA-1144), S. ureus (ATCC® 11632) | NA, 12 h. (overnight), 37 °C | BS | TiO2 NPs are found to have the maximum antibacterial activity against Gram-negative bacterial strains rather than Gram-positive bacteria. TiO2 NPs have been shown to prevent or destroy bacterial cells by adhering to the cell wall, causing the leakage and damage of intracellular contents, hydroxyl radicals, the generation of reactive oxygen species, and the release of Ti4+ ions. | [184] |
| 33 | Hydrothermal post-treatment of amorphous titania at different temperatures (250 °C or 310 °C) without using any additives or doping agent | TiO2 | ~10–80 | Sph, faceted | 500 µg/mL >> >> >> | Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr− | A. vitis E. amylovora P. syringae X. juglandis | LB agar plates, 48 h, 30 °C | BS | Under UV-irradiation, A310C (310 °C) showed a pronounced antimicrobial activity on all the investigated plant pathogenic bacteria. The kinetic curves reveal that the order of susceptibility of tested bacteria using A310C is the following: A. vitis >> E. amylovora > P. syringae > X. juglandis. | [17] |
| 34 | Sol−gel and electrospinning approaches in the presence of different amounts of air–argon mixtures | TiO2 | 50–300 | Electrospun nanofibers | 3000 µg/mL 6000 µg/mL | Gr+ Gr− | MRSA P. aeruginosa | TSB, 18 h, 30 °C | BC | TiO2 NFs were more operative against Gram-negative P. aeruginosa than Gram-positive S. aureus. | [159] |
| 35 | Microwave-assisted method | TiO2 Ba-TiO2 | 8–18 4–10 | Sph | 100 µg/mL >> >> >> | Gr+ Gr− Gr− Gr− | B. subtilis V. cholera P. aeruginosa S. flexneri | NA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | The antibacterial activity was found to be higher for Ba-doped TiO2 nanoparticles compared to pure TiO2 NPs due to reduced particle size and high specific surface area, leading to enhanced particle surface reactivity to light and H2O adsorption. | [60] |
| 36 | Ultrasonic vibration of Ag-TiO2 compound nanoparticles (obtained by picosecond laser ablation in deionized water) | TiO2/Ag (TiO2 core, Ag shell) | ~10–180 (average: 27) | Sph | 20 μg/mL | Gr− | E. coli | Lysogeny broth (LB), 6 h, 37 °C + LB agar dish, 2 d, ~22 °C | BS | The antibacterial activity of the core-shell NPs was slightly better than that of the compound NPs at the same concentration under standard laboratory light conditions, and both were better than the TiO2 NPs but not as good as the Ag NPs. | [133] |
| 37 | Green synthesis of Ag-doped TiO2 nanoparticles using maple leaf extract | Ag/TiO2 | 45.90 | Rods | 4000 μg/mL >> | Gr+ Gr− | S. aureus E. coli | NA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | The doping of Ag into TiO2 reveals the enhancement of inhibition growth against Gram-positive (S. aureus) and Gram-negative (E. coli). | [185] |
| 38 | A low-temperature sol−gel process using organic solvents (TO) and aqueous extract of mangrove leaves (TM) as media | TiO2 | 13.1 (TO) 8.3 (TM) | Amorph | 5 μg/mL >> >> | Gr+ Gr+ Gr− | S. aureus, E. faecalis, V. damsela | NA, 12 h. (overnight), 37 ± 2 °C | BS | The green method utilising TM demonstrated resistance to all three bacteria types, while TO exhibited greater resistance, specifically against V. damsela. Notably, TM NPs exhibited inhibition comparable to Ciprofloxacin when used as a positive control. | [186] |
| 39 | Sol−gel method loaded with cardamom essential oil (CEO) | CEO@ TiO2 | 100–1000 (average: 335.6) | Capsule-like | 18.75 μg/mL 25 μg/mL 18.75 μg/mL | Gr− Gr+ Gr− | E. coli, B. subtilis, K. pneumoniae | NB, 24 h, 37 °C | BC | The results demonstrate that CEO/TiO2 conjugates exhibit more potent antibacterial activity against all the tested bacteria than CEO or TiO2 nanoparticles alone. | [187] |
| 40 | Synthesis from TiOSO4 (NPs) and hydrothermal method (NWs) | TiO2 | ~80 ~100 | Sph, Wire | 20,000 μg/mL | Gr+ | S. aureus | LB agar, 12 h. (overnight), 37 °C | BC | The anti-staphylococcal activity of TiO2 nanowires was better than the nanoparticles. | [188] |
| 41 | Green synthesis using an enzyme alpha-amylase | TiO2 | 30–70 (average: 50) | Sph | 62.50 μg/mL >> | Gr+ Gr− | S. aureus, E. coli | NA, 18 h, 37 °C | BC | The morphology and shape depend upon the concentration of the alpha-amylase enzyme. The biosynthesized NPs show good bactericidal effects against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. | [174] |
| 42 | Green synthesis using Azadirachta indica leaf extract | TiO2 | 25–87 (SEM) | Sph | 20.83 μg/mL 16.66 μg/mL 25 μg/mL 10.42 μg/mL 10.42 μg/mL | Gr+ Gr− Gr+ Gr− Gr− | S. aureus, K. pneumoniae, B. subtilis, S. typhi, E. coli, | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BC | Green synthesis of TiO2 NPs was achieved because of the presence of terpenoids, flavonoids, and proteins in Azadirachta indica, as these bioactive compounds were responsible for the synthesis of these NPs. | [189] |
| 43 | Sol−gel method | TiO2 | 64.77 ± 0.14 | Irregular sph | 8–64 μg/mL (av: 46.90) <1 μg/mL | Gr− >> | 22 P. aeruginosa Isolates (wound exudate, ear discharge) 3 P. aeruginosa Isolates (urine specimen) | MHA, 18–24 h, 37 °C | BS | The combination of TiO2 NPs and cefepime was found to show synergistic activity against all tested isolates, followed by ceftriaxone (96%), amikacin (88%), and ciprofloxacin (80%). | [190] |
| 44 | Hydrothermal and solvothermal conditions. | TiO2 | 3~8 | - | 100 μg/mL >> >> | Gr+ Gr− Gr− | MRSA, P. aeruginosa, E. coli | LB agar, 12 h. (overnight), 37 °C | BS | The antibacterial activity against pathogens was as follows: MRSA > E. coli > P. aeruginosa. The synthesized TiO2 NPs were genotoxic/mutagenic. | [140] |
| 45 | Microwave-irradiation-assisted hybrid chemical approach | TiO2 | 28.3 ± 3.1 | - | 15 µg/mL | Gr− | E. coli | LB, 37 °C | BC | The one reason that can be assured for microbial cell death after treatment with nano-titania is reactive oxygen generation and an increase in membrane permeabilization, not superoxide generation. | [191] |
| 46 | Hydrothermal technique | TiO2 TiO2 TiO2 S-TiO2 S-TiO2 S-TiO2 | 25–32 >> >> 27–45 >> >> | Sph >> >> Sph >> >> | 0.1 µg/mL 0.1 µg/mL 100 µg/mL 0.01 µg/mL 0.1 µg/mL 0.1 µg/mL | Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr− | V. cholerae, E. coli, P. aeruginosa V. cholera E. coli, P. aeruginosa | LB, 24 h, 37 °C | BS, BC | The 40% Sulfur (S) doped TiO2 sample showed the highest antibacterial activity against the V. cholerae by killing 71% bacteria at a minimum inhibitory concentration of 0.01 μg/mL. NPs are non-cytotoxic against hepatocellular carcinoma (Huh-7) human cell lines | [136] |
| 47 | Ultrasound method | TiO2 | 33.56 | Amorph | 9.7 µg/mL 19.5 µg/mL 19.0 µg/mL 9.7 µg/mL 19.5 µg/mL | Gr− Gr+ Gr− Fungus Gr+ | E. coli, S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, C. albicans, B. subtilis | NA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS, FS | The TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized by ultrasound method can be good inorganic antimicrobial agents. | [192] |
| 48 | Hydrothermal synthesis | TiO2 | 70.80 | Sph | 50 µg/mL >> >> | Gr+ Gr− Gr− | B. subtilis, K. pneumoniae, S. typhi | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | At the maximum concentration tested (150 mg/L), TiO2 NPs showed strong inhibitory action against B. subtilis (zone of inhibition 8.4 mm), K. pneumoniae (zone of inhibition 8.8 mm), and S. typhi (zone of inhibition 9.3 mm). | [193] |
| 49 | Sol−gel method using diethanolamine, acetic acid, and propionic acid solvents | TiO2 | 5–25 | Sph | 250 mg/mL >> >> >> | Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr− | ATCC. E. coli, MDR. E. coli, ATCC P. aeruginosa, MDR. P. aeruginosa | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | The diethanolamine, acetic acid, and propionic acid solvents showed comparatively good antibacterial activity due to the rutile phase and pH of these solvents, which modify the properties of TiO2. | [194] |
| 50 | Sol–gel method | TiO2 | 68 | Sph | 50,000 µg/mL >> | Gr− Gr+ | E. coli, S. aureus | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | MMT test showed no toxicity of TiO2 NPs; the antibacterial inhibitory effect of TiO2 NPs at 200 mg/mL concentrations exhibited superior antibacterial activity at 15.9 ± 0.1 and 14.0 ± 0.1 against S. aureus and E. coli, respectively. In conclusion, colloidal solutions with high stability were successfully synthesized, contributing to decreased dimensions and increased antibacterial properties. | [195] |
| 51 | Green synthesis using Iranian propolis extracts | TiO2 | 21 | Quasi-sph | 10 mg/mL 1.25 mg/mL 5 mg/mL 2.5 mg/mL 5 mg/mL 5 mg/mL | Fungus Gr+ Gr+ Gr+ Gr+ Gr+ | C. albicans, S. sobrinus, S. mutans, S. sanguinis, S. salivarius, L. acidophilus | TSB (bacteria) or YPD (fungus), 24 h, 37 °C | BC | There were no significant cytotoxicity effects. NPs from propolis extracts have less toxic effects and are user-friendly, eco-friendly, and economical materials. Pro1TiO2 (Khalkhal sample) NPs may be considered the best candidate for clinical application. | [196] |
| 52 | Green synthesis from Juniperus phoenicea (L.) leaf extract | TiO2 | 10–30 | Sph | 40 µg/mL 40 µg/mL 80 µg/mL 80 µg/mL 40 µg/mL 20 µg/mL 40 µg/mL | Gr+ Gr+ Gr− Gr− Fungus Fungus Fungus | S. aureus, B. subtilis, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, S. cerevisiae, Asp. niger, Pen. digitatum | SDA (fungus) and MHA (bacteria), 24 h, 37 °C | BS, FS | Some components such as elemol, linalool, and hydrocinnamic acid in Juniperus phoenicea plant due to having hydroxyl functional groups act as reducing agents. | [197] |
| 53 | Synthesis NPs by sonication with Ganoderma lucidum extract | TiO2 + Ganoderma extract | - | - | 156.2 µg/mL 78.12 µg/mL | Gr− Gr+ | P. aeruginosa, MRSA | TSB, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | Collectively, the combination of TiO2 NPs and Ganoderma extract was more able to reduce viable cells, especially against MRSA isolate, and had almost the same effect as vancomycin. | [198] |
| 54 | Synthesis by plant extracts | TiO2 | 12 | hexagonal | 25 µg/mL >> >> >> >> >> >> >> >> >> >> | Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr+ Fungus Fungus Fungus Fungus Fungus | E. coli, P. mirabilis, V. cholerae, P. aeruginosa, S. typhimurium, S. aureus, A. nidulans, A. fumigatus, A. niger, A. terreus, A. flavu | MHA, 48 h, 37 °C (bacteria), PDA, 5 d, 28 °C (fungus) | BS FS | TiO2 NPs have concentration-dependent antibacterial activity against bacterial pathogens such as E. coli, P. mirabilis, V. cholerae, P. aeruginosa, S. typhimurium, and S. aureus at 100 μg/mL concentration. Furthermore, these TiO2 NPs showed remarkable antifungal activity against aspergillosis-causing fungal pathogens such as A. niger, A. fumigatus, A. nidulans, and A. flavus at 100 μg/mL. | [199] |
| 55 | Green synthesis mediated by extract of clove and ginger herbal formulation | TiO2 | - | - | 25 µL | Gr+ | Lactobacillus | MHA, 4 h, 37 °C | BS | The results show that as the concentration increases, the value of optical density decreases, which proves that a bactericidal process occurs that results in a reduced bacterial count. | [200] |
| 56 | The metabolic doping of cultured diatom cells with titanium, pyrolysis of the doped biomass, and chemical doping of silver | AgNPs/TiO2/DBP | 10–20 | Quasi-sph | 2.5 mg/mL 1.25 mg/mL 2.5 mg/mL | Gr+ Gr− Gr− | S. aureus, K. pneumonia, E. coli | - | BS | Remarkably high antibacterial activity was observed for the synthesized nanocomposites against Gram-positive S. aureus and Gram-negative K. pneumoniae and E. coli strains, both laboratory-cultivated and clinical isolates. DPB—diatom pyrolysed biomass | [161] |
| 57 | Hydrothermal-assisted synthesis using a novel β-galactosidase isolated from the seed extract of Melilots indica | β-gal-TiO2 | 27 | Sph | 10 µg/mL 5 µg/mL | Gr− Gr+ | E. coli, S. aureus | NA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | The decrease in inhibitory efficacy at increased β-gal-TiO2 NPs concentrations could be attributed to the aggregation of some particles, thereby increasing the particle size and reducing the accessible surface area for nanoparticles. | [201] |
| 58 | Co-precipitation method using titanium tetra isopropoxide and hydrochloric acid as a precursor | α-TiO2 (Rutile) | 16.65 | Cuboid | 10 g/disc | Gr− Gr− Gr+ | K. pneumoniae, E. coli, S. aureus | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | TiO2-based NPs have highly developed surface chemistry, chemical stability, and a smaller size than a microorganism, making it easier for them to interact with the microorganisms. | [61] |
| 59 | Bio-modification of TiO2 nanoparticles surface | Tryptophan-TiO2 | 5–27 | Amorph | 45.7 µg/mL (EC_50) | Parasite | T. gondii | DMEM, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | Tryptophan-TiO2 nanoparticles (NPs) show selective anti-parasitic activity. Surface modification with amino acids, such as l-tryptophan not only enhanced the anti-parasitic action of TiO2 but also improved the host biocompatibility. | [202] |
| 60 | Green synthesis from leaf extracts of two plant species (Trianthema portulacastrum, Chenopodium quinoa) | TiO2 | 6–8 | Granule | 25 μL/mL | Fungus | U. Tritici | PDA, 5 days., 25 ± 2 °C | FS | The calcinated TiO2 NPs exhibited substantial antifungal activity against U. tritici compared to non-calcinated NPS. All of the NPs produced using different procedures (also used the sol−gel method for comparison) and at different doses showed considerable antifungal activity against U. tritici. | [203] |
| 61 | Biosynthesis using Aloe vera L. aqueous leaf extract | TiO2 + T. cf. asperellum extract | 10–25 | Tetragonal | 25 µg/mL | Fungus | B. sorokiniana | PDA, 5 d, 28 °C | BS, BC | Green synthesized TiO2 NPs positively increased the host plant’s tolerance against this disease by inducing osmolytes and antioxidant defense-related enzyme production. | [204] |
| 62 | Commercial from US Research Nanomaterials | TiO2 | 30 | - | 200 µg/mL >> >> >> | Gr+ Gr+ Gr+ Gr+ | L. reuteri, L. gasseri, B. animalis, B. longum | MRS, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | The inhibitory effects of TiO2 NPs were associated with cell membrane damage. TiO2 NPs caused alterations in multiple metabolic pathways of gut bacteria. | [205] |
| 63 | Synthesis using Beta vulgaris (beetroot) extract | TiO2/Beta vulgaris extract | 12 | Sph | 1000 µg/mL 500 µg/mL Nil Nil | Gr− Gr− Gr+ Gr+ | E. coli, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, S. mutans | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | Antibacterial assays reveal moderate activity against Gram-negative bacterial strains, while no activity is observed against Gram-positive bacterial strains. | [206] |
| 64 | Biosynthesis using probiotic Bifidobacterium bifidum | TiO2/B. bifidum components | 81 | Oval | 16 mg/mL 16 mg/mL 16 mg/mL 32 mg/mL 32 mg/mL | Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr− | P. aeruginosa, A. baumani, K. pneumonia, E. coli, S. typhi | NA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | Bifidobacteria were found to engage in huge inhibition activity against Gram-negative bacteria, i.e., intestinal Salmonella serovar Typhimurium SL1344 and Escherichia coli C1845. The inhibition mechanism was examined and found to be dependent on lowering the pH in the medium and producing organic acids, especially acetic acid and lactic acid. | [207] |
| 65 | Hydrothermal route using novel biogenic source Piper betel leaf extract and chemogenic source nitric acid as capping and reducing agents | TiO2/Piper betel extract | 8 75 | Sph | 25 µg/mL 50 µg/mL | Gr+ Gr− | S. aureus, E. coli | NA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | Biogenic synthesized NPs act as more effective antibacterial agents than chemogenic-synthesized NPs. | [208] |
| 66 | Modification of commercial PAMAM and TiO2 to novel nanocomposite | PAMAM/TiO2 | 50 | Sph | 4 µg/mL 2 µg/mL | Gr+ Gr− | S. aureus, E. coli | NB, 24 h, 37 °C | BC | FE-SEM analysis revealed morphological variations and the mechanism of killing and trapping the bacteria by nanocomposite. In the MIC and MBC values range, the cytotoxicity effect of nanocomposite on the AGS cell line was relatively lower. PAMAM—poly-amidoamine dendrimer macromolecule | [209] |
| 67 | Green synthesis method using Orange peel extract (Citrus sinensis) and chemical method | TiO2/Citrus sinensi extract | 21.61 17.30 | Porous angular | 6.75 mg/mL >> >> | Gr+ Gr− Gr− | S. aureus, E. coli, P. aeruginosa | NB, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | TiO2 nanoparticles prepared using the biological method exhibit good results compared to nanoparticles prepared by the chemical method. | [72] |
| 68 | Hydrothermal method | CQD-TiO2 BC/CQD-TiO2 | 22.23 | Porous fibers | Nil 0.5 µg/mL | Gr− Gr+ | E. coli, S. aureus | Netrin agar, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | The antibacterial activity against E. coli was much lower than when it was against S. aureus. This concept is because of the discrepancy in the structure of the cell walls between Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. | [68] |
| 69 | Synthesis porous TiO2 NPs and PVA-PEG/TiO2 composites using the sol−gel technique | PVA-PEG/TiO2 | 15 | Sph | 100 µL | Gr− | E. coli | LB, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | Antibacterial activity experiments, TiO2 19.9%, PVA/TiO2 24.4%, and PEG/TiO2 26.2% eliminated E. coli bacteria. | [210] |
| 70 | Microwave-assisted green method using Andrographis paniculata as fuel | TiO2/Andrographis paniculata extract | 25 | Sph | 41 µg/mL 36 µg/mL 35 µg/mL 42 µg/mL 30 µg/mL | Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr+ Gr− | E. coli, S. flexneri, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, K. pneumoniae | NB, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | NPs TiO2 NPs led to mechanical damage of cell membrane and significant cell division inhibition compared to standard antibiotics (Streptomycin). | [211] |
| 71 | Sol−gel technique using titanium tetra isopropoxide (TTIP) as a precursor | TiO2 Ag-TiO2 | 15 16 | Sph | 1 µg/mL >> >> | Gr− Gr− Gr+ | E. coli, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus | NA, 12 h, 37 °C | BS | Significant increases in the sizes of zones of inhibition with the increase in silver capping (3–7%) as compared to pure TiO2-NPs were observed against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. | [212] |
| 72 | One-pot and one-step green synthesis using Grape seed extract (GSE) proanthocyanin (PAC) polyphenols | Grape seed extract/TiO2 | 18.42 ± 1.3 | Sph | 1.56 µg/mL 0.78 µg/mL | Gr− Gr+ | P. aeruginosa, S. saprophyticus | BHI, 24 h, 37 °C | BC | PACs on the GSE-TiO2-NPs surface significantly enhanced the antibacterial activities in terms of confinement of the biofilm formation, plausibly through the entrapment of AL-2 QS signal molecules, attenuating the bio-actives (e.g., proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids, and EPS), biofilm matrix, increasing cellular uptake and ROS mediated robust oxidative stress. | [162] |
| 73 | Biosynthesis using titanium tetrabutoxide as a precursor in the presence of Kniphofia foliosa root extract within different ratios | TiO2/Kniphofia foliosa extract | ~9 | Sph | 35 mg/mL >> >> >> | Gr+ Gr+ Gr− Gr− | S. aureus, S. pyogenes, E. coli, K. pneumonia | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | Among the different ratios, TiO2 (1:1) NP shows better performance towards Gram-negative bacteria due to its smaller average crystalline size and uniform morphology than the other two ratios of TiO2 NPs. The antibacterial activity of the ethanolic root extract of Kniphofia foliosa itself showed better performance towards Gram-negative bacteria than NPs of TiO2, which might be due to the antibacterial activity of the residue of ethanol left with the plant extract. | [63] |
| 74 | Green synthesis using aqueous extract of Acacia nilotica as bio-reductant | Ag-TiO2/Acacia nilotica extract | 11.25 | Sph | 64 µg/mL 64 µg/mL 128 µg/mL 64 µg/mL | Gr− Gr+ Gr− Yeast | E. coli, S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, C. albicans | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | The order of antimicrobial activity was found to be E. coli > C. albicans > MRSA > P. aeruginosa. | [213] |
| 75 | Green synthesis using aqueous leaf extract of Coleus aromaticus | TiO2/Coleus aromaticus extract | 12–33 | Sph | 15 µg/mL >> >> >> >> >> | Gr− Gr− Gr+ Gr− Gr+ Gr+ | S. boydii, V. cholerae, B. cereus, A. hydrophila, E. faecalis, B. megaterium | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | The synthesized TiO2 NPs had an excellent antibacterial potential against E. faecalis (33 mm), followed by S. boydii (30 mm) | [214] |
| 76 | Green synthesis using Cymodocea serrulate aqueous extract | TiO2/Cymodocea serrulate extract | 55–117 | Sph | 180 μg/mL 160 μg/mL | Gr+ Gr− | MRSA, V. cholerae | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | The TiO2 NPs treated results were exhibited maximum antibacterial activity against MRSA and V. cholerae comparatively. | [215] |
| 77 | Green synthesis mediated Spirulina | TiO2/Spirulina components | 55 ± 15 | Sph | 3.906 µg/mL 15.625 µg/mL 15.625 µg/mL 31.25 µg/mL | Gr+ Gr− Gr+ Gr− | S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, E. faecalis, E. coli | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | The nanoparticles exhibited significant inhibitory zones of 22 ± 3, 17 ± 4, 11 ± 2, and 15 ± 3 nm at 80 μg/mL against MRSA, P. aeruginosa, E. coli, and E. faecalis, respectively. | [216] |
| 78 | Green synthesis using leaf extract of Mentha arvensis | TiO2/Mentha arvensis extracts | 20–70 | Sph | 10 mg/mL Nil Nil 10 mg/mL Nil Nil | Gr− Gr+ Gr− Fungus Fungus Fungus | P. vulgaris, S. aureus, E. coli, A. niger, A. cuboid, A. fumigates | NA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | Synthesized TiO2 nanoparticles show maximum zone of inhibition against the Proteus vulgaris bacteria (at 30 mg/mL) and show significant antifungal activity against Aspergillus niger. | [217] |
| 79 | Green synthesis using Psidium guajava extract | TiO2/Psidium guajava extract | 32.58 | Sph | 20 µg/mL >> >> >> >> | Gr+ Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr− | S. aureus, E. coli, A. hydrophila, P. mirabilis, P. aeruginosa | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | The synthesized TiO2 NPs showed more antibacterial activity than the standard tetracycline antibiotic | [218] |
| 80 | Green synthesis using Acorus calamus leaf extract | TiO2/Acorus calamus extract | 15–40 | Globular | 10 µg/mL >> >> >> | Gr− Gr− Gr+ Gr+ | E. coli, P. aeruginosa, B. subtilis, S. aureus | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | Biosynthesized TiO2 showed excellent antimicrobial activity against the selected Gram-positive over Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria in comparison to bare TiO2. NPs disrupt the outer cell of bacteria, which is primarily responsible for bacterial death. | [219] |
| 81 | Green Synthesis via Eucalyptus globulus L. Extract | Ag-TiO2/Eucalyptus globulus extract | 11–14 | Sph | 13.33 μg/μL | Gr+ Gr− | S. aureus, E. coli | LB, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | The effect of NPs is more significant for Gram-negative bacteria because of their thinner cell wall, compared to 30 nm for Gram-positive bacteria. | [220] |
| 82 | Green synthesis using aqueous extract of W. somnifera | TiO2/W. somnifera extract | 50–90 | Sph, Square | 64 µg/mL 8 µg/mL 32 µg/mL 32 µg/mL 32 µg/mL 64 µg/mL | Gr+ Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr+ Yeast | L. monocytogenes, S. marcescens, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, MRSA, C. albicans | NB, 24 h, 37 °C | BC | Among bacteria, the highest inhibition of 71% was recorded in MRSA, and the lowest was recorded in L. monocytogenes (43%). | [221] |
| 83 | Green synthesis using Aloe barbadensis mill | TiO2/Aloe barbadensis extract | 20 | Sph | 31.25 µg/mL | Gr− | P. aeruginosa | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BC | A noticeable suppression in the cell viability by 30.76 ± 3.96% of P. aeruginosa in the biofilm mode was found in the presence of TiO2 NPs | [222] |
| 84 | Bacterial-mediated Bacillus subtilis MTCC 8322 using TiCl4 as a precursor | TiO2/Bacillus subtilis components | 80–120 | Sph | 5 µg/mL 8 µg/mL | Gr+ Gr− | B. subtilis, E. coli | NA | BS | The TiO2 NPs exhibited antibacterial activity against Bacillus subtilis MTCC 8322 at a lower dose, while against E. coli 8933, only a higher dose exhibited antibacterial activity. | [64] |
| 85 | Bacterial-mediated Staphylococcus aureus | TiO2/Staphylococcus aureus components | 20 | Sph | 10 mg/mL >> | Gr− Gr+ | E. coli, B. subtilis | NA, 12 h. (overnight), 37 °C | BS | The differential sensitivity of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria towards nanoparticles may depend upon their cell outer layer attribute and their interaction with the charged TiO2 nanoparticles. It was observed that Gram-negative bacteria are more sensitive than Gram-positive bacteria. | [70] |
| 86 | Green synthesis using Caesalpinia pulcherrima flower extract, Nervilia aragoana leaf extract, and Manihot esculenta peel extract | TiO2/C. pulcherrima, N. aragoana, M. esculenta plants extracts | 15–28 | Sph | 50 µg/mL >> >> >> | Gr+ Gr− Gr− Yeast | S. aureus, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, C. albicans | MHA, 12 h. | BS | The obtained results showed that the TiO2 sample revealed better antibacterial activity in S. aureus than in the E. coli bacterial strain. | [223] |
| 87 | Synthesis using Planomicrobium sp. | TiO2/Planomicrobium components | >8.89 | Amorph | 0.1 µg/mL >> | Gr+ Gr− | B. subtilis, K. Planticola | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | The differential sensitivity of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria towards NPs may depend upon their cell outer layer attribute and their interaction with the charged TiO2 NPs. | [224] |
| 88 | Green synthesis using Edible Mushroom (Pleurotus djamor) Extract | TiO2/Pleurotus djamor) extract | 31 | Sph | 5 mg/mL >> >> >> >> >> >> | Gr+ Gr+ Gr+ Gr− Gr+ Gr− Gr− | B. cereus, B. subtilis MDB, C. diphtheriae, E. coli, S. aureus, P. fluorescens, Serratia sp. | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | The highest rate of inhibition zone was recorded in P. fluorescens (33 ± 0.2 mm), S. aureus (32 ± 0.4 mm), and C. diphtheriae (32 ± 0.1 mm) followed by others. | [69] |
| 89 | Commercial Degussa-P25 TiO2 | TiO2 | 25 | - | 350 μg/mL | Gr− | P. aeruginosa | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | Exposure to UV irradiation of 60 min has been shown to greatly enhance the antibacterial efficacy of TiO2 nanoparticles against MDR P. aeruginosa. | [225] |
| 90 | Biosynthesis-mediated Avicennia marina | TiO2/Avicennia marina extract | 30 | Sph | 100 μg/mL >> | Gr− Gr+ | E. coli, S. aureus | LB, 24 h, 37 °C | BS | It was found that the bactericidal effect of the biosynthesized TiO2 increased with increasing concentrations from 100 to 300 μg/mL; thereafter, a decrease was observed, and again, the bactericidal effect was increased from 400 to 1000 μg/mL. This trend was observed for both E. coli and S. aureus. | [66] |
| 91 | Green synthesis using Artemisia haussknechtii leaf extract | TiO2/Artemisia haussknechtii extract | 92.58 ± 56.98 | Sph | 40 μg/mL 20 μg/mL 4 μg/mL 4 μg/mL | Gr− Gr+ Gr+ Gr− | E. coli, S. aureus, S. epidermidis, S. marcescens | MHA, 24 h, 37 °C | BC | TiO2 NPs had no significant effect on E. coli ATCC 25,922 and S. aureus ATCC 43300, but there was antibacterial impact on S epidermidis ATCC 12258, S. marcescens ATTC13880 as lack of growth. The results of the synthesis and antibacterial properties of silver and copper nanoparticles were also presented in the study. | [65] |
| 92 | Green synthesis using Limon citrus extract | TiO2/Limon citrus extract | 200 * | Sph | 12.5 µg/mL 12.5 µg/mL 18.75 µg/mL 12.5 µg/mL | Gr− Gr− Gr+ Gr+ | E. coli, Klebsiella sp., MRSA, Bacillus | NB, 24 h, 37 °C | The most accepted mechanism for antibacterial activity is based on the generation of reactive oxygen species associated with the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanostructures. Also, the antibacterial efficiency of the green-prepared TiO2 NPs was compared with NPs prepared via a chemical process. | [226] | |
| 93 | Sol−gel method | TiO2 | 22.41 | Sph | 65 mg/mL 200 mg/mL 100 mg/mL 144 mg/mL 72 mg/mL 100 mg/mL 100 mg/mL 20 mg/mL | Gr+ Gr+ Gr+ Gr+ Gr− Gr− Gr− Gr− | S. fecalis S. pyogenes S. saprophyticus S. epidermidis E.coli MDR E.coli A. hydrophila S. dysenteriae | MHA, 24–48 h, 37 ± 2 °C | BS | Titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles demonstrated antifungal and antibacterial activities. | [227] |
| 94 | Hydrothermal method | Commercial TiO2 | 8–10 (*) 90–100 (*) | - | 10 µg/mL (*) 50 µg/mL (**) 10 µg/mL (*) 50 µg/mL (**) | Gr− Gr+ | E. coli NCIM 2065 S. aureus ATCC 6538 | NB, 12 h. (overnight), 37 °C | BC | TiO2 NPs 8–10 nm have profound action on E. coli, while S. aureus was not affected. TiO2 NPs 90–100 nm have very little effect on both organisms. | [142] |
| 95 | Hydrothermal method | TiO2 | 67.60 | Rods | 240 µg/mL | Gr− | R. solanacearum | - | BS | Genomic DNA injury might be due to the intracellular production of reactive oxygen species (O2, O2− and OH) which was stimulated by TiO2 NPs. | [228] |
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AV | Antivirus |
| BC | Bacterial cellulose |
| BC | bactericidal effect |
| BHI | Brain heart infusion broth |
| BS | bacteriostatic effect |
| CQD | Carbon Quantum Dots; |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| DMEM | Modified Eagle Medium |
| LB | Luria brother |
| MDR | multidrug-resistant |
| MHA | Mueller-Hinton agar |
| MHB | Mueller-Hinton Brotherhood |
| MRSA | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| NA | Nutrient agar |
| NB | Nutrient broth |
| PAMAM | poly-amidoamine dendrimer macromolecule |
| PDA | Potato Dextrose Agar |
| PEG | polyethylene glycol |
| PVA | Polyvinyl alcohol |
| SDA | Sabouraud dextrose agar |
| TSB | Trypticase soy broth |
| YNB | Yeast nitrogen base |
| YPD | Yeast peptone dextrose broth |
References
- Ventola, C.L. The antibiotic resistance crisis: Part 1: Causes and threats. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spellberg, B.; Gilbert, D.N. The Future of Antibiotics and Resistance: A Tribute to a Career of Leadership by John Bartlett. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, S71–S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, S.; Chattopadhyay, M.K.; Grossart, H.-P. The multifaceted roles of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in nature. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The antibiotic alarm. Nature 2013, 495, 141. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annunziato, G. Strategies to overcome antimicrobial resistance (AMR) making use of non-essential target inhibitors: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, M. Antibiotics in crisis. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, R1063–R1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gostev, V.; Ivanova, K.; Kruglov, A.; Kalinogorskaya, O.; Ryabchenko, I.; Zyryanov, S.; Kalisnikova, E.; Likholetova, D.; Lobzin, Y.; Sidorenko, S. Comparative genome analysis of global and Russian strains of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST22, a ‘Gaza clone’. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2021, 57, 106264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skachkova, T.S.; Zamyatin, M.N.; Orlova, O.A.; Yumtsunova, N.A.; Lashenkova, N.N.; Fomina, V.S.; Gusarov, V.G.; Mikhaylova, Y.V.; Shelenkov, A.A.; Goloveshkina, E.N.; et al. Monitoring Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus strains in the Moscow Medical and Surgical Center using Molecular-Biological Methods. Epidemiol. Vaccinal Prev. 2021, 20, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.A.; Sharma-Kuinkel, B.K.; Maskarinec, S.A.; Eichenberger, E.M.; Shah, P.P.; Carugati, M.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An overview of basic and clinical research. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crank, C.; O’Driscoll, T. Vancomycin-resistant enterococcal infections: Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and optimal management. Infect. Drug Resist. 2015, 8, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodzieva, V. Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium prevalent in Russian neonatal intensive care units. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 16, e376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M.R. Drug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae: Rational antibiotic choices. Am. J. Med. 1999, 106, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.H.; Lee Nam, Y.; Ichiyama, S.; Yoshida, R.; Hirakata, Y.; Fu, W.; Chongthaleong, A.; Aswapokee, N.; Chiu, C.H.; Lalitha, M.K.; et al. Spread of Drug—Resistant Streptococcus pneumoniaein Asian Countries: Asian Network for Surveillance of Resistant Pathogens (ANSORP) Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 28, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setchanova, L.; Alexandrova, A.; Pencheva, D.; Sirakov, I.; Mihova, K.; Kaneva, R.; Mitov, I. Rise of multidrug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae clones expressing non-vaccine serotypes among children following introduction of the 10-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in Bulgaria. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 15, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savinova, T.; Brzhozovskaya, E.; Alyabieva, N.; Lazareva, A.; Shagin, D.; Mayanskiy, N. Multiple-Drug Resistant Nasopharyngeal Streptococcus pneumoniae Isolated in Russia: Serotypes, Antimicrobial Susceptibility, and Molecular Characterization of the Emergent Serotype 13/ST2754 Lineage. Microb. Drug Resist. 2022, 28, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomino, J.; Martin, A. Drug Resistance Mechanisms in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antibiotics 2014, 3, 317–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostyukova, I.; Pasechnik, O.; Mokrousov, I. Epidemiology and Drug Resistance Patterns of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in High-Burden Area in Western Siberia, Russia. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, Z.; Dong, D.; Fang, H.; Wang, C.; Dong, Y.; Wu, J.; Tan, X.; Zhu, P.; et al. Antibiotic resistant bacteria: A bibliometric review of literature. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1002015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugaiyan, J.; Kumar, P.A.; Rao, G.S.; Iskandar, K.; Hawser, S.; Hays, J.P.; Mohsen, Y.; Adukkadukkam, S.; Awuah, W.A.; Jose, R.A.M.; et al. Progress in Alternative Strategies to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance: Focus on Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryakova, I.; Afoshin, A.; Tarlachkov, S.; Leontyevskaya, E.; Suzina, N.; Leontyevskaya, N.L. Lysobacter gummosus 10.1.1, a Producer of Antimicrobial Agents. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clatworthy, A.E.; Pierson, E.; Hung, D.T. Targeting virulence: A new paradigm for antimicrobial therapy. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udegova, E.S.; Gildeeva, K.A.; Rukosueva, T.V.; Baker, S. Metal nanoparticle antibacterial effect on antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria. Russ. J. Infect. Immun. 2021, 11, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudkov, S.V.; Sarimov, R.M.; Astashev, M.E.; Pishchalnikov, R.Y.; Yanykin, D.V.; Simakin, A.V.; Shkirin, A.V.; Serov, D.A.; Konchekov, E.M.; Gusein-Zade, N.G.; et al. Modern physical methods and technologies in agriculture. Phys. Usp. 2024, 67, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, A.O.; Odeyemi, A.T.; Akinjogunla, O.J.; Adeyeye, A.B.; Ayo-ajayi, I. Review of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes within the one health framework. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2024, 14, 2312953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.C.; Wang, A.Z. Nanoparticles and their applications in cell and molecular biology. Integr. Biol. 2014, 6, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santás-Miguel, V.; Arias-Estévez, M.; Rodríguez-Seijo, A.; Arenas-Lago, D. Use of metal nanoparticles in agriculture. A review on the effects on plant germination. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 334, 122222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenova, N.A.; Burmistrov, D.E.; Shumeyko, S.A.; Gudkov, S.V. Fertilizers Based on Nanoparticles as Sources of Macro- and Microelements for Plant Crop Growth: A Review. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurygina, I.A.; Shurygin, M.G. Perspectives of Metal Nanoparticles Application for the Purposes of Regenerative Medicine. Sib. Med. Rev. 2018, 4, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, C.; Almeida, A. Metallic Nanoparticles in the Food Sector: A Mini-Review. Foods 2022, 11, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Naushad, M.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Iqbal, J. Engineered nanoparticles for removal of pollutants from wastewater: Current status and future prospects of nanotechnology for remediation strategies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassaei, L.; Marken, F.; Sillanpää, M.; Amiri, M.; Cirtiu, C.M.; Sillanpää, M. Nanoparticles in electrochemical sensors for environmental monitoring. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 1704–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silant’ev, V.E.; Shmelev, M.E.; Belousov, A.S.; Patlay, A.A.; Shatilov, R.A.; Farniev, V.M.; Kumeiko, V.V. How to Develop Drug Delivery System Based on Carbohydrate Nanoparticles Targeted to Brain Tumors. Polymers 2023, 15, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, P.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Chu, P.K. Degradable and Photocatalytic Antibacterial Au-TiO2/Sodium Alginate Nanocomposite Films for Active Food Packaging. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golubev, S.S.; Sekerin, V.D.; Gorokhova, A.E.; Gayduk, N.V. Nanotechnology market research: Development and prospects. Rev. Espac. 2018, 39, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bratan, S.; Inshakova, E.; Inshakov, O.; Gorbatyuk, S.; Leonov, S.; Roshchupkin, S. World market for nanomaterials: Structure and trends. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 129, 02013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meija, J.; Coplen, T.B.; Berglund, M.; Brand, W.A.; De Bièvre, P.; Gröning, M.; Holden, N.E.; Irrgeher, J.; Loss, R.D.; Walczyk, T.; et al. Atomic weights of the elements 2013 (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2016, 88, 265–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanavicius, S.; Ramanavicius, A. Insights in the Application of Stoichiometric and Non-Stoichiometric Titanium Oxides for the Design of Sensors for the Determination of Gases and VOCs (TiO2−x and TinO2n−1 vs. TiO2). Sensors 2020, 20, 6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Sohn, H.Y.; Mohassab, Y.; Lan, Y. Structures, preparation and applications of titanium suboxides. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 79706–79722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. A Review: Synthesis and Applications of Titanium Sub-Oxides. Materials 2023, 16, 6874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammendolia, M.G.; De Berardis, B. Nanoparticle Impact on the Bacterial Adaptation: Focus on Nano-Titania. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gialanella, S.; Malandruccolo, A. Titanium and Titanium Alloys. In Aerospace Alloys; Topics in Mining, Metallurgy and Materials Engineering; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 129–189. [Google Scholar]
- Sevost’yanov, M.A.; Nasakina, E.O.; Baikin, A.S.; Sergienko, K.V.; Konushkin, S.V.; Kaplan, M.A.; Seregin, A.V.; Leonov, A.V.; Kozlov, V.A.; Shkirin, A.V.; et al. Biocompatibility of new materials based on nano-structured nitinol with titanium and tantalum composite surface layers: Experimental analysis in vitro and in vivo. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villechaise, P.; Oryshchenko, A.S.; Leonov, V.P.; Mikhailov, V.I.; Kuznetsov, P.A.; Alexandrov, A.V.; Appolaire, B.; Castany, P.; Dehmas, M.; Delaunay, C.; et al. Titanium in Shipbuilding and Other Technical Applications. MATEC Web Conf. 2020, 321, 02001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushp, P.; Dasharath, S.M.; Arati, C. Classification and applications of titanium and its alloys. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 54, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.J.; Kopac, J.; Balazic, M.; Bombac, D.; Brojan, M.; Kosel, F. Titanium and Titanium Alloy Applications in Medicine. In Surgical Tools and Medical Devices; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 475–517. [Google Scholar]
- Sarraf, M.; Rezvani Ghomi, E.; Alipour, S.; Ramakrishna, S.; Liana Sukiman, N. A state-of-the-art review of the fabrication and characteristics of titanium and its alloys for biomedical applications. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2021, 5, 371–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutalik, C.; Lin, I.H.; Krisnawati, D.I.; Khaerunnisa, S.; Khafid, M.; Widodo; Hsiao, Y.-C.; Kuo, T.-R. Antibacterial Pathways in Transition Metal-Based Nanocomposites: A Mechanistic Overview. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 6821–6842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.G. Titanium dioxide–based nanomaterials: Application of their smart properties in biomedicine. In Titanium Dioxide (Tio2) and Its Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 337–352. [Google Scholar]
- Amiri, M.R.; Alavi, M.; Taran, M.; Kahrizi, D. Antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, and photocatalytic activities of TiO2 nanoparticles, nanocomposites, and bio-nanocomposites: Recent advances and challenges. J. Public Health Res. 2022, 11, 22799036221104151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudkov, S.V.; Burmistrov, D.E.; Serov, D.A.; Rebezov, M.B.; Semenova, A.A.; Lisitsyn, A.B. A Mini Review of Antibacterial Properties of ZnO Nanoparticles. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 641481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudkov, S.V.; Burmistrov, D.E.; Serov, D.A.; Rebezov, M.B.; Semenova, A.A.; Lisitsyn, A.B. Do Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Have Significant Antibacterial Properties? Antibiotics 2021, 10, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, A.B.; Haddad, Y.; Kosaristanova, L.; Smerkova, K. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: Recent progress in antimicrobial applications. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechn. 2022, 15, e1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonidi Jafari, A.; Moslemzadeh, M. The effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on bacterial growth: The effect of particle size and their structure—A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2023, 34, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, F.; Roudbar Mohammadi, S.; Mohammadi, P.; Hosseinkhani, S.; Shidpour, R. Antifungal activity of TiO2 nanoparticles and EDTA on Candida albicans biofilms. Infect. Epidemiol. Med. 2013, 1, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Priyanka, K.P.; Sukirtha, T.H.; Balakrishna, K.M.; Varghese, T. Microbicidal activity of TiO2 nanoparticles synthesised by sol–gel method. IET Nanobiotechn. 2016, 10, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anandgaonker, P.; Kulkarni, G.; Gaikwad, S.; Rajbhoj, A. Synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles by electrochemical method and their antibacterial application. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, S.; Shahzad, K.; Mushtaq, S.; Ali, I.; Rafe, M.H.; Fazal-ul-Karim, S.M. Antibacterial and antiviral potential of colloidal Titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles suitable for biological applications. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 105409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundrarajan, M.; Bama, K.; Bhavani, M.; Jegatheeswaran, S.; Ambika, S.; Sangili, A.; Nithya, P.; Sumathi, R. Obtaining titanium dioxide nanoparticles with spherical shape and antimicrobial properties using M. citrifolia leaves extract by hydrothermal method. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 171, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, G.; Tamilarasu, S. Visible Light Photocatalyst Anatase Phased TiO2 Nanoparticles for Enhanced Antibacterial Performance. J. Clust. Sci. 2020, 32, 1701–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayalakshmi, K.; Sivaraj, D. Synergistic antibacterial activity of barium doped TiO2 nanoclusters synthesized by microwave processing. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 9663–9671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, M.; Allwin Joseph, L.; Joel Abraham, J.; Isaac Emmanuel, J.; Prince Joshua, J. Structural and biological effects of rutile (α-TiO2) nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. Mater. Today Proc. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Ding, J.; Xu, J.; Deng, J.; Guo, J. TiO2 Nanoparticles Co-Doped with Silver and Nitrogen for Antibacterial Application. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 4868–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekele, E.T.; Gonfa, B.A.; Zelekew, O.A.; Belay, H.H.; Sabir, F.K. Synthesis of titanium oxide nanoparticles using root extract of Kniphofia foliosa as a template, characterization, and its application on drug resistance bacteria. J. Nanomater. 2020, 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, C.; Yadav, V.K.; Amari, A.; Meena, A.; Chinedu Egbosiuba, T.; Verma, R.K.; Mahdhi, N.; Choudhary, N.; Sahoo, D.K.; Chundawat, R.S.; et al. Synthesis and characterization of titanium dioxide nanoparticles from Bacillus subtilis MTCC 8322 and its application for the removal of methylene blue and orange G dyes under UV light and visible light. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 11, 1323249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subhapriya, S.; Gomathipriya, P. Green synthesis of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles by Trigonella foenum-graecum extract and its antimicrobial properties. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 116, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahin Lefteh, M.; Sourinejad, I.; Ghasemi, Z. Avicennia marina mediated synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles: Its antibacterial potential against some aquatic pathogens. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2020, 51, 1775–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Li, X.; Guo, X.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Yang, H.; Shui, Y.; et al. Effects of Different TiO2 Nanoparticles Concentrations on the Physical and Antibacterial Activities of Chitosan-Based Coating Film. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmir, S.; Karbalaei, A.; Pourmadadi, M.; Hamedi, J.; Yazdian, F.; Navaee, M. Antibacterial properties of a bacterial cellulose CQD-TiO2 nanocomposite. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 234, 115835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manimaran, K.; Murugesan, S.; Ragavendran, C.; Balasubramani, G.; Natarajan, D.; Ganesan, A.; Seedevi, P. Biosynthesis of TiO2 Nanoparticles Using Edible Mushroom (Pleurotus djamor) Extract: Mosquito Larvicidal, Histopathological, Antibacterial and Anticancer Effect. J. Clust. Sci. 2020, 32, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landage, K.S.; Arbade, G.K.; Khanna, P.; Bhongale, C.J. Biological approach to synthesize TiO2 nanoparticles using Staphylococcus aureus for antibacterial and antibiofilm applications. J. Microbiol. Exp. 2020, 8, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozova, M.V.; Korkina, V.I.; Makarova, M.A.; Litvinova, E.A. Effect of the Bacillus subtilis BS20 on physiological and immune parameters in mutant mice Muc2−/−. J. Microbiol. Epidemiol. Immunobiol. 2024, 101, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobeen Amanulla, A.; Sundaram, R. Green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles using orange peel extract for antibacterial, cytotoxicity and humidity sensor applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 8, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, K.; Shashank, M.; Revathi, V.; Tatarchuk, T. Facile microwave-assisted green synthesis of NiO nanoparticles from Andrographis paniculata leaf extract and evaluation of their photocatalytic and anticancer activities. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2019, 673, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfryyan, N.; Kordy, M.G.M.; Abdel-Gabbar, M.; Soliman, H.A.; Shaban, M. Characterization of the biosynthesized intracellular and extracellular plasmonic silver nanoparticles using Bacillus cereus and their catalytic reduction of methylene blue. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khashan, K.S.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Abdulameer, F.A.; Albukhaty, S.; Ibrahem, M.A.; Al-Muhimeed, T.; AlObaid, A.A. Antibacterial Activity of TiO2 Nanoparticles Prepared by One-Step Laser Ablation in Liquid. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Raturi, S.; Kulshrestha, S.; Chauhan, K.; Dhingra, S.; András, K.; Thu, K.; Khargotra, R.; Singh, T. A comprehensive review on various techniques used for synthesizing nanoparticles. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 1739–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Du, X.W.; Singh, S.C.; Kulinich, S.A.; Yang, S.; He, J.; Cai, W. Nanomaterials via Laser Ablation/Irradiation in Liquid: A Review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 1333–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simakin, A.V.; Baimler, I.V.; Uvarov, O.V.; Rakov, I.I.; Gudkov, S.V. Laser ablation method for the generation of chromium, iron, manganese, nickel, scandium, titanium and vanadium, nanoparticles: Control of size and properties. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 921, 012024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzeh, M.; Sunahara, G.I. In vitro cytotoxicity and genotoxicity studies of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles in Chinese hamster lung fibroblast cells. Toxicology in Vitro 2013, 27, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, C.; Yadav, V.K.; Gacem, A.; AbdelRahim, S.K.; Verma, R.K.; Chundawat, R.S.; Gnanamoorthy, G.; Yadav, K.K.; Choudhary, N.; Sahoo, D.K.; et al. Microbial synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles and their importance in wastewater treatment and antimicrobial activities: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1270245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakevich, P.V.; Simakin, A.V.; Voronov, V.V.; Shafeev, G.A. Laser induced synthesis of nanoparticles in liquids. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 4373–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bykov, I.; Malyshko, V.V.; Shashkov, D.I.; Moiseev, A.V.; Basov, A.; Sokolov, M.E.; Pavlyuchenko, I.; Esaulenko, E.E. Dependence of the size and number of silver nanoparticles on the ligand concentration in the reaction system. Med. News North Cauc. 2024, 19, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagajyothi, P.C.; Sreekanth, T.V.M.; Tettey, C.O.; Jun, Y.I.; Mook, S.H. Characterization, antibacterial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic activities of ZnO nanoparticles using Coptidis Rhizoma. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 4298–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.; Imran, M.; Jabri, T.; Ali, I.; Perveen, S.; Shafiullah; Ahmed, S.; Shah, M.R. Gum tragacanth stabilized green gold nanoparticles as cargos for Naringin loading: A morphological investigation through AFM. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Hrbek, J.; Osgood, R. Formation of TiO2 Nanoparticles by Reactive-Layer-Assisted Deposition and Characterization by XPS and STM. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, B.; Dash, S.K.; Mandal, D.; Ghosh, T.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Tripathy, S.; Das, S.; Dey, S.K.; Das, D.; Roy, S. Green synthesized silver nanoparticles destroy multidrug resistant bacteria via reactive oxygen species mediated membrane damage. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, N.C.; Minelli, C.; Tompkins, J.; Stevens, M.M.; Shard, A.G. Emerging Techniques for Submicrometer Particle Sizing Applied to Stöber Silica. Langmuir 2012, 28, 10860–10872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varenne, F.; Botton, J.; Merlet, C.; Vachon, J.-J.; Geiger, S.; Infante, I.C.; Chehimi, M.M.; Vauthier, C. Standardization and validation of a protocol of zeta potential measurements by electrophoretic light scattering for nanomaterial characterization. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 486, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.D.; Rizzello, L.; Avila-Olias, M.; Gaitzsch, J.; Contini, C.; Magoń, M.S.; Renshaw, S.A.; Battaglia, G. Purification of Nanoparticles by Size and Shape. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigimaga, V.A. Pulsed conductometer for biological cells and liquid media. Meas. Tech. 2013, 55, 1294–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriquez, R.R.; Ito, T.; Sun, L.; Crooks, R.M. The resurgence of Coulter counting for analyzing nanoscale objects. Analyst 2004, 129, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehara, K.; Sakurai, H. Metrology of airborne and liquid-borne nanoparticles: Current status and future needs. Metrologia 2010, 47, S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, F.; Broderick, M.J.F.; Gibson, T.; Millner, P.A. Fabrication and Activity of Silicate Nanoparticles and Nanosilicate-Entrapped Enzymes Using Polyethyleneimine As a Biomimetic Polymer. Langmuir 2011, 27, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Shrivastava, A.; Wahi, N. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by plants crude extracts and their characterization using UV, XRD, TEM and EDX. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 2554–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaseelan, C.; Rahuman, A.A.; Roopan, S.M.; Kirthi, A.V.; Venkatesan, J.; Kim, S.-K.; Iyappan, M.; Siva, C. Biological approach to synthesize TiO2 nanoparticles using Aeromonas hydrophila and its antibacterial activity. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 107, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naraginti, S.; Li, Y. Preliminary investigation of catalytic, antioxidant, anticancer and bactericidal activity of green synthesized silver and gold nanoparticles using Actinidia deliciosa. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 170, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zad, Z.R.; Davarani, S.S.H.; Taheri, A.; Bide, Y. A yolk shell Fe3O4 @PA-Ni@Pd/Chitosan nanocomposite -modified carbon ionic liquid electrode as a new sensor for the sensitive determination of fluconazole in pharmaceutical preparations and biological fluids. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 253, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajakumar, G.; Rahuman, A.A.; Roopan, S.M.; Khanna, V.G.; Elango, G.; Kamaraj, C.; Zahir, A.A.; Velayutham, K. Fungus-mediated biosynthesis and characterization of TiO2 nanoparticles and their activity against pathogenic bacteria. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 91, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswarlu, S.; Natesh Kumar, B.; Prasad, C.H.; Venkateswarlu, P.; Jyothi, N.V.V. Bio-inspired green synthesis of Fe3O4 spherical magnetic nanoparticles using Syzygium cumini seed extract. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2014, 449, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmistrov, D.E.; Serov, D.A.; Simakin, A.V.; Baimler, I.V.; Uvarov, O.V.; Gudkov, S.V. A Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and Nano-Al2O3 Based Composite Coating with a Bacteriostatic Effect against E. coli and Low Cytotoxicity. Polymers 2022, 14, 4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simakin, A.V.; Sarimov, R.M.; Smirnova, V.V.; Astashev, M.E.; Serov, D.A.; Yanykin, D.V.; Chausov, D.N.; Shkirin, A.V.; Uvarov, O.V.; Rotanov, E.; et al. New Structural Nanocomposite Based on PLGA and Al2O3 NPs as a Balance between Antibacterial Activity and Biocompatibility with Eukaryotic Cells. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühling, M.; Bradford, A.; Readman, J.W.; Somerfield, P.J.; Handy, R.D. An investigation into the effects of silver nanoparticles on antibiotic resistance of naturally occurring bacteria in an estuarine sediment. Mar. Environ. Res. 2009, 68, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochapski, D.J.; Carvalho Dos Santos, C.; Leite, G.W.; Pulcinelli, S.H.; Santilli, C.V. Zeta Potential and Colloidal Stability Predictions for Inorganic Nanoparticle Dispersions: Effects of Experimental Conditions and Electrokinetic Models on the Interpretation of Results. Langmuir 2021, 37, 13379–13389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Németh, Z.; Csóka, I.; Semnani Jazani, R.; Sipos, B.; Haspel, H.; Kozma, G.; Kónya, Z.; Dobó, D.G. Quality by design-driven zeta potential optimisation study of liposomes with charge imparting membrane additives. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doua, J.; Geurtsen, J.; Rodriguez-Baño, J.; Cornely, O.A.; Go, O.; Gomila-Grange, A.; Kirby, A.; Hermans, P.; Gori, A.; Zuccaro, V.; et al. Epidemiology, clinical features, and antimicrobial resistance of invasive Escherichia coli disease in patients admitted in tertiary care hospitals. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2023, 10, ofad026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelstein, M.V.; Sukhorukova, M.V.; Skleenova, E.Y.; Ivanchik, N.V.; Mikotina, A.V.; Sheck, E.A.; Dekhnich, A.V.; Azizov, I.S.; Kozlov, R.S. The antibiotic resistance of nosocomial strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Russian hospitals: The results of multicenter epidemiological study MARAFON 2013–2014. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 19, 27–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kolotova, O.N.; Kataeva, L.V.; Bakshtanovskaya, I.V.; Stepanova, T.F.; Stepanova, K.B. Resistance factors of Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteria during COVID-19 pandemic. Russ. J. Infect. Immun. 2022, 12, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noskov, A.K.; Kruglikov, V.D.; Moskvitina, E.A.; Monakhova, E.V.; Levchenko, D.A.; Yanovich, E.G.; Vodop’yanov, A.S.; Pisanov, R.V.; Nepomnyashchaya, N.B.; Ezhova, M.I.; et al. Characteristics of the Epidemiological Situation on Cholera in the World and in the Russian Federation in 2020 and Forecast for 2021. Probl. Part. Danger. Infect. 2021, 1, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, S.A.; Kuleshov, K.V.; Kaftyreva, L.A.; Matveeva, Z.N. The antimicrobial susceptibility, resistance mechanisms and phylogenetic structure of S. Typhi isolated in 2005–2018 in the Russian Federation. Russ. J. Infect. Immun. 2020, 10, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gostev, V.; Kruglov, A.; Kalinogorskaya, O.; Dmitrenko, O.; Khokhlova, O.; Yamamoto, T.; Lobzin, Y.; Ryabchenko, I.; Sidorenko, S. Molecular epidemiology and antibiotic resistance of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus circulating in the Russian Federation. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 53, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamski, P.; Byczkowska-Rostkowska, Z.; Gajewska, J.; Zakrzewski, A.J.; Kłębukowska, L. Prevalence and antibiotic resistance of Bacillus sp. Isolated from raw milk. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesvizhsky, Y.V.; Voropaev, A.D.; Afanasiev, S.S.; Volchkova, E.V.; Afanasiev, M.S.; Voropaeva, E.A.; Suleimanova, M.E.; Budanova, E.V.; Urban, Y.N. The association between Candida albicans sensitivity to antimycotic drugs and the architecture of their microbial community in the oropharynx of HIV infected patients. J. Microbiol. Epidemiol. Immunobiol. 2023, 100, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levina, A.S.; Repkova, M.N.; Ismagilov, Z.R.; Shikina, N.V.; Malygin, E.G.; Mazurkova, N.A.; Zinov’ev, V.V.; Evdokimov, A.A.; Baiborodin, S.I.; Zarytova, V.F. High-performance method for specific effect on nucleic acids in cells using TiO2~DNA nanocomposites. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutte-Smith, M.; Erasmus, E.; Mogale, R.; Marogoa, N.; Jayiya, A.; Visser, H.G. Using visible light to activate antiviral and antimicrobial properties of TiO2 nanoparticles in paints and coatings: Focus on new developments for frequent-touch surfaces in hospitals. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2023, 20, 789–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Jubeh, B.; Karaman, R. Resistance of Gram-Negative Bacteria to Current Antibacterial Agents and Approaches to Resolve It. Molecules 2020, 25, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudkov, S.V.; Serov, D.A.; Astashev, M.E.; Semenova, A.A.; Lisitsyn, A.B. Ag2O Nanoparticles as a Candidate for Antimicrobial Compounds of the New Generation. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudkov, S.V.; Burmistrov, D.E.; Smirnova, V.V.; Semenova, A.A.; Lisitsyn, A.B. A Mini Review of Antibacterial Properties of Al2O3 Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadiyala, U.; Kotov, N.A.; VanEpps, J.S. Antibacterial Metal Oxide Nanoparticles: Challenges in Interpreting the Literature. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroui, H.; Wilson, D.S.; Dalmasso, G.; Salaita, K.; Murthy, N.; Sitaraman, S.V.; Merlin, D. Nanomedicine in GI. Am. J. Physiol. -Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, G371–G383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnur, J.M.; Li, L.-H.; Yen, M.-Y.; Ho, C.-C.; Wu, P.; Wang, C.-C.; Maurya, P.K.; Chen, P.-S.; Chen, W.; Hsieh, W.-Y.; et al. Non-Cytotoxic Nanomaterials Enhance Antimicrobial Activities of Cefmetazole against Multidrug-Resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, H.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles of different particle size against Vibrio natriegens. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skomorokhova, E.A.; Sankova, T.P.; Orlov, I.A.; Savelev, A.N.; Magazenkova, D.N.; Pliss, M.G.; Skvortsov, A.N.; Sosnin, I.M.; Kirilenko, D.A.; Grishchuk, I.V.; et al. Size-Dependent Bioactivity of Silver Nanoparticles: Antibacterial Properties, Influence on Copper Status in Mice, and Whole-Body Turnover. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2020, 13, 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kladko, D.V.; Falchevskaya, A.S.; Serov, N.S.; Prilepskii, A.Y. Nanomaterial Shape Influence on Cell Behavior. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menichetti, A.; Mavridi-Printezi, A.; Mordini, D.; Montalti, M. Effect of Size, Shape and Surface Functionalization on the Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleimani, F.F.; Saleh, T.; Shojaosadati, S.A.; Poursalehi, R. Green Synthesis of Different Shapes of Silver Nanostructures and Evaluation of Their Antibacterial and Cytotoxic Activity. BioNanoScience 2017, 8, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jog, R.; Burgess, D.J. Pharmaceutical Amorphous Nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 39–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Chan, W.L.; Szeto, Y.S. Nanocomposite of chitosan and silver oxide and its antibacterial property. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 108, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, S.; Rehan, Z.A.; Khan, S.A.; Akhtar, K.; Khan, M.A.; Khan, M.I.; Rashid, M.I.; Asiri, A.M.; Khan, S.B. Antibacterial PES-CA-Ag2O nanocomposite supported Cu nanoparticles membrane toward ultrafiltration, BSA rejection and reduction of nitrophenol. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 230, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, S.; Rehman, W.; Waseem, M.; Meynen, V.; Awan, S.U.; Saeed, S.; Iqbal, N. Fabrication of pure and moxifloxacin functionalized silver oxide nanoparticles for photocatalytic and antimicrobial activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 186, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, M.; Namratha, K.; Alghamdi, S.; Mohammad, Y.H.E.; Hezam, A.; Zare, M.; Drmosh, Q.A.; Byrappa, K.; Chandrashekar, B.N.; Ramakrishna, S.; et al. Novel Green Biomimetic Approach for Synthesis of ZnO-Ag Nanocomposite; Antimicrobial Activity against Food-borne Pathogen, Biocompatibility and Solar Photocatalysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eremeeva, N. Nanoparticles of metals and their compounds in films and coatings: A review. Foods Raw Mater. 2023, 12, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iudin, D.; Vasilieva, M.; Knyazeva, E.; Korzhikov-Vlakh, V.; Demyanova, E.; Lavrentieva, A.; Skorik, Y.; Korzhikova-Vlakh, E. Hybrid Nanoparticles and Composite Hydrogel Systems for Delivery of Peptide Antibiotics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, A.H.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, X.L.; Wang, T. Sequential laser and ultrasonic wave generation of TiO2@Ag core-shell nanoparticles and their anti-bacterial properties. Lasers Med. Sci. 2015, 31, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithya, N.; Bhoopathi, G.; Magesh, G.; Kumar, C.D.N. Neodymium doped TiO2 nanoparticles by sol-gel method for antibacterial and photocatalytic activity. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2018, 83, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Patel, V.; Verma, H.; Kumar Akhani, T.; Singh Rathore, M. Structural, optical and antibacterial performance of the Mg doped TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized using sol–gel method. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 67, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, F.; Hussain, R.; Noreen, Z.; Javed, A.; Shah, A.; Mahmood, A.; Sajjad, M.; Bokhari, H.; Rahman, S.u. Enhanced antibacterial activity of visible light activated sulfur-doped TiO2 nanoparticles against Vibrio cholerae. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2022, 147, 106731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubacka, A.; Diez, M.S.; Rojo, D.; Bargiela, R.; Ciordia, S.; Zapico, I.; Albar, J.P.; Barbas, C.; Martins dos Santos, V.A.P.; Fernández-García, M.; et al. Understanding the antimicrobial mechanism of TiO2-based nanocomposite films in a pathogenic bacterium. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulit-Prociak, J.; Długosz, O.; Staroń, A.; Radomski, P.; Domagała, D.; Banach, M. In vitro studies of titanium dioxide nanoparticles modified with glutathione as a potential drug delivery system. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2023, 12, 20230126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ion, R.; Necula, M.G.; Mazare, A.; Mitran, V.; Neacsu, P.; Schmuki, P.; Cimpean, A. Drug Delivery Systems Based on Titania Nanotubes and Active Agents for Enhanced Osseointegration of Bone Implants. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 854–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadrami, H.A.; Shoudri, R.A.M. Titanium Oxide (TiO2) Nanoparticles for Treatment of Wound Infection (Preprint). Preprints 2020, 2020, 110307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Kuang, W.; Shi, L.; Ye, X.; Yang, Y.; Xie, X.; Shi, Q.; Tan, S. Carbon quantum dot-decorated TiO2 for fast and sustainable antibacterial properties under visible-light. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 777, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khater, M.S.; Kulkarni, G.R.; Khater, S.S.; Gholap, H.; Patil, R. Study to elucidate effect of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on bacterial membrane potential and membrane permeability. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 035005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, J.R.; Rice, C.V. Solid-state NMR studies of bacterial lipoteichoic acid adsorption on different surfaces. Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson. 2008, 34, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagnout, C.; Jomini, S.; Dadhwal, M.; Caillet, C.; Thomas, F.; Bauda, P. Role of electrostatic interactions in the toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles toward Escherichia coli. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 92, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitre, S.P.; Yoon, T.P.; Scaiano, J.C. Titanium dioxide visible light photocatalysis: Surface association enables photocatalysis with visible light irradiation. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 4335–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Hasan, N.; Lintang, H.O.; Shamsuddin, M.; Yuliati, L. Photocatalytic removal of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid herbicide on copper oxide/titanium dioxide prepared by co-precipitation method. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 107, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, S.; Yadav, V.K.; Choudhary, N.; Alswieleh, A.M.; Sharma, A.K.; Bhardwaj, A.K.; Khan, S.H.; Yadav, K.K.; Cheon, J.-K.; Jeon, B.-H. Onion Peel Waste Mediated-Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Phytotoxicity on Mung Bean and Wheat Plant Growth. Materials 2022, 15, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López de Dicastillo, C.; Guerrero Correa, M.; Martínez, F.B.; Streitt, C.; José Galotto, M. Antimicrobial Effect of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. In Antimicrobial Resistance—A One Health Perspective; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2021; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Gomaa, E.Z. Silver nanoparticles as an antimicrobial agent: A case study on Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli as models for Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 63, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Kovochich, M.; Brant, J.; Hotze, M.; Sempf, J.; Oberley, T.; Sioutas, C.; Yeh, J.I.; Wiesner, M.R.; Nel, A.E. Comparison of the abilities of ambient and manufactured nanoparticles to induce cellular toxicity according to an oxidative stress paradigm. Nano Lett 2006, 6, 1794–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruskov, V.I.; Karp, O.E.; Garmash, S.A.; Shtarkman, I.N.; Chernikov, A.V.; Gudkov, S.V. Prolongation of oxidative stress by long-lived reactive protein species induced by X-ray radiation and their genotoxic action. Free Radic. Res. 2012, 46, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruskov, V.I.; Malakhova, L.V.; Masalimov, Z.K.; Chernikov, A.V. Heat-induced formation of reactive oxygen species and 8-oxoguanine, a biomarker of damage to DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmistrov, D.E.; Simakin, A.V.; Smirnova, V.V.; Uvarov, O.V.; Ivashkin, P.I.; Kucherov, R.N.; Ivanov, V.E.; Bruskov, V.I.; Sevostyanov, M.A.; Baikin, A.S.; et al. Bacteriostatic and Cytotoxic Properties of Composite Material Based on ZnO Nanoparticles in PLGA Obtained by Low Temperature Method. Polymers 2022, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, S.H.; Abd Salam, N.R.; Zainal, N.; Kadir Basha, R.; Talib, R.A. Antimicrobial Activity of TiO2 Nanoparticle-Coated Film for Potential Food Packaging Applications. Int. J. Photoenergy 2014, 2014, 945930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Kumar, S.; Ahmed, S. Microwave-assisted one-step biosynthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: Antibacterial, antioxidant, and photocatalytic properties. Kuwait J. Sci. 2024, 51, 100203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimbone, M.; Buccheri, M.A.; Cacciato, G.; Sanz, R.; Rappazzo, G.; Boninelli, S.; Reitano, R.; Romano, L.; Privitera, V.; Grimaldi, M.G. Photocatalytical and antibacterial activity of TiO2 nanoparticles obtained by laser ablation in water. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 165, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, M.A.; Rodríguez-Páez, J.E. Amorphous TiO2 nanoparticles: Synthesis and antibacterial capacity. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2017, 459, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahjat, H.H.; Ismail, R.A.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Jabir, M.S. Magnetic Field-Assisted Laser Ablation of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Water for Anti-Bacterial Applications. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2021, 31, 3649–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Albetran, H.M.; Alheshibri, M.H.; Timoumi, A.; Algarou, N.A.; Akhtar, S.; Slimani, Y.; Almessiere, M.A.; Alahmari, F.S.; Baykal, A.; et al. Synthesis of Electrospun TiO2 Nanofibers and Characterization of Their Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Potential against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.S.; Parveen, A.; Koppalkar, A.R.; Prasad, M.V.N.A. Effect of nano-titanium dioxide with different antibiotics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechn. 2010, 1, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowska, W.; Wojtczak, I.; Railean, V.; Bekissanova, Z.; Trykowski, G.; Buszewski, B.; Sprynskyy, M. Pyrolized Diatomaceous Biomass Doped with Epitaxially Growing Hybrid Ag/TiO2 Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterisation and Antibacterial Application. Materials 2023, 16, 4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomary, M.N.; Ansari, M.A. Proanthocyanin—Capped biogenic TiO2 nanoparticles with enhanced penetration, antibacterial and ros mediated inhibition of bacteria proliferation and biofilm formation: A comparative approach. Chem. A Eur. J. 2021, 27, 5817–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlović, V.P.; Vujančević, J.D.; Mašković, P.; Ćirković, J.; Papan, J.M.; Kosanović, D.; Dramićanin, M.D.; Petrović, P.B.; Vlahović, B.; Pavlović, V.B. Structure and enhanced antimicrobial activity of mechanically activated nano TiO2. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 102, 7735–7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumdieck, S.P.; Boichot, R.; Gorthy, R.; Land, J.G.; Lay, S.; Gardecka, A.J.; Polson, M.I.J.; Wasa, A.; Aitken, J.E.; Heinemann, J.A.; et al. Nanostructured TiO2 anatase-rutile-carbon solid coating with visible light antimicrobial activity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, F.; Tucci, P. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: A Risk for Human Health? Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, B.; Gao, W.; Wang, S.; Xu, F.; Lu, T. Cytotoxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles differs in four liver cells from human and rat. Compos. Part B Eng. 2011, 42, 2136–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacova, J.; Knotek, P.; Kopecka, K.; Hromadko, L.; Capek, J.; Nyvltova, P.; Bruckova, L.; Schröterova, L.; Sestakova, B.; Palarcik, J.; et al. Evaluating the Use of TiO2 Nanoparticles for Toxicity Testing in Pulmonary A549 Cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 4211–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopiuk, V.; Yefimova, S.; Onishchenko, A.; Kapustnik, V.; Myasoedov, V.; Maksimchuk, P.; Butov, D.; Bespalova, I.; Tkachenko, A. Assessing the Cytotoxicity of TiO2−x Nanoparticles with a Different Ti3+(Ti2+)/Ti4+ Ratio. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 201, 3117–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahamed, M.; Khan, M.A.M.; Akhtar, M.J.; Alhadlaq, H.A.; Alshamsan, A. Ag-doping regulates the cytotoxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles via oxidative stress in human cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ul-Hamid, A.; Baig, N.; Haider, A.; Hakeem, A.S.; Ikram, M. Using biologically synthesized TiO2 nanoparticles as potential remedy against multiple drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus of bovine mastitis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Hassan, I.A.; Abbas, A.K.; Ibrahim, I.M.; Shallal, Z.S. Characterization and antimicrobial effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles produced by laser ablation. Indian J. Nat. Sci. 2018, 8, 14286–14292. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.S.; Amna, T.; Mishra, A.; Yun, S.-I.; Kim, H.-C.; Kim, H.-Y.; Khil, M.-S. Fabrication, Characterization and Antibacterial Effect of Novel Electrospun TiO2 Nanorods on a Panel of Pathogenic Bacteria. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2012, 8, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ağçeli, G.K.; Hammachi, H.; Kodal, S.P.; Cihangir, N.; Aksu, Z. A Novel Approach to Synthesize TiO2 Nanoparticles: Biosynthesis by Using Streptomyces sp. HC1. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 3221–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Mohsin, M.; Ahmad, T.; Sardar, M. Alpha amylase assisted synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles: Structural characterization and application as antibacterial agents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niño-Martínez, N.; Salas Orozco, M.F.; Martínez-Castañón, G.-A.; Torres Méndez, F.; Ruiz, F. Molecular Mechanisms of Bacterial Resistance to Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, M.T.; Bakr, B.A.; Shahin, Y.H.; Elwakil, B.H.; Abu-Serie, M.M.; Aljohani, F.S.; Bekhit, A.A.; Keramidas, A. Novel Synthesis of Titanium Oxide Nanoparticles: Biological Activity and Acute Toxicity Study. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2021, 2021, 8171786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadrami, H.A.; Baqasi, A.; Iqbal, J.; Shoudri, R.A.; Ashshi, A.M.; Azhar, E.I.; Al-Hazmi, F.; Al-Ghamdi, A.; Wageh, S. Antibacterial Applications of Anatase TiO2 Nanoparticle. Am. J. Nanomater. 2017, 5, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashan, K.S.; Sulaima, G.M.; Ameer, F.A.A.; Marzoog, T.R. Antibacterial Activity of TiO2 Nanoparticles Suspension Induced by Laser Ablation in Liquid. Eng. Technol. J. 2014, 32, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.Y.; Aly, U.F.; Abd El-Baky, R.M.; Waly, N.G.F.M. Effect of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the expression of efflux pump and quorum-sensing genes in MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Alrazaq Hassan, M.; Hassan, N.A.; Khudhair Khalaf, S.; Hakiem Tawfieq, A. Nanoparticles on pathogenic strains of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Diyala J. Med. 2024, 26, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimi, A.K.; Ahmed, H.M.; Wahab, M.; Katheria, S.; Wabaidur, S.M.; Eldesoky, G.E.; Islam, M.A.; Rane, K.P.; Zeng, W. Synthesis and Applications of Green Synthesized TiO2 Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic Dye Degradation and Antibacterial Activity. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 060388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, A.B.; Milosavljevic, V.; Fialova, T.; Smerkova, K.; Michalkova, H.; Svec, P.; Antal, P.; Kopel, P.; Adam, V.; Zurek, L.; et al. Synthesis and characterization of TiO2 nanoparticles combined with geraniol and their synergistic antibacterial activity. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunath, K.; Reddy Yadav, L.S.; Jayalakshmi, T.; Reddy, V.; Rajanaika, H.; Nagaraju, G. Ionic liquid assisted hydrothermal synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles: Photocatalytic and antibacterial activity. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2018, 7, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaq, Z.; Khalid, A.; Ahmad, P.; Farooq, M.; Khandaker, M.U.; Sulieman, A.; Rehman, I.U.; Shakeel, S.; Khan, A. Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Potency of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: A Cost-Effective and Environmentally Friendly Media for Treatment of Air and Wastewater. Catalysts 2021, 11, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, R.; Fadillah, G.; Ohira, S.-I.; Fajarwati, F.I.; Setyorini, D.A.; Saputra, A. Facile green synthesis of Ag doped TiO2 nanoparticles using maple leaf for bisphenol-A degradation and its antibacterial properties. Mater. Today Sustain. 2024, 26, 100752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baamer, D.F.; Helmy, E.T.; Mostafa, M.M.M.; Pan, J.H. Synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles using different routes with enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial properties. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 15780–15789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouerghi, O.; Geesi, M.H.; Ibnouf, E.O.; Ansari, M.J.; Alam, P.; Elsanousi, A.; Kaiba, A.; Riadi, Y. Sol-gel synthesized rutile TiO2 nanoparticles loaded with cardamom essential oil: Enhanced antibacterial activity. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 64, 102581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraj, N.; Anjusree, G.S.; Madhavan, A.A.; Priyanka, P.; Sankar, D.; Nisha, N.; Lakshmi, S.V.; Jayakumar, R.; Balakrishnan, A.; Biswas, R. Synthesis and Anti-Staphylococcal Activity of TiO2 Nanoparticles and Nanowires in Ex Vivo Porcine Skin Model. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, B.K.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, D. Green synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica leaf extract and evaluation of their antibacterial activity. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 124, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, F.; Farghaly, U.; Abd El-Baky, R.M.; Waly, N. Comparative Study of Antibacterial Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Alone and in Combination with Antibiotics on MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 3393–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, S.; Ramalingam, C. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce bacterial membrane rupture by reactive oxygen species generation. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2016, 14, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pişkin, S.; Palantöken, A.; Yılmaz, M.S. Antimicrobial activity of synthesized TiO2 nanoparticles. In Proceedings of the ICETET, Phuket, Thailand, 7–8 December 2013; pp. 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Murugan, K.; Dinesh, D.; Kavithaa, K.; Paulpandi, M.; Ponraj, T.; Alsalhi, M.S.; Devanesan, S.; Subramaniam, J.; Rajaganesh, R.; Wei, H.; et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: Mosquitocidal potential and anticancer activity on human breast cancer cells (MCF-7). Parasitol. Res. 2015, 115, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Ambreen, B.; Ali, J.; Shahid, I. Effects of solvent on the structure and properties of titanium dioxide nanoparticles and their antibacterial activity. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2019, 38, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albukhaty, S.; Al-Bayati, L.; Al-Karagoly, H.; Al-Musawi, S. Preparation and characterization of titanium dioxide nanoparticles andin vitroinvestigation of their cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Anim. Biotechnol. 2020, 33, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, E.; Mohammadi, M.; Yazdanian, M.; Alam, M.; Abbasi, K.; Hosseini, H.M.; Tavakolizadeh, M.; Khayatan, D.; Hassani, Z.; Tebyaniyan, H. Antimicrobial properties of green synthesized novel TiO2 nanoparticles using Iranian propolis extracts. J. Basic Microbiol. 2023, 63, 1030–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Masoudi, L.M.; Alqurashi, A.S.; Abu Zaid, A.; Hamdi, H. Characterization and Biological Studies of Synthesized Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles from Leaf Extract of Juniperus phoenicea (L.) Growing in Taif Region, Saudi Arabia. Processes 2023, 11, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzhoseyni, Z.; Rashki, S.; Nazari-Alam, A. Evaluation of the inhibitory effects of TiO2 nanoparticle and Ganoderma lucidum extract against biofilm-producing bacteria isolated from clinical samples. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anupong, W.; On-uma, R.; Jutamas, K.; Salmen, S.H.; Alharbi, S.A.; Joshi, D.; Jhanani, G.K. Antibacterial, antifungal, antidiabetic, and antioxidant activities potential of Coleus aromaticus synthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieshy, V.; Chokkattu, J.J.; Rajeshkumar, S.; Neeharika, S. Mechanism of Action of Clove and Ginger Herbal Formulation-Mediated TiO2 Nanoparticles Against Lactobacillus Species: An In Vitro Study. J. Adv. Oral Res. 2023, 14, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korde, S.A.; Thombre, P.B.; Dipake, S.S.; Sangshetti, J.N.; Rajbhoj, A.S.; Gaikwad, S.T. Neem gum (Azadirachta indicia) facilitated green synthesis of TiO2 and ZrO2 nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 153, 110777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, O.S.; Ishii, K.; Kato, K. L-tryptophan-titanium oxide nanoparticles showed selective anti-Toxoplasma gondii activity and improved host biocompatibility. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alabdallah, N.M.; Irshad, M.A.; Rizwan, M.; Nawaz, R.; Inam, A.; Mohsin, M.; Khurshid, I.; Alharby, H.F.; Bamagoos, A.A.; Ali, S. Synthesis, characterization and antifungal potential of titanium dioxide nanoparticles against fungal disease (Ustilago tritici) of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Environ. Res. 2023, 228, 115852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metwally, R.A.; Soliman, S.A.; Abdalla, H.; Abdelhameed, R.E. Trichoderma cf. asperellum and plant-based titanium dioxide nanoparticles initiate morphological and biochemical modifications in Hordeum vulgare L. against Bipolaris sorokiniana. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cao, X.; Du, H.; Guo, X.; Han, Y.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.; Xing, B.; Xiao, H. Adverse effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on beneficial gut bacteria and host health based on untargeted metabolomics analysis. Environ. Res. 2023, 228, 115921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, A.M.; Harisankar, A.; Salini, P.S.; John, B.; SarojiniAmma, S.; Devassy, M.T. Green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles using Beta vulgaris extract and the evaluation of their photocatalytic and antibacterial activity. Ionics 2024, 30, 4257–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hkeem Ibrahem, K.; Ali, F.A.; Abdulla Sorchee, S.M. Biosynthesis and characterization with antimicrobial activity of TiO2 nanoparticles using probiotic Bifidobacterium bifidum. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2020, 66, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunagund, S.M.; Desai, V.R.; Kadadevarmath, J.S.; Barretto, D.A.; Vootla, S.; Sidarai, A.H. Biogenic and chemogenic synthesis of TiO2 NPs via hydrothermal route and their antibacterial activities. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 97438–97444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matboo, S.A.; Nazari, S.; Niapour, A.; Niri, M.V.; Asgari, E.; Mokhtari, S.A. Antibacterial effect of TiO2 modified with poly-amidoamine dendrimer—G3 on S. aureus and E. coli in aqueous solutions. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 85, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, D.; Birhan, D.; Kiziltas, H. Thermal, photocatalytic, and antibacterial properties of calcinated nano-TiO2/polymer composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 251, 123067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, K.; Vijayalakshmi, S.; Phuruangrat, A.; Revathi, V.; Verma, U. Multifunctional Applications of Microwave-Assisted Biogenic TiO2 Nanoparticles. J. Clust. Sci. 2019, 30, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, J.; Agrawal, S.; Panwar, V.; Parveen, A.; Pal, K. Antibacterial properties of silver doped TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized via sol-gel technique. Macromol. Res. 2016, 24, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, T.N.; Riyazuddin; Babji, P.; Ahmad, N.; Khan, R.A.; Hassan, I.; Shahzad, S.A.; Husain, F.M. Green synthesis and structural classification of Acacia nilotica mediated-silver doped titanium oxide (Ag/TiO2) spherical nanoparticles: Assessment of its antimicrobial and anticancer activity. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, M.; Vigneshwari, P.; Natarajan, D.; Kandasamy, S.; Alsehli, M.; Elfasakhany, A.; Pugazhendhi, A. Synthesis and characterization of TiO2 NPs by aqueous leaf extract of Coleus aromaticus and assess their antibacterial, larvicidal, and anticancer potential. Environ. Res. 2021, 200, 111335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, M.; Srinivasan, S.; Gnanasekaran, C.; Ramachandran, G.; Chelliah, C.K.; Rajivgandhi, G.; Maruthupandy, M.; Quero, F.; Li, W.-J.; Hayder, G.; et al. Synthesis and characterization of marine seagrass (Cymodocea serrulata) mediated titanium dioxide nanoparticles for antibacterial, antibiofilm and antioxidant properties. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 189, 106595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathesh, A.; Mohanprasanth, A.; Saravanan, M. Synthesis and characterization of Spirulina-mediated titanium dioxide nanoparticles: Antimicrobial activity against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2024, 39, 101225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Jaiswal, K.K.; Soni, S. Green synthesis of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles by using Mentha arvensis leaves extract and its antimicrobial properties. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2020, 50, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhoshkumar, T.; Rahuman, A.A.; Jayaseelan, C.; Rajakumar, G.; Marimuthu, S.; Kirthi, A.V.; Velayutham, K.; Thomas, J.; Venkatesan, J.; Kim, S.-K. Green synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Psidium guajava extract and its antibacterial and antioxidant properties. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2014, 7, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, A.; Siddiqui, V.U.; Rehman, W.U.; Akram, M.K.; Siddiqi, W.A.; Alosaimi, A.M.; Hussein, M.A.; Rafatullah, M. Green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles using Acorus calamus leaf extract and evaluating its photocatalytic and in vitro antimicrobial activity. Catalysts 2022, 12, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Limiñana, J.; Feregrino-Pérez, A.A.; Vega-González, M.; Escobar-Alarcón, L.; Cervantes-Chávez, J.A.; Esquivel, K. Green Synthesis via Eucalyptus globulus L. Extract of Ag-TiO2 Catalyst: Antimicrobial Activity Evaluation toward Water Disinfection Process. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shabib, N.A.; Husain, F.M.; Qais, F.A.; Ahmad, N.; Khan, A.; Alyousef, A.A.; Arshad, M.; Noor, S.; Khan, J.M.; Alam, P.; et al. Phyto-Mediated Synthesis of Porous Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles From Withania somnifera Root Extract: Broad-Spectrum Attenuation of Biofilm and Cytotoxic Properties Against HepG2 Cell Lines. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumari, J.; Magdalane, C.M.; Siddhardha, B.; Madhavan, J.; Ramalingam, G.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Arasu, M.V.; Ghilan, A.K.M.; Duraipandiayan, V.; Kaviyarasu, K. Synthesis of titanium oxide nanoparticles using Aloe barbadensis mill and evaluation of its antibiofilm potential against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 201, 111667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, V.H.; Jeice, A.R. Green fabrication of titanium dioxide nanoparticles and their applications in photocatalytic dye degradation and microbial activities. Chem. Phys. Impact 2023, 6, 100197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malarkodi, C.; Chitra, K.; Rajeshkumar, S.; Gnanajobitha, G.; Paulkumar, K.; Vanaja, M.; Annadurai, G. Novel eco-friendly synthesis of titanium oxide nanoparticles by using Planomicrobium sp. and its antimicrobial evaluation. Der Pharm. Sin. 2013, 4, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, B.; Murar, M.; Dhumale, V. Antimicrobial potential of TiO2 nanoparticles against MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2014, 10, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouerghi, O.; Geesi, M.H.; Riadi, Y.; Ibnouf, E.O. Limon-citrus extract as a capping/reducing agent for the synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: Characterization and antibacterial activity. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2022, 15, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, S.; Iftikhar, A.; Tauseef, S.; Ahmed, F.; Shuja, A.; Sherwani, S. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles. Fuuast J. Biol 2016, 6, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Nie, D.; Guo, X.; Xu, S.; Zhang, D.; Cao, F.; Guan, X. Effective control of the tomato wilt pathogen using TiO2 nanoparticles as a green nanopesticide. Environ.Sci. Nano 2023, 10, 1441–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
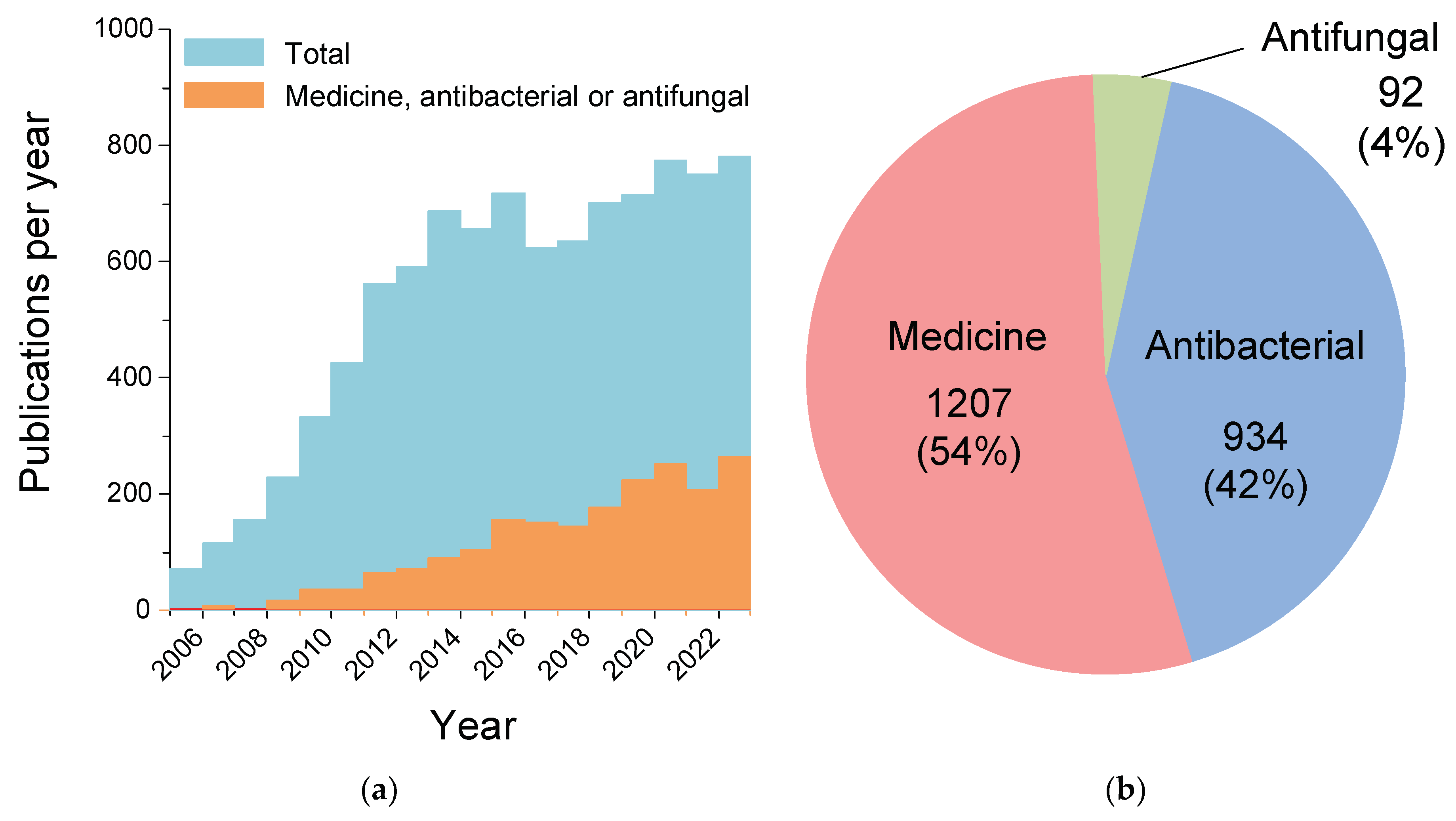
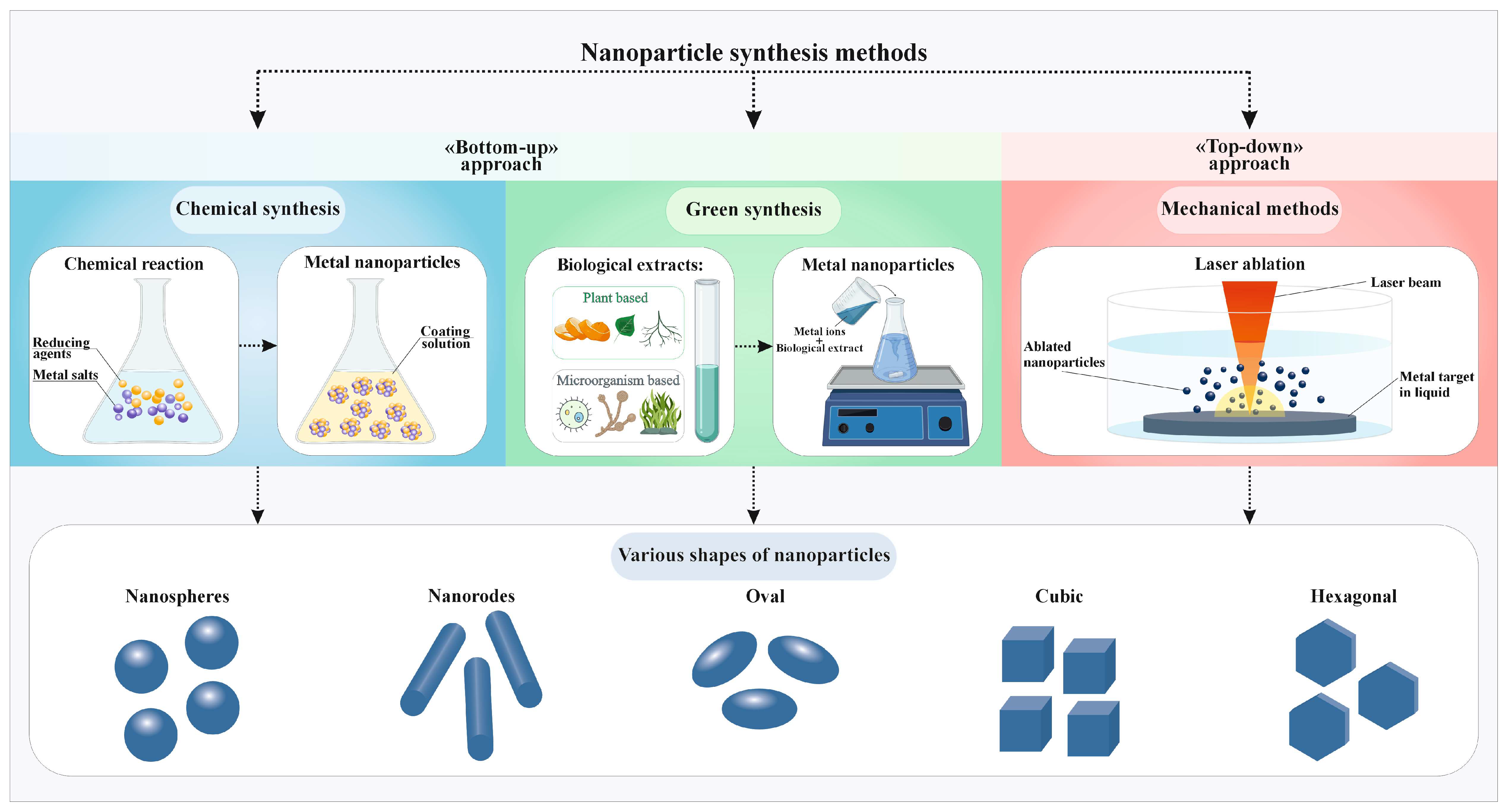
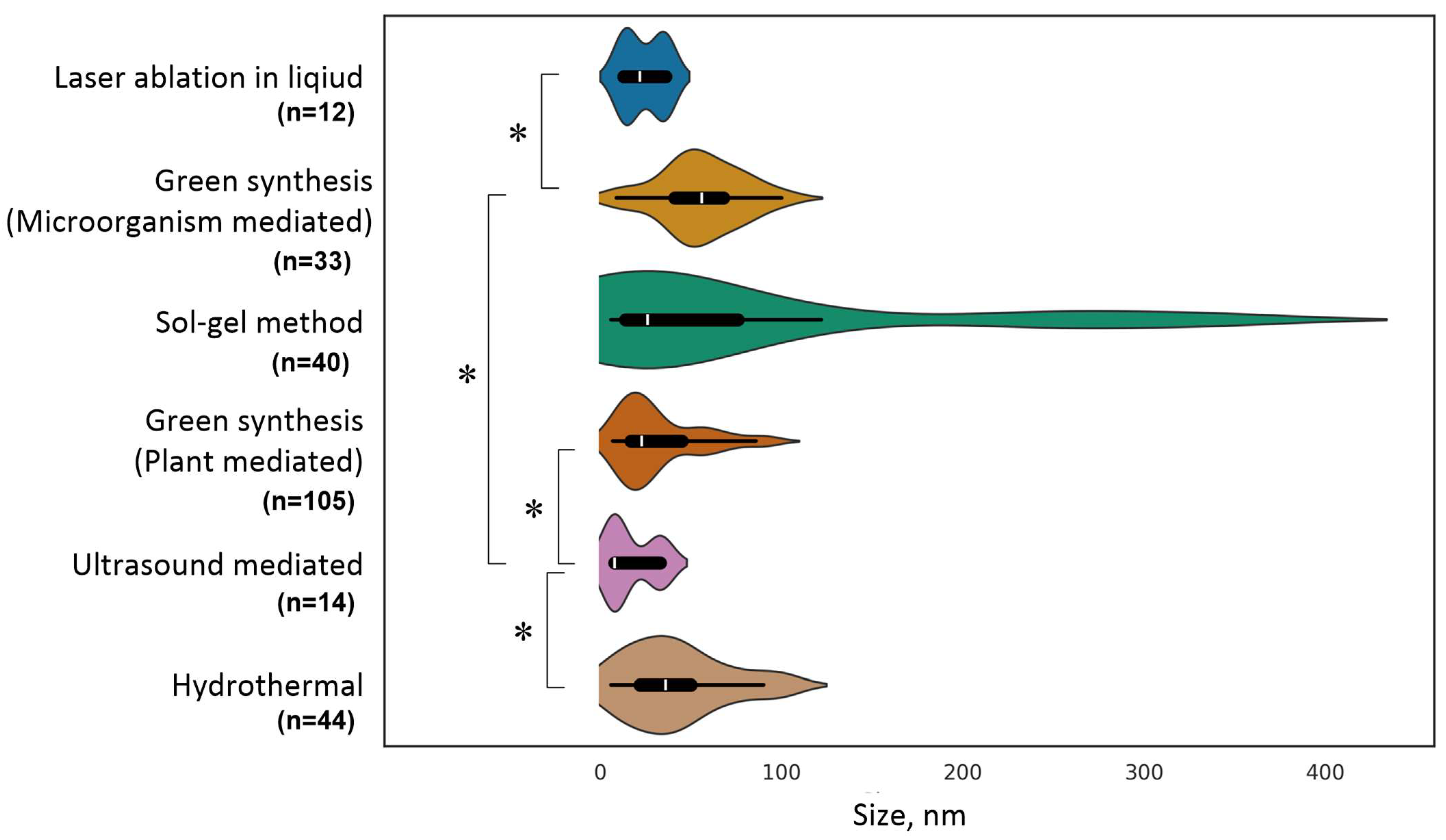
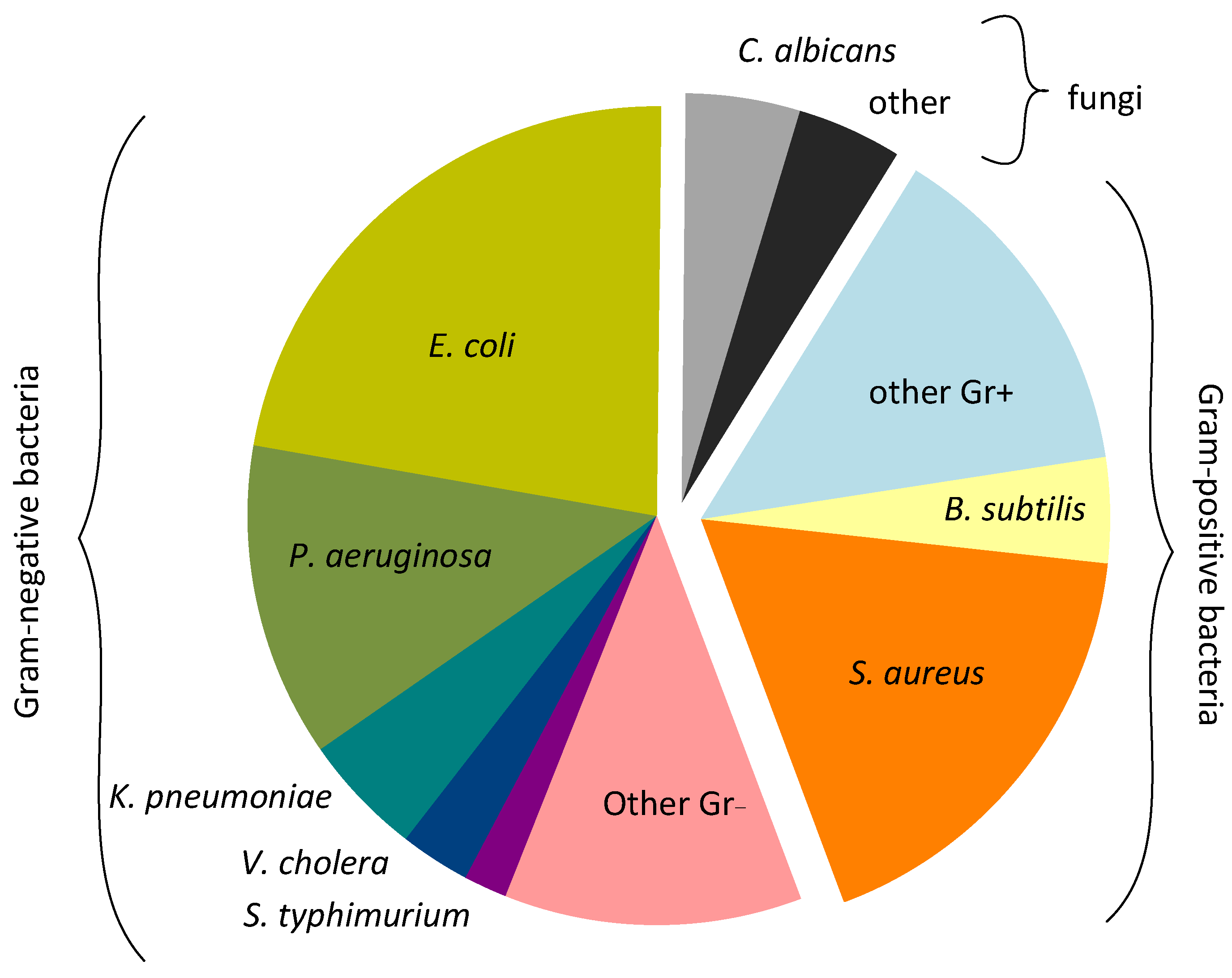
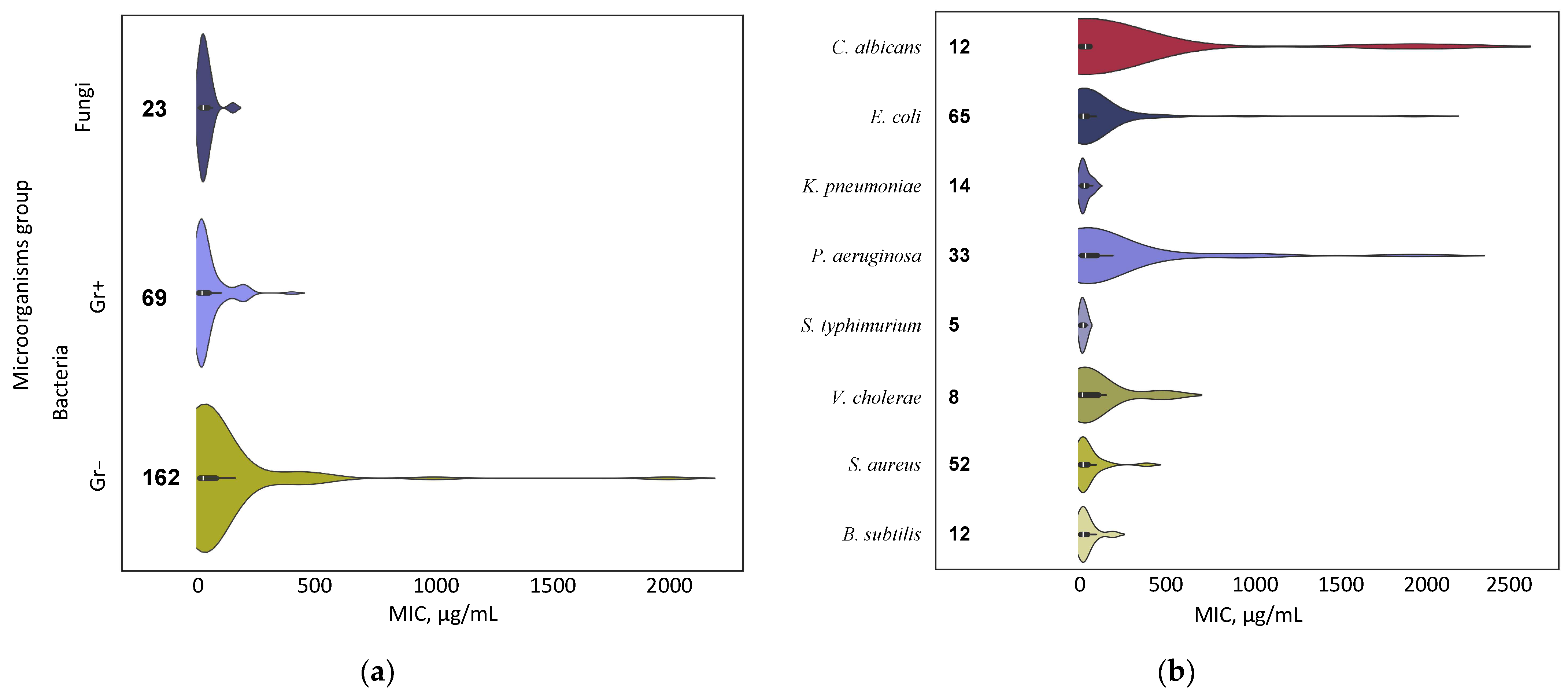
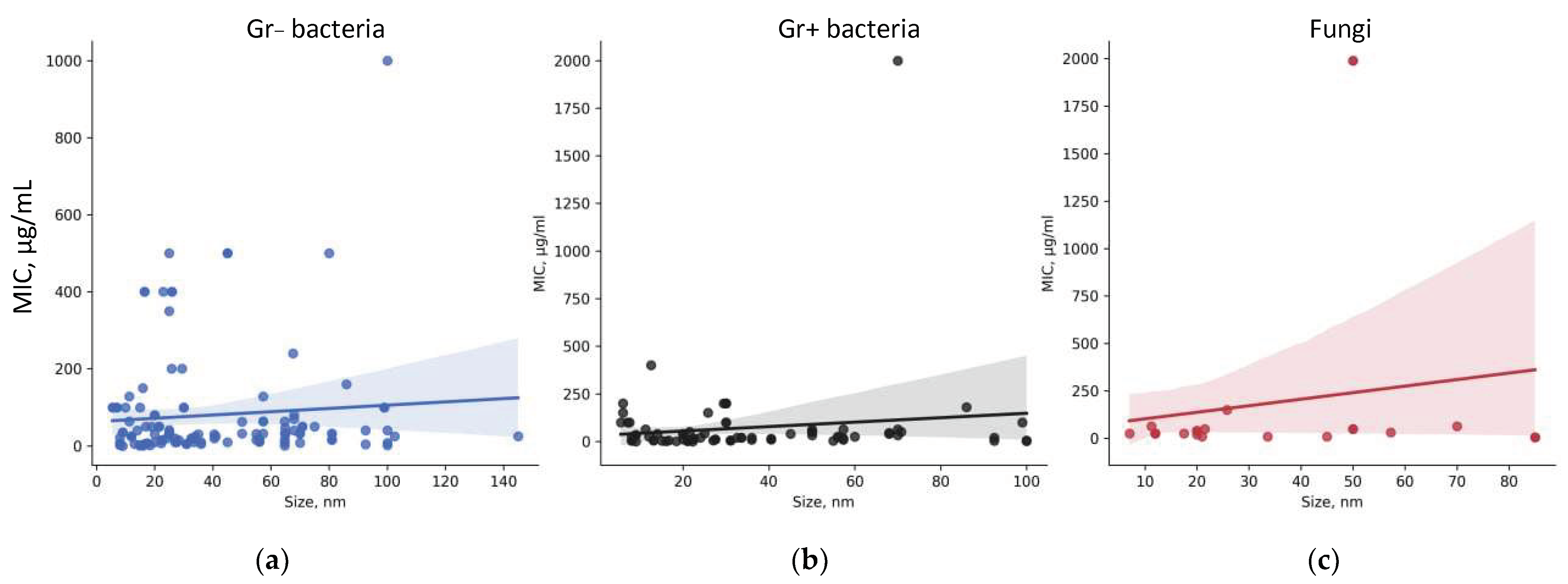
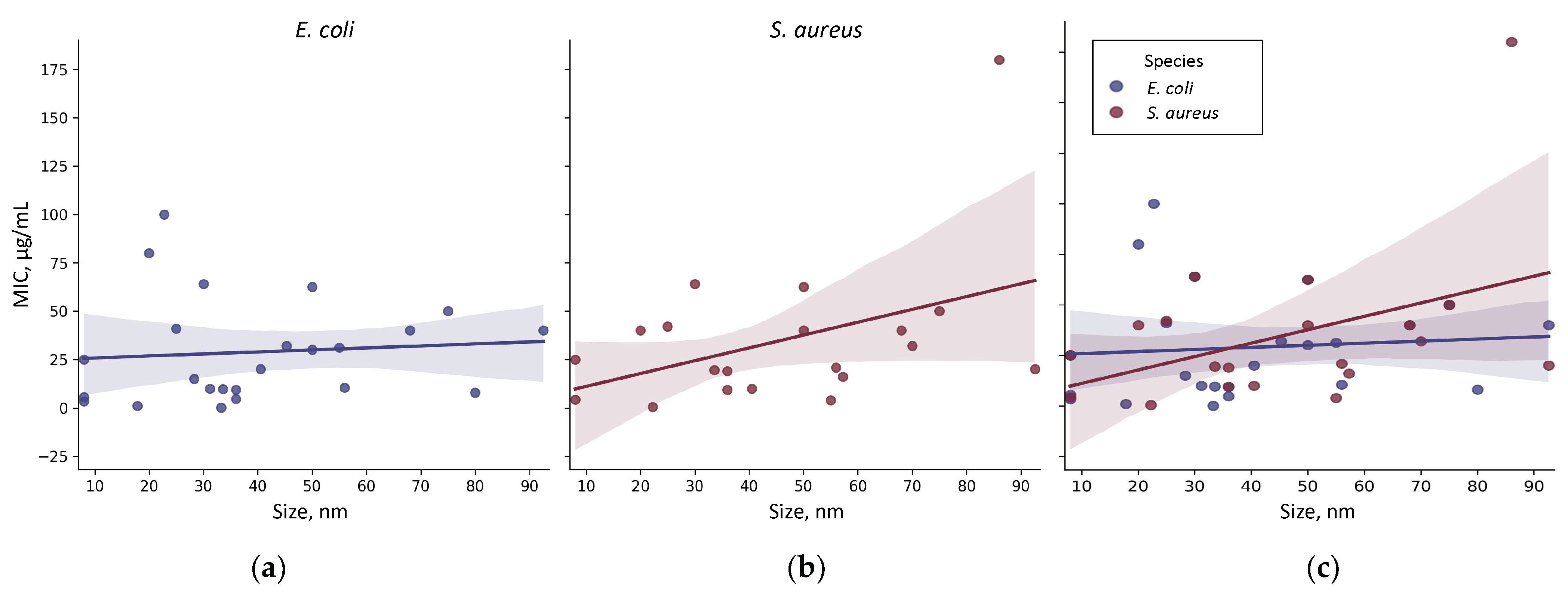

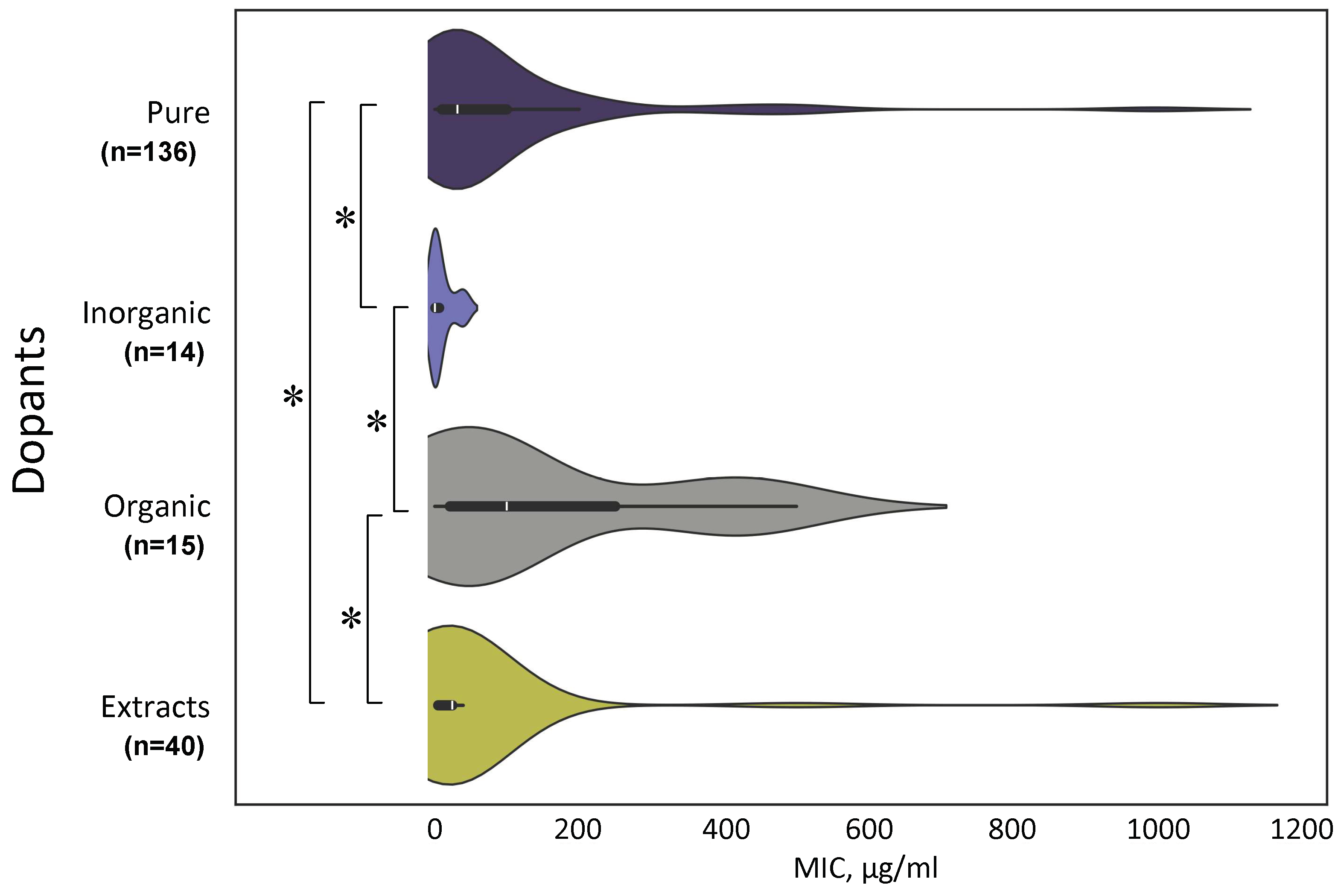

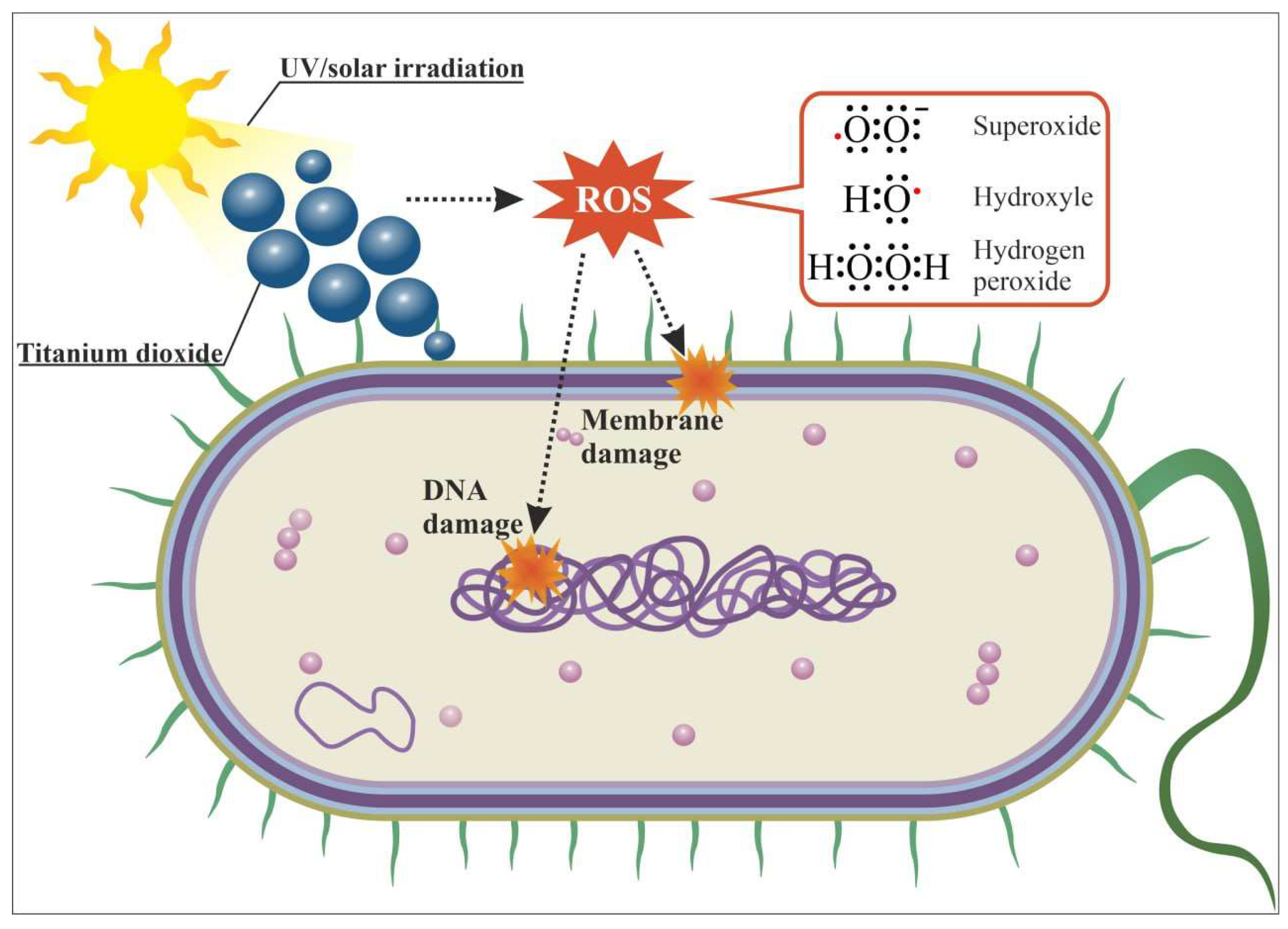
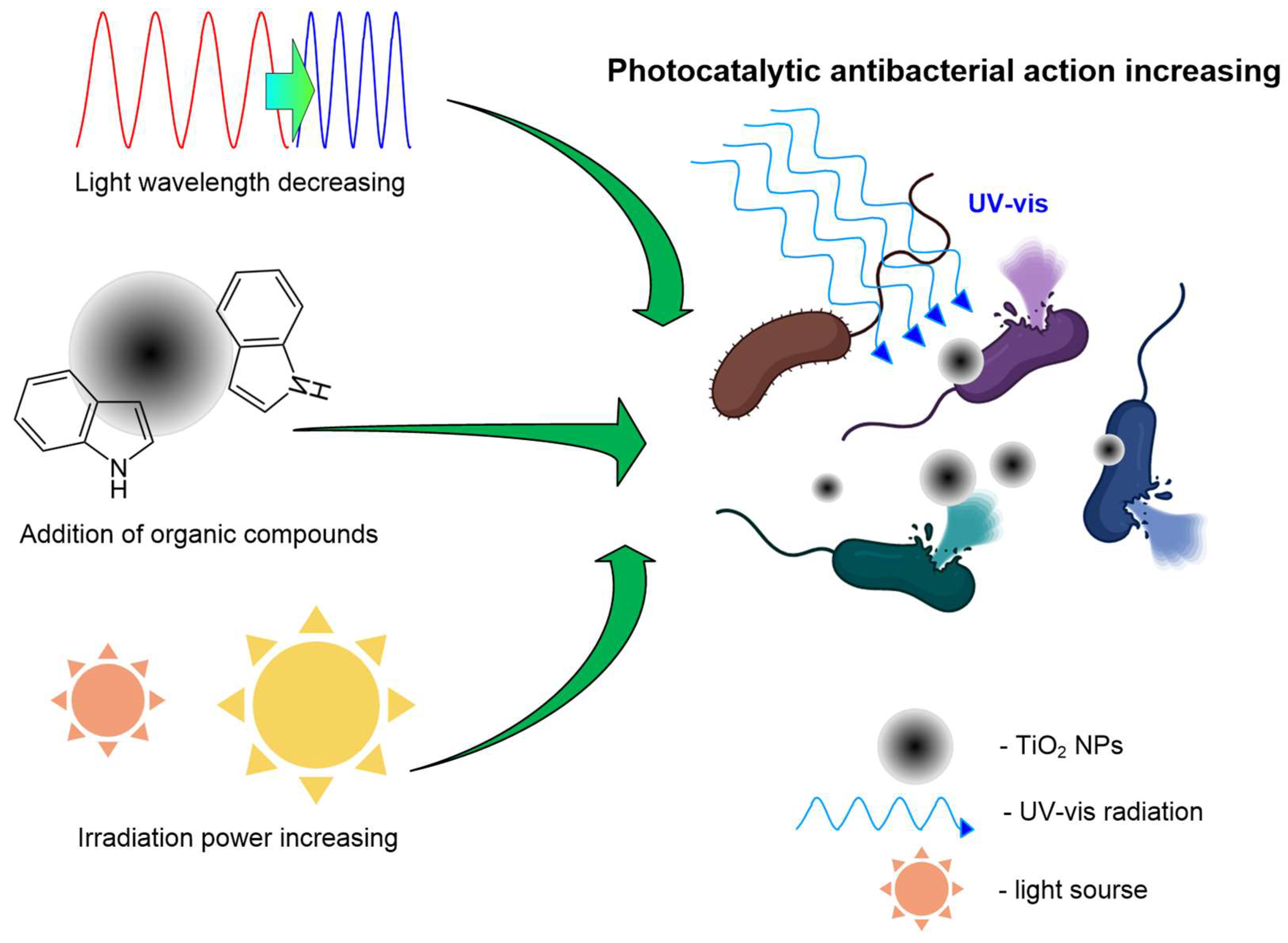
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serov, D.A.; Gritsaeva, A.V.; Yanbaev, F.M.; Simakin, A.V.; Gudkov, S.V. Review of Antimicrobial Properties of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910519
Serov DA, Gritsaeva AV, Yanbaev FM, Simakin AV, Gudkov SV. Review of Antimicrobial Properties of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(19):10519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910519
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerov, Dmitriy A., Ann V. Gritsaeva, Fatikh M. Yanbaev, Alexander V. Simakin, and Sergey V. Gudkov. 2024. "Review of Antimicrobial Properties of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 19: 10519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910519
APA StyleSerov, D. A., Gritsaeva, A. V., Yanbaev, F. M., Simakin, A. V., & Gudkov, S. V. (2024). Review of Antimicrobial Properties of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(19), 10519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910519








