CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated fech Knockout Zebrafish: Unraveling the Pathogenesis of Erythropoietic Protoporphyria and Facilitating Drug Screening
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
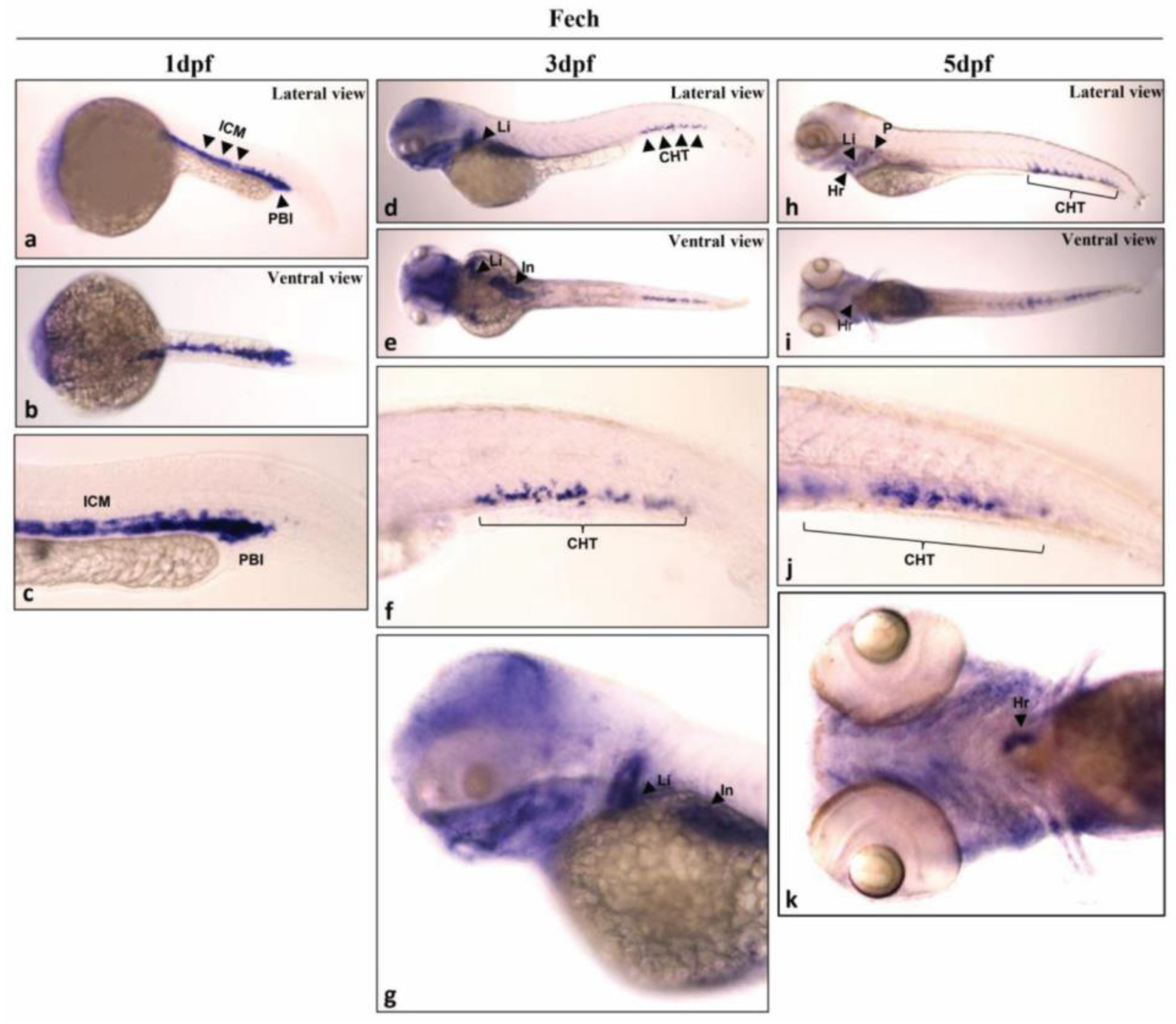
2.1. Analysis of Fech Expression in Different Larval Stages and Tissues of Zebrafish
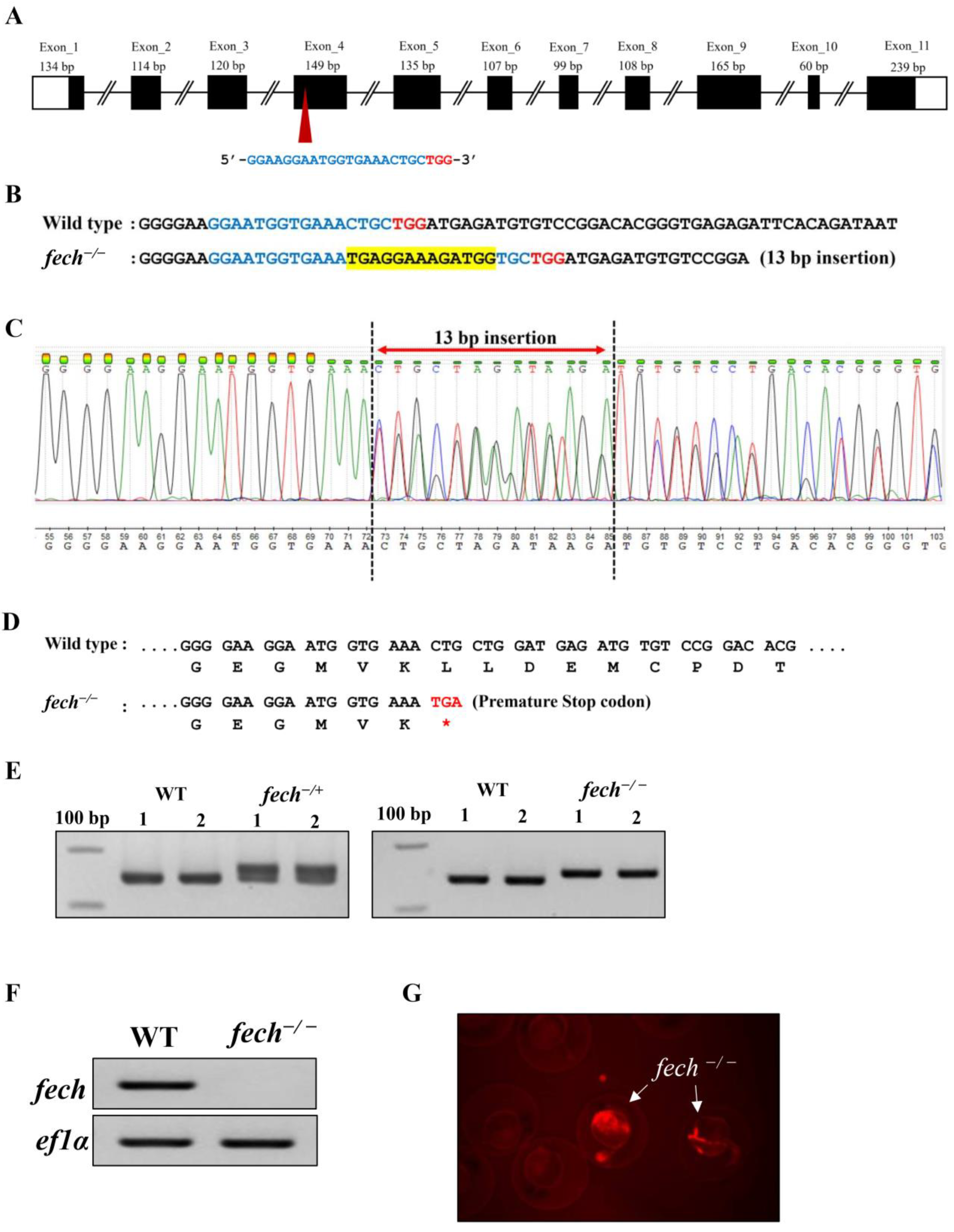
2.2. Generation of a Fech-Knockout Zebrafish Model Using CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing
2.3. Phenotypic and Physiological Effects of Fech Deletion in Zebrafish Larvae
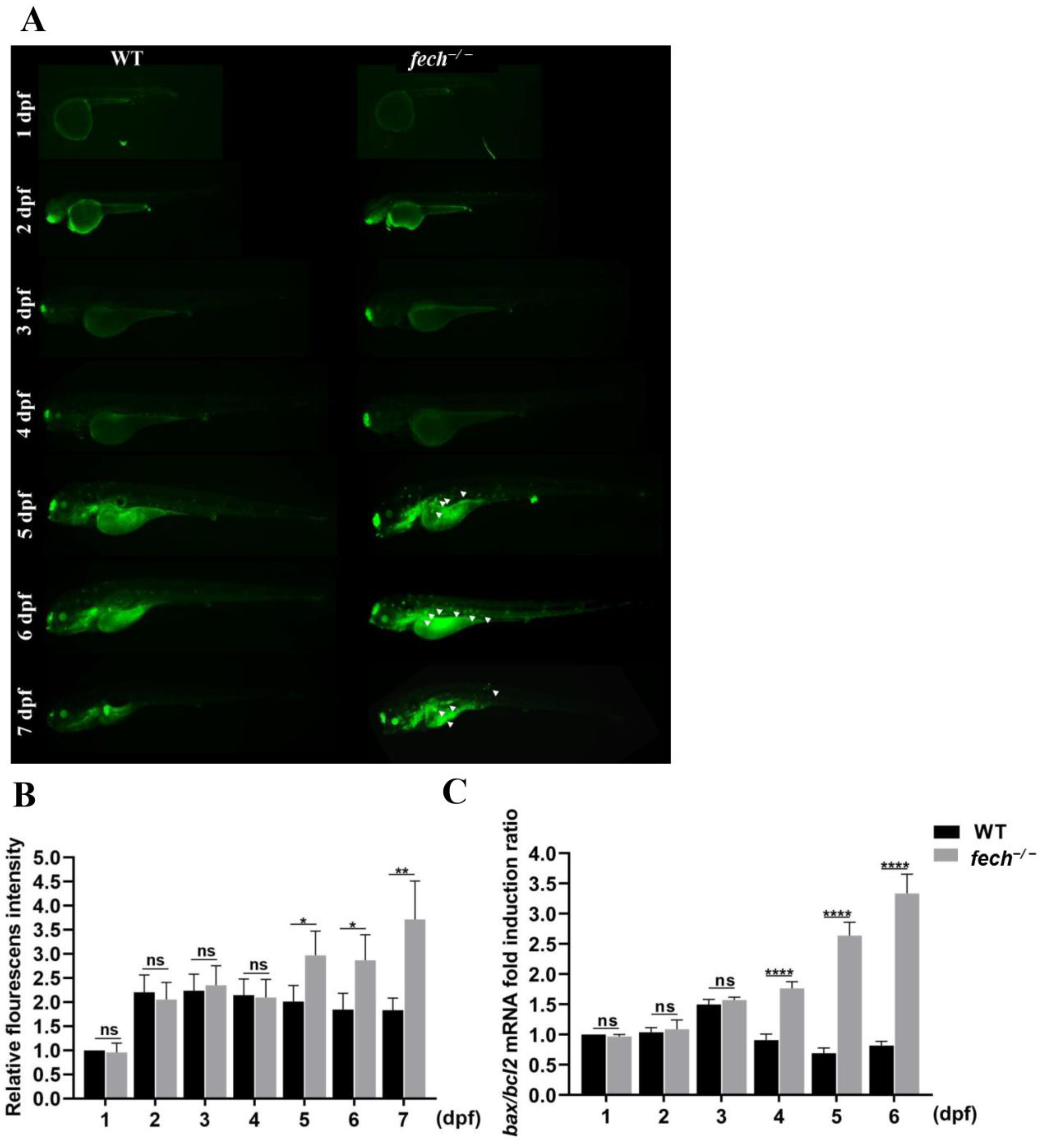
2.4. The Dynamics of PPIX Accumulation in fech−/− Larvae at Various Life Stages
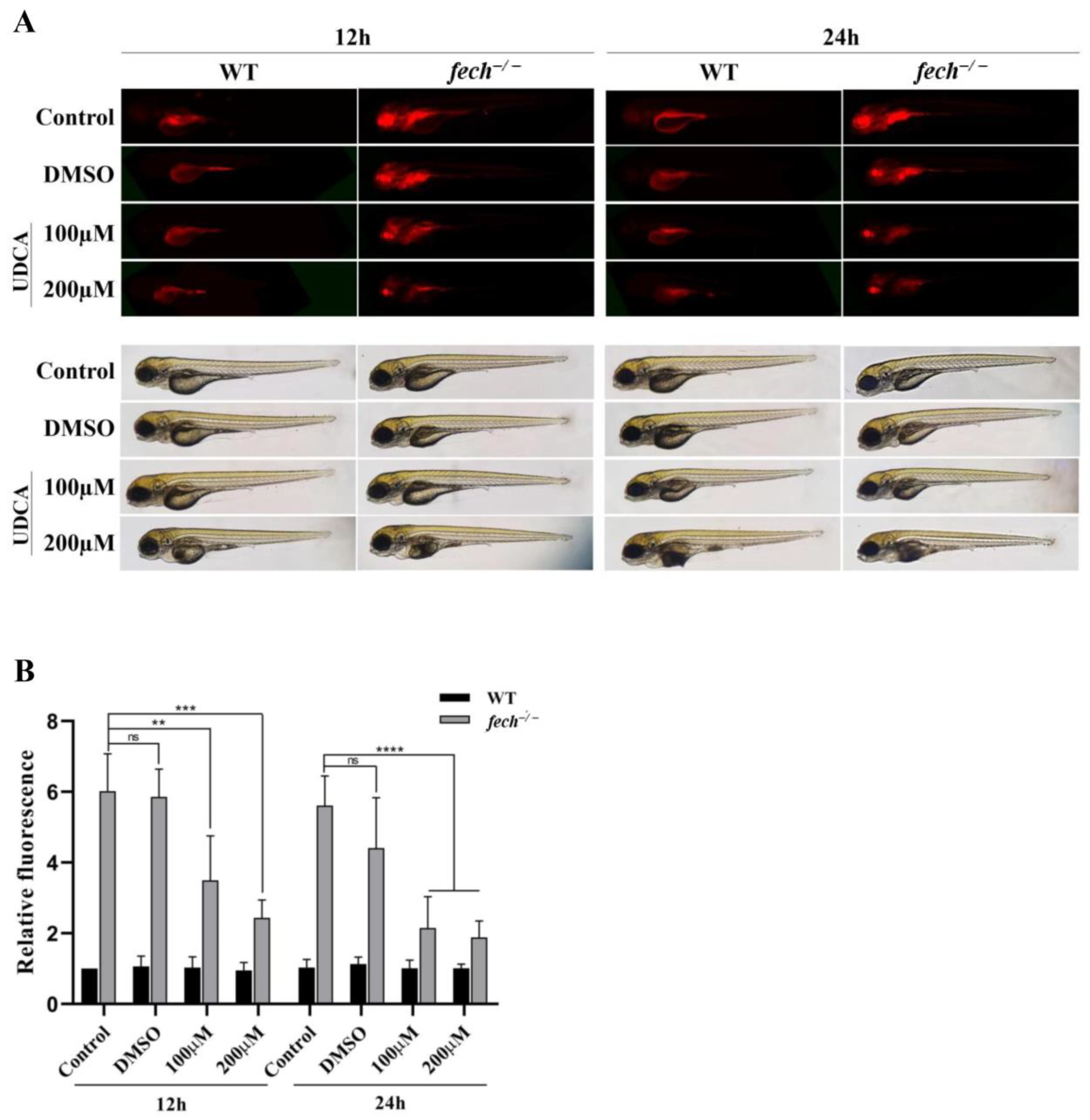
2.5. Attenuation of PPIX Accumulation in fech−/− Larvae following UDCA Treatment
2.6. Suppression of Apoptosis by UDCA Treatment of fech−/− Larvae
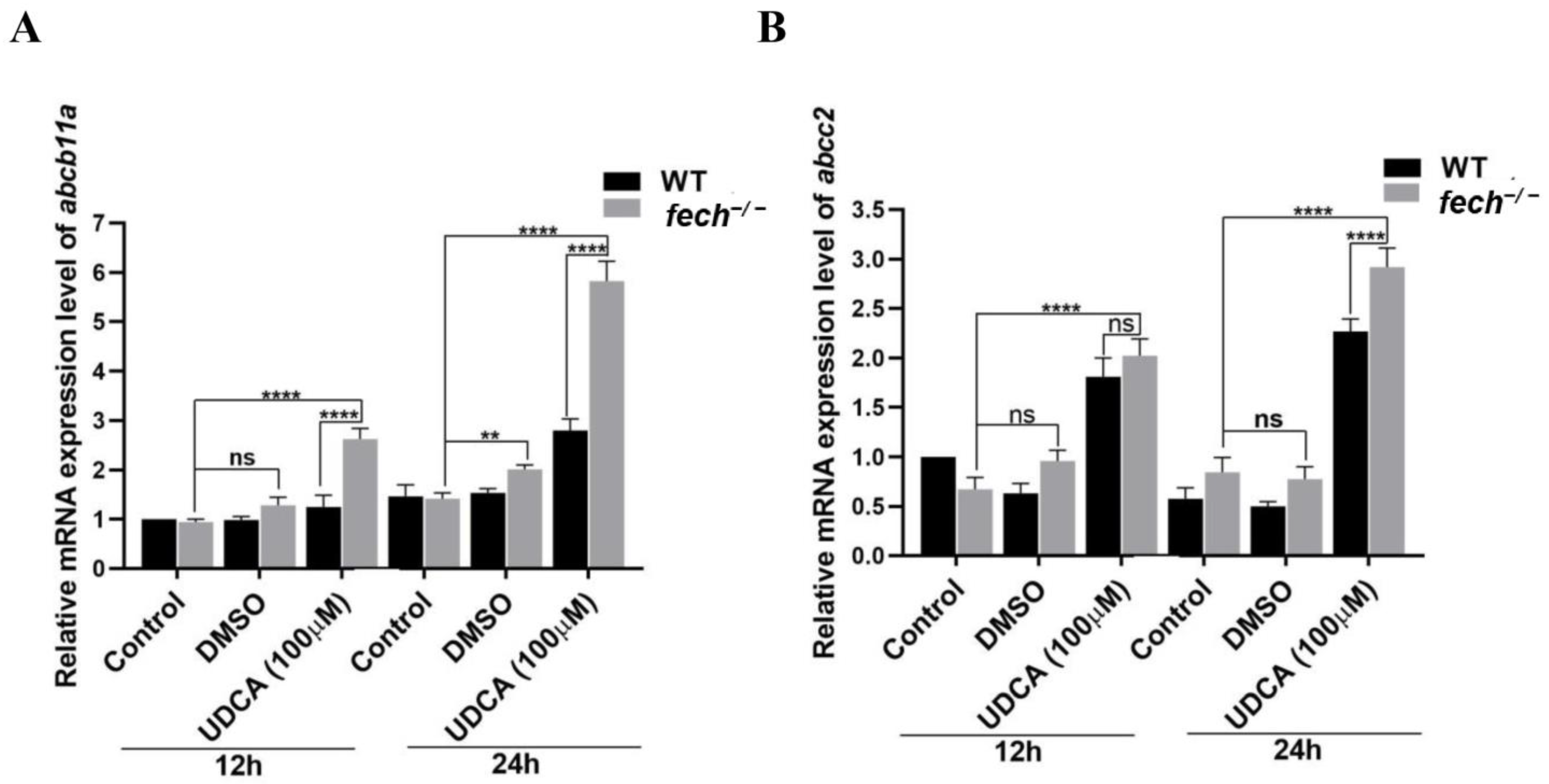
2.7. Activation of Bile Transportation-Related Genes by UDCA Treatment
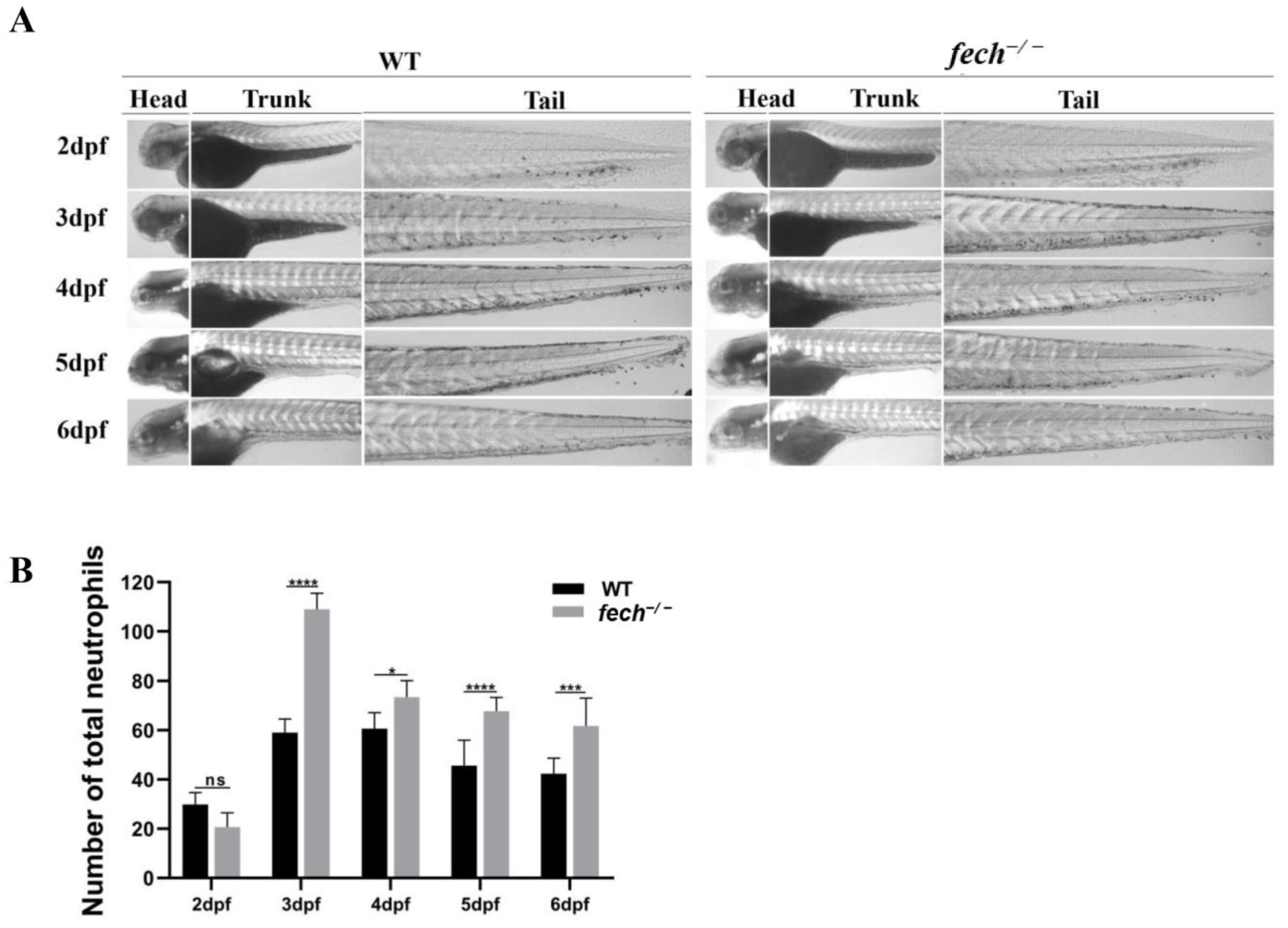
2.8. Temporal Changes in Neutrophil Production and Attenuation of Neutrophil Accumulation via UDCA Treatment in fech−/− Larvae
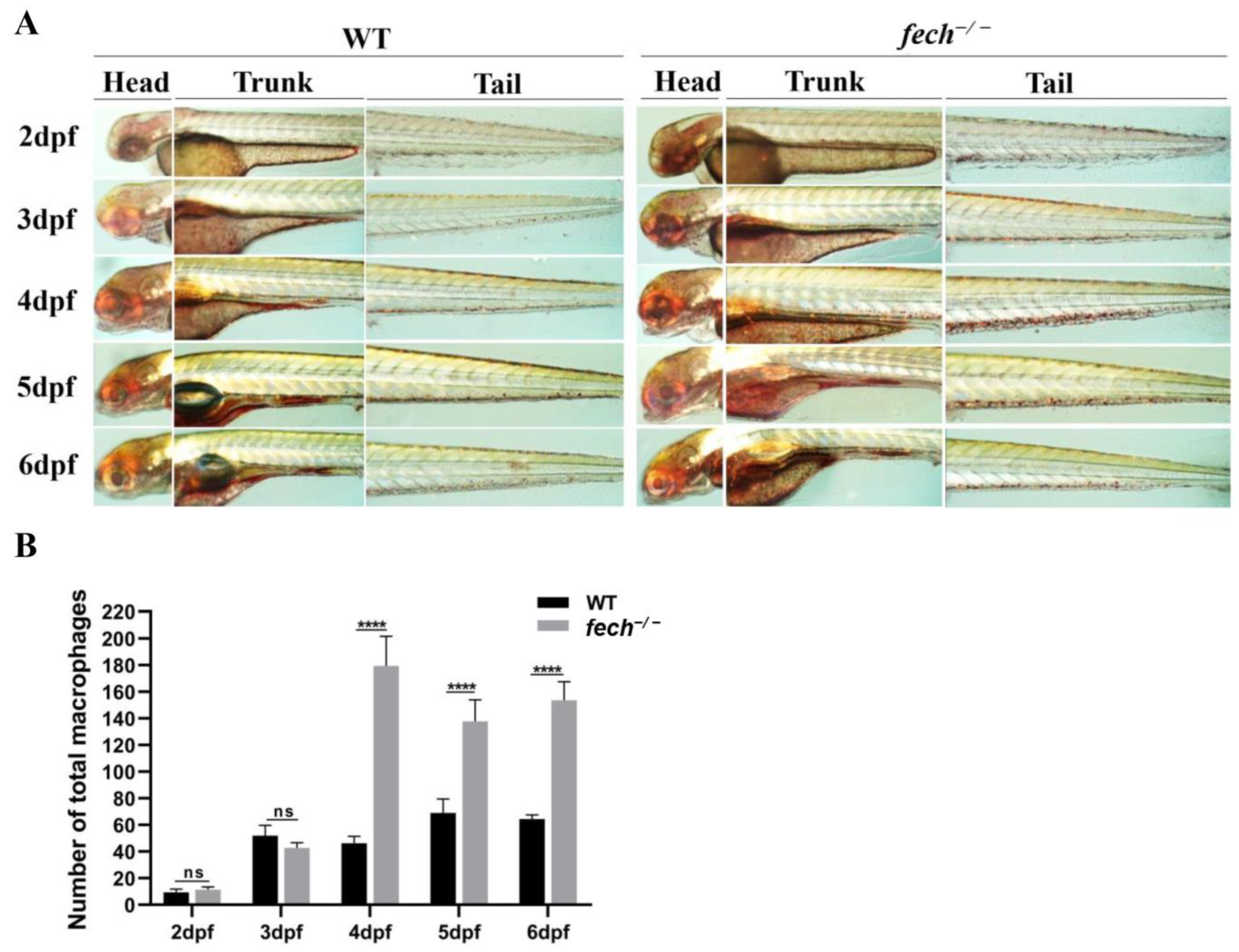
2.9. Temporal Changes in Macrophage Production and Attenuation of Macrophage Accumulation by UDCA Treatment in fech−/− Larvae
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Zebrafish Maintenance
4.2. Generation of Fech-Knockout Zebrafish Using CRISPR/Cas9 Technology
4.3. Assessing Phenotypic and Physiological Effects of Fech Deletion in Zebrafish Larvae
4.4. Tissue Collection for Fech Tissue Distribution Analysis
4.5. Total RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR
4.6. Whole-Mount In Situ Hybridization
4.7. Visualization of PPIX Accumulation in fech−/− Zebrafish Embryos and Larvae
4.8. Analyzing the Effect of UDCA on PPIX Accumulation in fech−/− Larvae
4.9. Analyzing the Impact of Fech Deletion in Zebrafish on Apoptosis Using Acridine Orange Staining
4.10. Analyzing the Effect of UDCA on Apoptosis Resulting from PPIX in fech−/− Larvae Using Acridine Orange Staining
4.11. Analyzing the Impact of UDCA Treatment on the Expression of Bile Acid Transporter-Related and Apoptosis-Related Genes
4.12. Analyzing the Effect of Fech Deletion on Neutrophil and Macrophage Production
4.13. Analyzing the Impact of UDCA Treatment on Neutrophil and Macrophage Production in fech−/− Larvae
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ardalan, Z.S.; Chandran, S.; Vasudevan, A.; Angus, P.W.; Grigg, A.; He, S.; Macdonald, G.A.; Strasser, S.I.; Tate, C.J.; Kennedy, G.A.; et al. Management of Patients with Erythropoietic Protoporphyria–Related Progressive Liver Disease. Liver Transplant. 2019, 25, 1620–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholnick, P.; Marver, H.S.; Schmid, R. Erythropoietic protoporphyria: Evidence for multiple sites of excess protoporphyrin formation. J. Clin. Investig. 1971, 50, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, B.D.; Harber, L.C. Erythropoietic Protoporphyria: Lipid Peroxidation and Red Cell Membrane Damage Associated with Photohemolysis. J. Clin. Investig. 1972, 51, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Sachar, M.; Guo, G.L.; Shehu, A.I.; Lu, J.; Zhong, X.-B.; Ma, X. Liver metabolomics in a mouse model of erythropoietic protoporphyria. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 154, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, G.C.; Franco, R.; Lloyd, S.G.; Moura, I.; Moura, J.J.G.; Huynh, B.H. Structure and function of ferrochelatase. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 1995, 27, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloomer, J.; Bruzzone, C.; Zhu, L.; Scarlett, Y.; Magness, S.; Brenner, D. Molecular defects in ferrochelatase in patients with protoporphyria requiring liver transplantation. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouya, L.; Puy, H.; Robreau, A.-M.; Bourgeois, M.; Lamoril, J.; Da Silva, V.; Grandchamp, B.; Deybach, J.-C. The penetrance of dominant erythropoietic protoporphyria is modulated by expression of wildtype FECH. Nat. Genet. 2002, 30, 27–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, G.C. Ferrochelatase. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1999, 31, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketani, S.; Inazawa, J.; Nakahashi, Y.; Abe, T.; Tokunaga, R. Tokunaga, Structure of the human ferrochelatase gene. Exon/intron gene organization and location of the gene to chromosome 18. Eur. J. Biochem. 1992, 205, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, J.D.; Viana, R.J.; Ramalho, R.M.; Steer, C.J.; Rodrigues, C.M. Bile acids: Regulation of apoptosis by ursodeoxycholic acid. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1721–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roma, M.G.; Toledo, F.D.; Boaglio, A.C.; Basiglio, C.L.; Crocenzi, F.A.; Pozzi, E.J.S. Ursodeoxycholic acid in cholestasis: Linking action mechanisms to therapeutic applications. Clin. Sci. 2011, 121, 523–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piffaretti, D.; Burgio, F.; Thelen, M.; Kaelin-Lang, A.; Paganetti, P.; Reinert, M.; D’Angelo, M.L. Protoporphyrin IX tracer fluorescence modulation for improved brain tumor cell lines visualization. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 201, 111640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groß, U.; Frank, M.; Doss, M.O. Hepatic complications of erythropoietic protoporphyria. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 1998, 14, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, A.; Frieri, C.; Lefebvre, T.; Delforge, J.; Mirmiran, A.; Talbi, N.; Moulouel, B.; Six, M.; Paradis, V.; Parquet, N.; et al. Management of erythropoietic protoporphyria with cholestatic liver disease: A case report. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2023, 37, 101018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hempfling, W.; Dilger, K.; Beuers, U. Ursodeoxycholic acid—Adverse effects and drug interactions. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 18, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streisinger, G.; Walker, C.; Dower, N.; Knauber, D.; Singer, F. Production of clones of homozygous diploid zebra fish (Brachydanio rerio). Nature 1981, 291, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunwald, D.J.; Streisinger, G. Induction of recessive lethal and specific locus mutations in the zebrafish with ethyl nitrosourea. Genet. Res. 1992, 59, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedell, V.M.; Wang, Y.; Campbell, J.M.; Poshusta, T.L.; Starker, C.G.; Krug, R.G., 2nd; Tan, W.; Penheiter, S.G.; Ma, A.C.; Leung, A.Y.H.; et al. In vivo genome editing using a high-efficiency TALEN system. Nature 2012, 491, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyon, Y.; McCammon, J.M.; Miller, J.C.; Faraji, F.; Ngo, C.; Katibah, G.E.; Amora, R.; Hocking, T.D.; Zhang, L.; Rebar, E.J.; et al. Heritable targeted gene disruption in zebrafish using designed zinc-finger nucleases. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.D.; Lander, E.S.; Zhang, F. Development and Applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for Genome Engineering. Cell 2014, 157, 1262–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.H.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, H.-T.; Lee, J.; Jeon, J.; Jin, Y.; Choi, J.-H.; Ban, Y.H.; Ha, S.-J.; Kim, C.-H.; et al. Highly efficient gene knockout in mice and zebrafish with RNA-guided endonucleases. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parng, C.; Seng, W.L.; Semino, C.; McGrath, P. Zebrafish: A Preclinical Model for Drug Screening. ASSAY Drug Dev. Technol. 2002, 1, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dooley, K.A.; Fraenkel, P.G.; Langer, N.B.; Schmid, B.; Davidson, A.J.; Weber, G.; Chiang, K.; Foott, H.; Dwyer, C.; Wingert, R.A.; et al. montalcino, A zebrafish model for variegate porphyria. Exp. Hematol. 2008, 36, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Long, Q.; Marty, S.D.; Sassa, S.; Lin, S. A zebrafish model for hepatoerythropoietic porphyria. Nat. Genet. 1998, 20, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childs, S.; Weinstein, B.M.; Mohideen, M.-A.P.; Donohue, S.; Bonkovsky, H.; Fishman, M.C. Zebrafish dracula encodes ferrochelatase and its mutation provides a model for erythropoietic protoporphyria. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, 1001–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsch, R.E.; Meissner, P.N.; Hift, R.J. Variegate Porphyria. Semin. Liver Dis. 1998, 18, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, S.; Phillips, J. Bonkovsky, Porphyrias consortium of the rare diseases clinical research network, hepatoerythropoietic porphyria. In GeneReviews; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; GeneReviews®, University of Washington, Seattle: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK169003/ (accessed on 7 September 2024).
- Song, H.-D.; Sun, X.-J.; Deng, M.; Zhang, G.-W.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, X.-Y.; Sheng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ruan, Z.; Jiang, C.-L.; et al. Hematopoietic gene expression profile in zebrafish kidney marrow. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16240–16245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Floris, F.; Rensing, M.; Andersson-Engels, S. Fluorescence Spectroscopy Study of Protoporphyrin IX in Optical Tissue Simulating Liquid Phantoms. Materials 2020, 13, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paumgartner, G.; Beuers, U. Mechanisms of action and therapeutic efficacy of ursodeoxycholic acid in cholestatic liver disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2004, 8, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Yan, Z.; Feng, Q.; Yu, L.; Wang, H. The Roles of Neutrophils in the Pathogenesis of Liver Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 625472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thisse, B.; Thisse, C. Fast Release Clones: A High Throughput Expression Analysis. ZFIN Direct Data Submission. 2004. Available online: https://zfin.org/ZDB-PUB-040907-1#summary (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Thisse, C.; Thisse, B. High-resolution in situ hybridization to whole-mount zebrafish embryos. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, J.Y.; Kim, A.D.; Violette, E.P.; Stachura, D.L.; Cisson, J.L.; Traver, D. Definitive hematopoiesis initiates through a committed erythromyeloid progenitor in the zebrafish embryo. Development 2007, 134, 4147–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasighaemi, P.; Basheer, F.; Liongue, C.; Ward, A.C. Zebrafish as a model for leukemia and other hematopoietic disorders. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dailey, H.A.; Meissner, P.N. Erythroid Heme Biosynthesis and Its Disorders. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a011676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponka, P. Cell Biology of Heme. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1999, 318, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hamza, I. Zebrafish as a model system to delineate the role of heme and iron metabolism during erythropoiesis. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 128, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carradice, D.; Lieschke, G.J. Zebrafish in hematology: Sushi or science? Blood 2008, 111, 3331–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelster, B.; Bagatto, B. Respiration. In Fish Physiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 289–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-J.; Thomas, P.; Zhu, Y. Pgrmc1 Knockout Impairs Oocyte Maturation in Zebrafish. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atella, G.C.; Gondim, K.C.; Machado, E.A.; Medeiros, M.N.; Silva-Neto, M.A.; Masuda, H. Oogenesis and egg development in triatomines: A biochemical approach. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2005, 77, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, A. Metabolism of the stimulated rat spleen. J. Clin. Investig. 1968, 47, 2230–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapar, M.; Bonkovsky, H.L. The diagnosis and management of erythropoietic protoporphyria. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 4, 561–566. [Google Scholar]
- Kalra, A.; Yetiskul, E.; Wehrle, C.J.; Tuma, F. Physiology, Liver. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535438/ (accessed on 12 October 2023).
- Balwani, M. Erythropoietic Protoporphyria and X-linked Protoporphyria; National Organization for Rare Disorders: Danbury, Connecticut, 2022; Available online: https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/erythropoietic-protoporphyria/#complete-report (accessed on 13 October 2023).
- Farid, Y.; Bowman, N.S.; Lecat, P. Biochemistry, hemoglobin synthesis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536912/ (accessed on 13 October 2023).
- Belele, C.L.; English, M.A.; Chahal, J.; Burnetti, A.; Finckbeiner, S.M.; Gibney, G.; Kirby, M.; Sood, R.; Liu, P.P. Differential requirement for Gata1 DNA binding and transactivation between primitive and definitive stages of hematopoiesis in zebrafish. Blood 2009, 114, 5162–5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, A.; Sandberg, S. Mechanisms of photosensitivity in porphyric patients with special emphasis on erythropoietic protoporphyria. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 1991, 10, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachar, M.; Anderson, K.E.; Ma, X. Protoporphyrin IX: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 356, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotb, M.A. Molecular Mechanisms of Ursodeoxycholic Acid Toxicity & Side Effects: Ursodeoxycholic Acid Freezes Regeneration & Induces Hibernation Mode. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 8882–8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, A.; Wakai, E.; Tada, T.; Koiwa, J.; Adachi, Y.; Shiromizu, T.; Goto, H.; Tanaka, T.; Nishimura, Y. Generation of a Transgenic Zebrafish Line for In Vivo Assessment of Hepatic Apoptosis. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Sadler, K.C. New school in liver development: Lessons from zebrafish. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1656–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, N.; Shiraishi, H.; Hanada, T. Zebrafish as a Useful Model System for Human Liver Disease. Cells 2023, 12, 2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Yacoub, A.; Studer, E.; Gupta, S.; Pei, X.Y.; Grant, S.; Hylemon, P.B.; Dent, P. Inhibition of the MAPK and PI3K pathways enhances UDCA-induced apoptosis in primary rodent hepatocytes. Hepatology 2002, 35, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solá, S.; Aranha, M.M.; Steer, C.J.; Rodrigues, C.M. Game and Players: Mitochondrial Apoptosis and the Therapeutic Potential of Ursodeoxycholic Acid. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2007, 9, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lu, H.; Lu, Y.-F.; Lei, X.; Cui, J.Y.; Ellis, E.; Strom, S.C.; Klaassen, C.D. Potency of Individual Bile Acids to Regulate Bile Acid Synthesis and Transport Genes in Primary Human Hepatocyte Cultures. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 141, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puy, H.; Gouya, L.; Deybach, J.-C. Porphyrias. Lancet 2010, 375, 924–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyoumi, S.; Abitbol, M.; Rainteau, D.; Karim, Z.; Bernex, F.; Oustric, V.; Millot, S.; Lettéron, P.; Heming, N.; Guillmot, L.; et al. Protoporphyrin Retention in Hepatocytes and Kupffer Cells Prevents Sclerosing Cholangitis in Erythropoietic Protoporphyria Mouse Model. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1509–1519.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstey, A.V.; Hift, R.J. Liver disease in erythropoietic protoporphyria: Insights and implications for management. Postgrad. Med. J. 2007, 83, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balwani, M.; Naik, H.; Anderson, K.E.; Bissell, D.M.; Bloomer, J.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Phillips, J.D.; Overbey, J.R.; Wang, B.; Singal, A.K.; et al. Clinical, Biochemical, and Genetic Characterization of North American Patients with Erythropoietic Protoporphyria and X-linked Protoporphyria. JAMA Dermatol. 2017, 153, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Desert, R.; Das, S.; Song, Z.; Athavale, D.; Ge, X.; Nieto, N. Danger signals in liver injury and restoration of homeostasis. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 933–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Figueroa, E.; Álvarez-Carrasco, P.; Ortega, E.; Maldonado-Bernal, C. Neutrophils: Many Ways to Die. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 631821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Cai, N.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, Y.; Yi, S.; Song, W.; Kang, L.; He, H. Acute stress induces an inflammation dominated by innate immunity represented by neutrophils in mice. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1014296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhao, M.; Jia, S. Macrophage: Key player in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1080310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, N.; Kobayashi, K. Macrophages in Inflammation. Curr. Drug Target. Inflamm. Allergy 2005, 4, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Saeed, A.F.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, H.; Xiao, G.G.; Rao, L.; Duo, Y. Macrophages in immunoregulation and therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, T.; Ouchida, R.; Yoshikawa, N.; Okamoto, K.; Makino, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Morimoto, C.; Makino, I.; Tanaka, H. Functional Modulation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor and Suppression of NF-κB-dependent Transcription by Ursodeoxycholic Acid. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 47371–47378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Tsujii, T.; Matsumura, K.; Yamao, J.; Matsumura, Y.; Kubo, R.; Fukui, H.; Ishizaka, S. Immunomodulatory effects of ursodeoxycholic acid on immune responses. Hepatology 1992, 16, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishizaki, K.; Iwaki, T.; Kinoshita, S.; Koyama, M.; Fukunari, A.; Tanaka, H.; Tsurufuji, M.; Sakata, K.; Maeda, Y.; Imada, T.; et al. Ursodeoxycholic acid protects concanavalin A-induced mouse liver injury through inhibition of intrahepatic tumor necrosis factor-α and macrophage inflammatory protein-2 production. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 578, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avdesh, A.; Chen, M.; Martin-Iverson, M.T.; Mondal, A.; Ong, D.; Rainey-Smith, S.; Taddei, K.; Lardelli, M.; Groth, D.M.; Verdile, G.; et al. Regular Care and Maintenance of a Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Laboratory: An Introduction. JoVE J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 69, e4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jao, L.-E.; Wente, S.R.; Chen, W. Efficient multiplex biallelic zebrafish genome editing using a CRISPR nuclease system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13904–13909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, G.K.; Pei, W.; LaFave, M.C.; Idol, J.; Xu, L.; Gallardo, V.; Carrington, B.; Bishop, K.; Jones, M.; Li, M.; et al. High-throughput gene targeting and phenotyping in zebrafish using CRISPR/Cas9. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1030–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.; Cho, S.W.; Kim, J.-S. Targeted genome editing in human cells with zinc finger nucleases constructed via modular assembly. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, B.; Lardelli, M. A Rapid Apoptosis Assay Measuring Relative Acridine Orange Fluorescence in Zebrafish Embryos. Zebrafish 2007, 4, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosowski, E.E.; Raffa, N.; Knox, B.P.; Golenberg, N.; Keller, N.P.; Huttenlocher, A. Macrophages inhibit Aspergillus fumigatus germination and neutrophil-mediated fungal killing. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbomel, P.; Levraud, J.-P. Imaging early macrophage differentiation, migration, and behaviors in live zebrafish embryos. Methods Mol. Biol. 2005, 105, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, T. The Ensembl genome database project. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, D.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 2963–2965. [Google Scholar]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. The clustal omega multiple alignment package. In Multiple Sequence Alignment; Katoh, K., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 2231, pp. 3–16. Available online: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-1-0716-1036-7_1 (accessed on 5 October 2023).
- Rice, P.; Longden, I.; Bleasby, A. EMBOSS: The european molecular biology open software suite. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 276–277. [Google Scholar]
- Paffett-Lugassy, N.N.; Zon, L.T. Analysis of hematopoietic development in the zebrafish. In Developmental Hematopoiesis; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 171–198. Available online: http://link.springer.com/10.1385/1-59259-826-9:171 (accessed on 7 October 2023).





| Application | Primer Sequence (5′ to 3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| sgRNA synthesis | T7-sgRNA (Forward) | GAAATTAATACGACTCACTATAGGAAGGAATGGTGAAACTGCgtttTagagctagaaatagcaagttAaaat |
| Universal reverse primer | gatccgcaccgactcggtgccactttttcaagtTgataaCggactagccttatttTaacttgctatttctag | |
| T7E1 assay | F | ATTGCCAAAAGACGCACCCCAAAGATC |
| R | CTCACCCGTGTCCGGACACATCTCAT | |
| Mutation confirmation (RT-qPCR) | F | GGTGAAACTGCTGGATGAGATGTGT |
| R | ACTGTGGGTACTGTGTGAAGGCC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wijerathna, H.M.S.M.; Shanaka, K.A.S.N.; Raguvaran, S.S.; Jayamali, B.P.M.V.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, M.-J.; Jung, S.; Lee, J. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated fech Knockout Zebrafish: Unraveling the Pathogenesis of Erythropoietic Protoporphyria and Facilitating Drug Screening. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910819
Wijerathna HMSM, Shanaka KASN, Raguvaran SS, Jayamali BPMV, Kim S-H, Kim M-J, Jung S, Lee J. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated fech Knockout Zebrafish: Unraveling the Pathogenesis of Erythropoietic Protoporphyria and Facilitating Drug Screening. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(19):10819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910819
Chicago/Turabian StyleWijerathna, Hitihami M. S. M., Kateepe A. S. N. Shanaka, Sarithaa S. Raguvaran, Bulumulle P. M. V. Jayamali, Seok-Hyung Kim, Myoung-Jin Kim, Sumi Jung, and Jehee Lee. 2024. "CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated fech Knockout Zebrafish: Unraveling the Pathogenesis of Erythropoietic Protoporphyria and Facilitating Drug Screening" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 19: 10819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910819
APA StyleWijerathna, H. M. S. M., Shanaka, K. A. S. N., Raguvaran, S. S., Jayamali, B. P. M. V., Kim, S.-H., Kim, M.-J., Jung, S., & Lee, J. (2024). CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated fech Knockout Zebrafish: Unraveling the Pathogenesis of Erythropoietic Protoporphyria and Facilitating Drug Screening. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(19), 10819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910819






