Effects of Pharmaceutical Substances with Obesogenic Activity on Male Reproductive Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
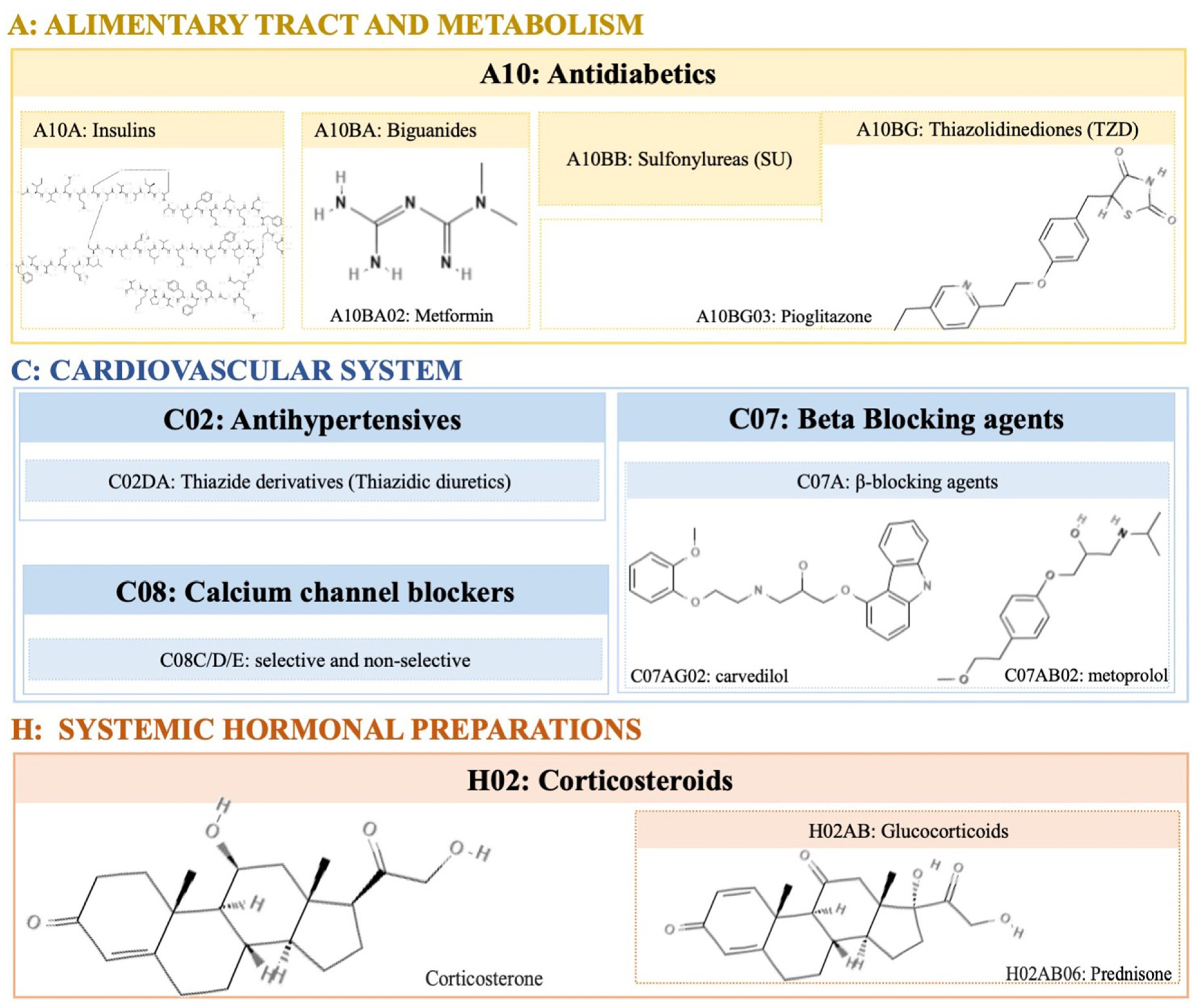
2. Pharmacological Agents with Obesogenic Activity
2.1. Corticosteroids
2.2. Antidiabetics
2.3. Antihypertensive
2.4. Psychotropic
2.4.1. Antidepressants
2.4.2. Lithium
2.4.3. Antipsychotics
2.4.4. Antiepileptics
3. Effects of Pharmacological Agents on Male Fertility Parameters
3.1. Antidiabetics
3.2. Antihypertensive Drugs
3.3. Psychotropics
3.3.1. Antidepressants
3.3.2. Antipsychotics
3.3.3. Antiepileptics
| Types of Pharmaceuticals | Samples/Subjects | Outcomes | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antidiabetics | |||
| TZDs | |||
| Pioglitazone | Human Sertoli cells | ↓ lactate production | [68] |
| Antihypertensives | |||
| Alpha Blockers Tamsulosin Alfuzosin | Human (Clinical trial) | Alterations in semen | [106,107] |
| Calcium Channel Blockers Nifedipine Amlodipine Verapamil Diltiazem | Human (Clinical trial) | Reduced fertilizing ability of spermatozoa (not under in vivo conditions) | [81,82,83] |
| Amlodipine | Human | ↓ Sperm viability ↓ Sperm motility | [64,80,81,82,83] [81,82,83] |
| Antidepressants | |||
| Tricyclic (Imipramine) | Human | ↓ Sperm motility | [82,85,91] |
| SSRI | [82,85,91] [82,85,89] [82,97,100] | ||
| Fluoxetine | Human | ↓ Sperm morphology ↓ Sperm count | |
| Paroxetine | |||
| Sertraline | |||
| Fluvoxamine | |||
| MAOIs | |||
| Bupropion | Human | No effects observed | [72,78,79,86,92,93,94] |
| Mirtazapine | |||
| Buspirone | |||
| Mocoblemide | Human | ↓ Sperm motility under in vitro conditions | [85] |
| Antiephyletics | |||
| Carbamazepine | Human | ↓ Sperm motility ↓ Sperm count ↓ Sperm morphology | [64] [97,98,101,108] [82,97,100] [97,98,101,108] |
| Phenytoin | |||
| Valproate | |||
| Oxcarbazepine | |||
| Phenobarbital | |||
| Lithium | Human | ↓ Sperm motility | [109] |
| ↓ Sperm count | |||
| ↓ Sperm morphology |
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heindel, J.; Schug, T. The Obesogen Hypothesis: Current Status and Implications for Human Health. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2014, 1, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, L.; Lind, P.M.; Lejonklou, M.H.; Dunder, L.; Bergman, Å.; Guerrero-Bosagna, C.; Lampa, E.; Lee, H.K.; Legler, J.; Nadal, A.; et al. Uppsala Consensus Statement on Environmental Contaminants and the Global Obesity Epidemic. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, A81–A83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Coster, S.; Van Larebeke, N. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: Associated disorders and mechanisms of action. J. Environ. Public Health 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janesick, A.S.; Blumberg, B. Obesogens: An emerging threat to public health. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 2016, 214, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darbre, P.D. Endocrine disruptors and obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, O.; Kim, H.L.; Weon, J.-I.; Seo, Y.R. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: Review of toxicological mechanisms using molecular pathway analysis. J. Can. Prev. 2015, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Bourguignon, J.-P.; Giudice, L.C.; Hauser, R.; Prins, G.S.; Soto, A.M.; Zoeller, R.T.; Gore, A.C. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: An Endocrine Society scientific statement. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 293–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gore, A.C.; Chappell, V.A.; Fenton, S.E.; Flaws, J.A.; Nadal, A.; Prins, G.S.; Toppari, J.; Zoeller, R.T. EDC-2: The Endocrine Society’s second scientific statement on endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Endocr. Rev. 2015, 36, E1–E150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tontonoz, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Fat and beyond: The diverse biology of PPARγ. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2008, 77, 289–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lustig, R.H.; Collier, D.; Kassotis, C.; Roepke, T.A.; Ji Kim, M.; Blanc, E.; Barouki, R.; Bansal, A.; Cave, M.C.; Chatterjee, S.; et al. Obesity I: Overview and molecular and biochemical mechanisms. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 115012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siersbaek, R.; Nielsen, R.; Mandrup, S. PPARgamma in adipocyte differentiation and metabolism—Novel insights from genome-wide studies. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 3242–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, V.; Huang, P.; Hamuro, Y.; Raghuram, S.; Wang, Y.; Burris, T.P.; Rastinejad, F. Structure of the intact PPAR-gamma-RXR- nuclear receptor complex on DNA. Nature 2008, 456, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.Q.; Lane, M.D. Adipogenesis: From stem cell to adipocyte. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 715–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, A.C.; Pastorinho, M.R.; Takahashi, S.; Tanabe, S. Organotin compounds from snails to humans. In Pollutant Diseases, Remediation and Recycling; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 215–275. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, E.D. TBT An environmental dilemma. Environment 1986, 28, 17–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heindel, J.J.; Blumberg, B.; Cave, M.; Machtinger, R.; Mantovani, A.; Mendez, M.A.; Nadal, A.; Palanza, P.; Panzica, G.; Sargis, R. Metabolism disrupting chemicals and metabolic disorders. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 68, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heindel, J.J.; Howard, S.; Agay-Shay, K.; Arrebola, J.P.; Audouze, K.; Babin, P.J.; Barouki, R.; Bansal, A.; Blanc, E.; Cave, M.C.; et al. Obesity II: Establishing Causal Links Between Chemical Exposures and Obesity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 115015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casals-Casas, C.; Desvergne, B. Endocrine disruptors: From endocrine to metabolic disruption. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2011, 73, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quagliariello, V.; Rossetti, S.; Cavaliere, C.; Di Palo, R.; Lamantia, E.; Castaldo, L.; Nocerino, F.; Ametrano, G.; Cappuccio, F.; Malzone, G. Metabolic syndrome, endocrine disruptors and prostate cancer associations: Biochemical and pathophysiological evidences. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 30606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaegen, A.A.; Van Gaal, L.F. Drug-induced obesity and its metabolic consequences: A review with a focus on mechanisms and possible therapeutic options. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2017, 40, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, N.O.; Bakos, H.W.; Fullston, T.; Lane, M. Impact of obesity on male fertility, sperm function and molecular composition. Spermatogenesis 2012, 2, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mínguez-Alarcón, L.; Gaskins, A.J.; Meeker, J.D.; Braun, J.M.; Chavarro, J.E. Endocrine disrupting chemicals and male reproductive health. Fertil. Steril. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thacharodi, A.; Hassan, S.; Acharya, G.; Vithlani, A.; Hoang Le, Q.; Pugazhendhi, A. Endocrine disrupting chemicals and their effects on the reproductive health in men. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.C.A.; Alves, M.G.; Oliveira, P.F.; Silva, B.M.; Rato, L. Male Infertility in the XXI Century: Are Obesogens to Blame? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, J.R.; Westfall, A.O.; Allison, J.; Bijlsma, J.W.; Freeman, A.; George, V.; Kovac, S.H.; Spettell, C.M.; Saag, K.G. Population-based assessment of adverse events associated with long-term glucocorticoid use. Arthritis Care Res. 2006, 55, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell-Jones, D.; Khan, R. Insulin-associated weight gain in diabetes–causes, effects and coping strategies. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2007, 9, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gaal, L.; Scheen, A. Weight management in type 2 diabetes: Current and emerging approaches to treatment. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, S.E.; Haffner, S.M.; Heise, M.A.; Herman, W.H.; Holman, R.R.; Jones, N.P.; Kravitz, B.G.; Lachin, J.M.; O’Neill, M.C.; Zinman, B. Glycemic durability of rosiglitazone, metformin, or glyburide monotherapy. New Eng. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2427–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.C. The UK prospective diabetes study: A review. Diabetes Care 1998, 21 (Suppl. 3), C35–C38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inzucchi, S.E. Oral antihyperglycemic therapy for type 2 diabetes: Scientific review. JAMA 2002, 287, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domecq, J.P.; Prutsky, G.; Leppin, A.; Sonbol, M.B.; Altayar, O.; Undavalli, C.; Wang, Z.; Elraiyah, T.; Brito, J.P.; Mauck, K.F. Drugs commonly associated with weight change: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medici, V.; McClave, S.A.; Miller, K.R. Common medications which lead to unintended alterations in weight gain or organ lipotoxicity. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2016, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messerli, F.H.; Bell, D.S.; Fonseca, V.; Katholi, R.E.; McGill, J.B.; Phillips, R.A.; Raskin, P.; Wright Jr, J.T.; Bangalore, S.; Holdbrook, F.K. Body weight changes with β-blocker use: Results from GEMINI. Am. J. Med. 2007, 120, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.M.; Pischon, T.; Hardt, S.; Kunz, I.; Luft, F.C. Hypothesis: β-adrenergic receptor blockers and weight gain: A systematic analysis. Hypertension 2001, 37, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welle, S.; Schwartz, R.G.; Statt, M. Reduced metabolic rate during β-adrenergic blockade in humans. Metabolism 1991, 40, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, G.; Franz, I.-W.; Lohmann, F. Effects of Short-Term and Long-Term Treatment with Cardio-Selective and non-Selective β-Receptor Blockade on Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism and on Plasma Catecholamines at Rest and during Exercise. Clin. Sci. 1981, 61, 433s–435s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.L.; Fonseca, V.; Katholi, R.E.; McGill, J.B.; Messerli, F.H.; Phillips, R.A.; Raskin, P.; Wright, J.T., Jr.; Oakes, R.; Lukas, M.A.; et al. Metabolic effects of carvedilol vs metoprolol in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2004, 292, 2227–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripley, T.L.; Saseen, J.J. β-blockers: A review of their pharmacological and physiological diversity in hypertension. Annals Pharmacol. 2014, 48, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménard, C.; Pfau, M.L.; Hodes, G.E.; Russo, S.J. Immune and neuroendocrine mechanisms of stress vulnerability and resilience. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 42, 62–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naughton, M.; Dinan, T.G.; Scott, L.V. Corticotropin-releasing hormone and the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis in psychiatric disease. Handbook Clin. Neurol. 2014, 124, 69–91. [Google Scholar]
- Capuron, L.; Lasselin, J.; Castanon, N. Role of adiposity-driven inflammation in depressive morbidity. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, J.-C.; Krishnan, V.; Hana, G.Y.; Mason, B.; Cui, H.; Wilkinson, M.B.; Zigman, J.M.; Elmquist, J.K.; Nestler, E.J.; Lutter, M. A β3-adrenergic-leptin-melanocortin circuit regulates behavioral and metabolic changes induced by chronic stress. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, U.; Kraus, T.; Himmerich, H.; Schuld, A.; Pollmächer, T. Epidemiology, implications and mechanisms underlying drug-induced weight gain in psychiatric patients. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2003, 37, 193–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himmerich, H.; Minkwitz, J.; Kirkby, K.C. Weight gain and metabolic changes during treatment with antipsychotics and antidepressants. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2015, 15, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, D.E.; Zorn, S.H. The pharmacology of weight gain with antipsychotics. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2001, 62, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Serretti, A.; Chiesa, A. A meta-analysis of sexual dysfunction in psychiatric patients taking antipsychotics. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2011, 26, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingstone, C.; Rampes, H. Lithium: A review of its metabolic adverse effects. J. Psychopharmacol. 2006, 20, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spertus, J.; Horvitz-Lennon, M.; Abing, H.; Normand, S.L. Risk of weight gain for specific antipsychotic drugs: A meta-analysis. NPJ Schizophr. 2018, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, D.B.; Mentore, J.L.; Heo, M.; Chandler, L.P.; Cappelleri, J.C.; Infante, M.C.; Weiden, P.J. Antipsychotic-induced weight gain: A comprehensive research synthesis. Am. J. Psychiatry 1999, 156, 1686–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balf, G.; Stewart, T.D.; Whitehead, R.; Baker, R.A. Metabolic adverse events in patients with mental illness treated with antipsychotics: A primary care perspective. Prim. Care Companion J. Clin. Psychiatry 2008, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Menachem, E. Weight issues for people with epilepsy—A review. Epilepsia 2007, 48 (Suppl. 9), 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agró, L.; Demurtas, R.; Sander, J.W. Anticonvulsant Agents: Gabapentin and Pregabalin. In NeuroPsychopharmacotherapy; Riederer, P., Laux, G., Mulsant, B., Le, W., Nagatsu, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Verrotti, A.; D’Egidio, C.; Mohn, A.; Coppola, G.; Chiarelli, F. Weight gain following treatment with valproic acid: Pathogenetic mechanisms and clinical implications. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, e32–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcastro, V.; D’Egidio, C.; Striano, P.; Verrotti, A. Metabolic and endocrine effects of valproic acid chronic treatment. Epilepsy Res. 2013, 107, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swann, A.C. Major system toxicities and side effects of anticonvulsants. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2001, 62, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Campion, S.; Catlin, N.; Heger, N.; McDonnell, E.V.; Pacheco, S.E.; Saffarini, C.; Sandrof, M.A.; Boekelheide, K. Male reprotoxicity and endocrine disruption. Mol. Clin. Environ. Toxicol. 2012, 315–360. [Google Scholar]
- Creasy, D.M. Evaluation of testicular toxicity in safety evaluation studies: The appropriate use of spermatogenic staging. Toxicol. Pathol. 1997, 25, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, A.M.; Alves, M.G.; Mathur, P.P.; Oliveira, P.F.; Cavaco, J.E.; Rato, L. Obesogens and male fertility. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rato, L.; Sousa, A.C.A. The Impact of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals in Male Fertility: Focus on the Action of Obesogens. J. Xenobiot. 2021, 11, 163–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traggiai, C.; Stanhope, R. Disorders of pubertal development. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obst. Gynaecol. 2003, 17, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.; Davies, D. The control of sexual differentiation of the reproductive system and brain. Reproduction 2007, 133, 331–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, S.; Moret, C.; Kaaks, R.; Biessy, C.; Kurzer, M.; Dechaud, H.; Peeters, P.; Van Noord, P. Reproducibility over time of measurements of androgens, estrogens and hydroxy estrogens in urine samples from post-menopausal women. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 18, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, V.; Eugster, E.A. Etiology and treatment of hypogonadism in adolescents. Pediatr. Clin. 2011, 58, 1181–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semet, M.; Paci, M.; Saïas-Magnan, J.; Metzler-Guillemain, C.; Boissier, R.; Lejeune, H.; Perrin, J. The impact of drugs on male fertility: A review. Andrology 2017, 5, 640–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung, J.; Henry, R.R. Thiazolidinedione safety. Exp. Opin. Drug Safety 2012, 11, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.G.; Martins, A.D.; Vaz, C.V.; Correia, S.; Moreira, P.I.; Oliveira, P.F.; Socorro, S. Metformin and male reproduction: Effects on Sertoli cell metabolism. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krentz, A.J.; Bailey, C.J. Oral antidiabetic agents: Current role in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs 2005, 65, 385–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, M.J.; Bernardino, R.L.; Sa, R.; Silva, J.; Barros, A.; Sousa, M.; Silva, B.M.; Oliveira, P.F.; Alves, M.G. Pioglitazone increases the glycolytic efficiency of human Sertoli cells with possible implications for spermatogenesis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 79, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, C.M.; Levy, P. Sexual dysfunction in patients with hypertension: Implications for therapy. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2002, 4, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm Jr, R.H.; Grandits, G.A.; Prineas, R.J.; McDonald, R.H.; Lewis, C.E.; Flack, J.M.; Yunis, C.; Svendsen, K.; Liebson, P.R.; Elmer, P.J. Long-term effects on sexual function of five antihypertensive drugs and nutritional hygienic treatment in hypertensive men and women: Treatment of Mild Hypertension Study (TOMHS). Hypertension 1997, 29, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolis, A.; Doumas, M. Antihypertensive treatment and sexual dysfunction. Curr. Hypert. Rep. 2012, 14, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.; Norman, A.; Horwich, A.; Hendry, W. Ejaculatory dysfunction after retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy. Eur. Urol. 1993, 23, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindel, A.; Kishore, S.; Lue, T. Drugs designed to improve endothelial function: Effects on erectile dysfunction. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 3758–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, A.J.; Ückert, S.; Stief, C.G.; Scheller, F.; Knapp, W.H.; Hartmann, U.; Jonas, U. Plasma levels of angiotensin II during different penile conditions in the cavernous and systemic blood of healthy men and patients with erectile dysfunction. Urology 2001, 58, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droupy, S. Epidemiology and Physiopathology of Erectile Dysfunction. Ann. Urol. 2005, 39, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavitakis, M.; Komninos, C.; Theodorakis, P.N.; Politis, V.; Lefakis, G.; Mitsios, K.; Koritsiadis, S.; Doumanis, G. Evaluation of sexual function in hypertensive men receiving treatment: A review of current guidelines recommendation. J. Sex. Med. 2011, 8, 2405–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindel, A.W.; Althof, S.E.; Carrier, S.; Chou, R.; McMahon, C.G.; Mulhall, J.P.; Paduch, D.A.; Pastuszak, A.W.; Rowland, D.; Tapscott, A.H. Disorders of ejaculation: An AUA/SMSNA guideline. J. Urol. 2022, 207, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratzke, C.; Angulo, J.; Chitaley, K.; Dai, Y.-t.; Kim, N.N.; Paick, J.-S.; Simonsen, U.; Ückert, S.; Wespes, E.; Andersson, K.E. Anatomy, physiology, and pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2010, 7 Pt 2, 445–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nudell, D.M.; Monoski, M.M.; Lipshultz, L.I. Common medications and drugs: How they affect male fertility. Urol. Clin. 2002, 29, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosser, J.; Nakib, I.; Carré-Pigeon, F.; Staerman, F. Infertilité Masculine: Définition et Physiopathologie. Ann. Urol. 2007, 41, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoff, S.; Cooper, G.W.; Hurley, I.; Mandel, F.S.; Rosenfeld, D.L.; Scholl, G.M.; Gilbert, B.R.; Hershlag, A. The effect of calcium ion channel blockers on sperm fertilization potential. Fertil. Steril. 1994, 62, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezina, P.R.; Yunus, F.N.; Zhao, Y. Effects of pharmaceutical medications on male fertility. J. Reprod. Infertil. 2012, 13, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar, U.; Anand, R.; Sanyal, S. The effect of nifedipine, a calcium channel blocker, on human spermatozoal functions. Contraception 1993, 48, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, M.; Zarrilli, S.; Di Sarno, A.; Milano, N.; Gaccione, M.; Boggia, B.; Lombardi, G.; Colao, A. Hyperprolactinemia in men: Clinical and biochemical features and response to treatment. Endocrine 2003, 20, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanrikut, C.; Schlegel, P.N. Antidepressant-associated changes in semen parameters. Urology 2007, 69, 185.e5–185.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, D.; Mayers, A. Sexual side-effects of antidepressant and antipsychotic drugs. Adv. Psychiatr. Treat. 2003, 9, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dording, C.M.; Fisher, L.; Papakostas, G.; Farabaugh, A.; Sonawalla, S.; Fava, M.; Mischoulon, D. A double-blind, randomized, pilot dose-finding study of maca root (L. meyenii) for the management of SSRI-induced sexual dysfunction. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2008, 14, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montejo, A.L.; Llorca, G.; Izquierdo, J.A.; Rico-Villademoros, F. Incidence of sexual dysfunction associated with antidepressant agents: A prospective multicenter study of 1022 outpatients. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2001, 62, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Erdemir, F.; Atilgan, D.; Firat, F.; Markoc, F.; Parlaktas, B.S.; Sogut, E. The effect of sertraline, paroxetine, fluoxetine and escitalopram on testicular tissue and oxidative stress parameters in rats. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2014, 40, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montejo, A.L.; Montejo, L.; Navarro-Cremades, F. Sexual side-effects of antidepressant and antipsychotic drugs. Curr. Opin. Psych. 2015, 28, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarinejad, M.R. Sperm DNA damage and semen quality impairment after treatment with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors detected using semen analysis and sperm chromatin structure assay. J. Urol. 2008, 180, 2124–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althof, S.E.; McMahon, C.G.; Waldinger, M.D.; Serefoglu, E.C.; Shindel, A.W.; Adaikan, P.G.; Becher, E.; Dean, J.; Giuliano, F.; Hellstrom, W.J.; et al. An Update of the International Society of Sexual Medicine’s Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Premature Ejaculation (PE). J. Sex. Med. 2014, 2, 60–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.J.; Rudkin, L.; Bullemor-Day, P.; Lubin, J.; Chukwujekwu, C.; Hawton, K. Strategies for managing sexual dysfunction induced by antidepressant medication. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, R.C.; Marin, H. Prevalence of antidepressant-associated erectile dysfunction. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2003, 64, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Panidis, D.; Rousso, D.; Skiadopoulos, S.; Panidou, E.; Mamopoulos, M. Evaluation of semen parameters in man with hyperprolactinemia induced by metoclopramide. Arch. Androl. 1997, 39, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Howes, O.D.; Wheeler, M.J.; Pilowsky, L.S.; Landau, S.; Murray, R.M.; Smith, S. Sexual function and gonadal hormones in patients taking antipsychotic treatment for schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2007, 68, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.S.; Shen, M.R.; Chen, T.J.; Lai, S.L. Effects of antiepileptic drugs on sperm motility of normal controls and epileptic patients with long-term therapy. Epilepsia 1992, 33, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isojärvi, J.; Löfgren, E.; Juntunen, K.; Pakarinen, A.; Päivänsalo, M.; Rautakorpi, I.; Tuomivaara, L. Effect of epilepsy and antiepileptic drugs on male reproductive health. Neurology 2004, 62, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, A.G. Disorders of reproduction in patients with epilepsy: Primary neurological mechanisms. Seizure 2008, 17, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lossius, M.I.; Taubøll, E.; Mowinckel, P.; Mørkrid, L.; Gjerstad, L. Reversible Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs on Reproductive Endocrine Function in Men and Women with Epilepsy—A Prospective Randomized Double-Blind Withdrawal Study. Epilepsia 2007, 48, 1875–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rättyä, J.; Turkka, J.; Pakarinen, A.J.; Knip, M.; Kotila, M.; Lukkarinen, O.; Myllylä, V.; Isojärvi, J. Reproductive effects of valproate, carbamazepine, and oxcarbazepine in men with epilepsy. Neurology 2001, 56, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, M.P.; Hauser, W.A.; Ottman, R.; Annegesr, J.F. Fertility in persons with epilepsy: 1935–1974. Epilepsia 1986, 27, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocek, L.; Tarhan, H.; Uludag, F.I.; Sariteke, A.; Kose, C.; Colak, A.; Zorlu, F.; Zorlu, Y. Evaluation of sex hormones and sperm parameters in male epileptic patients. Acta. Neurol. Scand. 2018, 137, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isojärvi, J.I.; Taubøll, E.; Herzog, A.G. Effect of antiepileptic drugs on reproductive endocrine function in individuals with epilepsy. CNS Drugs 2005, 19, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, S.U.; Scarano, W.R.; Okada, F.K.; Miraglia, S.M. Harmful effects of carbamazepine on the postnatal development of the rat ventral prostate. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2012, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellstrom, W.J.; Sikka, S.C. Effects of alfuzosin and tamsulosin on sperm parameters in healthy men: Results of a short-term, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. J. Androl. 2009, 30, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellstrom, W.J.; Sikka, S.C. Effects of acute treatment with tamsulosin versus alfuzosin on ejaculatory function in normal volunteers. J. Urol. 2006, 176 Pt 1, 1529–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Røste, L.; Taubøll, E.; Mørkrid, L.; Bjørnenak, T.; Saetre, E.; Mørland, T.; Gjerstad, L. Antiepileptic drugs alter reproductive endocrine hormones in men with epilepsy. Eur. J. Neurol. 2005, 12, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadirian, A.M.; Annable, L.; Belanger, M.C. Lithium, benzodiazepines, and sexual function in bipolar patients. Am. J. Psychiatry 1992, 149, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mascarenhas, C.; Sousa, A.C.A.; Rato, L. Effects of Pharmaceutical Substances with Obesogenic Activity on Male Reproductive Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042324
Mascarenhas C, Sousa ACA, Rato L. Effects of Pharmaceutical Substances with Obesogenic Activity on Male Reproductive Health. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(4):2324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042324
Chicago/Turabian StyleMascarenhas, Caio, Ana C. A. Sousa, and Luís Rato. 2024. "Effects of Pharmaceutical Substances with Obesogenic Activity on Male Reproductive Health" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 4: 2324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042324
APA StyleMascarenhas, C., Sousa, A. C. A., & Rato, L. (2024). Effects of Pharmaceutical Substances with Obesogenic Activity on Male Reproductive Health. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(4), 2324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042324







