The Construction of a Multi-Gene Risk Model for Colon Cancer Prognosis and Drug Treatments Prediction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. DEGs Identification
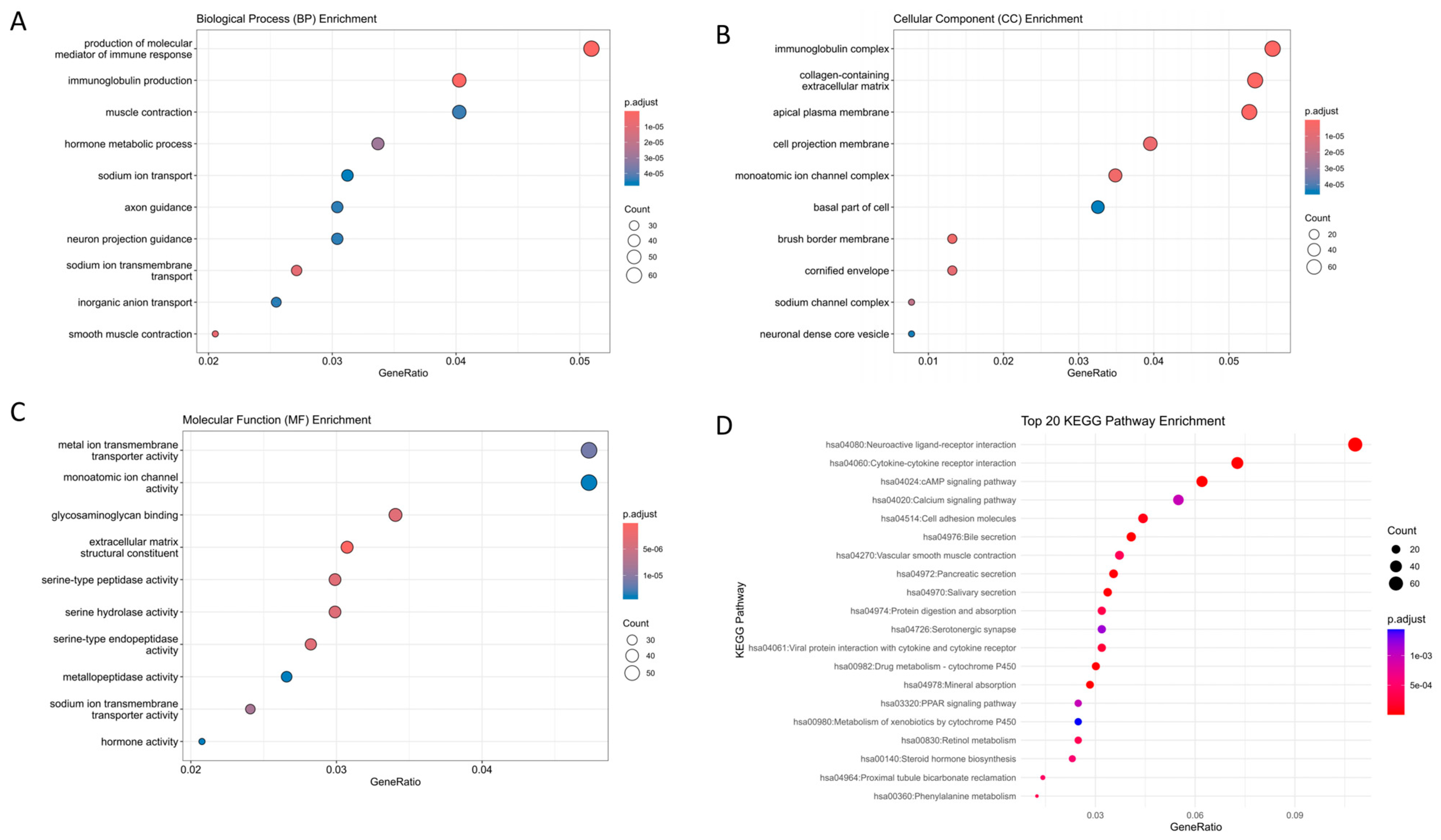
2.2. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
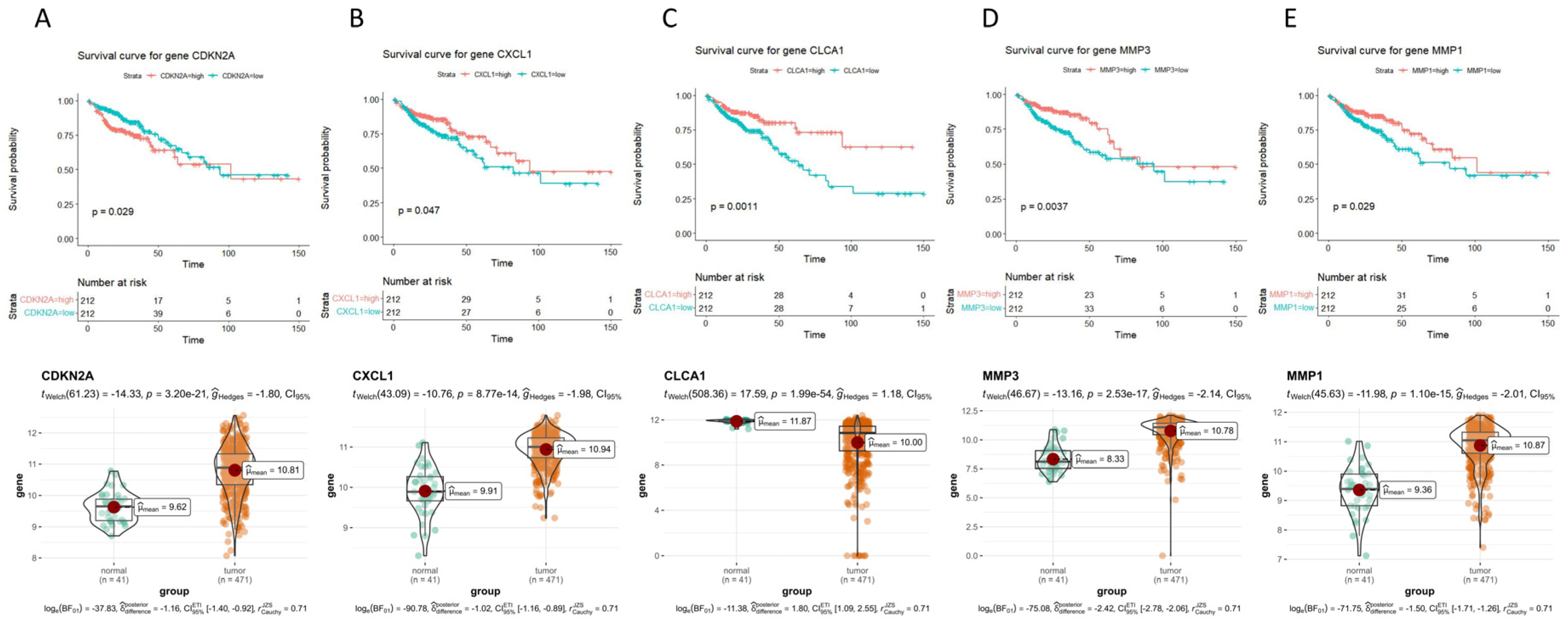
2.3. Survival Curves of 47 Hub Genes and Their Expression Levels in COAD
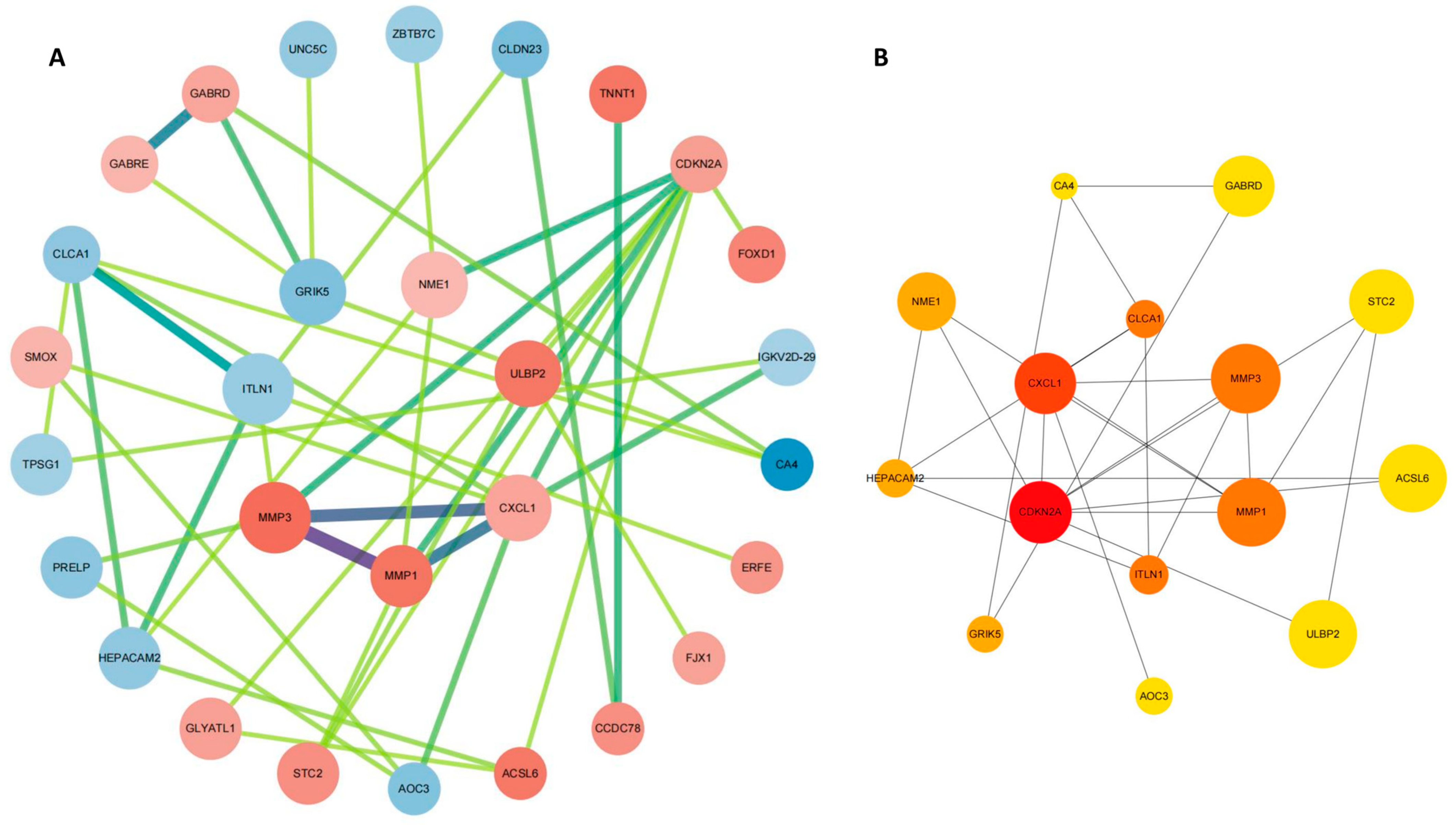
2.4. PPI Network Construction
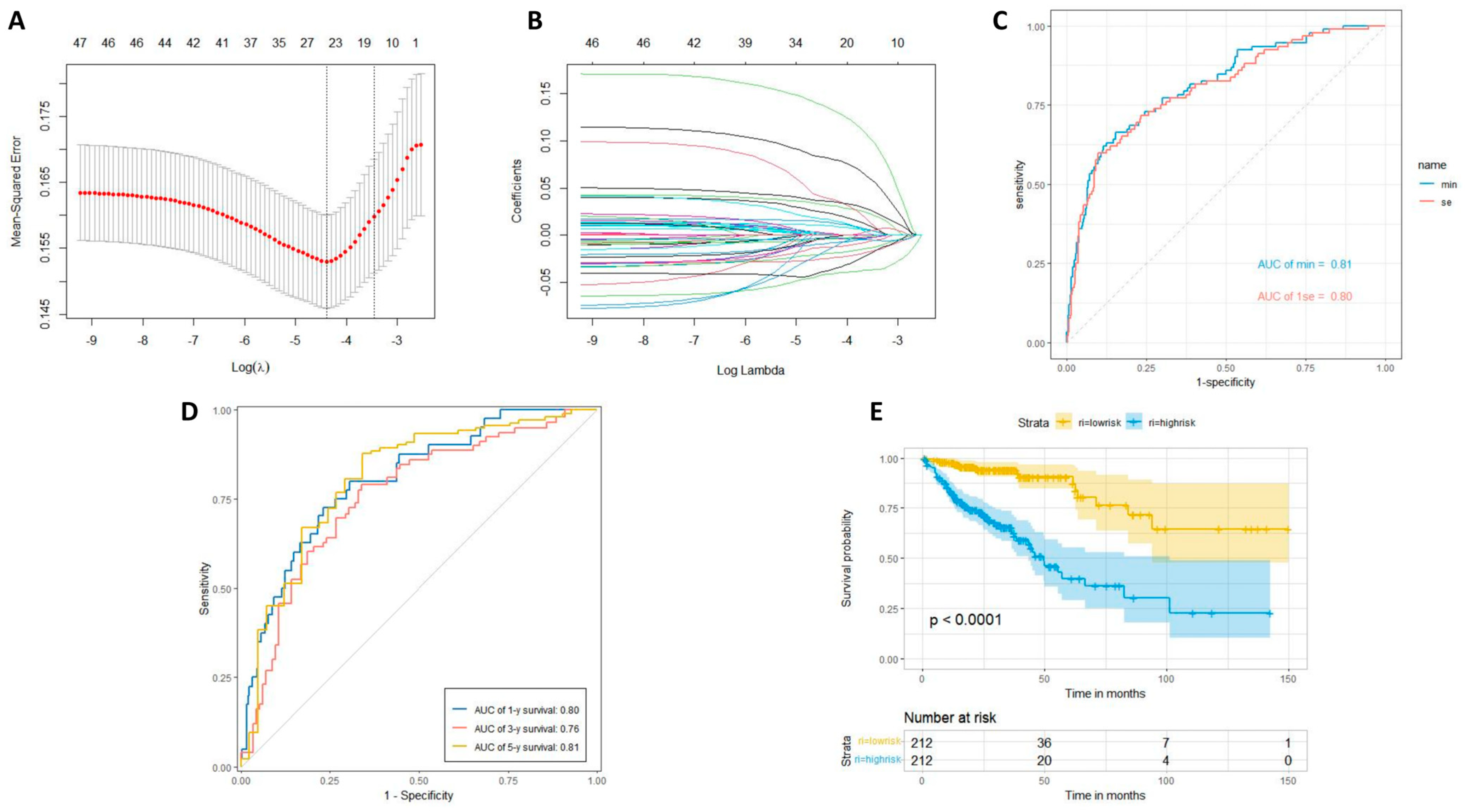
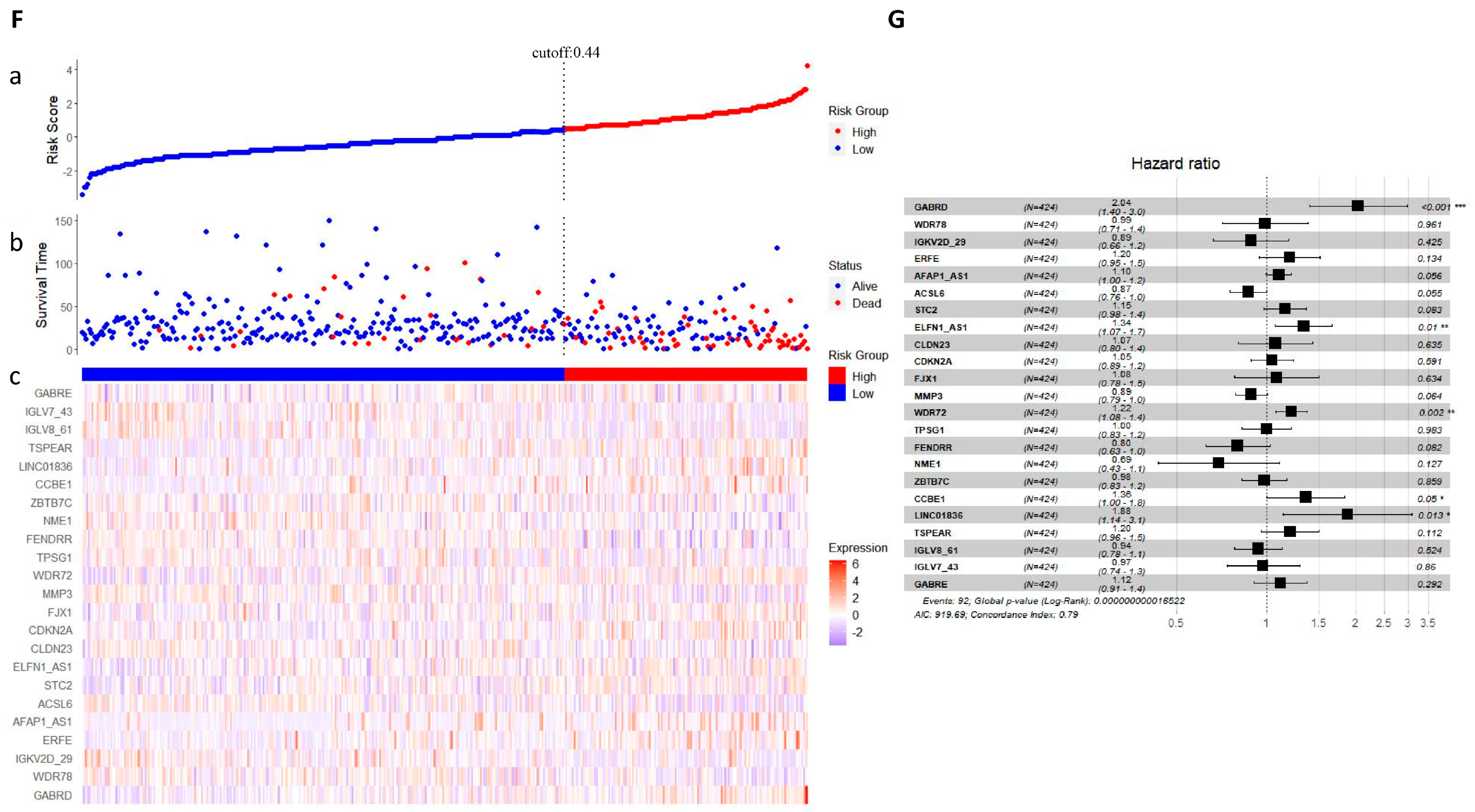
2.5. LASSO Regression Analysis
2.6. Immune Cell Infiltration Analysis
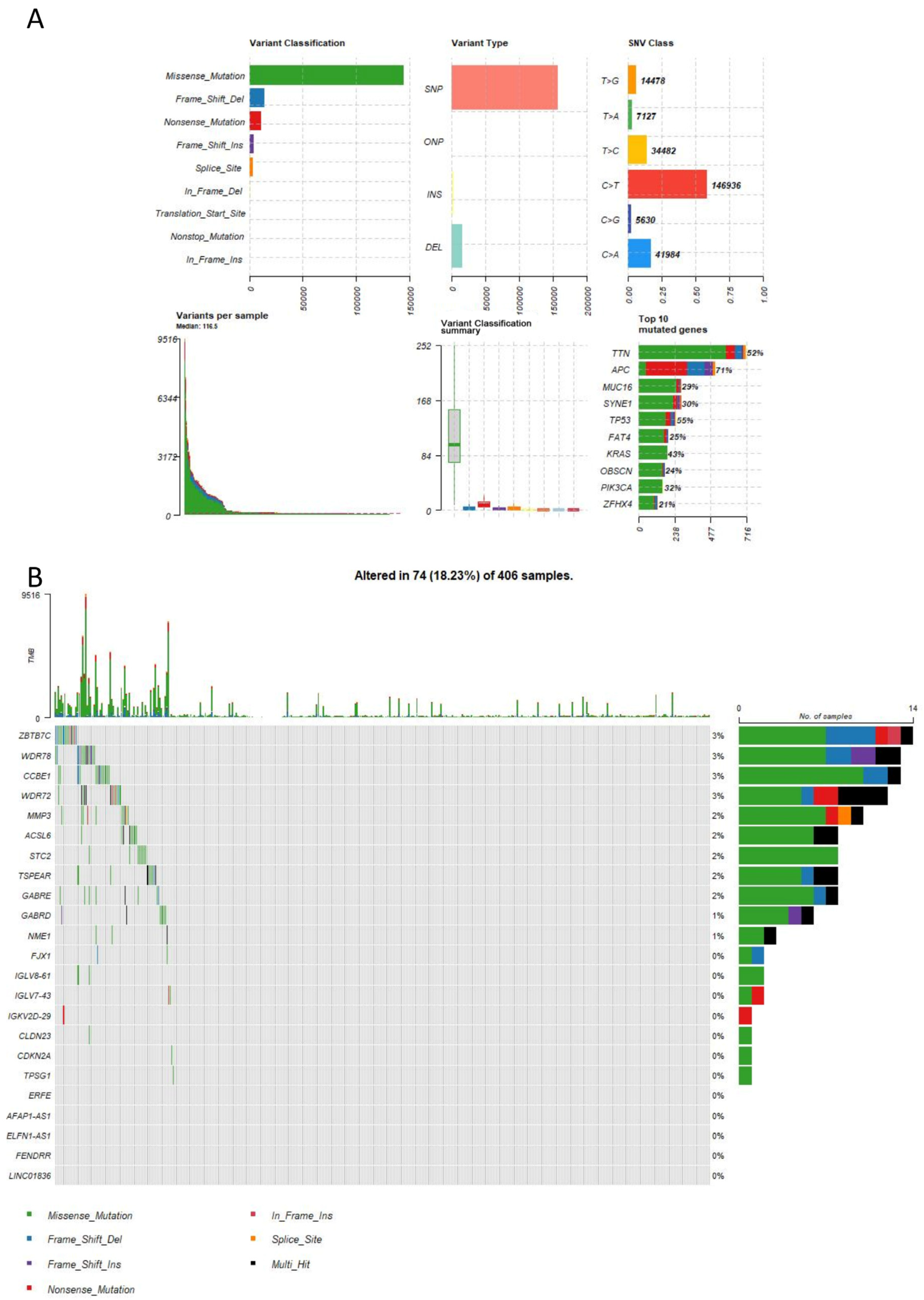
2.7. Mutation Analysis
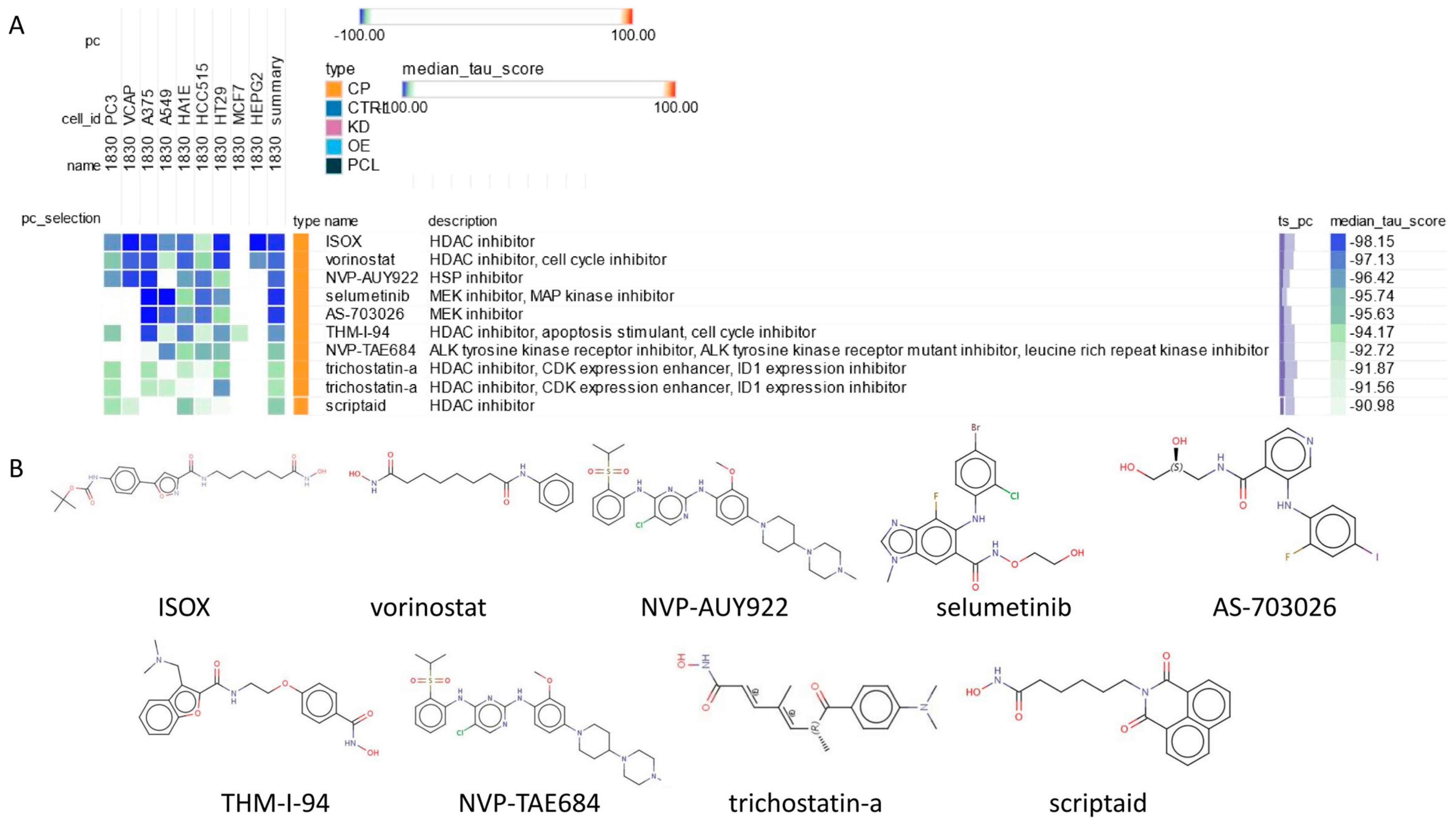
2.8. Connectivity Map (cMAP) Analysis
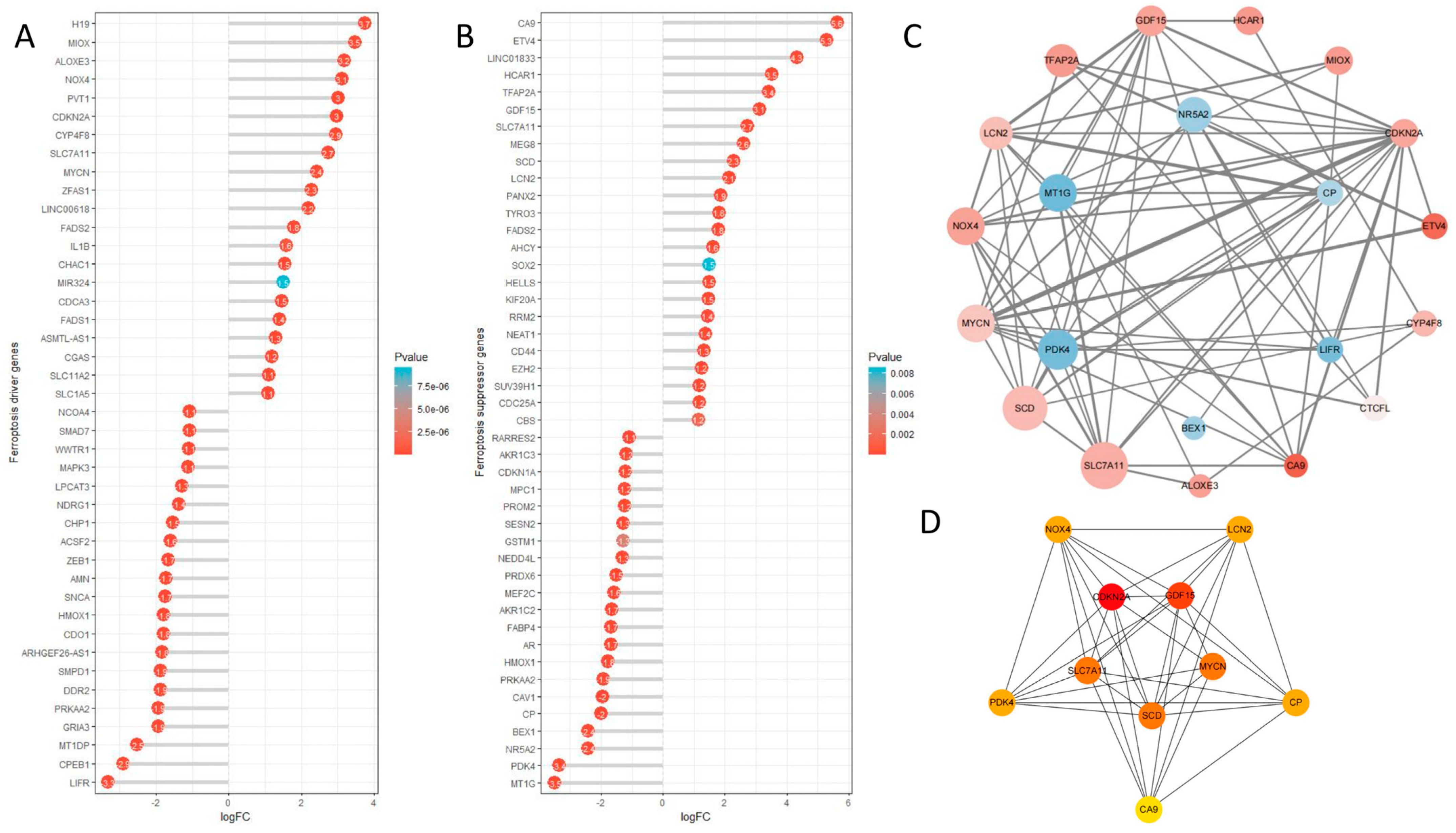
2.9. Ferroptosis Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Collection
4.2. Performing Differential Gene Expression Analysis Using the Three Major R Packages, DESeq2, edgeR, and Limma
4.3. Functional Enrichment Analysis
4.4. Survival Analysis
4.5. PPI Network Construction
4.6. LASSO Regression Analysis
4.7. Immune Cell Infiltration Analysis
4.8. Mutation Analysis
4.9. Connectivity Map (cMAP) Analysis
4.10. Ferroptosis Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.; Yang, F.; He, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, W.; Xing, J.; Zhu, Z.; Jiang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; et al. Alteration of tumor suppressor BMP5 in sporadic colorectal cancer: A genomic and transcriptomic profiling based study. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature 2012, 487, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, F.D.S.E.; Wang, X.; Jansen, M.; Fessler, E.; Trinh, A.; De Rooij, L.P.M.H.; De Jong, J.H.; de Boer, O.J.; Van Leersum, R.; Bijlsma, M.F.; et al. Poor-prognosis colon cancer is defined by a molecularly distinct subtype and develops from serrated precursor lesions. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuger, I.Z.; Slieker, R.C.; van Groningen, T.; van Doorn, R. Therapeutic Strategies for Targeting CDKN2A Loss in Melanoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 143, 18–25.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, B.; Li, M.; Song, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; et al. CXCL1 derived from tumor-associated macrophages promotes breast cancer metastasis via activating NF-κB/SOX4 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Hu, W.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Y.; Peng, J.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, J.; Zheng, S. CLCA1 suppresses colorectal cancer aggressiveness via inhibition of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2017, 15, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabasa, M.; Radisky, E.S.; Ikemori, R.; Bertolini, G.; Arshakyan, M.; Hockla, A.; Duch, P.; Rondinone, O.; Llorente, A.; Maqueda, M.; et al. MMP1 drives tumor progression in large cell carcinoma of the lung through fibroblast senescence. Cancer Lett. 2021, 507, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehner, C.; Miller, E.; Khauv, D.; Nassar, A.; Oberg, A.L.; Bamlet, W.R.; Zhang, L.; Waldmann, J.; Radisky, E.S.; Crawford, H.C.; et al. Tumor cell-derived MMP3 orchestrates Rac1b and tissue alterations that promote pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2014, 12, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au-Yeung, C.-L.; Yeung, T.-L.; Achreja, A.; Zhao, H.; Yip, K.-P.; Kwan, S.-Y.; Onstad, M.; Sheng, J.; Zhu, Y.; Baluya, D.L.; et al. ITLN1 modulates invasive potential and metabolic reprogramming of ovarian cancer cells in omental microenvironment. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Visser, K.E.; Joyce, J.A. The evolving tumor microenvironment: From cancer initiation to metastatic outgrowth. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 374–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.-F.; Liu, C.-J.; Liu, L.-L.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, A.-Y. Expression profile of immune checkpoint genes and their roles in predicting immunotherapy response. Briefings Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, F.; Chen, J.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, Z. TNFSF9 promotes metastasis of pancreatic cancer through Wnt/Snail signaling and M2 polarization of macrophages. Aging 2021, 13, 21571–21586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podojil, J.R.; Miller, S.D. Potential targeting of B7-H4 for the treatment of cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 276, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, R.D.M.; Roberts, N.A.; Dart, R.J.; Vantourout, P.; Jandke, A.; Nussbaumer, O.; Deban, L.; Cipolat, S.; Hart, R.; Iannitto, M.L.; et al. Epithelia Use Butyrophilin-like Molecules to Shape Organ-Specific γδ T Cell Compartments. Cell 2016, 167, 203–218.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Zhu, C.; Kondo, Y.; Anderson, A.C.; Gandhi, A.; Russell, A.F.; Dougan, S.K.; Petersen, B.-S.; Melum, E.; Pertel, T.; et al. CEACAM1 regulates TIM-3-mediated tolerance and exhaustion. Nature 2015, 517, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; Luo, P. CD209 signaling pathway as a biomarker for cisplatin chemotherapy response in small cell lung cancer. Genes Dis. 2023, 11, 101038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Xu, J.; Huang, Q.; Huang, M.; Li, K.; Qu, K.; Wen, H.; Lin, R.; Zheng, M.; Wei, H.; et al. Reduced CD160 Expression Contributes to Impaired NK-cell Function and Poor Clinical Outcomes in Patients with HCC. Cancer Res 2018, 78, 6581–6593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.; Ren, Z.; Yang, F.; Yang, P.; Zhang, T. Clinical significance and immune landscape of KIR2DL4 and the senescence-based signature in cutaneous melanoma. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 3947–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Bodycombe, N.E.; Haskell, K.M.; Sun, Y.L.; Wang, E.T.; Morris, C.A.; Jones, L.H.; Wood, L.D.; Pletcher, M.T. A flow cytometry-based screen identifies MBNL1 modulators that rescue splicing defects in myotonic dystrophy type I. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 3056–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liao, Y.; Sun, P.; Tu, J.; Zou, Y.; Fang, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Peng, Y.; et al. Construction of an ER stress-related prognostic signature for predicting prognosis and screening the effective anti-tumor drug in osteosarcoma. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Hu, K.; Zeng, S.; Wu, L.; Liu, S.; Zhi, C.; Lai, M.; Chen, D.; Xie, L.; et al. Histone deacetylase 6 promotes growth of glioblastoma through the MKK7/JNK/c-Jun signaling pathway. J. Neurochem. 2020, 152, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, S.; Phillips, A.C.; Clark, P.A.; Stott, F.; Peters, G.; Ludwig, R.L.; Vousden, K.H. p14ARF links the tumour suppressors RB and p53. Nature 1998, 395, 124–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Choi, B.Y.; Lee, M.-H.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z. Implications of Genetic and Epigenetic Alterations of CDKN2A (p16INK4a) in Cancer. EBioMedicine 2016, 8, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xie, J.; Mao, J. CDKN2A inhibits cell proliferation and invasion in cervical cancer through LDHA-mediated AKT/mTOR pathway. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 23, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, J.K.; Morrow, D.; Bayley, N.A.; Fernandez, E.G.; Salinas, J.J.; Tse, C.; Zhu, H.; Su, B.; Plawat, R.; Jones, A.; et al. CDKN2A deletion remodels lipid metabolism to prime glioblastoma for ferroptosis. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 1048–1060.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, D.; Ye, Z.; Shen, R.; Yu, G.; Wu, J.; Xiong, Y.; Zhou, R.; Qiu, W.; Huang, N.; Sun, L.; et al. IOBR: Multi-Omics Immuno-Oncology Biological Research to Decode Tumor Microenvironment and Signatures. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 687975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, T.R.; Marton, M.J.; Jones, A.R.; Roberts, C.J.; Stoughton, R.; Armour, C.D.; Bennett, H.A.; Coffey, E.; Dai, H.; He, Y.D.; et al. Functional discovery via a compendium of expression profiles. Cell 2000, 102, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, J.; Crawford, E.D.; Peck, D.; Modell, J.W.; Blat, I.C.; Wrobel, M.J.; Lerner, J.; Brunet, J.-P.; Subramanian, A.; Ross, K.N.; et al. The Connectivity Map: Using Gene-Expression Signatures to Connect Small Molecules, Genes, and Disease. Science 2006, 313, 1929–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Narayan, R.; Corsello, S.M.; Peck, D.D.; Natoli, T.E.; Lu, X.; Gould, J.; Davis, J.F.; Tubelli, A.A.; Asiedu, J.K.; et al. A next generation connectivity map: L1000 platform and the first 1,000,000 profiles. Cell 2017, 171, 1437–1452.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Gao, M.; Guo, B.; Gao, M.; Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, L.; Kong, W.; et al. Prediction of drug efficacy from transcriptional profiles with deep learning. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variables | Patients | Percentages (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| gender | male | 298 | 52.19 |
| female | 271 | 47.46 | |
| A/D | Alive | 442 | 77.41 |
| Dead | 127 | 22.24 | |
| Age, years | ≦69 | 272 | 47.80 |
| >69 | 297 | 52.20 | |
| T stage | T1 | 11 | 1.93 |
| T2 | 95 | 16.64 | |
| T3 | 390 | 68.30 | |
| T4 | 39 | 6.83 | |
| N stage | N0 | 335 | 58.67 |
| N1 | 129 | 22.59 | |
| N2 | 105 | 18.39 | |
| M stage | M0 | 416 | 72.85 |
| M1 | 81 | 14.19 | |
| MX | 64 | 11.21 | |
| Name | Count | % | p-Value | Genes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO-BP | production of molecular mediator of immune response | 62 | 5.09 | 9.13 × 10−13 | CD22, PGC, SLC7A5, AICDA, CD160, CCR2, TREM1, VPREB3, CD36, APOA2, SLAMF9, TLR3, KLK7, MZB1, KIR2DL4, ELANE, IGKV4-1, IGKV6-21, IGKV3D-20, IGKV3D-11, IGKV1D-42, IGLV4-69, IGLV8-61, IGLV4-60, IGLV10-54, IGLV1-50, IGLV5-48, IGLV7-46, IGLV5-45, IGLV1-44, IGLV7-43, IGLV2-33, IGLV2-14, IGLV3-10, IGLV3-9, IGLV4-3, TRDV1, IGKV3D-15, IGKV6D-21, IGKV2D-30, IGKV1-6, IGKV3-20, IGKV1D-33, IGKV1-17, IGKV1-8, IGKV1-16, MIF, IGKV2-24, IGKV2D-24, IGKV1-9, IGKV1-39, IGKV2D-28, IGKV1D-17, IGKV3-7, IGKV2-30, IGKV2D-29, IGKV1-12, IGKV2-28, IGKV1-27, IGKV1D-39, IGLV2-8, IGKV1D-12 |
| immunoglobulin production | 49 | 4.03 | 1.29 × 10−17 | CD22, AICDA, VPREB3, MZB1, IGKV4-1, IGKV6-21, IGKV3D-20, IGKV3D-11, IGKV1D-42, IGLV4-69, IGLV8-61, IGLV4-60, IGLV10-54, IGLV1-50, IGLV5-48, IGLV7-46, IGLV5-45, IGLV1-44, IGLV7-43, IGLV2-33, IGLV2-14, IGLV3-10, IGLV3-9, IGLV4-3, TRDV1, IGKV3D-15, IGKV6D-21, IGKV2D-30, IGKV1-6, IGKV3-20, IGKV1D-33, IGKV1-17, IGKV1-8, IGKV1-16, IGKV2-24, IGKV2D-24, IGKV1-9, IGKV1-39, IGKV2D-28, IGKV1D-17, IGKV3-7, IGKV2-30, IGKV2D-29, IGKV1-12, IGKV2-28, IGKV1-27, IGKV1D-39, IGLV2-8, IGKV1D-12 | |
| GO-CC | immunoglobulin complex | 72 | 5.58 | 5.46696 × 10−49 | CD79A, JCHAIN, IGKV4-1, IGKV6-21, IGKV3D-20, IGKV3D-11, IGKV1D-42, IGLV4-69, IGLV8-61, IGLV4-60, IGLV10-54, IGLV1-50, IGLV5-48, IGLV7-46, IGLV5-45, IGLV1-44, IGLV7-43, IGLV2-33, IGLV2-14, IGLV3-10, IGLV3-9, IGLV4-3, IGLC7, IGHA2, IGHA1, IGHV6-1, IGHV2-5, IGHV3-7, IGHV3-11, IGHV3-13, IGHV3-15, IGHV3-21, IGHV3-23, IGHV3-35, IGHV4-39, IGHV3-48, IGHV3-49, IGHV5-51, IGHV3-53, IGHV1-58, IGHV3-66, IGHV3-73, IGKV3D-15, IGHV4-59, IGHV3-74, IGKV6D-21, IGHV3-72, IGKV2D-30, IGKV1-6, IGKV3-20, IGKV1D-33, IGKV1-17, IGKV1-8, IGKV1-16, IGKV2-24, IGKV2D-24, IGKV1-9, IGKV1-39, IGKV2D-28, IGKV1D-17, IGKV3-7, IGKV2-30, IGKV2D-29, IGKV1-12, IGKV2-28, IGKV1-27, IGKV1D-39, IGLL5, IGLV2-8, IGKV1D-12, IGHV7-4-1, IGHV3-64D |
| collagen-containing extracellular matrix | 69 | 5.35 | 3.37778 × 10−13 | COL11A1, NTN1, FGFR2, COL19A1, ADAMTS2, CMA1, CTSG, BMP7, LAMA1, SRPX, SRPX2, SFRP1, COMP, WNT2, PTPRZ1, SERPINE1, OGN, CXCL12, COL1A1, COL7A1, ANGPTL1, MFAP2, MMP8, TGFBI, CLU, ITIH5, COL10A1, F13A1, AMELX, FGL2, GDF15, MATN3, ADAMDEC1, CILP, MMRN1, INHBE, DPT, AHSG, HAPLN1, HMCN2, NCAM1, SPARCL1, ABI3BP, ACAN, AZGP1, CLEC3B, EDIL3, SHH, CTHRC1, VWA2, MFAP4, KRT1, TNXB, FGB, ANGPTL7, COL6A5, ZG16, F2, BGN, EMILIN3, ANGPTL5, VWC2, PRELP, ELANE, COL4A6, MFAP5, EGFL6, VIT, MMP28 | |
| apical plasma membrane | 68 | 5.28 | 9.77371 × 10−14 | SLC13A2, CEACAM7, DPEP1, CLCA4, CASR, SLC9A3, CYBRD1, ABCB11, CDHR2, CA12, CEACAM1, PTPRH, KCNK2, SLC15A1, SLC4A11, SI, SLC26A3, CDHR5, SLC7A5, AQP8, FOLR1, CLIC5, SLC9A2, PAPPA2, ABCG2, TRPM6, ECRG4, CNTFR, SLC17A1, ATP1B2, SLC6A6, SLC14A2, CBLIF, CD36, PRKG2, SLC4A10, ANK2, SLC17A4, ATP6V0D2, SLC26A2, KCNMA1, KCNB1, SLC5A11, STC1, IL6R, PTH1R, CD300LG, AQP5, CLDN1, SCNN1G, MYO1A, CA4, NAALADL1, SLC22A11, SCNN1B, P2RY1, SLC23A1, KISS1, MAL, SPTBN2, SLC6A19, SLC26A9, OXTR, SAPCD2, P2RY4, P2RX2, SLC6A14, GPIHBP1 | |
| cell projection membrane | 51 | 3.95 | 6.88773 × 10−8 | DPEP1, PHLPP2, PSD, SLC9A3, CNGB1, CYBRD1, CDHR2, ITGA8, FAP, CEACAM1, PTPRH, EPB41L3, TESC, SLC26A3, CDHR5, BMX, GABRE, SLC7A5, AQP8, CA9, FOLR1, BVES, GABRG2, ABCG2, TRPM6, ATP1B2, SLC6A6, PDE6A, CD36, SLC17A4, SLC7A11, SLC26A2, KCNB1, PDE9A, S100P, HHIP, GPER1, PRKCB, CA4, FAM107A, P2RY12, DRD5, GAP43, SLC6A19, TSPEAR, ITLN1, DDN, MAPT, CYS1, NME1, SSTR3 | |
| monoatomic ion channel complex | 45 | 3.49 | 4.70643 × 10−8 | BEST2, TRPC7, CNGB1, KCNK2, GABRE, SLC17A7, GRIN2D, GRIK5, CLIC5, GABRG2, CASQ2, OLFM3, BEST3, DPP6, SCN7A, CACNG8, BEST4, CNGA3, KCNMB1, SCN2B, KCNA6, GRIA4, SCN3A, KCNJ16, KCNMA1, KCNB1, GRIK3, HTR3A, SCNN1G, SCN11A, SCNN1B, SCN9A, LRRC8E, KCNG3, SCN4B, KCNA3, SLC17A8, GRIN2A, CLCNKB, KCNIP4, HTR3E, GABRD, VWC2, TMEM249, GRIN2B | |
| GO-MF | metal ion transmembrane transporter activity | 57 | 4.73 | 8.3773 × 10−8 | SLC13A2, SLC11A1, ATP1A2, SLC9A3, ATP2B3, TRPC7, SLC4A4, KCNK2, SLC4A11, SLC17A7, GRIN2D, GRIK5, CLDN16, SLC9A2, SLC5A7, SLC8A2, TRPM6, SLC17A1, SLC6A6, SNAP25, SCN7A, CACNG8, KCNN3, SLC4A10, KCNMB1, SLC17A4, SCN2B, GPM6A, KCNA6, SCN3A, KCNJ16, KCNMA1, SLC13A3, KCNB1, SLC5A11, GRIK3, SLC30A8, PKD1L2, SCNN1G, TRPV3, SCN11A, SCNN1B, SCN9A, SLC23A1, KCNG3, TMEM37, KCNK3, SCN4B, KCNA3, SLC17A8, SLC9A9, GRIN2A, KCNH8, KCNIP4, SLC30A10, SLC6A14, GRIN2B |
| monoatomic ion channel activity | 57 | 4.73 | 1.48449 × 10−7 | CLCA1, CLCA4, BEST2, TRPC7, CNGB1, KCNK2, SLC4A11, GABRE, SLC17A7, GRIN2D, GRIK5, P2RX1, CLIC5, GABRG2, TRPM6, BEST3, SNAP25, SCN7A, CACNG8, BEST4, KCNN3, CNGA3, KCNMB1, SCN2B, GPM6A, KCNA6, GRIA4, SCN3A, KCNJ16, KCNMA1, KCNB1, GRIK3, PKD1L2, HTR3A, SCNN1G, TRPV3, SCN11A, SCNN1B, SCN9A, LRRC8E, KCNG3, TMEM37, KCNK3, ANO5, SLC26A9, SCN4B, KCNA3, SLC17A8, OTOP2, GRIN2A, KCNH8, CLCNKB, KCNIP4, HTR3E, GABRD, P2RX2, GRIN2B | |
| glycosaminoglycan binding | 41 | 3.41 | 1.40577 × 10−8 | ANOS1, COL11A1, CCN5, FGFR2, EPYC, SERPIND1, CTSG, BMP7, CEMIP, SFRP1, CCN4, COMP, PTN, CCL8, CCN6, JCHAIN, LYVE1, STAB2, HAPLN1, RSPO2, HABP2, ACAN, PCOLCE2, CLEC3B, SHH, TNXB, RSPO1, CXCL11, CXCL8, CEL, REG3A, ZG16, F2, GREM2, BGN, SLIT3, PRELP, SPOCK3, ELANE, VIT, CCL23 | |
| extracellular matrix structural constituent | 37 | 3.07 | 9.57517 × 10−11 | ANOS1, COL11A1, COL19A1, LAMA1, SRPX, SRPX2, COMP, OGN, COL1A1, COL7A1, MFAP2, TGFBI, COL10A1, AMELX, FGL2, MATN3, CHI3L1, CILP, MMRN1, DPT, HAPLN1, HMCN2, ABI3BP, ACAN, EDIL3, CTHRC1, MFAP4, TNXB, FGB, COL6A5, BGN, EMILIN3, MUC6, PRELP, COL4A6, MFAP5, MUC5AC | |
| serine-type peptidase activity | 36 | 2.99 | 1.1059 × 10−8 | PRSS22, TLL1, FAP, CMA1, PCSK5, MMP11, CTSG, PRSS33, TPSG1, MMP8, PLAU, PCSK2, MASP1, KLK10, KLK8, DPP6, MMP7, MMP13, TMPRSS13, CORIN, HABP2, MMP3, TMPRSS3, MMP10, TMPRSS5, KLK6, KLK7, PCSK9, F2, RELN, MMP1, ELANE, CFD, PRSS41, PRSS56, PRSS2 | |
| serine hydrolase activity | 36 | 2.99 | 1.79471 × 10−8 | PRSS22, TLL1, FAP, CMA1, PCSK5, MMP11, CTSG, PRSS33, TPSG1, MMP8, PLAU, PCSK2, MASP1, KLK10, KLK8, DPP6, MMP7, MMP13, TMPRSS13, CORIN, HABP2, MMP3, TMPRSS3, MMP10, TMPRSS5, KLK6, KLK7, PCSK9, F2, RELN, MMP1, ELANE, CFD, PRSS41, PRSS56, PRSS2 | |
| serine-type endopeptidase activity | 34 | 2.82 | 1.19537 × 10−8 | PRSS22, TLL1, FAP, CMA1, PCSK5, MMP11, CTSG, PRSS33, TPSG1, MMP8, PLAU, PCSK2, MASP1, KLK10, KLK8, MMP7, MMP13, TMPRSS13, CORIN, HABP2, MMP3, TMPRSS3, MMP10, TMPRSS5, KLK6, KLK7, PCSK9, F2, MMP1, ELANE, CFD, PRSS41, PRSS56, PRSS2 | |
| metallopeptidase activity | 32 | 2.66 | 1.54386 × 10−7 | PDPEP1, CLCA1, CLCA4, TLL1, ADAMTS6, TRHDE, ADAMTS2, MMP11, MEP1A, PAPPA2, MMP8, CPXM2, XPNPEP2, CPA4, ADAMDEC1, CPM, MMP7, MMP13, MEP1B, ADAM12, ADAM33, MMP3, ADAMTS12, CPB1, MMP10, ANPEP, NAALADL1, KLK7, LVRN, MMP1, MMP28, PRSS2 | |
| KEGG | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | 61 | 3.87 | 1.61 × 10−11 | CHRM2, OXTR, THRB, NPFFR1, GRIK5, CHRM4, GRIK3, PTH1R, HTR4, ADRA1A, GHR, HTR7, UCN2, ADORA3, CTSG, PRSS2, INSL5, LYNX1, EDN2, AVPR1B, EDN3, GLP2R, NPY1R, TACR2, SSTR2, F2, SSTR3, GABRG2, SSTR5, ADRB3, AGTR1, NPSR1, CALCA, ADCYAP1R1, GRP, LPAR1, GRIN2A, APELA, P2RY4, CNR2, CNR1, NPY, P2RY1, PENK, GABRE, GABRD, DRD5, GRIA4, P2RY14, HTR1D, SCTR, GCG, GRIN2B, APLN, GRIN2D, KISS1, PYY, P2RX2, SST, P2RX1, VIP |
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | 41 | 2.60 | 7.87972 × 10−6 | CCL13, CNTFR, CSF3, CSF2, CXCL8, TNFRSF13B, IL24, CXCR5, CXCL17, CXCL1, CXCL3, CXCL2, CXCL5, GHR, CCL8, TNFRSF17, CCL19, AMH, IL6R, CCR2, IL11, CCL23, TNFRSF12A, CCL21, GDF15, OSM, LIFR, PPBP, INHBA, BMP7, BMP5, INHBE, EDAR, BMP3, IL1A, CXCL11, CXCL12, IL23A, TNFSF9, CCL28, IL17C | |
| cAMP signaling pathway | 35 | 2.22 | 3.09924 × 10−6 | CHRM2, OXTR, ADCYAP1R1, HHIP, ATP1A2, HTR4, ADCY5, GRIN2A, PLN, CREB3L3, NPY, PLCE1, TNNI3, CNGA3, AMH, BVES, PRKACB, GRIA4, DRD5, EDN2, EDN3, HTR1D, NPY1R, ATP2B3, GCG, ATP1B2, SSTR2, GRIN2B, GRIN2D, SSTR5, SST, VIP, KCNK2, MYL9, CNGB1 | |
| Calcium signaling pathway | 31 | 1.97 | 0.000983789 | CHRM2, OXTR, HTR4, ADRA1A, SLC8A2, MYLK, GRIN2A, HTR7, PLN, FGF20, PLCE1, NOS1, PRKACB, DRD5, PRKCG, AVPR1B, PRKCB, TACR2, ATP2B3, VEGFD, GRIN2B, GRIN2D, ADRB3, P2RX2, P2RX1, FGF19, CASQ2, AGTR1, PLCD4, PLCD1, FGFR2 | |
| Cell adhesion molecules | 25 | 1.59 | 8.07266 × 10−5 | NLGN1, NRXN1, VTCN1, CLDN2, CLDN1, CDH3, SLITRK2, MPZ, SLITRK3, CLDN23, NCAM1, MADCAM1, JAM2, NTNG1, CADM3, NEGR1, CLDN11, IGSF11, CLDN14, CLDN8, ITGA8, CNTN1, CNTN2, CLDN16, CD22 |
| Name | Genes | |
|---|---|---|
| GO-BP | production of molecular mediator of immune response | IGKV2-24, IGKV2D-29, IGLV7-43, IGLV8-61 |
| immunoglobulin production | IGKV2-24, IGKV2D-29, IGLV7-43, IGLV8-61 | |
| GO-CC | immunoglobulin complex | IGKV2-24, IGKV2D-29, IGLV7-43, IGLV8-61 |
| collagen-containing extracellular matrix | PRELP | |
| apical plasma membrane | CA4 | |
| cell projection membrane | CA4, GABRE, NME1, TSPEAR, ITLN1 | |
| monoatomic ion channel complex | GABRD, GABRE, GRIK5 | |
| GO-MF | metal ion transmembrane transporter activity | GRIK5 |
| monoatomic ion channel activity | GABRD, GABRE, GRIK5, CLCA1 | |
| glycosaminoglycan binding | PRELP | |
| extracellular matrix structural constituent | PRELP | |
| serine-type peptidase activity | MMP1, MMP3, TPSG1 | |
| serine hydrolase activity | MMP1, MMP3, TPSG1 | |
| serine-type endopeptidase activity | MMP1, MMP3, TPSG1 | |
| metallopeptidase activity | MMP1, MMP3, CLCA1 | |
| IGKV2-24, IGKV2D-29, IGLV7-43, IGLV8-61, PRELP, CA4, GABRE, NME1, TSPEAR, ITLN1, GABRD, GRIK5, CLCA1, MMP1, MMP3, TPSG1 (Summarize: A total of 16 genes) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, L.; Tian, Y.; Chen, E. The Construction of a Multi-Gene Risk Model for Colon Cancer Prognosis and Drug Treatments Prediction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3954. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25073954
Gao L, Tian Y, Chen E. The Construction of a Multi-Gene Risk Model for Colon Cancer Prognosis and Drug Treatments Prediction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(7):3954. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25073954
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Liyang, Ye Tian, and Erfei Chen. 2024. "The Construction of a Multi-Gene Risk Model for Colon Cancer Prognosis and Drug Treatments Prediction" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 7: 3954. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25073954
APA StyleGao, L., Tian, Y., & Chen, E. (2024). The Construction of a Multi-Gene Risk Model for Colon Cancer Prognosis and Drug Treatments Prediction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(7), 3954. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25073954





