PfbZIP85 Transcription Factor Mediates ω-3 Fatty Acid-Enriched Oil Biosynthesis by Down-Regulating PfLPAT1B Gene Expression in Plant Tissues
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
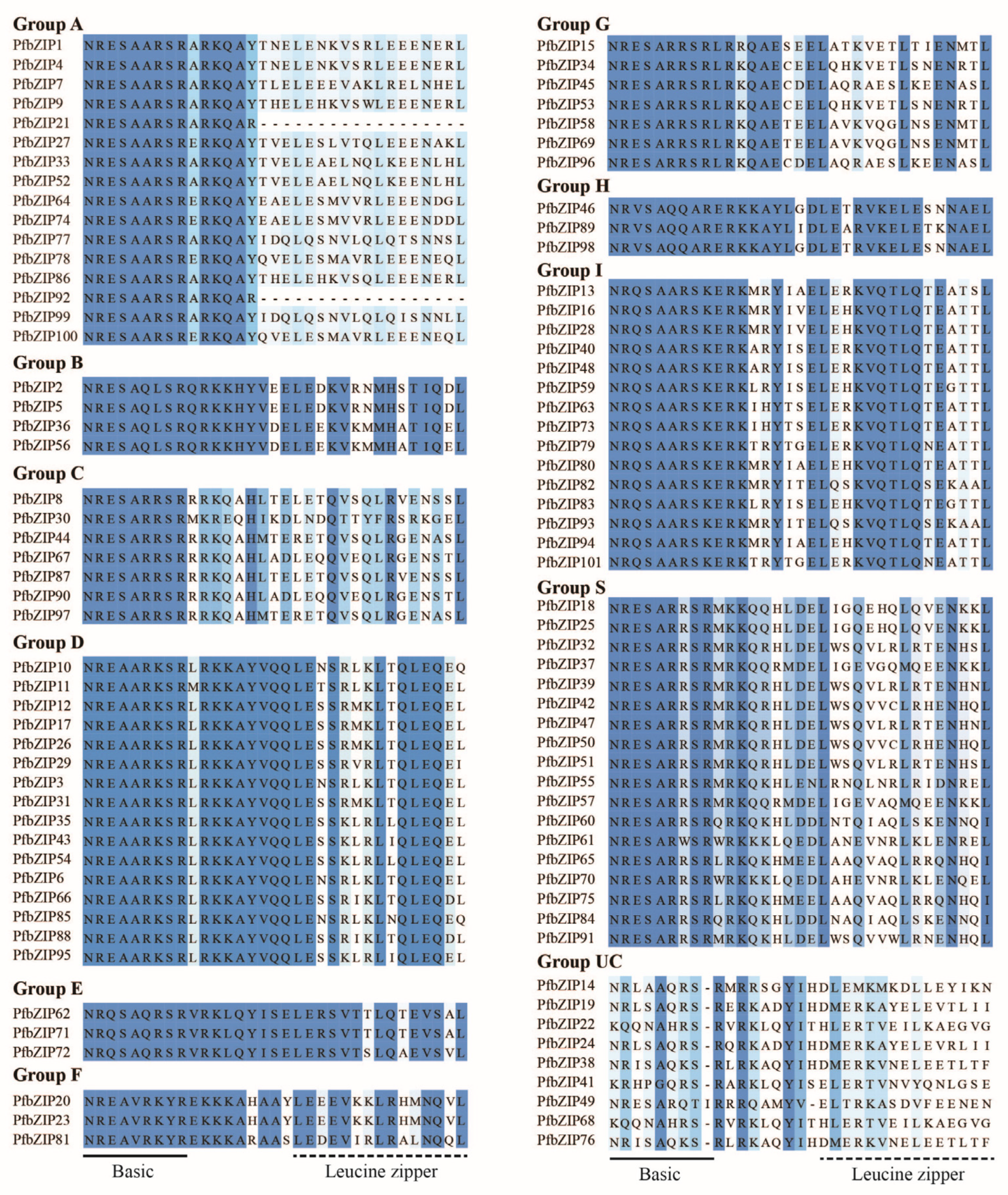
2.1. A Total of 101 PfbZIP Transcription Factors Were Identified from P. frutescens
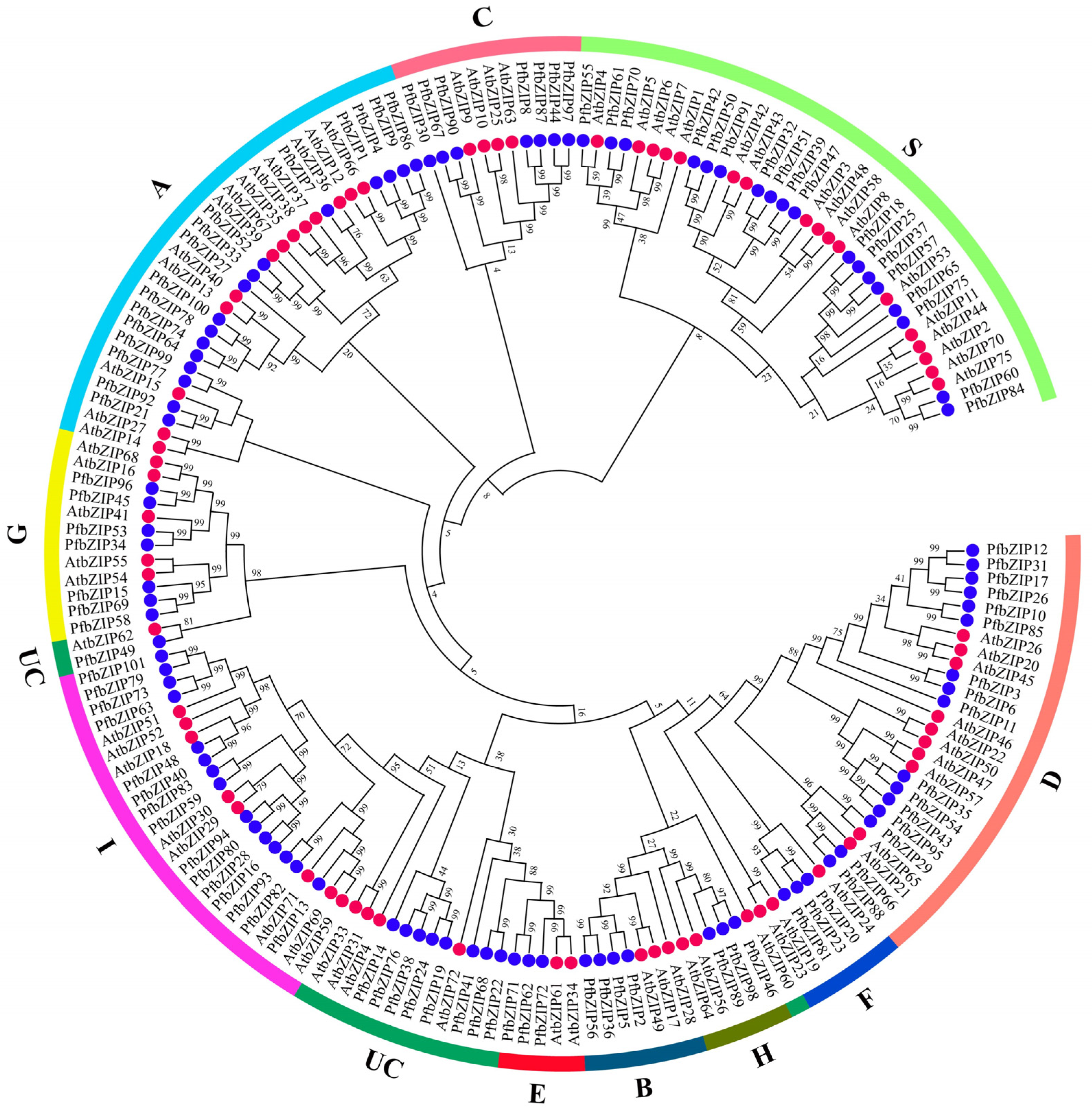
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of PfbZIP Proteins
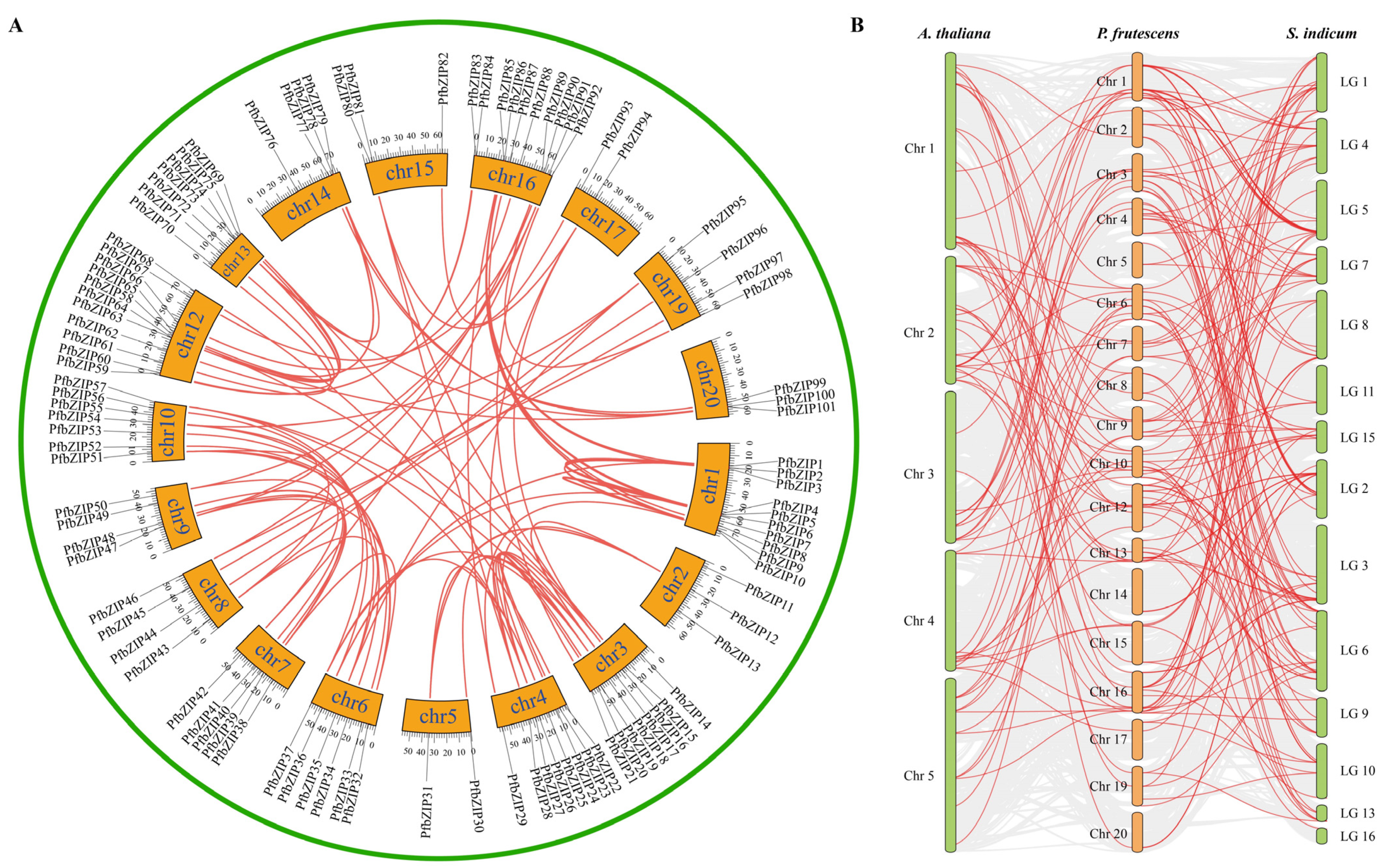
2.3. Segmental Duplication and Synteny Analysis of PfbZIP Genes
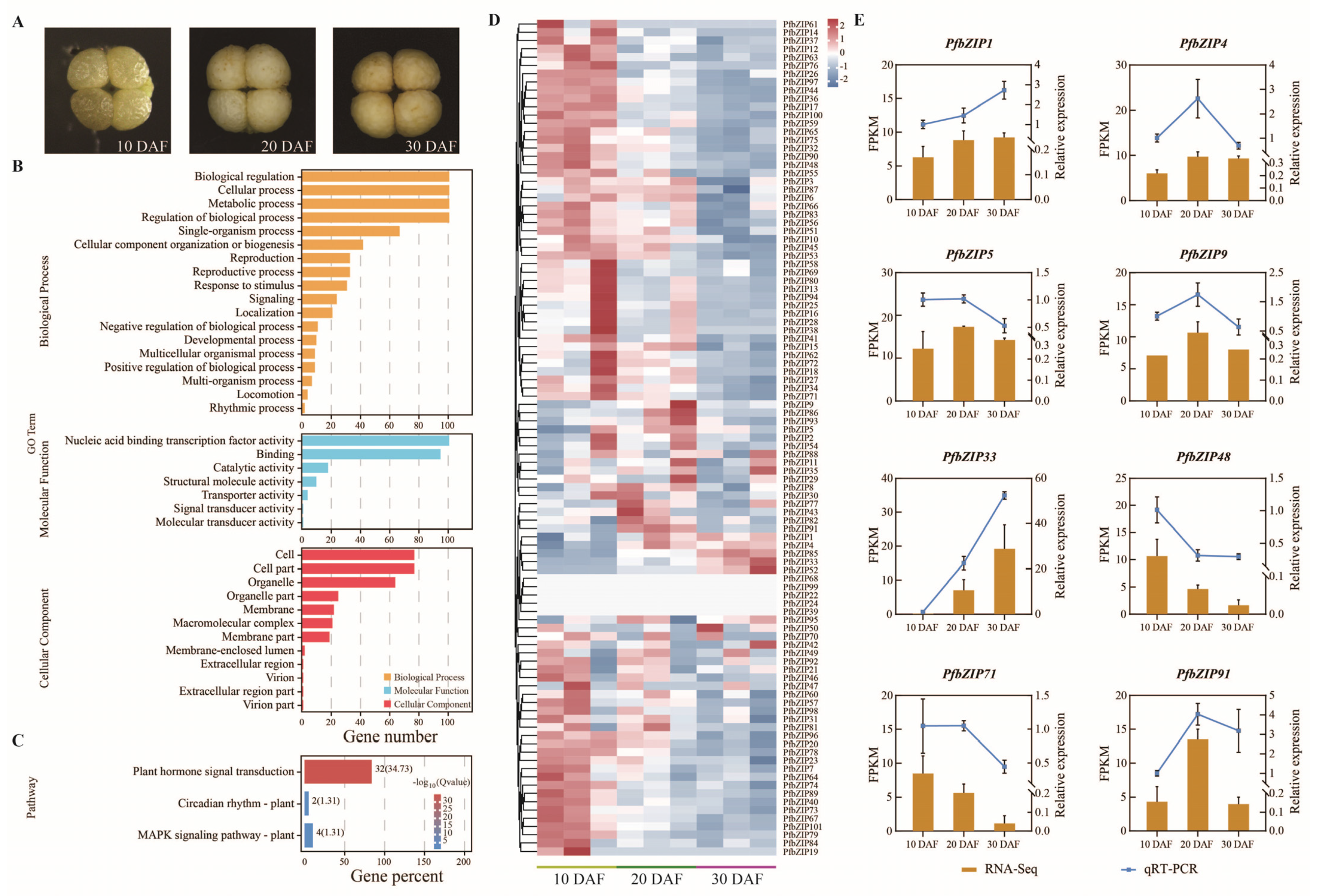
2.4. Functional Classification of PfbZIP Genes by GO and KEGG
2.5. Analysis of the Expression Patterns of the PfbZIP Genes during Perilla Seed Development
2.6. Identification of Candidate PfbZIP TFs Mediating Transcription and Regulation of Enzyme Genes Involved in Lipid Metabolism
2.7. PfbZIP85 Rather than PfbZIP52 Physically Interacts with Promoters of the Downstream Target Genes Revealed by the Yeast One-Hybrid Assay
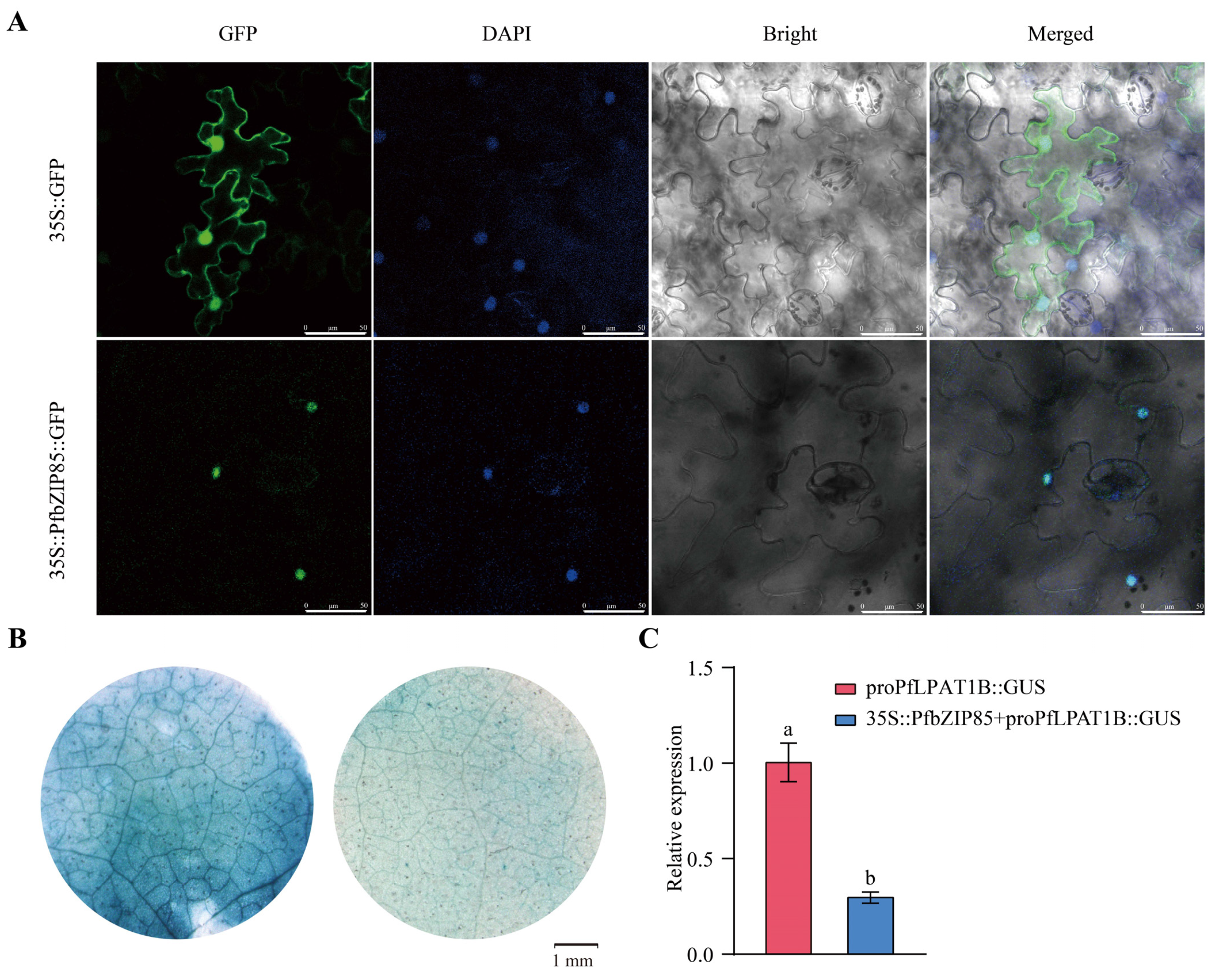
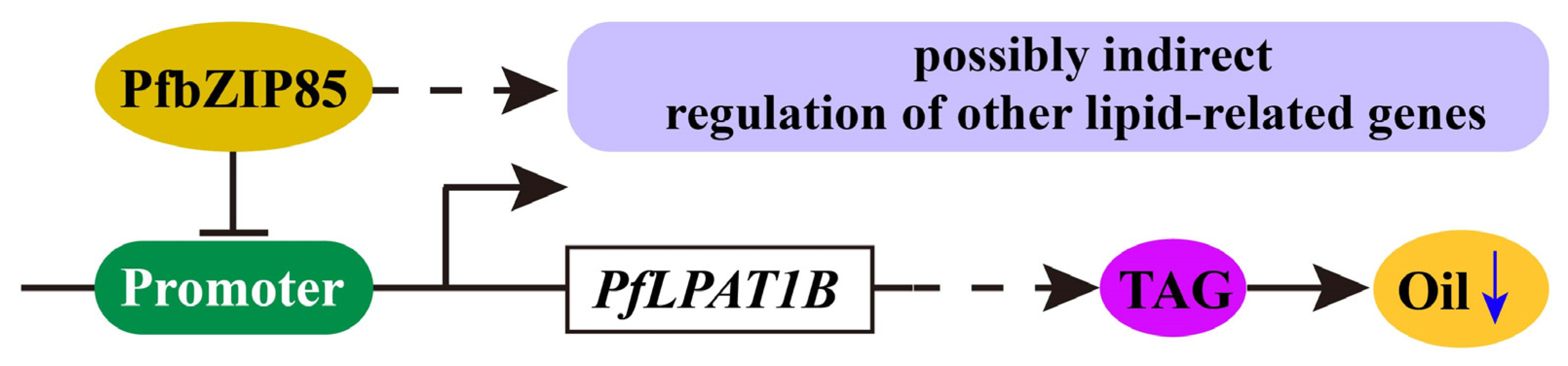
2.8. PfbZIP85 Is Localized in the Nucleus and Negatively Regulates the Expression of the PfLPAT1B Gene
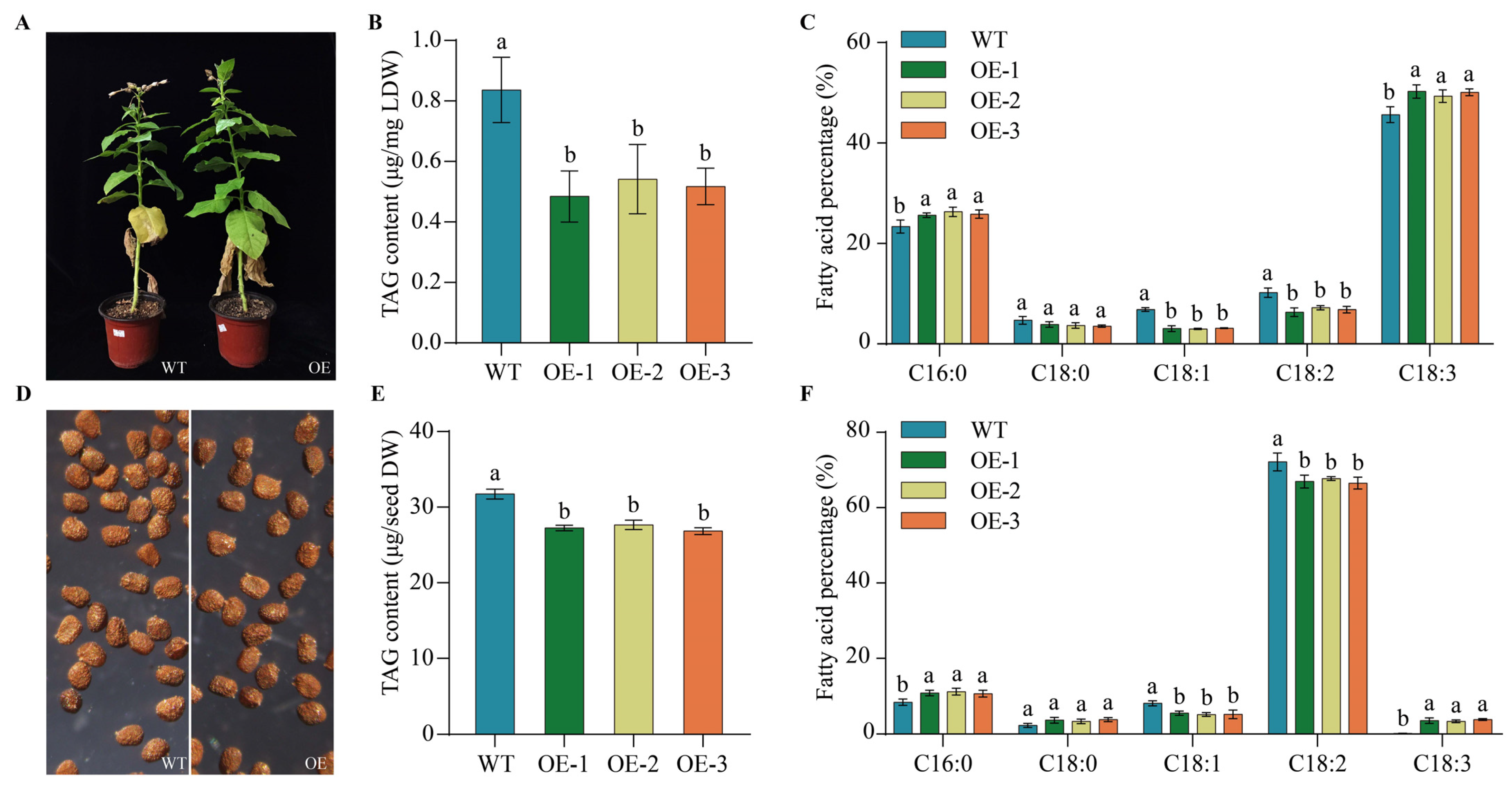
2.9. Heterogeneous Expression of PfbZIP85 Resulted in a Reduction of TAG Content and an Alternation of TAG-Associated FAs in Transgenic Tobacco Lines
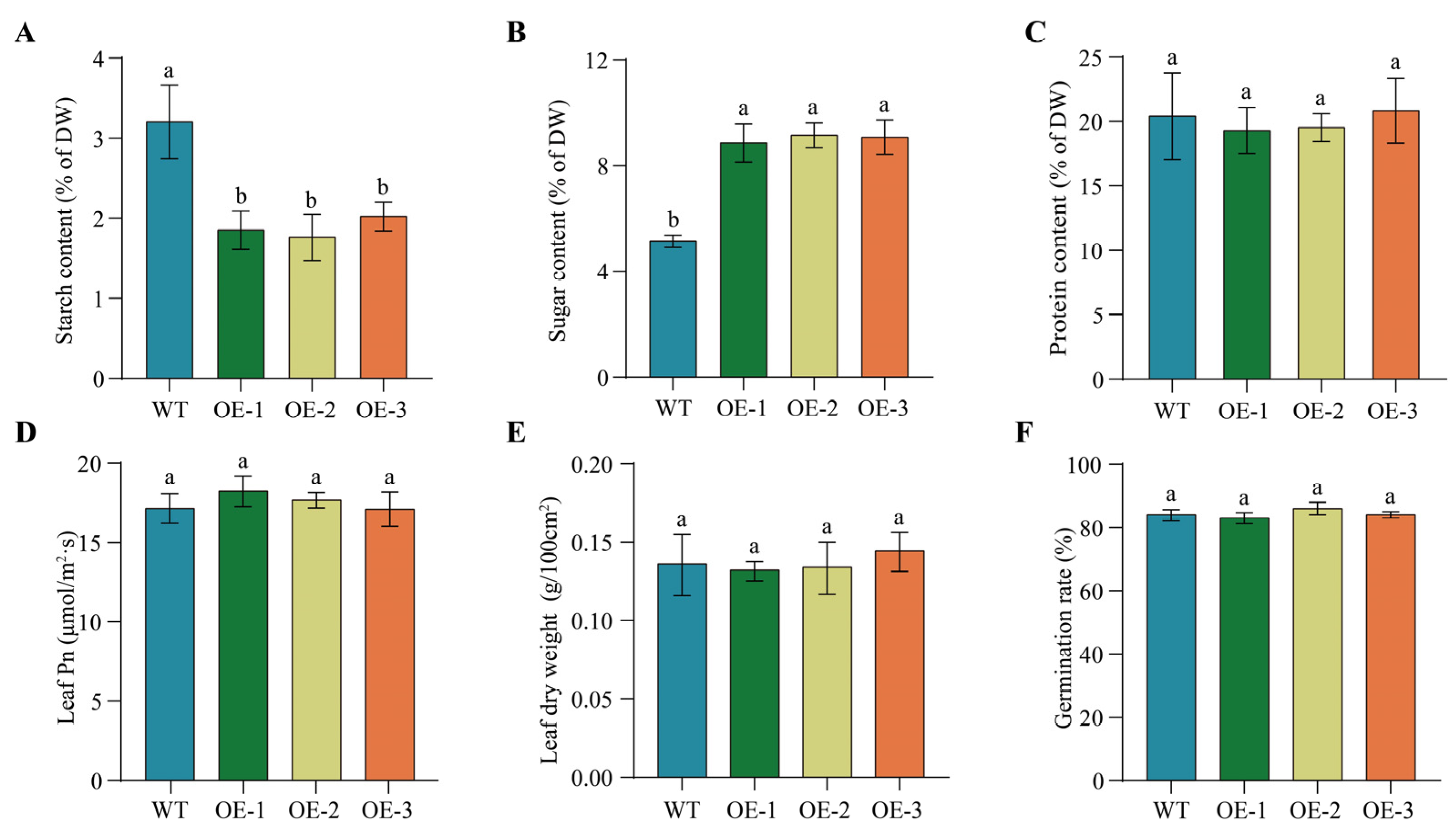
2.10. Overexpression of PfbZIP85 Results in No Significantly Negative Impacts on Other Agronomic Traits of Tobacco Plants
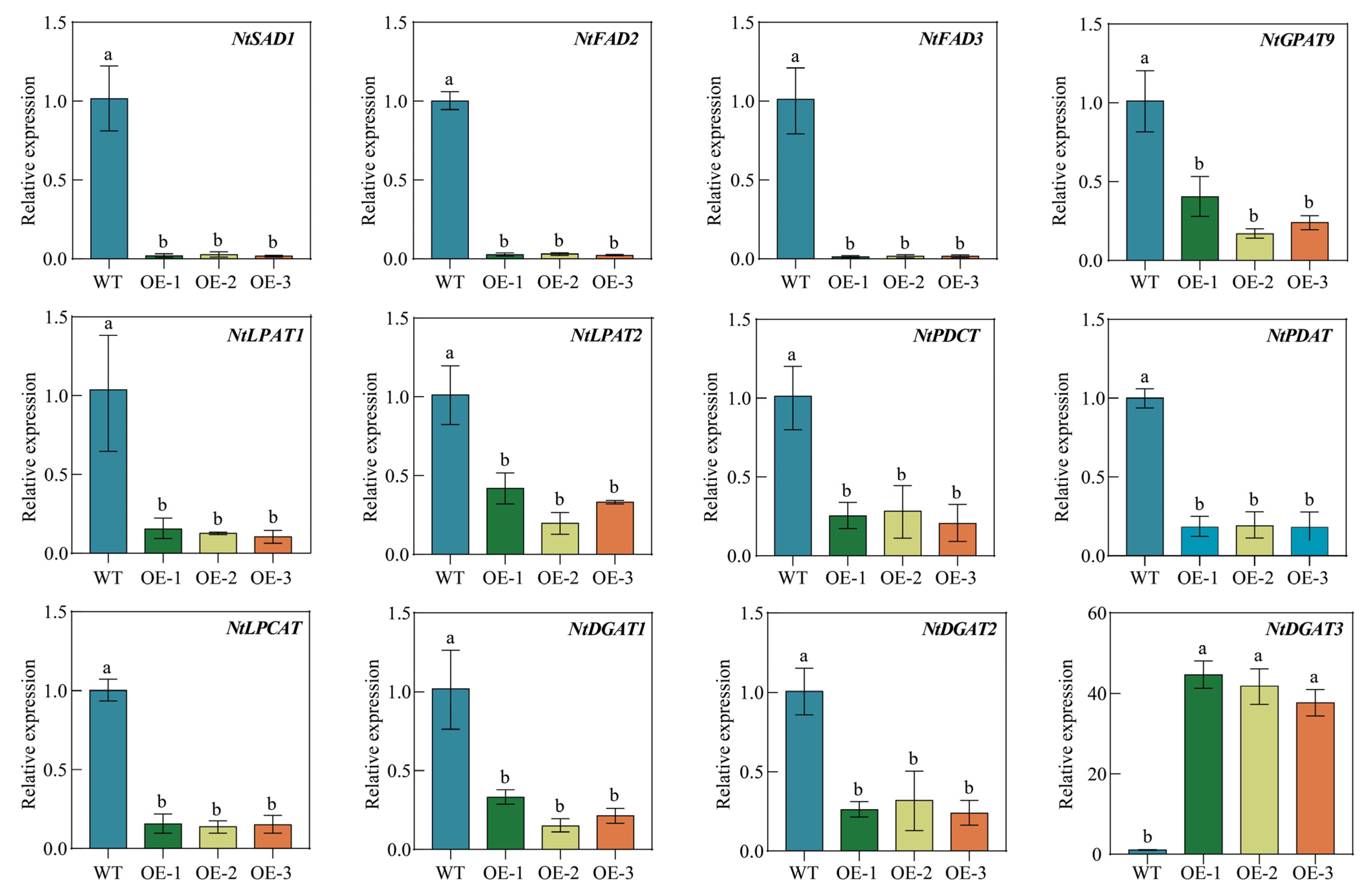
2.11. Overexpression of PfbZIP85 Affects the Expression of Genes Associated with Lipid Metabolism in Tobacco Plants
3. Discussion
3.1. Characteristics and Evolution of PfbZIP Family Members
3.2. PfbZIP Members May Play Significant Roles in Lipid Biosynthesis by Regulating the Expression of Lipid-Associated Genes
3.3. PfbZIP85 Can Be Used as a Genetic Modification Target to Enhance Oil Production and Quality in Plant Seed or Non-Seed Tissues
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biological Materials
4.2. Identification and Chromosomal Localization of bZIP Gene Family Members in P. frutescens
4.3. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Construction of a Phylogenetic Tree
4.4. Analysis of Gene Duplication Events
4.5. GO Annotation and KEGG Enrichment Analysis
4.6. Expression Profiling of PfbZIP Genes Based on RNA-Seq and RT-qPCR
4.7. Prediction of Target Genes Regulated by the bZIP Transcription Factor
4.8. Gene Cloning and Plasmid Construction
4.9. The Yeast One-Hybrid (Y1H) Assay
4.10. Subcellular Localization of PfbZIP85 Protein and GUS Activity Assay
4.11. GUS Stain and GUS Activity Assays
4.12. Heterologous Overexpression of PfbZIP85 in Tobacco Plant
4.13. Lipid Extraction and Fatty Acid Analysis
4.14. Analysis of Other Agronomy Traits in Transgenic Tobacco Lines
4.15. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nitta, M.; Lee, J.K.; Ohnishi, O. Asian Perilla crops and their weedy forms: Their cultivation, utilization and genetic relationships. Econ. Bot. 2003, 57, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.U.; Lee, K.R.; Shim, D.; Lee, J.H.; Chen, G.Q.; Hwang, S. Transcriptome analysis and identification of genes associated with ω-3 fatty acid biosynthesis in Perilla frutescens (L.) var. frutescens. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitta, M.; Lee, J.K.; Kang, C.W.; Katsuta, M.; Yasumoto, S.; Liu, D.; Nagamine, T.; Ohnishi, O. The Distribution of Perilla Species. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2005, 52, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Dixit, A.; Ma, K.H.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, M.H.; Chung, C.S.; Nitta, M.; Okuno, K.; Kim, T.S.; Cho, E.G.; et al. Evaluation of genetic diversity and relationships within an on-farm collection of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. using microsatellite markers. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2008, 55, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yang, S.M.; Shang, Z.W.; Xu, J.; Zhao, D.G.; Wang, H.B.; Shen, Q. Genome-Wide Analysis of the Fatty Acid Desaturase Gene Family Reveals the Key Role of PfFAD3 in α-Linolenic Acid Biosynthesis in Perilla Seeds. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 735862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.; Hu, T.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.; Yin, M.; Li, R.; Wang, J.; Jia, X. Genome-Wide Analysis of Glycerol-3-Phosphate Acyltransferase (GPAT) Family in Perilla frutescens and Functional Characterization of PfGPAT9 Crucial for Biosynthesis of Storage Oils Rich in High-Value Lipids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, M.; Miyazaki, Y. A review on bioactivities of perilla: Progress in research on the functions of perilla as medicine and food. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 925342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mungmai, L.; Preedalikit, W.; Aunsri, N.; Amornlerdpison, D. Efficacy of Cosmetic Formulation Containing Perilla frutescens Leaves Extract for Irritation and Aging Skin. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2020, 13, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M. Health effects of omega-3,6,9 fatty acids: Perilla frutescens is a good example of plant oils. Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med. 2011, 11, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, H. Fatty acid-derived signals in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, E.J.; Miles, E.A.; Burdge, G.C.; Yaqoob, P.; Calder, P.C. Metabolism and functional effects of plant-derived omega-3 fatty acids in humans. Prog. Lipid Res. 2016, 64, 30–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.; Song, Y.; Gao, H.; Wang, M.; Cui, H.; Ji, C.; Wang, J.; Yuan, L.; Li, R. Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of Dof transcription factor family in Camelina sativa. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhercke, T.; El Tahchy, A.; Shrestha, P.; Zhou, X.-R.; Singh, S.P.; Petrie, J.R. Synergistic effect of WRI1 and DGAT1 coexpression on triacylglycerol biosynthesis in plants. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Xie, L.; Chen, G.Q.; Lee, M.Y.; Loque, D.; Scheller, H.V. A transgene design for enhancing oil content in Arabidopsis and Camelina seeds. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roscoe, T.T.; Guilleminot, J.; Bessoule, J.J.; Berger, F.; Devic, M. Complementation of Seed Maturation Phenotypes by Ectopic Expression of ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE3, FUSCA3 and LEAFY COTYLEDON2 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Q.; Yang, Y.; Guo, L.; Yuan, L.; Ma, W. Molecular Basis of Plant Oil Biosynthesis: Insights Gained from Studying the WRINKLED1 Transcription Factor. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldoni, E.; Genga, A.; Cominelli, E. Plant MYB Transcription Factors: Their Role in Drought Response Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 15811–15851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.Y.; Du, Y.T.; Ma, J.; Min, D.H.; Jin, L.G.; Chen, J.; Chen, M.; Zhou, Y.B.; Ma, Y.Z.; Xu, Z.S.; et al. The WRKY Transcription Factor GmWRKY12 Confers Drought and Salt Tolerance in Soybean. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumalaikumar, V.P.; Devkar, V.; Mehterov, N.; Ali, S.; Ozgur, R.; Turkan, I.; Mueller-Roeber, B.; Balazadeh, S. NAC transcription factor JUNGBRUNNEN1 enhances drought tolerance in tomato. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qiu, X.; Yang, Y.; Kim, H.S.; Jia, X.; Yu, H.; Kwak, S.S. Sweetpotato bZIP Transcription Factor IbABF4 Confers Tolerance to Multiple Abiotic Stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, M.; Zhou, W.; Dong, Q.; Jiang, H.; Cheng, B. The DOF-Domain Transcription Factor ZmDOF36 Positively Regulates Starch Synthesis in Transgenic Maize. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baloglu, M.C.; Eldem, V.; Hajyzadeh, M.; Unver, T. Genome-wide analysis of the bZIP transcription factors in cucumber. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Vanitha, J.; Ramachandran, S.; Jiang, S.Y. Genome-wide expansion and expression divergence of the basic leucine zipper transcription factors in higher plants with an emphasis on sorghum. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2011, 53, 212–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gai, W.x.; Ma, X.; Qiao, Y.M.; Shi, B.H.; ul Haq, S.; Li, Q.H.; Wei, A.M.; Liu, K.k.; Gong, Z.H. Characterization of the bZIP Transcription Factor Family in Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.): CabZIP25 Positively Modulates the Salt Tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Xu, W.; Liu, A. Genomic surveys and expression analysis of bZIP gene family in castor bean (Ricinus communis L.). Planta 2014, 239, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakoby, M.; Weisshaar, B.; Dröge-Laser, W.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J.; Tiedemann, J.; Kroj, T.; Parcy, F. bZIP Transcription Factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhawan, A.; Jain, M.; Tyagi, A.K.; Khurana, J.P. Genomic survey and gene expression analysis of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family in rice. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 333–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riechmann, J.L.; Heard, J.E.; Martin, G.M.; Reuber, T.L.; Jiang, C.Z.; Keddie, J.S.; Adam, L.; Pineda, O.; Ratcliffe, O.J.; Samaha, R.; et al. Arabidopsis transcription factors: Genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science 2000, 290, 2105–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, K.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Lin, Y.; Pan, S.; Zhong, X.; Xie, D. Genome-wide analysis of bZIP-encoding genes in maize. DNA Res. 2012, 19, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, L.G.; Riano-Pachon, D.M.; Schrago, C.G.; dos Santos, R.V.; Mueller-Roeber, B.; Vincentz, M. The role of bZIP transcription factors in green plant evolution: Adaptive features emerging from four founder genes. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, D.; Jia, L.; Huang, X.; Ma, G.; Wang, S.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, A.; Guan, M.; Lu, K.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Structural Analysis of bZIP Transcription Factor Genes in Brassica napus. Genes 2017, 8, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Shi, H.; Guo, M.; Chai, M.; He, Q.; Yan, M.; Cao, D.; Zhao, L.; Cai, H.; et al. Evolutionary and expression analyses of soybean basic Leucine zipper transcription factor family. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Dossa, K.; Yu, J.; Li, D.; Liu, A.; Mmadi, M.A.; Zhang, X.; You, J. Identification and characterization of the bZIP transcription factor family and its expression in response to abiotic stresses in sesame. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yan, L.; Wan, L.; Huai, D.; Kang, Y.; Shi, L.; Jiang, H.; Lei, Y.; Liao, B. Genome-wide systematic characterization of bZIP transcription factors and their expression profiles during seed development and in response to salt stress in peanut. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, K.; Seki, M.; Sakurai, T.; Satou, M.; Akiyama, K.; Toyoda, T.; Konagaya, A.; Shinozaki, K. RARTF: Database and tools for complete sets of Arabidopsis transcription factors. DNA Res. 2005, 12, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibalová, A.; Rĕnák, D.; Matczuk, K.; Dupl’áková, N.; Cháb, D.; Twell, D.; Honys, D. AtbZIP34 is required for Arabidopsis pollen wall patterning and the control of several metabolic pathways in developing pollen. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 70, 581–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iven, T.; Strathmann, A.; Bottner, S.; Zwafink, T.; Heinekamp, T.; Guivarc’h, A.; Roitsch, T.; Droge-Laser, W. Homo- and heterodimers of tobacco bZIP proteins counteract as positive or negative regulators of transcription during pollen development. Plant J. 2010, 63, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, S.; McCourt, P.; Tsuchiya, Y. HY5 is involved in strigolactone-dependent seed germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 556–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baena-Gonzalez, E.; Rolland, F.; Thevelein, J.M.; Sheen, J. A central integrator of transcription networks in plant stress and energy signalling. Nature 2007, 448, 938–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciceri, P.; Locatelli, F.; Genga, A.; Viotti, A.; Schmidt, R. The activity of the maize Opaque2 transcriptional activator is regulated diurnally. Plant Physiol. 1999, 121, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weltmeier, F.; Ehlert, A.; Mayer, C.S.; Dietrich, K.; Wang, X.; Schutze, K.; Alonso, R.; Harter, K.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J.; Droge-Laser, W. Combinatorial control of Arabidopsis proline dehydrogenase transcription by specific heterodimerisation of bZIP transcription factors. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3133–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, P.; Onate-Sanchez, L.; Abraham, Z.; Ferrandiz, C.; Diaz, I.; Carbonero, P.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J. Synergistic activation of seed storage protein gene expression in Arabidopsis by ABI3 and two bZIPs related to OPAQUE2. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 21003–21011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, O.; Popova, O.V.; Suthoff, U.; Luking, I.; Dietz, K.J.; Golldack, D. The Arabidopsis basic leucine zipper transcription factor AtbZIP24 regulates complex transcriptional networks involved in abiotic stress resistance. Gene 2009, 436, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, F.; Maeta, E.; Terashima, A.; Takumi, S. Positive role of a wheat HvABI5 ortholog in abiotic stress response of seedlings. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 134, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Zhang, J.S.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhang, W.-K. Role of soybean GmbZIP132 under abscisic acid and salt stresses. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2008, 50, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Zou, H.F.; Wei, W.; Hao, Y.J.; Tian, A.G.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhang, J.S.; Chen, S.Y. Soybean GmbZIP44, GmbZIP62 and GmbZIP78 genes function as negative regulator of ABA signaling and confer salt and freezing tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Planta 2008, 228, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.A.; Cho, J.I.; Han, M.; Ahn, C.H.; Jeon, J.S.; An, G.; Park, P.B. The ABRE-binding bZIP transcription factor OsABF2 is a positive regulator of abiotic stress and ABA signaling in rice. J. Plant Physiol. 2010, 167, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md, A.H.; Lee, Y.; Cho, J.I.; Ahn, C.H.; Lee, S.K.; Jeon, J.S.; Kang, H.; Lee, C.H.; An, G.; Park, P.B. The bZIP transcription factor OsABF1 is an ABA responsive element binding factor that enhances abiotic stress signaling in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2010, 72, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, S.; Wu, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Huang, Q. Genome-Wide Identification, Evolutionary Patterns, and Expression Analysis of bZIP Gene Family in Olive (Olea europaea L.). Genes 2020, 11, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, A.; Kelly, A.A.; Van Erp, H.; Shaw, E.; Powers, S.J.; Kurup, S.; Eastmond, P. bZIP67 Regulates the Omega-3 Fatty Acid Content of Arabidopsis Seed Oil by Activating FATTY ACID DESATURASE3. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 3104–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.X.; Li, Q.T.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhang, F.X.; Ma, B.; Zhang, W.K.; Man, W.Q.; Du, W.G.; Wang, G.D.; Chen, S.Y.; et al. Soybean GmbZIP123 gene enhances lipid content in the seeds of transgenic Arabidopsis plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 4329–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J. A bZIP transcription factor is involved in regulating lipid and pigment metabolisms in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Algal Res. 2021, 59, 102450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Kang, N.K.; Koh, H.G.; Shin, S.-E.; Lee, B.; Jeong, B.-r.; Chang, Y.K. Enhancement of biomass and lipid productivity by overexpression of a bZIP transcription factor in Nannochloropsis salina. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2018, 115, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Leng, L.; Zhang, D.; Chen, S.; Shi, Y.; Ning, Z.; Chen, S. Incipient diploidization of the medicinal plant Perilla within 10,000 years. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voorrips, R.E. MapChart: Software for the Graphical Presentation of Linkage Maps and QTLs. J. Hered. 2002, 93, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çiftçi, O.N.; Przybylski, R.; Rudzińska, M. Lipid components of flax, perilla, and chia seeds. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2012, 114, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Roychoudhury, A. Abscisic-acid-dependent basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors in plant abiotic stress. Protoplasma 2017, 254, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, C.; Xu, X.; Su, C.; Li, J.; Song, H.; Zhang, X.; Pan, Y. SlbZIP38, a Tomato bZIP Family Gene Downregulated by Abscisic Acid, Is a Negative Regulator of Drought and Salt Stress Tolerance. Genes 2017, 8, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leene, J.; Blomme, J.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Cannoot, B.; De Winne, N.; Eeckhout, D.; Persiau, G.; Van De Slijke, E.; Vercruysse, L.; Vanden Bossche, R.; et al. Functional characterization of the Arabidopsis transcription factor bZIP29 reveals its role in leaf and root development. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 5825–5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, S.B.; Mitra, A.; Baumgarten, A.; Young, N.D.; May, G. The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2004, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, N.; Chen, F.; Cai, B.; Dal Santo, S.; Tornielli, G.; Pezzotti, M.; Cheng, Z. Genome-Wide Analysis and Expression Profile of the bZIP Transcription Factor Gene Family in Grapevine (Vitis vinifera). BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, K.L.; Wendel, J.F. Polyploidy and genome evolution in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2005, 8, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Nicolae, D.; Lu, H.H.; Li, W.H. Rapid divergence in expression between duplicate genes inferred from microarray data. Trends Genet. 2002, 18, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendel, J.F. Genome evolution in polyploids. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000, 42, 225–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dröge-Laser, W.; Weiste, C. The C/S1 bZIP Network: A Regulatory Hub Orchestrating Plant Energy Homeostasis. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorca, C.M.; Potschin, M.; Zentgraf, U. bZIPs and WRKYs: Two large transcription factor families executing two different functional strategies. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Kong, Q.; Tee, W.T.; Li, Y.; Low, P.M.; Patra, B.; Guo, L.; Yuan, L.; Ma, W. Transcription factor bZIP52 modulates Arabidopsis seed oil biosynthesis through interaction with WRINKLED1. Plant Physiol. 2023, 192, 2628–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, G.; Mu, X.; Grabowski, P.; Schmutz, J.; Lu, C. Enhancing microRNA167A expression in seed decreases the α-linolenic acid content and increases seed size in Camelina sativa. Plant J. 2019, 98, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Kong, Q.; Lim, A.R.Q.; Lu, S.; Zhao, H.; Guo, L.; Yuan, L.; Ma, W. Transcriptional regulation of oil biosynthesis in seed plants: Current understanding, applications, and perspectives. Plant Commun. 2022, 3, 100328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Gao, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Xue, J.; Jia, X.; Li, R. Correction to: Ectopic overexpression of a type-II DGAT (CeDGAT2-2) derived from oil-rich tuber of Cyperus esculentus enhances accumulation of oil and oleic acid in tobacco leaves. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2021, 14, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Yu, K.; Hildebrand, D.F. DGAT1, DGAT2 and PDAT expression in seeds and other tissues of epoxy and hydroxy fatty acid accumulating plants. Lipids 2010, 45, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene Name | Gene ID | Binding Sequence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PfKAS2 | β-Ketoacyl-acp synthase 2 | C2S51_000860 | CACGTA |
| PfSAD2 | Δ9-Stearoyl-ACP desaturase 2 | C2S51_009736 | TACGTG |
| PfFAD6 | ω-6 fatty acid desaturase 6 | C2S51_002817 | GACGTC/TACGTA |
| PfGPAT1 | Glycerol-3-Phosphate Acyltransferase 1 | C2S51_037878 | AACGTG/CAACGTTA |
| PfLPAT1B | lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase 1B | C2S51_002830 | TACGTG/AACGTG/AACGTT |
| PfDGAT2A | Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase 2A | C2S51_029109 | CACGTG/TACGTG |
| PfDGAT3A | Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase 3A | C2S51_015166 | CACGTT/CACGTC/TACGTG |
| PfPDAT2B | Phospholipid Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase | C2S51_011488 | CACGTG/TACGTG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, X.; Wen, J.; Sun, Y.; Chen, S.; Hu, T.; Li, R.; Wang, J.; Jia, X. PfbZIP85 Transcription Factor Mediates ω-3 Fatty Acid-Enriched Oil Biosynthesis by Down-Regulating PfLPAT1B Gene Expression in Plant Tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4375. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084375
Huang X, Zhou Y, Shi X, Wen J, Sun Y, Chen S, Hu T, Li R, Wang J, Jia X. PfbZIP85 Transcription Factor Mediates ω-3 Fatty Acid-Enriched Oil Biosynthesis by Down-Regulating PfLPAT1B Gene Expression in Plant Tissues. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(8):4375. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084375
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xusheng, Yali Zhou, Xianfei Shi, Jing Wen, Yan Sun, Shuwei Chen, Ting Hu, Runzhi Li, Jiping Wang, and Xiaoyun Jia. 2024. "PfbZIP85 Transcription Factor Mediates ω-3 Fatty Acid-Enriched Oil Biosynthesis by Down-Regulating PfLPAT1B Gene Expression in Plant Tissues" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 8: 4375. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084375
APA StyleHuang, X., Zhou, Y., Shi, X., Wen, J., Sun, Y., Chen, S., Hu, T., Li, R., Wang, J., & Jia, X. (2024). PfbZIP85 Transcription Factor Mediates ω-3 Fatty Acid-Enriched Oil Biosynthesis by Down-Regulating PfLPAT1B Gene Expression in Plant Tissues. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(8), 4375. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084375





