The Role and Mechanisms of the Hypocretin System in Zebrafish (Danio rerio)
Abstract
1. Introduction
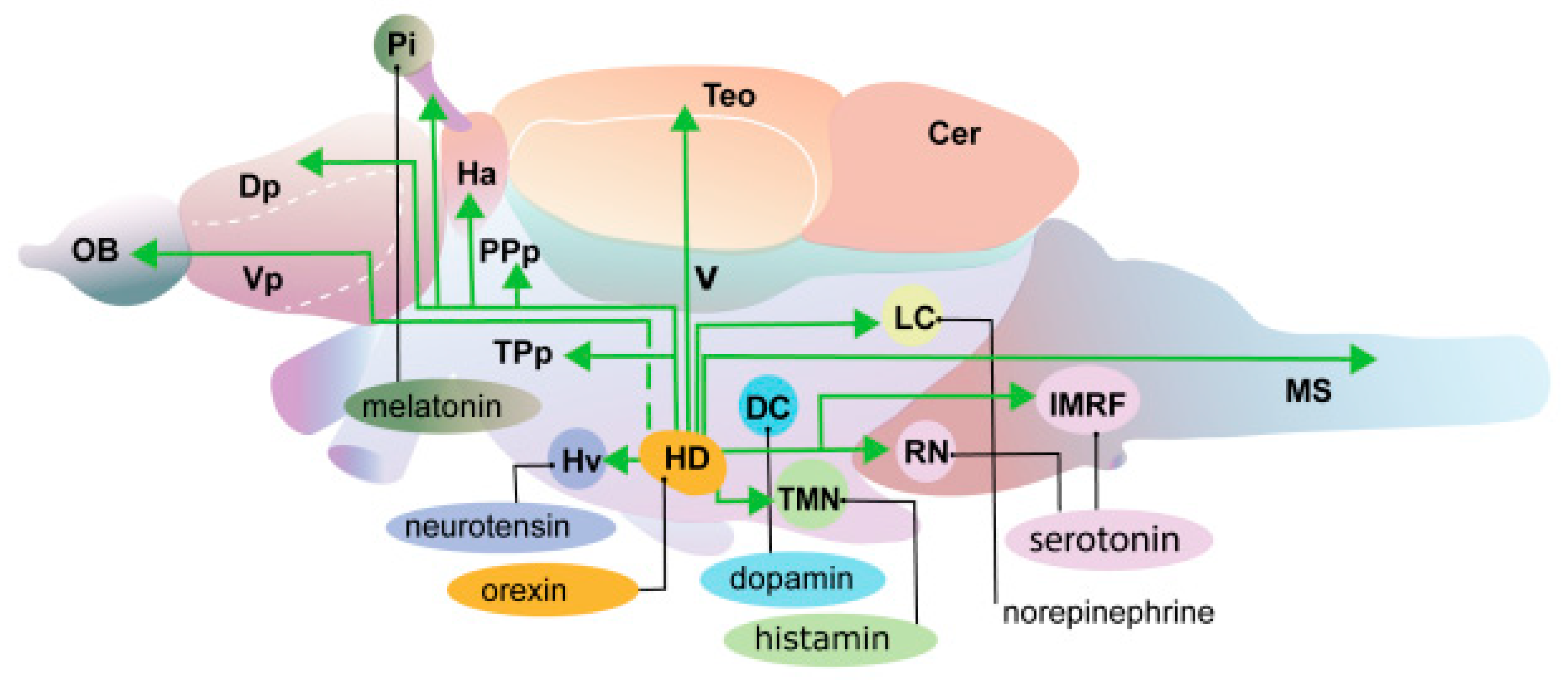
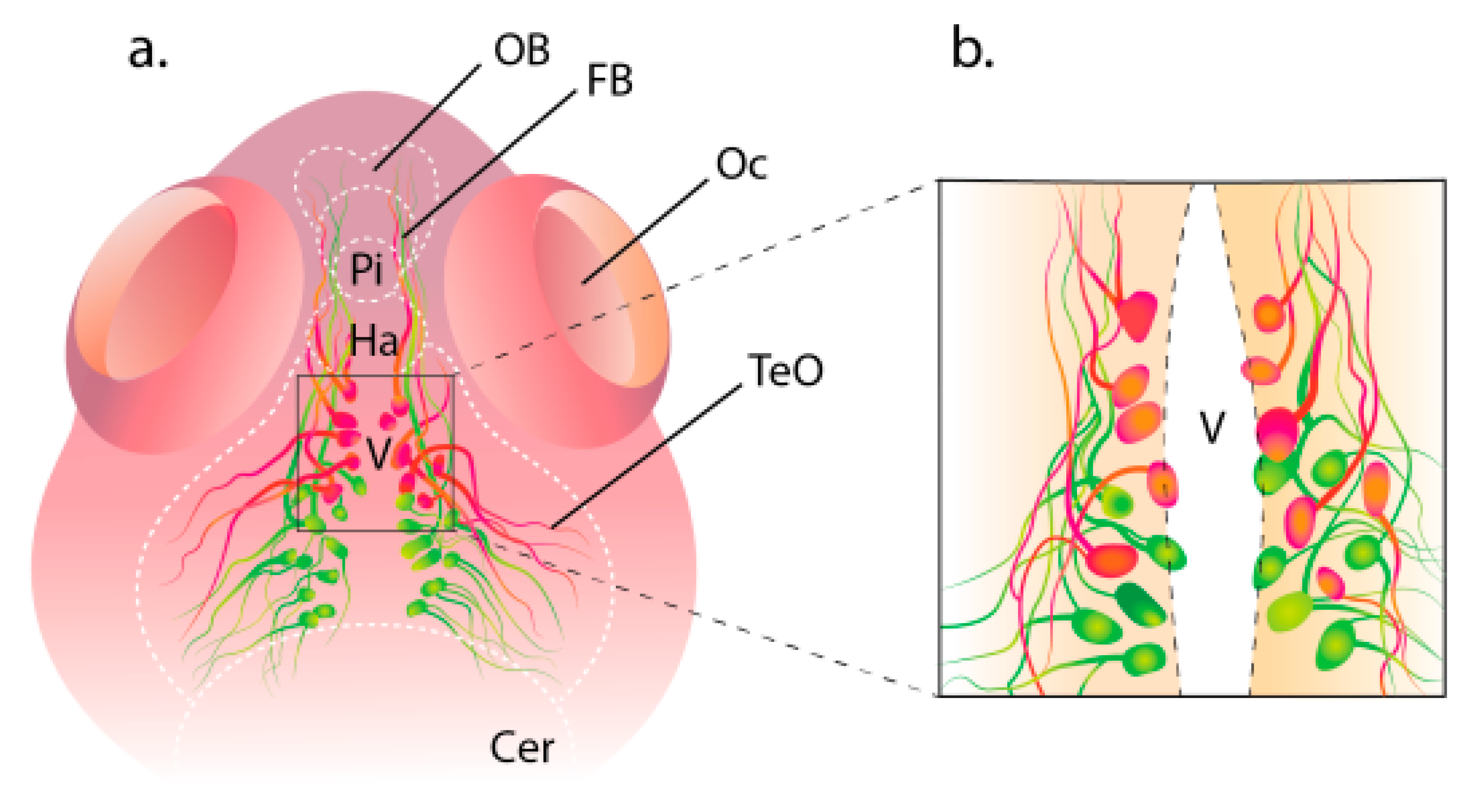
2. Structure of the Hypocretin System in Zebrafish
3. Functions of the Hypocretin System
4. Effect of Genetic Ablation of HCRT Neurons
5. Expression of the HCRT Receptor (HCRTR) in the Ablation of HCRT Neurons
6. Regulation of HCRT Cell Specification in D. rerio
7. Heterogeneity of HCRT Neurons
8. Interaction Between Systems of HCRT and GnRH3 Neurons
9. Expression of the HCRT Receptor in GnRH3:EMD Neurons
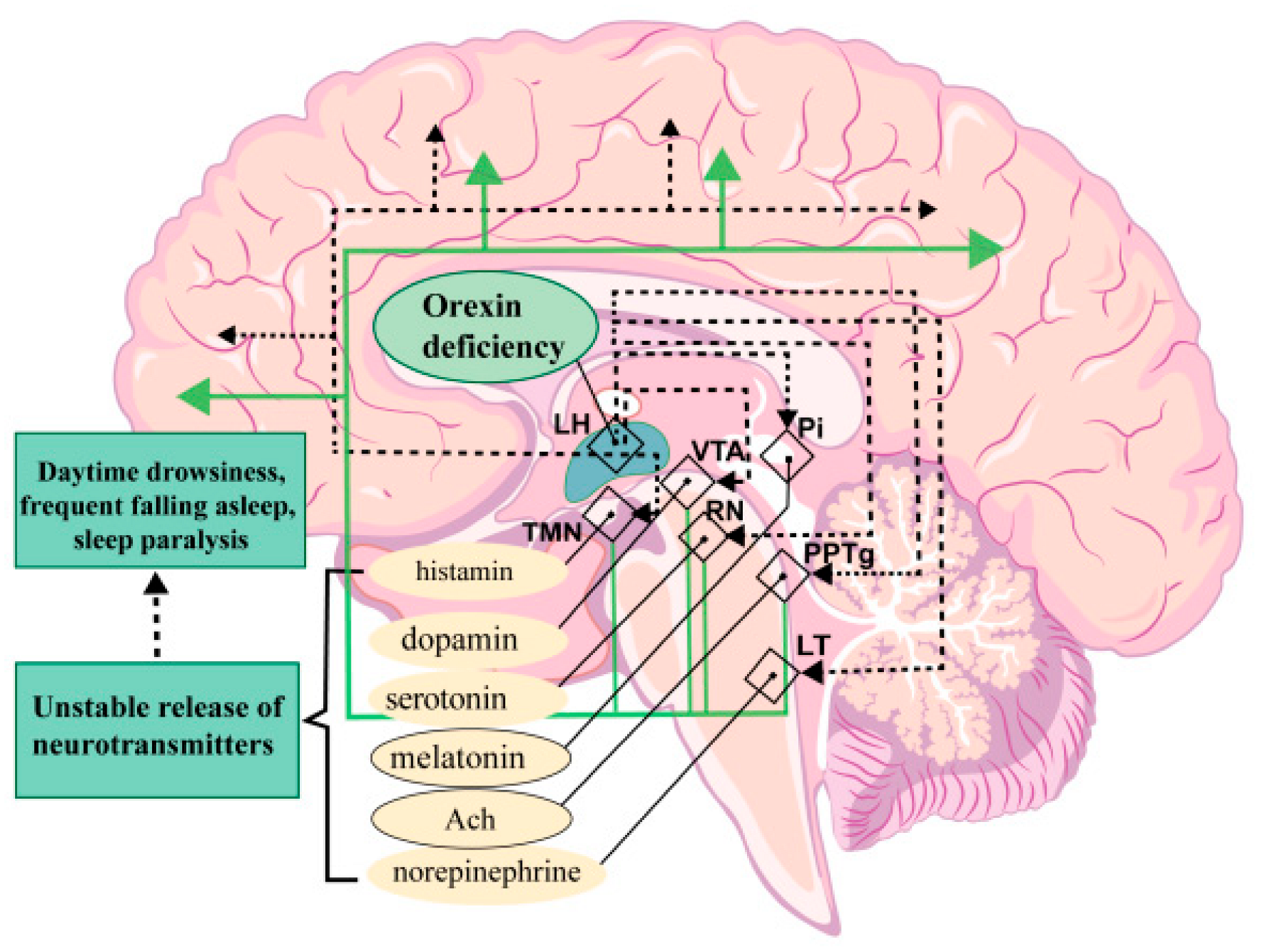
10. Diseases Associated with the Human Hypocretin System
11. Disadvantages of the Danio rerio Model in Studies of Sleep and Circadian Rhythms
12. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, P.; Wang, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, S.; Jiang, W.; Wang, Z.; Sun, C.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z. Functional Characterization of an Orexin Neuropeptide in Amphioxus Reveals an Ancient Origin of Orexin/Orexin Receptor System in Chordate. Sci. China Life Sci. 2019, 62, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbaz, I.; Yelin-Bekerman, L.; Nicenboim, J.; Vatine, G.; Appelbaum, L. Genetic Ablation of Hypocretin Neurons Alters Behavioral State Transitions in Zebrafish. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 12961–12972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz, I.; Foulkes, N.S.; Gothilf, Y.; Appelbaum, L. Circadian Clocks, Rhythmic Synaptic Plasticity and the Sleep-Wake Cycle in Zebrafish. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz, I.; Zada, D.; Tovin, A.; Braun, T.; Lerer-Goldshtein, T.; Wang, G.; Mourrain, P.; Appelbaum, L. Sleep-Dependent Structural Synaptic Plasticity of Inhibitory Synapses in the Dendrites of Hypocretin/Orexin Neurons. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 6581–6597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaslin, J.; Nystedt, J.M.; Ostergård, M.; Peitsaro, N.; Panula, P. The Orexin/Hypocretin System in Zebrafish Is Connected to the Aminergic and Cholinergic Systems. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 2678–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amores, A.; Catchen, J.; Ferrara, A.; Fontenot, Q.; Postlethwait, J.H. Genome Evolution and Meiotic Maps by Massively Parallel DNA Sequencing: Spotted Gar, an Outgroup for the Teleost Genome Duplication. Genetics 2011, 188, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A.; Schartl, M. Gene and Genome Duplications in Vertebrates: The One-to-Four (-to-Eight in Fish) Rule and the Evolution of Novel Gene Functions. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1999, 11, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunwald, D.J.; Eisen, J.S. Headwaters of the Zebrafish—Emergence of a New Model Vertebrate. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitas-Djerbi, T.; Appelbaum, L. Modeling Sleep and Neuropsychiatric Disorders in Zebrafish. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2017, 44, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.H. The Physiology of Fishes, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-8493-8427-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, W.Y.; Fu, Y.; Reyon, D.; Maeder, M.L.; Tsai, S.Q.; Sander, J.D.; Peterson, R.T.; Yeh, J.-R.J.; Joung, J.K. Efficient Genome Editing in Zebrafish Using a CRISPR-Cas System. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelbaum, L.; Wang, G.; Yokogawa, T.; Skariah, G.M.; Smith, S.J.; Mourrain, P.; Mignot, E. Circadian and Homeostatic Regulation of Structural Synaptic Plasticity in Hypocretin Neurons. Neuron 2010, 68, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbaz, I.; Levitas-Djerbi, T.; Appelbaum, L. The Hypocretin/Orexin Neuronal Networks in Zebrafish. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 33, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, M.; van Eeden, F.J.; Schach, U.; Trowe, T.; Brand, M.; Furutani-Seiki, M.; Haffter, P.; Hammerschmidt, M.; Heisenberg, C.P.; Jiang, Y.J.; et al. Genes Controlling and Mediating Locomotion Behavior of the Zebrafish Embryo and Larva. Development 1996, 123, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihel, J.; Prober, D.A.; Arvanites, A.; Lam, K.; Zimmerman, S.; Jang, S.; Haggarty, S.J.; Kokel, D.; Rubin, L.L.; Peterson, R.T.; et al. Zebrafish Behavioral Profiling Links Drugs to Biological Targets and Rest/Wake Regulation. Science 2010, 327, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prober, D.A.; Rihel, J.; Onah, A.A.; Sung, R.-J.; Schier, A.F. Hypocretin/Orexin Overexpression Induces an Insomnia-like Phenotype in Zebrafish. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 13400–13410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokogawa, T.; Marin, W.; Faraco, J.; Pézeron, G.; Appelbaum, L.; Zhang, J.; Rosa, F.; Mourrain, P.; Mignot, E. Characterization of Sleep in Zebrafish and Insomnia in Hypocretin Receptor Mutants. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zada, D.; Appelbaum, L. Behavioral Criteria and Techniques to Define Sleep in Zebrafish. In Behavioral and Neural Genetics of Zebrafish; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 141–153. ISBN 978-0-12-817528-6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhdanova, I.V.; Wang, S.Y.; Leclair, O.U.; Danilova, N.P. Melatonin Promotes Sleep-like State in Zebrafish. Brain Res. 2001, 903, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagi, D.; de Lecea, L.; Appelbaum, L. Heterogeneity of Hypocretin/Orexin Neurons. Front. Neurol. Neurosci. 2021, 45, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arendt, J.; Deacon, S.; English, J.; Hampton, S.; Morgan, L. Melatonin and Adjustment to Phase Shift. J. Sleep Res. 1995, 4, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, D.C.; Coon, S.L.; Roseboom, P.H.; Weller, J.L.; Bernard, M.; Gastel, J.A.; Zatz, M.; Iuvone, P.M.; Rodriguez, I.R.; Bégay, V.; et al. The Melatonin Rhythm-Generating Enzyme: Molecular Regulation of Serotonin N-Acetyltransferase in the Pineal Gland. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 1997, 52, 307–357; discussion 357–358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Appelbaum, L.; Wang, G.X.; Maro, G.S.; Mori, R.; Tovin, A.; Marin, W.; Yokogawa, T.; Kawakami, K.; Smith, S.J.; Gothilf, Y.; et al. Sleep-Wake Regulation and Hypocretin-Melatonin Interaction in Zebrafish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21942–21947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, M.E.; Brill, J.; Bonnavion, P.; Huguenard, J.R.; Huerta, R.; de Lecea, L. Mechanism for Hypocretin-Mediated Sleep-to-Wake Transitions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2635–E2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, R.; Nardone, S.; Grace, K.P.; Venner, A.; Cristofolini, M.; Bandaru, S.S.; Sohn, L.T.; Kong, D.; Mochizuki, T.; Viberti, B.; et al. Orexin Neurons Inhibit Sleep to Promote Arousal. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A.; Kumar, S.; McGinty, D.; Alam, M.N.; Szymusiak, R. Neuronal Activity in the Preoptic Hypothalamus during Sleep Deprivation and Recovery Sleep. J. Neurophysiol. 2014, 111, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Greco, M.A.; Shiromani, P.; Saper, C.B. Effect of Lesions of the Ventrolateral Preoptic Nucleus on NREM and REM Sleep. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 3830–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Miracca, G.; Yu, X.; Harding, E.C.; Miao, A.; Yustos, R.; Vyssotski, A.L.; Franks, N.P.; Wisden, W. Galanin Neurons Unite Sleep Homeostasis and A2-Adrenergic Sedation. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 3315–3322.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherin, J.E.; Shiromani, P.J.; McCarley, R.W.; Saper, C.B. Activation of Ventrolateral Preoptic Neurons during Sleep. Science 1996, 271, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, M.E.; Adamantidis, A.; Ohtsu, H.; Deisseroth, K.; de Lecea, L. Sleep Homeostasis Modulates Hypocretin-Mediated Sleep-to-Wake Transitions. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 10939–10949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggermann, E.; Serafin, M.; Bayer, L.; Machard, D.; Saint-Mleux, B.; Jones, B.E.; Mühlethaler, M. Orexins/Hypocretins Excite Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Neurones. Neuroscience 2001, 108, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyron, C.; Tighe, D.K.; van den Pol, A.N.; de Lecea, L.; Heller, H.C.; Sutcliffe, J.G.; Kilduff, T.S. Neurons Containing Hypocretin (Orexin) Project to Multiple Neuronal Systems. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 9996–10015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nambu, T.; Sakurai, T.; Mizukami, K.; Hosoya, Y.; Yanagisawa, M.; Goto, K. Distribution of Orexin Neurons in the Adult Rat Brain. Brain Res. 1999, 827, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlet, S.; Tyler, C.J.; Leonard, C.S. Direct and Indirect Excitation of Laterodorsal Tegmental Neurons by Hypocretin/Orexin Peptides: Implications for Wakefulness and Narcolepsy. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 2862–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inutsuka, A.; Yamanaka, A. The Physiological Role of Orexin/Hypocretin Neurons in the Regulation of Sleep/Wakefulness and Neuroendocrine Functions. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraco, J.H.; Appelbaum, L.; Marin, W.; Gaus, S.E.; Mourrain, P.; Mignot, E. Regulation of Hypocretin (Orexin) Expression in Embryonic Zebrafish. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 29753–29761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Bai, L.; Gan, X.; Li, L.; Han, C. Molecular Evolutionary Analysis of the HCRTR Gene Family in Vertebrates. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8120263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curado, S.; Stainier, D.Y.R.; Anderson, R.M. Nitroreductase-Mediated Cell/Tissue Ablation in Zebrafish: A Spatially and Temporally Controlled Ablation Method with Applications in Developmental and Regeneration Studies. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panula, P. Hypocretin/Orexin in Fish Physiology with Emphasis on Zebrafish. Acta Physiol. 2010, 198, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, S.; Ripley, B.; Overeem, S.; Lammers, G.J.; Mignot, E. Hypocretin (Orexin) Deficiency in Human Narcolepsy. Lancet 2000, 355, 39–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalal, J.; Roh, J.H.; Maloney, S.E.; Akuffo, A.; Shah, S.; Yuan, H.; Wamsley, B.; Jones, W.B.; de Guzman Strong, C.; Gray, P.A.; et al. Translational Profiling of Hypocretin Neurons Identifies Candidate Molecules for Sleep Regulation. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Miyazaki, R.; Yamada, T. Intracerebroventricular Administration of 26RFa Produces an Analgesic Effect in the Rat Formalin Test. Peptides 2009, 30, 1683–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayasu, S.; Sakurai, T.; Iwasaki, S.; Teranishi, H.; Yamanaka, A.; Williams, S.C.; Iguchi, H.; Kawasawa, Y.I.; Ikeda, Y.; Sakakibara, I.; et al. A Neuropeptide Ligand of the G Protein-Coupled Receptor GPR103 Regulates Feeding, Behavioral Arousal, and Blood Pressure in Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 7438–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, L.C.; Wang, G.X.; Madelaine, R.; Skariah, G.; Kawakami, K.; Deisseroth, K.; Urban, A.E.; Mourrain, P. Neural Signatures of Sleep in Zebrafish. Nature 2019, 571, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, M.; Eriksson, K.S.; Zhang, S.; Tanaka, S.; Lin, L.; Salehi, A.; Hesla, P.E.; Maehlen, J.; Gaus, S.E.; Yanagisawa, M.; et al. IGFBP3 Colocalizes with and Regulates Hypocretin (Orexin). PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Singh, C.; Prober, D.A.; Wayne, N.L. Morphological and Physiological Interactions Between GnRH3 and Hypocretin/Orexin Neuronal Systems in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Endocrinology 2016, 157, 4012–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, S.; Lee, W.; Navarre, S.; Kozlowski, D.J.; Wayne, N.L. Acquisition of Spontaneous Electrical Activity during Embryonic Development of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone-3 Neurons Located in the Terminal Nerve of Transgenic Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 168, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Lin, M.-C.A.; Farajzadeh, M.; Wayne, N.L. Early Development of the Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Neuronal Network in Transgenic Zebrafish. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, A.; Mignot, E. Genetics of Sleep and Sleep Disorders. Cell 2011, 146, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fronczek, R.; van Geest, S.; Frölich, M.; Overeem, S.; Roelandse, F.W.C.; Lammers, G.J.; Swaab, D.F. Hypocretin (Orexin) Loss in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 1642–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fronczek, R.; Overeem, S.; Lee, S.Y.Y.; Hegeman, I.M.; van Pelt, J.; van Duinen, S.G.; Lammers, G.J.; Swaab, D.F. Hypocretin (Orexin) Loss in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain 2007, 130, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thannickal, T.C.; Lai, Y.-Y.; Siegel, J.M. Hypocretin (Orexin) Cell Loss in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain 2007, 130, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Chen, Z.; Han, J.; Ma, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.-D.; Ji, Y. Orexin-A in Patients with Lewy Body Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 765701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzardo, A.M.; Johnson, L.; Miller, J.L.; Driscoll, D.J.; Butler, M.G. Higher Plasma Orexin a Levels in Children with Prader-Willi Syndrome Compared with Healthy Unrelated Sibling Controls. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2016, 170, 2328–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omokawa, M.; Ayabe, T.; Nagai, T.; Imanishi, A.; Omokawa, A.; Nishino, S.; Sagawa, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Kanbayashi, T. Decline of CSF Orexin (Hypocretin) Levels in Prader-Willi Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2016, 170A, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nollet, M.; Leman, S. Role of Orexin in the Pathophysiology of Depression: Potential for Pharmacological Intervention. CNS Drugs 2013, 27, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blouin, A.M.; Fried, I.; Wilson, C.L.; Staba, R.J.; Behnke, E.J.; Lam, H.A.; Maidment, N.T.; Karlsson, K.Æ.; Lapierre, J.L.; Siegel, J.M. Human Hypocretin and Melanin-Concentrating Hormone Levels Are Linked to Emotion and Social Interaction. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estabrooke, I.V.; McCarthy, M.T.; Ko, E.; Chou, T.C.; Chemelli, R.M.; Yanagisawa, M.; Saper, C.B.; Scammell, T.E. Fos Expression in Orexin Neurons Varies with Behavioral State. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 1656–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.G.; Hassani, O.K.; Jones, B.E. Discharge of Identified Orexin/Hypocretin Neurons across the Sleep-Waking Cycle. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 6716–6720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniz Behn, C.G.; Klerman, E.B.; Mochizuki, T.; Lin, S.-C.; Scammell, T.E. Abnormal Sleep/Wake Dynamics in Orexin Knockout Mice. Sleep 2010, 33, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, C.R.; Scammell, T.E. Narcolepsy: Neural Mechanisms of Sleepiness and Cataplexy. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 12305–12311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, C.R.; Oishi, Y.; Mochizuki, T.; Peever, J.H.; Scammell, T.E. Amygdala Lesions Reduce Cataplexy in Orexin Knock-out Mice. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 9734–9742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meletti, S.; Vaudano, A.E.; Pizza, F.; Ruggieri, A.; Vandi, S.; Teggi, A.; Franceschini, C.; Benuzzi, F.; Nichelli, P.F.; Plazzi, G. The Brain Correlates of Laugh and Cataplexy in Childhood Narcolepsy. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 11583–11594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, Y.; Williams, R.H.; Agostinelli, L.; Arrigoni, E.; Fuller, P.M.; Mochizuki, T.; Saper, C.B.; Scammell, T.E. Role of the Medial Prefrontal Cortex in Cataplexy. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 9743–9751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donadio, V.; Liguori, R.; Vandi, S.; Pizza, F.; Dauvilliers, Y.; Leta, V.; Giannoccaro, M.P.; Baruzzi, A.; Plazzi, G. Lower Wake Resting Sympathetic and Cardiovascular Activities in Narcolepsy with Cataplexy. Neurology 2014, 83, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohayon, M.M. Narcolepsy Is Complicated by High Medical and Psychiatric Comorbidities: A Comparison with the General Population. Sleep Med. 2013, 14, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knez, R.; Niksic, M.; Omerovic, E. Orexin/Hypocretin System Dysfunction in Patients with Takotsubo Syndrome: A Novel Pathophysiological Explanation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 1016369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, N.J.; Rodriguez, M.L.; Waters, K.A.; Machaalani, R. Changes in Orexin (Hypocretin) Neuronal Expression with Normal Aging in the Human Hypothalamus. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, M.D.; Sakurai, T.; Rainero, I.; Maj, M.C.; Kukkonen, J.P. Orexin Receptor Multimerization versus Functional Interactions: Neuropharmacological Implications for Opioid and Cannabinoid Signalling and Pharmacogenetics. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, Y.-L.; Liu, C.-M.; Shan, J.-C.; Lee, H.-J.; Hsieh, M.H.; Hwu, H.-G.; Chiou, L.-C. Elevated Plasma Orexin A Levels in a Subgroup of Patients with Schizophrenia Associated with Fewer Negative and Disorganized Symptoms. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2015, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglass, A.B. Narcolepsy: Differential Diagnosis or Etiology in Some Cases of Bipolar Disorder and Schizophrenia? CNS Spectr. 2003, 8, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Huang, M.-L.; Li, J.-H.; Jin, K.-Y.; Li, H.-M.; Mou, T.-T.; Fronczek, R.; Duan, J.-F.; Xu, W.-J.; Swaab, D.; et al. Changes of Hypocretin (Orexin) System in Schizophrenia: From Plasma to Brain. Schizophr. Bull. 2021, 47, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angom, R.S.; Nakka, N.M.R. Zebrafish as a Model for Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease: The Future of Precision Medicine. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia, L.; Sutcliffe, J.G. The hypocretins/orexins: Novel hypothalamic neuropeptides involved in different physiological systems. CMLS Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1999, 56, 473–480. [Google Scholar]
- Oikonomou, G.; Prober, D.A. Attacking Sleep from a New Angle: Contributions from Zebrafish. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2017, 44, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dyachuk, V. The Role and Mechanisms of the Hypocretin System in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010256
Dyachuk V. The Role and Mechanisms of the Hypocretin System in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(1):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010256
Chicago/Turabian StyleDyachuk, Vyacheslav. 2025. "The Role and Mechanisms of the Hypocretin System in Zebrafish (Danio rerio)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 1: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010256
APA StyleDyachuk, V. (2025). The Role and Mechanisms of the Hypocretin System in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(1), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010256





