Integrated Physiological, Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analyses of the Response of Rice to Aniline Toxicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Changes in Physiological Indicators
2.2. Transcriptomic Analysis
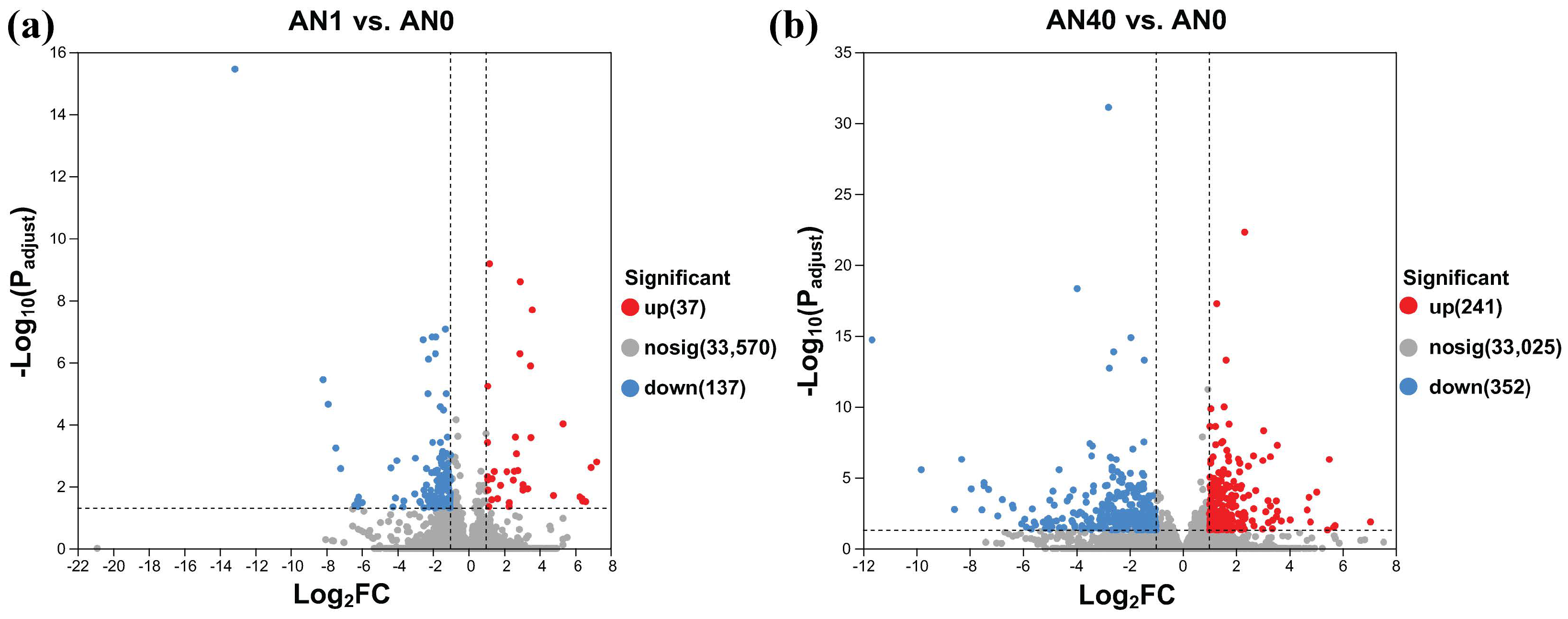
2.2.1. Transcriptome Sequencing and DEG Identification
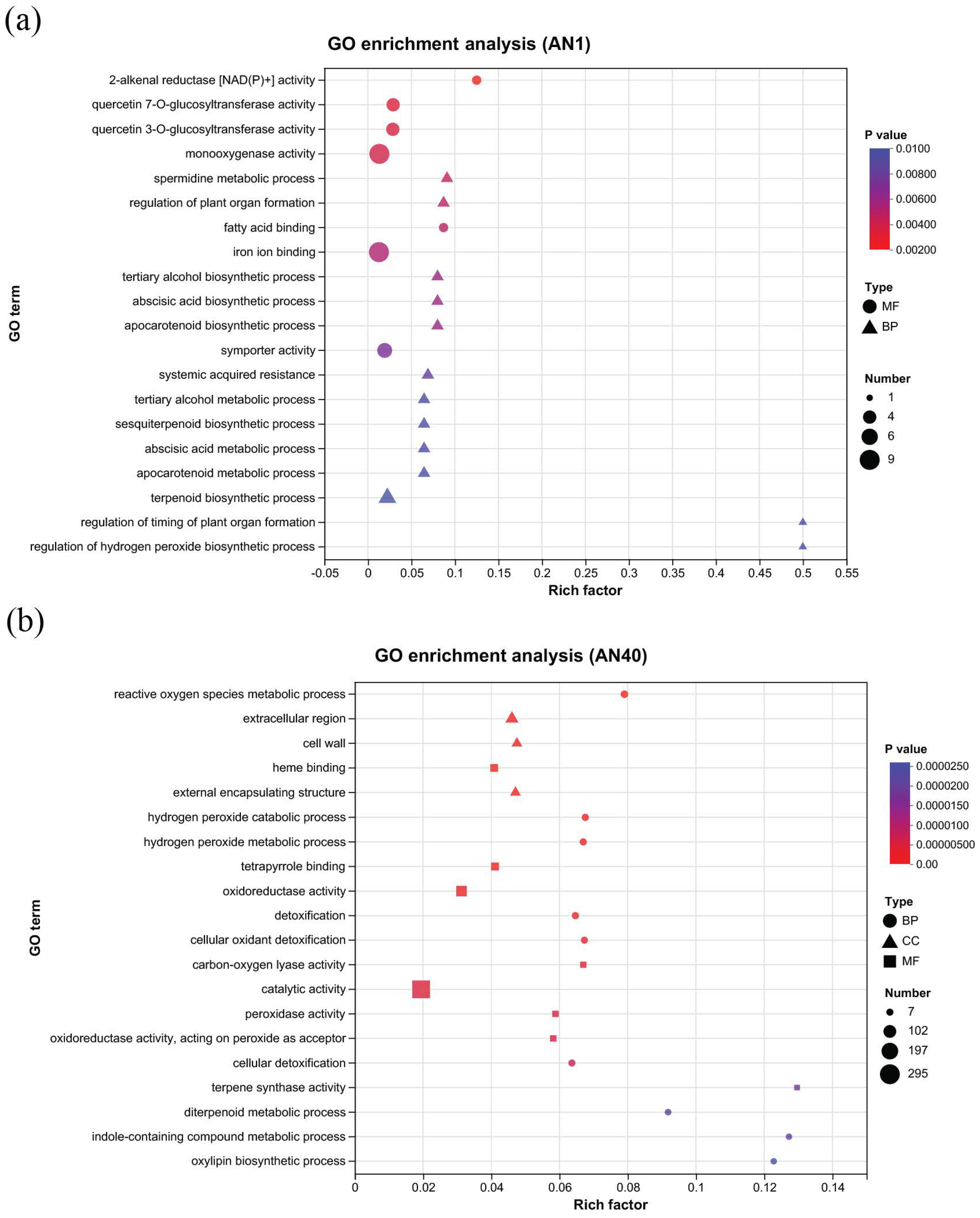
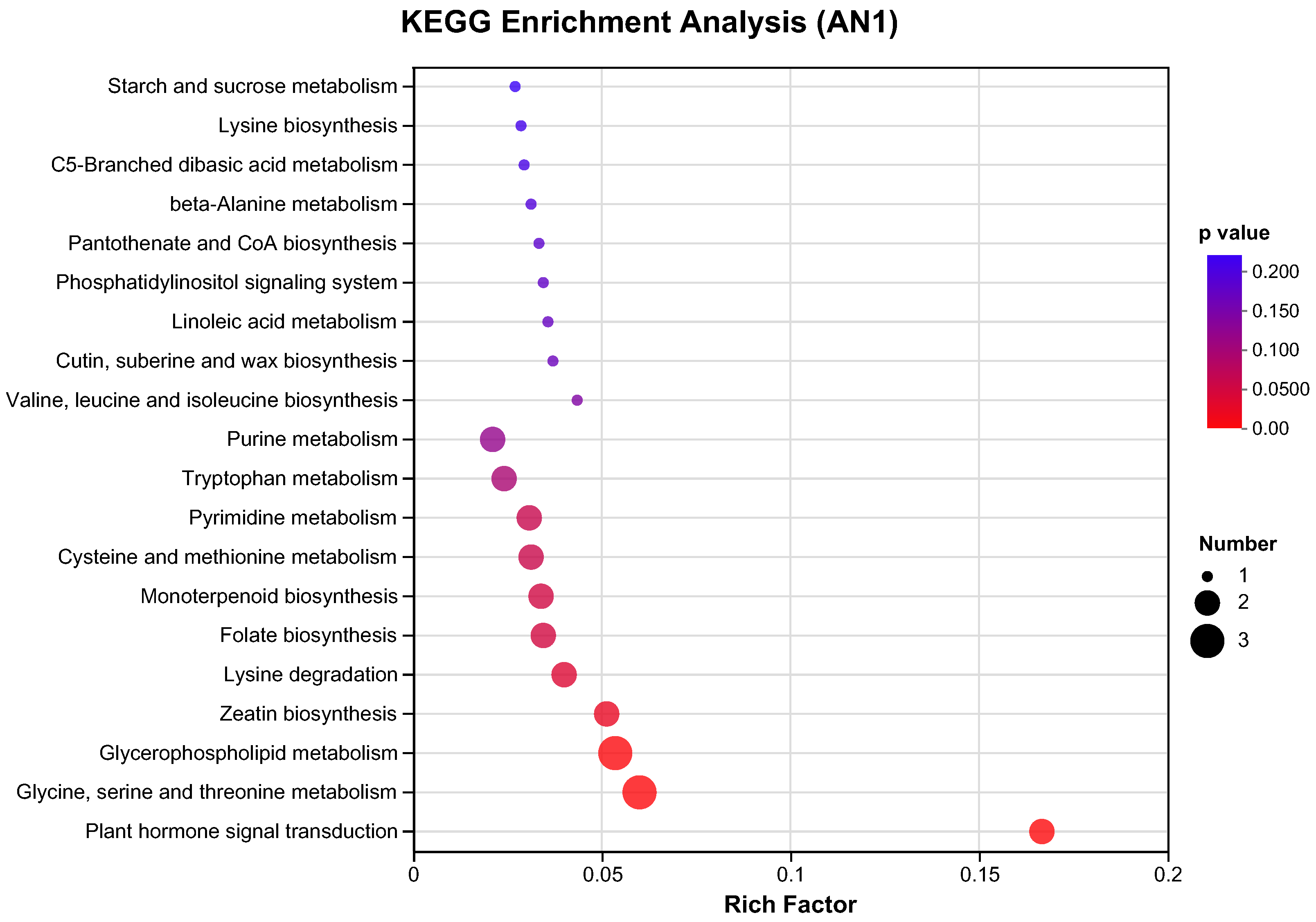
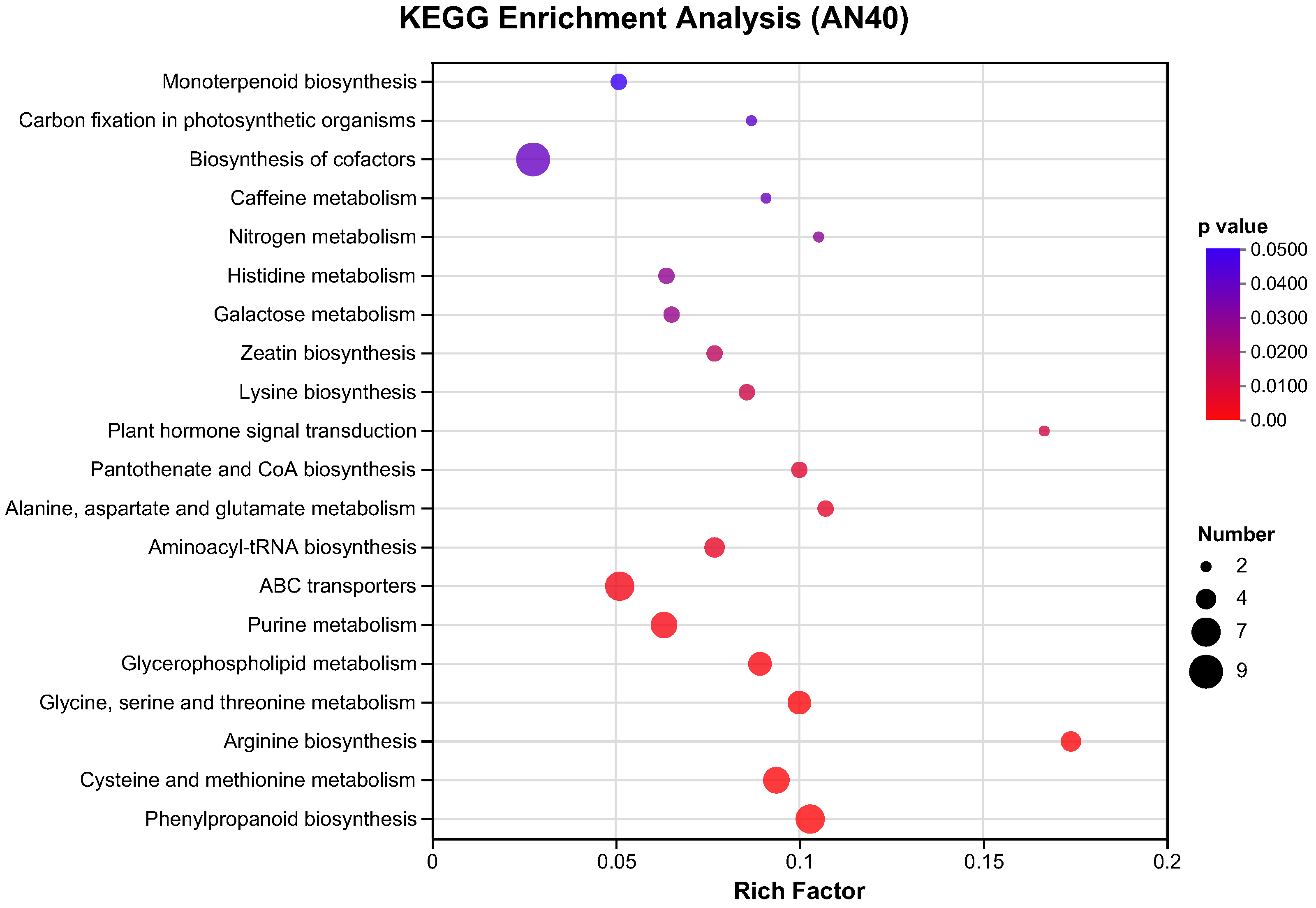
2.2.2. GO and KEGG Pathway Analysis
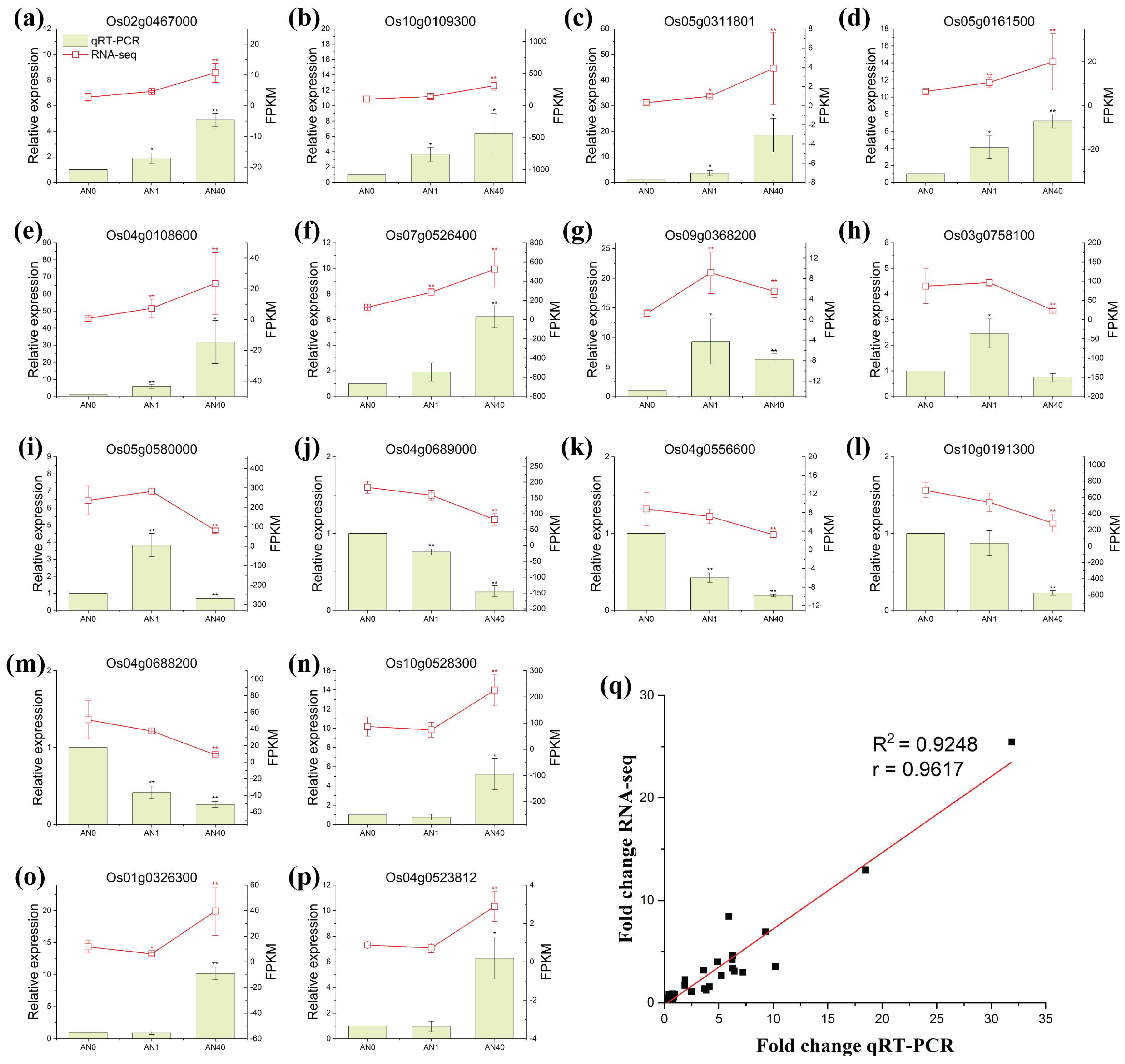
2.2.3. qRT-PCR Verification of Gene Expression
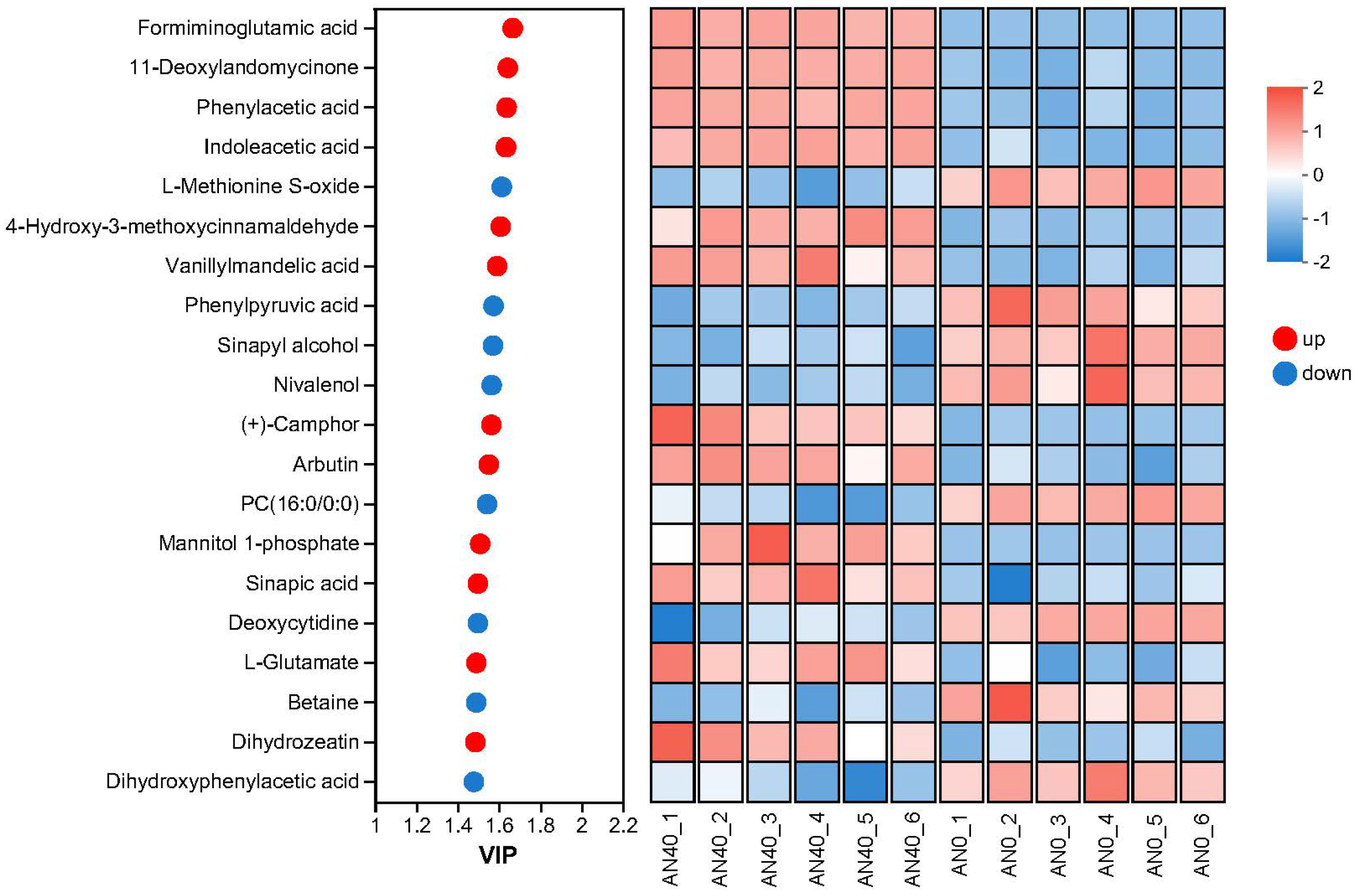
2.3. Metabolomic Analysis
2.3.1. Quality Assessment of Metabolomic Data
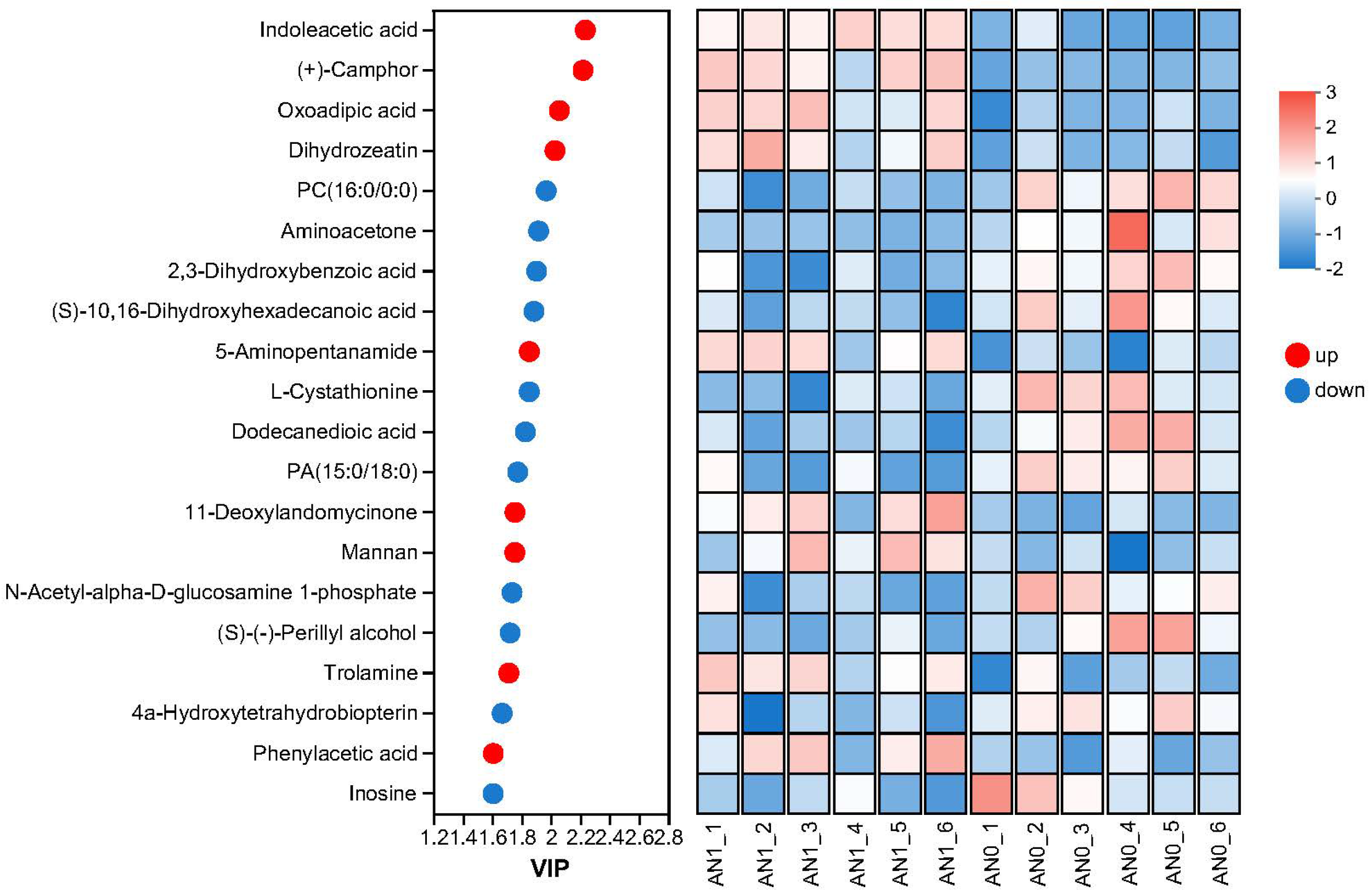
2.3.2. Identification and Analysis of DAMs
2.4. Integrated Analysis of Transcriptomics and Metabolomics
3. Discussion
3.1. Physiological Responses of Rice to Aniline Stress
3.2. The Phenylpropanoid Biosynthesis Pathway Responded to Aniline Stress
3.3. The Amino Acid Metabolism Pathways Responded to Aniline Stress
3.4. The Lipid and Puring Metabolism Pathways Responded to Aniline Stress
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Rice Cultivation
4.2. Determination of Physiological Indicators
4.2.1. Determination of MDA Content
4.2.2. Determination of H2O2 Content
4.2.3. Determination of Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
4.2.4. Determination of Soluble Sugar Content
4.2.5. Determination of Soluble Protein Content
4.3. Transcriptomics Analysis
4.4. Metabolomics Profiling
4.5. qRT-PCR Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis and Visualization
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
- The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AN | aniline |
| MDA | malondialdehyde |
| H2O2 | hydrogen peroxide |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| POD | peroxidase |
| CAT | catalase |
| AN1 | AN1 represents an aniline solution with a concentration of 1 mg/L, and so on. |
| AN0 | AN0 represents the control group, where 0 indicates zero aniline content. |
| SP | Soluble Protein |
| QC | Quality Controlled |
| GC | Guanine and Cytosine |
| DEGs | Differentially Expressed Genes |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| OPLS-DA | Orthogonal Partial Least Squares-Discriminant Analysis |
| DAMs | Differentially Accumulated Metabolites |
| VIP | Variable Importance in the Projection |
| C4H | cinnamate 4-hydroxylase |
| CAD | cinnamylalcohol dehydrogenase |
| HCT | Hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA shikimate/quinate hydroxycinnamoyltransferase |
| CCR | Cinnamoyl-CoA reductase |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| CoA | coenzyme A |
| PRX | peroxidase |
| TCA | tricarboxylic acid |
| GST | glutathione S-transferase |
| GSH | glutathione |
| IAA | indole-3-acetic acid |
| ALDH | acetaldehyde dehydrogenase |
| PA | phosphatidic acid |
| PG | phosphatidylglycerol |
| PC | phosphatidylcholine |
| AC | adenylate cyclase |
| GC | guanylate cyclase |
| cGMP | cyclic guanosine monophosphate |
| cAMP | cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| FPKM | Fragments Per Kilobase of transcript per Million mapped reads |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| UHPLC-MS/MS | Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| FC | Fold Change |
| LC-MS | Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometer |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
References
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Priority Pollutant List. 1981. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-09/documents/priority-pollutant-list-epa.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, X.; Xie, L.H.; Li, J.; Xie, Y.; Li, J.R. A copper (II)-paddlewheel metal–organic framework with exceptional hydrolytic stability and selective adsorption and detection ability of aniline in water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 27027–27035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mones, E. Handbook of Environmental Fate and Exposure Data for Organic Chemicals. J. Test. Eval. 1990, 18, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Xie, H. Phytoremediation of aniline by Salix babylonica cuttings: Removal, accumulation, and photosynthetic response. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 214, 112124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, G.; Xie, H. Tolerance and Phytoremediation Capacity of Salix matsudana to Aniline Wastewater. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 32, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, N.; Liu, G.; Bai, L.; Tang, L.; Guo, C. Genotoxicity and growth inhibition effects of aniline on wheat. Chemosphere 2017, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, N.; Zhang, W.; Si, L.; Zhang, R.; Wang, D.; Guo, C. Effects of aniline on growth, oxidative and DNA damage of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, M.A.; Shibl, M.F.; El-Demerdash, S.H.; El-Nahas, A.M. Simulated kinetics of the atmospheric removal of aniline during daytime. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 127031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bus, J.; Popp, J. Perspectives on the mechanism of action of the splenic toxicity of aniline and structurally-related compounds. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1987, 25, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blondel, C.; Khelalfa, F.; Reynaud, S.; Fauvelle, F.; Raveton, M. Effect of organochlorine pesticides exposure on the maize root metabolome assessed using high-resolution magic-angle spinning 1H NMR spectroscopy. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, S.I.; Figueiredo, P.I.; Barros, A.S.; Dias, M.C.; Santos, C.; Duarte, I.F.; Gil, A.M. Changes in the metabolome of lettuce leaves due to exposure to mancozeb pesticide. Food Chem. 2014, 154, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Le, X.C.; Zhu, L. Metabolomics and transcriptomics reveal defense mechanism of rice (Oryza sativa) grains under stress of 2,2’,4,4’-tetrabromodiphenyl ether. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Zhu, L. Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Investigation of Metabolic Perturbations in Oryza sativa L. Triggered by Three Pesticides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6115–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujahid, M.; Prasuna, M.L.; Sasikala, C.; Ramana, C.V. Integrated Metabolomic and Proteomic Analysis Reveals Systemic Responses of Rubrivivax benzoatilyticus JA2 to Aniline Stress. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 711–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, G.; Sun, P.; Kong, X.; Han, X.; Sun, Q.; Fouillen, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Genome editing of a rice CDP-DAG synthase confers multipathogen resistance. Nature 2023, 618, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legg, S. World Population Prospects 2024: Summary of Results. Interaction 2024, 52, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Gnanamanickam, S.S. Rice and Its Importance to Human Life. In Biological Control of Rice Diseases; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izawa, T.; Shimamoto, K. Becoming a model plant: The importance of rice to plant science. Trends Plant Sci. 1996, 1, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennicke, C.; Cochemé, H.M. Redox metabolism: ROS as specific molecular regulators of cell signaling and function. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 3691–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, H.; Wang, R.; Hu, H.; Lu, T.; Chen, X.; Ye, H.; Liu, W.; Fu, Z. Enantioselective Phytotoxicity of the Herbicide Imazethapyr and its Effect on Rice Physiology and Gene Transcription. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7036–7043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, M.; Prado, C.; Podazza, G.; Interdonato, R.; González, J.A.; Hilal, M.; Prado, F.E. Soluble sugars: Metabolism, sensing and abiotic stress: A complex network in the life of plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2009, 4, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, H.; Qian, T.; He, L.; Jin, H.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, J. Nutrient Concentrations Induced Abiotic Stresses to Sweet Pepper Seedlings in Hydroponic Culture. Plants 2022, 11, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Zhao, W.; Liang, Q.; Cai, M.; Fan, X.; Hu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Xie, H.; Peng, C.; Liu, J. Polystyrene microplastics enhanced the toxicity of cadmium to rice seedlings: Evidence from rice growth, physiology, and element metabolism. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 945, 173931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, S.; Chaudhary, N.; Singh, N.K. Role of Soluble Sugars in Metabolism and Sensing Under Abiotic Stress. In Plant Growth Regulators: Signalling Under Stress Conditions; Aftab, T., Hakeem, K.R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 305–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R. Protein synthesis by plants under stressful conditions. Handb. Plant Crop Stress 1999, 2, 365–397. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, I.; Rodrigues, C.M.; Neuhaus, H.E.; Pommerrenig, B. Improved resource allocation and stabilization of yield under abiotic stress. J. Plant Physiol. 2021, 257, 153336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Choi, B.; Natarajan, S.; Bae, H. Expression analysis of kenaf cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H) ortholog during developmental and stress responses. Plant Omics 2013, 6, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Besseau, S.; Hoffmann, L.; Geoffroy, P.; Lapierre, C.; Pollet, B.; Legrand, M. Flavonoid Accumulation in Arabidopsis Repressed in Lignin Synthesis Affects Auxin Transport and Plant Growth. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacombe, E.; Hawkins, S.; Van Doorsselaere, J.; Piquemal, J.; Goffner, D.; Poeydomenge, O.; Boudet, A.M.; Grima-Pettenati, J. Cinnamoyl CoA reductase, the first committed enzyme of the lignin branch biosynthetic pathway: Cloning, expression and phylogenetic relationships. Plant J. 1997, 11, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Wu, J.; Lin, L.; Li, P.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, Q.; Liang, J.; Wang, Y. Overexpression of Cinnamoyl-CoA Reductase 2 in Brassica napus Increases Resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum by Affecting Lignin Biosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 732733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, T. Metabolons in plant primary and secondary metabolism. Phytochem. Rev. 2019, 18, 1483–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Fonseca-Pereira, P.; Monteiro-Batista, R.d.C.; Araújo, W.L.; Nunes-Nesi, A. Harnessing enzyme cofactors and plant metabolism: An essential partnership. Plant J. 2023, 114, 1014–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, P.V. Phenolic Compounds of Cereals and Their Antioxidant Capacity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashiane, P.; Manhivi, V.E.; Shoko, T.; Slabbert, R.M.; Sultanbawa, Y.; Sivakumar, D. Cooking African Pumpkin Leaves (Momordica balsamina L.) by Stir-Frying Improved Bioactivity and Bioaccessibility of Metabolites—Metabolomic and Chemometric Approaches. Foods 2021, 10, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, A.; Fiorentino, A.; Abrosca, B.; Izzo, A.; Cefarelli, G.; Golino, A.; Monaco, P. Potential allelopathic interference of Melilotus neapolitana metabolites on three coexisting species of Mediterranean herbaceous plant community. J. Plant Interact. 2008, 3, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dong, S.; Li, M.; Gu, F.; Yang, G.; Guo, T.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J. The class III peroxidase gene OsPrx30, transcriptionally modulated by the AT-hook protein OsATH1, mediates rice bacterial blight-induced ROS accumulation. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trovato, M.; Funck, D.; Forlani, G.; Okumoto, S.; Amir, R. Editorial: Amino Acids in Plants: Regulation and Functions in Development and Stress Defense. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 772810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Zhang, C.; Suglo, P.; Sun, S.; Wang, M.; Su, T. l-Aspartate: An Essential Metabolite for Plant Growth and Stress Acclimation. Molecules 2021, 26, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Yang, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, X. Application of glutamic acid improved As tolerance in aromatic rice at early growth stage. Chemosphere 2023, 322, 138173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, S.S.; Anjum, N.A.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Gill, R.; Tuteja, N. Glutathione and glutathione reductase: A boon in disguise for plant abiotic stress defense operations. Plant Physiol. Biochem. Ppb 2013, 70, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Suo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xing, N.; Gao, Z.; Lin, X.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Y. Glutaredoxin like protein (RtGRL1) regulates H2O2 and Na+ accumulation by maintaining the glutathione pool during abiotic stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 159, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumdar, R.; Barchi, B.; Turlapati, S.A.; Gagne, M.; Minocha, R.; Long, S.; Minocha, S.C. Glutamate, Ornithine, Arginine, Proline, and Polyamine Metabolic Interactions: The Pathway Is Regulated at the Post-Transcriptional Level. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhamid, E.M.A.; Sadak, M.S.; Tawfik, M.M. Alleviation of Adverse Effects of Salt Stress in Wheat Cultivars by Foliar Treatment with Antioxidant 2—Changes in Some Biochemical Aspects, Lipid Peroxidation, Antioxidant Enzymes and Amino Acid Contents. Agric. Sci. 2014, 5, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Yuan, M.; Liu, H.; Hui, S.; Qin, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Q.; et al. The versatile functions of OsALDH2B1 provide a genic basis for growth–defense trade-offs in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3867–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Han, B. Evolutionary and expression study of the aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) gene superfamily in rice (Oryza sativa). Gene 2009, 431, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takato, S.; Kakei, Y.; Mitsui, M.; Ishida, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Yamazaki, C.; Hayashi, K.i.; Ishii, T.; Nakamura, A.; Soeno, K.; et al. Auxin signaling through SCFTIR1/AFBs mediates feedback regulation of IAA biosynthesis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 1320–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Lin, F.; Chen, J.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L. Multistage Defense System Activated by Tetrachlorobiphenyl and its Hydroxylated and Methoxylated Derivatives in Oryza sativa. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 4889–4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mithaishvili, T.; Scalla, R.; Ugrekhelidze, D.; Tsereteli, B.; Sadunishvili, T.; Kvesitadze, G. Degradation of Aromatic Compounds in Plants Grown under Aseptic Conditions. Z. FüR Naturforschung C 2005, 60, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, K.; Li, M. Functions and interaction of plant lipid signalling under abiotic stresses. Plant Biol. 2023, 25, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Shao, W.; He, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Membrane Lipids’ Metabolism and Transcriptional Regulation in Maize Roots Under Cold Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 639132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Q.; Ufer, G.; Bartels, D. Lipid signalling in plant responses to abiotic stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 1029–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsikas, D. Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: Analytical and biological challenges. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 524, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulukapi, K.; Nasircilar, A.G. The role of exogenous glutamine on germination, plant development and transcriptional expression of some stress-related genes in onion under salt stress. Folia Hortic. 2024, 36, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, P.; Li, B.; Wang, W.; Zhu, B. Phosphoribosyltransferases and Their Roles in Plant Development and Abiotic Stress Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duszyn, M.; Świeżawska, B.; Szmidt-Jaworska, A.; Jaworski, K. Cyclic nucleotide gated channels (CNGCs) in plant signalling—Current knowledge and perspectives. J. Plant Physiol. 2019, 241, 153035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, D.; Burroughs, R. Disinfection of seed surfaces with sodium hypochlorite. Phytopathology 1986, 76, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemm, E.; Willis, A. The estimation of carbohydrates in plant extracts by anthrone. Biochem. J. 1954, 57, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Guo, Z.; Yao, Y.; Xia, L.; Liu, R.; Song, H.; Zhang, S. Acetic acid alters rhizosphere microbes and metabolic composition to improve willows drought resistance. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, P.; Gommers, R.; Oliphant, T.E.; Haberland, M.; Reddy, T.; Cournapeau, D.; Burovski, E.; Peterson, P.; Weckesser, W.; Bright, J.; et al. SciPy 1.0: Fundamental Algorithms for Scientific Computing in Python. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Liu, L.; Zhang, W.; Yin, Z.; Guo, R.; Wang, D.; Guo, C. Integrated Physiological, Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analyses of the Response of Rice to Aniline Toxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020582
Wang J, Wang R, Liu L, Zhang W, Yin Z, Guo R, Wang D, Guo C. Integrated Physiological, Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analyses of the Response of Rice to Aniline Toxicity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(2):582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020582
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jingjing, Ruixin Wang, Lei Liu, Wenrui Zhang, Zhonghuan Yin, Rui Guo, Dan Wang, and Changhong Guo. 2025. "Integrated Physiological, Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analyses of the Response of Rice to Aniline Toxicity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 2: 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020582
APA StyleWang, J., Wang, R., Liu, L., Zhang, W., Yin, Z., Guo, R., Wang, D., & Guo, C. (2025). Integrated Physiological, Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analyses of the Response of Rice to Aniline Toxicity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(2), 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020582





