Growth-Inhibitory Effect of Chicken Egg Yolk Polyclonal Antibodies (IgY) on Zoonotic Pathogens Campylobacter jejuni, Salmonella spp. and Escherichia coli, In Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
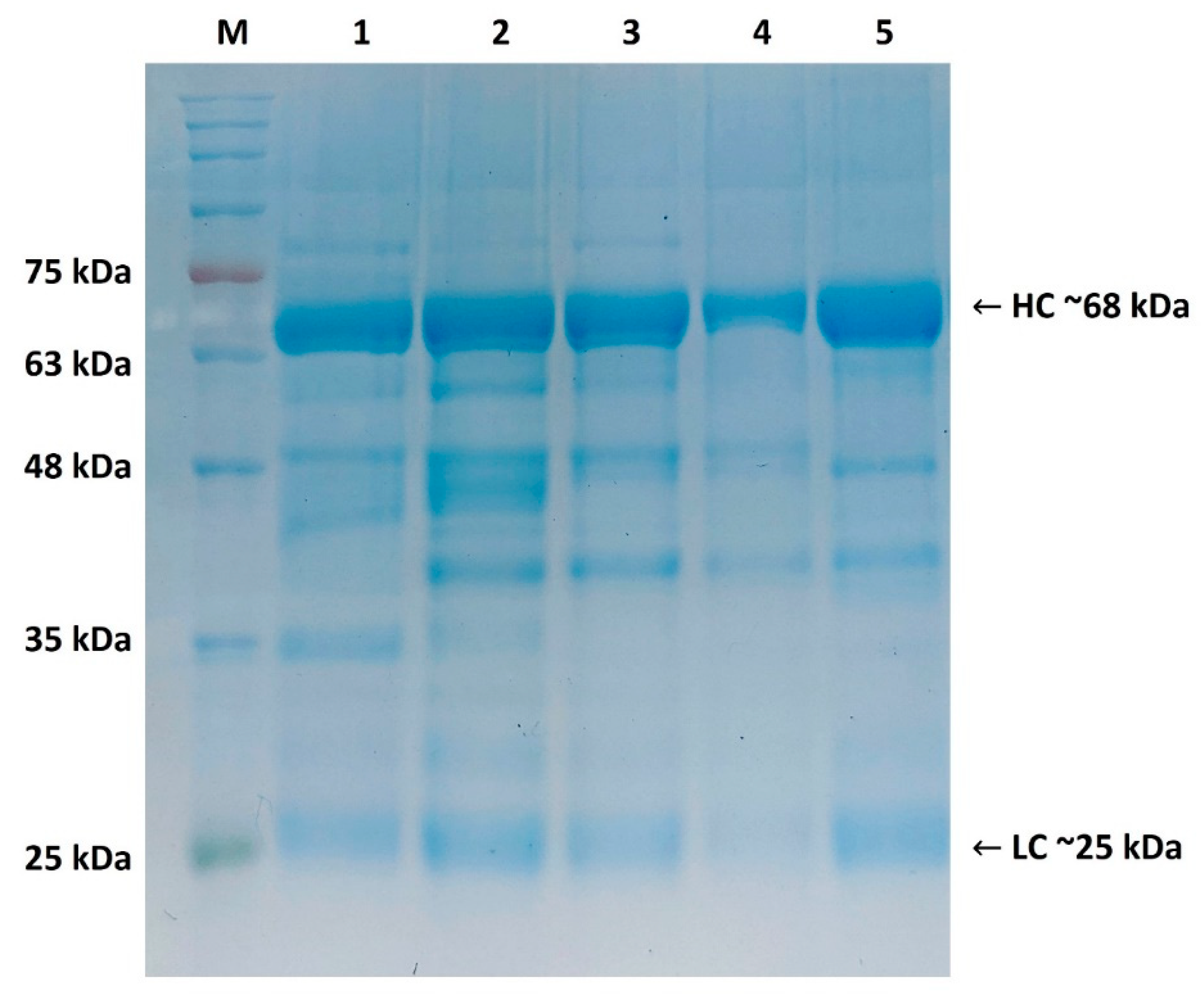
2.1. Purity Assessment of Isolated IgY by SDS-PAGE (Reducing Conditions)
2.2. Evaluation of Specific IgY Titers Assessment in Tube Agglutination Test
2.3. Growth Inhibition Assay
2.3.1. Campylobacter jejuni
2.3.2. Escherichia coli (STEC)
2.3.3. Salmonella spp.
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacteria Strains and Growing Conditions
4.1.1. Campylobacter jejuni
4.1.2. Escherichia coli
4.1.3. Salmonella spp.
4.1.4. Storage and Handling
4.2. Antigen Preparation for Hen Immunization
4.2.1. Campylobacter jejuni
4.2.2. Escherichia coli
4.2.3. Salmonella spp.
4.2.4. Bacteria Inactivation
4.3. Hen Immunization Protocol
4.4. IgY Isolation and Purification
4.5. Purity Assessment (SDS-Page)
4.6. IgY Titer Assessment (Tube Agglutination Test)
4.7. Growth Inhibition Assay
4.7.1. Campylobacter jejuni
4.7.2. Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp.
4.7.3. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sinclair, J.R. Importance of a One Health approach in advancing global health security and the Sustainable Development Goals. Rev. Sci. Tech. (Int. Off. Epizoot.) 2019, 38, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filter, M.; Buschhardt, T.; Dórea, F.; de Abechuco, E.L.; Günther, T.; Sundermann, E.M.; Gethmann, J.; Dups-Bergmann, J.; Lagesen, K.; Ellis-Iversen, J. One Health Surveillance Codex: Promoting the adoption of One Health solutions within and across European countries. One Health 2021, 12, 100233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union One Health 2020 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06971. [Google Scholar]
- McEwen, S.A.; Collignon, P.J. Antimicrobial Resistance: A One Health Perspective. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, H.K.; Trachsel, J.; Looft, T.; Casey, T.A. Finding alternatives to antibiotics. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1323, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernando-Amado, S.; Coque, T.M.; Baquero, F.; Martínez, J.L. Defining and combating antibiotic resistance from One Health and Global Health perspectives. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudjarwo, S.A.; Eraiko, K.; Sudjarwo, G.W.; Koerniasari. The potency of chicken egg yolk immunoglobulin (IgY) specific as immunotherapy to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2017, 8, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.; Samardzic, K.; Wallach, M.; Frumkin, L.R.; Mochly-Rosen, D. Immunoglobulin Y for Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications in Infectious Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 696003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Schubert, A.; Zajac, J.; Dyck, T.; Oelkrug, C. IgY antibodies in human nutrition for disease prevention. Nutr. J. 2015, 14, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, E.P.V.; van Tilburg, M.F.; Florean, E.O.P.T.; Guedes, M.I.F. Egg yolk antibodies (IgY) and their applications in human and veterinary health: A review. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 73, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustos, C.P.; Leiva, C.L.; Gambarotta, M.; Guida, N.; Chacana, P.A. In vitro Inhibitory Activity of IgY Antibodies Against Salmonella Ser. Newport Isolated from Horses. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2021, 103, 103657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassim, N.; Mtenga, A.B.; Shim, W.B.; Chung, D.H. The in vitro and in vivo efficacy of hen IgY against Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 22, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solhi, R.; Alebouyeh, M.; Khafri, A.; Rezaeifard, M.; Aminian, M. In vitro evaluation of cross-strain inhibitory effects of IgY polyclonal antibody against H. pylori. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 110, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, F.L.; Garcia, L.N.N.; Kanashiro, M.M.; Medina-Acosta, E.; Brom-De-Luna, J.G.; de Almeida, C.M.C.; Junior, R.R.A.; Lemos, M.; Vieira-Da-Motta, O. Growth Inhibition of Staphylococcus Aureus and Escherichia Coli Strains by Neutralizing Igy Antibodies From Ostrich Egg Yolk. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2012, 43, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, E.S.M.; Rahman, A.S.; Isoda, R.; Umeda, K.; Van Sa, N.; Kodama, Y. In vitro and in vivo effectiveness of egg yolk antibody against Candida albicans (anti-CA IgY). Vaccine 2008, 26, 2073–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, H.; Xu, Y.; Xu, F.; Wang, L.; You, J.; Li, S.; Jin, L. Chicken egg yolk antibody (IgY) controls solobacterium moorei under in vitro and in vivo conditions. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 168, 1448–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battersby, T.; Walsh, D.; Whyte, P.; Bolton, D.J. Campylobacter growth rates in four different matrices: Broiler caecal material, live birds, Bolton broth, and brain heart infusion broth. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2016, 6, 31217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Štumpf, S.; Hostnik, G.; Primožič, M.; Leitgeb, M.; Bren, U. Generation times of E. coli prolong with increasing tannin concentration while the lag phase extends exponentially. Plants 2020, 9, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Wilkins, K.; Bowers, M.; Wynn, C.; Ndegwa, E. Influence of Ph and Temperature on Growth Characteristics of Leading Foodborne Pathogens in a Laboratory Medium and Select Food Beverages. Austin Food Sci. 2018, 3, 1031. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.N.; Sunwoo, H.H.; Menninen, K.; Sim, J.S. In Vitro Studies of Chicken Egg Yolk Antibody (IgY) Against Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella typhimurium. Poult. Sci. 2002, 81, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adiguzel, M.C.; Sigirci, B.D.; Celik, B.; Kahraman, B.B.; Metiner, K.; Ikiz, S.; Bagcigil, A.F.; Ak, S.; Ozgur, N.Y. Phenotypic and genotypic examination of antimicrobial resistance in thermophilic Campylobacter species isolated from poultry in Turkey. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 62, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, R.; Yadav, J.; Maherchandani, S.; Kashyap, S.K. Typing of Campylobacter jejuni isolated from poultry on the basis of flaA-RFLP by various restriction enzymes. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2018, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Shoffner, M.A.; Hvichia, G.E.; Kricka, L.J.; Wilding, P. Chip PCR. II. Investigation of different PCR amplification systems in microfabricated silicon-glass chips. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, D.; Hannon, S.J.; Townsend, H.G.; Potter, A.; Allan, B.J. Genes coding for virulence determinants of Campylobacter jejuni in human clinical and cattle isolates from Alberta, Canada, and their potential role in colonization of poultry. Int. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Talukder, K.A.; Aslam, M.; Islam, Z.; Azmi, I.J.; Dutta, D.K.; Hossain, S.; Nur-E-Kamal, A.; Nair, G.B.; Cravioto, A.; Sack, D.A.; et al. Prevalence of virulence genes and cytolethal distending toxin production in Campylobacter jejuni isolates from diarrheal patients in Bangladesh. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1485–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, E.; McMullen, L.M.; Chui, L.; Jeon, B. Differential Survival of Hyper-Aerotolerant Campylobacter jejuni under Different Gas Conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, S.; Brahmbhatt, M.N.; Chatur, Y.A.; Nayak, J.B. Prevalence of Campylobacter species in milk and milk products, their virulence gene profile and antibiogram. Vet. World 2015, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabat, G.; Rose, P.; Hickey, W.J.; Harkin, J.M. Selective and Sensitive Method for PCR Amplification of Escherichia coli 16S rRNA Genes in Soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zijlstra, R.T.; Gänzle, M.G. Identification and quantification of virulence factors of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by high-resolution melting curve quantitative PCR. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, E.; Hanrieder, J.; Bergquist, J.; Larsson, A. Proteomic characterization of IgY preparations purified with a water dilution method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 11638–11642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bižanov, G. IgY extraction and purification from chicken egg yolk. J. Hell. Vet. Med. Soc. 2017, 68, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| IgY Type | Antigen Used for Agglutination | Titer (Highest Dilution with Visible Agglutination) |
|---|---|---|
| IgY-CJ | CJ6 | 1:320 |
| IgY-OB | S. Typhimurium | 1:640 |
| IgY-OD | S. Enteritidis | 1:640 |
| IgY-EC | K3 | 1:320 |
| Symbol | Species | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CJ6 | Campylobacter jejuni | CDT, CadF, CiaB, FlgR |
| K3 | Escherichia coli | O:139, F5, Stx2e, STb |
| ST | Salmonella serovar Typhimurium | [1, 4, 12 : i : 1, 2] O:B |
| SE | Salmonella serovar Enteritidis | [1, 9, 12 : gm ; -] O:D |
| SK | Salmonella serovar Kapemba | [1, 9, 12 : lv : 1, 7] O:D |
| SP | Salmonella serovar Paratyphi B | [1, 4, 12 : b : 1, 2] O:B |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Czoska, P.; Tarsalewska, K.; Ponichtera, M.; Rybicka, M.; Sowa-Rogozinska, N.; Sominka-Pierzchlewicz, H.; Stodolna, A.; Ogonowska, P.; Kosciuk, A.; Glosnicka, R.; et al. Growth-Inhibitory Effect of Chicken Egg Yolk Polyclonal Antibodies (IgY) on Zoonotic Pathogens Campylobacter jejuni, Salmonella spp. and Escherichia coli, In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031040
Czoska P, Tarsalewska K, Ponichtera M, Rybicka M, Sowa-Rogozinska N, Sominka-Pierzchlewicz H, Stodolna A, Ogonowska P, Kosciuk A, Glosnicka R, et al. Growth-Inhibitory Effect of Chicken Egg Yolk Polyclonal Antibodies (IgY) on Zoonotic Pathogens Campylobacter jejuni, Salmonella spp. and Escherichia coli, In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(3):1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031040
Chicago/Turabian StyleCzoska, Paulina, Karolina Tarsalewska, Magdalena Ponichtera, Magda Rybicka, Natalia Sowa-Rogozinska, Hanna Sominka-Pierzchlewicz, Aleksandra Stodolna, Patrycja Ogonowska, Aleksandra Kosciuk, Renata Glosnicka, and et al. 2025. "Growth-Inhibitory Effect of Chicken Egg Yolk Polyclonal Antibodies (IgY) on Zoonotic Pathogens Campylobacter jejuni, Salmonella spp. and Escherichia coli, In Vitro" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 3: 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031040
APA StyleCzoska, P., Tarsalewska, K., Ponichtera, M., Rybicka, M., Sowa-Rogozinska, N., Sominka-Pierzchlewicz, H., Stodolna, A., Ogonowska, P., Kosciuk, A., Glosnicka, R., & Bielawski, K. P. (2025). Growth-Inhibitory Effect of Chicken Egg Yolk Polyclonal Antibodies (IgY) on Zoonotic Pathogens Campylobacter jejuni, Salmonella spp. and Escherichia coli, In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(3), 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031040






