Markers of Type 2 Inflammation and Immunosenescence Are Upregulated in Localized Scleroderma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Demographics and Clinical Characteristics
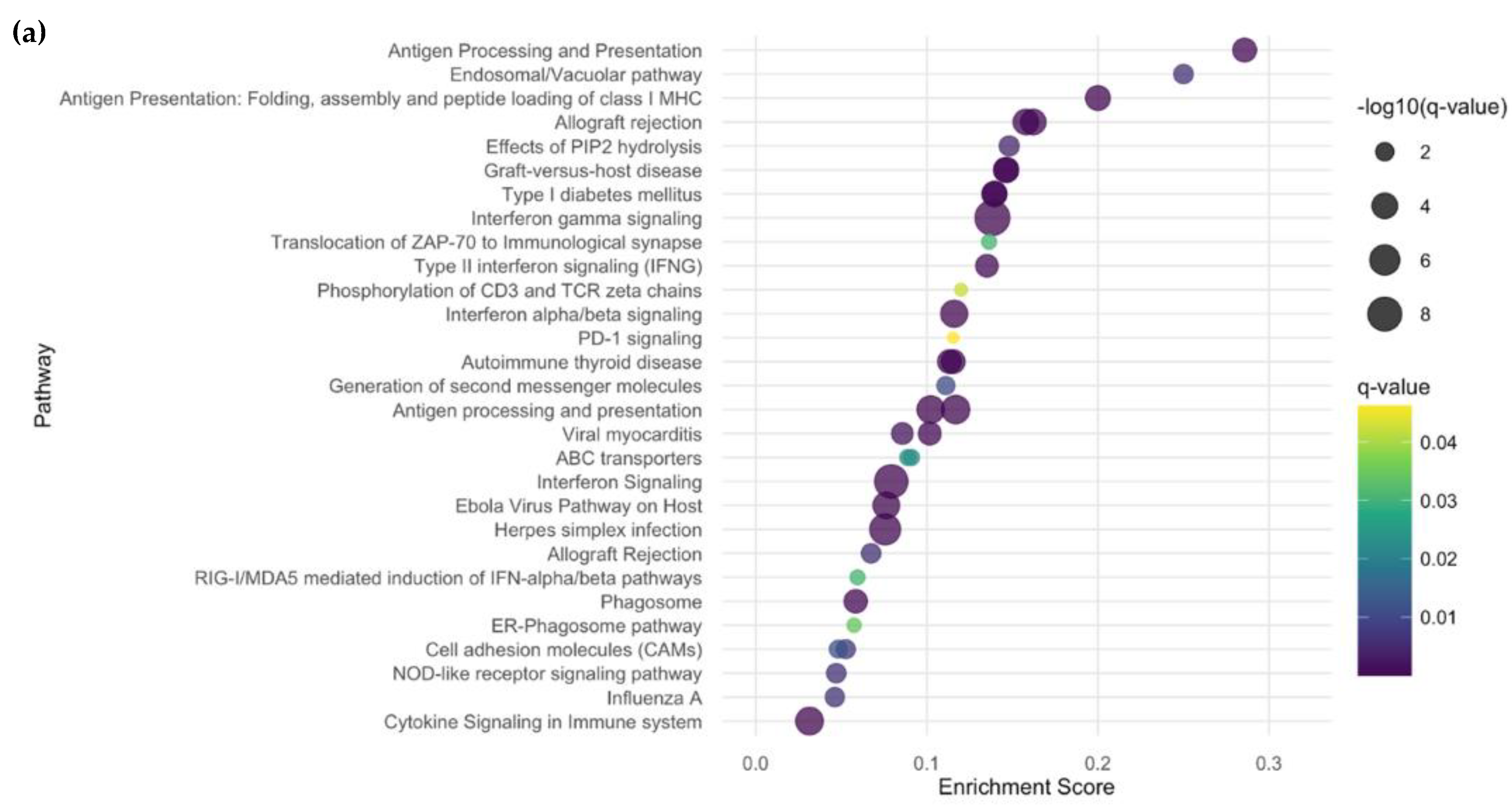
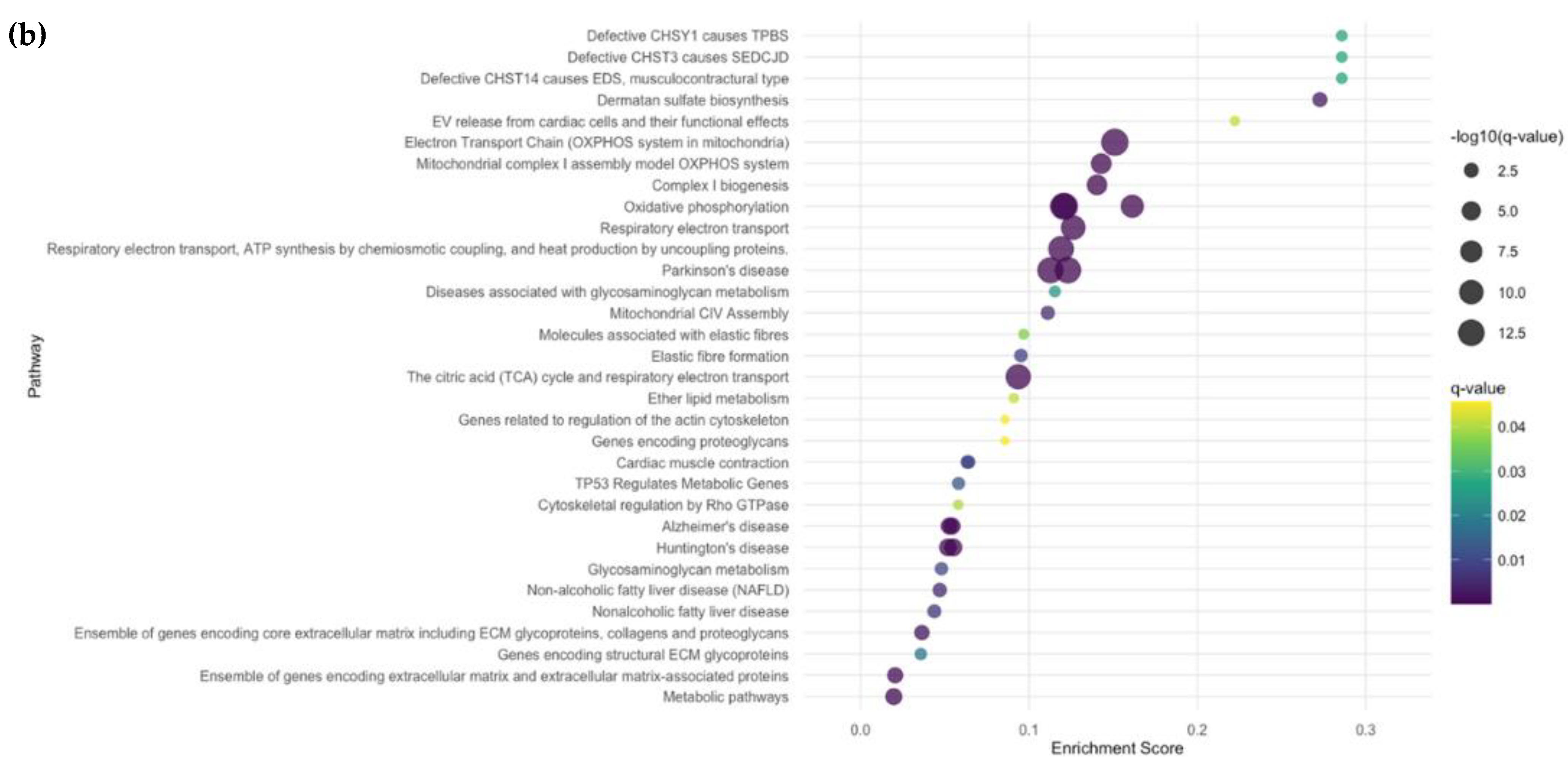
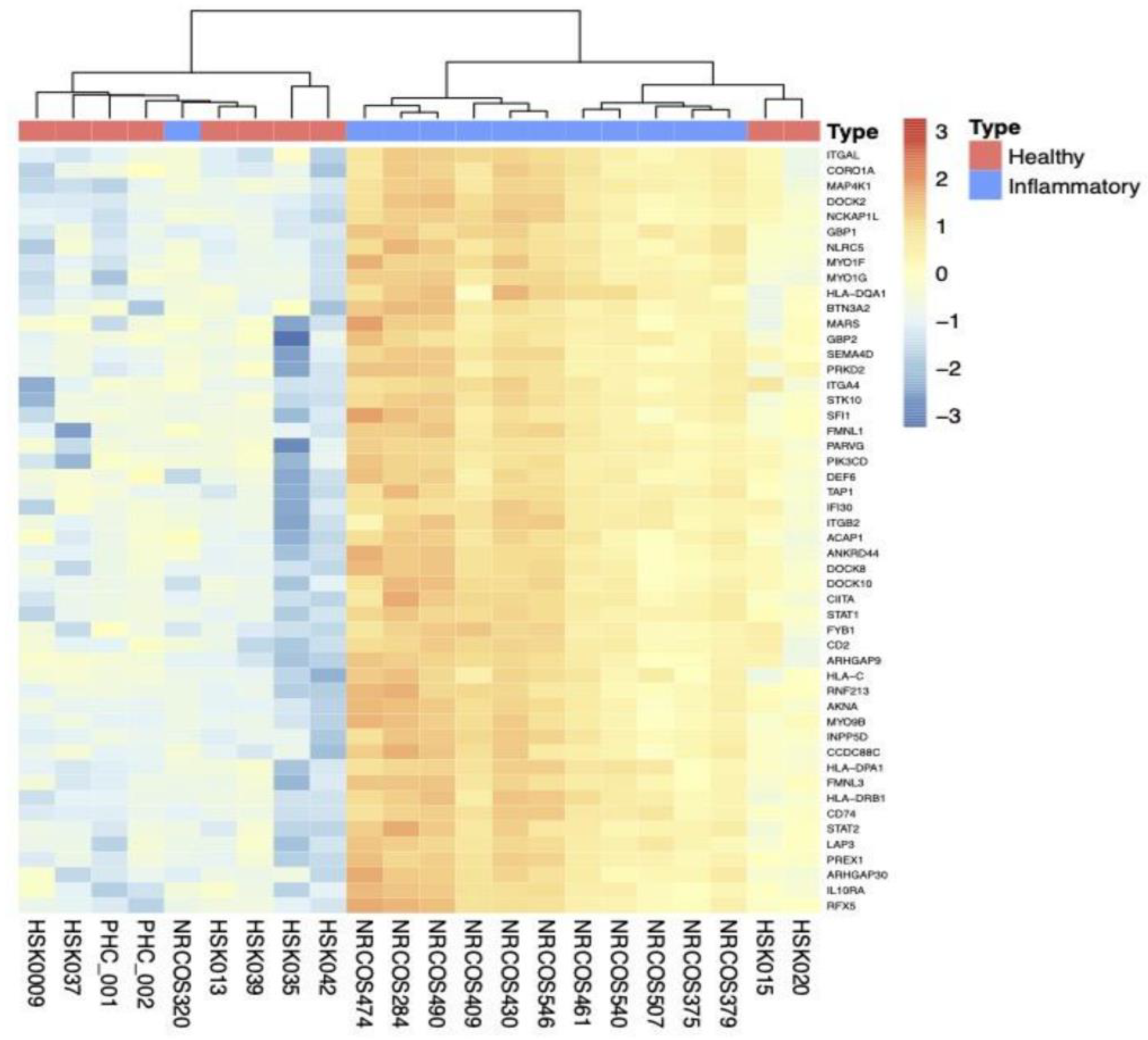
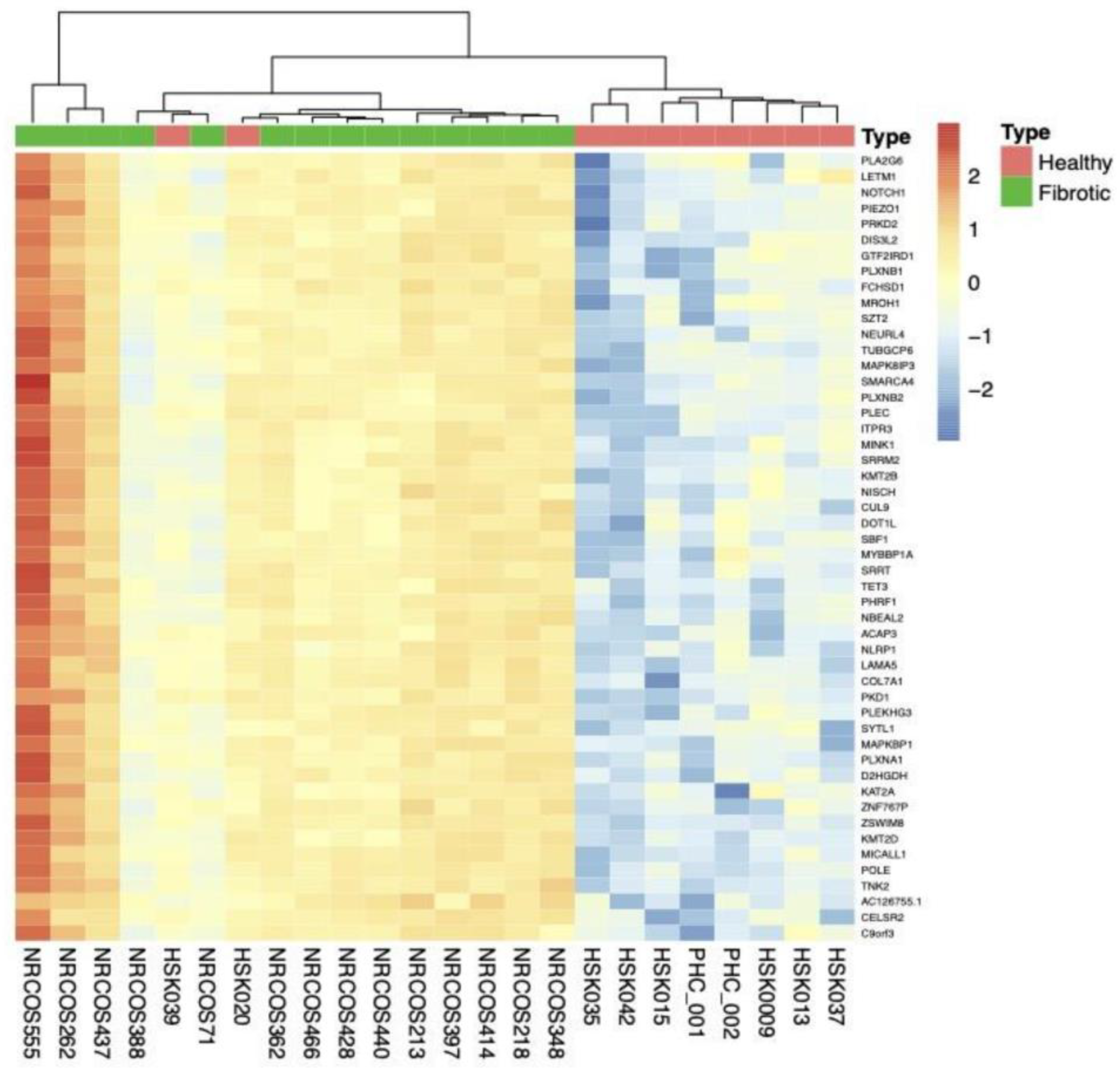
2.2. Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs), Clustering, Pathway Analyses, and Deconvolution
2.2.1. Subgroup Analyses: Linear, Circumscribed, Generalized LS vs. HC
2.2.2. Subgroup Analyses: Active vs. Inactive LS
2.2.3. Subgroup Analyses: Inflammatory vs. HC
2.2.4. Subgroup Analyses: Fibrotic vs. HC
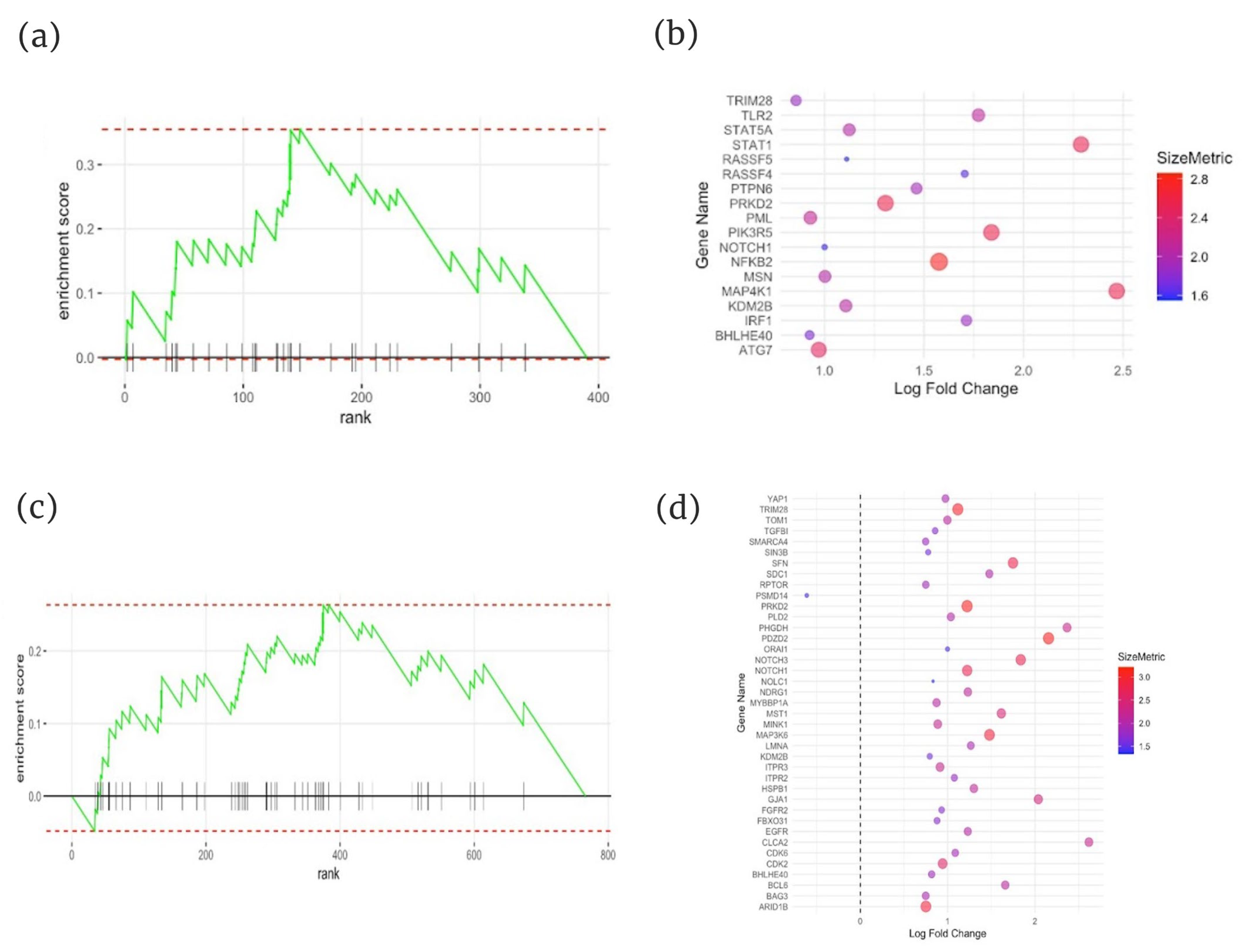
2.3. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) of Immunosenescence-Associated Genes
2.4. Fusion Transcript Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. Comparisons
3.3. Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs), Violin Plots, Unsupervised Clustering, Pathway Analyses, Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
3.4. Cell Type Estimation
3.5. Identification of Fusion Transcripts
3.6. Statistical Analyses
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laxer, R.M.; Zulian, F. Localized scleroderma. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2006, 18, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schutt, C.; Mirizio, E.; Salgado, C.; Reyes-Mugica, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Grunwaldt, L.; Schollaert, K.L.; Torok, K.S. Transcriptomic Evaluation of Juvenile Localized Scleroderma Skin With Histologic and Clinical Correlation. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CPapara; De Luca, D.A.; Bieber, K.; Vorobyev, A.; Ludwig, R.J. Morphea: The 2023 update. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1108623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, P.-S.; Shi, B.; Varga, J. Role of cellular senescence in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2022, 34, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Cai, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, J.; Wei, F. Immunosenescence of T cells: A key player in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 71, 1449–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulian, F.; Culpo, R.; Sperotto, F.; Anton, J.; Avcin, T.; Baildam, E.M.; Boros, C.; Chaitow, J.; Constantin, T.; Kasapcopur, O.; et al. Consensus-based recommendations for the management of juvenile localised scleroderma. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Li, W. RSeQC: Quality control of RNA-seq experiments. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2184–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graubert, A.; Aguet, F.; Ravi, A.; Ardlie, K.G.; Getz, G. RNA-SeQC 2: Efficient RNA-seq quality control and quantification for large cohorts. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 3048–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, K.E.; Buj, R.; Lesko, E.; Dahl, E.S.; Chen, C.-W.; Tangudu, N.K.; Imamura-Kawasawa, Y.; Kossenkov, A.V.; Hobbs, R.P.; Aird, K.M. DOT1L modulates the senescence-associated secretory phenotype through epigenetic regulation of IL1A. J. Cell Biol. 2021, 220, e202008101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzanka, M.; Piekiełko-Witkowska, A. The Role of Gene in Health and Disease: Beyond Treacher Collins Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.; Domrachev, M.; Lash, A.E. Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirizio, E.; Liu, C.; Yan, Q.; Waltermire, J.; Mandel, R.; Schollaert, K.L.; Konnikova, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Torok, K.S. Genetic Signatures From RNA Sequencing of Pediatric Localized Scleroderma Skin. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 669116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, Y.; Fujimoto, M.; Ishikawa, O.; Sato, S.; Jinnin, M.; Takehara, K.; Hasegawa, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Ihn, H. Diagnostic criteria, severity classification and guidelines of localized scleroderma. J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, 755–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y. Discovering the false discovery rate: False Discovery Rate. J. R. Stat. Soc. Series B Stat. Methodol. 2010, 72, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W. DAVID: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolde. Pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps, R Package Version, Kolde: St Marys, KS, USA, 2019.
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Bardes, E.E.; Aronow, B.J.; Jegga, A.G. ToppGene Suite for gene list enrichment analysis and candidate gene prioritization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W305–W311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacutu, R.; Thornton, D.; Johnson, E.; Budovsky, A.; Barardo, D.; Craig, T.; Diana, E.; Lehmann, G.; Toren, D.; Wang, J.; et al. Human Ageing Genomic Resources: New and updated databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1083–D1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mootha, V.K.; Lindgren, C.M.; Eriksson, K.-F.; Subramanian, A.; Sihag, S.; Lehar, J.; Puigserver, P.; Carlsson, E.; Ridderstråle, M.; Laurila, E.; et al. PGC-1alpha-responsive genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aran, D.; Hu, Z.; Butte, A.J. xCell: Digitally portraying the tissue cellular heterogeneity landscape. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, B.J.; Dobin, A.; Stransky, N.; Li, B.; Yang, X.; Tickle, T.; Bankapur, A.; Ganote, C.; Doak, T.G.; Pochet, N.; et al. STAR-Fusion: Fast and Accurate Fusion Transcript Detection from RNA-Seq. bioRxiv 2017, 120295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhrig, S.; Ellermann, J.; Walther, T.; Burkhardt, P.; Fröhlich, M.; Hutter, B.; Toprak, U.H.; Neumann, O.; Stenzinger, A.; Scholl, C.; et al. Accurate and efficient detection of gene fusions from RNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2021, 31, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PEwels; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Käller, M. MultiQC: Summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdassarian, H.; Blackstone, S.A.; Clay, O.S.; Philips, R.; Matthiasardottir, B.; Nehrebecky, M.; Hua, V.K.; McVicar, R.; Liu, Y.; Tucker, S.M.; et al. Variant and Response to Ruxolitinib in an Autoinflammatory Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 2241–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobe, H.; Ahn, C.; Arnett, F.C.; Reveille, J.D. Major histocompatibility complex class I and class II alleles may confer susceptibility to or protection against morphea: Findings from the Morphea in Adults and Children cohort. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 3170–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saracino, A.M.; Denton, C.P.; Orteu, C.H. The molecular pathogenesis of morphoea: From genetics to future treatment targets. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laetsch, B.; Hofer, T.; Lombriser, N.; Lautenschlager, S. Irradiation-Induced Morphea: X-Rays as Triggers of Autoimmunity. Dermatology 2011, 223, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigi, P.K.M. The Immunogenetics of Morphea and Lichen Sclerosus. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022, 1367, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partl, R.; Regitnig, P.; Lukasiak, K.; Winkler, P.; Kapp, K.S. Incidence of Morphea following Adjuvant Irradiation of the Breast in 2,268 Patients. Breast Care 2020, 15, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanami, Y.; Ohtsuka, M.; Yamamoto, T. Paraneoplastic eosinophilic fasciitis with generalized morphea and vitiligo in a patient working with organic solvents. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 67–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aounallah, A.; Lahouel, I.; Mokni, S.; Ksiaa, M.; Hayouni, M.; Belajouza, C.; Kotti, F.; Saidi, W.; Boussofara, L.; El Maalel, O.; et al. Atypical generalized morphea-like scleroderma occurring in a patient exposed to organic solvents and having chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2018, 84, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truchetet, M.E.; Brembilla, N.C.; Chizzolini, C. Current concepts on the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 64, 262–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.C.; Nymeyer, H.; Green, A.; Jacobe, H.T. Changes in Disease Activity and Damage Over Time in Patients With Morphea. JAMA Dermatol. 2020, 156, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, B.; Sinha, S.C.; Amin, S.; Gan, L. Mechanism and therapeutic potential of targeting cGAS-STING signaling in neurological disorders. Mol. Neurodegener. 2023, 18, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lood, C.; Blanco, L.P.; Purmalek, M.M.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; De Ravin, S.S.; Smith, C.K.; Malech, H.L.; A Ledbetter, J.; Elkon, K.B.; Kaplan, M.J. Neutrophil extracellular traps enriched in oxidized mitochondrial DNA are interferogenic and contribute to lupus-like disease. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gniadecki, R.; Iyer, A.; Hennessey, D.; Khan, L.; O’Keefe, S.; Redmond, D.; Storek, J.; Durand, C.; Cohen-Tervaert, J.W.; Osman, M. Genomic instability in early systemic sclerosis. J. Autoimmun. 2022, 131, 102847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALonde, C.; Fernandez-Ruiz, R.; Julio, P.R.; Appenzeller, S.; Niewold, T.B. Type I Interferons in Autoimmunity: Implications in Clinical Phenotypes and Treatment Response. J. Rheumatol. 2023, 50, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Gabrielli, S.; Khoury, L.; Osman, M.; Litvinov, I.V.; Iannattone, L.; Lefrançois, P.; Netchiporouk, E. Immunosenescence, Inflammaging, and Dermatology: Insights and Opportunities. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2023, 27, 532–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogilenko, D.A.; Shchukina, I.; Artyomov, M.N. Immune ageing at single-cell resolution. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 22, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, C.; Han, Y.; Gu, Z.; Sun, C. Immunosenescence, aging and successful aging. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 942796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, P.; Wang, S.; Yang, M.; Wu, H. The ABC-associated Immunosenescence and Lifestyle Interventions in Autoimmune Disease. Rheumatol. Immunol. Res. 2022, 3, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly-Chevrier, M.; Gélinas, A.; Ghazal, S.; Moussa, S.; McCuaig, C.C.; Piram, M.; Mereniuk, A.; Litvinov, I.V.; Osman, M.; Pehr, K.; et al. Morphea, Eosinophilic Fasciitis and Cancer: A Scoping Review. Cancers 2023, 15, 4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijsenbeek, M.; Swigris, J.J.; Inoue, Y.; Kreuter, M.; Maher, T.M.; Suda, T.; Baldwin, M.; Mueller, H.; Rohr, K.B.; Flaherty, K.R.; et al. Effects of nintedanib on symptoms in patients with progressive pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 63, 2300752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonowski, S.; Goldman, N.; Kassamali, B.; Shahriari, N.; LaChance, A.; Vleugels, R.A. Tocilizumab for refractory morphea in adults: A case series. JAAD Case Rep. 2022, 30, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damsky, W.; Patel, D.; Garelli, C.J.; Garg, M.; Wang, A.; Dresser, K.; Deng, A.; Harris, J.E.; Richmond, J.; King, B. Jak Inhibition Prevents Bleomycin-Induced Fibrosis in Mice and Is Effective in Patients with Morphea. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 1446–1449.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient Characteristics | LS (n = 28) |
|---|---|
| Female sex (n, %) | 17 (61) |
| Age at the time of biopsy, median (IQR) | 13 (10–16) |
| Race White (n, %) Other (n, %) | 25 (89) 3 (11) |
| Disease subtype Linear trunk/limbs (n, %) Linear head (n, %) Circumscribed (n, %) Generalized (n, %) | 8 (29) 4 (14) 8 (29) 8 (29) |
| Disease activity Active (n, %) Inactive (n, %) | 19 (68) 9 (32) |
| Histologic subtype Inflammatory | |
| Yes (n, %) No (n, %) | 12 (43) 16 (57) |
| Severity grade None/mild (n, %) Moderate (n, %) Severe (n, %) | 19 (68) 3 (11) 6 (21) |
| Collagen thickness in μm Papillary dermis (range) Upper reticular dermis (range) Lower reticular dermis (range) | 1.92–7.44 6.17–41.09 12.10–74.25 |
| Comorbid Th2 Diseases Eczema (n, %) Seasonal Allergies (n, %) Asthma (n, %) | 5 (18) 3 (11) 1 (4) |
| ssDNA antibody positivity (n, %) | 8 (29) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khoury, L.; Prosty, C.; Ghazal, S.; Gabrielli, S.; Torok, K.S.; Osman, M.; Martinez-Jaramillo, E.; Lefrançois, P.; Netchiporouk, E. Markers of Type 2 Inflammation and Immunosenescence Are Upregulated in Localized Scleroderma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031258
Khoury L, Prosty C, Ghazal S, Gabrielli S, Torok KS, Osman M, Martinez-Jaramillo E, Lefrançois P, Netchiporouk E. Markers of Type 2 Inflammation and Immunosenescence Are Upregulated in Localized Scleroderma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(3):1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031258
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhoury, Lauren, Connor Prosty, Stephanie Ghazal, Sofianne Gabrielli, Kathryn S. Torok, Mohammed Osman, Elvis Martinez-Jaramillo, Philippe Lefrançois, and Elena Netchiporouk. 2025. "Markers of Type 2 Inflammation and Immunosenescence Are Upregulated in Localized Scleroderma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 3: 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031258
APA StyleKhoury, L., Prosty, C., Ghazal, S., Gabrielli, S., Torok, K. S., Osman, M., Martinez-Jaramillo, E., Lefrançois, P., & Netchiporouk, E. (2025). Markers of Type 2 Inflammation and Immunosenescence Are Upregulated in Localized Scleroderma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(3), 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031258







