Hydrogels for Cardiac Tissue Regeneration: Current and Future Developments
Abstract
1. Introduction
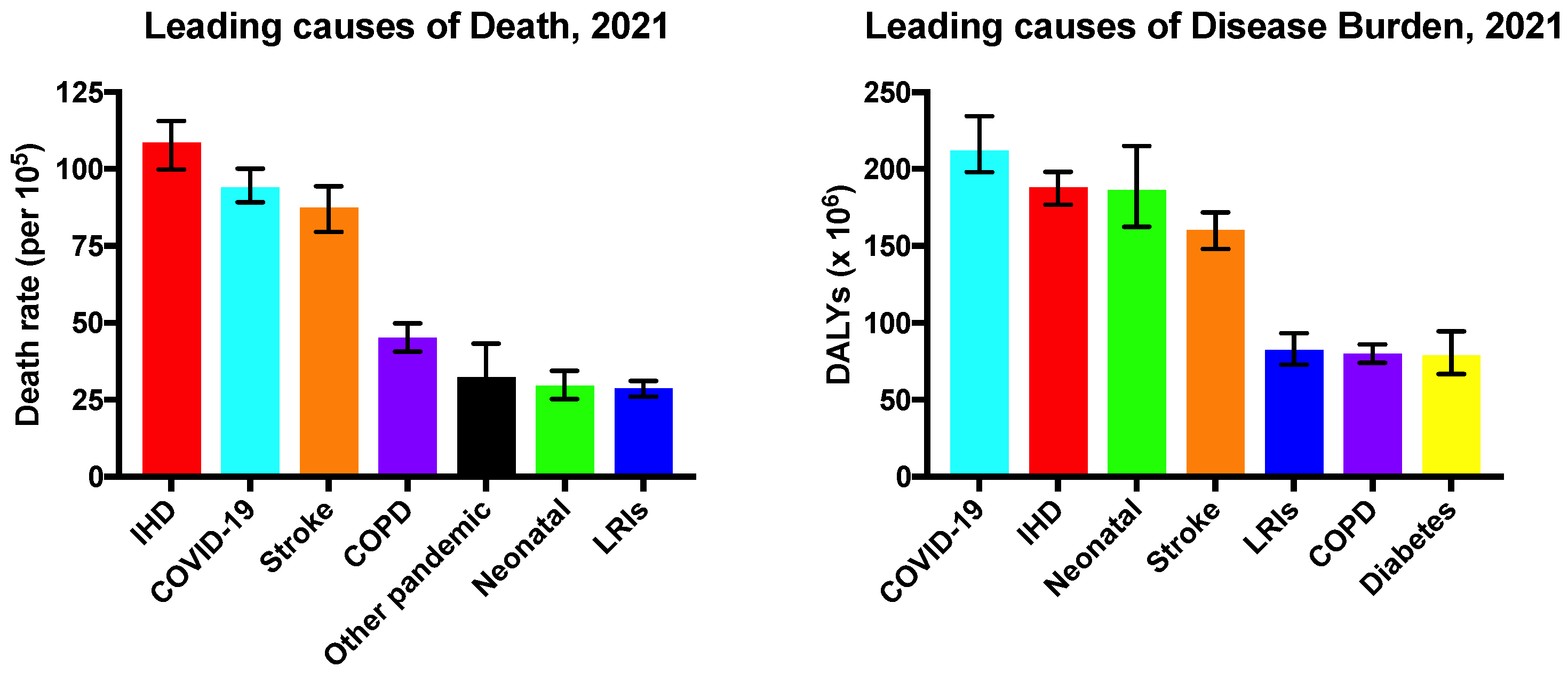
2. Myocardial Infarction
Current Treatments for MI
3. Development of Novel Therapies for Cardiac Regeneration
3.1. Cell-Based Therapies
3.1.1. Skeletal Myoblasts
3.1.2. Mesenchymal Stem Cells
3.1.3. Embryonic Stem Cells
3.1.4. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
4. Application of Biomaterials to Enhance Cell-Based Regenerative Therapies
4.1. Hydrogels
4.2. Hydrogel Crosslinking
4.2.1. Physical Crosslinking
4.2.2. Chemical Crosslinking
4.3. Hydrogels: Natural vs. Synthetic Polymers
4.4. Hybrid Hydrogels
4.5. Self-Assembling Peptide Hydrogels
4.6. Cardiac Patches
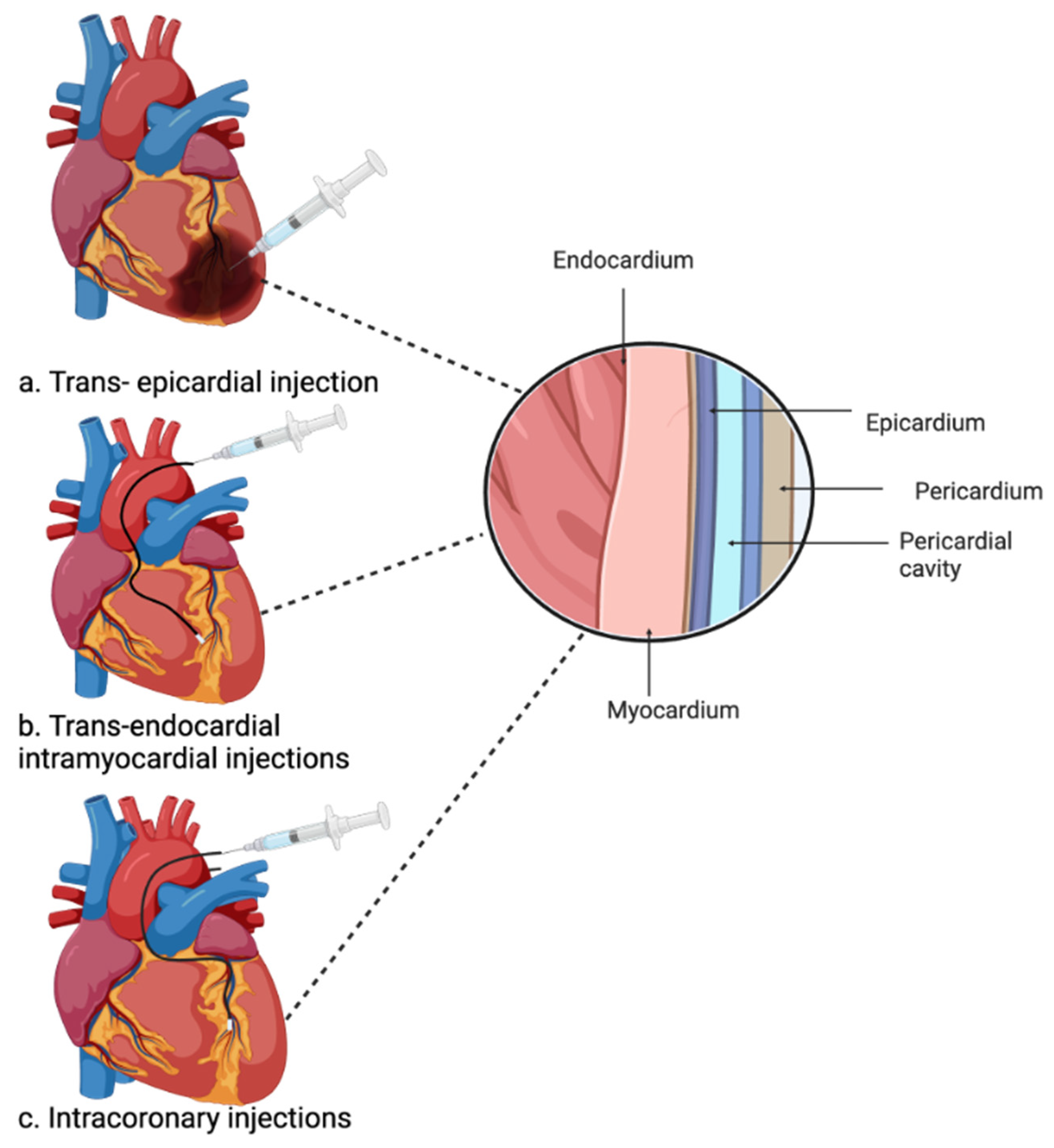
4.7. Injectable Hydrogels
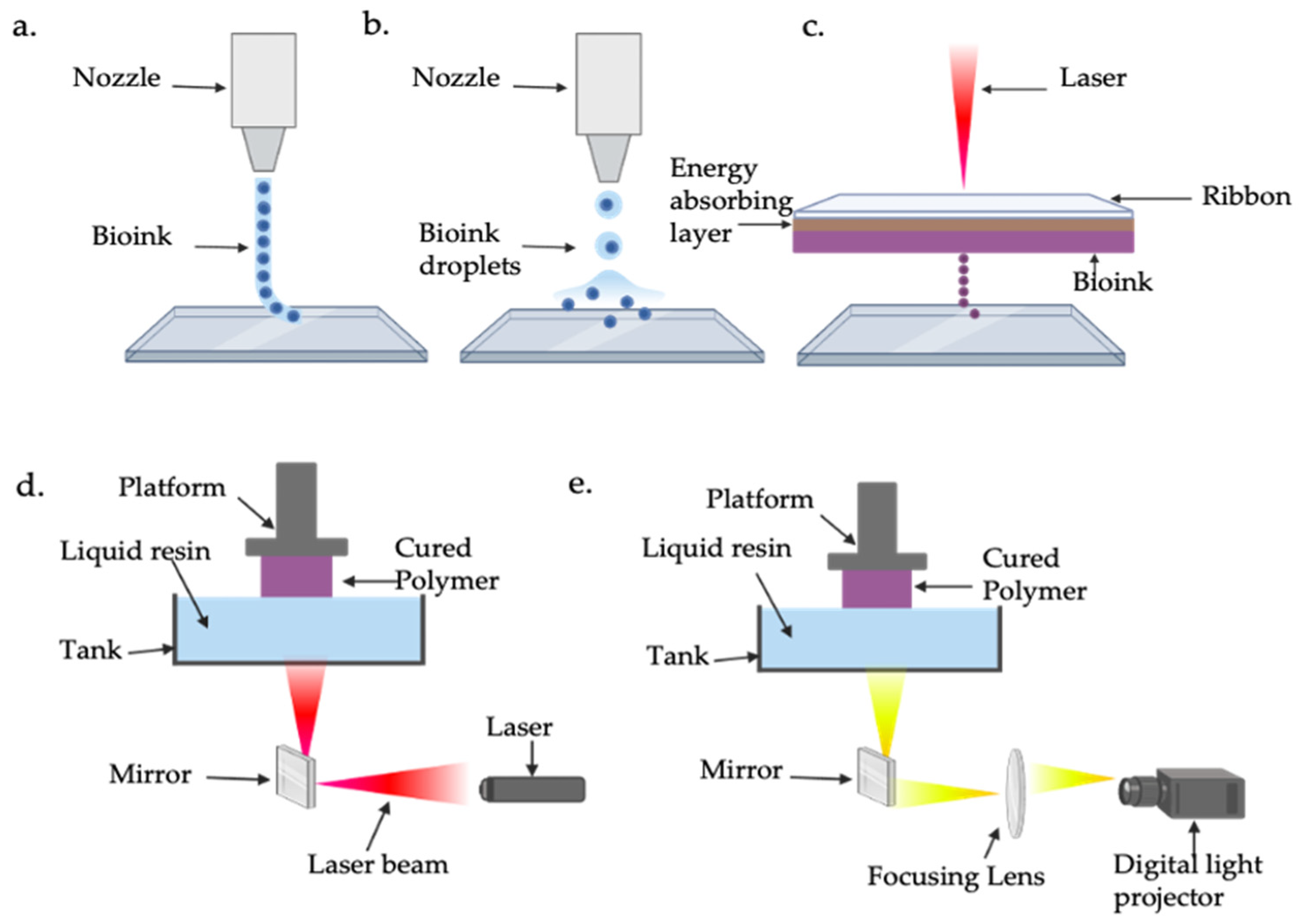
4.8. Current Progress of Organoids and 3D Bioprinting in Cardiac Regeneration
5. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
5.1. Hydrogel Composition
5.2. Hydrogel Delivery Methods
5.3. Current and Future Prospects of Bioprinting in Cardiac Regeneration
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Perez-Quilis, C.; Leischik, R.; Lucia, A. Epidemiology of coronary heart disease and acute coronary syndrome. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mensah, G.A.; Fuster, V.; Murray, C.J.L.; Roth, G.A. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risks, 1990–2022. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 82, 2350–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Burden of Disease Collaborative Network. Global Burden of Disease Study 2021 (GBD 2021); Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME): Seattle, WA, USA, 2024; Available online: http://www.healthdata.org/research-analysis/library/global-burden-disease-2021-findings-gbd-2021-study (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- World Health Organization. UN Decade of Healthy Ageing: Plan of Action 2021–2030. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/decade-of-healthy-ageing/decade-proposal-final-apr2020-en.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Mensah, G.A.; Fuster, V.; Roth, G.A. A Heart-Healthy and Stroke-Free World: Using Data to Inform Global Action. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 82, 2343–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine Committee on Social Security Cardiovascular Disability Criteria. Cardiovascular Disability: Updating the Social Security Listings; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mendis, S.; Thygesen, K.; Kuulasmaa, K.; Giampaoli, S.; Mähönen, M.; Ngu Blackett, K.; Lisheng, L. World Health Organization definition of myocardial infarction: 2008-09 revision. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, A.P.; Virmani, R. Pathophysiology of Acute Myocardial Infarction. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 91, 553–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüscher, T.F. Myocardial infarction: Mechanisms, diagnosis, and complications. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 947–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damluji, A.A.; van Diepen, S.; Katz, J.N.; Menon, V.; Tamis-Holland, J.E.; Bakitas, M.; Cohen, M.G.; Balsam, L.B.; Chikwe, J. Mechanical Complications of Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 144, e16–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jernberg, T.; Hasvold, P.; Henriksson, M.; Hjelm, H.; Thuresson, M.; Janzon, M. Cardiovascular risk in post-myocardial infarction patients: Nationwide real world data demonstrate the importance of a long-term perspective. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Liu, M.; Sun, R.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, P. Myocardial Infarction: Symptoms and Treatments. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 72, 865–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Mehta, P.; Reddivari, A.K.R.; Mungee, S. Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mousaei Ghasroldasht, M.; Seok, J.; Park, H.S.; Liakath Ali, F.B.; Al-Hendy, A. Stem Cell Therapy: From Idea to Clinical Practice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrami, A.P.; Urbanek, K.; Kajstura, J.; Yan, S.M.; Finato, N.; Bussani, R.; Nadal-Ginard, B.; Silvestri, F.; Leri, A.; Beltrami, C.A.; et al. Evidence that human cardiac myocytes divide after myocardial infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1750–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, O.; Bhardwaj, R.D.; Bernard, S.; Zdunek, S.; Barnabé-Heider, F.; Walsh, S.; Zupicich, J.; Alkass, K.; Buchholz, B.A.; Druid, H.; et al. Evidence for cardiomyocyte renewal in humans. Science 2009, 324, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beliën, H.; Evens, L.; Hendrikx, M.; Bito, V.; Bronckaers, A. Combining stem cells in myocardial infarction: The road to superior repair? Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 343–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duval, K.; Grover, H.; Han, L.H.; Mou, Y.; Pegoraro, A.F.; Fredberg, J.; Chen, Z. Modeling Physiological Events in 2D vs. 3D Cell Culture. Physiology 2017, 32, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaicharoenaudomrung, N.; Kunhorm, P.; Noisa, P. Three-dimensional cell culture systems as an in vitro platform for cancer and stem cell modeling. World J. Stem Cells 2019, 11, 1065–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisone, I.; Cecchettini, A.; Ceccherini, E.; Persiani, E.; Morales, M.A.; Vozzi, F. Cardiac tissue engineering: Multiple approaches and potential applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 980393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Choo, A.B.H. Stem Cells. In Comprehensive Biotechnology, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Burlington, VT, USA, 2011; pp. 341–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, R.; Dan, P.; Hasan, A.; Khalaf, I.M.; Prasad, P.; Ghosal, K.; Gentile, C.; McClements, L.; Maureira, P. Stem cell-based approaches in cardiac tissue engineering: Controlling the microenvironment for autologous cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, D.; Buttery, L.D.; Shakesheff, K.M.; Roberts, S.J. Tissue engineering: Strategies, stem cells and scaffolds. J. Anat. 2008, 213, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochazkova, M.; Chavez, M.G.; Prochazka, J.; Felfy, H.; Mushegyan, V.; Klein, O.D. Chapter 18: Embryonic Versus Adult Stem Cells. In Stem Cell Biology and Tissue Engineering in Dental Sciences; Vishwakarma, A., Sharpe, P., Shi, S., Ramalingam, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 249–262. [Google Scholar]
- Akter, F.; Hamid, H. Chapter 6-Cardiovascular Tissue Engineering. In Tissue Engineering Made Easy; Akter, F., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Liew, L.C.; Ho, B.X.; Soh, B.S. Mending a broken heart: Current strategies and limitations of cell-based therapy. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turksen, K. Adult stem cells and cardiac regeneration. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2013, 9, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ott, H.C.; Rajab, T.K. Chapter 13-Tissue-Derived Matrices. In In Situ Tissue Regeneration; Lee, S.J., Yoo, J.J., Atala, A., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 229–250. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, J.A.; Itskovitz-Eldor, J.; Shapiro, S.S.; Waknitz, M.A.; Swiergiel, J.J.; Marshall, V.S.; Jones, J.M. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 1998, 282, 1145–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghodsizad, A.; Ruhparwar, A.; Bordel, V.; Mirsaidighazi, E.; Klein, H.M.; Koerner, M.M.; Karck, M.; El-Banayosy, A. Clinical application of adult stem cells for therapy for cardiac disease. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2013, 31, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Tanabe, K.; Ohnuki, M.; Narita, M.; Ichisaka, T.; Tomoda, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 2007, 131, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.L.; Xue, Q.; Xu, X.H.; Hu, F.; Shao, H. Recent progress in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived 3D cultures for cardiac regeneration. Cell Tissue Res. 2021, 384, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chachques, J.C.; Acar, C.; Herreros, J.; Trainini, J.C.; Prosper, F.; D’Attellis, N.; Fabiani, J.N.; Carpentier, A.F. Cellular cardiomyoplasty: Clinical application. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2004, 77, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraniak, P.R.; McDevitt, T.C. Stem cell paracrine actions and tissue regeneration. Regen. Med. 2010, 5, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menasché, P.; Hagège, A.A.; Scorsin, M.; Pouzet, B.; Desnos, M.; Duboc, D.; Schwartz, K.; Vilquin, J.T.; Marolleau, J.P. Myoblast transplantation for heart failure. Lancet 2001, 357, 279–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muqresh, M.A.; Harbieh, I.; Haider, K.H. Myogenic Cardiac Regeneration: Clinical Studies Using Skeletal Myoblasts. In Handbook of Stem Cell Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hare, J.M.; Fishman, J.E.; Gerstenblith, G.; DiFede Velazquez, D.L.; Zambrano, J.P.; Suncion, V.Y.; Tracy, M.; Ghersin, E.; Johnston, P.V.; Brinker, J.A.; et al. Comparison of allogeneic vs autologous bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stem cells delivered by transendocardial injection in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy: The POSEIDON randomized trial. JAMA 2012, 308, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, H.; Olson, E.N.; Bassel-Duby, R. Therapeutic approaches for cardiac regeneration and repair. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiasen, A.B.; Qayyum, A.A.; Jørgensen, E.; Helqvist, S.; Fischer-Nielsen, A.; Kofoed, K.F.; Haack-Sørensen, M.; Ekblond, A.; Kastrup, J. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cell treatment in patients with severe ischaemic heart failure: A randomized placebo-controlled trial (MSC-HF trial). Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 1744–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.J.; Yang, X.; Don, C.W.; Minami, E.; Liu, Y.W.; Weyers, J.J.; Mahoney, W.M.; Van Biber, B.; Cook, S.M.; Palpant, N.J.; et al. Human embryonic-stem-cell-derived cardiomyocytes regenerate non-human primate hearts. Nature 2014, 510, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Wu, Q.; Ni, C.; Zhang, P.; Zhong, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Kong, M.; Cheng, H.; et al. Lack of Remuscularization Following Transplantation of Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Cardiovascular Progenitor Cells in Infarcted Nonhuman Primates. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.W.; Chen, B.; Yang, X.; Fugate, J.A.; Kalucki, F.A.; Futakuchi-Tsuchida, A.; Couture, L.; Vogel, K.W.; Astley, C.A.; Baldessari, A.; et al. Human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes restore function in infarcted hearts of non-human primates. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, C.; Song, K. Cellular reprogramming of fibroblasts in heart regeneration. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2023, 180, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Huang, G.N.; Payumo, A.Y. Two decades of heart regeneration research: Cardiomyocyte proliferation and beyond. WIREs Mech. Dis. 2024, 16, e1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiba, Y.; Gomibuchi, T.; Seto, T.; Wada, Y.; Ichimura, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Ogasawara, T.; Okada, K.; Shiba, N.; Sakamoto, K.; et al. Allogeneic transplantation of iPS cell-derived cardiomyocytes regenerates primate hearts. Nature 2016, 538, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Sai, X.; Li, Z.; Ye, X.; Jin, L.; Liu, G.; Li, G.; Yang, P.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, S.; et al. Maturation of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes and its therapeutic effect on myocardial infarction in mouse. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 20, 286–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shida, M.; Miyagawa, S.; Saito, A.; Fukushima, S.; Harada, A.; Ito, E.; Ohashi, F.; Watabe, T.; Hatazawa, J.; Matsuura, K.; et al. Transplantation of Human-induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-derived Cardiomyocytes Is Superior to Somatic Stem Cell Therapy for Restoring Cardiac Function and Oxygen Consumption in a Porcine Model of Myocardial Infarction. Transplantation 2019, 103, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, M.; Miyagawa, S.; Miki, K.; Saito, A.; Fukushima, S.; Higuchi, T.; Kawamura, T.; Kuratani, T.; Daimon, T.; Shimizu, T.; et al. Feasibility, safety, and therapeutic efficacy of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocyte sheets in a porcine ischemic cardiomyopathy model. Circulation 2012, 126, S29–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishino, Y.; Tohyama, S.; Morita, Y.; Soma, Y.; Tani, H.; Okada, M.; Kanazawa, H.; Fukuda, K. Cardiac Regenerative Therapy Using Human Pluripotent Stem Cells for Heart Failure: A State-of-the-Art Review. J. Card. Fail. 2023, 29, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, M.; Yang, B.; Zhang, F.; Cao, K. Intramyocardial transplantation of undifferentiated rat induced pluripotent stem cells causes tumorigenesis in the heart. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rienks, M.; Papageorgiou, A.P.; Frangogiannis, N.G.; Heymans, S. Myocardial extracellular matrix: An ever-changing and diverse entity. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 872–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristen, L.; Zhijie, W. Chapter 2: Extracellular Matrix in Cardiac Tissue Mechanics and Physiology: Role of Collagen Accumulation. In Extracellular Matrix; Rama Sashank, M., Joseph Orgel, P.R.O., Zvi, L., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Zhang, L. Cardiac ECM: Its Epigenetic Regulation and Role in Heart Development and Repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisenbrey, E.A.; Murphy, W.L. Synthetic alternatives to Matrigel. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funaki, M.; Janmey, P.A. Chapter 23-Technologies to Engineer Cell Substrate Mechanics in Hydrogels. In Biology and Engineering of Stem Cell Niches; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 363–373. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, N.C. From bench to cageside: Risk assessment for rodent pathogen contamination of cells and biologics. ILAR J. 2008, 49, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Shmeis, R.M. Chapter Four-Nanotechnology in wastewater treatment. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Turan, N.B., Engin, G.O., Bilgili, M.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 99, pp. 105–134. [Google Scholar]
- Spicer, C.D. Hydrogel scaffolds for tissue engineering: The importance of polymer choice. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 184–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Chakraborty, E. Hydrogel based tissue engineering and its future applications in personalized disease modeling and regenerative therapy. Beni Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2022, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, J.L.; Mooney, D.J. Hydrogels for tissue engineering: Scaffold design variables and applications. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4337–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Florit, M.; Pardo, A.; Domingues, R.M.A.; Graça, A.L.; Babo, P.S.; Reis, R.L.; Gomes, M.E. Natural-Based Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madduma-Bandarage, U.S.K.; Madihally, S.V. Synthetic hydrogels: Synthesis, novel trends, and applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkouri, H.; Chamkouri, M. A review of hydrogels, their properties and applications in medicine. Am. J. Biomed. Sci. Res. 2021, 11, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J. Advances in crosslinking strategies of biomedical hydrogels. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.M. Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojkov, G.; Niyazov, Z.; Picchioni, F.; Bose, R.K. Relationship between Structure and Rheology of Hydrogels for Various Applications. Gels 2021, 7, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama, R.; Ulziibayar, A.; Reinhardt, J.W.; Watanabe, T.; Kelly, J.; Shinoka, T. Recent Developments in Biopolymer-Based Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Chen, Y.; Rehman, H.U.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, M.; Li, H.; Liu, H. Ultratough, Self-Healing, and Tissue-Adhesive Hydrogel for Wound Dressing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33523–33531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.L.; Yu, A.C.; Agmon, G.; Appel, E.A. Supramolecular polymeric biomaterials. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 10–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Ye, H.; Wu, D. Recent advances on polymeric hydrogels as wound dressings. APL Bioeng. 2021, 5, 011504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klouda, L.; Mikos, A.G. Thermoresponsive hydrogels in biomedical applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 68, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacesa, P. Alginates. Carbohydr. Polym. 1988, 8, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, M.; Diao, Y.; Li, B.; Shi, L.; Ran, R. Preparation and properties of polyacrylamide/polyvinyl alcohol physical double network hydrogel. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 112468–112476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascone, M.G.; Maltinti, S.; Barbani, N.; Laus, M. Effect of chitosan and dextran on the properties of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1999, 10, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasution, H.; Harahap, H.; Dalimunthe, N.F.; Ginting, M.H.S.; Jaafar, M.; Tan, O.O.H.; Aruan, H.K.; Herfananda, A.L. Hydrogel and Effects of Crosslinking Agent on Cellulose-Based Hydrogels: A Review. Gels 2022, 8, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermis, M.; Calamak, S.; Calibasi Kocal, G.; Guven, S.; Durmus, N.G.; Rizvi, I.; Hasan, T.; Hasirci, N.; Hasirci, V.; Demirci, U. Chapter 15-Hydrogels as a New Platform to Recapitulate the Tumor Microenvironment. In Handbook of Nanomaterials for Cancer Theranostics; Conde, J., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 463–494. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Lu, F.; Liu, Y. A Review of the Mechanism, Properties, and Applications of Hydrogels Prepared by Enzymatic Cross-linking. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 10238–10249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heck, T.; Faccio, G.; Richter, M.; Thöny-Meyer, L. Enzyme-catalyzed protein crosslinking. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyles, D.A.; Castro, L.D.; Silva, J.O.C.; Ribeiro-Costa, R.M. A review of the designs and prominent biomedical advances of natural and synthetic hydrogel formulations. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 88, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Raines, R.T. Review collagen-based biomaterials for wound healing. Biopolymers 2014, 101, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassiri, Z.; Khokha, R. Myocardial extra-cellular matrix and its regulation by metalloproteinases and their inhibitors. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 93, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreazza, R.; Morales, A.; Pieniz, S.; Labidi, J. Gelatin-Based Hydrogels: Potential Biomaterials for Remediation. Polymers 2023, 15, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Guo, S.; Yu, G.; Yang, H. Synthesis and Properties of Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMA) Hydrogels and Their Recent Applications in Load-Bearing Tissue. Polymers 2018, 10, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lierova, A.; Kasparova, J.; Filipova, A.; Cizkova, J.; Pekarova, L.; Korecka, L.; Mannova, N.; Bilkova, Z.; Sinkorova, Z. Hyaluronic Acid: Known for Almost a Century, but Still in Vogue. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Jha, A.K.; Harrington, D.A.; Farach-Carson, M.C.; Jia, X. Hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels: From a natural polysaccharide to complex networks. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 3280–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catoira, M.C.; Fusaro, L.; Di Francesco, D.; Ramella, M.; Boccafoschi, F. Overview of natural hydrogels for regenerative medicine applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2019, 30, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionkowska, A. Collagen blended with natural polymers: Recent advances and trends. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021, 122, 101452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.; Khattab, A.; Islam, M.A.; Hweij, K.A.; Zeitouny, J.; Waters, R.; Sayegh, M.; Hossain, M.M.; Paul, A. Injectable Hydrogels for Cardiac Tissue Repair after Myocardial Infarction. Adv. Sci. 2015, 2, 1500122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christman, K.L.; Vardanian, A.J.; Fang, Q.; Sievers, R.E.; Fok, H.H.; Lee, R.J. Injectable fibrin scaffold improves cell transplant survival, reduces infarct expansion, and induces neovasculature formation in ischemic myocardium. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagarsamy, K.N.; Yan, W.; Srivastava, A.; Desiderio, V.; Dhingra, S. Application of injectable hydrogels for cardiac stem cell therapy and tissue engineering. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 20, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, A.; Zamani, M.; Huang, N.F. Extracellular Matrix-Based Biomaterials for Cardiovascular Tissue Engineering. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2021, 8, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.; Bhatia, A.; Chopra, S.; Dua, K.; Prasher, P.; Gupta, G.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Chellappan, D.K.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Sharma, M.; et al. Chapter 28: Advancements on microparticles-based drug delivery systems for cancer therapy. In Advanced Drug Delivery Systems in the Management of Cancer; Dua, K., Mehta, M., de Jesus Andreoli Pinto, T., Pont, L.G., Williams, K.A., Rathbone, M.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 351–358. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, R.S.; Myers, K.A.; Gardel, M.L.; Waterman, C.M. Stiffness-controlled three-dimensional extracellular matrices for high-resolution imaging of cell behavior. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 2056–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, L.; Worch, J.C.; Dove, A.P.; Gehmlich, K. The Utilisation of Hydrogels for iPSC-Cardiomyocyte Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J. Bioactive modification of poly (ethylene glycol) hydrogels for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4639–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guan, J. Hydrogels for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. Polymers 2011, 3, 740–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, A.; Ajazuddin; Khan, J.; Saraf, S.; Saraf, S. Polyethylene glycol (PEG)–Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm) based thermosensitive injectable hydrogels for biomedical applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 88, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, S.; Feng, W. PVA hydrogel properties for biomedical application. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 4, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saludas, L.; Pascual-Gil, S.; Prósper, F.; Garbayo, E.; Blanco-Prieto, M. Hydrogel based approaches for cardiac tissue engineering. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 523, 454–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, B.J.; Gawlitta, D.; Rosenberg, A.J.W.P.; Malda, J.; Melchels, F.P.W. Gelatin-Methacryloyl Hydrogels: Towards Biofabrication-Based Tissue Repair. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, K.; Trujillo-de Santiago, G.; Alvarez, M.M.; Tamayol, A.; Annabi, N.; Khademhosseini, A. Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomaterials 2015, 73, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, B.; Laughter, M.; Jett, S.; Rowland, T.J.; Taylor, M.R.G.; Mestroni, L.; Park, D. Injectable Hydrogels for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. Macromol. Biosci. 2018, 18, 1800079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kougkolos, G.; Golzio, M.; Laudebat, L.; Valdez-Nava, Z.; Flahaut, E. Hydrogels with electrically conductive nanomaterials for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 2036–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtari, K.; Nazari, H.; Ko, H.; Tebon, P.; Akhshik, M.; Akbari, M.; Alhosseini, S.N.; Mozafari, M.; Mehravi, B.; Soleimani, M.; et al. Electrically conductive nanomaterials for cardiac tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 144, 162–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-P.; Qu, K.-Y.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Abodunrin, O.D.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, N.-P. Electrical stimulation of neonatal rat cardiomyocytes using conductive polydopamine-reduced graphene oxide-hybrid hydrogels for constructing cardiac microtissues. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 205, 111844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Lee, A.L.; Li, Z.; Fu, M.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.Y.; Yuan, P. Synthetic peptide hydrogels as 3D scaffolds for tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 160, 78–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, K.M.; Somasuntharam, I.; Davis, M.E. Self-assembling peptide-based delivery of therapeutics for myocardial infarction. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 96, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zou, X. Self-assemble peptide biomaterials and their biomedical applications. Bioact. Mater. 2019, 4, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Gao, J.; Shang, Y.; Hua, Y.; Ye, M.; Yang, Z.; Ou, C.; Chen, M. Folic Acid Derived Hydrogel Enhances the Survival and Promotes Therapeutic Efficacy of iPS Cells for Acute Myocardial Infarction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 24459–24468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, K.A.; Frati, C.; Meade, K.; Gao, J.; Castillo Diaz, L.; Madeddu, D.; Graiani, G.; Cavalli, S.; Miller, A.F.; Oceandy, D.; et al. Functionalised peptide hydrogel for the delivery of cardiac progenitor cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 119, 111539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caplan, M.R.; Schwartzfarb, E.M.; Zhang, S.; Kamm, R.D.; Lauffenburger, D.A. Control of self-assembling oligopeptide matrix formation through systematic variation of amino acid sequence. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplan, M.R.; Schwartzfarb, E.M.; Zhang, S.; Kamm, R.D.; Lauffenburger, D.A. Effects of systematic variation of amino acid sequence on the mechanical properties of a self-assembling, oligopeptide biomaterial. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2002, 13, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mie, M.; Oomuro, M.; Kobatake, E. Hydrogel scaffolds composed of genetically synthesized self-assembling peptides for three-dimensional cell culture. Polym. J. 2013, 45, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.-D.; Wu, J.-H.; Wang, H.-J.; Tan, Y.-Z. Delivery of Stem Cells and BMP-2 With Functionalized Self-Assembling Peptide Enhances Regeneration of Infarcted Myocardium. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2024, 20, 1540–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Hu, B.; Gu, N. Recent fabrications and applications of cardiac patch in myocardial infarction treatment. View 2022, 3, 20200153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, M.P.; Venugopal, J.; Kai, D.; Ramakrishna, S. Biomimetic material strategies for cardiac tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2011, 31, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, E.; Colombo, T.; Fratto, P.; Russo, C.; Bruschi, G.; Frigerio, M. Surgical therapy in advanced heart failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2003, 91, 88F–94F. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, H.; Bai, A.; Jiang, W.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Mao, Y.; Lu, C.; Qian, R.; Guo, F.; et al. Functional engineered human cardiac patches prepared from nature’s platform improve heart function after acute myocardial infarction. Biomaterials 2016, 105, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passier, R.; van Laake, L.W.; Mummery, C.L. Stem-cell-based therapy and lessons from the heart. Nature 2008, 453, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Chang, Y.H.; Xiong, Q.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, L.; Somasundaram, P.; Lepley, M.; Swingen, C.; Su, L.; Wendel, J.S.; et al. Cardiac repair in a porcine model of acute myocardial infarction with human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiovascular cells. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 15, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasu, S.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J.; Johnston, P.V.; Kim, D.H. Biomaterials-based Approaches for Cardiac Regeneration. Korean Circ. J. 2021, 51, 943–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Gregorich, Z.R.; Zhu, W.; Mattapally, S.; Oduk, Y.; Lou, X.; Kannappan, R.; Borovjagin, A.V.; Walcott, G.P.; Pollard, A.E.; et al. Large Cardiac Muscle Patches Engineered from Human Induced-Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiac Cells Improve Recovery from Myocardial Infarction in Swine. Circulation 2018, 137, 1712–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Huang, K.; Daniele, M.A.; Hensley, M.T.; Young, A.T.; Tang, J.; Allen, T.A.; Vandergriff, A.C.; Erb, P.D.; Ligler, F.S.; et al. Cardiac Stem Cell Patch Integrated with Microengineered Blood Vessels Promotes Cardiomyocyte Proliferation and Neovascularization after Acute Myocardial Infarction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33088–33096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pupkaite, J.; Sedlakova, V.; Eren Cimenci, C.; Bak, M.; McLaughlin, S.; Ruel, M.; Alarcon, E.I.; Suuronen, E.J. Delivering More of an Injectable Human Recombinant Collagen III Hydrogel Does Not Improve Its Therapeutic Efficacy for Treating Myocardial Infarction. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 4256–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetter, V.C.; Bouten, C.V.C.; van der Pol, A. Hydrogels for Cardiac Restorative Support: Relevance of Gelation Mechanisms for Prospective Clinical Use. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2023, 20, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C. The Role of Hydrogel in Cardiac Repair and Regeneration for Myocardial Infarction: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, N.; Linke, A.; Süselbeck, T.; Müller-Ehmsen, J.; Vermeersch, P.; Schoors, D.; Rosenberg, M.; Bea, F.; Tuvia, S.; Leor, J. Intracoronary Delivery of Injectable Bioabsorbable Scaffold (IK-5001) to Treat Left Ventricular Remodeling After ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2014, 7, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, S.D.; Coats, A.J.S.; Cristian, G.; Dragomir, D.; Pusineri, E.; Piredda, M.; Bettari, L.; Dowling, R.; Volterrani, M.; Kirwan, B.-A.; et al. A prospective comparison of alginate-hydrogel with standard medical therapy to determine impact on functional capacity and clinical outcomes in patients with advanced heart failure (AUGMENT-HF trial). Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 2297–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, R.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y. Advances in Injectable Hydrogel Strategies for Heart Failure Treatment. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2300029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, C.B.; Lee, M.E.; Wang, H.; Takebayashi, S.; Takayama, T.; Kawamura, T.; Arkles, J.S.; Dusaj, N.N.; Dorsey, S.M.; Witschey, W.R.T.; et al. Injectable Shear-Thinning Hydrogels for Minimally Invasive Delivery to Infarcted Myocardium to Limit Left Ventricular Remodeling. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2016, 9, e004058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Pedrosa, R.; Salgado, A.J.; Ferreira, P.E. Revolutionizing Disease Modeling: The Emergence of Organoids in Cellular Systems. Cells 2023, 12, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Hu, H.; Kung, H.; Zou, R.; Dai, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, T.; Lv, T.; Yu, J.; Li, F. Organoids: The current status and biomedical applications. MedComm 2023, 4, e274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, W.; Tipparaju, S.M.; Ashraf, M. Transformational Applications of Human Cardiac Organoids in Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 936084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahara, M. Recent Advances in Generation of In Vitro Cardiac Organoids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenreiro, M.F.; Louro, A.F.; Alves, P.M.; Serra, M. Next generation of heart regenerative therapies: Progress and promise of cardiac tissue engineering. NPJ Regen. Med. 2021, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Zhao, J.; Leung, E.; Flandes-Iparraguirre, M.; Vernon, M.; Silberstein, J.; De-Juan-Pardo, E.M.; Jansen, S. Three-Dimensional Bioprinting in Cardiovascular Disease: Current Status and Future Directions. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gungor-Ozkerim, P.S.; Inci, I.; Zhang, Y.S.; Khademhosseini, A.; Dokmeci, M.R. Bioinks for 3D bioprinting: An overview. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 915–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Ye, X.; Yao, B.; Zhao, M.; Wu, P.; Liu, G.; Zhuang, D.; Jiang, H.; Chen, X.; He, Y.; et al. Advances in 3D bioprinting technology for cardiac tissue engineering and regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 1388–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatimi, A.; Okoro, O.V.; Podstawczyk, D.; Siminska-Stanny, J.; Shavandi, A. Natural Hydrogel-Based Bio-Inks for 3D Bioprinting in Tissue Engineering: A Review. Gels 2022, 8, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, T.; Liu, S.; Guo, B.; Huang, W.; Wu, Y. 3D bioprinting in cardiac tissue engineering. Theranostics 2021, 11, 7948–7969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlarz, M.; Ferreira, A.M.; Gentile, P.; Russell, S.J.; Dalgarno, K. Droplet-based bioprinting enables the fabrication of cell–hydrogel–microfibre composite tissue precursors. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2022, 5, 512–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudapati, H.; Dey, M.; Ozbolat, I. A comprehensive review on droplet-based bioprinting: Past, present and future. Biomaterials 2016, 102, 20–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, R.D. An Overview of Laser-assisted Bioprinting (LAB) in Tissue Engineering Applications. Med. Lasers 2021, 10, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.A.; Zhu, Y.; Woo, Y.J. Advances in 3D Bioprinting: Techniques, Applications, and Future Directions for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, M.; Ma, H.; Chapa-Villarreal, F.A.; Lobo, A.O.; Zhang, Y.S. Stereolithography apparatus and digital light processing-based 3D bioprinting for tissue fabrication. iScience 2023, 26, 106039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boularaoui, S.; Al Hussein, G.; Khan, K.A.; Christoforou, N.; Stefanini, C. An overview of extrusion-based bioprinting with a focus on induced shear stress and its effect on cell viability. Bioprinting 2020, 20, e00093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusmão, A.; Sanjuan-Alberte, P.; Ferreira, F.C.; Leite, M. Design, fabrication, and testing of a low-cost extrusion based 3D bioprinter for thermo-sensitive and light sensitive hydrogels. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 70, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.A.; Zhu, Y.; Venkatesh, A.; Stark, C.J.; Lee, S.H.; Woo, Y.J. Optimization of Freeform Reversible Embedding of Suspended Hydrogel Microspheres for Substantially Improved Three-Dimensional Bioprinting Capabilities. Tissue Eng. Part. C Methods 2023, 29, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Hudson, A.R.; Shiwarski, D.J.; Tashman, J.W.; Hinton, T.J.; Yerneni, S.; Bliley, J.M.; Campbell, P.G.; Feinberg, A.W. 3D bioprinting of collagen to rebuild components of the human heart. Science 2019, 365, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Xia, Y.; Zhao, H.; Xu, X.; Ma, X.; Tao, L. Stem cell-based therapy in cardiac repair after myocardial infarction: Promise, challenges, and future directions. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2024, 188, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Xiao, Z.; Yang, Q.; Yu, T.; Deng, X.; Chen, N.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Wang, J. Hydrogel-based cardiac repair and regeneration function in the treatment of myocardial infarction. Mater. Today Bio 2024, 25, 100978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhoury, K.; Morsink, M.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, L.; Kahn, C.; Tamayol, A.; Arab-Tehrany, E. Biofabrication of natural hydrogels for cardiac, neural, and bone Tissue engineering Applications. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 3904–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liang, H.; Chen, X.; Tan, H. Natural Polymer-Based Hydrogels: From Polymer to Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.-C.; Chang, C.-C.; Chan, H.-P.; Chung, T.-W.; Shu, C.-W.; Chuang, K.-P.; Duh, T.-H.; Yang, M.-H.; Tyan, Y.-C. Hydrogels: Properties and Applications in Biomedicine. Molecules 2022, 27, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, S.; Naghib, S.M.; Garshasbi, H.R.; Ghorbanzadeh, S.; Zhang, W. Smart stimuli-responsive injectable gels and hydrogels for drug delivery and tissue engineering applications: A review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1104126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guvendiren, M.; Lu, H.D.; Burdick, J.A. Shear-thinning hydrogels for biomedical applications. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Zhu, D.; Huang, K.; Caranasos, T.G. Minimally invasive delivery of a hydrogel-based exosome patch to prevent heart failure. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2022, 169, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Ye, G.; He, Y.; Li, B.; Guan, Y.; Gong, B.; Mequanint, K.; Xing, M.M.Q.; Qiu, X. Injectable and conductive cardiac patches repair infarcted myocardium in rats and minipigs. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 1157–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, K.; Patel, N.R.; Ashammakhi, N.; Nguyen, K.-L. 3-Dimensional Bioprinting of Cardiovascular Tissues: Emerging Technology. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2021, 6, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardin, C.; Ferroni, L.; Latremouille, C.; Chachques, J.C.; Mitrečić, D.; Zavan, B. Recent Applications of Three Dimensional Printing in Cardiovascular Medicine. Cells 2020, 9, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia Carreira, S.; Begum, R.; Perriman, A.W. 3D Bioprinting: The Emergence of Programmable Biodesign. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, e1900554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, Z.U.; Khalid, M.Y.; Zolfagharian, A.; Bodaghi, M. 4D bioprinting of smart polymers for biomedical applications: Recent progress, challenges, and future perspectives. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 179, 105374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabirian, F.; Mela, P.; Heying, R. 4D Printing Applications in the Development of Smart Cardiovascular Implants. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 873453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cells Type | Origins | Pros | Cons | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skeletal myoblasts | Progenitor cells located within skeletal muscle. | Rapidly divide Resist ischemia | Limited electrical integration Do not fully differentiate into cardiomyocytes Increased risk of ischemia | [25,26] |
| Mesenchymal stem cells | Multipotent cells originate from various tissues/organs, such as bone marrow and adipose tissue. | Anti-inflammatory effects Easy isolation and expansion | Low cell retention Limited cell engraftment and survival | [26,27] |
| Embryonic stem cells | A pluripotent stem cell that originates from in the inner cell mass of human blastocysts, at early stages of the embryo’s development. | Pluripotency High proliferation | Risk of tumour formation Ethical concerns Higher risks of immune rejection | [28,29,30] |
| Induced pluripotent stem cells | A pluripotent stem cell that can be generated directly from a somatic cell using specific growth factors. | Pluripotency Patient specific High proliferation No ethical concerns | Immature differentiation and maturation Risk of tumour formation High costs | [31,32,33] |
| Polymers | Attributes | Pros | Cons | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collagen | Provides structural support to cardiac cells and contributes to the heart’s stiffness and rigidity. Assists in force transmission ensuring efficient force is generated by the heart to pump blood around the body. | Biocompatible Biodegradable Incorporated with other polymers to enhance its physical properties | Unstable Poor mechanical properties | [19,24,81,82] |
| Gelatin | Partially hydrolysed from collagen Functions as a crosslinking polymer, imparting essential properties like structure and texture to the gel. Retains the arginine-glycine- aspartic acid (RGD) peptide sequence which promotes cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation. | Non-immunogenic Biocompatible Biodegradable | Low thermostability Weak mechanical strength | [27,83,84] |
| Hyaluronic acid (HA) | Natural, linear polysaccharide that contains multiple acid and hydroxyl groups chemically modifiable to improve its mechanical properties. | Biocompatible Biodegradable Non-immunogenic Non-thrombogenic | Weak mechanical strength High degradation rate | [85,86] |
| Elastin | Provides elasticity to various tissues and organs Tropoelastin is a soluble precursor of elastin that has similar biochemical properties to elastin. | Can be hydrolysed to form smaller chains such as peptides and polypeptides, which are soluble | Insoluble nature Weak mechanical properties Batch-to-batch variation | [62,87,88] |
| Chitosan | Linear polysaccharide attained by the partial deacetylation of chitin. | Low toxicity Antibacterial properties Encourages angiogenesis | Weak mechanical properties Batch-to-batch variation | [62,89] |
| Fibrin | Plays a role in the body’s natural tissue repair mechanism. | Biologically compatible Ability to promote repair Increased survival rate of CMs | Poor mechanical strength Hydrogel shrinkage Batch to batch variation | [87,89,90] |
| Decellularized ECM (dECM) | Developed through decellularization, which involves the elimination of cells from the ECM to generate a natural matrix. | Supports cell growth, adhesion, and remodelling Non-immunogenic | Poor mechanical properties Cytotoxicity Batch-to-batch variation | [89,91,92] |
| Synthetic Polymers | Attributes | Advantages | Disadvantages | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyacrylamide (PAA) | Developed via crosslinking of acrylamide monomers. | Stable Non-toxic Hydrophilic Highly adaptable | Short lifespan, which limits cell culture studies | [93,94,95] |
| Polyethylene glycol (PEG) | FDA-approved water-soluble polymer. Modifying this hydrogel with an RGD peptides improves cell proliferation and survival. | Biocompatible Non-immunogenic Strong mechanical properties | Not soluble Inadequate cell specific adhesion | [80,96,97] |
| Poly-N-isopropyl acrylamide (PNIPAAm) | Changes from liquid to gel above temperatures over 32 °C. | Thermo-responsive behaviour | Weak mechanical strength Low biodegradability | [89,91,98] |
| Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) | Developed via the hydrolysis of polyvinyl acetate. As a hydrogel, it has high elasticity and can enhance the dispersion of mechanical signals. | Hydrophilic Biocompatible Biodegradable | Low adhesion Low biodegradability Poor thermo-responsive behaviour | [80,89,99] |
| Bioprinting Technique | Pros | Cons | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extrusion-based | Not complex Affordable Scalable | Cell damage through sheer stress Limited available biomaterials Low resolution Clogging of the nozzle | [147] |
| Droplet-based | Affordable Accessible High cell viability >90% High resolution | Limited available biomaterials Issues with fabricating porous tissue structures Clogging of the printer’s injector | [143] |
| Laser-assisted | Nozzle free High resolution Wide range of available biomaterials High cell viability Low mechanical stress | High cost Time consuming | [145] |
| Stereolithography (SLA) and Digital Light Processing (DLP) | High resolution High speed High cell viability Nozzle free | Cytotoxic effects Limited available bio-inks | [146] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Holme, S.; Richardson, S.M.; Bella, J.; Pinali, C. Hydrogels for Cardiac Tissue Regeneration: Current and Future Developments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052309
Holme S, Richardson SM, Bella J, Pinali C. Hydrogels for Cardiac Tissue Regeneration: Current and Future Developments. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(5):2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052309
Chicago/Turabian StyleHolme, Sonja, Stephen M. Richardson, Jordi Bella, and Christian Pinali. 2025. "Hydrogels for Cardiac Tissue Regeneration: Current and Future Developments" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 5: 2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052309
APA StyleHolme, S., Richardson, S. M., Bella, J., & Pinali, C. (2025). Hydrogels for Cardiac Tissue Regeneration: Current and Future Developments. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(5), 2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052309





