The Mechanism by Which Estrogen Level Affects Knee Osteoarthritis Pain in Perimenopause and Non-Pharmacological Measures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. KOA Pain
2.1. Concept of KOA
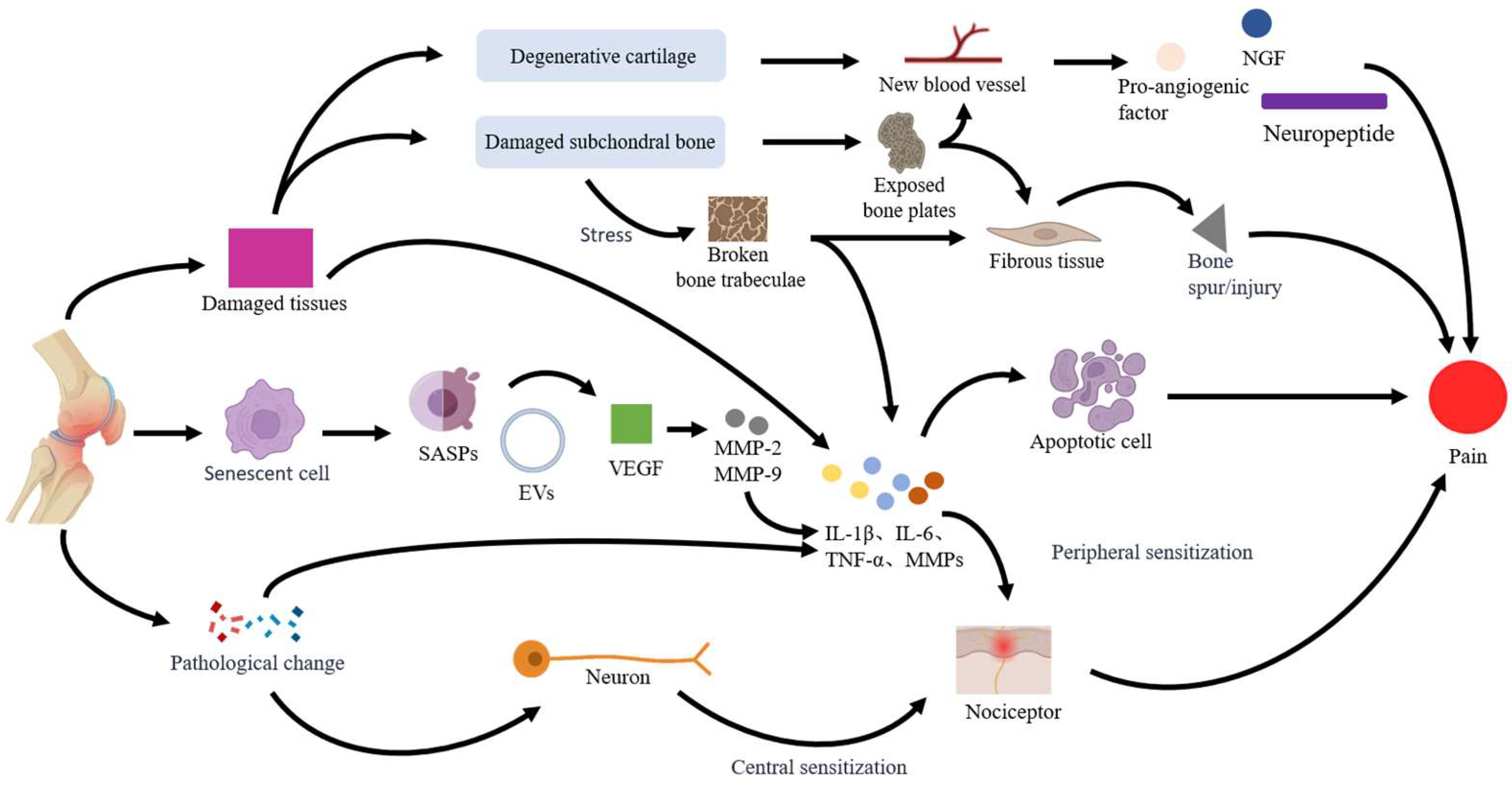
2.2. Mechanisms of KOA Pain
2.2.1. Tissue Damage
2.2.2. Cell Senescence and Apoptosis
2.2.3. Nerve Sensitization
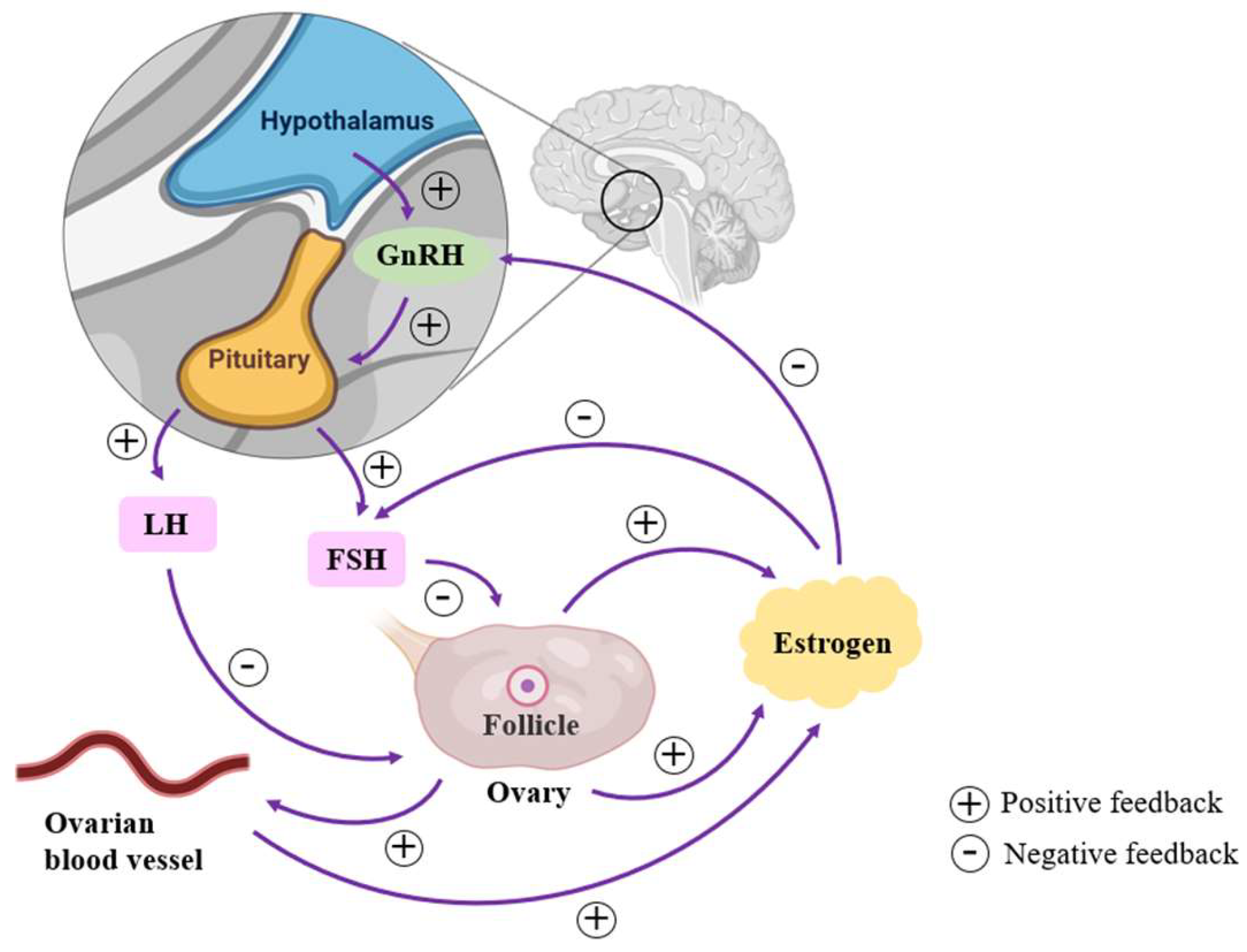
3. Perimenopausal Estrogen Level and KOA Pain
3.1. Changes in Estrogen Levels of Perimenopausal Women
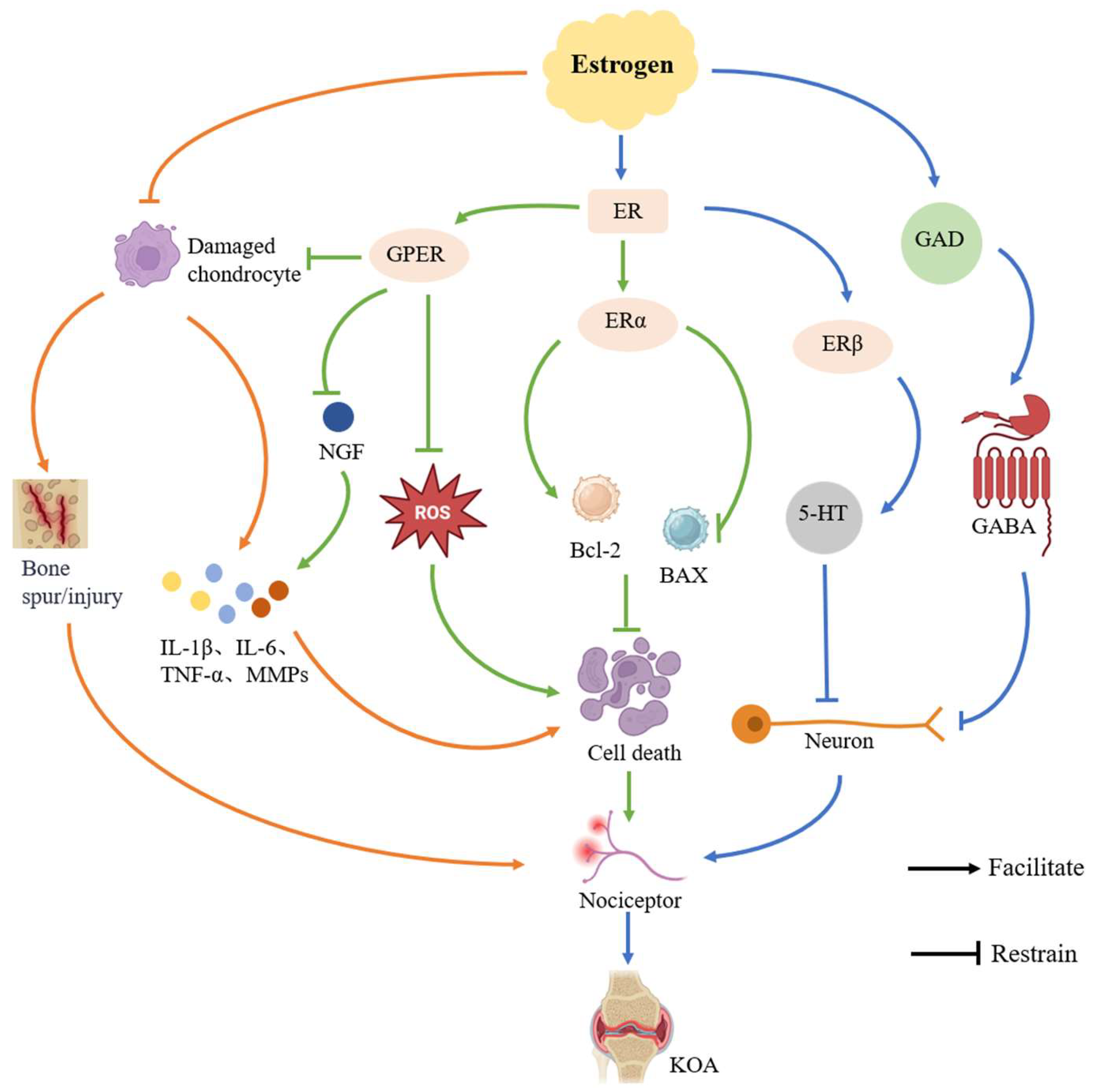
3.2. Mechanisms of Estrogen Levels on KOA Pain
3.2.1. Regulation of Inflammatory Response
3.2.2. Inhibition of Cellular Senescence and Apoptosis
3.2.3. Modulation of Neurotransmitters
4. Non-Pharmacological Measures in Perimenopausal Women with KOA
4.1. Physical Therapy
4.1.1. Aerobic Exercise
4.1.2. Resistance Training
4.1.3. Mind–Body Exercise
4.2. Physical Factor Therapy
4.2.1. Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound
4.2.2. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation
4.3. Traditional Chinese Medicine
4.4. Diet
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Talaulikar, V. Menopause transition: Physiology and symptoms. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2022, 81, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camon, C.; Garratt, M.; Correa, S.M. Exploring the effects of estrogen deficiency and aging on organismal homeostasis during menopause. Nat. Aging 2024, 4, 1731–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, H.G.; Hale, G.E.; Dennerstein, L.; Robertson, D.M. Cycle and hormone changes during perimenopause: The key role of ovarian function. Menopause 2008, 15, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.L.; Eisenlohr-Moul, T.A.; Rubinow, D.R.; Schrubbe, L.; Girdler, S.S. Naturally Occurring Changes in Estradiol Concentrations in the Menopause Transition Predict Morning Cortisol and Negative Mood in Perimenopausal Depression. Clin. Psychol. Sci. 2016, 4, 919–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.L.; Hodara, E.; Sriprasert, I.; Shoupe, D.; Stanczyk, F.Z. Estrogen deficiency in the menopause and the role of hormone therapy: Integrating the findings of basic science research with clinical trials. Menopause 2024, 31, 926–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman-Blas, J.A.; Castañeda, S.; Largo, R.; Herrero-Beaumont, G. Osteoarthritis associated with estrogen deficiency. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, P.A.; Bradford, J.C.; Brahmachary, P.; Ulman, S.; Robinson, J.L.; June, R.K.; Cucchiarini, M. Unraveling sex-specific risks of knee osteoarthritis before menopause: Do sex differences start early in life? Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2024, 32, 1032–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, F.; Wirth, W.; Putz, R. Sexual dimorphism in articular tissue anatomy–Key to understanding sex differences in osteoarthritis? Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2024, 32, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primorac, D.; Molnar, V.; Rod, E.; Jeleč, Ž.; Čukelj, F.; Matišić, V.; Vrdoljak, T.; Hudetz, D.; Hajsok, H.; Borić, I. Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review of Pathogenesis and State-Of-The-Art Non-Operative Therapeutic Considerations. Genes 2020, 11, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, H. Evidence on risk factors for knee osteoarthritis in middle-older aged: A systematic review and meta analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumaran, A.J.; Deveza, L.A.; Atukorala, I.; Hunter, D.J. Assessment of Pain in Osteoarthritis of the Knee. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zheng, H.; Ye, B.; Guo, T.; Xu, Y.; Fu, Z.; Ji, X.; Chai, X.; Li, S.; Deng, Q. Identification of biomarkers for knee osteoarthritis through clinical data and machine learning models. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panwar, P.; Chaurasia, S.; Gangrade, J.; Bilandi, A.; Pruthviraja, D. Optimizing knee osteoarthritis severity prediction on MRI images using deep stacking ensemble technique. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocco, E.; Emmi, A.; De Caro, R.; Porzionato, A.; Macchi, V. Knee adipose tissue: From its implication in osteoarthritis to its supposed role in tissue engineering. NPJ Aging 2025, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvet, J.; Berenguer-Llergo, A.; Orellana, C.; García-Manrique, M.; Rusiñol, M.; Garcia-Cirera, S.; Llop, M.; Arévalo, M.; Garcia-Pinilla, A.; Galisteo, C.; et al. Specific-cytokine associations with outcomes in knee osteoarthritis subgroups: Breaking down disease heterogeneity with phenotyping. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2024, 26, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainese, P.; Wyngaert, K.V.; De Mits, S.; Wittoek, R.; Van Ginckel, A.; Calders, P. Association between knee inflammation and knee pain in patients with knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2022, 30, 516–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiser, M.; Preiss, S.; Ferguson, S.J.; Stadelmann, V.A. High-resolution microCT analysis of sclerotic subchondral bone beneath bone-on-bone wear grooves in severe osteoarthritis. Bone 2025, 193, 117388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Sheng, P.; Mobasheri, A. The role of metabolism in chondrocyte dysfunction and the progression of osteoarthritis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 66, 101249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, J.H.; Rai, V.; Dilisio, M.F.; Agrawal, D.K. Damage-associated molecular patterns in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Potentially novel therapeutic targets. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2017, 434, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Yu, H.; Huang, X.; Shen, J.; Xiao, G.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Xing, L.; Chen, D. Current understanding of osteoarthritis pathogenesis and relevant new approaches. Bone Res. 2022, 10, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, S.; Jing, Y.; Su, J. Subchondral bone microenvironment in osteoarthritis and pain. Bone Res. 2021, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanamas, S.K.; Wluka, A.E.; Pelletier, J.P.; Martel-Pelletier, J.; Abram, F.; Wang, Y.; Cicuttini, F.M. The association between subchondral bone cysts and tibial cartilage volume and risk of joint replacement in people with knee osteoarthritis: A longitudinal study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muratovic, D.; Findlay, D.M.; Cicuttini, F.M.; Wluka, A.E.; Lee, Y.R.; Edwards, S.; Kuliwaba, J.S. Bone marrow lesions in knee osteoarthritis: Regional differences in tibial subchondral bone microstructure and their association with cartilage degeneration. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2019, 27, 1653–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhen, G.; Hu, Y.; An, S.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wan, M.; et al. Subchondral bone osteoclasts induce sensory innervation and osteoarthritis pain. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1076–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Lu, L.; Yu, X. Research progress of cellular senescence in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi 2021, 35, 519–526. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, T.; Miyaki, S.; Ishitobi, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Nakasa, T.; Lotz, M.K.; Ochi, M. Exosomes from IL-1β stimulated synovial fibroblasts induce osteoarthritic changes in articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Huang, R.; Wu, G. Construction and validation of a senescence-related gene signature for early prediction and treatment of osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 31862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, M.G.; Núñez-Carro, C.; Blanco-Blanco, M.; Blanco, F.J.; de Andrés, M.C. Inflammaging contributes to osteoarthritis development and human microbiota variations and vice versa: A systematic review. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2025, 33, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, T.; Luo, Q.; Wang, R.; Dai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Wu, G. Network pharmacology combined with experimental validation to investigate the effect of Rongjin Niantong Fang on chondrocyte apoptosis in knee osteoarthritis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2024, 29, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfander, D.; Körtje, D.; Zimmermann, R.; Weseloh, G.; Kirsch, T.; Gesslein, M.; Cramer, T.; Swoboda, B. Vascular endothelial growth factor in articular cartilage of healthy and osteoarthritic human knee joints. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2001, 60, 1070–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belotti, D.; Paganoni, P.; Manenti, L.; Garofalo, A.; Marchini, S.; Taraboletti, G.; Giavazzi, R. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP9 and MMP2) induce the release of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) by ovarian carcinoma cells: Implications for ascites formation. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 5224–5229. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, H.; Sarmento-Ribeiro, A.B.; Andrade, J.P.; Dourado, M. Apoptosis and (in) Pain-Potential Clinical Implications. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, Y.; Uchida, K.; Fukushima, K.; Inoue, G.; Takaso, M. Mechanisms of Peripheral and Central Sensitization in Osteoarthritis Pain. Cureus 2023, 15, e35331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Shi, X.; Liao, T.; Jie, L.; Yu, L.; Wang, P. NGF Signaling Exacerbates KOA Peripheral Hyperalgesia via the Increased TRPV1-Labeled Synovial Sensory Innervation in KOA Rats. Pain. Res. Manag. 2024, 2024, 1552594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havelin, J.; King, T. Mechanisms Underlying Bone and Joint Pain. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2018, 16, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volcheck, M.M.; Graham, S.M.; Fleming, K.C.; Mohabbat, A.B.; Luedtke, C.A. Central sensitization, chronic pain, and other symptoms: Better understanding, better management. Cleve Clin. J. Med. 2023, 90, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Méndez, J.; Cuyul-Vásquez, I.; Viscay-Sanhueza, N.; Morales-Verdugo, J.; Mendez-Rebolledo, G.; Ponce-Fuentes, F.; Lluch-Girbés, E. Structural and functional brain changes in people with knee osteoarthritis: A scoping review. PeerJ 2023, 11, e16003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, T.; Lou, J.; Zhang, T.; Wu, S.; Xie, R.; Xu, J. The beneficial roles and mechanisms of estrogens in immune health and infection disease. Steroids 2024, 207, 109426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreier, R.; Ising, T.; Ramroth, M.; Rellmann, Y. Estradiol Inhibits ER Stress-Induced Apoptosis in Chondrocytes and Contributes to a Reduced Osteoarthritic Cartilage Degeneration in Female Mice. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 913118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendis, P.C.; Zimmerman, S.; Onisiforou, A.; Zanos, P.; Georgiou, P. The impact of estradiol on serotonin, glutamate, and dopamine systems. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1348551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeta, M.; Digumarti, L.; Agarwal, N.; Vaze, N.; Shah, R.; Malik, S. Clinical Practice Guidelines on Menopause: *An Executive Summary and Recommendations: Indian Menopause Society 2019–2020. J. Midlife Health 2020, 11, 55–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, H.G.; Dudley, E.C.; Hopper, J.L.; Shelley, J.M.; Green, A.; Smith, A.; Dennerstein, L.; Morse, C. The endocrinology of the menopausal transition: A cross-sectional study of a population-based sample. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995, 80, 3537–3545. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spicer, J.; Malaspina, D.; Blank, S.V.; Goosens, K.A. Follicle-stimulating hormone: More than a marker for menopause: FSH as a frontier for women’s mental health. Psychiatry Res. 2024, 345, 116239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Khoudary, S.R.; Greendale, G.; Crawford, S.L.; Avis, N.E.; Brooks, M.M.; Thurston, R.C.; Karvonen-Gutierrez, C.; Waetjen, L.E.; Matthews, K. The menopause transition and women’s health at midlife: A progress report from the Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation (SWAN). Menopause 2019, 26, 1213–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlow, S.D.; Gass, M.; Hall, J.E.; Lobo, R.; Maki, P.; Rebar, R.W.; Sherman, S.; Sluss, P.M.; de Villiers, T.J. Executive summary of the Stages of Reproductive Aging Workshop + 10: Addressing the unfinished agenda of staging reproductive aging. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turek, J.; Gąsior, Ł. Estrogen fluctuations during the menopausal transition are a risk factor for depressive disorders. Pharmacol. Rep. 2023, 75, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Xiang, W. Mechanisms of ovarian aging in women: A review. J. Ovarian Res. 2023, 16, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S.; Wu, C.; Chen, D.; Xue, L.; Guo, Y.; Dai, Y.; Wei, S.; et al. Towards prolonging ovarian reproductive life: Insights into trace elements homeostasis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 97, 102311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Wang, G.; Yang, X.; Liang, J.; Tong, H.; Li, L.; Geng, K.; Bo, Y.; Hu, X.; Yang, R.; et al. Physiological premature aging of ovarian blood vessels leads to decline in fertility in middle-aged mice. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaprara, A.; Huhtaniemi, I.T. The hypothalamus-pituitary-gonad axis: Tales of mice and men. Metabolism 2018, 86, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, R.; Cariboni, A.M.; Marelli, M.M.; Moretti, R.M.; Andrè, V.; Marzagalli, M.; Limonta, P. GnRH and GnRH receptors in the pathophysiology of the human female reproductive system. Hum. Reprod. Update 2016, 22, 358–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, K.J.; Hewitt, S.C.; Arao, Y.; Korach, K.S. Estrogen Hormone Biology. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2017, 125, 109–146. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X.; Ying, P.; Ding, W.; Li, H.; Xu, P.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Liu, J. Genetic estrogen receptor alpha gene PvuII polymorphism in susceptibility to knee osteoarthritis in a Chinese Han population: A southern Jiangsu study. Knee 2020, 27, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.M.; Ribeiro, A.C.; Botelho, J.; Proença, L.; Noronha, S.; Alves, R.C. The Influence of Genetic Polymorphisms on the Expression of Interleukin-1beta, Prostaglandin E2 and Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha in Peri-Implant Crevicular Fluid: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tateiwa, D.; Yoshikawa, H.; Kaito, T. Cartilage and Bone Destruction in Arthritis: Pathogenesis and Treatment Strategy: A Literature Review. Cells 2019, 8, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, A.; Baek, D.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.; Notario, G.R.; Lee, D.W.; Kim, H.J.; Cho, S.R. Polydeoxyribonucleotide ameliorates IL-1β-induced impairment of chondrogenic differentiation in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Park, H.; Lee, Y.L.; Weon, S.; Kim, Y.G.; Yang, J.H.; Nam, B.; Jo, S.; Kim, T.H. Blocking TNFα attenuates progressive cartilage matrix degradation in inflammatory arthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegeto, E.; Benedusi, V.; Maggi, A. Estrogen anti-inflammatory activity in brain: A therapeutic opportunity for menopause and neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 29, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmer, G.; Iijima, H.; Hettinger, Z.R.; Jackson, N.; Bergmann, J.; Bean, A.C.; Shahshahan, N.; Creed, E.; Kopchak, R.; Wang, K.; et al. Menopause-induced 17β-estradiol and progesterone loss increases senescence markers, matrix disassembly and degeneration in mouse cartilage. Nat. Aging 2025, 5, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, A.; Wang, J.; Han, K.; Gao, H. Estrogen alleviates post-traumatic osteoarthritis progression and decreases p-EGFR levels in female mouse cartilage. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Chen, S.; Klyne, D.M.; Harrich, D.; Ding, W.; Yang, S.; Han, F.Y. Low back pain and osteoarthritis pain: A perspective of estrogen. Bone Res. 2023, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Chen, H.; Lin, Y.; Cheng, K.; Zhou, D.; Chen, R.; Song, C.; Zeng, L.; Yu, H. Mechanical stress abnormalities promote chondrocyte senescence—The pathogenesis of knee osteoarthritis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Wang, K.; Ding, S.; Zhang, M. Cross-talk of inflammation and cellular senescence: A new insight into the occurrence and progression of osteoarthritis. Bone Res. 2024, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, F.J.; Riley, J.S. When cell death goes wrong: Inflammatory outcomes of failed apoptosis and mitotic cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2023, 30, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Lu, Y.; Rothrauff, B.B.; Zheng, A.; Lamb, A.; Yan, Y.; Lipa, K.E.; Lei, G.; Lin, H. Mechanotransduction pathways in articular chondrocytes and the emerging role of estrogen receptor-α. Bone Res. 2023, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X.; Xia, L.; Cai, J.; Huang, N.; Luo, Y.; Wu, W. Icaritin alleviates motor impairment and osteoporosis in Parkinson’s disease mice via the ER-PI3K/Akt pathway. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Xu, Z.; Tang, X.; Cao, H.; Zhang, G.; Tan, J. Estrogen-Related Receptor α: A Significant Regulator and Promising Target in Bone Homeostasis and Bone Metastasis. Molecules 2022, 27, 3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorsch, Z.S.; Loh, Y.E.; Purushothaman, I.; Walker, D.M.; Parise, E.M.; Salery, M.; Cahill, M.E.; Hodes, G.E.; Pfau, M.L.; Kronman, H.; et al. Estrogen receptor α drives pro-resilient transcription in mouse models of depression. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Leng, P.; Guo, P.; Gao, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H. G protein coupled estrogen receptor attenuates mechanical stress-mediated apoptosis of chondrocyte in osteoarthritis via suppression of Piezo1. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Anglemont de Tassigny, X. Outlook on the neuroprotective effect of estrogen. Neural Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 1799–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Im, H.J. Serotonin Transporter (5-Hydroxytryptamine Transporter, SERT, SLC6A4) and Sodium-dependent Reuptake Inhibitors as Modulators of Pain Behaviors and Analgesic Responses. J. Pain. 2024, 25, 618–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.H.; Zhang, W.X.; Xu, Q.; Wu, H.; Jiao, C.C.; Chen, X.Z. Estrogen modulation of visceral pain. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2019, 20, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, S.; Lu, S.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, H. Estradiol reduced 5-HT reuptake by downregulating the gene expression of Plasma Membrane Monoamine Transporter (PMAT, Slc29a4) through estrogen receptor β and the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 924, 174939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, S.; Hickman, T.M.; Lopez-Ramirez, A.; McDonald, H.; Lockhart, L.M.; Darwish, O.; Averitt, D.L. Estrogen modulation of the pronociceptive effects of serotonin on female rat trigeminal sensory neurons is timing dependent and dosage dependent and requires estrogen receptor alpha. Pain 2022, 163, e899–e916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Zhao, X.; Yu, L.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, X.D.; Wang, L.; Li, J.X.; Zhu, Q.; Luo, J.L. Current status of GABA receptor subtypes in analgesia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 168, 115800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, W.; Sadana, N.; Chen, X. Estrogen receptors in pain modulation: Cellular signaling. Biol. Sex Differ. 2021, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athnaiel, O.; Cantillo, S.; Paredes, S.; Knezevic, N.N. The Role of Sex Hormones in Pain-Related Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Martínez, B.S.; Sommer, B.; Solís-Chagoyán, H.; Calixto, E.; Aquino-Gálvez, A.; Jaimez, R.; Gomez-Verjan, J.C.; González-Avila, G.; Flores-Soto, E.; Montaño, L.M. Estrogenic Modulation of Ionic Channels, Pumps and Exchangers in Airway Smooth Muscle. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Dominguez, F.; Tibesku, C.; McAlindon, T.; Freitas, R.; Ivanavicius, S.; Kandaswamy, P.; Sears, A.; Latourte, A. Literature Review to Understand the Burden and Current Non-surgical Management of Moderate-Severe Pain Associated with Knee Osteoarthritis. Rheumatol. Ther. 2024, 11, 1457–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, M.J.; Driban, J.B.; McAlindon, T.E. Pharmaceutical treatment of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2023, 31, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duralde, E.R.; Sobel, T.H.; Manson, J.E. Management of perimenopausal and menopausal symptoms. BMJ 2023, 382, e072612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, D.F.; Carvalho, C.; Moreira Padovez, R.F.C.; Braz de Oliveira, M.P.; Mendes da Silva Serrão, P.R. Effects of physical exercise on muscle function of the knee, pain and quality of life in postmenopausal women with knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2024, 71, 102929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniela, M.; Catalina, L.; Ilie, O.; Paula, M.; Daniel-Andrei, I.; Ioana, B. Effects of Exercise Training on the Autonomic Nervous System with a Focus on Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidants Effects. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, F.; Demirgüç, A.; Arslan, S.A.; Keskin, E.D.; Aras, M. The effect of aerobic exercise training on postmenopausal patients with knee osteoarthritis. J. Back. Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2020, 33, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, M.; Moafi-Madani, M.; Qureshi, R.; Roberts, M.B.; Allison, M.; Manson, J.E.; LaMonte, M.J.; Liu, S.; Eaton, C.B. Heart rate variability and the risk of heart failure and its subtypes in post-menopausal women: The Women’s Health Initiative study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, C.; Spanos, M.; Li, G.; Lu, R.; Bei, Y.; Xiao, J. Exercise training maintains cardiovascular health: Signaling pathways involved and potential therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzak, Z.A.; Khan, A.A.; Farooqui, S.I. Effect of aerobic and anaerobic exercise on estrogen level, fat mass, and muscle mass among postmenopausal osteoporotic females. Int. J. Health Sci. 2019, 13, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Cheng, L.; Wang, J. Effects of three types of resistance training on knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0309950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forti, L.N.; Van Roie, E.; Njemini, R.; Coudyzer, W.; Beyer, I.; Delecluse, C.; Bautmans, I. Effects of resistance training at different loads on inflammatory markers in young adults. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 117, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, M.A.; Soleimanpour, S.; Mayo, S.J.; Myers, J.S.; Panesar, P.; Ameri, F. The effect of mind-body exercise on cognitive function in cancer survivors: A systematic review. Can. Oncol. Nurs. J. 2022, 32, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Figueroa, A. Effects of Acute Stretching Exercise and Training on Heart Rate Variability: A Review. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2021, 35, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.L.; Newman, J.W.; Elmassry, M.M.; Borkowski, K.; Chyu, M.C.; Kahathuduwa, C.; Neugebauer, V.; Watkins, B.A. Tai Chi exercise reduces circulating levels of inflammatory oxylipins in postmenopausal women with knee osteoarthritis: Results from a pilot study. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1210170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Kang, Y.; Zhuang, Y.C. Effects of Tai Chi Ball on Estrogen Levels, Bone Metabolism Index, and Muscle Strength of Perimenopausal Women. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2015, 63, 2629–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carcelén-Fraile, M.D.C.; Hita-Contreras, F.; Martínez-Amat, A.; Loureiro, V.B.; Loureiro, N.E.M.; Jiménez-García, J.D.; Fábrega-Cuadros, R.; Aibar-Almazán, A. Impact of Qigong exercises on the severity of the menopausal symptoms and health-related quality of life: A randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Sport. Sci. 2023, 23, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shan, W.; Li, Q.; Yang, N.; Shan, W. Tai Chi Exercise for the Quality of Life in a Perimenopausal Women Organization: A Systematic Review. Worldviews Evid. Based Nurs. 2017, 14, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajković, N.; Bogataj, Š. Effects of Neuromuscular Training on Motor Competence and Physical Performance in Young Female Volleyball Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, A.; Alt, V. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) for stimulation of bone healing—A narrative review. Injury 2021, 52 (Suppl. 2), S91–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Sun, M. Effects of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Rehabil. 2022, 36, 1153–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Hou, J.; Wang, Y.; Shu, H.; Huang, Y. Effects of Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound on the Migration and Homing of Human Amnion-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Ovaries in Rats With Premature Ovarian Insufficiency. Cell Transplant. 2022, 31, 9636897221129171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Lu, F.; Hao, X.; Deng, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, K.; Hou, W.; Shang, X.; Chi, R.; Guo, F.; et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound delays the progression of osteoarthritis by regulating the YAP-RIPK1-NF-κB axis and influencing autophagy. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Li, D.; Wei, X.; Chen, J.; Zuo, D.; Chen, W. Efficacy and safety of focused low-intensity pulsed ultrasound versus pulsed shortwave diathermy on knee osteoarthritis: A randomized comparative trial. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gozani, S.N. Remote Analgesic Effects Of Conventional Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation: A Scientific And Clinical Review With A Focus On Chronic Pain. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 3185–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Z.J.; Liu, J.E.; Lei, L.L.; Wang, S.Y. Effects of Transcutaneous Electrical Acupoint Stimulation on Ovarian Responses and Pregnancy Outcomes in Patients Undergoing IVF-ET: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2022, 28, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dørmænen, A.; Heimdal, M.R.; Wang, C.E.; Grimsgaard, A.S. Depression in postmenopause: A study on a subsample of the Acupuncture on Hot Flushes Among Menopausal Women (ACUFLASH) study. Menopause 2011, 18, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.W.; Tang, Z.Y.; Zhang, F.R.; Li, H.; Kong, Y.Z.; Iannetti, G.D.; Hu, L. Neurobiological mechanisms of TENS-induced analgesia. Neuroimage 2019, 195, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Yu, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, T.; Battulga, O.; Wang, L.; Guo, C. A comparison of the effects of electroacupuncture versus transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for pain control in knee osteoarthritis: A Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Acupunct. Med. 2021, 39, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, J.J.; Jauregui, J.J.; Leichliter, A.K.; Elmallah, R.K.; Bhave, A.; Mont, M.A. The effects of various physical non-operative modalities on the pain in osteoarthritis of the knee. Bone Jt. J. 2016, 98-B, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, Q.; Luo, Y.; Feng, J.; Deng, Y.; Li, G.; Li, M.; Sun, J. Efficacy and immune-inflammatory mechanism of acupuncture-related therapy in animal models of knee osteoarthritis: A preclinical systematic review and network meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2024, 19, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Chang, Y.; Yan, X.; Feng, X.; Wu, N. Effect of acupuncture for patients with knee osteoarthritis: Study protocol for a double-dummy randomized controlled trial. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.H.; Kim, S.N. A Literature Review of Women’s Sex Hormone Changes by Acupuncture Treatment: Analysis of Human and Animal Studies. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 3752723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.Y.; Fu, Q.Q.; Spencer, S.J.; Kennedy, G.A.; Conduit, R.; Zhang, W.J.; Zheng, Z. Acupuncture: A Promising Approach for Comorbid Depression and Insomnia in Perimenopause. Nat. Sci. Sleep. 2021, 13, 1823–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Ai, B.; Shen, M. Effectiveness of Mild Moxibustion for Sub-Health Conditions in Pre- and Post-Menopausal Women: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 2907–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.X.; Shi, L.; Liang, S.J.; Fang, C.C.; Xu, Q.Q.; Lu, G.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, J.; Shen, J.; Shen, M.H. Moxibustion alleviates decreased ovarian reserve in rats by restoring the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J. Integr. Med. 2022, 20, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Duan, Y.S.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Tu, J.F.; Bao, X.Y.; Yang, J.W.; Lee, M.S.; Wang, L.Q. Clinical effect and contributing factors of acupuncture for knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and pairwise and exploratory network meta-analysis. BMJ Evid. Based Med. 2024, 29, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, T.Y.; Lee, M.S.; Kim, J.I.; Zaslawski, C. Moxibustion for the treatment of osteoarthritis: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Maturitas 2017, 100, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk-Warunek, A.; Winiarska-Mieczan, A.; Blicharski, T.; Blicharski, R.; Kowal, F.; Pano, I.T.; Tomaszewska, E.; Muszyński, S. Consumption of Phytoestrogens Affects Bone Health by Regulating Estrogen Metabolism. J. Nutr. 2024, 154, 2611–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.N.; Lin, C.C.; Liu, C.F. Efficacy of phytoestrogens for menopausal symptoms: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Climacteric 2015, 18, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagari, V.S.; Levis, S. Phytoestrogens and bone health. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2010, 17, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allred, C.D.; Allred, K.F.; Ju, Y.H.; Clausen, L.M.; Doerge, D.R.; Schantz, S.L.; Korol, D.L.; Wallig, M.A.; Helferich, W.G. Dietary genistein results in larger MNU-induced, estrogen-dependent mammary tumors following ovariectomy of Sprague-Dawley rats. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.O.; Simon, S.; Chae, K.; Metzler, M.; Korach, K.S. Phytoestrogens and their human metabolites show distinct agonistic and antagonistic properties on estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) and ERbeta in human cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 80, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.S. Current Perspectives on the Beneficial Effects of Soybean Isoflavones and Their Metabolites for Humans. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellavia, D.; Dimarco, E.; Costa, V.; Carina, V.; De Luca, A.; Raimondi, L.; Fini, M.; Gentile, C.; Caradonna, F.; Giavaresi, G. Flavonoids in Bone Erosive Diseases: Perspectives in Osteoporosis Treatment. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 32, 76–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, J.D.; Ward, W.E.; Lewis, J.E.; Hilditch, J.; Nickell, L.; Wong, E.; Thompson, L.U. Supplementation with flaxseed alters estrogen metabolism in postmenopausal women to a greater extent than does supplementation with an equal amount of soy. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, A.; Liu, R.H.; Gao, X.; Li, D.; Kou, X.; Xue, Z. Nutritional constituent and health benefits of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): A review. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150 Pt A, 110790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, F.; Alimoradi, Z.; Haqi, P.; Mahdizad, F. Effects of phytoestrogens on bone mineral density during the menopause transition: A systematic review of randomized, controlled trials. Climacteric 2016, 19, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinuta, K.; Tanaka, H.; Moriwake, T.; Aya, K.; Kato, S.; Seino, Y. Vitamin D is an important factor in estrogen biosynthesis of both female and male gonads. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yuan, M.; Wang, G. Copper homeostasis and cuproptosis in gynecological disorders: Pathogenic insights and therapeutic implications. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2024, 84, 127436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Li, L.S.; Lan, M.F.; Shang, J.Z.; Zhang, J.X.; Xiong, W.J.; Lai, X.L.; Duan, X. Zinc deficiency deteriorates ovarian follicle development and function by inhibiting mitochondrial function. J. Ovarian Res. 2024, 17, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Non-Pharmacological Measures | Types | Suggestion | Changes | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PT | AE | 40 min, 5 times a week; Intensity: a moderate level of 50–70% of the maximum heart rate (220-age); walking and cycling are recommended. | Central β-endo fibular peptide↑ Estrogen↑ TNF-α↓ IL-6↓ HRV↓ Cardiovascular risk↓ | [83,84,85,86] |
| RT | 60 min, 2–3 times a week; squats, push-ups, and hard pulls are recommended. | Estrogen↑ C reactive protein↓ TNF-α↓ IL-6↓ | [87,88,89] | |
| MBE | 60 min, 3–4 times a week; Tai Chi, Qigong, and Baduanjin are recommended. | Estrogen↑ IL-10↑ TNF-α↓ IL-6↓ | [91,92,93,94,95] | |
| PFT | LIPUS | 20 min, 3–5 times a week. | GDF9↑ BMP15↑ IL-1β↓ TNF-α↓ IL-6↓ | [98,99,100,101] |
| TENS | 20–40 min, 5 times a week; attach to specific acupoints (uterus point, Tianshu point, etc.); high-frequency TENS is more recommended. | Estrogen↑ Endorphin↑ TNF-α↓ IL-6↓ Cortisol↓ | [103,104,105,106,107] | |
| TCM | Acupuncture | 20–30 min, 3–4 times a week; recommended acupoints: SP6 KI3 ST35 GB34 SP9 ST36 | Estrogen↑ ER↑ IL-1β↓ TNF-α↓ IL-6↓ | [108,109,110,111] |
| Moxibustion | 15–20 min, 3–5 times a week; recommended acupoints: CV4 SP6 KI3 ST35 GB34 SP9 ST36 | [112,113,114,115] | ||
| Diet | Phytoestrogens | Recommended: soybeans soy products flaxseeds chickpeas | Estrogen↑ Osteoblast↑ Osteoclast↓ | [119,120,121,122,123,124,125] |
| Vitamin | Vitamin D | Estrogen↑ | [126] | |
| Minerals | copper zinc | [127,128] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, H.; Yu, F.; Wu, W. The Mechanism by Which Estrogen Level Affects Knee Osteoarthritis Pain in Perimenopause and Non-Pharmacological Measures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062391
Zhao H, Yu F, Wu W. The Mechanism by Which Estrogen Level Affects Knee Osteoarthritis Pain in Perimenopause and Non-Pharmacological Measures. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062391
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Huiying, Fan Yu, and Wei Wu. 2025. "The Mechanism by Which Estrogen Level Affects Knee Osteoarthritis Pain in Perimenopause and Non-Pharmacological Measures" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062391
APA StyleZhao, H., Yu, F., & Wu, W. (2025). The Mechanism by Which Estrogen Level Affects Knee Osteoarthritis Pain in Perimenopause and Non-Pharmacological Measures. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062391






