Clinical and Molecular Barriers to Understanding the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
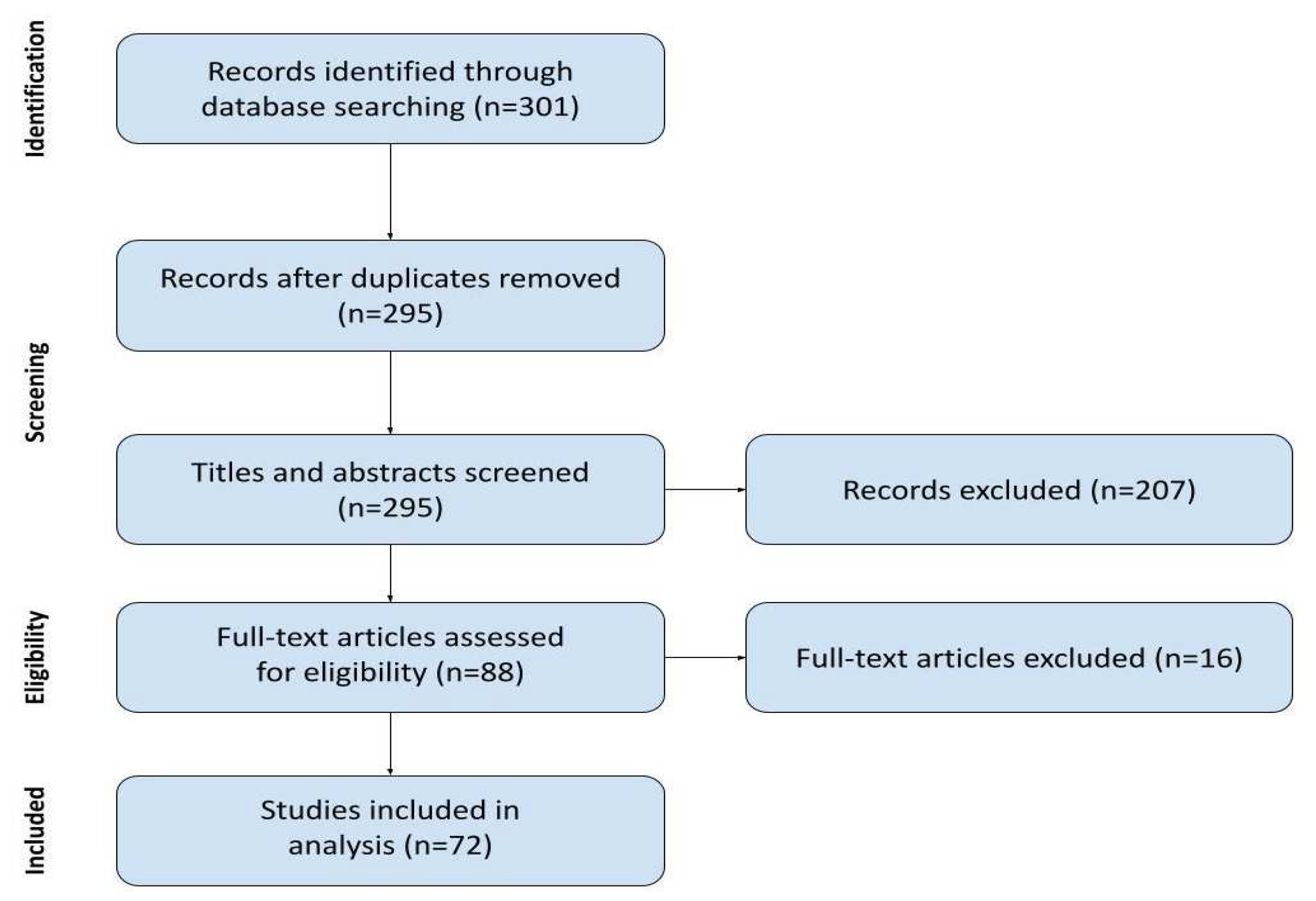
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Searching Strategy
- Clinical studies with CRPS as the main research interest (mentioned in the name of the paper);
- Including at least three patients with a diagnosis of CRPS;
- Describing challenges the research team encountered;
- Published after January of 2018 in English.
2.2. Data Charting Process
- Author and date: all listed authors and year of publication.
- Title of the study.
- Study type: available information on the study design to confirm the clinical setting and original nature of the study.
- Number of subjects: only patients with CRPS were included in our review; we did not include healthy controls or patients with other diagnoses.
- Diagnostic tools used: all tools and measurements utilized by authors to diagnose CRPS and assess disease activity, inflammation mediators, biomarkers, signs, and symptoms; we excluded measurements not pertinent to CRPS, performed solely for the purpose of the study.
- Challenges encountered: both expected and unexpected issues that were deemed by authors to be important enough to be included in the research paper; these include direct drawbacks in conducting CRPS research, methodological shortcomings, bias, confounding factors, insufficient information, etc. We included the authors’ opinions but excluded referenced statements.
2.3. Synthesis of Results
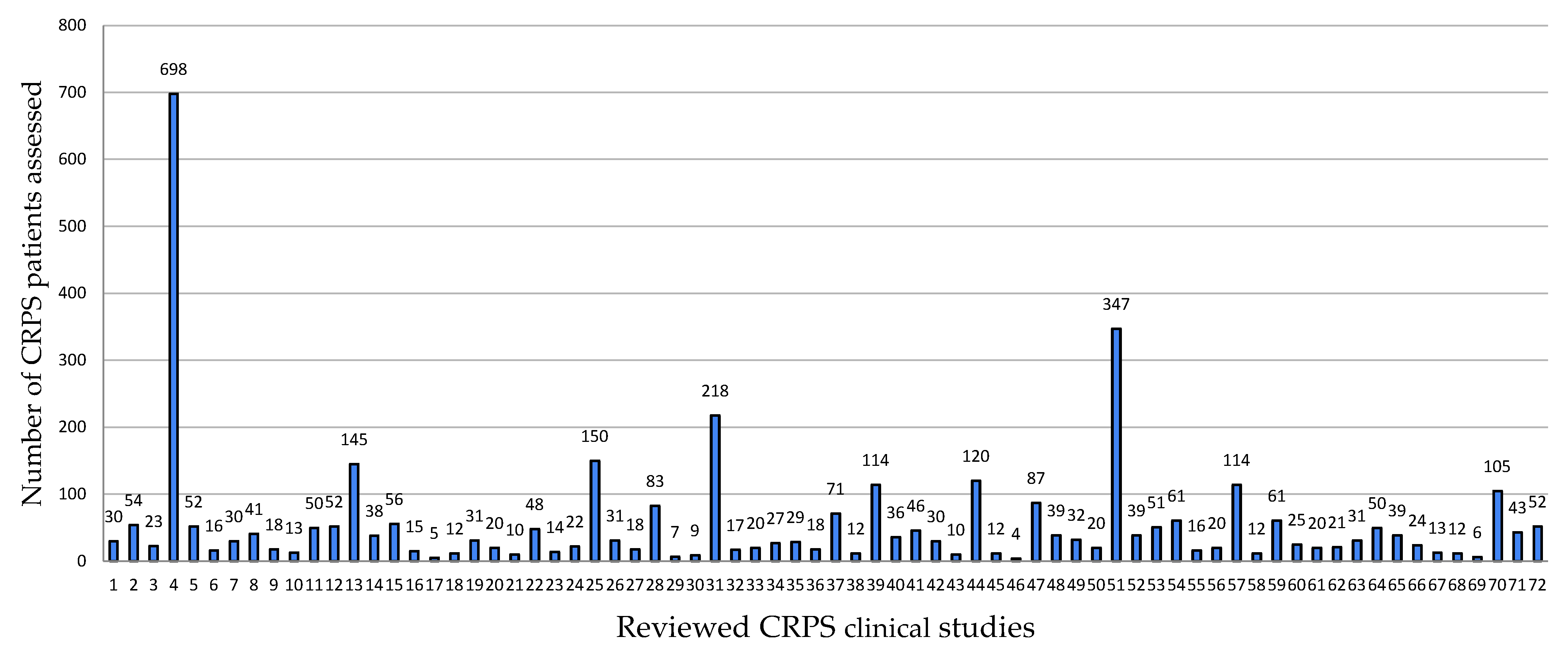
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
3.2. Diagnostic Tools Used
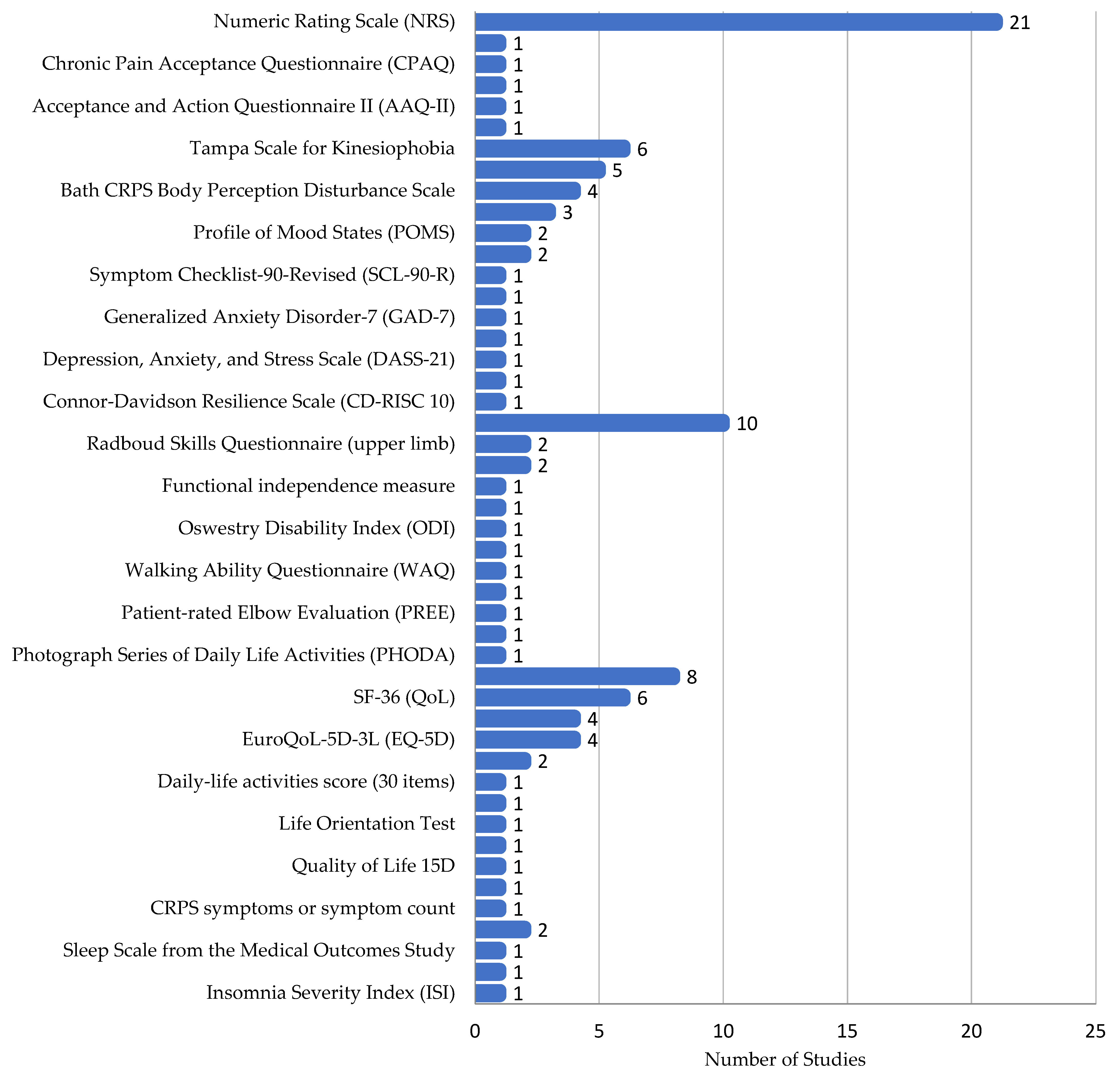
3.3. Patient-Reported Outcome Measures
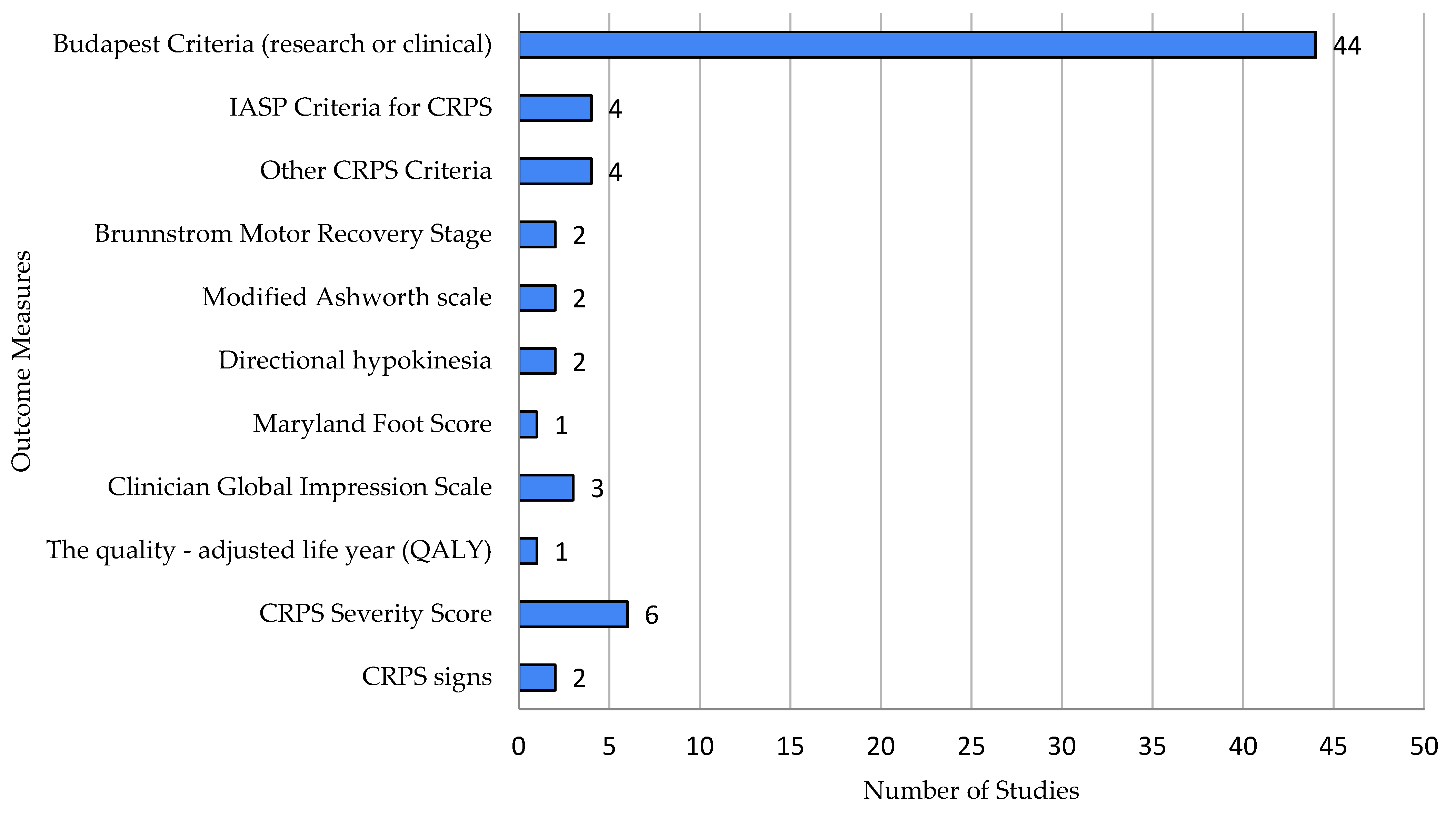
3.4. Clinician-Reported Outcome Measures
- Motor Function: Four assessments were used across five studies, including the Brunnstrom Motor Recovery Stage and Modified Ashworth Scale.
- Quality of Life: Clinician-assessed quality of life was measured in four studies using tools like the Clinician Global Impression Scale.
- Neuropathic Pain: DN4 and the Mainz Pain Staging System were used.
- Other CRPS Features: Three methods tracked CRPS features, including the CRPS severity score (CSS). One study assessed lateralization with a Mental Number Line Bisection task (Figure 5).
3.5. Clinical Measures
3.6. Immunological, Biochemical and Molecular Aspects of CRPS
3.6.1. Cytokines/Inflammation in CRPS
3.6.2. miRNA
3.6.3. Biomarkers of Therapy Effectiveness
4. Challenges in Clinical and Immunological/Biochemical/Molecular Studies
4.1. Challenges Encountered by Authors in Clinical Studies
- Difficulty in recruiting participants (60% of the studies)
- 2.
- Difficulty in controlling for confounds (60% of the studies)
- 3.
- Heterogeneity and complexity of the disorder (49% of the studies)
- 4.
- Difficulty in measuring outcomes (47% of the studies)
- 5.
- Poor quality of existing data (44% of the studies)
- 6.
- Lack of standardized, validated assessment tools (40% of the studies)
- 7.
- Difficulty in conducting long-term treatment and follow-up (27% of the studies)
- 8.
- Variability and lack of standardization in treatment approaches (25% of the studies)
- 9.
- Difficulty in blinding the study (11% of the studies)
- 10.
- Ethical considerations (7% of the studies)
- 11.
- Limited understanding of the underlying mechanisms (7% of the studies)
- 12.
- Inadequate training for healthcare providers (5% of the studies)
- 13.
- Limited access to specialized care (4% of the studies)
- 14.
- The stigma surrounding chronic pain (4% of the studies)
- 15.
- Limited funding (2% of the studies)
4.2. Challenges Encountered by Authors in Immunological/Biochemical/Molecular Studies
- Difficulty in recruiting participants (82% of the studies)
- 2.
- Inflammatory response assessed in vitro may not reflect the inflammatory processes in vivo (29% of the studies)
- 3.
- Findings for early CRPS might not generalize to persistent CRPS and vice versa (35% of the studies).
- 4.
- Heterogeneity and complexity of the disorder (41,18% of the studies)
- 5.
- Difficulty in controlling for confounds (41% of the studies).
- 6.
- Variability and lack of standardization in treatment approaches (47% of the studies)
- 7.
- Lack of standardized, validated assessment tools (47% of the studies)
- 8.
- Lack of a comparison baseline, distinguishing CRPS subtypes, and experimental control (47% of the studies).
5. Discussion
- Given patient heterogeneity, scarcity, and insufficient data on treatment efficacy, CRPS research should focus on small, high-quality studies, including case reports and n-of-1 studies, but with rigorous methodological detail.
- Studies with experimental designs should include at least 30 patients with CRPS.
- All studies should utilize the Budapest criteria, either clinical or research-based, to diagnose CRPS and explicitly state the criteria used.
- Due to ethical concerns surrounding the administration of a placebo in the treatment of severe pain, study designs should favor head-to-head comparisons and avoid placebo-controlled designs.
- Patients should be followed for at least 24 months to assess long-term treatment efficacy.
- Disease activity measurements should be reproducible and include quantitative assessments of pain, anxiety, functional disability, quality of life, sleep quality, kinesiophobia, and cognition.
- Ease of execution—The tool must be feasible in an outpatient setting, without the need for specialized equipment. It should focus on patient-reported outcomes through a self-reported questionnaire.
- Brevity—It must be as concise as possible to increase the likelihood of widespread clinical adoption.
- Simplicity—The tool must consist of straightforward tasks and questions. Patients often experience pain and may have cognitive impairments (due to pain, disease, or medication), which could hinder their understanding of more complex or abstract questions.
- Multidimensionality—It should assess multiple aspects of the disease, including pain, anxiety, functional disability, quality of life, sleep quality, kinesiophobia, and cognition. It may also incorporate a graphic representation of the affected area.
Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van Rijn, M.A.; Marinus, J.; Putter, H.; Bosselaar, S.R.J.; Moseley, G.L.; van Hilten, J.J. Spreading of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Not a Random Process. J. Neural Transm. 2011, 118, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Mos, M.; de Bruijn, A.G.J.; Huygen, F.J.P.M.; Dieleman, J.P.; Stricker, B.H.C.; Sturkenboom, M.C.J.M. The Incidence of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Population-Based Study. Pain 2007, 129, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieve, S.; Perez, R.S.; Birklein, F.; Brunner, F.; Bruehl, S.; Harden, R.N.; Packham, T.; Gobeil, F.; Haigh, R.; Holly, J.; et al. Recommendations for a First Core Outcome Measurement Set for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Clinical Studies (COMPACT). Pain 2017, 158, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, R.N.; McCabe, C.S.; Goebel, A.; Massey, M.; Suvar, T.; Grieve, S.; Bruehl, S. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Practical Diagnostic and Treatment Guidelines, 5th ed. Pain Med. 2022, 23, S1–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesaroli, G.; Hundert, A.; Birnie, K.A.; Campbell, F.; Stinson, J. Screening and Diagnostic Tools for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Pain 2021, 162, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Cowell, F.; Gillespie, S.; Goebel, A. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: What Is the Outcome? A Systematic Review of the Course and Impact of CRPS at 12 Months from Symptom Onset and Beyond. Eur. J. Pain 2022, 26, 1203–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misidou, C.; Papagoras, C. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: An Update. Mediterr. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 30, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Pan, Y.; Cheng, J.; Xu, L.; Xu, J. The Role of Neuroinflammation in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review. J. Pain Res. 2023, 16, 3061–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, M.H.; Meyer, C.; Legrain, V.; Berquin, A. Biological and Psychological Early Prognostic Factors in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Pain 2023, 27, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birklein, F.; Ajit, S.; Goebel, A.; Perez, R.S.G.M.; Sommer, C. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome—Phenotypic Characteristics and Potential Biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, L. Guides: Scoping Reviews: Protocol. Available online: https://guides.library.unisa.edu.au/ScopingReviews/Protocol (accessed on 4 March 2022).
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Velzen, G.A.J.; Huygen, F.J.P.M.; van Kleef, M.; van Eijs, F.V.; Marinus, J.; van Hilten, J.J. Sex Matters in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Eur. J. Pain 2019, 23, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, M.G.; Cavazzuti, L.; Mosca, M.; Fusaro, I.; Zati, A. Bio-Electro-Magnetic-Energy-Regulation (BEMER) for the Treatment of Type I Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Pilot Study. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2020, 36, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGee, C.; Skye, J.; Van Heest, A. Graded Motor Imagery for Women at Risk for Developing Type I CRPS Following Closed Treatment of Distal Radius Fractures: A Randomized Comparative Effectiveness Trial Protocol. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2018, 19, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halicka, M.; Vittersø, A.D.; McCullough, H.; Goebel, A.; Heelas, L.; Proulx, M.J.; Bultitude, J.H. Prism Adaptation Treatment for Upper-Limb Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Pain 2021, 162, 471–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunden, L.K.; Jorum, E. The Challenge of Recognizing Severe Pain and Autonomic Abnormalities for Early Diagnosis of CRPS. Scand. J. Pain 2021, 21, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beales, D.; Carolan, D.; Chuah-Choong, J.; Hammond, S.; O’Brien, E.; Boyle, E.; Ranelli, S.; Holthouse, D.; Mitchell, T.; Slater, H. Exploring Peoples’ Lived Experience of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome in Australia: A Qualitative Study. Scand. J. Pain 2021, 21, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, M.J.; Mekhjian, H.S.; Goad, J.A.; Lou, M.; Ding, M.; Richeimer, S.H. Topical Ketamine in the Treatment of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Int. J. Pharm. Compd. 2018, 22, 172–175. [Google Scholar]
- Canós-Verdecho, A.; Abejón, D.; Robledo, R.; Argente, P.; Peraita-Costa, I.; Morales-Suárez-Varela, M. Randomized Prospective Study in Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome of the Upper Limb with High-Frequency Spinal Cord Stimulation (10-kHz) and Low-Frequency Spinal Cord Stimulation. Neuromodulation 2021, 24, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defina, S.; Niedernhuber, M.; Shenker, N.; Brown, C.A.; Bekinschtein, T.A. Attentional Modulation of Neural Dynamics in Tactile Perception of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Patients. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 54, 5601–5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.S.; Kellett, S.; McCullough, R.; Tapper, A.; Tyler, C.; Viner, M.; Palmer, S. Body Perception Disturbance and Pain Reduction in Longstanding Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Following a Multidisciplinary Rehabilitation Program. Pain Med. 2019, 20, 2213–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlatkovic-Svenda, M.I.; Leitner, C.; Lazovic, B.; Petrovic, D.M. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (Sudeck Atrophy) Prevention Possibility and Accelerated Recovery in Patients with Distal Radius at the Typical Site Fracture Using Polarized, Polychromatic Light Therapy. Photobiomodul. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2019, 37, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.M.; Mekhail, N.; Kramer, J.; Poree, L.; Amirdelfan, K.; Grigsby, E.; Staats, P.; Burton, A.W.; Burgher, A.H.; Scowcroft, J.; et al. Therapy Habituation at 12 Months: Spinal Cord Stimulation Versus Dorsal Root Ganglion Stimulation for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I and II. J. Pain 2020, 21, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, E.D. A Prospective, Randomized Cross-Over Trial of T2 Paravertebral Block as a Sympathetic Block in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Pain Physician 2019, 22, E417–E424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumowski, N.; Hegelmaier, T.; Kolbenschlag, J.; Mainka, T.; Michel-Lauter, B.; Maier, C. Short-Term Glucocorticoid Treatment Normalizes the Microcirculatory Response to Remote Ischemic Conditioning in Early Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Pain Pract. 2019, 19, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrier, E.; Geertzen, J.H.B.; Scheper, J.; Dijkstra, P.U. Psychosocial Factors Associated with Poor Outcomes After Amputation for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type-I. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y.; Lee, C.S.; Kim, J.; Jo, D.; Moon, J.Y. Botulinum Toxin Type A for Lumbar Sympathetic Ganglion Block in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Randomized Trial. Anesthesiology 2022, 136, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallico, N.; Padmanabhan, R.; Rahman, S.; Somma, F.; Spagnoli, A.M. A Randomised Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial on the Efficacy of Local Lidocaine Injections and Oral Citalopram for the Treatment of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2022, 75, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriek, N.; de Vos, C.C.; Groeneweg, J.G.; Baart, S.J.; Huygen, F.J.P.M. Allodynia, Hyperalgesia, (Quantitative) Sensory Testing and Conditioned Pain Modulation in Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Before and After Spinal Cord Stimulation Therapy. Neuromodulation 2023, 26, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzad, M.; MacDermid, J.C.; Packham, T.; Khodabandeh, B.; Vahedi, M.; Shafiee, E. Factors Associated with Disability and Pain Intensity in Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Disabil. Rehabil. 2022, 44, 8243–8251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokopienko, M.; Sobstyl, M. Spinal Cord Stimulation for Treatment of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Single-Centre Retrospective Case Series Study. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2022, 56, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paicius, R.; White, Z.S.; Smith, C.; Lightner, A.L.; Ransom, J.T.; Lee, D.W.; Speare, S. Safety and Efficacy of Intravenous ExoFlo in the Treatment of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Pain Physician 2023, 26, E851–E857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.S.; Wallace, C.S.; White, P.; Mottram, L.; Ockenden, G.; Rehm, K.; Walker, K. Early versus Persistent Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Is There a Difference in Patient-Reported Outcomes Following Rehabilitation? Eur. J. Pain 2024, 28, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhanen, J.; Kujala, J.; Liljeström, M.; Kalso, E.; Virkkala, J.; Harno, H. rTMS Targeted to the Secondary Somatosensory Cortex Influences Sleep in CRPS Patients, as Measured with the OURA Ring. Brain Behav. 2023, 13, e3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, J.H.; Oh, J.; Choi, K. A Pilot Study of Autonomic Function Screening Tests for Differentiating Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type II and Traumatic Neuropathic Pain. Medicina 2023, 59, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovaira, M.; Cañada-Soriano, M.; García-Vitoria, C.; Calvo, A.; De Andrés, J.A.; Moratal, D.; Priego-Quesada, J.I. Clinical Results of Lumbar Sympathetic Blocks in Lower Limb Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Using Infrared Thermography as a Support Tool. Pain Pract. 2023, 23, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filbrich, L.; Kuzminova, A.; Molitor, V.; Verfaille, C.; Mouraux, D.; Berquin, A.; Barbier, O.; Libouton, X.; Legrain, V. Characterizing Biased Visuospatial Perception in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Eur. J. Pain 2023, 27, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliffe, S.; Arkilo, D.; Asgharnejad, M.; Bhattacharya, S.; Harden, R.N. Randomized Controlled Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Soticlestat as Adjunctive Therapy in Adults with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Pain Med. 2023, 24, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.P.; Khunsriraksakul, C.; Yoo, Y.; Parker, E.; Samen-Akinsiku, C.D.K.; Patel, N.; Cohen, S.J.; Yuan, X.; Cheng, J.; Moon, J.Y. Sympathetic Blocks as a Predictor for Response to Ketamine Infusion in Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Multicenter Study. Pain Med. 2023, 24, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, A.; Jacob, A.; Frank, B.; Sacco, P.; Alexander, G.; Philips, C.; Bassett, P.; Moots, R. Mycophenolate for Persistent Complex Regional Pain Syndrome, a Parallel, Open, Randomized, Proof of Concept Trial. Scand. J. Pain 2018, 18, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkpatrick, A.F.; Saghafi, A.; Yang, K.; Qiu, P.; Alexander, J.; Bavry, E.; Schwartzman, R. Optimizing the Treatment of CRPS with Ketamine. Clin. J. Pain 2020, 36, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vittersø, A.D.; Buckingham, G.; Halicka, M.; Proulx, M.J.; Bultitude, J.H. Altered Updating of Bodily and Spatial Representations After Tool-Use in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Pain 2020, 161, 1609–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacques, H.; Jérôme, V.; Antoine, C.; Lucile, S.; Valérie, D.; Amandine, L.; Theofylaktos, K.; Olivier, B. Prospective Randomized Study of the Vitamin C Effect on Pain and Complex Pain Regional Syndrome After Total Knee Arthroplasty. Int. Orthop. 2021, 45, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernigou, J.; Labadens, A.; Ghistelinck, B.; Bui Quoc, E.; Maes, R.; Bhogal, H.; Callewier, A.; Bath, O.; Chahidi, E.; Safar, A. Vitamin C Prevention of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome After Foot and Ankle Surgery: A Prospective Randomized Study of Three Hundred and Twenty-Nine Patients. Int. Orthop. 2021, 45, 2453–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habig, K.; Lautenschläger, G.; Maxeiner, H.; Birklein, F.; Krämer, H.H.; Seddigh, S. Low Mechano-Afferent Fibers Reduce Thermal Pain but Not Pain Intensity in CRPS. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román-Veas, J.; Gutiérrez-Monclus, R.; López-Gil, J.F.; Valenzuela-Fuenzalida, J.; Araya-Quintanilla, F.; Gutiérrez-Espinoza, H.; Hagert, E. Baseline Predictors Related to Functional Outcomes in Patients Older Than Sixty Years with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1 After Distal Radius Fracture Treated Conservatively: A Prospective Observational Study. Int. Orthop. 2023, 47, 2275–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoehr, J.R.; Sood, R.; Jordan, S.W.; Dumanian, G.A. Targeted Muscle Reinnervation at the Time of Amputation in the Management of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome of the Lower Extremity. Microsurgery 2020, 40, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Zhao, G.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Z. Determinants of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I in Patients with Scaphoid Waist Fracture—A Multicenter Prospective Observational Study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamroz, A.; Berger, M.; Winston, P. Prednisone for Acute Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Pain Res. Manag. 2020, 2020, 8182569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Ren, C.; Shi, X.; Shi, T.; Sun, D.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, K.; Du, H.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, W. Relative Prevalence and Associated Factors of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I in Patients with Radial Head Fractures Treated with Open Reduction and Internal Fixation: A Cross-Sectional Study. Pain Res. Manag. 2022, 2022, 9214404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llewellyn, A.; McCabe, C.S.; Hibberd, Y.; White, P.; Davies, L.; Marinus, J.; Perez, R.G.S.M.; Thomassen, I.; Brunner, F.; Sontheim, C.; et al. Are You Better? A Multi-Centre Study of Patient-Defined Recovery from Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Eur. J. Pain 2018, 22, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turgeman Dahan, N.; Vatine, J.J.; Weissman-Fogel, I.; Karpin, H.; Shmuely, S.; Bar-Shalita, T. Quantitative Dynamic Allodynograph—A Standardized Measure for Testing Dynamic Mechanical Allodynia in Chronic Limb Pain. Sensors 2023, 23, 7949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagueux, É.; Bernier, M.; Bourgault, P.; Whittingstall, K.; Mercier, C.; Léonard, G.; Laroche, S.; Tousignant-Laflamme, Y. The Effectiveness of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation as an Add-on Modality to Graded Motor Imagery for Treatment of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Randomized Proof of Concept Study. Clin. J. Pain 2018, 34, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhoorn, K.; Staal, J.B.; van Dongen, R.T.; Frölke, J.P.M.; Klomp, F.P.; van de Meent, H.; Adang, E.; Nijhuis-van der Sanden, M.W. Pain Exposure Physical Therapy versus Conventional Treatment in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1—A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis alongside a Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2018, 32, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halicka, M.; Vittersø, A.D.; McCullough, H.; Goebel, A.; Heelas, L.; Proulx, M.J.; Bultitude, J.H. Disputing space-based biases in unilateral complex regional pain syndrome. Cortex A J. Devoted Study Nerv. Syst. Behav. 2020, 127, 248–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederico, T.N.; da Silva Freitas, T. Peripheral Nerve Stimulation of the Brachial Plexus for Chronic Refractory CRPS Pain of the Upper Limb: Description of a New Technique and Case Series. Pain Med. 2020, 21 (Suppl. 1), S18–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elomaa, M.; Hotta, J.; de C Williams, A.C.; Forss, N.; Äyräpää, A.; Kalso, E.; Harno, H. Symptom Reduction and Improved Function in Chronic CRPS Type 1 After 12-Week Integrated, Interdisciplinary Therapy. Scand. J. Pain 2019, 19, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verfaille, C.; Filbrich, L.; Cordova Bulens, D.; Lefèvre, P.; Berquin, A.; Barbier, O.; Libouton, X.; Fraselle, V.; Mouraux, D.; Legrain, V. Robot-Assisted Line Bisection in Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz Keleş, B.; Önder, B.; Kesiktaş, F.N.; Öneś, K.; Paker, N. Acute Effects of Contrast Bath on Sympathetic Skin Response in Patients with Poststroke Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 2020, 37, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaribas, I.M.; Peccora, C.; Skaribas, E. Single S1 Dorsal Root Ganglia Stimulation for Intractable Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Foot Pain After Lumbar Spine Surgery: A Case Series. Neuromodulation 2019, 22, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheuren, P.S.; De Schoenmacker, I.; Rosner, J.; Brunner, F.; Curt, A.; Hubli, M. Pain-Autonomic Measures Reveal Nociceptive Sensitization in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Eur. J. Pain 2023, 27, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezgin Ozcan, D.; Tatli, H.U.; Polat, C.S.; Oken, O.; Koseoglu, B.F. The Effectiveness of Fluidotherapy in Poststroke Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Study. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2019, 28, 1578–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Hollander, M.; Heijnders, N.; de Jong, J.R.; Vlaeyen, J.W.S.; Smeets, R.J.E.M.; Goossens, M.E.J.B. Exposure in Vivo Versus Pain-Contingent Physical Therapy in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. Int. J. Technol. Assess. Health Care 2018, 34, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, F.; Wang, A.P.; Schira, M.M.; Isherwood, Z.J.; McAuley, J.H.; Iannetti, G.D.; Sereno, M.I.; Moseley, G.L.; Rae, C.D. Fine-Grained Mapping of Cortical Somatotopies in Chronic Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 9185–9196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, A.; Palomba, A.; Paoletta, M.; Liguori, S.; Toro, G.; Iolascon, G. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome in Athletes: Scoping Review. Medicina 2021, 57, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, L.E.; Terkelsen, A.J.; Blichfeldt-Eckhardt, M.R.; Sørensen, J.C.H.; Meier, K. Spinal Cord Stimulation in Severe Cases of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Retrospective Cohort Study with Long-Term Follow-Up. Eur. J. Pain 2021, 25, 2212–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walfish, L.; Sbrocchi, A.M.; Rivera, G.; Ricaurte Gracia, Y.L.N.; Mohamed, N.; González Cárdenas, V.H.; Stoopler, M.; Ingelmo, P. Use of bisphosphonates in a retrospective case series of children and adolescents with complex regional pain syndrome. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2021, 31, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, N.R.; Bruehl, S.; Perez, R.S.G.M.; Birklein, F.; Marinus, J.; Maihofner, C.; Lubenow, T.; Buvanendran, A.; Mackey, S.; Graciosa, J.; et al. Validation of proposed diagnostic criteria (the “Budapest Criteria”) for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Pain 2010, 150, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Gao, M.; Li, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhao, Y. Animal Models of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I. J. Pain Res. 2021, 14, 3711–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhold, A.K.; Kindl, G.K.; Dietz, C.; Dietz, C.; Scheu, N.; Mehling, K.; Brack, A.; Birklein, F.; Rittner, H.L. Molecular and Clinical Markers of Pain Relief in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: An Observational Study. Eur. J. Pain 2023, 27, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, A.K.; Malik, A.; Singh, A.; Chilkoti, G.T.; Bhardwaj, N.; Bajaj, M.; Banerjee, B.D.; Rehan-Ul-Haq. Modulation of mTORC1 and IL-6 Following Mirror Therapy and Pregabalin in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1. Pain Manag. 2023, 13, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravius, N.; Chaudhry, S.R.; Muhammad, S.; Boström, A.; Gravius, S.; Randau, T.; Scheele, D.; Westhofen, P.; Kruppenbacher, J.; Stoffel-Wagner, B.; et al. Selective L4 Dorsal Root Ganglion Stimulation Evokes Pain Relief and Changes of Inflammatory Markers: Part I Profiling of Saliva and Serum Molecular Patterns. Neuromodulation 2019, 22, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharmalingam, B.; Singh, P.; Schramm, P.; Birklein, F.; Kaps, M.; Lips, K.S.; Szalay, G.; Blaes, F.; Tschernatsch, M. Autoantibodies from Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Induce Pro-inflammatory Effects and Functional Disturbances on Endothelial Cells in Vitro. Pain 2022, 163, 2446–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, S.; Douglas, S.R.; Alexander, G.M.; Shenoda, B.B.; Barrett, J.E.; Aradillas, E.; Sacan, A.; Ajit, S.K. Exosome MicroRNA Signatures in Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Undergoing Plasma Exchange. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, H.H. Immunological Aspects of the Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS). Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 4546–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, P.D.; Drummond, E.S.; Dawson, L.F.; Mitchell, V.; Finch, P.M.; Vaughan, C.W.; Phillips, J.K. Upregulation of α1-Adrenoceptors on Cutaneous Nerve Fibres after Partial Sciatic Nerve Ligation and in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type II. Pain 2014, 155, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, P.D.; Morellini, N.; Finch, P.M.; Birklein, F.; Knudsen, L.F. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Intradermal Injection of Phenylephrine Evokes Pain and Hyperalgesia in a Subgroup of Patients with Upregulated α1-Adrenoceptors on Dermal Nerves. Pain 2018, 159, 2296–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, P.M.; Drummond, E.S.; Dawson, L.F.; Phillips, J.K.; Drummond, P.D. Up-Regulation of Cutaneous α1-Adrenoceptors in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I. Pain Med. 2014, 15, 1945–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, L.K.; Morici, M.V.; Stumbles, P.A.; Finch, P.M.; Drummond, P.D. Stimulation of Alpha-1 Adrenoceptors May Intensify Cutaneous Inflammation in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Pain 2023, 164, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birklein, F.; Drummond, P.D.; Li, W.; Schlereth, T.; Albrecht, N.; Finch, P.M.; Dawson, L.F.; Clark, J.D.; Kingery, W.S. Activation of Cutaneous Immune Responses in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. J. Pain 2014, 15, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heijmans-Antonissen, C.; Wesseldijk, F.; Munnikes, R.J.; Huygen, F.J.; van der Meijden, P.; Hop, W.C.; Hooijkaas, H.; Zijlstra, F.J. Multiplex Bead Array Assay for Detection of 25 Soluble Cytokines in Blister Fluid of Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1. Mediat. Inflamm. 2006, 2006, 28398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huygen, F.J.; De Bruijn, A.G.; De Bruin, M.T.; Groeneweg, J.G.; Klein, J.; Zijlstra, F.J. Evidence for Local Inflammation in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1. Mediat. Inflamm. 2002, 11, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munnikes, R.J.; Muis, C.; Boersma, M.; Heijmans-Antonissen, C.; Zijlstra, F.J.; Huygen, F.J. Intermediate Stage Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1 Is Unrelated to Proinflammatory Cytokines. Mediat. Inflamm. 2005, 2005, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesseldijk, F.; Huygen, F.J.; Heijmans-Antonissen, C.; Niehof, S.P.; Zijlstra, F.J. Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha and Interleukin-6 Are Not Correlated with the Characteristics of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1 in 66 Patients. Eur. J. Pain 2008, 12, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nance, D.M.; Sanders, V.M. Autonomic Innervation and Regulation of the Immune System (1987–2007). Brain Behav. Immun. 2007, 21, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisanti, L.A.; Perez, D.M.; Porter, J.E. Modulation of Immune Cell Function by α(1)-Adrenergic Receptor Activation. Curr. Top. Membr. 2011, 67, 113–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisanti, L.A.; Woster, A.P.; Dahlman, J.; Sauter, E.R.; Combs, C.K.; Porter, J.E. α1-Adrenergic Receptors Positively Regulate Toll-Like Receptor Cytokine Production from Human Monocytes and Macrophages. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 338, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijnen, C.J.; Rouppe van der Voort, C.; Wulffraat, N.; van der Net, J.; Kuis, W.; Kavelaars, A. Functional Alpha 1-Adrenergic Receptors on Leukocytes of Patients with Polyarticular Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Neuroimmunol. 1996, 71, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestroni, G.J. Dendritic Cell Migration Controlled by Alpha 1b-Adrenergic Receptors. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 6743–6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roupe van der Voort, C.; Heijnen, C.J.; Wulffraat, N.; Kuis, W.; Kavelaars, A. Stress Induces Increases in IL-6 Production by Leukocytes of Patients with the Chronic Inflammatory Disease Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Putative Role for Alpha(1)-Adrenergic Receptors. J. Neuroimmunol. 2000, 110, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casale, T.B.; Kaliner, M. Demonstration that Circulating Human Blood Cells Have No Detectable Alpha 1-Adrenergic Receptors by Radioligand Binding Analysis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1984, 74, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavelaars, A. Regulated Expression of Alpha-1 Adrenergic Receptors in the Immune System. Brain Behav. Immun. 2002, 16, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, A.; Bronzetti, E.; Conterno, A.; Greco, S.; Mulatero, P.; Schena, M.; Schiavone, D.; Tayebati, S.K.; Veglio, F.; Amenta, F. Alpha1-Adrenergic Receptor Subtypes in Human Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes. Hypertension 1999, 33, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, S.A.; Schmidlin, H.; Nagasawa, M.; Blom, B.; Spits, H. IL-6 Triggers IL-21 Production by Human CD4+ T Cells to Drive STAT3-Dependent Plasma Cell Differentiation in B Cells. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Mehta, H.; Drevets, D.A.; Coggeshall, K.M. IL-6 Increases B-Cell IgG Production in a Feed-Forward Proinflammatory Mechanism to Skew Hematopoiesis and Elevate Myeloid Production. Blood 2010, 115, 4699–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, E.H.; Panayi, G.S. Cytokine Pathways and Joint Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.Y.; Moudgil, K.D. Immunomodulation of Autoimmune Arthritis by Pro-inflammatory Cytokines. Cytokine 2017, 98, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Lutz, I.; Railton, P.; Wiley, J.P.; McAllister, J.; Powell, J.; Krawetz, R.J. Serum and Synovial Fluid Cytokine Profiling in Hip Osteoarthritis: Distinct from Knee Osteoarthritis and Correlated with Pain. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2018, 19, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, A.I.; Beekhuizen, M.; ‘t Hart, M.C.; Radstake, T.R.; Dhert, W.J.; Saris, D.B.; van Osch, G.J.; Creemers, L.B. Cytokine Profiles in the Joint Depend on Pathology, but Are Different between Synovial Fluid, Cartilage Tissue, and Cultured Chondrocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, L.K.; Stumbles, P.A.; Finch, P.M.; Drummond, P.D. Inflammation Induces α1-Adrenoceptor Expression in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 115, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijaya, L.K.; Stumbles, P.A.; Drummond, P.D. A Positive Feedback Loop between Alpha1-Adrenoceptors and Inflammatory Cytokines in Keratinocytes. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 391, 112008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubuis, E.; Thompson, V.; Leite, M.I.; Blaes, F.; Maihöfner, C.; Greensmith, D.; Vincent, A.; Shenker, N.; Kuttikat, A.; Leuwer, M.; et al. Longstanding Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Is Associated with Activating Autoantibodies against Alpha-1a Adrenoceptors. Pain 2014, 155, 2408–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohr, D.; Singh, P.; Tschernatsch, M.; Kaps, M.; Pouokam, E.; Diener, M.; Kummer, W.; Birklein, F.; Vincent, A.; Goebel, A.; et al. Autoimmunity against the β2 Adrenergic Receptor and Muscarinic-2 Receptor in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Pain 2011, 152, 2690–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaes, F.; Schmitz, K.; Tschernatsch, M.; Kaps, M.; Krasenbrink, I.; Hempelmann, G.; Bräu, M.E. Autoimmune Etiology of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (M. Sudeck). Neurology 2004, 63, 1734–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, A.; Blaes, F. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome, Prototype of a Novel Kind of Autoimmune Disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.Z.; Wei, T.; Tajerian, M.; Clark, J.D.; Birklein, F.; Goebel, A.; Li, W.W.; Sahbaie, P.; Escolano, F.L.; Herrnberger, M.; et al. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Patient Immunoglobulin M Has Pronociceptive Effects in the Skin and Spinal Cord of Tibia Fracture Mice. Pain 2020, 161, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohr, D.; Tschernatsch, M.; Schmitz, K.; Singh, P.; Kaps, M.; Schäfer, K.H.; Diener, M.; Mathies, J.; Matz, O.; Kummer, W.; et al. Autoantibodies in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Bind to a Differentiation-Dependent Neuronal Surface Autoantigen. Pain 2009, 143, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tékus, V.; Hajna, Z.; Borbély, É.; Markovics, A.; Bagoly, T.; Szolcsányi, J.; Thompson, V.; Kemény, Á.; Helyes, Z.; Goebel, A. A CRPS-IgG-Transfer-Trauma Model Reproducing Inflammatory and Positive Sensory Signs Associated with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Pain 2014, 155, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aradillas, E.; Schwartzman, R.J.; Grothusen, J.R.; Goebel, A.; Alexander, G.M. Plasma Exchange Therapy in Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Pain Physician 2015, 18, 383–394. [Google Scholar]
- Goebel, A.; Bisla, J.; Carganillo, R.; Cole, C.; Frank, B.; Gupta, R.; James, M.; Kelly, J.; McCabe, C.; Milligan, H.; et al. A Randomised Placebo-Controlled Phase III Multicenter Trial: Low-Dose Intravenous Immunoglobulin Treatment for Long-Standing Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (LIPS Trial). NIHR Journals Library: Southampton, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Goebel, A.; Netal, S.; Schedel, R.; Sprotte, G. Human Pooled Immunoglobulin in the Treatment of Chronic Pain Syndromes. Pain Med. 2002, 3, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.W.; Guo, T.Z.; Shi, X.; Czirr, E.; Stan, T.; Sahbaie, P.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Kingery, W.S.; Clark, J.D. Autoimmunity Contributes to Nociceptive Sensitization in a Mouse Model of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Pain 2014, 155, 2377–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.W.; Yang, Y.; Guo, T.Z.; Sahbaie, P.; Shi, X.Y.; Guang, Q.; Kingery, W.S.; Herzenberg, L.A.; Clark, J.D. IL-6 Signaling Mediates the Germinal Center Response, IgM Production and Nociceptive Sensitization in Male Mice after Tibia Fracture. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 94, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkitny, L.; McAuley, J.H.; Herbert, R.D.; Di Pietro, F.; Cashin, A.G.; Ferraro, M.C.; Moseley, G.L. Post-fracture serum cytokine levels are not associated with a later diagnosis of complex regional pain syndrome: A case-control study nested in a prospective cohort study. BMC Neurol. 2022, 22, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kalita, J.; Pandey, P.C.; Shukla, R.; Misra, U.K. Prednisolone 20 mg vs. 40 mg in complex regional pain syndrome type I: A randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2023, 113, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpin, H.; Vatine, J.J.; Bachar Kirshenboim, Y.; Markezana, A.; Weissman-Fogel, I. Central Sensitization and Psychological State Distinguishing Complex Regional Pain Syndrome from Other Chronic Limb Pain Conditions: A Cluster Analysis Model. Biomedicines 2022, 11, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kavelaars, A.; Heijnen, C.J. T cells as guardians of pain resolution. Trends Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Krukowski, K.; Laumet, G.O.; Weis, D.; Alexander, J.F.; Heijnen, C.J.; Kavelaars, A. CD8+ T cell-derived IL-13 increases macrophage IL-10 to resolve neuropathic pain. JCI Insight 2022, 7, 154–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Vlist, M.; Raoof, R.; Willemen, H.; Prado, J.; Versteeg, S.; Martin Gil, C.; Vos, M.; Lokhorst, R.E.; Pasterkamp, R.J.; Kojima, T.; et al. Macrophages transfer mitochondria to sensory neurons to resolve inflammatory pain. Neuron 2022, 110, 613–626.e619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova, I.A.; Alexander, G.M.; Qureshi, R.A.; Sacan, A.; Graziano, A.; Barrett, J.E.; Schwartzman, R.J.; Ajit, S.K. MicroRNA modulation in complex regional pain syndrome. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dietz, C.; Müller, M.; Reinhold, A.K.; Karch, L.; Schwab, B.; Forer, L.; Vlckova, E.; Brede, E.M.; Jakubietz, R.; Üçeyler, N.; et al. What is normal trauma healing and what is complex regional pain syndrome I? An analysis of clinical and experimental biomarkers. Pain 2019, 160, 2278–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, M.K.; Ramanathan, S.; Touati, A.; Zhou, Y.; Thanawala, R.U.; Alexander, G.M.; Sacan, A.; Ajit, S.K. Regulation of proinflammatory genes by the circulating microRNA hsa-miR-939. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Che, Y.; Zheng, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, X.; Shi, F. miR-223: An immune regulator in infectious disorders. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 781815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yu, J. circCUL3 drives malignant progression of cervical cancer by activating autophagy through sponge miR-223-3p upregulation of ATG7. Gene 2024, 925, 148572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.A.; Blandford, S.N.; Berry, T.; Williams, J.B.; Stefanelli, M.; Ploughman, M.; Moore, C.S. miR-223 promotes regenerative myeloid cell phenotype and function in the demyelinated central nervous system. Glia 2019, 67, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Peng, Z.; Tang, M.; Xue, Q. MiR-144-3p inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of lung cancer A549 cells via targeting HGF. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2022, 17, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madè, A.; Greco, S.; Vausort, M.; Miliotis, M.; Schordan, E.; Baksi, S.; Zhang, L.; Baryshnikova, E.; Ranucci, M.; Cardani, R.; et al. Association of miR-144 levels in the peripheral blood with COVID-19 severity and mortality. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, P.J.; Hines, S.; Eisenberg, E.; Pud, D.; Finlay, D.R.; Connolly, K.M.; Paré, M.; Davar, G.; Rice, F.L. Pathologic alterations of cutaneous innervation and vasculature in affected limbs from patients with complex regional pain syndrome. Pain 2006, 120, 244–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinç, M.; Soydemir, Ö.C. Efficacy of N-acetylcysteine in reducing inflammation and oxidative stress to prevent complex regional pain syndrome type 1. Medicine 2024, 103, e39742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mehling, K.; Becker, J.; Chen, J.; Scriba, S.; Kindl, G.; Jakubietz, R.; Sommer, C.; Hartmannsberger, B.; Rittner, H.L. Bilateral deficiency of Meissner corpuscles and papillary microvessels in patients with acute complex regional pain syndrome. Pain 2024, 165, 1613–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- König, S.; Bayer, M.; Dimova, V.; Herrnberger, M.; Escolano-Lozano, F.; Bednarik, J.; Vlckova, E.; Rittner, H.; Schlereth, T.; Birklein, F. The serum protease network—One key to understand complex regional pain syndrome pathophysiology. Pain 2019, 160, 1402–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harnik, M.A.; Sodmann, A.; Hartmannsberger, B.; Kindl, G.; Becker, J.; Reinhold, A.K.; Herrmann, E.; Buck, A.K.; Dischinger, U.; Birklein, F.; et al. Bone metabolism in complex regional pain syndrome. Pain Rep. 2024, 9, e1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kinfe, T.M.; Asif, M.; Chakravarthy, K.V.; Deer, T.R.; Kramer, J.M.; Yearwood, T.L.; Hurlemann, R.; Hussain, M.S.; Motameny, S.; Wagle, P.; et al. Unilateral L4-dorsal root ganglion stimulation evokes pain relief in chronic neuropathic postsurgical knee pain and changes of inflammatory markers: Part II whole transcriptome profiling. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zalewski, A.; Andreieva, I.; Wiśniowska, J.; Tarnacka, B.; Gromadzka, G. Clinical and Molecular Barriers to Understanding the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2514. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062514
Zalewski A, Andreieva I, Wiśniowska J, Tarnacka B, Gromadzka G. Clinical and Molecular Barriers to Understanding the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2514. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062514
Chicago/Turabian StyleZalewski, Adam, Iana Andreieva, Justyna Wiśniowska, Beata Tarnacka, and Grażyna Gromadzka. 2025. "Clinical and Molecular Barriers to Understanding the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2514. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062514
APA StyleZalewski, A., Andreieva, I., Wiśniowska, J., Tarnacka, B., & Gromadzka, G. (2025). Clinical and Molecular Barriers to Understanding the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2514. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062514






