Punishment-Induced Suppression of Methamphetamine Self-Administration Is Accompanied by the Activation of the CPEB4/GLD2 Polyadenylation Complex of the Translational Machinery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Meth Self-Administration and Effects of Footshocks
2.2. The Effect of DRD1 Antagonist, SCH23390, on Compulsive METH-Taking Behaviors in the Presence of Punishment
2.3. Prolonged Forced Abstinence of METH Showed Greater Incubation of METH Seeking in Compulsive Rats
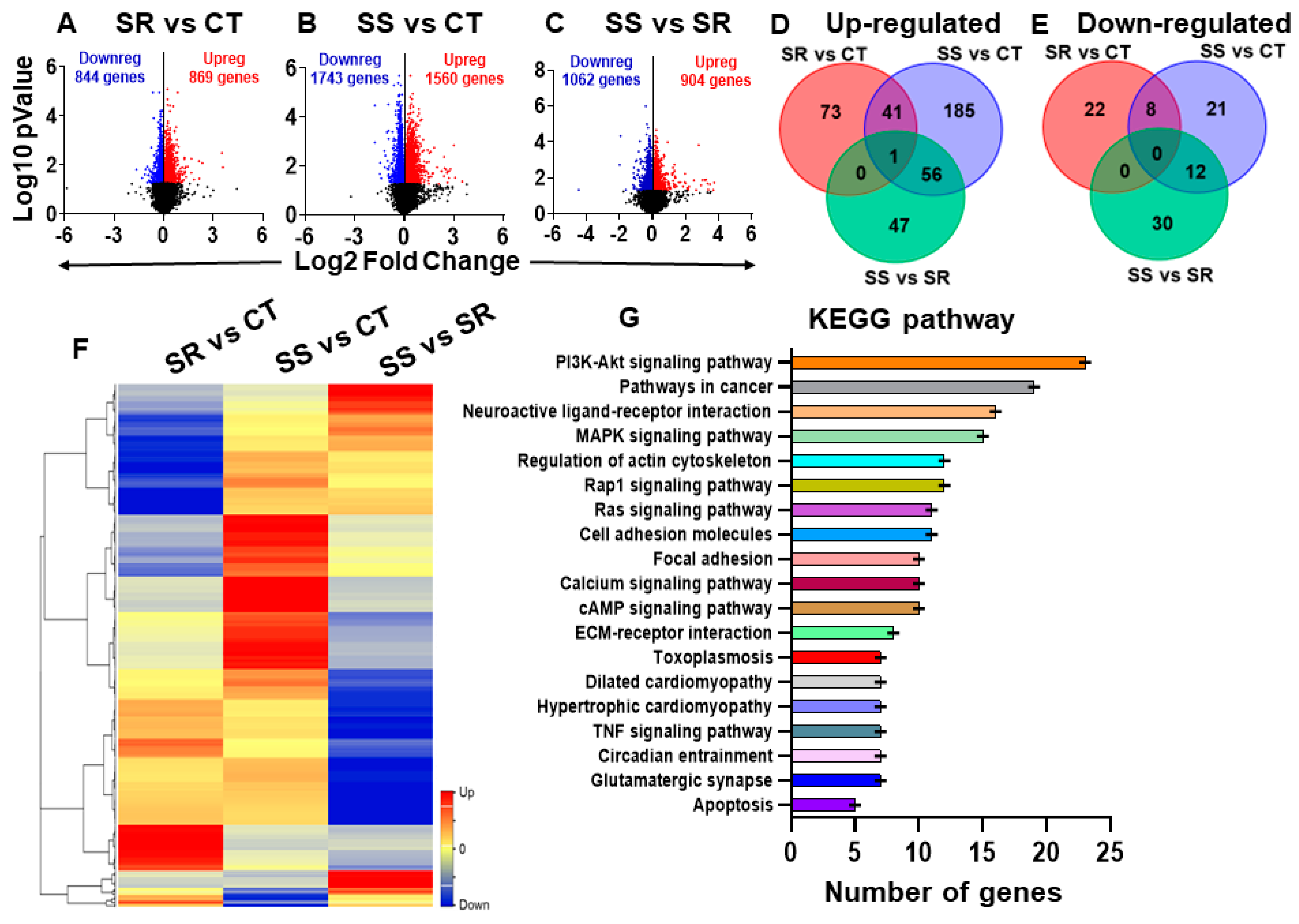
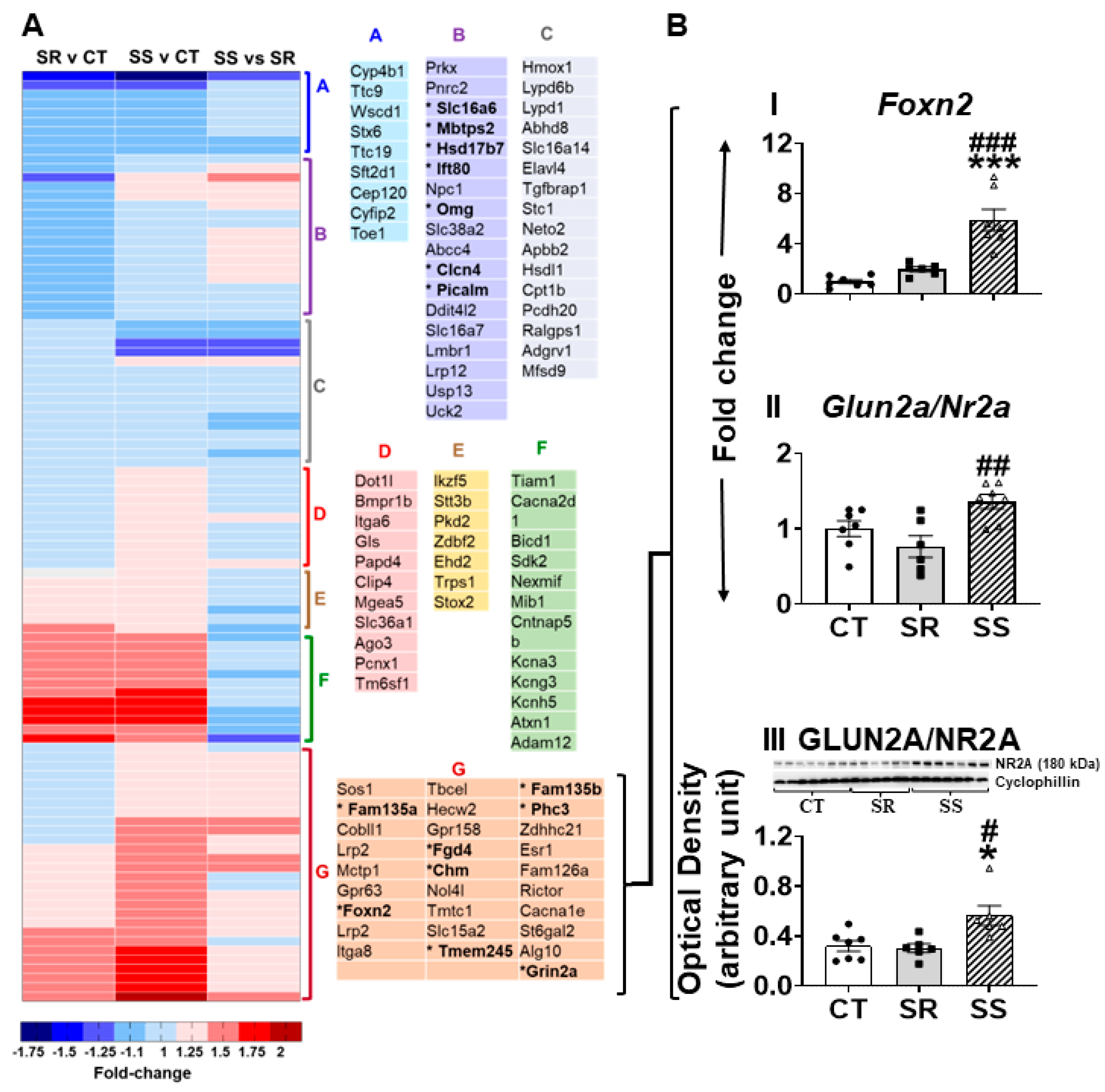
2.4. Global Transcriptional Profiling of Long-Term METH SA Reveals Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) in Compulsive and Non-Compulsive Rats
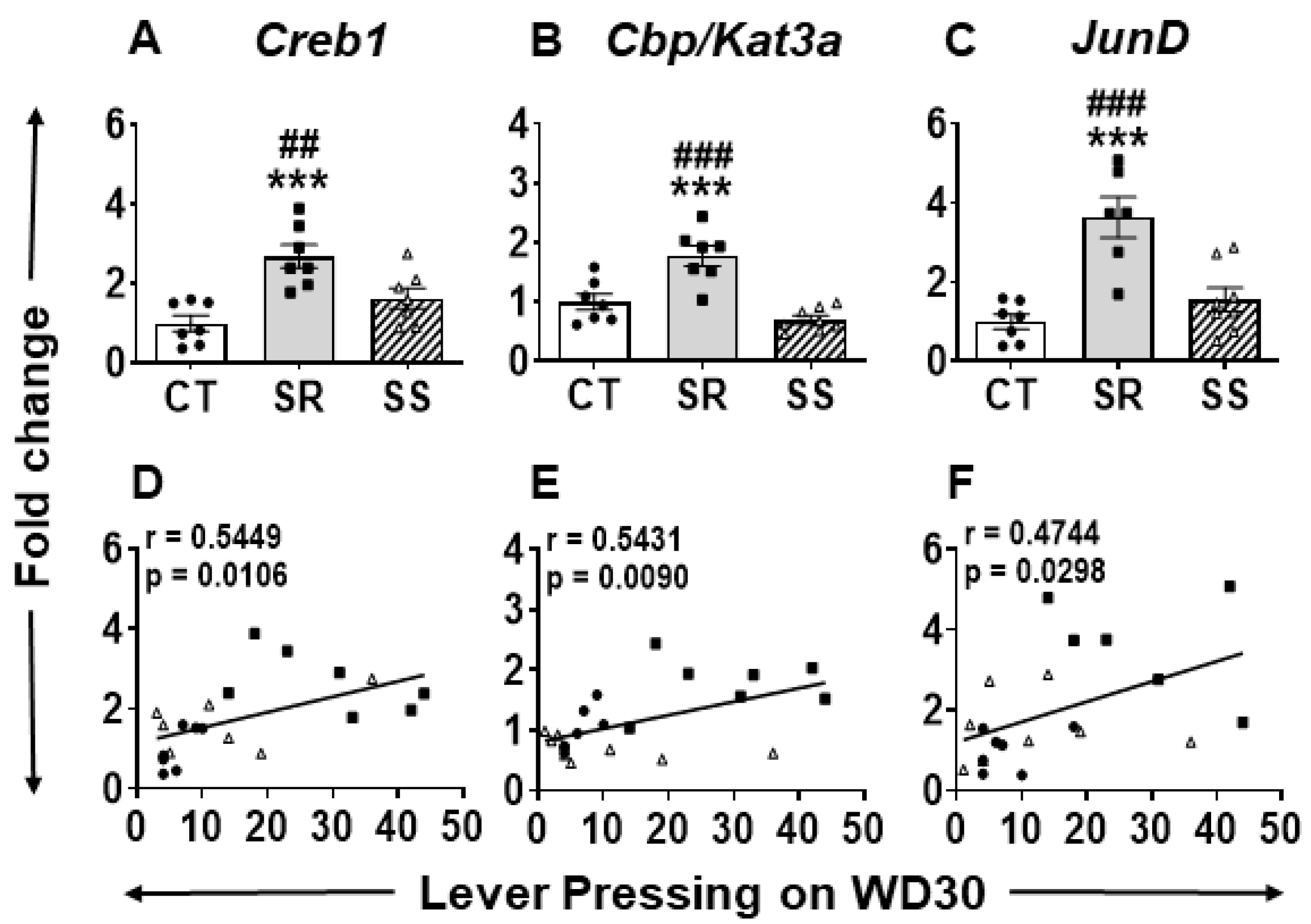
2.5. Specific Striatal Genes Are Differentially Expressed in Rats Prone to Relapse
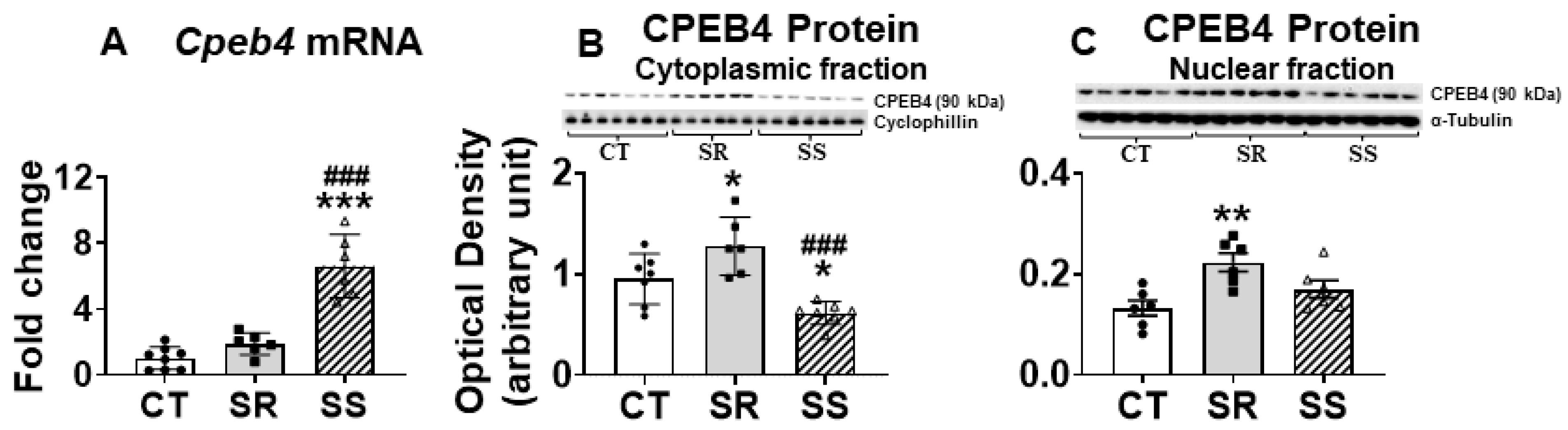
2.6. Non-Compulsive METH Takers Show Differential Expression of CPEB4
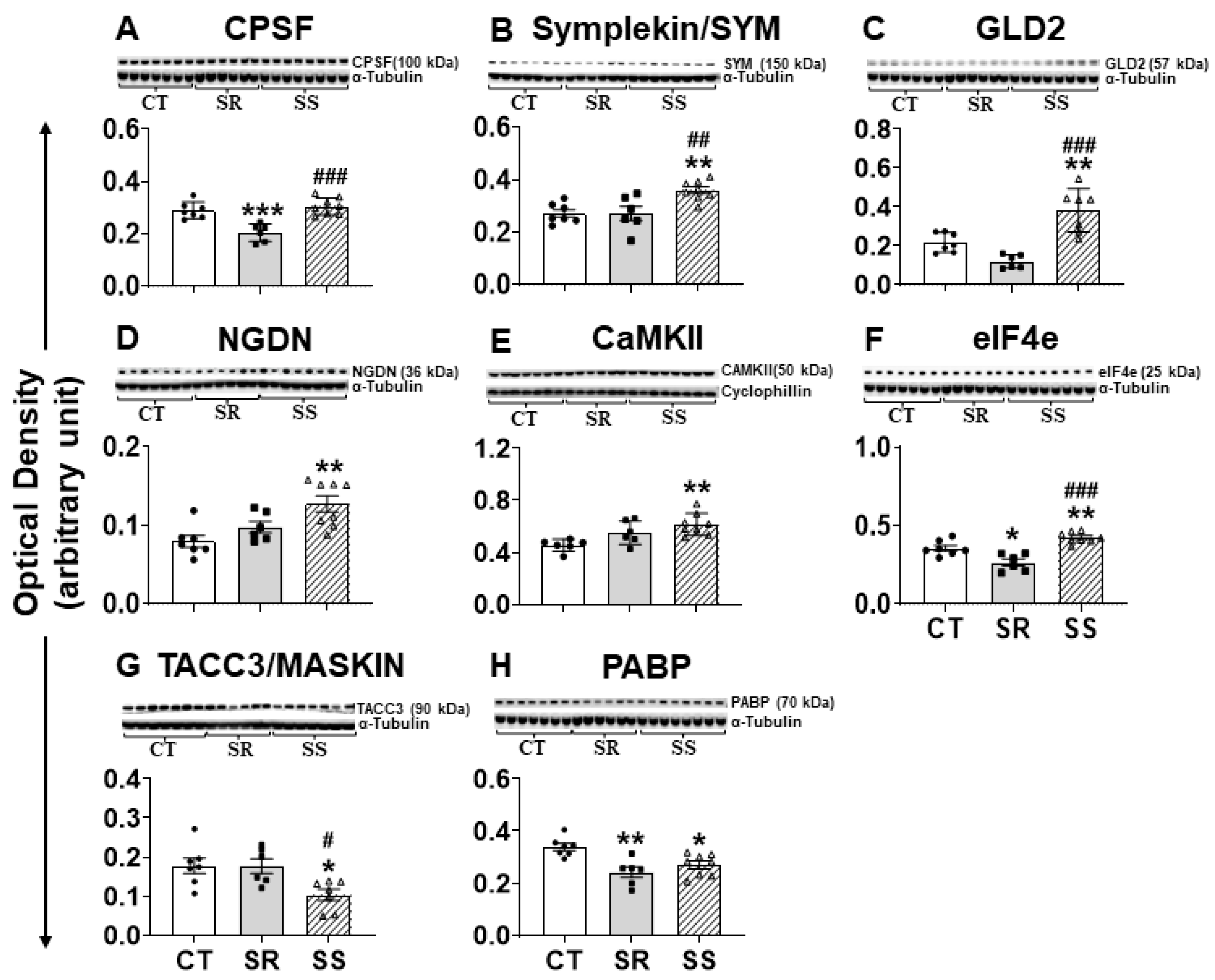
2.7. Altered CPEB4 Expression in Non-Compulsive METH-Taking Rats Is Associated with Changes in the Expression of CPEB4-Interacting Proteins
3. Discussion
3.1. Effects of the DRD1 Antagonist on Compulsive METH SA
3.2. Compulsive METH-Taking Rats Are Prone to Relapse
3.3. CPEB and Dynamic Transcriptional Reprogramming in Non-Compulsive Animals
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Drugs
4.3. METH Self-Administration and Foothocks
4.4. DRD1 Antagonist, SCH23390, Treatment During METH SA, and Footshock Punishment
4.5. Measurements of Incubation of METH Craving
4.6. RNA Extraction and Sequencing
4.7. Quantification of mRNA Levels by qRT-PCR Analysis
4.8. Western Blot
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanson, K.L.; Luciana, M.; Sullwold, K. Reward-related decision-making deficits and elevated impulsivity among MDMA and other drug users. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2008, 96, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernheim, A.; See, R.E.; Reichel, C.M. Chronic methamphetamine self-administration disrupts cortical control of cognition. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 69, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potvin, S.; Pelletier, J.; Grot, S.; Hébert, C.; Barr, A.M.; Lecomte, T. Cognitive deficits in individuals with methamphetamine use disorder, A meta-analysis. Addict. Behav. 2018, 80, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groman, S.M.; Morales, A.M.; Lee, B.; London, E.D.; Jentsch, J.D. Methamphetamine-induced increases in putamen gray matter associate with inhibitory control. Psychopharmacology 2013, 229, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balleine, B.W.; Delgado, M.R.; Hikosaka, O. The role of the dorsal striatum in reward and decision making. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 8161–8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everitt, B.J.; Robbins, T.W. Drug addiction: Updating actions to habits to compulsions ten years on. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2016, 67, 23–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, D.M.; Gonzales, B.J.; Citri, A. Dorsal Striatal Circuits for Habits, Compulsions and Addictions. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Compton, W.M.; Jones, C.M.; Einstein, E.B.; Volkow, N.D. Methamphetamine use, methamphetamine use disorder and associated overdose deaths among us adults. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 1329–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAMSHA—Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Key Substance Use and Mental Health Indicators in the United States, Results from the 2020 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (HHS Publication No. PEP21-07-01-003, NSDUH Series H-56); Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration: Rockville, MD, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, O.V.; Jayanthi, S.; Ladenheim, B.; McCoy, M.T.; Krasnova, I.N.; Cadet, J.L. Compulsive methamphetamine taking under punishment is associated with greater cue-induced drug seeking in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 326, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnova, I.N.; Gerra, M.C.; Walther, D.; Jayanthi, S.; Ladenheim, B.; McCoy, M.T.; Brannock, C.; Cadet, J.L. Compulsive methamphetamine taking in the presence of punishment is associated with increased oxytocin expression in the nucleus accumbens of rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadet, J.L.; Brannock, C.; Krasnova, I.N.; Jayanthi, S.; Ladenheim, B.; McCoy, M.T.; Walther, D.; Godino, A.; Pirooznia, M.; Lee, R.S. Genome-wide DNA hydroxymethylation identifies potassium channels in the nucleus accumbens as discriminators of methamphetamine addiction and abstinence. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1196–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadet, J.L.; Patel, R.; Jayanthi, S. Compulsive methamphetamine taking and abstinence in the presence of adverse consequences, Epigenetic and transcriptional consequences in the rat brain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2019, 179, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subu, R.; Jayanthi, S.; Cadet, J.L. Compulsive methamphetamine taking induces autophagic and apoptotic markers in the rat dorsal striatum. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 3515–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthi, S.; Ladenheim, B.; Sullivan, P.; McCoy, M.T.; Krasnova, I.N.; Goldstein, D.S.; Cadet, J.L. Biochemical neuroadaptations in the rat striatal dopaminergic system after prolonged exposure to methamphetamine self-administration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayanthi, S.; Peesapati, R.; McCoy, M.T.; Ladenheim, B.; Cadet, J.L. Footshock-induced abstinence from compulsive methamphetamine self-administration in rat model is accompanied by increased hippocampal expression of cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2). Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everitt, B.J. Neural and psychological mechanisms underlying compulsive drug seeking habits and drug memories indications for novel treatments of addiction. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2014, 40, 2163–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, K.M.; Kim, T.H.; Castro, M.; Drieu, C.; Padovan-Hernandez, Y.; Chen, B.; Pat, F.; Ottenheimer, D.J.; Janak, P.H. Encoding and context-dependent control of reward consumption within the central nucleus of the amygdala. iScience 2024, 27, 109652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koob, G.F.; Volkow, N.D. Neurobiology of addiction: A neurocircuitry analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti-Prats, L.; Giuliano, C.; Domi, A.; Puaud, M.; Peña-Oliver, Y.; Fouyssac, M.; McKenzie, C.; Everitt, B.J.; Belin, D. The development of compulsive coping behavior depends on dorsolateral striatum dopamine-dependent mechanisms. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 4666–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daiwile, A.P.; McCoy, M.T.; Ladenheim, B.; Subramaniam, J.; Cadet, J.L. Incubation of methamphetamine craving in punishment-resistant individuals is associated with activation of specific gene networks in the rat dorsal striatum. Mol. Psychiatry 2024, 29, 990–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhadi, K.; Daiwile, A.P.; Cadet, J.L. Modeling methamphetamine use disorder and relapse in animals: Short- and long-term epigenetic.; transcriptional.; and biochemical consequences in the rat brain. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 155, 105440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, G.E.; Crutcher, M.D. Functional architecture of basal ganglia circuits: Neural substrates of parallel processing. Trends Neurosci. 1990, 13, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, S.N. Corticostriatal circuitry. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 18, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, F.A.; Strick, P.L. Basal ganglia output and cognition: Evidence from anatomical, behavioral, and clinical studies. Brain Cogn. 2000, 42, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, J.C.; Warner, L.A.; Kessler, R.C. Comparative epidemiology of dependence on tobacco, alcohol. controlled substances, and inhalants: Basic findings from the National Comorbidity Survey. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 1994, 2, 244–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivshina, M.; Lasko, P.; Richter, J.D. Cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding proteins in development, health, and disease. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 393–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlov, E.; Shidlovskii, Y.V.; Gilmutdinov, R.; Schedl, P.; Zhukova, M. The role of CPEB family proteins in the nervous system function in the norm and pathology. Cell Biosci. 2012, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, R.; Richter, J.D. Translational control by CPEB: A means to the end. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, K.; Giustetto, M.; Etkin, A.; Hsu, R.; Janisiewicz, A.M.; Miniaci, M.C.; Kim, J.-H.; Zhu, H.; Kandel, E.R. A neuronal isoform of CPEB regulates local protein synthesis and stabilizes synapse-specific long-term facilitation in aplysia. Cell 2003, 115, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioriti, L.; Myers, C.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Li, X.; Stephan, J.S.; Trifilieff, P.; Colnaghi, L.; Kosmidis, S.; Drisaldi, B.; Pavlopoulos, E.; et al. The persistence of hippocampal-based memory requires protein synthesis mediated by the prion-like protein CPEB3. Neuron 2015, 86, 1433–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Han, J.; A Chinn, C.; Rounds, J.S.; Li, X.; Nikan, M.; Myszka, M.; Tong, L.; Passalacqua, L.F.; Bredy, T.; et al. Inhibition of Cpeb3 ribozyme elevates CPEB3 protein expression and polyadenylation of its target mRNAs and enhances object location memory. Elife 2024, 13, e90116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theis, M.; Si, K.; Kandel, E.R. Two previously undescribed members of the mouse CPEB family of genes and their inducible expression in the principal cell layers of the hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9602–9607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groisman, I.; Huang, Y.S.; Mendez, R.; Cao, Q.; Richter, J.D. Translational control of embryonic cell division by CPEB and maskin. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2001, 66, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drisaldi, B.; Colnaghi, L.; Levine, A.; Huang, Y.; Snyder, A.M.; Metzger, D.J.; Theis, M.; Kandel, D.B.; Kandel, E.R.; Fioriti, L. Cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding proteins cpeb1 and cpeb3 regulate the translation of fosb and are required for maintaining addiction-like behaviors induced by cocaine. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nousch, M.; Minasaki, R.; Eckmann, C.R. Polyadenylation is the key aspect of GLD-2 function in C. elegans. RNA 2017, 23, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, J.D. CPEB: A life in translation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2007, 32, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur, F.; Alarcon, J.M.; Stackpole, E.E.; Wang, R.; Richter, J.D. Noncanonical cytoplasmic poly(A) polymerases regulate RNA levels, alternative RNA processing, and synaptic plasticity but not hippocampal-dependent behaviours. RNA Biol. 2012, 18, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udagawa, T.; Swanger, S.A.; Takeuchi, K.; Kim, J.H.; Nalavadi, V.; Shin, J.; Lorenz, L.J.; Zukin, R.S.; Bassell, G.J.; Richter, J.D. Bidirectional control of mRNA translation and synaptic plasticity by the cytoplasmic polyadenylation complex. Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avchalumov, Y.; Trenet, W.; Piña-Crespo, J.; Mandyam, C. SCH23390 Reduces Methamphetamine self-administration and prevents methamphetamine-induced striatal LTD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, K.A.; Carati, C.; Lea, R.A.; Fitzmaurice, P.S.; Schenk, S. Effect of D1-like and D2-like receptor antagonists on methamphetamine and 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine self-administration in rats. Behav. Pharmacol. 2009, 20, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedel, C.C.; Dölken, L.; Ruzsics, Z.; Koszinowski, U.H.; Zimmer, R. Conserved principles of mammalian transcriptional regulation revealed by RNA half-life. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duran-Arqué, B.; Cañete, M.; Castellazzi, C.L.; Bartomeu, A.; Ferrer-Caelles, A.; Reina, O.; Caballé, A.; Gay, M.; Arauz-Garofalo, G.; Belloc, E.; et al. Comparative analyses of vertebrate CPEB proteins define two subfamilies with coordinated yet distinct functions in post-transcriptional gene regulation. Genome Biol. 2022, 23, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, A.; Chang, T.-C.; Yamashita, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhong, Z.; A Chen, C.-Y.; Shyu, A.-B. Concerted action of poly(A) nucleases and decapping enzyme in mammalian mRNA turnover. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giangarrà, V.; Igea, A.; Castellazzi, C.L.; Bava, F.A.; Mendez, R. Global analysis of CPEBs reveals sequential and non-redundant functions in mitotic cell cycle. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igea, A.; Méndez, R. Meiosis requires a translational positive loop where CPEB1 ensues its replacement by CPEB4. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 2182–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoa, I.; Gallego, J.; Ferreira, P.G.; Mendez, R. Mitotic cell-cycle progression is regulated by CPEB1 and CPEB4-dependent translational control. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, M.-C.; Oruganty-Das, A.; Cooper-Morgan, A.; Jin, G.; Swanger, S.A.; Bassell, G.J.; Florman, H.; van Leyen, K.; Richter, J.D. CPEB4 is a cell survival protein retained in the nucleus upon ischemia or endoplasmic reticulum calcium depletion. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 5658–5671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.L.; Evans, V.; Shen, S.; Xing, Y.; Richter, J.D. The nuclear experience of CPEB: Implications for RNA processing and translational control. RNA 2010, 16, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.Y.; Lorenz, L.; Richter, J.D. Translational control by neuroguidin, a eukaryotic initiation factor 4E and CPEB binding protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 4277–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgoni, B.; Gray, N.K. The roles of cytoplasmic poly(A)-binding proteins in regulating gene expression: A developmental perspective. Brief. Funct. Genom. Proteom. 2004, 3, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkocki, Z.; Liudkovska, V.; Gewartowska, O.; Mroczek, S.; Dziembowski, A. Terminal nucleotidyl transferases (TENTs) in mammalian RNA metabolism. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20180162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhana, L.; Wang, L.; Buter, N.; Kwak, J.E.; Schiltz, C.A.; Gonzalez, T.; Kelley, A.E.; Landry, C.F.; Wickens, M. Vertebrate GLD2 poly(A) polymerases in the germline and the brain. RNA 2005, 11, 1117–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnard, D.C.; Ryan, K.; Manley, J.L.; Richter, J.D. Symplekin and xGLD-2 are required for CPEB-mediated cytoplasmic polyadenylation. Cell 2004, 119, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Eckmann, C.R.; Kadyk, L.C.; Wickens, M.; Kimble, J. A regulatory cytoplasmic poly(A) polymerase in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 2002, 419, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, S.; Lin, R. The Maternal-to-Zygotic Transition in C. elegans. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2015, 113, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Swanger, S.A.; He, Y.A.; Richter, J.D.; Bassell, G.J. Dendritic GluN2A synthesis mediates activity-induced NMDA receptor insertion. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 8898–8908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlong, T.M.; Corbit, L.H.; Brown, R.A.; Balleine, B.W. Methamphetamine promotes habitual action and alters the density of striatal glutamate receptor and vesicular proteins in dorsal striatum. Addict. Biol. 2018, 23, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szumlinski, K.K.; Lominac, K.D.; Campbell, R.R.; Cohen, M.; Fultz, E.K.; Brown, C.N.; Miller, B.W.; Quadir, S.G.; Martin, D.; Thompson, A.B.; et al. Methamphetamine addiction vulnerability: The glutamate, the bad, and the ugly. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 81, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnova, I.N.; Chiflikyan, M.; Justinova, Z.; McCoy, M.T.; Ladenheim, B.; Jayanthi, S.; Quintero, C.; Brannock, C.; Barnes, C.; Adair, J.E.; et al. CREB phosphorylation regulates striatal transcriptional responses in the self-administration model of methamphetamine addiction in the rat. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 58, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Rubio, F.J.; Zeric, T.; Bossert, J.M.; Kambhampati, S.; Cates, H.M.; Kennedy, P.J.; Liu, Q.-R.; Cimbro, R.; Hope, B.T. Incubation of methamphetamine craving is associated with selective increases in expression of Bdnf and trkb, glutamate receptors, and epigenetic enzymes in cue-activated fos-expressing dorsal striatal neurons. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 8232–8244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, F.J.; Liu, Q.R.; Li, X.; Cruz, F.C.; Leão, R.M.; Warren, B.L.; Kambhampati, S.; Babin, K.R.; McPherson, K.B.; Cimbro, R.; et al. Context-induced reinstatement of methamphetamine seeking is associated with unique molecular alterations in fos-expressing dorsolateral striatum neurons. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 5625–5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadet, J.L.; Brannock, C.; Jayanthi, S.; Krasnova, I.N. Transcriptional and epigenetic substrates of methamphetamine addiction and withdrawal: Evidence from a long-access self-administration model in the rat. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 51, 696–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, O.V.; McCoy, M.T.; Ladenheim, B.; Jayanthi, S.; Brannock, C.; Tulloch, I.; Krasnova, I.N.; Cadet, J.L. CAMKII-conditional deletion of histone deacetylase 2 potentiates acute methamphetamine-induced expression of immediate early genes in the mouse nucleus accumbens. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasnova, I.N.; Justinova, Z.; Cadet, J.L. Methamphetamine addiction: Involvement of CREB and neuroinflammatory signaling pathways. Psychopharmacology 2016, 233, 1945–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthi, S.; Gonzalez, B.; McCoy, M.T.; Ladenheim, B.; Bisagno, V.; Cadet, J.L. Methamphetamine Induces TET1- and TET3-dependent DNA hydroxymethylation of Crh and Avp genes in the rat nucleus accumbens. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 5154–5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollà, I.; Pardiñas, A.F.; Parras, A.; Hernández, I.H.; Santos-Galindo, M.; Picó, S.; Callado, L.F.; Elorza, A.; Rodríguez-López, C.; Fernández-Miranda, G.; et al. Pathogenic mis-splicing of CPEB4 in Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 94, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker-Andresen, D.; Zhao, Q.; Li, X.; Jupp, B.; Chesworth, R.; Lawrence, A.J.; Bredy, T.W. Persistent variations in neuronal DNA methylation following cocaine self-administration and protracted abstinence in mice. Neuroepigenetics 2015, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.M.; Mason-Parker, S.E.; Abraham, W.C.; Tate, W.P. Biphasic changes in the levels of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-2 subunits correlate with the induction and persistence of long-term potentiation. Mol. Brain Res. 1998, 60, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosshans, D.R.; Clayton, D.A.; Coultrap, S.J.; Browning, M.D. LTP leads to rapid surface expression of NMDA but not AMPA receptors in adult rat CA1. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daiwile, A.P.; Ladenheim, B.; Jayanthi, S.; Cadet, J.L. Punishment-Induced Suppression of Methamphetamine Self-Administration Is Accompanied by the Activation of the CPEB4/GLD2 Polyadenylation Complex of the Translational Machinery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062734
Daiwile AP, Ladenheim B, Jayanthi S, Cadet JL. Punishment-Induced Suppression of Methamphetamine Self-Administration Is Accompanied by the Activation of the CPEB4/GLD2 Polyadenylation Complex of the Translational Machinery. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062734
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaiwile, Atul P., Bruce Ladenheim, Subramaniam Jayanthi, and Jean Lud Cadet. 2025. "Punishment-Induced Suppression of Methamphetamine Self-Administration Is Accompanied by the Activation of the CPEB4/GLD2 Polyadenylation Complex of the Translational Machinery" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062734
APA StyleDaiwile, A. P., Ladenheim, B., Jayanthi, S., & Cadet, J. L. (2025). Punishment-Induced Suppression of Methamphetamine Self-Administration Is Accompanied by the Activation of the CPEB4/GLD2 Polyadenylation Complex of the Translational Machinery. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062734





