Reparixin as a Potential Antiepileptogenic Agent: Modulation of the CXCL1–CXCR1/2 Axis and Seizure Activity in a Kindling Rat Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
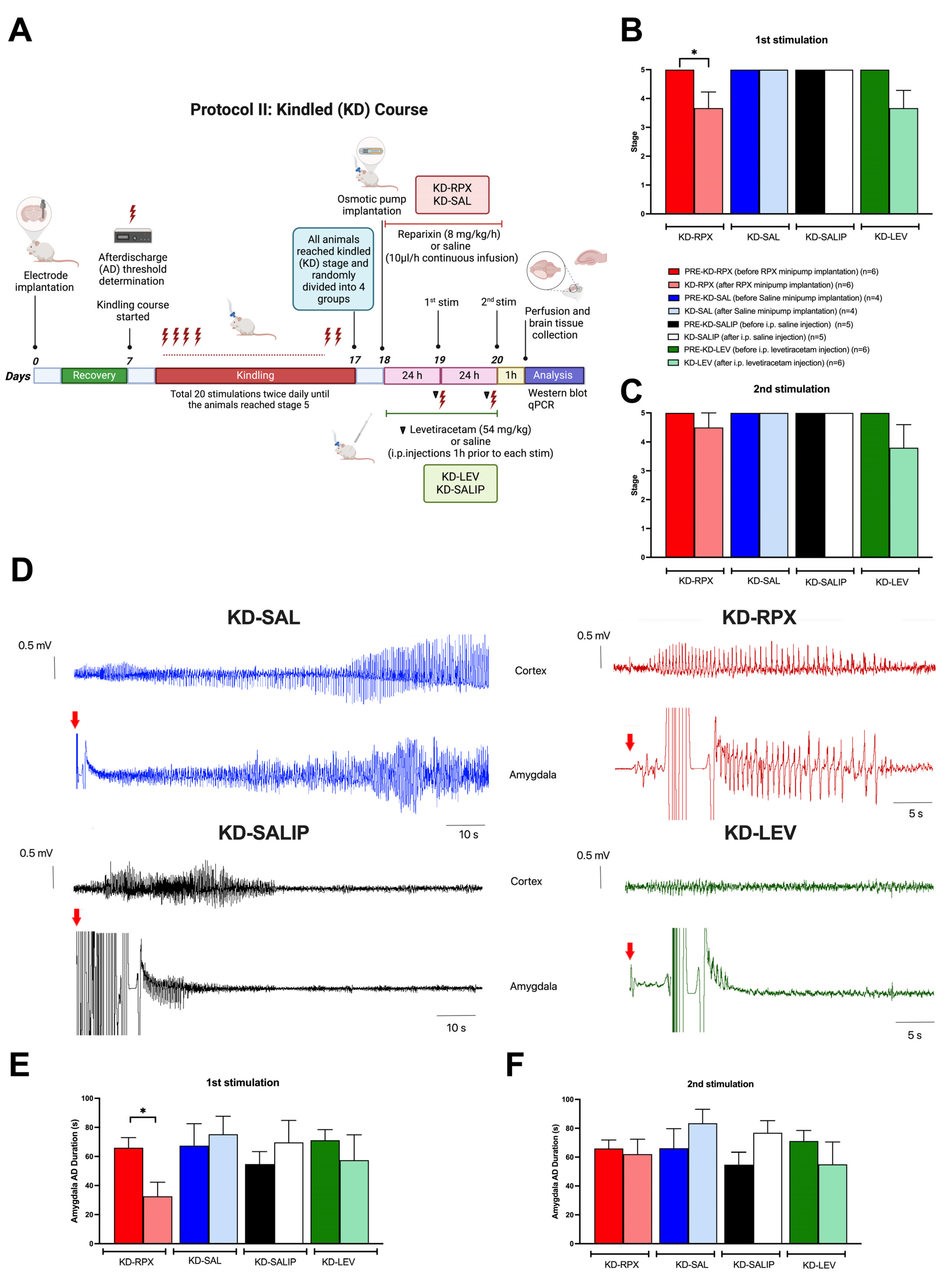
2.1. Antiepileptogenic Effect of Reparixin in the Kindling Process
2.2. Antiseizure Effect of Reparixin in Kindled (KD) Rats
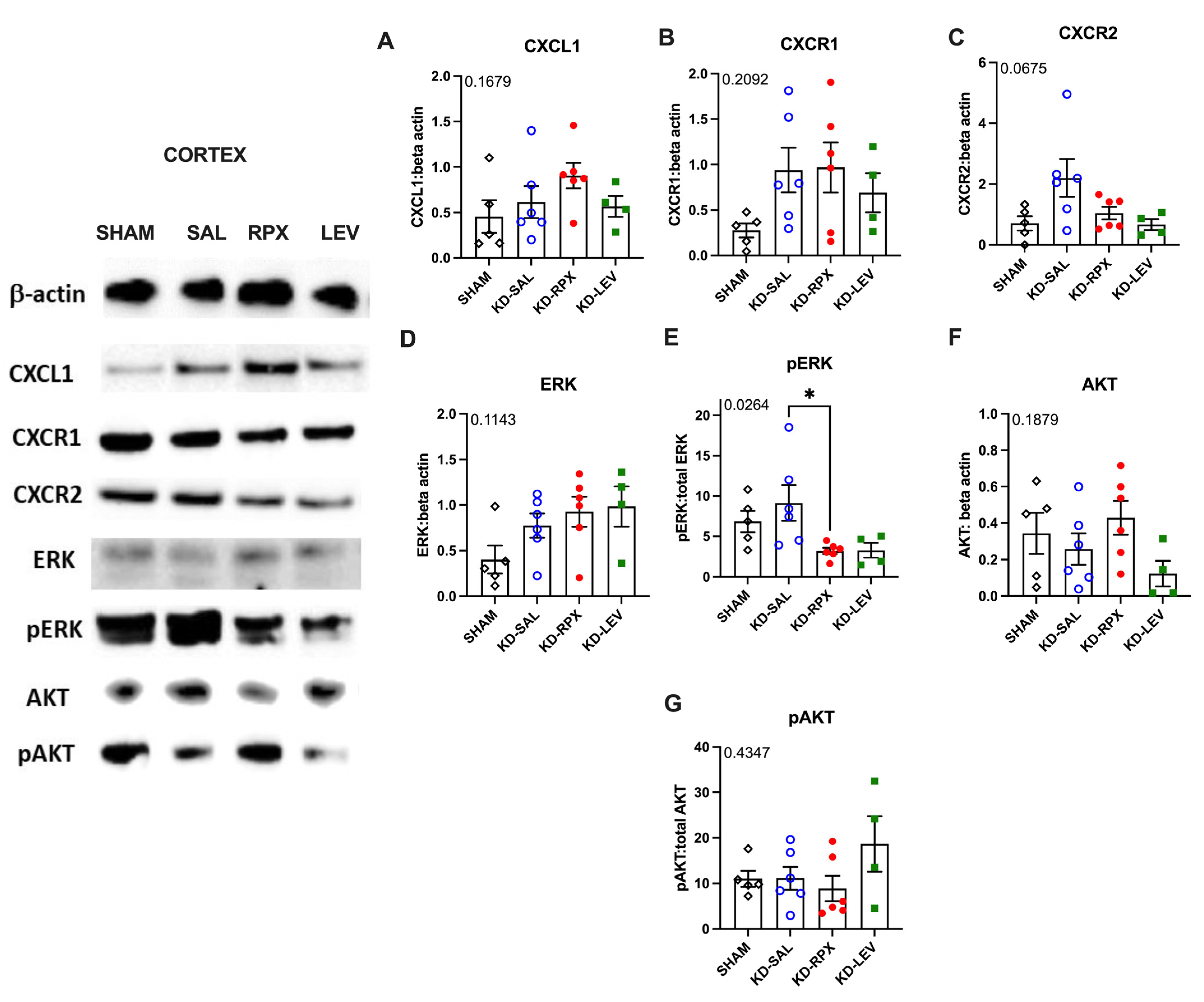
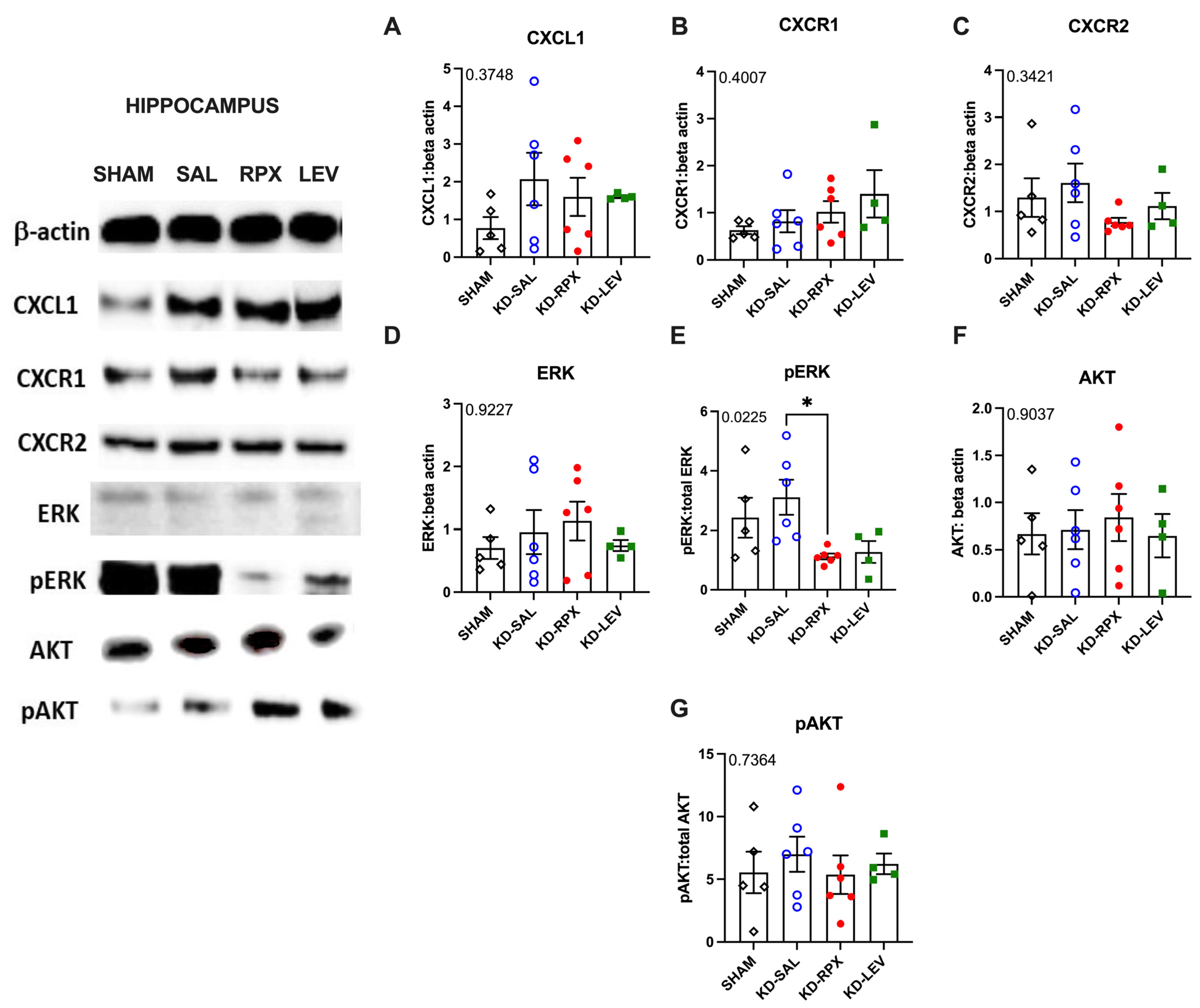
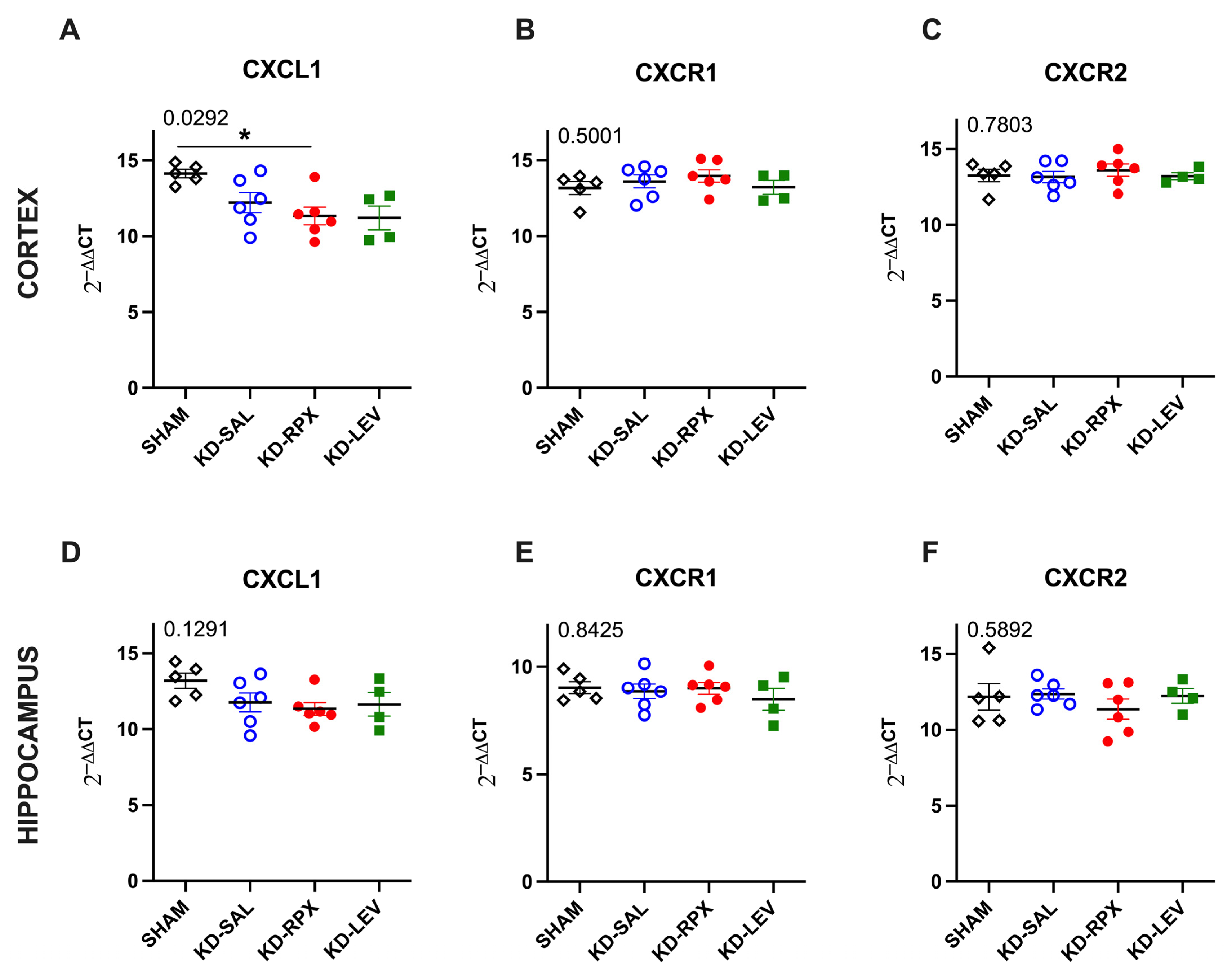
2.3. Analysis of CXCL1–CXCR1/2 Signaling in a Rodent Model of Acquired Epilepsy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Study Design and Experimental Groups
4.3. Implantation of Electrodes and Determination of After-Discharge Threshold
4.4. Kindling Protocol
4.5. Drug Preparation
4.6. Osmotic Pump Implantation
4.7. Brain Tissue Preparation
4.8. Western Blotting
4.9. Real-Time PCR
4.10. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stafstrom, C.E.; Carmant, L. Seizures and epilepsy: An overview for neuroscientists. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a022426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motovilov, K.; Maguire, C.; Briggs, D.; Melamed, E. Altered cytokine profile in clinically suspected seronegative autoimmune associated epilepsy. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauhari, P.; Kaur, P.; Gulati, S.; Meena, A.K.; Pandey, T.; Upadhyay, A. Diagnostic and prognostic significance of serum interleukins in epileptic encephalopathy with spike wave activation in sleep (EE-SWAS) syndrome. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2024, 53, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczorowska, M.; Czekuć-Kryśkiewicz, E.; Dądalski, M.; Kotulska, K. Immunological markers of drug resistant epilepsy and its response to immunomodulatory therapy with ACTH in children. Folia Neuropathol. 2023, 61, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milano, C.; Montali, M.; Barachini, S.; Burzi, I.S.; Pratesi, F.; Petrozzi, L.; Chico, L.; Morganti, R.; Gambino, G.; Rossi, L.; et al. Increased production of inflammatory cytokines by circulating monocytes in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: A possible role in drug resistance. J. Neuroimmunol. 2024, 386, 578272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.; Wilson, S.E.; Rubinos, C. SARS-CoV-2 infection and seizures: The perfect storm. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2022, 21, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Česká, K.; Papež, J.; Ošlejšková, H.; Slabý, O.; Radová, L.; Loja, T.; Libá, Z.; Svěráková, A.; Brázdil, M.; Aulická, Š. CCL2/MCP-1, interleukin-8, and fractalkine/CXC3CL1: Potential biomarkers of epileptogenesis and pharmacoresistance in childhood epilepsy. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2023, 46, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Sapia, R.; Zimmer, T.S.; Kebede, V.; Balosso, S.; Ravizza, T.; Sorrentino, D.; Castillo, M.A.M.; Porcu, L.; Cattani, F.; Ruocco, A.; et al. CXCL1-CXCR1/2 signaling is induced in human temporal lobe epilepsy and contributes to seizures in a murine model of acquired epilepsy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 158, 105468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, J.O. Kindling model of epilepsy. Adv. Neurol. 1986, 44, 303–318. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, D.G.; Bertini, R.; Vieira, A.T.; Cunha, F.Q.; Poole, S.; Allegretti, M.; Colotta, F.; Teixeira, M.M. Repertaxin, a novel inhibitor of rat CXCR2 function, inhibits inflammatory responses that follow intestinal ischaemia and reperfusion injury. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 143, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, E.S.; Trocóniz, I.F. Can pentylenetetrazole and maximal electroshock rodent seizure models quantitatively predict antiepileptic efficacy in humans? Seizure 2015, 24, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löscher, W.; Hönack, D.; Rundfeldt, C. Antiepileptogenic effects of the novel anticonvulsant levetiracetam (ucb L059) in the kindling model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 284, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.L.; Gao, M.M.; Gong, J.X.; Yang, L.Y. DUSP1 regulates hippocampal damage in epilepsy rats via ERK1/2 pathway. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2021, 118, 102032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.H.; Leiser, S.C.; Song, D.; Brunner, D.; Roberds, S.L.; Wong, M.; Bordey, A. Inhibition of MEK-ERK signaling reduces seizures in two mouse models of tuberous sclerosis complex. Epilepsy Res. 2022, 181, 106890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Yang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z. ERK1/2 Regulates Epileptic Seizures by Modulating the DRP1-Mediated Mitochondrial Dynamic. Synapse 2024, 78, e22309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Chen, X.; Lin, H.J.; Lin, J. Inhibition of interleukin 8/C-X-C chemokine receptor 1,/2 signaling reduces malignant features in human pancreatic cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Nie, S.; Chen, G.; Ma, K.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Papa, S.M.; Cao, X. Levetiracetam Ameliorates L-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia in Hemiparkinsonian Rats Inducing Critical Molecular Changes in the Striatum. Parkinsons Dis. 2015, 2015, 253878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.B.; An, J.Z.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, M.G.; Liu, S.B.; Yi, J. Elevated interleukin-8 enhances prefrontal synaptic transmission in mice with persistent inflammatory pain. Mol. Pain 2012, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.L.; Zhang, Z.J.; Xie, R.G.; Jiang, B.C.; Ji, R.R.; Gao, Y.J. Chemokine CXCL1 enhances inflammatory pain and increases NMDA receptor activity and COX-2 expression in spinal cord neurons via activation of CXCR2. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 261, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.H.; Xu, G.M.; Wang, Y. Up-regulation of CXCL1 and CXCR2 contributes to remifentanil-induced hypernociception via modulating spinal NMDA receptor expression and phosphorylation in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 626, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lax, P.; Limatola, C.; Fucile, S.; Trettel, F.; Di Bartolomeo, S.; Renzi, M.; Ragozzino, D.; Eusebi, F. Chemokine receptor CXCR2 regulates the functional properties of AMPA-type glutamate receptor GluR1 in HEK cells. J. Neuroimmunol. 2002, 129, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puma, C.; Danik, M.; Quirion, R.; Ramon, F.; Williams, S. The chemokine interleukin-8 acutely reduces Ca(2+) currents in identified cholinergic septal neurons expressing CXCR1 and CXCR2 receptor mRNAs. J. Neurochem. 2001, 78, 960–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.X.; Yang, L.; Shao, L.X.; He, Y.; Wu, G.; Bao, Y.H.; Lu, N.N.; Gong, D.M.; Lu, Y.P.; Cui, T.T.; et al. Endothelial Cdk5 deficit leads to the development of spontaneous epilepsy through CXCL1/CXCR2-mediated reactive astrogliosis. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20180992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.G.; Strong, J.A.; Xie, W.; Yang, R.H.; Coyle, D.E.; Wick, D.M.; Dorsey, E.D.; Zhang, J.M. The chemokine CXCL1/growth related oncogene increases sodium currents and neuronal excitability in small diameter sensory neurons. Mol. Pain 2008, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.H.; Strong, J.A.; Zhang, J.M. NF-kappaB mediated enhancement of potassium currents by the chemokine CXCL1/growth related oncogene in small diameter rat sensory neurons. Mol. Pain 2009, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Wan, Y.; Wang, X. CCL2 and CXCL1 trigger calcitonin gene-related peptide release by exciting primary nociceptive neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 82, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippo, K.; Henderson, R.B.; Laschinger, M.; Hogg, N. Neutrophil chemokines KC and macrophage-inflammatory protein-2 are newly synthesized by tissue macrophages using distinct TLR signaling pathways. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 4308–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, B.D.; Bricio-Moreno, L.; Sorensen, E.W.; Miyabe, Y.; Lian, J.; Solomon, T.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Luster, A.D. Astrocyte- and Neuron-Derived CXCL1 Drives Neutrophil Transmigration and Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability in Viral Encephalitis. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, S.E.; Zera, K.A.; Ivison, G.T.; Buckwalter, M.S.; Engleman, E.G. Brain profiling in murine colitis and human epilepsy reveals neutrophils and TNFα as mediators of neuronal hyperexcitability. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröer, S.; Pauletti, A. Microglia and infiltrating macrophages in ictogenesis and epileptogenesis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2024, 17, 1404022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, P.; Rubio, T.; Garcia-Gimeno, M.A. Neuroinflammation and Epilepsy: From Pathophysiology to Therapies Based on Repurposing Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klitgaard, H.; Matagne, A.; Gobert, J.; Wülfert, E. Evidence for a unique profile of levetiracetam in rodent models of seizures and epilepsy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 353, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George Paxinos, C.W. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 4th ed.; Academic Press: Sydney, Australia, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Racine, R.J. Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation. II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1972, 32, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandolini, L.; Benedetti, E.; Ruffini, P.A.; Russo, R.; Cristiano, L.; Antonosante, A.; d’Angelo, M.; Castelli, V.; Giordano, A.; Allegretti, M.; et al. CXCR1/2 pathways in paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 23188–23201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalieri, B.; Mosca, M.; Ramadori, P.; Perrelli, M.G.; De Simone, L.; Colotta, F.; Bertini, R.; Poli, G.; Cutrìn, J.C. Neutrophil recruitment in the reperfused-injured rat liver was effectively attenuated by repertaxin, a novel allosteric noncompetitive inhibitor of CXCL8 receptors: A therapeutic approach for the treatment of post-ischemic hepatic syndromes. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2005, 18, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löscher, W.; Hönack, D. Profile of ucb L059, a novel anticonvulsant drug, in models of partial and generalized epilepsy in mice and rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 232, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Frw Primer (5′-3′) | Rev Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| CXCL1 | CTCGCTTCTCTGTGCAGC | AGTGTGGCTATGACTTCGGT |
| CXCR1 | ACCGATGTCTACGTGCTGAA | GATGGCCAGGTATCGATCCA |
| CXCR2 | TGTCCCTGCCCATCTTCATT | CGAGGACCACAGCAAAGATG |
| GAPDH | ATGGTGAAGGTCGGTGTGAAC | TGTAGTTGAGGTCAATGAAGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Çarçak, N.; Mutlu, N.; Erdeve, E.T.; Turan, T.T.; Sarıyıldız, Ö.; Ulusoy, C.; Şanlı, E.; Tüzün, E.; Küçükali, C.İ.; Brandolini, L.; et al. Reparixin as a Potential Antiepileptogenic Agent: Modulation of the CXCL1–CXCR1/2 Axis and Seizure Activity in a Kindling Rat Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2831. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072831
Çarçak N, Mutlu N, Erdeve ET, Turan TT, Sarıyıldız Ö, Ulusoy C, Şanlı E, Tüzün E, Küçükali Cİ, Brandolini L, et al. Reparixin as a Potential Antiepileptogenic Agent: Modulation of the CXCL1–CXCR1/2 Axis and Seizure Activity in a Kindling Rat Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):2831. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072831
Chicago/Turabian StyleÇarçak, Nihan, Nursima Mutlu, Elif Tuğçe Erdeve, Talat Taygun Turan, Özge Sarıyıldız, Canan Ulusoy, Elif Şanlı, Erdem Tüzün, Cem İsmail Küçükali, Laura Brandolini, and et al. 2025. "Reparixin as a Potential Antiepileptogenic Agent: Modulation of the CXCL1–CXCR1/2 Axis and Seizure Activity in a Kindling Rat Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 2831. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072831
APA StyleÇarçak, N., Mutlu, N., Erdeve, E. T., Turan, T. T., Sarıyıldız, Ö., Ulusoy, C., Şanlı, E., Tüzün, E., Küçükali, C. İ., Brandolini, L., Aramini, A., Allegretti, M., Onat, F., & De Filippis, L. (2025). Reparixin as a Potential Antiepileptogenic Agent: Modulation of the CXCL1–CXCR1/2 Axis and Seizure Activity in a Kindling Rat Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 2831. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072831







