Genome-Wide Characterization of CaM/CML Gene Family in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata): Expression Profiling and Functional Implications During Hyaloperonospora parasitica Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Characterization of BoCaM/BoCML Genes in B. oleracea
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis, Protein Motifs, and Gene Structure of BoCaM/BoCML Genes
2.3. Phylogenetic Relationship of CaM/CML Genes Among B. oleracea, Arabidopsis, and Rice
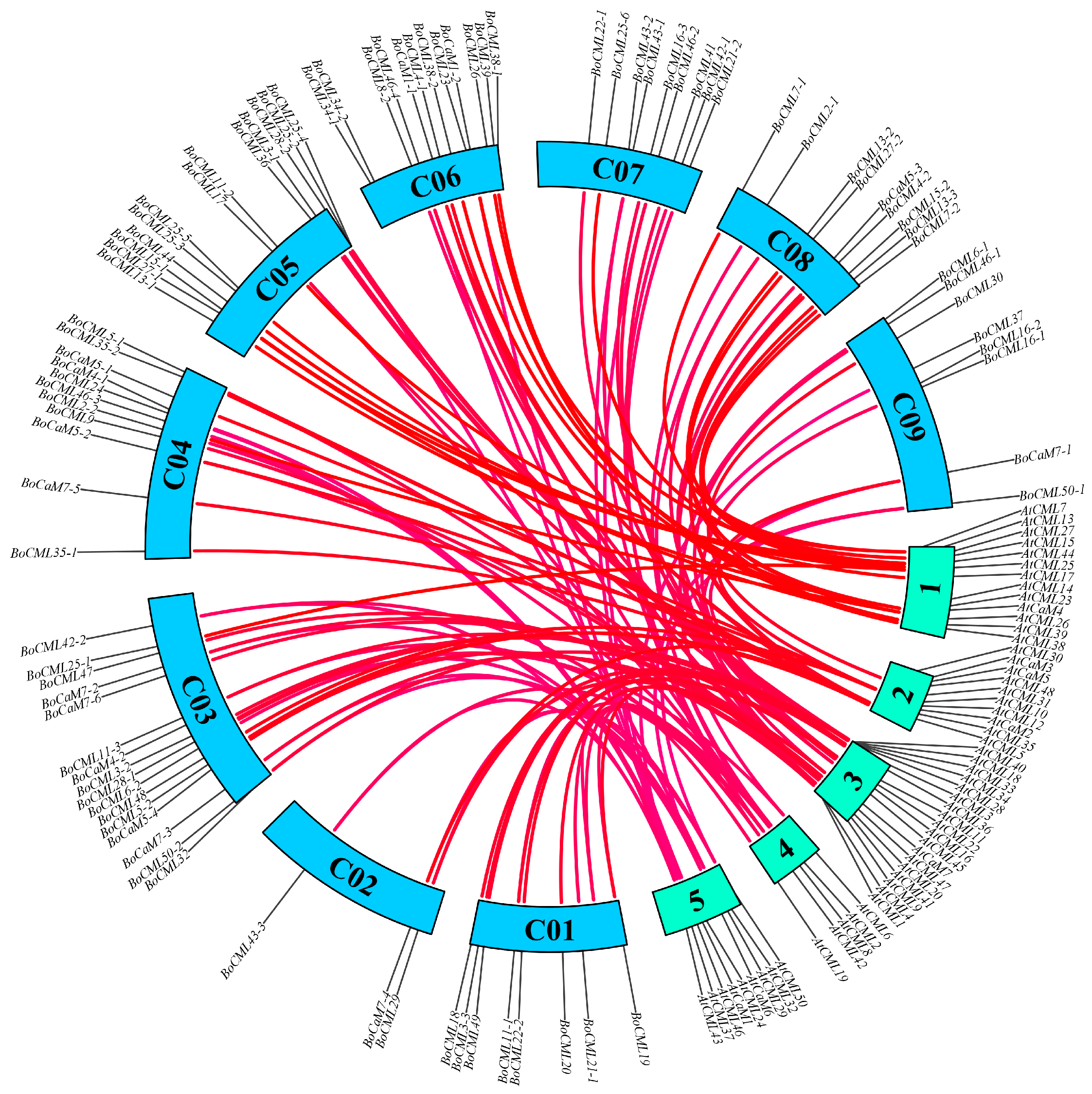
2.4. Chromosome Distribution and Collinearity Analysis of BoCaM/BoCML Genes
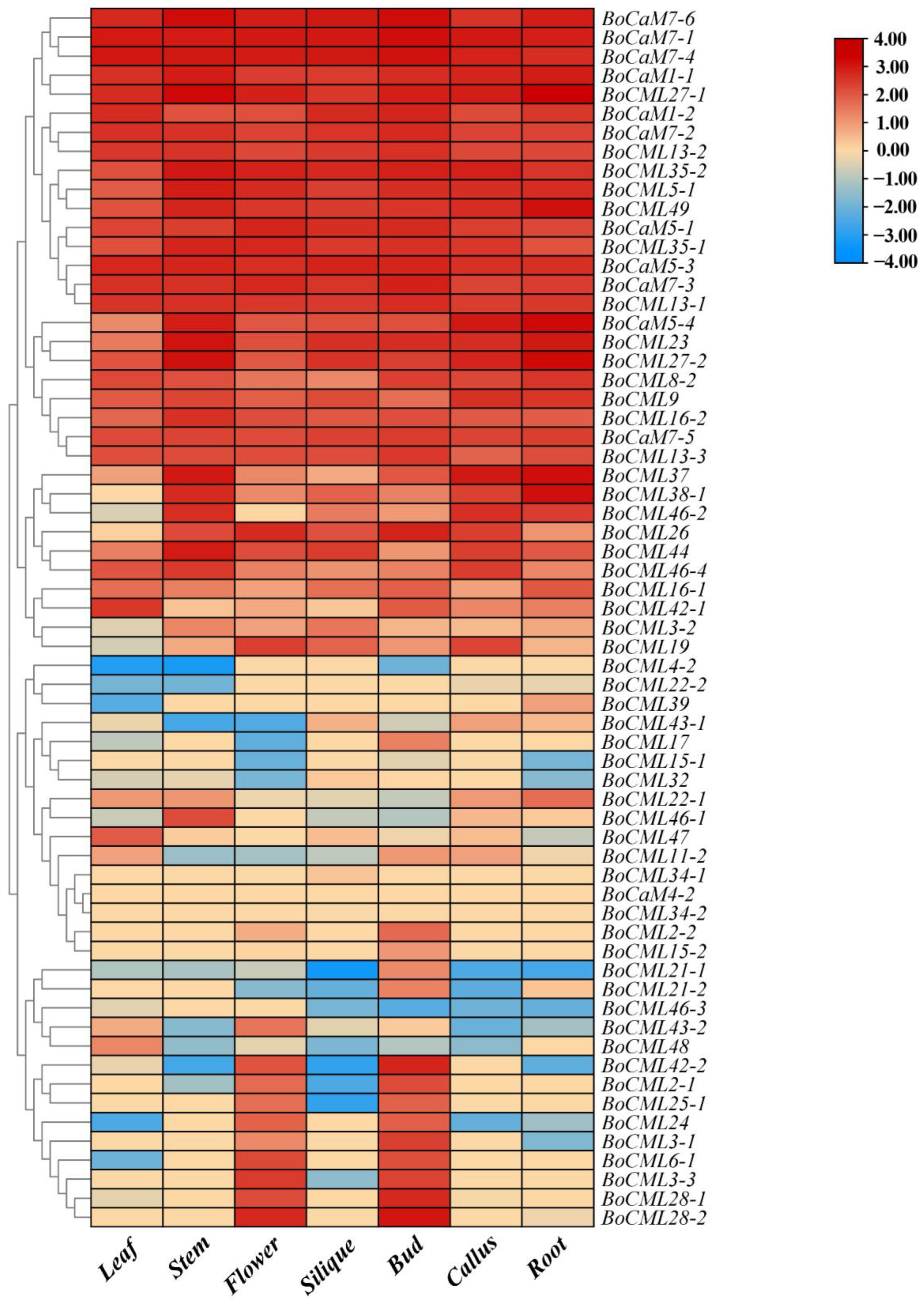
2.5. Expression Profiling of BoCaM/BoCML Genes in Different Tissues
2.6. The Relative Expression of BoCaM/BoCML Genes Under H. parasitica Infection
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Genome-Wide Identification of BoCaM/BoCML Genes in B. oleracea
4.2. Prediction of Basic Infomation of BoCaM/BoCML Genes
4.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.4. Chromosome Location and Collinearity Analysis
4.5. Expression Analysis of BoCaM/BoCML Genes Using RNA-Seq Data
4.6. Plant Materials and Treatments
4.7. Total RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and qRT-PCR Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nawaz, M.; Sun, J.; Shabbir, S.; Khattak, W.A.; Ren, G.; Nie, X.; Bo, Y.; Javed, Q.; Du, D.; Sonne, C. A review of plants strategies to resist biotic and abiotic environmental stressors. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 165832. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reddy, A.S.N.; Ali, G.S.; Celesnik, H.; Day, I.S. Coping with Stresses: Roles of Calcium- and Calcium/Calmodulin-Regulated Gene Expression. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 2010–2032. [Google Scholar]
- Kudla, J.; Batistič, O.; Hashimoto, K. Calcium Signals: The Lead Currency of Plant Information Processing. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 541–563. [Google Scholar]
- Kudla, J.; Becker, D.; Grill, E.; Hedrich, R.; Hippler, M.; Kummer, U.; Parniske, M.; Romeis, T.; Schumacher, K. Advances and current challenges in calcium signaling. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 414–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-H.; Willmann, M.R.; Chen, H.-C.; Sheen, J. Calcium Signaling through Protein Kinases. The Arabidopsis Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinase Gene Family. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 469–485. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Day, I.S.; Reddy, V.S.; Shad Ali, G.; Reddy, A.S.N. Analysis of EF-hand-containing proteins in Arabidopsis. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, research0056.1. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Poovaiah, B.W. Calcium/calmodulin-mediated signal network in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2003, 8, 505–512. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, S. The CBL—CIPK network in plant calcium signaling. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Boudsocq, M.; Sheen, J. CDPKs in immune and stress signaling. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-P.; Munyampundu, J.-P.; Xu, Y.-P.; Cai, X.-Z. Phylogeny of Plant Calcium and Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinases (CCaMKs) and Functional Analyses of Tomato CCaMK in Disease Resistance. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1075. [Google Scholar]
- Perochon, A.; Aldon, D.; Galaud, J.-P.; Ranty, B. Calmodulin and calmodulin-like proteins in plant calcium signaling. Biochimie 2011, 93, 2048–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormack, E.; Braam, J. Calmodulins and related potential calcium sensors of Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2003, 159, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gifford, J.L.; Walsh, M.P.; Vogel, H.J. Structures and metal-ion-binding properties of the Ca2+-binding helix–loop–helix EF-hand motifs. Biochem. J. 2007, 405, 199–221. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Liu, W.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Xie, P.; Kang, Y.; Liao, L.; Qian, L.; Liu, Z.; et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of CaM/CML genes in Brassica napus under abiotic stress. J. Plant Physiol. 2020, 255, 153251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonburapong, B.; Buaboocha, T. Genome-wide identification and analyses of the rice calmodulin and related potential calcium sensor proteins. BMC Plant Biol. 2007, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, R.-G.; Gao, Y.-J.; Zheng, S.-Z.; Xu, P.; Zhang, S.-Q.; Sun, D.-Y. Molecular and Genetic Evidence for the Key Role of AtCaM3 in Heat-Shock Signal Transduction in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2009, 149, 1773–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Perez, M.; Aldon, D.; Galaud, J.-P. Respective contribution of CML8 and CML9, two arabidopsis calmodulin-like proteins, to plant stress responses. Plant Signal. Behav. 2017, 12, e1322246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Smigel, A.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Braam, J.; Berkowitz, G.A. Innate Immunity Signaling: Cytosolic Ca2+ Elevation Is Linked to Downstream Nitric Oxide Generation through the Action of Calmodulin or a Calmodulin-Like Protein. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 818–828. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.-Q.; Han, L.-B.; Yang, C.-L.; Wu, X.-M.; Zhong, N.-Q.; Wu, J.-H.; Wang, F.-X.; Wang, H.-Y.; Xia, G.-X. The cotton MYB108 forms a positive feedback regulation loop with CML11 and participates in the defense response against Verticillium dahliae infection. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 1935–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Yang, S.; Guan, D.; He, S. CaCML13 Acts Positively in Pepper Immunity Against Ralstonia solanacearum Infection Forming Feedback Loop with CabZIP63. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhai, W.; Jiang, G.; Li, C. Inducible Enrichment of Osa-miR1432 Confers Rice Bacterial Blight Resistance through Suppressing OsCaML2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zou, A.; Wen, Y.; Wei, X.; Liu, C.; Lv, X.; Ma, X.; Fan, G.; Sun, X. SlCML55, a novel Solanum lycopersicum calmodulin-like gene, negatively regulates plant immunity to Phytophthora pathogens. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 299, 111049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Ren, W.; Chen, L.; Yang, L.; Zhuang, M.; Lv, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. A Whole-Genome Assembly for Hyaloperonospora parasitica, A Pathogen Causing Downy Mildew in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.). J. Fungi 2023, 9, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiasson, D.; Ekengren, S.K.; Martin, G.B.; Dobney, S.L.; Snedden, W.A. Calmodulin-like Proteins from Arabidopsis and Tomato are Involved in Host Defense Against Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005, 58, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xiong, X.; Arif, S.; Gao, L.; Zhao, L.; Shah, I.H.; Zhang, Y. A calmodulin-like CmCML13 from Cucumis melo improved transgenic Arabidopsis salt tolerance through reduced shoot’s Na+, and also improved drought resistance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 155, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, H.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, P.; Huang, R.; Guo, Z. A calmodulin-like protein (CML10) interacts with cytosolic enzymes GSTU8 and FBA6 to regulate cold tolerance. Plant Physiol. 2022, 190, 1321–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Tan, Q.; Gao, Q.; Zheng, S.; Chen, W.; Galaud, J.-P.; Li, X.; Zhu, X. Calmodulin-like protein CML15 interacts with PP2C46/65 to regulate papaya fruit ripening via integrating calcium, ABA and ethylene signals. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2024, 22, 1703–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffares, D.C.; Penkett, C.J.; Bähler, J. Rapidly regulated genes are intron poor. Trends Genet. 2008, 24, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheval, C.; Aldon, D.; Galaud, J.-P.; Ranty, B. Calcium/calmodulin-mediated regulation of plant immunity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Cell Res. 2013, 1833, 1766–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Su, W.; Li, W.; Wang, B.; Peng, D.; Gheysen, G.; Peng, H.; Dai, L. The nematode effector calreticulin competes with the high mobility group protein OsHMGB1 for binding to the rice calmodulin-like protein OsCML31 to enhance rice susceptibility to Meloidogyne graminicola. Plant Cell Environ. 2024, 47, 1732–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Chen, T.; Wu, Y.; Tang, H.; Yu, J.; Dai, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wan, X.; Yang, Y.; Tan, X. Genome-wide analysis of the peanut CaM/CML gene family reveals that the AhCML69 gene is associated with resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 200. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Truman, W.; Liu, X.; Bethke, G.; Zhou, M.; Myers, C.L.; Katagiri, F.; Glazebrook, J. Different Modes of Negative Regulation of Plant Immunity by Calmodulin-Related Genes. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 3046–3061. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lamesch, P.; Berardini, T.Z.; Li, D.; Swarbreck, D.; Wilks, C.; Sasidharan, R.; Muller, R.; Dreher, K.; Alexander, D.L.; Garcia-Hernandez, M.; et al. The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): Improved gene annotation and new tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1202–D1210. [Google Scholar]
- McCormack, E.; Braam, J. Handling calcium signaling: Arabidopsis CaMs and CMLs. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, S.; Zhu, W.; Hamilton, J.; Lin, H.; Campbell, M.; Childs, K.; Thibaud-Nissen, F.; Malek, R.L.; Lee, Y.; Zheng, L.; et al. The TIGR Rice Genome Annotation Resource: Improvements and new features. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35 (Suppl. S1), D883–D887. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Wang, T.; He, X.; Cai, X.; Lin, R.; Liang, J.; Wu, J.; King, G.; Wang, X. BRAD V3.0: An upgraded Brassicaceae database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1432–D1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L.; Tosatto, S.C.E.; Paladin, L.; Raj, S.; Richardson, L.J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D412–D419. [Google Scholar]
- Paysan-Lafosse, T.; Blum, M.; Chuguransky, S.; Grego, T.; Pinto, B.L.; Salazar, G.A.; Bileschi, M.L.; Bork, P.; Bridge, A.; Colwell, L.; et al. InterPro in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D418–D427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Lu, S.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; Thanki, N.; Yamashita, R.A.; et al. The conserved domain database in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D384–D388. [Google Scholar]
- Letunic, I.; Khedkar, S.; Bork, P. SMART: Recent updates, new developments and status in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D458–D460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.E.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Walker, J.M., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Savojardo, C.; Martelli, P.L.; Fariselli, P.; Profiti, G.; Casadio, R. BUSCA: An integrative web server to predict subcellular localization of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W459–W466. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yao, X.; Yang, L.; Zhuang, M.; Lv, H.; Wang, Y.; Ji, J.; Hou, X.; Zhang, Y. Genome-Wide Characterization of CaM/CML Gene Family in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata): Expression Profiling and Functional Implications During Hyaloperonospora parasitica Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073208
Wu Y, Zhang B, Yao X, Yang L, Zhuang M, Lv H, Wang Y, Ji J, Hou X, Zhang Y. Genome-Wide Characterization of CaM/CML Gene Family in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata): Expression Profiling and Functional Implications During Hyaloperonospora parasitica Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073208
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yuankang, Bin Zhang, Xuehui Yao, Limei Yang, Mu Zhuang, Honghao Lv, Yong Wang, Jialei Ji, Xilin Hou, and Yangyong Zhang. 2025. "Genome-Wide Characterization of CaM/CML Gene Family in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata): Expression Profiling and Functional Implications During Hyaloperonospora parasitica Infection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073208
APA StyleWu, Y., Zhang, B., Yao, X., Yang, L., Zhuang, M., Lv, H., Wang, Y., Ji, J., Hou, X., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Genome-Wide Characterization of CaM/CML Gene Family in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata): Expression Profiling and Functional Implications During Hyaloperonospora parasitica Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073208








